Nature and Scope of Strategic Management
Strategic management is well-organized approach that is based on effective principles and process of management to recognize the corporate objective or mission of business. It establishes suitable target to assure the objective, identify existing opportunities and restraints in the environment, and develop a logical realistic process to accomplish company objective. Strategic management is both the process and beliefs to determine and control the organizational affiliation in its vibrant environment. It is a process to describe approaches and procedures to help management become accustomed to the current business environment through the use of objectives and strategies. As a philosophy, it changes the viewpoint of manager to deal with competitors, customers, markets and even the organization itself. Its purpose is to motivate management's wakefulness of the strategic implication of environmental events and internal decision.
Theoretical review: Strategic management in literature is thoroughly described by several theorists. In the beginning of 1980, Glueck (1984) explained Strategic Management as "a stream of decisions and actions, which leads to the development of an effective strategy or strategies to help achieve corporate objectives". Another group of theorists like Hofer and others (1984) stated that strategic management is "the process which deals with the fundamental organizational renewal and growth with the development of strategies, structures, and systems necessary to achieve such renewal and growth, and with the organizational systems needed to effectively manage the strategy formulation and implementation processes". According to Sharplin (1985), strategic management is "the formulation and implementation of plans and carrying out of activities relating to the matters which are of vital, pervasive or continuing importance to the total organization" Lawrence and William (1988) delineated strategic management as a stream of decisions and actions, which leads to the development of an efficient strategy or strategies to help achieve corporate objectives.
Copious studies have shown that the strategic management process is the technique in which strategists decide objectives and take effective strategic decisions. Main concentration of strategic management is the accomplishment of organizational goals taking into consideration the internal and external environmental factors. Porter (1985) squabbled that the spirit of formulating comprehensive strategy is associated with company to its environment. Strategic management allows the systematic management of change. It facilitates organization to decisively organize resources towards a desired future. Chandler (1962) also speculated that any successful policy is dependent on structure, to accomplish any effective economic performance. The organization needs to change its structure. In the decade of 1998, Harrison and St. John (1998) explained the concept of Strategic Management as "the process through which organizations analyse and learn from their internal and external environments, establish strategic direction, create strategies that area intended to help achieve established goals, and execute these strategies, all in an effort to satisfy key organizational stakeholders". It is appraised that several theorists have dissimilar viewpoint for the notion of strategic management but there are several common elements in the way it is understood. Strategic Management is regarded as either decision making and planning, or a set of activities interrelated to the formulation and execution of strategies to accomplish Organizational Objectives. It is also set of managerial decisions and actions that decide the long term performance of firms. It comprises of Strategic Intent, Environmental scanning (both internal and external), and strategy formulation (strategic planning), strategy implementation and evaluation and control. It can be recognized that Strategic Management is the process by which an organization try to establish the ways by which company can accomplish long term goals.
overview of strategic management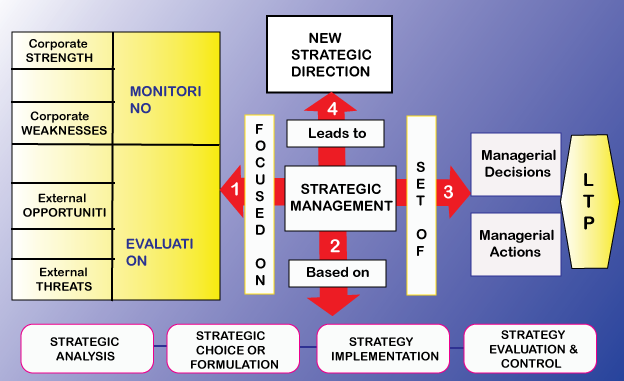
Strategic management is an organized approach to manage strategic change, which consists of the following:
- Positioning of the firm through strategy and capability planning.
- Real-time strategic response through issue management.
- Systematic management of resistance during strategic implementation.
Strategy and market positions are necessary to set directions for a firm and to overcome competitors or facilitate to conquer threatening environment. A good strategy when effectively implemented can ensure an uppermost position for the weakest firm among other leading competitors.
Nature and Scope of Strategic Management
Strategic management is both an Art and science of formulating, implementing, and evaluating, cross-functional decisions that facilitate an organization to accomplish its objectives. The purpose of strategic management is to use and create new and different opportunities for future. The nature of Strategic Management is dissimilar form other facets of management as it demands awareness to the "big picture" and a rational assessment of the future options. It offers a strategic direction endorsed by the team and stakeholders, a clear business strategy and vision for the future, a method for accountability, and a structure for governance at the different levels, a logical framework to handle risk in order to guarantee business continuity, the capability to exploit opportunities and react to external change by taking ongoing strategic decisions.
Strategic management process encompasses of three phases.
- Establishing the hierarchy of strategic intent
- Strategic formulation.
- Implementation
- Evaluation and control.
Strategy formulation comprises of developing a vision and mission, identifying an organization's external opportunities and threats, determining internal strengths and weaknesses, establishing long-term objectives, creating alternative strategies, and choosing particular strategies to follow.
Strategy implementation needs a company to ascertain annual objectives, formulate policies, stimulate employees, and assign resources so that formulated strategies can be implemented. Strategy implementation includes developing a strategy-supportive culture, creating an effective organizational structure, redirecting marketing efforts, preparing budgets, developing and utilizing information systems, and relating employee reward to organizational performance.
Strategy evaluation is the last stage in strategic management. Managers must know when particular strategies are not working well. Strategy evaluation is the main process for obtaining this information.
Figure: Phases of Strategic management process (Source: Azhar Kozami, 2002):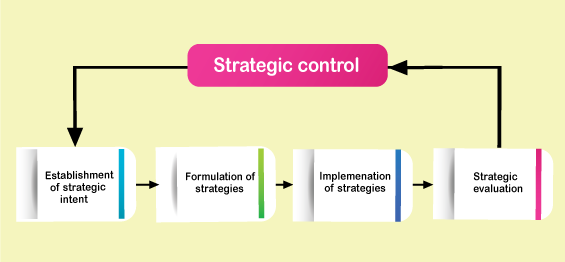
Strategic Intent
Strategic Intent is very important concept of management that is explained as a high level statement of the means by which an organisation achieves its vision. In present business scenario, management team make extreme efforts to go with the competitive advantage of their international competitors but most of them only imitating the activities of rivals. Imitation does not really produce the Strategic Intent as competitors have already implemented those techniques and get advantage. Imitation is not a solution of competitive revival. Strategic Intent drives organisations, individuals and groups to overcome the challenge of change in business. Strategic Intent is a notion that emerged in Post-World war as world leader in economy. Japanese Organizations had set goals for themselves that might have been considered by most of the Western Organizations of that time as highly impractical. But with very few resources and highly committed labour force, Japan was then able to lay the foundation for 10-15 years of leadership in terms of economy. From Japan, all international business leaders learnt how to surpass when there is limited resources and company face huge challenges.
Strategic intent
Strategic Intent is a management notion that is elucidated by theorists Hamel and Parahalad as: an ambitious and compelling dream that energizes; which provides the emotional and intellectual energy for the journey to the future. Strategic intent gives direction, focus and motivation for the whole organization. Additionally, it has imperative role as an organizing concept in the firm's architectural and organizational progress. If strategic intent is the organizational and motivational power in the organization, core competencies are the foundation. Though instant success is the result of market recognition of current product or service offerings, future success depends upon the capability to foresee market possibilities, customer needs and the skills necessary to develop the organizational capabilities and future successful products.
Strategic intent is a functional model in accounting for purpose and stability of goals in an organization adapting to internal and external developmental pressures. The administrative role of strategic intent is to go beyond environment sensitive strategic planning to represent objectives "for which one cannot plan" (Hamel and Prahalad, 1989). As such, strategic intent characterizes a practical mode in strategizing, a symbol of the organization's will about the future, which invigorates all organizational levels for a combined purpose. Strategic intent mirrors the 'corporate context' in which bottom up business ideas are considered (Lovas and Ghoshal, 2000). It directs the accretion of necessary competencies (Hamel and Prahalad, 1989), giving the intra organizational evolution processes a common target, "something to 'aim' for" (Lovas & Ghoshal, 2000).
Strategic intent in earlier literature: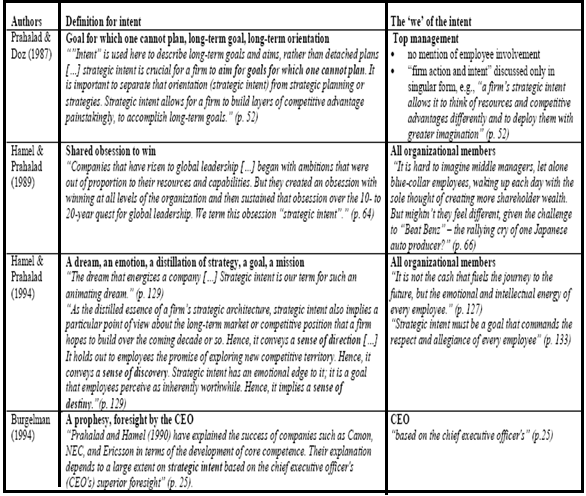
Features of Strategic Intent: Attributes of Strategic Intent:
There are three major attributes of Strategic Intent:
- Sense of Direction,
- Sense of Discovery
- Sense of Destiny.
Sense of Direction is described as the "Long-Term Market or Competitive Position.
The Sense of Discovery denotes to "the competitively unique point of view about future. It states that Strategic Intent is differentiated because here in this case the employees are allied and they are convinced about the concept of Strategic Intent".
Sense of Destiny refers to the emotional edge that is involved with the Strategic Intent. This takes Strategic Intent to an all-together new level by including the employee's emotions with the organization aspirations. This leads to an all over harmonic progress for everyone.
Hamel & Prahalad stressed that strategic intent is more than simply unfettered ambition. It encompasses the active management process which include focusing on organization's attention on the essence of winning, motivating people by communicating the value of target, leaving room for individual and team contributions, sustaining the enthusiasm by providing new operational definitions as circumstances change and using intent consistently to guide resource allocation. Therefore underlying concept of strategic intent is that strategic planning should be based on setting an ambitious vision and goals that stretch a company and then explore ways to build resources and capabilities necessary to accomplish vision and goals. Strategic intent is more internally focused (Charles Hill, 2008).
Vision: Aspirations expressed as strategic intent should lead to an end. That end is vision of an organization. A vision is more dreamt of than it is articulated. Vision has been described in different manner. Kotter defined vision as description of something such as an organization, corporate culture, a business, a technology, an activity in future (1990). EL Namaki considers it as a mental perception of the kind of environment of an individual, organization aspires to create with in a broad time horizon and underlying conditions for the acquisition of this perception (1992). Miller and Dess visualized vision as category of intentions that are broad, all inclusive and forward thinking. Major benefits of having vision are designated by Parikh and Neubauer (1993). Good visions are inspiring and exhilarating. Vision represents a discontinuity, a step function and jump ahead so that company knows what is to be done. Good vision assists to create common identity and a shared sense of purpose. Good vision is competitive, original and unique. They make sense in the marketplace as they are practical. Good vision foster risk taking and experimentation. It also promotes long term thinking. Visions represent integrity (Azhar Kozami, 2002).
Objectives: Objectives are described as specific results that an organization gets to accomplish for its basic mission. Long term means more than one year. Objectives state direction, aid in evaluation, create synergy, reveal priorities, focus synchronization, and provide a basis for effective planning, organizing, motivating and controlling activities. Objectives should be challenging, assessable, reliable, reasonable, and apparent. Objectives plays vital role in strategic management. Objectives define organizational relationships with its environment. By stating its objective, an organization commits itself to what it has to achieve for its employees, customers and society at large. Objectives help organization to pursue mission and vision. By defining long term position that organization wishes to attain and the short term targets to be achieved, organization help an organization to pursue its mission and vision. Objectives provide the basis for strategic decision making. By directing attention of strategists to those areas where strategic decisions need to be taken, objectives lead to desirable standard of behaviour and this way help to coordinate decision making. Objectives provide the standards for performance appraisal. By stating the target to be achieved in a given period of time, and the measures to be adopted to attain them, objectives lay down the standards against which organizational as well as individual performance could be judged. In the absence of objectives, an organization would have no clear and definite basis for evaluating its performance (Azhar Kozami, 2002).
Features of objectives: Objectives have certain characteristics to get success in business (Azhar Kozami, 2002).
- Objectives must be understandable. Objectives has vital role in strategic management therefore these should be comprehensive to accomplish them.
- Objectives should be concrete and specific.
- Objectives should be related to a time frame.
- Objectives should be measurable and controllable.
- Objectives should be challenging.
- Different objectives should correlate with each other.
- Objectives should be set with in constraints.
Objective setting is complex process. There are numerous issues associated with Objective setting.
- Specificity: Objectives may be stated at different level of specificity. Many organizations state corporate as well as general, specific, functional and operational objectives. The issue of specificity is resolved through stating objectives at different level and prefixing terms.
- Multiplicity: Since objectives deal with numerous performance areas, a variety of them to be formulated to include all aspect of functioning of an organization. No organization operates on the basis of single objective. Other issue of Multiplicity is number and type of objectives to be set. Organizations need to set adequate and appropriate objective to cover all performance areas.
- Periodicity: Objectives are devised for different time periods. It is possible to establish long term, medium term and shot term objectives. Generally, companies set long and short term objectives. When they do so, objectives for different time periods must have to be integrated with each other. Long term objectives are less certain and short term objectives are certain, specific and comprehensive.
- Verifiability: Each objective is to be tested on the basis of its Verifiability. Only Verifiable objectives can be meaningfully used in strategic management. Verifiability is also related quantification.
- Reality: Generally, organizations have two sets of objectives- official and operative. Official objectives are those which organization professes to attain while operative objectives are those which seek to attain in reality.
- Quality: Objectives may be good or bad. The quality of the objectives can be judged on the basis of its ability to give specific direction and tangible basis for evaluating the performance.
It is assesses that Strategic objectives are used to operationalize the mission statement. They help to provide supervision for the organization to fulfil or move toward the high goals in the goal hierarchy of the mission and vision. Consequently, they tend to be more particular and cover a more well-defined time frame. Most of strategic objectives are directed toward generating more profits and returns for the owners of the business, others are directed at customers or society at large. It can be established that objectives are set in all those performance areas which have strategic importance to organization. Drucker stated that objectives are established in areas of market standing, innovation, productivity, physical and financial resources, profitability, manager performance and development, worker performance and attitude and public responsibility (Azhar Kozami, 2002).
Major factors in Formulating Strategic Objectives
The first factor when Formulating Strategic Objectives is the mission of the organization.
Formulating Strategic Objectives depends on the environment in which the organization operates i.e. the influence of external factors such as market conditions legislation, political and economic trends have an influence on the desired end result.
Formulating Strategic Objectives also depends on the values held by the management. Management values have an important influence on the formulation of target. They may value from ethical standards to the position held on social welfare.
The management experience is also an important factor in Formulating Strategic Objectives. This relates to the management experience of a specific market.
The strong and weak points of the business is where the organization plans should not be made to expose the weak points of the business but instead exploit on the strength of the business. The cost of each alternative should be considered against the benefits offered.
There are many benefits for the organization. They facilitate to channel employees throughout the organization toward common goals. This helps to focus and conserve valuable resources in the organization and to work jointly in a timelier manner. Challenging objectives can help to encourage workers throughout the organization to higher levels of commitment and effort. Meaningful objectives help to resolve conflicts when they arise. Appropriate objectives provide a standard for rewards and incentives.
Policies: Policies are the devices by which annual objectives will be attained. Policies include guidelines, rules, and procedures established to support efforts to achieve stated objectives. Policies are most often stated in terms of management, marketing, finance/accounting, production/operations, research and development, and computer information systems activities. Business policies are concerned with developing the general management point of view with demands that the manager sublimates his departmental, functional or specialist perspective in order to take balanced companywide look. The process of strategic planning encompasses the formation of specific polices. Policies help to ensure that all units of organization operate under the same ground rules. They also facilitate coordination and communication between various organizational units. Policies of competitors also influence organizational policies. According to Terry George, a business policy is an implied over all guide setting up boundaries that supply the general limits and directions in which managerial actions will take place (Satya Sekhar, 2009).
Effectiveness of Strategic Management
Alli (1992) stated following attributes of an effective strategic management:
- Clear direction and purpose
- Objectives, goals, and strategic consistency
- Continuous monitoring of internal and external (environment)
- Integration of operating budget and profit plans with strategic plan
- Continuous monitoring of progress with revision of plan and programs as appropriate
- Creation of strategic atmosphere that foresters a team spirit
- Commitment of necessary resources and the development of system to provide necessary management information.
Fundamentally, there are three major viewpoints to understand strategic management efficacy in management studies.
First is the use of goal cantered approach to gauge organizational effectiveness. In this situation, individual organization scrutinizes the extent of completion of important planning objectives. Theorists like Cameron and Whitton (1983), King (1987) and Steiner (1979) supported this statement.
Secondly, specific capabilities to develop a 'generic view' if system capabilities as stated by Lorange (1979) a generic capability required of every formal strategic planning system is the ability to persuade both creativity and control (Camillus 1975). In this viewpoint, creativity and control are used as requisite properties of a successful planning method.
The third perspective usually scrutinizes the role and impact of corporate planning on organizational efficacy. Although, the link may be quite difficult however, there are strong arguments that the crucial test of the system's effectiveness and rationalization for its existence is the impact on organizational performance (Henry 1979).
Benefits of strategic management: The major benefit of strategic management is to facilitate organizations to devise viable policies through the use of a more systematic, logical, and rational approach to strategic choice. Communication is main factor to successful strategic management. The chief aim of the communication process is to accomplish understanding and commitment throughout the organization. It results in huge benefit of empowerment. More and more organizations are decentralizing the strategic-management process.
Financial Benefits: Numerous management Researches have revealed that organizations using strategic-management concepts are more gainful and successful than those that do not. Successful firms tend to do methodical planning to prepare for future fluctuations in the external and internal environments. Firms with planning systems more strongly resembling strategic-management theory generally exhibit superior long-term financial performance relative to their industries.
Non-financial Benefits: Strategic management provides other tangible benefits, such as an enhanced wakefulness of external threats, better understanding of competitors' strengths, increased employee productivity, reduced resistance to change, and a clearer understanding of performance-reward relationships. In addition to empowering managers and employees, strategic management often brings order and discipline to an otherwise struggling firm.
According to Greenley, strategic management has following benefits:
- It allocates for identification, prioritization, and exploitation of opportunities.
- It provides an objective outlook of management problems.
- It characterizes a framework for improved synchronization and control of activities.
- It reduces the effects of adverse conditions and changes.
- It allows major decisions to better support established objectives.
- It allows more effective distribution of time and resources to identified opportunities.
- It permits fewer resources and less time to be devoted to correcting erroneous or ad hoc decisions.
- It generates a framework for internal communication among personnel.
- It helps integrate the behaviour of individuals into a total effort.
- It provides a foundation to clarify individual responsibilities.
- It promotes forward thinking.
- It provides a cooperative, integrated, and enthusiastic approach to tackling problems and opportunities.
- It encourages a positive attitude toward change.
- It gives a degree of discipline and formality to the management of a business
Limitation
Besides numerous benefits, Strategic Management has following disadvantages:
Strategic Management is based on certain principles and if the properties do not hold suitable the strategy or plans based on them would not be sensible or effectual. SWOT analysis is an important exercise in Strategic Management which requires lot of action and information. When these two are lacking the usefulness of the SWOT analysis is questionable and it could even lead to formulation of wrong or effective strategies. In Strategic Management, effective implementation is essential that demands many factors such as resource allocation, leadership implementation, right structure and effective evaluation and control. The cause for the failure of many strategies is the implementation failure. Company may face serious issues if there is lack of involvement of the internal people in the strategy formulation and when they are not equally taken into confidence. Strategic Planning is a multifaceted and complex task which requires people with vision, expertise and commitment and an appropriate system. Strategic Management is an expensive process. Major drawback of Strategic Management is that it sometimes makes the organization over determined and resultant failure to reach the goals cause disturbance. Impractical strategies may lead to serious problems.
To summarize, Strategic management facilitate an organization to make its decisions based on long-term prediction. It also allows the establishment to make action at an early stage of new trend and consider the lead-time for effective management. The study of strategic management stresses the monitoring and evaluating of external opportunities and threats in the view of a company's strengths and weaknesses in order to create and implement innovative strategic direction for company.

