Enterprise Resource Planning
Business software has indispensable role to accelerate business activities of global organization. Enterprise Resource Planning Systems, briefly abbreviated as ERP is specially designed for distributors, retailers and expert services firms as per for their requirements. The company named SAP Aktiengesellschaft is leader in offering ERP systems (Benjamin et,al., 2004). Though it is beneficial for organizations, some management studies have shown that Enterprise resource planning systems are highly complex information systems. The implementation of these systems is a challenging and high cost proposition that places tremendous demands on corporate time and resources. Many ERP implementations have been categorized as failures because they did not accomplish predetermined corporate goals.
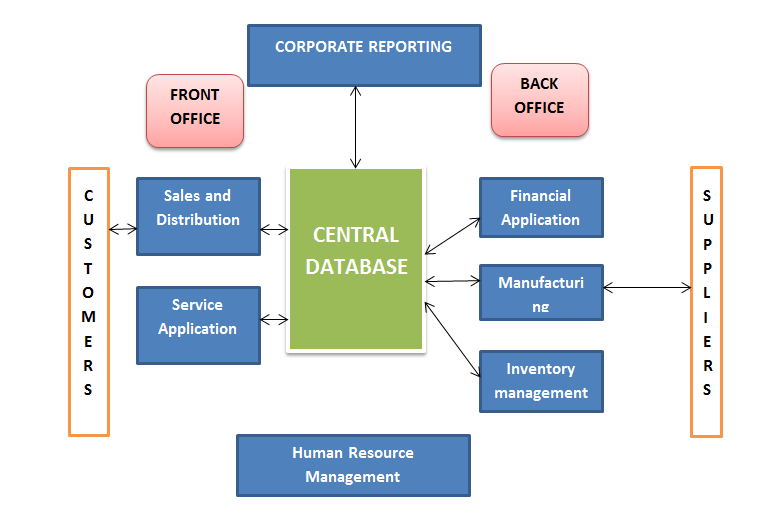
A true Enterprise Resource Planning system incorporates both internal and external information flows used by the organization within a single, comprehensive solution. An Enterprise resource planning solution incorporates the practical systems used by organizations to manage the basic business functions like planning, inventory/materials management, purchasing, manufacturing, finance, accounting, human resources, marketing and sales, services etc. The objective of the Enterprise resource planning solution is to drive the flow of information between all internal business functions as well as managing functions related to outside stakeholders.
Enterprise resource planning system is implemented in organization to provide more precise information and safe time, decrease asset costs and financial cycles, increase customer satisfaction, and globally assimilate information across the enterprise supply chain. ERP system use relational database technology to incorporate various units of an organization's information system which integrated all business process and sub-processes related and combined into a single system. This process is designed to focus on four main areas in a firm such as financial, human resources, marketing and supply chain management. Irrespective of the alignment, characteristically, Enterprise resource planning solutions use a common database to hold information from the numerous business functions that is accessible in some form or another by different customers. The use of an integrated database to manage the solution's multi-module application framework within a common information system is one of the primary ERP benefits.
Enterprise resource planning systems are basically software systems for business management, incorporating modules supporting functional areas such as planning, manufacturing, sales, marketing, distribution, accounting, financial, human resource management, project management, inventory management, service and maintenance, transportation and e-business. The planning of the software enables clear integration of modules, providing flow of information between all functions within the enterprise in a steadily visible manner.
Management practitioners and experts described that Enterprise resource planning systems are computer-based systems designed to process an organization's transactions and facilitate integrated and real-time planning, production, and customer response (O'Leary, 2001).
The concept of the ERP system, Davenport, 1998
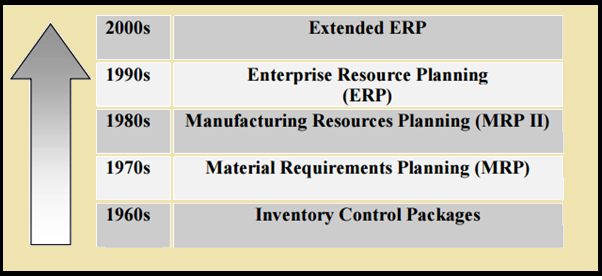
The development towards ERP: In the decade of 1960s, main focus of manufacturing systems was to control inventory. Companies could afford to keep lots of ''just-in-case'' inventory on hand to fulfil the needs of customer and gain competitive advantage in market. Subsequently, techniques focused on effective way to manage huge inventory. Most software packages were designed to manage inventory based on conventional inventory concepts (Schragenheim, 2000). In the decade of 1970s, it became apparent that companies could no longer afford the luxury high cost of maintaining large quantities of inventory. This led to the introduction of material requirements planning (MRP) systems. MRP signified a huge step forward in the materials planning process. By the use of accurate inventory record files, the available quantity of on-hand or scheduled-to-arrive materials could then be used to decide net material requirements. This prompted an activity such as placing an order, cancelling an existing order, or modifying the timing of existing orders. For the first time in manufacturing, there was a formal mechanism for keeping priorities valid in a fluctuating manufacturing environment. The capability of the planning system to methodically and efficiently schedule all parts was a major step forward for productivity and quality (Oden, 1993).
Enterprise Resource Planning system was first evolved in the late 1980s and the beginning of the 1990s with the power of enterprise-wide inter-functional management and integration. Based on the technological foundations of MRP and MRP II, Enterprise Resource Planning systems assimilate business processes including manufacturing, distribution, accounting, financial, human resource management, project management, inventory management, service and maintenance, and transportation, providing accessibility, visibility and consistency across the enterprise. In the period of the 1990s, ERP vendors added more modules and functions as "add-ons" to the core modules which created extended ERPs. These Enterprise Resource Planning extensions include advanced planning and scheduling (APS), e-business solutions such as customer relationship management (CRM) and supply chain management (SCM).
Evolution of ERP
Enterprise Resource Planning system is required by all types of firms and can be used in any kind of organization, regardless of the business objectives, size, and area of operations. Enterprise Resource Planning improves the efficiency of the average existing work process. In contemporary business world, without ERP system, organizations cannot operate their business function competitively. The main reason for this is because it can be configured to accommodate different work processes and this lead it to become popular not only in large corporations but medium companies also often used it because it provides a seamless incorporation of their business. During the 1990s, Global 2000 companies spent huge amount in implementing Enterprise Resource Planning systems (Dan Everett, 2003).
Major features of enterprise resource planning: ERP systems alter disparate, complex, and fragmentary sets of data into a clear and logically structured format which helps decision-makers to take action to manage the material in a quick manner. ERP also facilitates sophisticated processes which allow firms to assume complex volume and timing decisions relating both to the present and future. Main features of ERP are as follows:
- Enterprise resource planning provides multi-platform, multi-facility, multi-mode manufacturing, multi-currency, multi-lingual facilities.
- This system supports strategic and business planning activities, operational planning and execution activities, creation of Materials and Resources.
- Enterprise resource planning cover all functional areas like manufacturing, selling and distribution, payables, receivables, inventory, accounts, human resources, purchases.
- Enterprise resource planning performs major activities and increases customer service, thereby enhancing the corporate image.
- Enterprise resource planning bridges the information gap across organisations.
- Enterprise resource planning provides complete integration of systems not only across departments but also across companies under the same management.
Implementation steps in ERP: Enterprise Resource Planning systems can be multifaceted and difficult to implement, but a structured and well-organized approach can facilitate the implementation. There are numerous steps for an effective implementation of Enterprise Resource Planning (Ptak, 2000).
- Review the pre-implementation process to date. Make sure the system selection process has been satisfactorily completed and all factors critical to implementation success are in place.
- Install and test any new hardware. Before attempting to install any software, it is essential to make sure that the hardware is reliable and is running as expected.
- Install the software and perform the computer room pilot. A technical support person from the software supplier will often install the software and run a few tests to make sure it is installed correctly.
- Attend system training. Software training will teach users the keystrokes and transactions required to run the system.
- Train on the conference room pilot. The conference room pilot exercises the systems and tests the users understanding of the system. The project team creates a skeletal business case test environment which takes the business processes from the beginning, when a customer order is received, to the end, when the customer order is shipped.
- Establish security and necessary permissions. Once the training phase is finished, during the conference room pilot, begin setting the security and permissions necessary to ensure that everyone has access to the information they need.
- Ensure that all data bridges are sufficiently robust and the data are sufficiently accurate. The data brought across from the old system must be sufficiently accurate for people to start trusting the new system.
- Document policies and procedures. The policy statement is a statement of what is intended to be accomplished. The procedural steps to accomplish that statement may be detailed in a flowchart format.
- Bring the entire organization on-line, either in a total cutover or in a phased approach. In a ''cold turkey'' approach, the whole company is eventually brought onto the new system. The entire company prepares for the cutover date, which would preferably be during a plant shutdown of one to two weeks. In a phased approach, modules/products/plants are brought on-line sequentially. After the first module/product/plant is live, procedures may be refined and adjusted, then the remaining modules/products/plants are sequentially implemented. The phased approach may allow for improvements to be made during the implementation.
- Celebrate. This can be the most important step. The company has just completed a major project, the celebration recognizes this, and clearly demonstrates the importance of the project to the organization.
- Improve continually. The organization can only engage a limited amount of change during a finite time period. Change is an on-going process, successful companies understand this, and encourage their employees to use the system to continue to improve.
Advantages:
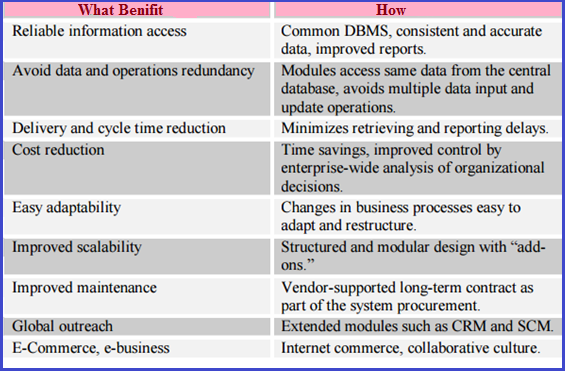
Major advantage of implementing ERP system is, it helps organization to decrease costs and cycle time, increase the productivity and quality and improve the customer service by automating basic and repetitive operations. Enterprise Resource Planning systems automatically assess the demand for a product, order the raw materials, provide production schedules, track down the entire inventory, allocate costs, and keep historical customer. The ERP systems repeat all the operation and keep the information so that company can analyse the impact of changes in product mix and volumes in order to maximize corporate profit margins. Enterprise Resource Planning systems also offer informational benefits to management. ERP system helps an organization to accomplish better resource management for instance, in workforce management improved the manpower allocation, in inventory management, improved inventory turn and stock allocation, in production management, optimized supply chain and production schedules. It also helps in taking wise decision by increase the market responsiveness, has a better profit and also controls the cost and also flexible the customer services, increase the service adjustment and response customer demand.
Enterprise Resource Planning systems also offer E-business by using the web integration capability. It provides benefit to business to business (B2B) interactive customer service, for example through customer directs feedback, it can improve product design, and most importantly deliver real time and reliable data enquiries.
In brief, ERP provide following advantages to firms:
- ERP enhances business process efficiency
- It offers a platform for improved communication channels which enable speedier actions between units.
- It is a mechanism for seeing the organizational whole and not simply distinct parts of the overall business.
- ERP facilitates an all-encompassing and seamless merging of the entire supply chain network
Benefits of ERP
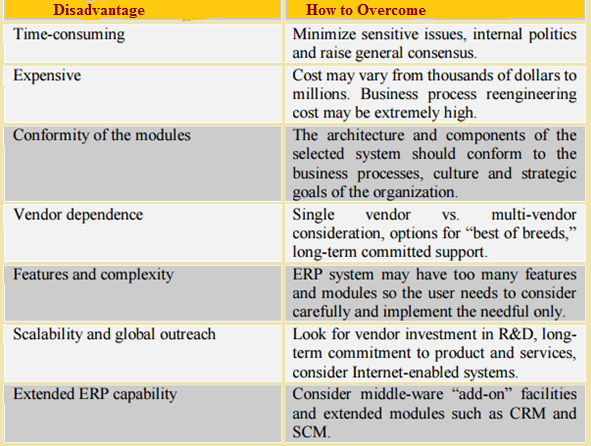
Limitations of Enterprise Resource Planning: The disadvantage for implementing Enterprise Resource Planning system is the high cost of installation. The ERP system be installed by ERP consulting organization and the fees to modify the system is also expensive (Benjamin B. Bae, and Paul Ashcroft, 2004). Besides that, installing an Enterprise Resource Planning systems take a long period. "ERP system is an intricate system and it often takes 12-18 months to be installed and operating (Benjamin B. Bae, and Paul Ashcroft, 2004). It takes longer period because a thorough study must be made and reviewed before installing Enterprise Resource Planning system to match the business requirement. If there is any mistake in planning of ERP systems, it will affect the whole performance system. Some management consultant has indicated that Enterprise Resource Planning systems are inflexible and does not meet specific organization and industry requirements (Booth et al., 2000).
Table: Drawbacks of ERP
To summarize, Enterprise Resource Planning has emerged as the major option for enterprise management systems among software such as SAP, Oracle and Microsoft, and from the small software developers in their own places. Enterprise Resource Planning software is composed of many software components. Each component represent major functional area of organization such as Logistics, Production, Finance, Accounting and Human Resources.

