Vendor Evaluation and Audit
Since last two decades, there has been considerable growth in the industries around the globe. With this rapid progression, the competition in the market is also increasing. The high quality of vendors' products is vital factor to the success of the company's quality control function. Therefore, the quality commitment of vendors is indispensable. To attain the company's goals through the quality assurance/quality control function, it is important to issue instructions and procedures for the evaluation, approval and auditing of incoming-material from suppliers or manufacturers. It is well realized that Supplier Evaluation and audits can be considered as an integral part of assessment in any type of industry or organization. As the entire industry routine depends on the type of materials supplied for the production. These raw materials will only shape up into the actual end product or the final product. So, it becomes necessary to guarantee that the person who supplies the raw material in an industry is of good quality and standard and the materials they supply comply with all the industry set standards and policies. Good quality products become standard and reliable end products that can satisfy customers.
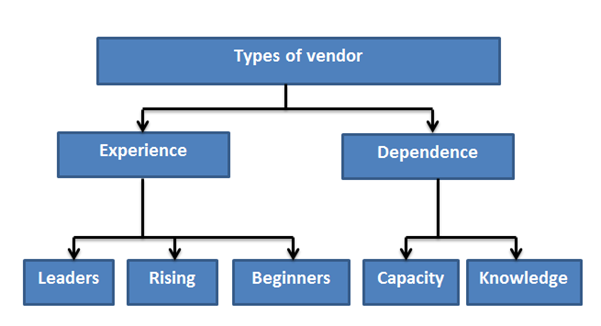
Type of vendors:
Figure: (Source: Mark Power, 2006)
The evaluation of the quality program is a joint vendor-vendee activity. It is efficiently achieved, it provides mutual benefit for all parties concerned. The vendor evaluates his quality program to ensure that the program is accomplishing its intended functions effectively and economically. The vendee appraise his vendor's quality program to check whether his vendor is adept to produce the desired quality product. Additionally, he may establish a ranking system by providing a numerical value. This value, which will be assigned to each vendor, should have recognition and can be used as the basis of the vendee and vendor remedial action and vendor comparisons within the vendee's organization. The vendee may establish a comprehensive audit program to cover all phases of plant design, procurement, construction and operation, either within his organizational structure, or by contractual requirements i.e. specified in the purchaser order to audit the vendor's facilities. The main aim of the quality audits is to guarantee compliance with the quality assurance program requirements. Basically vendor management is vital for company because it improves cash flow, provide excellent services, improve reliability of supply, and help reduce reliance on capital assets, provide advanced technology trends.
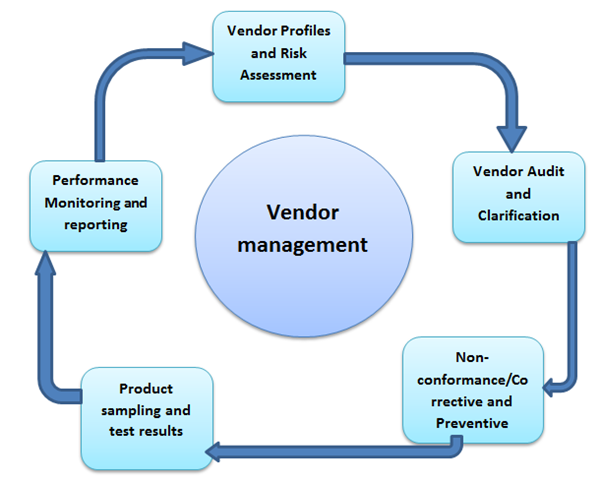
Vendor management
Vendor Evaluation:
There are basically three different types of vendor evaluation. These are:
-Informal use of records
-After-The-Fact Evaluation
-Before-The-Fact Designed
- Informal use of records: In this type of vender evaluation, data is collected from many sources such as journals, diaries, log books, or financial records, and knowing what happened in the past allow one to evaluate an event in order to make better decisions for the future.
- After-The-fact-Evaluation: When event has occurred, a manager may ask questions like What happened? How did it happen? Why did it succeed? or why did it fail? How well did it do? Responses to such questions give data for decisions and future planning after an event has been completed.
- Before-The-Fact-Designed, evaluation: In this type of evaluation, the evaluator plans and starts gathering data early in the history of the project. Evaluation vendor capabilities is an example.
According to Frank Caplan, the vendor surveys and capability determination is an important tasks to the purchaser's organization to determine, in advance, the capability of the vendor to produce quality products on schedule. Efficacious companies hold their suppliers and vendors, consider them as partners to assist in their business. It is viewed as mutually beneficial partnership. If a supplier/vendor is major part or service to operation invite that supplier or vendor to strategic meetings that involve the product they work with.
There are numerous tips and tools through which companies need to effectively rate their suppliers and vendors, track their performance, and ultimately increase company's overall productivity.
1. Establish Performance Indicators: At the beginning of the vendor relationship, managers have to determine what characteristics a vendor needs to have, demonstrate, or maintain to continue doing business with company. It is important to create specific performance criteria for tracking and evaluating suppliers and vendors regularly on monthly, quarterly, and/or annually. Considerations include size of the company, number of certifications, quality management systems, complaint history, and financial stability.
A basic consideration for all business owner should be whether the supplier has a quality management system in place. This does not just apply to manufacturing but any business including service providers. If the supplier has a certain set of procedures in place then its people are expected to follow.
2. Classify Multiple Suppliers and Vendors: If company has a huge number of suppliers and vendors and managers intend to craft a survey to evaluate them, it will be burdensome to apply the same survey to each and every one. It is better to separate suppliers into levels based on how critical they are. Decide the classification that is best for company and evaluate suppliers according to the effect they have on your product or service in order of importance.
3. Devise an Evaluation Method: There are common methods to rate a supplier's performance including evaluation forms, surveys, system metrics, and software applications.
Company professionals can craft a survey where they ask their own employees to answer questions and to rate suppliers and vendors. Then, evaluators can review how many corrective actions they have to issue a supplier or vendor, how many products they have to scrap or return because the supplier or vendor failed to meet specifications, or how many customer complaints they receive due to a bad part or service from a vendor. Evaluators must also monitor suppliers and vendors by doing an audit periodically. They need to generate measurements or reports at the onset of the purchase and throughout the course of the supplier and vendor relationship.
Vender quality evaluation:
|
Delivery |
Customer Service |
|
-
Deliver on time
-
Delivers proper item
-
Delivers proper quantities
-
Meets due date without constant follow up
-
Product lead time competitiveness
-
Accurate documentation/ identification provided
-
Response on rush/emergency delivery
requirements |
-
Market insight
-
Invoicing efficiency
-
Order acknowledgement
-
Recognises cost effects
-
Compliance to special terms
-
Technical emergency support
-
Issuing credit memos promptly
-
Adherence to company policies
-
Technical support/ resolution
-
Inside sales support/customer service
-
Training provided on manufacturer's products |
|
Quality |
Pricing |
|
-
Warranty coverage
-
Product reliability/ durability meeting of
specifications including new features introductions
-
Product documentation, instructions, technical
manuals
-
Product packaging, including environmental aspects |
-
Price stability / accuracy
-
Competitive pricing / value
-
Advance notice of price changes |
Experts stated that periodic vendor reviews would also involve a discussion about what the company had been buying, how much it had been buying, what did that vendor have on the shelf or working on for push out six months or a year down the road and did it represent a significant improvement over what had been previously purchased, and what were competitors buying from a particular vendor.
4. Determine Who's Calling the Shots: Once evaluators of company establish the criteria for evaluating suppliers and vendors, it is to determine who in company will be responsible for reviewing the data. It depends on how much Resources Company has to dedicate to evaluate their suppliers.
5. Maintain Good Relationships: It is very important to retain healthy business relationship with suppliers and vendors as part of the team and treat them as such. Company managers must communicate often and openly. Also, it is advised to avoid supplier and vendor conflicts by paying on time or at least honestly addressing late payment issues and talking with supplier or vendor about it. Be frank and transparent with suppliers and vendors. Make sure they understand company needs and expectations.
6. Decide When to Issue a Red Flag: When evaluators of company monitor a supplier's performance, they have to decide when to praise them and when to issue a red flag.
7. Cut Loose Weak Links: Company should tolerate ongoing bad service. There may come a time when managers have to let go of an underperforming supplier or vendor. The relationship with supplier is a business partnership and if both parties are working to make sure that the partnership is a success it will be a success. In the long run, having a win-win supplier and vendor relationship will be a competitive advantage.
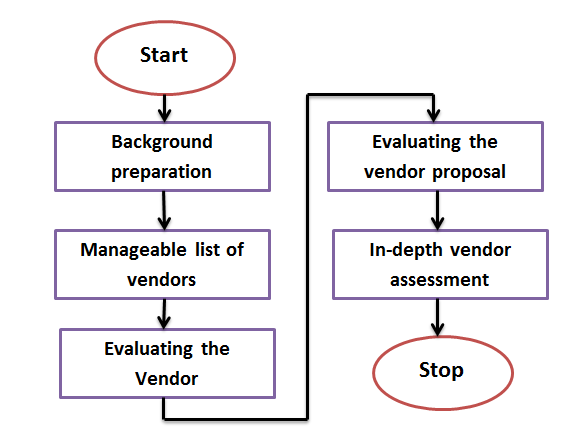
Vendor assessment process
Vendor Rating (Ranking) and Certification:
The vendor rating system is used by many companies around the globe. It is explained by Feigenbaum as a technique that provides vendor-to-vendor assessment, whereby each vendor is measured against another specific vendor or group of vendors for price, quality and delivery. Rating results are reported quarterly, and used to determine all future business activities with the vendor. There are different types of vendor ratings established to fit the changeable needs of plants and companies. The basic and extensively used vendor rating plan weighs the key factors as follows:
|
Quality |
40 points |
|
Price |
35 points |
|
Service |
25 points |
|
Total |
100 points |
Quality rating is based on:
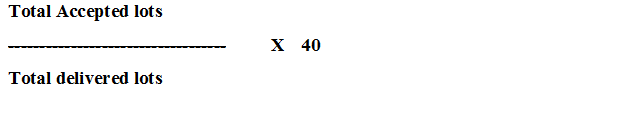
Price rating is:
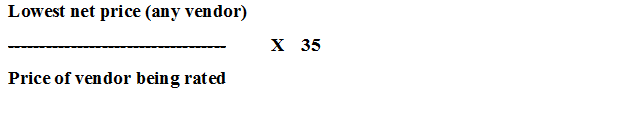
Service rating is based on the percentage of promises kept. If vendor kept 90% of his promises, then, service rating is equals 0.90 (25) = 22.5.
Vendor Audit:
All companies manage vendors to achieve SCM's deliverable of supplying safe and reliable goods and services to customers, the operations. In vendor management, auditing process is vital in offices and companies. It is done to do the required checks. It might be for the operations or it might also be done for the vendors who supply goods. Traditional vendor audit procedures are time-consuming and therefore very expensive for the average organization to undertake with the required scale and thoroughness. And they are often not particularly effective.
Generally, manufacturing, factories and industries use suppliers to get there raw materials. These goods should be of quality and standard. Anything bad cannot be used by the company, because the end product reaches the customer. If the customer gets poor or damaged product then it degrades the image of company and customers will purchase it from other company. Due to these reasons, supplier audits are conducted by giant companies. There are different vendors and suppliers who supply goods to companies. It is necessary for company to make a systematic check before approaching to any vendor for getting the raw materials. It is of paramount importance that the raw material is of good quality and standard. Once the product is developed in to finished good and it is circulated in the market, then it cannot be changed. So, if the raw material is of poor quality, then end product is definitely going to face lot of problems and issues. The customer might return the product with complaints.
Therefore trained supplier must be recruited. There are certification courses that an individual can take to become a supplier auditor. The certification gives the individual an upper hand over others. The auditor has thorough knowledge and practical knowledge of how to check and do the audits for the vendor's items. There is a checklist which the auditor should follow and comply with. Supplier audits are very essential for the organization. This audit makes sure the quality of the product and also the raw materials are such that it will last for long and will not get damaged within short period of time.
Vendor evaluation or supplier audits should be done once in a year. In this kind of audit, the vendor's location, the products and his manufacturing unit should be audited and checked well. The kind of audit and how many times it should be done depends on the kind of products and service the company is using or buying from the vendor. It also depends on how important is that vendor and his products for company's business. Based on that, one can decide on the kind and times an audit should be done.
Vendor audit
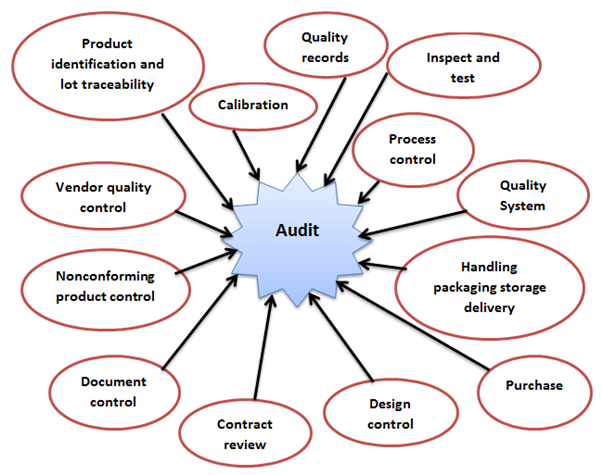
In supplier audits, the facilities of the vendor must be checked. The auditor should check and appraise short shipments, invoice to and fro from the supplier. The deliveries should always be checked in order to keep the quality standards intact. Auditing is a very crucial task and the supplier auditor should have the knowledge and ability to fulfil this responsibility with sincerity. It is not at all easy to check the vendor and his products. There needs to be smartness, ability and tact in doing this. Auditors should make sure that the vendor does not get upset and understands the importance of this check. This will make sure that the business relations remain good. The vendor also eagerly complies with the audit and checking procedures. It is the responsibility of any business owner to give importance to quality checks and audits. If company has to grow and flourish in the business, then it is always best to do proper checks of the equipment and raw material that the vendor is supplying for the said business.
It has been documented in many studies that Supplier quality management is a critical business practice for firms that gradually outsource business processes to strategic associates and have increased dependence on vendor products and services. The audit process guarantees that suppliers are continually performing at or above the levels delineated in procurement contracts. Incorporate industry practices for developing supplier audit procedures and checklists to recognise underperformance that might be timely improved and encourage support quality efforts in high-performing areas.
Procedure of Vendor Audit:
- Planning: Audit planning is done by the lead auditor charged with recognizing the scope of the audit. Here, an audit performance metric a combination of a checklist and scoring card, might be developed that identifies measurable performance areas that will be the subject of the audit. Measure factors might include such matters as on-time delivery, order response times, response times to requested corrections and product quality. Furthermore, audit plans should address the essential technical, capital and human resources necessary to adequately perform the audit.
- Audit Management: During audit period, performance data is secured, measured and recorded over a course of time. Information from the supplier is normally required to effectively perform the audit process such as acquiring and reviewing supplier's quality manuals, policy and procedures, as well as current certifications. There are many areas that require effective management during the procedure. It is important to be prepared for changes to audit schedules to the scope of supplier performance appraisal.
- Reporting: Audit reports comprises of measurements and data collected using the performance metric. Audit reporting highlights the major cause of identified performance problems. In reporting, remedial and preventive actions are included as recommendations. Furthermore, prior audits should be incorporated into reports as a way to track historical performance variations. Audit reports include qualitative data about the supplier, such as noted performance observations or internal interviews with staff members that work with the supplier. Also, industry performance data is generally incorporated as a comparison tool that provides additional supplier ranking against benchmark standards.
- Review: After report is made, a company must review the results of an audit report with supplier management. This should be a formal meeting that allows supplier representatives to provide feedback about the performance data contained in the audit. Audit review process is beneficial and gives an opportunity to support the collaboration between the vendors, but be honest about any underperformances. This is the time when supplier performance goals and objectives might be established to correct any existing problems.
To summarize, vendor evaluation is done to ensure a portfolio of good suppliers available for use. It is also a process applied to current suppliers to measure and monitor their performance to decrease costs, mitigate risk and improve continuously. It can be believed that there is a need to conduct vendor audits for quality control in an organization. This need for a closer monitoring of a vendor's qualities and practices stems from an ever-evolving quality control market, and an industry where quality products are a requirement. The main areas that need to be appraised in a vendor audit are vendor viability, management responsibility, system accuracy, and data integrity. The prime aim for a vendor audit are to evaluate the quality management of the whole organization, through its procedures and data processes. It is an assessment of quality control measures taken by the vendor to guarantee that their products and services are satisfactory for business transaction and beneficial for end users.

