Current Affairs October 2019
For the very purpose of getting you ready for the challenge that is Current Affairs In India, we are covering the 2016 October current affairs including politics current affair, current affair news, science current affairs, general knowledge current affair, current government affair and international current affairs. Only studying India's current affairs or political current affairs is not sufficient as you have to cover international events and current affairs along with the Indian current affairs, as well as those in the field of science and sports.
Current Affairs October 20 to October 26
Indian Policy
Indian Railways : Most advanced Electronic Interlocking System has been installed on the Grand Chord route which is one of the busiest section of railways by the Indian Railways. Indian railways has made possible this achievement by replacing the 65 years old obsolete mechanical signalling system. It was installed at Tundla Junction in Uttar Pradesh by railways as part of upgradation process which will become fully functional from November 17, 2019.
Indian Railways hopes that the measure will help Indian Railways speed up trains and to achieve its future objective of reducing the travel time between Delhi and Howrah to about 12 hours from the existing 17-19 hours.
This will not only improve the punctuality of trains on New Delhi-Howrah mainline but also the work will have manifold benefits during incoming foggy season through safe and detention free handling of trains at Tundla Junction
Grand Chord : It is actually a part of the Howrah-Gaya-Delhi line and Howrah-Allahabad-Mumbai line. It acts as a link between Sitarampur in West Bengal and Pundit Deen Dayal Upadhyay Junction, Uttar Pradesh. It covers a stretch of 450 kilometres of North Central Railway (NCR) zone of Indian Railways. The new Electronic system has replaced outdated 65-year old mechanical signalling system at Tundla Junction in Uttar Pradesh on the route. It is called the lifeline of the country because important goods like coal, steel are moved from Eastern India to Western and Northern parts of India. The Grand Chord route was first opened by Lord Minto in December 1906 at Gujhandi, Jharkhand. The distance with the opening of the Grand Chord Route between Delhi and Calcutta was reduced by 80 kilometres.
Bharat Ki Laxmi : It is a new initiative by Prime Minister Modi which aims to honor women across the country who have made a mark with their extraordinary achievements in various fields. The Bharat Ki Laxmi movement underscores the cause of women empowerment.
Actress Deepika Padukone and Indian badminton player P. V. Sindhu were named ambassadors for PM"s movement ‘Bharat Ki Laxmi’.
Some of the Indian Government Schemes for Women Empowerment are :-
Mahila E-haat: It is a direct online marketing platform launched by Ministry of Women and Child Development.
Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao: It is a joint initiative run by Ministry of Women and Child Development, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Ministry of Human Resource Development.
One Stop Centre Scheme: Popularly known as ‘Sakhi‘.
Working Women Hostels
Swadhar Greh The Swadhar scheme:It is a scheme for rehabilitation of women in difficult circumstances. It was launched by Union Ministry of Women and Child Developmentin 2002.
STEP Scheme: STEP stands for ‘The Support to Training and Employment Programme for Women’.
KVIC : It refers to The Khadi and Village Industries Commission. It is a statutory body formed by the Government of India, under the Act of Parliament, 'Khadi and Village Industries Commission Act of 1956. The commission took over the works of the former All India Khadi and Village Industries Board. The objectives of KVIC are providing employment, producing saleable articles and creating self-reliance amongst the poor and building up of a strong rural community spirit. In India, the crafts sector sustains over 20 million practitioners. Handicrafts bring in good fortune with minimal investment and have good value in the international markets.
KVIC and Goa govt join hands to generate employment opportunities in Goa. They inaugurated a series of initiatives. These initiatives are first of its kind in Goa because earlier there was no spinning and weaving activity there.
Pramod Sawant, the Chief Minister of Goa, along with Vinai Kumar Saxena, Chairman, KVIC recently distributed electric potter wheels to 160 families and new models charkhas (spinning wheels) to 50 trained women. This will create direct employment to 700 people. KVIC is also establishing a Lijjat Papad unit in Goa, which will create 200 direct jobs to the local women.
AYUSH Ministry : AYUSH (Ayurveda, Yoga & Naturopathy, Unani, Siddha, Sowa Rigpa and Homoeopathy) Ministry has signed an MoU (Memorandum of UNderstanding) with the Defence ministry to provide traditional medicine services at the armed forces’ hospitals and dispensaries under health establishments of Directorate General of Armed Forces Medical Services (DGAFMS).
Minister of State for AYUSH Shripad Naik on Monday inaugurated an Ayurveda Palliative Care Unit at Palliative Care Centrethe at the Base Hospital in the Delhi Cantonment.
Under the MoU, ayurveda units will also be established at palliative care centres at the Army Research and Referral Hospital, Air Force Hospital, Hindon in Ghaziabad and five identified ex-service men Contributory Health Scheme (ECHS) polyclinics in Delhi –NCR.
The important objective of MoU is that ayurveda and yoga can help Indian soldiers who work in challenging environmental conditions right from glaciers of Siachin to desserts of Thar, which takes a toll on their physical as well as mental health can attain the best of physical and mental health, and improve their endurance. Ayurveda medicines and Panchkarma procedures such as Snehana and Swedana are very effective in treating work-related musculoskeletal disorders.
The Government of Odisha: The Government of India, Government of Odisha and the World Bank have signed 165 million USD loan agreement for the Odisha Integrated Irrigation Project for Climate Resilient Agriculture. It is a project under the National Action Plan on Climate Change of the Government of India.
The project will be implemented in rural areas vulnerable to droughts and largely dependent on rainfed agriculture. It will not only support and benefit about 125,000 smallholder farmer households from 15 districts of Odisha managing 128,000 hactres of agricultural land but will also strengthen the resilience of their production systems as well as diversify and improve the marketing of their produce, for increased income. The project will irrigate 91,435 hectares of land with the support of the project which will rehabilitate 532 water tanks.
The scheme is very important because since 2009, the frequency of droughts in the state increased from 1 in 5 years to 1 in 2 years. About 70% in 2019 of the agricultural land in Odisha a prone to droughts as compared to 40% in 1970s. Agriculture in Odisha is also responsible for about 25% of the GHG emissions in the state.
The project will help to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals of the GoI’s National Action Plan on Climate Change that largely includes adaptation of climate-smart agricultural practices and technologies.
ATVM : It refers to Automatic Ticket Vending Machine. They work on Linux software. It provides tickets to consumers after a smart card, or a specially designed card is inserted into the machine. The user has to select the route and destination and when the machine confirms the details and ticket is printed money is deducted from the card.
Indian Railways has launched 'one touch ATVM' at 42 suburban stations of Central Railway to render fast ticketing to millions of commuters over Mumbai Suburban Network. Railway passenger can now avail the service of this new machine.
The purpose of the service is that the machine will help passengers get their tickets quickly instead of waiting long hour in a queue. The features of the one touch ATVM is that a passenger can obtain ticket in two steps instead of 6 steps that was used earlier. It will also ease the load on ticketing system of Mumbai Suburban Network. The machine will also provide platform tickets.
Indian polity
Indian Railways : Most advanced Electronic Interlocking System has been installed on the Grand Chord route which is one of the busiest section of railways by the Indian Railways. Indian railways has made possible this achievement by replacing the 65 years old obsolete mechanical signalling system. It was installed at Tundla Junction in Uttar Pradesh by railways as part of upgradation process which will become fully functional from November 17, 2019.
Indian Railways hopes that the measure will help Indian Railways speed up trains and to achieve its future objective of reducing the travel time between Delhi and Howrah to about 12 hours from the existing 17-19 hours.
This will not only improve the punctuality of trains on New Delhi-Howrah mainline but also the work will have manifold benefits during incoming foggy season through safe and detention free handling of trains at Tundla Junction
Grand Chord : It is actually a part of the Howrah-Gaya-Delhi line and Howrah-Allahabad-Mumbai line. It acts as a link between Sitarampur in West Bengal and Pundit Deen Dayal Upadhyay Junction, Uttar Pradesh. It covers a stretch of 450 kilometres of North Central Railway (NCR) zone of Indian Railways. The new Electronic system has replaced outdated 65-year old mechanical signalling system at Tundla Junction in Uttar Pradesh on the route. It is called the lifeline of the country because important goods like coal, steel are moved from Eastern India to Western and Northern parts of India. The Grand Chord route was first opened by Lord Minto in December 1906 at Gujhandi, Jharkhand. The distance with the opening of the Grand Chord Route between Delhi and Calcutta was reduced by 80 kilometres.
BSNL Revival Plan : The Union Cabinet approved the revival of the ?56,000 crore merger and revival plan for crisis-ridden telecom companies- Bharat Sanchar Nigam Ltd (BSNL) and Mahanagar Telecom Nigam Ltd (MTNL). MTNL operates in Delhi, Mumbai and Mauritius while BSNL in the rest of India.
The plan entails giving suitable package comprising components like voluntary retirement scheme (VRS) and raising sovereign bonds. It also allotted the 4G spectrum to the institutions and allowed monetisation of assets available with BSNL. A four-step revival plan has been announced for BSNL. The MTNL will act as a subsidy to BSNL. The Government of India(GoI) plans to raise Rs 15,000 crore through sovereign bonds
Both the telecom firms (MTNL and BSNL) have been incurring losses and have been facing problems in clearing staff salaries in the recent past.
International
Feed our Future: It is an cinema advertising campaign against hunger and malnutrition. The ad shows the reality of millions of people facing across the world. It has been launched by United Nations (UN) World Food Programme (WFP) in collaboration with UFO Moviez – India’s largest in-cinema advertising platform and SAWA -the Global Cinema Advertising Association. The United Nations World Food Program (UNWFP) has joined hands with Bollywood in India and it is also supported by Showbox Music TV Channel, LF (Living Foodz TV Channel) and Red FM 93.5. The event took place last week on Friday via a live broadcast from the social network's Mumbai office. WFP has launched this campaign for the second time in India.
The main aim of UNWFP is to create awareness and take steps against hunger and malnutrition in India.
WFP: It refers to World Food Program. The World Food Programme(WFP) is the food-assistance branch of the United Nations(UN) and the world's largest humanitarian organization addressing hunger and promoting food security. Its headquarters is in Rome. It was established in 1961 after Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) Conference 1960. According to the WFP, for more than 80 country offices around the world, the WFP works to help people who cannot produce or obtain enough food for themselves and their families. It is a member of the United Nations Development Group and part of its executive committee.
India-Nepal : Government of India is training a batch of officers of Government of Nepal on ‘Anti Money Laundering (AML) and Countering Financing of Terrorism (CFT)’ in India at the Regional Centre of National Academy of Customs, Indirect Taxes and Narcotics (NACIN) in Bengaluru. As many as 18 Nepali officers started their training the training on Anti-Money Laundering and Countering Financing of Terrorism underway. This is the second group of Nepali officials of Nepal undergoing the training. The first group of about 20 Nepal officials successfully completed their 6-days training module on 24 August 2019. The third batch of 21 officers will undergo training in December 2019. The course is supported by Government of India under Union Ministry of External Affairs’ Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) Programme.
NACIN : It refers to National Academy of Customs, Indirect Taxes and Narcotics.It is the apex institute of Government of India for capacity building of civil servants in the field of indirect taxation, particularly the areas of customs, GST, central excise, service tax and narcotics control administration. It is not only a training institute with state-of-the-art learning facilities in field of financial investigations and anti-money laundering matters but also an accredited Regional Training Centre of World Customs Organization (WCO) for Asia/Pacific Region. NACIN works in collaboration with other international organizations like UNEP, UNODC (United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime), SASEC (South Asia Subregional Economic Cooperation) etc.,
India-US : Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi has approved the proposal for Agreement on Science and Technology Cooperation between India and the United States of America.
India and US both have good cooperation in terms of science. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) of US and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) have several information exchanging programs. The defence sector of both the countries are also cooperative in terms of technology transfer and in safeguarding the Indo-Pacific region. So,the agreement will help in opening a new chapter in bilateral relations as both sides will leverage complementary strengths spurred by a significant convergence of mutual interests in science and technology. It will provide an opportunity to promote 'high quality' and 'high impact' research and innovation partnerships as well as broadening and expanding relationships between the extensive scientific and technological communities. The agreement would not only enable cooperation between the countries in training the scientists and experts according to the requirements, they will conduct cooperative research projects .
Kartarpur Corridor : The Kartarpur Corridor is an under-construction border corridor between the neighbouring nations of India and Pakistan, connecting the Sikh shrines of Dera Baba Nanak Sahib and Gurdwara Darbar Sahib Kartarpur. It was established on 28 November 2018. Kartarpur is a town near the city of Jalandhar and is located in the Doaba region of the state. Gurdwara Darbar Sahib in Norowal district of Pakistan is where Sikh Guru Nanak Dev,the founder of Sikhism, spent last 18 years of his life. The Gurudwara was founded by the fifth Guru of Sikhs, Sri Guru Arjan Dev Ji.
India and Pakistan have signed a histori agreement to operationalise the Kartarpur Sahib Corridor to allow Indian Sikh pilgrims to visit the holy Darbar Sahib in this country. The corridor connecst the Dera Baba Nanak shrine in India's Punjab with Darbar Sahib at Kartarpur, 4 km from the international border, located at Narowal district of Pakistan's Punjab province. The agreement signing ceremony took place at the Kartarpur Zero Point at the Pakistan-India border in Narowal.
National
Azad Hind Movement : It was a part of the freedom movement, originating in 1940s outside India with a purpose of allying with Axis powers to free India from British rule. The Provisional Government of Free India or Azad Hind was established in Singapore in 1943. It was supported by the Japanese Empire, Italian social Republic, Nazi Germany and other allies. The existence of the Azad Hind Government gave a greater legitimacy to the independence struggle against the British. The Azad Hind Government, founded on 21st October, 1943 was inspired by Neta ji Subhash Chandra Bose. Netaji was the leader of Azad Hind Government and also the Head of State of this Provisional Indian Government-in-exile during the 2nd world war.
The Union Minister of Culture and Tourism Shri Prahlad Singh attended the commemotation of the 76th anniversary of Azad Hind Movement at Red Fort, Delhi. Secretary General of the INA trust, its members and other higher officials from the Ministry of Culture were also present at the commemoration.
Last year,Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi had hoisted the National Flag at Red Fort, to commemorate the 75th Anniversary of formation of Azad Hind Government, formed by Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose. The national flag was hoisted at the Red Fort as it was the same place where soldiers of the Indian National Army or the Azad Hind Fauj faced trials by the British. Prime Minister will also lay the foundation stone of a museum dedicated to the Azad Hind Fauj.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Col. Chewang Rinchen Setu : It is a bridge named in honor of Colonel Chewang Rinchan who was one of the highly decorated officers in Indian Army from Ladakh. He was also a Maha Vir Chakara awardee (1952). It has been constructed at an altitude of 14,650 feet in the forward area of Ladakh region by the Border Road Organization (BRO). The construction of the Bridge was completed within 15 working months using 6900 cubic meters of concrete and 1984 metric tons of steel. It is built on the strategically important road Durbuk Shyok Daulat Beg Oldie in sub sector north in eastern Ladakh. It is 45 km east of Line of Actual Control (LAC) with China.
Defence Minister Rajnath Singh inaugurated Col. Chewang Rinchen Setu (Bridge) and dedicated it to the nation. It is 4.5 metres wide. It can accommodate vehicles of 70 tonnes class. It will not only reduce travel time by about half but also help in development of border areas and villages across Shyok River.
Art and Culture : Union Minister of State for Culture Prahlad Singh Patel inaugurated an e-portal and a YouTube channel of Rashtriya Centre for Cultural Resources and Training (CCRT) with support from Route to Route,in New Delhi. He also attended the “Digital Bharat - Digital Sanskriti” program which was organised by Rashtriya Centre for Cultural Resources and Training (CCRT) of the Ministry of Culture. The aim of the e-portal is to take India to a newer digital pinnacle and to promote Indian culture. The portal explores and understands the unknown aspects of India’s lesser-known places and their rural and semi-urban culture.
CCRT has produced a documentary film 'Rahas' with an objective of providing knowledge and understanding of different regional cultures and Indian traditions. It has also started publishing books from the series “Untold Tales of India’s Cities” in order to explore & understand the unknown aspects of India’s lesser known places and their rural and semi-urban culture. Union Minister also released a book titled ‘Dewas Ki Sanskritik Parampara’ written by Jeevan Singh Thakur and published by CCRT.
IAF: It refers ot Indian Air Force. It has carried out successful firing of BrahMos surface-to-surface missiles the 2.5-tonne surface-to-surface missile with a range of around 300 km from a mobile platform at Trak Island in Andaman Nicobar islands. The drill was conducted on Monday and Tuesday to check the IAF's capability to hit targets with "pin-point" accuracy at targets close to 300km
BrahMos Aerospace is an India-Russian joint venture which produces the missile that can be launched from submarines, ships, aircraft, or from land platforms.
‘Ex Ekuverin – 2019 : It is a name given to the Indo-Maldives joint exercise The joint exeercise culminated on Sunday, with an impressive closing ceremony held at Foreign Training Node, Aundh military station in the city, where the joint team from the two countries executed a drill counter-terrorism operation as per the United Nations mandate. The 14-day joint training was the 10th edition of the joint military exercise which commenced on October 7.
The word ‘Ekuverin’ means ‘Friends’ in Dhivehi language. As India and Maldives share very close cultural, ethnic, linguistic, religious and have good commercial ties with eachpther, the joint Exercise Ekuverin will assist in further strengthening of these ties between two nations and to share their best practices and acquaint each other with operating procedures being followed while undertaking counter insurgency and counter-terrorism operations.
Imnex-2019 : It is a name given to India Myanmar Naval Exercise which is being organised in Visakhapatnam from 19 to 22 October in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh. The opening ceremony of the second edition of Indo-Myanmar joint naval exercise was conducted onboard INS Ranvijay.
Myanmar naval ships UMS Sin Phyu Shin (F-14) and UMS Tabinshweti (773) arrived at Visakhapatnam where it would engage in professional interaction with Indian Navy personnel for sharing of expertise on various maritime issues between both the navies. It will aslo increase scope and complexity and is a testimony of growing maritime cooperation between two navies.
The exercise would be conducted in two phases, i.e., harbour phase and sea phase.
The harbour phase includes visits to Indian Naval units, training and maintenance facility at Visakhapatnam whereas the sea phase will include joint exercise with India's Navy’s INS Kuthar, a missile corvette and INS Ranvijay, a guided-missile destroyer and Myanmar's ships UMS Tabinshweti, a corvette and UMS Sin Phyu Shin, a frigate in the Bay of Bengal.
ITBP’s 58th Raising Day : Indo-Tibetian Border Police (ITBP) celebrates 58th Raising Day. the day is observed every year on the 24th of October. The Indo-Tibetian Border Police is one of the seven Central Armed Police Forces of India. ITBP has a total strength of 56 service battalion and four specialist battalions. It was raised on 24 October 1962, under the CRPF Act in the wake of the Sino-Indian War of 1962. The ITBP was intended for deployment along India's border with Tibet.
Union Minister G Kishan Reddy attended the 58th Raising Day Parade of the Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP) at the Lakhnawali Camp in Gautam Budh Nagar.
The Union Cabinet approved the proposal of cadre review of Group 'A' General Duty (Executive) cadre and non-GD cadre of Indo- Tibetan Border Police (ITBP) resulting in creation of over 3,000 new posts, and creation of two operational commands. The Cabinet meeting chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi. this decision was taken on the eve of the ITBP’s 58th Raising Day. The two new commands that is the Western Command at Chandigarh and Eastern Command at Guwahati will be headed by Additional Director General and assisted by Inspector General. The decision will help in effective domination and control of LAC that is marred by harsh weather and high-altitude locations.
People In News
Shri K Parasaran : He is scholar, legal luminary and former Attorney General of India. He was Advocate-General of Tamil Nadu during President's rule in 1976 and then, Attorney General of India under Indira Gandhi and Rajiv Gandhi. Parasaran was awarded the Padma Bhushan in the year 2003 and Padma Vibhushan in the year 2011. In June 2012, he received a presidential nomination to the Rajya Sabha, the upper house of India's parliament. He was born in 1927.
He was conferred the 'Most Eminent Senior Citizen Award' by the Vice President Shri Venkaiyah Naidu on the occasion of Elder’s Day celebration organized by Age Care India.
Advocate General of the state : He is the highest law officer of the state. Articles 165 deals with the Advocate General of the state and Article 177 deals with rights Advocate General in respective houses. He gives advices to the government in the legal matter. He also discharges duties assigned on him by the State Government. He defends and protects the interest of the state government. The office of the Advocate General in state corresponds to the office of Attorney General of India
Attorney General: He is the chief legal advisor to Government of India. He is a primary lawyer in the Supreme Court of India. He is appointed by the President of India on the advice of Union Cabinet. Article 76 deals with the Attorney General of India.
Sanjeev Nandan Sahai is a senior IAS officer. He is a 1986-batch IAS officer of union territories (UT) cadre. He is at present serving as the special secretary in power ministry. He has been appointed as the new power secretary. The order in this regard was issued by Union Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions. He would be replacing Subhash Chander Garg who superannuates on 31 October 2019 who had sought voluntary retirement after being shunted out from the post of finance secretary soon after the budget was passed by Parliament.
Tuhin Kanta Pandey, an Odisha cadre IAS officer. He has been appointed by the Appointments Committee of Cabinet as Secretary Department of Investment and Public Asset Management.
Braj Raj Sharma, a Jammu and Kashmir 1984 cadre batch IAS officer. He has been serving as Secretary in Border Roads Organisation (BRO) under the Home Ministry. He has been appointed Chairman of Staff Selection Commission.
Pankaj Kumar, a 1987 batch IAS officer. He will be the new CEO of Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI) which issues Aadhaar. He has been appointed Minority Affairs Secretary.
Pramod Kumar Das, a Madhya Pradesh Cadre IAS officer. He has been appointed Minority Affairs Secretary.
Sanjeev Gupta, a Himachal Cadre IAS officer. He will be the Secretary, Inter-State Council Secretariat while Minority Affairs Secretary Sailesh will be Secretary in the department of public enterprises, the ministry of heavy industries and public enterprises.
Alok Tandon, a 1986 batch officer will be Secretary in Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances and Nagendra Nath Sinha will be Secretary, Department of Border Management in the Home Ministry.
Rajesh Bhushan will be Secretary (Coordination) in the Cabinet Secretariat.
Nagendra Nath Sinha appointed NHAI Chairman- He is a 1987 batch IAS officer as the Chairman of National Highways Authority of India (NHAI). He is will take Sharma’s place in BRO.
Anil Kumar Khachi has been removed from the post of secretary, the department of investment and public asset management (DIPAM).
Emperor Naruhito: He is the Emperor of Japan. He is the 126th monarch according to Japan's traditional order of succession. He is an honorary member of the World Commission on Water for the 21st century and patron of the Global Water Partnership, established by the World Bank, the United Nations, and the Swedish Agency of Development. His birthday which falls on 23 February is named "Mount Fuji Day" because of his reported love of the mountain. Naruhito on 23 February 1991 was invested as the Crown Prince with the title 'Prince Hiro.' Naruhito, the first Japanese emperor born after WWII acceded to the Chrysanthemum Throne on 1 May 2019, beginning the Reiwa era, following the abdication of his father, Emperor Akihito.
President Ram Nath Kovind on Tuesday attended the enthronement ceremony of Japan's new Emperor Naruhito, 59, who completed his ascension to the Chrysanthemum Throne after his father's abdication earlier this year. The ceremony was attended by nearly 2000 guests including dignitaries from more than 180 countries international organizations. the ceremony was also attended by UK's Prince Charles. The 30-minute ceremony was held in the Imperial palace. The ceremony featured elements of ancient protocol which was immersed in the traditions and glory of a monarchy that claims 2,000 years of history
Places In News
Ladakh :The Government on Monday announced that Siachen area, the world's highest battlefield, is now open to tourists. The entire area from Siachen base camp to Kumar Post for tourism purposes has been opened.Defence Minister Rajnath Singh made the announcement on Siachen while inaugurating newly constructed ‘Colonel Chewang Rinchen Bridge’ over Shyok River in Eastern Ladakh.The main objective of the government is to boost tourism in Ladakh as well as to showcase and give people a window to appreciate the tough work done by Indian Army jawans and engineers posted in the extreme weather and inhospitable terrains.
Siachin Glacier : The Siachen Glacier is a glacier located in the eastern Karakoram range in the Himalayas at about 35.421226°N 77.109540°E, just northeast of the point NJ9842 where the Line of Control between India and Pakistan ends. It is the world's highest battlefield.
Egypt : Egypt : A team of Egyptians archaeologists find rare trove of 30 ornately decorated ancient wooden coffins 'belonging to family members of high priests' in Egypt's Valley of Kings. It was discovered at Asasif, a necropolis on the west bank of the River Nile near the Hatshepsut Temple. It is the first large human coffin cache ever discovered since the end of the 19th century. The wooden coffins of men, women and children were found just three feet underground stacked in two rows. The sarcophagi date back to the 22nd Dynasty, founded around 3,000 years ago in the 10th century BC. Despite their age, black, green, red and yellow paintings of snakes, birds, lotus flowers and hieroglyphics that cover the coffins are still clearly visible.
Indonesia : Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia. It is a country in Southeast Asia, between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It is the world's largest island country, with more than seventeen thousand islands, and at 1,904,569 square kilometres, the 14th largest by land area and 7th in the combined sea and land area.
Joko Widodo, the incumbent Indonesian President, won last month’s election by a comfortable 10% margin over his rival, retired General Prabowo Subianto, the country’s election commission announced early on Tuesday.
Mr Widodo is a moderate Muslim and popular reformist leader of Indonesia. He is also known as Jokowi. He is an Indonesian politician who is the seventh president of Indonesia. He is the first president elected in July 2014 who has not to come from an elite political or military background. He was previously the Mayor of Surakarta from 2005 to 2012, and the Governor of Jakarta from 2012 to 2014.
Abu Dhabi: An 8000 year old natural pearl has been discovered on an island off Abu Dhabi, the capital of the United Arab Emirates. According to the archeologists, it is said to be the world's oldest pearl. It was discovered by Abu Dhabi archaeologists during excavations at Marawah Island, off the capital of the United Arab Emirates. The natural pearl was found in the floor of a room discovered during excavations. The discovery of the natural pearl also revealed the earliest architecture found in the coountry.
Abu Dhabi's Department of Culture and Tourism said that the layers from which the pearl came have been carbon dated to 5800-5600 BC, during the Neolithic period. It has been dubbed as the ‘Abu Dhabi Pearl’.
As per the Emirates News Agency, the discovery is a proof that pearls and oysters were being used in the UAE nearly 8,000 years ago, and represents the earliest known evidence for pearling yet discovered anywhere in the world. Before this discovery, the earliest known pearl was found in a Neolithic site in Umm Al Qaiwain. Ancient pearls have also been found at a Neolithic cemetery close to Jebel Buhais, in the Emirate of Sharjah.
Marawah Island: It is a low-lying island off the coast of the Western Region of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi, the United Arab Emirates. Although privately owned, the island is a key center of archaeology. Marawah Island’s neolithic sites were first identified in 1992 during a survey carried out by the Abu Dhabi Islands Archaeological Survey (ADIAS). Subsequent excavations have shown them to include numerous collapsed stone structures, the earliest architecture yet discovered in the UAE. Archeologists identified 13 sites dating from the Neolithic to the Islamic Period (12-13 AD)
Canada : Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau won a second term on Monday, but he lost his majority in Canada's parliament. He won a narrow victory to form minority government. He has led the Liberal Party of Canada in 2015 and formed a majority government, which he won by defeating then-Prime Minister Stephen Harper and the Conservative Party of Canada. He has been prime minister since November 4, 2015. He has also stood for election to the House of Commons of Canada four times and was elected each time (2008, 2011, 2015, 2019). Trudeau was elected leader of the Liberal Party in 2013, succeeding Michael Ignatieff, who retired from politics after losing the general election of 2011.
Uttar Pradesh : The Yogi Adityanath cabinet approved the budget for construction of boundaries of Ramlila grounds across the state and allocated funds in the supplementary budget announced on Monday. Along with boundaries of Ramlila Grounds, cow shelters were also included in the supplementary budget.
The Culture Department of Uttar Pradesh government is going to organise the country’s first training and performance programme of world famous KHON Ramlila in collaboration with Thailand government on the 26th of October 2019. The participant artists will be trained by experts of KHON Ramlila in Thailand as part of the cultural exchange program between the two countries. The artists will perform at Grand Deepotsav function in Ayodhya. The Kohn Ramlila festivities of Thailand were declared as one of the 'Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity' in 2008 by by UNESCO.
KHON Ramlila: It is a masked form of Ramlila art of Thailand. It is a dance form depicting the scenes of Ramlila. There are no dialogues and background voices narrate the whole story of Ramayana. It is famous for its beautiful attire and golden masks.
Science and Technology
New Kiln technology : It is a technology where in the new kilns, the bricks that are to be baked are arranged in a zigzag pattern, allowing hot air to cover a longer path, unlike in traditional kilns, where the bricks were arranged in straight lines. As the air takes this zigzag path, it improves the heat transfer to the bricks, thus making the operation more efficient. The mixing of air and fuel in the new kilns allows for complete combustion, thus reducing coal consumption by about 20 per cent. The new kilns also use fans to regulate air. The new Kiln Technology not only cuts the emissions by 70-80% but also saves fuel for the users.
Bringing down pollution from brick kilns in the National Capital Region during winter turned out to be a major challenge for the Supreme Court-appointed Environment Pollution (Prevention and Control) Authority (EPCA).
The kiln industry in Punjab's kiln industry employs about 5 lakh workers and it contributes to 8% of brick production in the country producing 15-20 billion bricks. The pollution caused by Stubble burning and industrial and kiln smoke in Punjab and Haryana in northwest India has been cited as a major cause of air pollution in Delhi. Smoke from this burning produces a cloud of particulates visible from space, and has produced a "toxic cloud" in New Delhi, resulting in declarations of an air-pollution emergency.
The Punjab government after following orders from the National Green Tribunal (NGT) and guidelines from the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), ordered traditional kilns to stop operating by March 2019 to control the toxicity of the National Capital Region(NCR). The new technology is being implemented by the DST. Punjab has been successful in cutting emissions by an estimated 70 per cent. Districts such as Barnala and Sangrur have seen 100 per cent conversion to the new technology. The Department of Science and Technology (DST), through the Punjab State Council for Science and Technology, is providing technical assistance for the conversion.
New Catalyst : A new catalyst has been developed by the Engineers at the Stanford University that convert carbon dioxide from car exhaust pipes and other sources into natural gas or propane. The researchers succeeded in developing the new catalyst by combining ruthenium and iron oxide nanoparticles. The ruthenium nuggets sit in the core of the catalyst surrounded by an outer sheath of iron. This structure activates hydrocarbon formation from CO2 thus yielding four times as much fuel as previous approaches.
Catalyst : It is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself undergoing any permanent chemical change.
Ruthenium : It is a chemical element with the symbol Ru and atomic number 44. It is a rare transition metal belonging to the platinum group of the periodic table. Like the other metals of the platinum group, ruthenium is inert to most other chemicals
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Fire Resistant Lithium-Ion Batteries : Scientists at John Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, US, have developed Lithium-Ion batteries that wont catch fire. The batteries can operate under extreme conditions like submersion, ballistic impact, cutting and heat..
Lithium-Ion Batteries : A lithium-ion battery or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used for portable electronics and electric vehicles. It is also used in every household item starting from smartphones which are susceptible to catastrophic fire and explosion. Due to this, many phones are banned from airlines and ships. The US Navy had also prohibited the use of e-cigarettes on ships and submarines because of the danger the batteries possessed.
Govt Attempt to AFRS : It refers to National Automated Facial Recognition System (AFRS). It is Biometric Artificial Intelligence based application that can uniquely identify a person by analysing patterns based on the person's facial textures and shape. It is capable of identifying or verifying a person from a digital image or a video frame from a video source. There are multiple methods in which facial recognition systems work, but in general, they work by comparing selected facial features from given image with faces within a database.
The Government of India in an plan to curb soaring crime rates has started working on installing the building the world's biggest facial recognition system that is a centralized database – accessible to police across all states of the country that would match images from the network of CCTV cameras against a database encompassing criminal records. Many states, including Andhra Pradesh and Punjab, had adopted the facial recognition technology in 2018 to fight crime. National Crime Records Bureau has sought tenders to procure a facial recognition system.
New Dielectric capacitor : It is a device that can store 30 times more energy than best-performing commercially available dielectric capacitor. The researchers, including those from Queen Mary institute of London in the United Kingdom, have developed a new dielectric capacitor- a device that stores energy like a battery, taking inspiration from a French pastry, croissant which is made by folding multiple layers of dough. They found that by pressing and folding a polymer film capacitor (a capacitor with an insulating plastic film), they were able to store 30 times more energy than the best-performing commercially available dielectric capacitor.
According the the study published in the journal Nature Communications, the new dielectric capacitor is the highest energy density ever reported in a polymer film capacitor. The advance may pave the way for efficient, low-cost, and environmentally-friendly electric energy storage systems for wind and solar sources. As storing energy can be tricky, expensive and problematic especially with renewable energy sources, large amounts of renewable energy can be stored with the help of this new technique to be used when the sun is not shining and it is not windy. The study also noted that dielectric capacitors generally have ultrahigh power density making them suitable for technologies such as motor drives, and space vehicle power systems. These require accumulating energy over a period of time and then releasing it very quickly.
Until now, such capacitors were limited by the low amounts of energy they could store. This finding promises a significant impact on the field of pulse power applications and could produce a step-change in the field of dielectric capacitors, so far limited by their low energy storage density.
Plutonium : It is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation states. It is very unstable, which is of course what makes it both an incredibly powerful source of energy and a potentially-devastating environmental disaster. Some isotopes of plutonium can persist for tens of millions of years, which is bad news if it gets into the groundwater.
For the first time, an International team of scientists, led by Helmholtz Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) have accidentally discovered a new compound of plutonium (a radioactive chemical famously unstable for transport, storage and disposal) with an unexpected, pentavalent oxidation state, using the ESRF in France. The team was actually in the process of creating Plutonium Dioxide nano particles using different precursors. In the process, the plutonium at its pentavalent state showed a peculiar behavior. The scientists then learnt that the strange behavior of Plutonium at its pentavalent state was because it was stable! The team confirmed its stability using Pu M4 edge technology. the scientists repeated this experiment after 3 months and the element showed the same behavior, thus, confirming that Plutonium exhibited stability properties at its pentavalent state. The discovery of the new phase of plutonium could lead to new ways to tackle some of the challenges in handling the powerful compound.
Cosmic Ray Observatory : A huge cosmic ray observatory named High-Altitude Air Shower Observatory (LHAASO) is being constructed at China's southwest Sichuan Province. It is located in the mountains of the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau at an average altitude of 4,110 meters. Research teams from Australia and Thailand and other countries will participate in the project directly.
The cosmic ray observation station LHAASO covers an area equivalent to 200 soccer fields. The rocks left from Ice Age were blasted for the construction. Many different types of detectors are being installed to form a huge "net" to catch the particles generated by cosmic rays in the atmosphere, to help scientists study both the micro and the macro worlds in the universe. Three huge underground pools are to hold the detectors that will collect high energy photons generated by remote celestial bodies as well as 12 telescopes will be erected to conduct high-precision measurement of cosmic rays with the highest energy.
As per Cao Zhen, chief scientist of LHAASO and a researcher at the Institute of High Energy Physics (IHEP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences the observatory is due to be finished at the end of this year, and the whole project completed by June 2021.
Cosmic rays are highly penetrative rays from outer space. Their collisions with atmospheric particles create a variety of different particles, including neutrons, mesons and hyperons so the detection of ray showers will help pinpoint the sources of the rays and help decode the origins of the universe, solar activity and Earth's space environment. So the main objective of LHAASO is to search for the origin of cosmic rays, and study their acceleration and transmission mechanisms. The cosmic rays can be used for applications outside astronomy.
In 2017, a void was found at the The Great Pyramid of Giza using cosmic rays by a team of scientists.
Sports
Cricket : Indian cricketer Rohit Sharma, during his incredible knock at Ranchi on Sunday broke the record of Sir Donald Bradman in the third and final Test against South Africa on Sunday. He scored his maiden double century (212). He has an average of 99.84 whereas Sir Donald Bradman of Australia has 98.22.
Rohit Gurunath Sharma is an Indian international cricketer who plays for Mumbai in domestic cricket and captains Mumbai Indians in the Indian Premier League as a right-handed batsman and an occasional right-arm off break bowler.
India completed a clean sweep in the three Test series against South Africa, winning the third and final Test in Ranchi on Tuesday (October 22) by an innings and 202 runs.
International under–21 men's field hockey tournament : The Indian junior men's hockey team lost to Great Britain by 1-2 defeat in the International under–21 men's field hockey tournament final. Great Britain scored 20 seconds before full time and won the Sultan of Johor Cup 2019 held at Johor Bahru in Malaysia.
Sultan of Johor Cup : The Sultan of Johor Cup is an annual, international under–21 men's field hockey tournament held in Malaysia. Since the first edition held in 2011, five teams have emerged victorious. India and Australia have won the tournament twice, Germany and Malaysia have won the tournament once.
Champions League : The UEFA Champions League is an annual club football competition organised by the Union of European Football Associations and contested by top-division European clubs, deciding the best team in Europe.
Slavia Prague vs Barcelona: Lionel Messi's Historic Goal Helps Barcelona Edge a spirited Slavia Prague 2-1 on Wednesday to stay top of Champions League Group F. Messi opened the scoring after three minutes, beating Slavia goalkeeper Ondrej Kolar with a low left-footed shot to become the first player ever to score at least once in 15 consecutive Champions League seasons.
Wushu World Championship : The World Wushu Championships (WWC) is the official world championship event that is hosted by the International Wushu Federation. First held in 1991, the WWC takes place biennially and is the official pinnacle championships of the IWUF, featuring the highest competitive level within the sport of wushu. This official international Wushu competition sees many countries from around the world participating. Wushu originated in China.
Wushu Sanda : It is a Chinese martial art which combines full-contact kickboxing, including close-range punches and kicks, with wrestling, throws, takedowns, kick catch and sweeps. It is a Chinese self-defense system and combat sport. Wushu Sanshou or Wushu Sanda originated in China.
Praveen Kumar became the first Indian man to win a Wushu World Championships gold, beating Russel Diaz of Philippines in the 48kg category in Shanghai. The Indian saw off his Filipino opponent 2-1 in the men's Sanda event of the 15th World Wushu Championships.
The other Indian winners were Poonam in women’s 75kg category and Sanathoi Devi in women’s 52kg category secured silver medals. Vikrant Baliyan bagged bronze in men’s 60kg category.
In 2017, Pooja Kadian became the first Indian to be crowned world champion in wushu after she defeated Evgeniya Stepanova of Russia in the women's 75 kg sanda event.
French Open : It is an annual Badminton tournament held in France since 1909 and hosted by the Fédération française de badminton (FFBa). Batminton World Federation (BWF) categorised French Open as one of the five BWF World Tour Super 750 events as per new BWF events structure since 2018.
The Indian pair of Satwiksairaj Rankireddy and Chirag Shetty have advanced to the semi-finals of the ongoing French Open in Paris. The duo defeated Denmark's pair of Kim Astrup and Anders Skaarup Rasmussen 21-13, 22-20 in the quarter-finals. The Indian duo, who had claimed their maiden Super 500 title at the Thailand Open in August this year will take on the winner of the men's doubles clash between third seed Li Jun Hui-Liu Yu Chen of China and Hiroyuki Endo-Yuta Watanabe of Japan.
Saina Nehwal was knocked out of the French Open as she lost her quarter-final match against South Korea's An Se Young 20-22, 21-23 and Indian shuttler PV Sindhu too was knocked out of the ongoing French Open after she lost lost her quarter-final match against South Korea's An Se Young 20-22, 21-23.
Rugby World Cup : Rugby union, widely known simply as rugby, is a contact team sport which originated in England in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. The 2019 Rugby World Cup is the ongoing ninth Rugby World Cup, the quadrennial rugby union world championship.
The opening match of the 2019 Rugby World Cup took place at Tokyo Stadium in Chofu, Tokyo and the final match will be held at International Stadium Yokohama in Yokohama, Kanagawa Prefecture by World Rugby. Reigning champions New Zealand and England, ranked second will clash in a heavyweight Rugby World Cup semi-final for the spot in the finals. The All Blacks are defending a record 18-match World Cup winning streak dating back 12 years as they look to cement the legacy of departing coach Steve Hansen with their third straight title, and fourth overall.
Environment
Melting of ice glaciers : glaciers are melting at an alarming rate because of ongoing global warming. As the average global temperature increases, glaciers melt and retreat back up the valleys they flowed down. When glaciers disappear, the landscape stops being eroded by tons of ice and starts to be reclaimed by plant and animal life. With enough glacial melt, sea levels and landmasses can rise and fall.
The Russian Navy confirmed the discovery of five new islands. The new islands are located near the Vylki glacier off the coast of the remote Novaya Zemlya archipelago, which lies in the Arctic Ocean northwest of the Russian mainland. They range in area from 900 to 54,500 square meters (about 9,690 to 586,630 square feet) as big as 10 football fields.
As per Vice-Admiral Alexander Moiseyev, the head of the northern fleet. the melting, collapse and temperature changes led to these islands being uncovered. The islands are yet to be named.The Navy first spotted the islands in 2016 using satellite imagery, but only confirmed and mapped them in August and September during an expedition to the site.
Ozone : It is a highly reactive molecule comprised of three oxygen atoms that occurs naturally in small amounts. Roughly seven to 25 miles above Earth’s surface, in a layer of the atmosphere called the stratosphere, the ozone layer is a sunscreen, shielding the planet from potentially harmful ultraviolet radiation that can cause skin cancer and cataracts, suppress immune systems and also damage plants. Unfortunately, Ozone hole was created by the depletion of ozone in the atmosphere. The cause for the depletion was chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and halons—gases formerly found in aerosol spray cans and refrigerants which are released into the atmosphere and caused chemical reactions that break down ozone molecules,thus, reducing ozone's ultraviolet radiation-absorbing capacity. This led to thinning of the Ozone layer in the Southern Hemisphere. Apart from the chlorine compounds in refrigerators and aerosols,the climate change is also the cause of the Ozone depletion.
Researchers at the British Antarctic Survey discovered the ozone hole in 1985, and NASA’s satellite estimates of total column ozone from the Total Ozone Mapping Spectrometer confirmed the 1985 event, revealing the ozone hole’s continental scale. soon after the discovery, The International Montreal Protocol was framed in 1987.
It is the protocol ratified at the United Nations that bans chlorine compounds in refrigerators and aerosols.
NASA reported that ozone hole near south pole is in its smallest size since it was discovered. In 2006, the hole was 10.3 million square miles. However, recently it has reduced to 3.6 million square miles. Scientists say that the hole is smaller than it was found in 1985.
International Snow Leopard Day : International Snow Leopard Day is an annual holiday celebrated in different countries across the world. It is dedicated to saving one of the rarest wild cats on the planet. It is celebrated on the 23rd of October every year.
Project Snow Leoard is an initiative of the Union Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC). It aims to safeguard and conserve India’s unique natural heritage of high altitude wildlife populations and their habitats by promoting conservation via participatory policies and actions. There are about 400 to 700 snow leopards spread across Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim.The Snow Leopard Population Assessment in India (SPAI) will contribute to global ‘Population Assessment of the World’s Snow Leopard’s (PAWS) initiative.
Union Minister Prakash Jawadekar, on the occasion of International Snow Leopard Day, launched the country’s first national protocol for enumerating the population of snow leopards, an elusive predator found in the higher reaches of the Himalayas and other mountain ranges of Asia. It was announced at the inaugural session of 4th steering committee meeting of Global Snow Leopard and Ecosystem Protection Program (GSLEP), held in New Delhi. Conservation efforts and reviewed steps to be taken for future protection of the high-altitude predator was discussed by the delegates from countries including Nepal, Bhutan and Mongolia,in the GSLEP. It was decided that all Snow leopard range countries work together and enumerate the number of snow leopards and to strive to double snow leopard population in the coming decade.
Snow leopards : The snow leopard, also known as the ounce. The scientific name of the snow leopard is Panthera uncia. It is a large cat which live primarily in the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia. They are built for the cold and spend their lives crossing thousands of kilometres to feed and breed. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because the global population is estimated to number less than 10,000 mature individuals and is expected to decline about 10% by 2040. They are extremely difficult to spot thus making it difficult to accurately estimate their population.
Economics
BHIM : It refers to Bharat Interface for Money. It is a mobile payment App developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), based on the Unified Payments Interface (UPI). It is named after B. R. Ambedkar and was launched on 30 December 2016. Its aim is to to facilitate e-payments directly through banks as part of the 2016 Indian banknote demonetisation and drive towards cashless transactions. It is in line with government’s vision of Digital India.
Union Minister of Electronics and Information Technology (MeiTY) Ravi Shankar Prasad unveiled a slew of new initiatives and programmes including BHIM 2.0 upgraded version of BHIM with new functionalities, supports additional languages and has increased transaction limits on October 21. He also launched new initiatives that included MeitY Startup Hub (MSH) portal, Indian Software Product Registry and selected Incubation Centres under Technology Incubation Development for Entrepreneurs 2.0 (TIDE 2.0) at IT Ministry's MeitY Start-up Summit. The summit was a platform for start-ups and an opportunity to expand business plans.
BHIM 2.0 : It is a new upgarded version of BHIM. Additional features have been added to BHIM 2.0 making it more effective and useful. It supports three additional languages- Konkani, Haryanvi and Bhojpuri, over and above existing 13 and also enhanced transaction limits. The new developments in the application includes increasing the transaction limit, linking multiple bank accounts, offerings from shopkeepers, the option of applying for an Initial Public Offerings (IPO), gifting money and much more. The application also comes equipped with a dedicated gateway for donations.
TIDE 2.0 : It is aimed at strengthening nearly 2000 technology startups in areas of national concern by taking advantage of emerging technologies as well as empowering 51 incubation centers across the India. It will also digitally map innovative products by small entrepreneurs and artisans in villages across India.
Indian Railways : The Indian Railways, in a bid to increase revenue through the non-fare sources, has decided to allow carriage to goods of e-commerce giant Amazon on a pilot basis for three months during the non-peak hours. Under the pilot project initially about 7 MT of consignment per day will be carried. The project was earlier launched by the Eastern Railways for the first time in India when it allowed the Amazon consignments in its EMU local (suburban services). The partnership is the first in the e-commerce industry to enable the Railways build an e-commerce product for freight transport via rail.
According to Railway Ministry officials this project is likely to benefit both railways and e-commerce companies if implemented permanently. The growing e-commerce market will benefit railways as this will generate further revenue possibilities without putting any additional stress or burden on existing system whereas help the e-commerce giants in reducing transit time. The parcel business of Indian Railways will get a major boost.
Arts
Kamakhya Temple: The Kamakhya Temple also known as Kamrup-Kamakhya temple or Kamakhya Devalaya. The temple had been built in reverence to Goddess Kamakhya who is an important Hindu Tantric goddess of desire or Sati, who was one of the numerous incarnations of Goddess Durga or Goddess Shakti. She evolved in the Himalayan hills and she is worshiped as Siddha Kubjika. She is also identified as Kali and Maha Tripura Sundari. Her name means "renowned goddess of desire," and she resides at the presently rebuilt Kamakhya Temple in 1645 C. The priests believe the temple existed from the time of The Mahabharata. It is one of the oldest of the 51 Shakti Pithas. The temple built in the Nilachal type of architecture was created by the Mlechchha dynasty and was rebuilt by Koch King Nara Narayan and Ahom kings. It was completed in the 8th-17th century. The temple remains closed for three days during the mela for it is believed that mother earth becomes unclean for three days like the traditional women's menstrual seclusion.
Recently, Kamakhya Devalaya Management Committee in a press meet held at Kamakhya premisis announced that the biggest religious congregation of eastern India, the Ambubachi Mela, which is held at Kamakhya Temple in Guwahati every year is cancelled due to the outbreak of Corona Virus. For the first time in recorded history, the annual Ambubachi rituals at the sacred Kamakhya temple in Guwahati are wearing a deserted look. Even during the height of historic Assam Agitation or anti-immigrants’ agitation of early 1980s, the temple had the Mela although the turnout of devotees was very low.
The rituals of Ambubachi Mahayog was performed by the priests of the temple by maintaining the social distancing norms. The Mahayog will be performed at the Devalaya from 07:53:15 am- 22nd June to 8:16:55 pm- 25th June.
Ambubachi Mela: Ambubachi Mela is an annual Hindu mela held at Kamakhya Temple in Guwahati, Assam. It is a four-day fair to mark the annual menstruation of the goddess at Kamakhya temple. It is believed that the presiding goddess of the temple, Devi Kamakhya, the Mother Shakti, goes through her annual cycle of menstruation during this time stretch. This mela is celebrated during the monsoon season that happens to fall during the Assamese month Ahaar, around the middle of June when sun transit to the zodiac of Mithuna, when the Brahmaputra river is in spate. There is a strong belief that during the monsoon rains, the creative and nurturing power of the 'menses' of Mother Earth becomes accessible to devotees at this site during the mela. There is no idol of the presiding deity but she is worshipped in the form of a yoni-like stone instead over which a natural spring flows.
This celebration attracts lakhs of devotees and pilgrims from all the corners of the globe. This is a significant source of revenue for the temple and the state as well.
Rath Yatra: Ratha Yatra is also called as Car Festival or Chariot Festival. It is a Hindu festival associated with Lord Jagannath held at Puri in the state of Odisha, India. It is the oldest Ratha Yatra taking place in India and the World, whose descriptions can be found in Brahma Purana, Padma Purana, and Skanda Purana and Kapila Samhita. This annual festival is celebrated on Ashadha Shukla Paksha Dwitiya (second day in bright fortnight of Ashadha month). The festival commemorates Lord Jagannath's annual visit to Gundicha Temple via Mausi Maa Temple (maternal aunt's home) near Saradha Bali, Puri. Three richly decorated chariots, resembling temple structures, are pulled by devotees through the streets of Puri who consider this as an auspicious deed.
As part of Ratha Yatra, the deities Lord Jagannath, his elder brother Lord Balabhadra and younger sister Devi Subhadra, along with Sudarshan, are taken out in a procession out of the main shrine of Jagannath Temple and placed in the Ratha (Chariot) which are ready in front of the Temple. This process is called as 'Pahandi'. The procession starts with 'Madan Mohan' then 'Sudarshana' Balabhadra, Subhadra, and Jagannath Deva. After that, Gajapati Maharaja, the king of Puri, who is also known as the first servitor of the Lords, does 'Chhera Pahanra' (the holy cleaning of the chariots). Finally, the devotees pull the chariots up to the Gundicha Temple, which is also known as the birthplace of the Lords. The deities remain there for nine days and return back to the Main temple. The return journey of Puri Jagannath Ratha Jatra is known as Bahuda Jatra.
Recently, after the Supreme Court lifted its June 18 ban on the conduct of Puri Jagannath Rath Yatra after ensuring a complete lack of public attendance for the festival to avoid spread of infection amid the pandemic, for the first time ever, the annual Rath Yatra was performed in the absence of devotees amid COVID-19 restrictions. Chariots of Lord Jagannath, Lord Balabhadra, Devi Subhadra have reached Gundicha temple where hundreds of servitors and police personnel pulled the chariots of three Lords. They were permitted to do that only after they had tested negative for Covid-19.
Earlier, the Supreme Court has placed several conditions, including the imposition of a curfew in Puri during the festivities.
FÊTE DE LA MUSIQUE: The day is also popularly referred to as Fete de la Musique, French for Make Music Day or World Music Day. It is an annual celebration that was founded by Jack Lang and Maurice Fleuret in 1981 in Paris. It is celebrated on June 21. Free concerts are organized every year across the globe to make music accessible to all. It began in France in 1982. In 1981 French Minister of Culture Jack Lang conceived the idea. Since then the day has been celebrated every year as the World Music Day. It was so popular that is spread worldwide and people in every country celebrate music in their own unique way. The World Music Day is celebrated to promote peace and spread goodwill through music.
Recently, World Music Day 2020 was celebrated mostly indoors due to the COVID-19 pandemic. It is being celebrated along with Father's Day and International Yoga Day.
Cannes Film Festival: The Cannes Festival, until 2003 called the International Film Festival and known in English as the Cannes Film Festival and French as the Festival de Cannes, is an annual film festival held in Cannes, France, which previews new films of all genres, including documentaries, from all around the world. It was founded in 1946, the invitation-only festival is held annually (usually in May) at the Palais des Festivals et des Congrès. The main objective of this festival is to draw attention to and raise the profile of films with the aim of contributing towards the development of cinema, boosting the film industry worldwide and celebrating cinema at an international level.
Recently, Indian Participation at Cannes Film Festival 2020 began with the e-inauguration of the Virtual India Pavilion. The Festival will be held from 22-26 June 2020. The Virtual India Pavilion was e-inauguration by Minister of Information & Broadcasting Prakash Javadekar at the 1st Online Edition of Cannes Film Market 2020. He also launched the poster and information booklet for the 51st International Film Festival of India (IFFI) , slated to held in Goa from the 20th of November this year.
During the e-inauguration, he not only highlighted government's initiative of instituting Film Facilitation Centres for granting quick and easy clearances for shooting of International Films in the Country but also called upon global film makers to shoot movies in India and produce them for the global market. The Indian pavilion at Cannes Film Market has been jointly set up by Ministry of Information and Broadcasting and FICCI.
This year, India has sent two films for screening during the festival, namely: MaiGhat: Crime No 103/200 (Marathi) and Hellaro (Gujarati) which are National Film Awad Winners.
Cannes Film Festival had earlier postponed its 73rd edition of this year due to the Coronavirus pandemic. It is now being held virtually as a five day festival, which will culminate on 26 June 2020.
Economics
NIPFP: It refers to the National Institute of Public Finance and Policy. NIPFP is an autonomous body set up jointly by the Ministry of Finance, the erstwhile Planning Commission, and several state governments. It was founded in 1976 and is registered under the Societies Registration Act, 1860. It maintains an independent non-government character and pursues research in public policy, advising the Central government as well as states. Its Governing Council includes the Revenue Secretary, Economic Affairs Secretary and the Chief Economic Advisor from the Union Finance Ministry, besides representatives from Niti Aayog, RBI and three state governments.
Recently, Urjit Patel has been appointed as the chairman of the (NIPFP), India’s premier economic think tank. He was appointed almost 18 months after his early exit as Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Governor. He will be replacing former bureaucrat Vijay Kelkar, who chaired the institution for almost six years.
Co-operative Banks: Co-operative banks are the banks whose main objective is to provide financial assistance to economically weaker sections of the society. They are cooperative societies registered under co operative societies act and having license under Banking Regulation Act from RBI and they are owned by individual share holders from Public. These banks are governed by the Banking Regulations Act 1949 and Banking Laws (Co-operative Societies) Act, 1955 and regulated by RBI. These institutions play a crucial role in financial inclusion and cater to both rural and urban areas.
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved an ordinance to bring Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs) and Multi-state cooperative banks (MSCBs) under RBI supervision. This was announced by Union Information and Broadcasting Minister Prakash Javadekar during a virtual press meet on 24th June, 2020. The ordinance has been passed with a view to protect the depositors.
The decision was taken by the Government following the financial irregularities of the Punjab $ Maharashtra Cooperative (PMC) bank. The ordinance will immediately come into effect from the date of signature of the President of India.
Earlier, the Finance Minister, on 1st February 2020, during her Budget Speech had announced that the Cooperative Banks will be brought under the Supervision of RBI. The amendment Bill was cleared by the Cabinet on 5th February 2020 following which the Banking Regulations (Amendment) Bill, 2020 was introduced in Lok Sabha on 3rd March 2020. However, the Bill could not be passed as the Budget Session was curtailed due to the outbreak of the global COVID-19 pandemic.
AHIDF: It refers to Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund. The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) has recently approved setting up of Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund worth Rs. 15000 crore. The fund has been proposed as a part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat that was announced by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharam to revive economic growth.
AHIDF is expected to incentivize infrastructure investments in dairy, meat processing and animal feed plants.
The fund aims to provide loans at subsidized interest rate to State Governments / UTs and State entities, cooperatives, individuals and entrepreneurs etc., for taking up of the identified investment activities of fisheries development.
The eligible beneficiaries under the scheme include farmer producer organisations (FPOs) and MSMEs, Section 8 Companies, Private Companies and individual entrepreneur with minimum 10% margin money contribution by them.
The balance 90% would be the loan component which is to be made available by scheduled banks.
Centre will provide 3% interest subvention to eligible beneficiaries. There will be 2 years moratorium period for principal loan amount and 6 years repayment period thereafter. GoI would also set up Credit Guarantee Fund of Rs. 750 crore to be managed by National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD). Credit guarantee would be provided to those sanctioned projects which are covered under MSME defined ceilings.
Guarantee Coverage would be upto 25% of Credit facility of borrower.
Shishu Loan: Sishu Loans are those loans extended for income generating activities up to Rs 50,000 under Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY), The Member Lending Institutions such as Scheduled Commercial Banks, Non Banking Finance Companies and Micro Financial Institutions, registered with Mudra Ltd are responsible for extending the above loans. This initiative aims to promote entrepreneurship among the new generation aspiring youth. It is to ensure that more focus is given to Shishu Category Units and then Kishore and Tarun categories.
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the scheme for interest subvention of 2% to all Shishu loan accounts given under Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY) to eligible borrowers. The scheme would be operated by Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) for a period of 12 months.
PMMY: It refers to the Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana. PMMY was launched in April, 2015 with an objective to refinance collateral-free loans given by the lenders to small borrowers. Mudra’s unique features include a Mudra Card which permits access to Working Capital through ATMs and Card Machines.
Under PMMY, loans for income generating activities up to Rs. 50,000 are termed as Shishu loans. PMMY loans are extended by Member Lending Institutions viz. Scheduled Commercial Banks, Non-Banking Finance Companies and Micro Financial Institutions, registered with Mudra Ltd.
CGSSD: It refers to the Guarantee Scheme for Sub-ordinate Debt. It is also called Distressed Assets Fund–Sub-ordinate Debt for MSMEs.
Minister of MSME Nitin Gadkari recently launched Guarantee Scheme for Sub-ordinate Debt CGSSD. The Scheme will provide Rs. 20,000 crore of guarantee cover to two lakh MSMEs.
As per CGSSD, the guarantee cover worth Rs. 20,000 crores will be provided to the promoters who can take debt from the banks to further invest in their stressed MSMEs as equity. The scheme will be operationalised through Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for MSEs (CGTMSE).
Under the scheme, Promoters of the MSMEs will be given credit equal to 15 percent of their stake or 75 lakh rupees whichever is lower.
90% guarantee coverage for this sub-debt will be given under the Scheme and 10% would come from the concerned promoters.
There will be a moratorium of 7 years on payment of principal whereas maximum tenor for repayment will be 10 years.
Defence
Major General (Retd) Lachhman Singh Lehl: Major General (Retd) Lachhman Singh Lehl one of India’s finest military brains and one of its last surviving officers to have taken part in both the 1948 and 1971 wars passed away recently. He was commissioned in the Regiment of Artillery in 1943.
He took part within the 1948 war in Jhangar area of Jammu and Kashmir as a captain and commanded a division within the 1971 war. He received the Vir Chakra, the third highest gallantry award in India for his role as a forward observer within the 50 Para Brigade. He also commanded 3 Field Regiment, 301 Infantry Brigade and 20 Infantry Division.
EAG: It refers to the Eurasian Group on Combating Money Laundering and Financing of Terrorism. Indian officials recently attended the 32nd special Eurasian Group on Combating Money Laundering and Financing of Terrorism (EAG) plenary meeting, under the aegis of the Financial Action Task Force. The meeting was held online.
EAG is an FATF-style regional body. It was established in 2004 and is currently an associate member of the FATF. The main objective of EAG is to assist member-states in implementing the 40 FATF anti-money laundering Recommendations and the 9 Special FATF Recommendations on combating terrorist financing (FATF 40+9 Recommendations). It comprises nine countries: India, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, China, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan and Belarus.
Indian Navy: The Indian Navy is the naval branch of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Navy. The Chief of Naval Staff, a four-star admiral, commands the navy. It was founded in 5 September 1612. The current Chief of Navy Staff (CNS) is Karambir singh. The main objective of the Indian Navy is to protect the country’s maritime borders and help in the expansion of its forces.There are 3 commands under the Navy which are:
1. The Western Naval Command (Headquarters at Mumbai).
2. The Eastern Naval Command (Headquarters at Visakhapatnam)
3. The Southern Naval Command (Headquarters at Kochi)
Recently, the Indian Navy inducted indigenously developed Torpedo Decoy System called Maareech that is capable of being fired from all frontline ships. It is also capable of detecting, locating and neutralizing incoming torpedo.
The induction has increased the Anti-Submarine Warfare capability of the Indian Navy. Its induction not only stands testimony to the joint resolve of the Indian Navy and DRDO towards indigenous development of defence technology, but has also given a major fillip to the government’s ‘Make in India’ initiative and the country’s resolve to become ‘atmanirbhar’ (self-reliant) in niche technology,
Design and Development of Maareech has been undertaken indigenously by DRDO labs-(NSTL and NPOL). The Bharat Electronics Limited, a Defence PSU, would undertake the production of this decoy system.
Environment
DTEE Project: It refers to the Decarbonising Transport in Emerging Economies. DTEE is a project of International Transport Forum (ITF). The current participants under the program apart from India are Argentina, Azerbaijan, and Morocco. DTEE is also collaboration between ITF and the Wuppertal Institute, supported by the International Climate Initiative (IKI) of the German Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety. DTEE project helps governments of emerging nations to identify ways to reduce their transport CO2 emissions and meet their climate goals.
Recently, NITI Aayog and the International Transport Forum (ITF) of OECD jointly launched the ‘Decarbonizing Transport in Emerging Economies’ (DTEE) project in India. The launch was held on 24 June 2020 via a webinar and was inaugurated by ITF Secretary General Young Tae Kim and NITI Aayog CEO Amitabh Kant in the presence ofMinistry of Housing and Urban Affairs(MoHUA) Secretary D.S. Mishra, as well as Ministry of Road Transport and HighwaysJoint Secretary Priyank Bharti.
The ambitious five-year project is going to develop a pathway towards a low-carbon transport system for India. This project will design a tailor-made transport emissions assessment framework for India. It will also provide the government with a detailed understanding of current and future transport activity and the related CO2 emissions as a basis for their decision-making.
ITF: It refers to the International Transport Forum. It is an intergovernmental organization with the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OCED). It is administratively integrated with the OECD, yet politically autonomous. It is the only global body with a mandate for all modes of transport. It is a think tank for transport policy issues and it organises the Annual Summit of transport ministers. It is headquartered in Paris, France. It brings together 60 member countries with an aim to foster a deeper understanding of the role of transport in economic growth, environmental sustainability and social inclusion and to raise the public profile of transport policy.
India has been a member of ITF since 2008.
Iceland: It is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic. It is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. It is a country of extreme geological contrasts. Widely known as “The Land of Fire and Ice” Iceland is home to some of the largest glaciers in Europe, and some of the world's most active volcanoes. It is also the land of light and darkness. Iceland is known as one of the youngest landmasses on the planet and was one of the last places on earth to be settled by humans. Vikings from Norway discovered Iceland by accident over 1,100 years ago. The capital city of Iceland is Reykjavík. The currency used here is Icelandic króna.
Recently, Iceland was hit by thousands of quakes. As per Iceland’s meteorological service IMO around, 3,000 tremors had been registered on the northern coast of the country. The island nation has experienced increased seismic activity in the past month. Authorities also warn that its Grimsvotn volcano, Iceland's most active, could erupt soon. This is because the scientists have recorded high levels of sulfur dioxide, indicating the presence of so-called shallow magma.
Grimsvotn is located on the northwestern side of the Vatnajokull ice cap and had its last eruption in 2011, which led to the temporary closure of Reykjavik's Keflavik airport and the cancellation of some 900 flights in Europe.
Iceland sits on the boundary of the North American Plate and the Eurasian plate, with the Mid-Atlantic Ridge running through the middle and propping up a series of moving tectonic and volcanic zones.
The last eruption of Grimsvotn was preceded by the 2010 eruption of southern Iceland's Eyjafjallajokull, which caused a huge cloud of smoke and ash that left more than 100,000 flights canceled and 8 million passengers stranded. However, the Scientists have said that the effects of a possible Grimsvotn eruption would be less dramatic than that of Eyjafjallajokull.
Sakleshpur is a hill station in the Western Ghats mountain range, in India’s Karnataka state. It is surrounded by slopes covered with tea, coffee and spice plantations and fascinating mountains. Its biodiverse Bisle Reserve Forest is a home to cobras, deer and birds. To the northeast, Jenukallu Gudda peak offers vistas stretching as far as the Arabian Sea.
Recently, a new lizard species from Sakleshwar in central-western ghats of neighbouring Karnataka was discovered by Tejas Thackeray, younger son of Maharashtra Chief Minister Uddhav Thackeray, and his team.
The new species of big-bodied Cnemaspis has been named "Cnemaspis magnifica", with the suggested common name "Magnificent dwarf gecko".
The findings have been published in international taxonomic journal Zootaxa.
Indian Policy
MHRD: It refers to the Ministry of Human Resources and Development. The Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) was formerly known as the Ministry of Education. It was founded on 26 septenber 1985. It is headquartered in New Delhi. India. It is responsible for the development of human resources in India. The current Minister of MHRD is Ramesh Pokhriyal.
Recently, the Union Minister of Human Resource Development, Ramesh Pokhriyal 'Nishank' launched the second phase of YUKTI (Young India Combating COVID with Knowledge, Technology and Innovation). The second phase of YUKTI was launched virtually to help systematically assimilate technologies having commercial potential and information related to incubated start-ups in country's higher education institutions.
YUKTI 2.0 is the logical extension of the earlier version of ‘YUKTI’ that was launched on 11 April 2020. Ministry of HRD prepared the portal in view of Coronavirus which intended to cover different dimensions of COVID-19 challenges and also to monitor and record the efforts and initiatives of MHRD.
Through this portal, the MHRD will endeavour to ensure that teachers, students and researchers in higher educational institutions are getting appropriate support to meet the requirements needed to advance their technologies and innovations.
MoF: It refers to the Ministry of Finance. The MoF is the apex controlling authority of the Indian Revenue Service, Indian Economic Service, Indian Cost Accounts Service and Indian Civil Accounts Service. It is an important ministry within the Government of India (GoI) concerned with the economy of India, serving as the Indian Treasury Department. It was founded on 29 October 1946. The ministry of finance is charged with the task of raising the resources for the overall expenditure of the Government of India and to see to the desirability of the demands of other departments, taking into consideration the interest of taxpayers. It is headquartered in New Delhi. the current Minister of Finance is Nirmala Sitharaman.
Recently, the Finance Ministry nearly fifteen years after the Disaster Management Act was passed has given the approval to a proposal to allow individuals and institutions to contribute directly to the National Disaster Relief Fund (NDRF).
This is a significant development at a time when many have expressed concerns about donations sent to the PM CARES Fund or the Prime Minister’s National Relief Fund, as both claim they are not public authorities subject to questions under the Right to Information Act.
NDRF: It refers to the National Disaster Relief Fund. NDRF was set up in accordance with Section 46 of the Disaster Management Act, 2005. It is meant to “meet the expenses for emergency response, relief and rehabilitation” for any disaster situation. Although Section 46 includes a clause for grants made by any person or institution, provisions for such donations had not been made. NDRF was earlier named as National Calamity Contingency Fund (NCCF).
GeM: It stands for Government e-Marketplace. GeM is a Special Purpose Vehicle under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry that offers end to end solutions for all procurement needs of Central and State Government Departments, autonomous institutions, Public Sector Units (PSUs) and local bodies. It was launched on 9 August 2016 to bring transparency and efficiency in the government buying process. It has transformed public procurement in India by leveraging technology and making procurement contactless, paperless, and cashless. It has also provided the tools of e-bidding and reverse e-auction to facilitate the government users achieve the best value for their money. It has been continuously working towards the promotion of Make in India initiative. At present, GeM has more than 15 lakh products, around 20,000 services, and more than 40,000 Government buyer organizations.
Recently, Government e-Marketplace (GeM) has made it mandatory for sellers to mention their Country of Origin while registering all new products on GeM.
GeM has taken this significant step to promote PM Modi's call for ‘Make in India’ and ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’.
It has also enabled a provision for indication of the percentage of local content in products. With the introduction of this new feature, the buyers on the platform can now see the Country of Origin as well as the local content percentage that will be visible in the marketplace for all items.
As ‘Make in India’ filter has now been enabled on the portal, the buyers can choose to buy only those products that meet the minimum 50% local content criteria.
Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment: The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment is a ministry of Government of India (GoI). It is responsible for welfare, social justice and empowerment of disadvantaged and marginalized sections of society, including scheduled castes, Other Backward Classes, the disabled, the elderly, and the victims of drug abuse. The Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment holds cabinet rank as a member of the Council of Ministers. The Ministry of Welfare adopted the name Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment in May 1998. In October 1999, the Tribal Development Division left the ministry to become its own ministry, the Ministry of Tribal Affairs. The current Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment is Thawar Chand Gehlot, who is assisted by a Minister of State, Rattan Lal Kataria, Krishan Pal Gujjar and Ramdas Athavale.
Recently, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment launched Nasha Mukt Bharat Annual Action Plan (2020-21). The action plan has been launched for 272 Most Affected Districts, on the occasion of “International Day Against Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking”. A Logo and Tagline for National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction and awareness videos for Drug Abuse Prevention was also released by the Ministry.
This action plan is a three-pronged attack combining efforts of Narcotics Bureau, Outreach/Awareness by Social Justice and Treatment through the Health Department.
The Action Plan has the following components.
Awareness generation programmes; Focus on Higher Educational institutions, University Campuses and Schools; Community outreach and identification of dependent population; Focus on Treatment facilities in Hospital settings; and Capacity Building Programmes for Service Provider.
Its main aim is to reach out to Children and Youth for awareness about ill effect of drug use, increase community participation and public cooperation, support Government Hospitals for opening up De- addiction Centers in addition to existing Ministry Supported De-addiction Centers (IRCAs) and Conducting Training programme for participants.
The Ministry has also prepared a National Action Plan for Drug Demand Reduction for the period 2018-2025 which aims at reduction of adverse consequences of drug abuse through a multi-pronged strategy involving education, de-addiction and rehabilitation of affected individuals and their families.
According to a list of 272 most affected districts from Drug addiction and Illicit Trafficking in India are Uttar Pradesh (UP), Rajasthan and Punjab are the worst affected states.
Indian polity
Supreme Court: The Supreme Court of India is the highest judicial forum and final court of appeal under the Constitution of India, the highest constitutional court, with the power of constitutional review. It consists of the Chief Justice of India and a maximum of 34 judges, it has extensive powers in the form of original, appellate and advisory jurisdictions. It is regarded as the most powerful public institution in India. It was established on 26 January 1950. Its headquartered in New Delhi. The current CJI of the Supreme Court is Sharad Arvind Bobde.
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) in a recent judgment has held that secrecy of ballot is the cornerstone of free and fair elections. The judgment came on an appeal against the Allahabad High Court decision setting aside the voting of a no-confidence motion in a zila panchayat in Uttar Pradesh in 2018. The High Court had found that some of the panchayat members had violated the rule of secrecy of ballot. Relying on the CCTV footage it was found that they had either displayed the ballot papers or by their conduct revealed the manner in which they had voted.
Supreme Court held that:
1. The principle of secrecy of ballots is an important postulate of constitutional democracy. The choice of a voter should be free and the secret ballot system in a democracy ensures it.
2. The principle of secrecy of ballots is an important postulate of constitutional democracy and referred to Section 94 of the Representation of People Act (RPA) 1951.
3. Section 94 of the Representation of the People Act upholds the privilege of the voter to maintain confidentiality about her choice of vote.
4. The right of voters to the secrecy of the ballot must be protected by the Law. Even a remote or distinct possibility that a voter can be forced to disclose for whom she or he has voted would act as a positive constraint and a check on the freedom to exercise the franchise.
5. However, a voter can also voluntarily waive the privilege of non-disclosure. The privilege ends when the voter decides to waive it and decides voluntarily to disclose their vote. In such a case voters can neither be prevented from disclosing nor can be subjected to a complaint by anyone.
The apex court referred to Section 28(8) of the Uttar Pradesh Kshettra Panchayat and Zila Panchayat Adhiniyam, 1961. This provision states that a motion of no confidence shall be put to vote in the prescribed manner by secret ballot.
The apex court has ordered a re-vote of the motion within the next two months.
Secret Ballot: The secret ballot is also known as Australian ballot. It is a voting method in which a voter’s choices in an election or a referendum are anonymous. The main objective of secret ballot is forestalling attempts to influence the voter by intimidation, blackmailing, and potential vote-buying. The system is one means of achieving the goal of political privacy.
Rajya Sabha: The Rajya Sabha or Council of States is the upper house of the bicameral Parliament of India. It is a permanent body and is not subject to dissolution. At present the Rajya Sabha has a maximum membership of 245, of which 233 are elected by the legislatures of the states and union territories using single transferable votes through Open Ballot while the President has the power to appoint 12 members for their contributions to art, literature, science, and social services. The Upper House was founded on 3 April 1952 by the Constituent Assembly of India. It is headquartered in New Delhi. Its current Chairperson is Venkaiah Naidu.
Recently, another round of Rajya Sabha elections were completed. However, polls to some seats were postponed in view of the situation caused by the novel coronavirus outbreak.
The ruling Narendra Modi-led National Democratic Alliance (NDA) gained a significant advantage where Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) bagged 11 of 24 seats, YSR Congress 4 and NDA crossed 100 seats in upper house.
Rajya Sabha Polls: The Rajya Sabha elections are different from the Lok Sabha. The representatives of the States and of the Union Territories in the Rajya Sabha are elected by the method of indirect election. Only the elected members of the State Legislative Assemblies can vote in a Rajya Sabha election.
As per the constitution, since the Rajya Sabha is the Council of States, the allocation of seats for Rajya Sabha is made on the basis of the population of each state. Article 80 of the Constitution lays down the maximum strength of Rajya Sabha as 250, out of which 12 members are nominated by the President and 238 are representatives of the States and of the two Union Territories. At present, out of the 245, 233 are elected by the legislatures of the states and UTs using single transferable votes through Open Ballot. The remaining 12 members are appointed by the President for their contributions to art, literature, science, and social services. Voting is done by a system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote.
The legislators send a batch of new members to the Upper House every 2 years for a six-year term. A third of Members of Parliament in the Rajya Sabha, from each State retire once in two years and polls are held to fill up the vacancies.
The Supreme Court ruled that a member can vote in a Rajya Sabha election even before taking oath as legislator. It ruled that voting at the Rajya Sabha polls, being a non-legislative activity, can be performed without taking oath.
NOTA: "None of the above", or NOTA for short, also known as "against all" or a "scratch" vote, is a ballot option in some jurisdictions or organizations, designed to allow the voter to indicate disapproval of the candidates in a voting system.
The Election Commission of India (ECI) in 2014 and 2015 had issued 2 circulars , giving Rajya Sabha members the option to press the NOTA button in the Upper House polls but in 2018, the Supreme Court of India (SCI) struck down the provision, holding that the ‘none of the above’ option is only for general elections held on the basis of universal adult suffrage, and cannot be applied to indirect elections based on proportional representation.
International
China: China, officially the People's Republic of China, is a country in East Asia. It is governed by the Communist Party of China. It is a recognized nuclear weapons state and has the world's largest standing army, the People's Liberation Army, and the second-largest defense budget. The capital of China is Beijing. The currency used here is Yuan (CNY) and Renminbi (RMB). The yuan is the unit of account of the country's economic and financial system while Renminbi is the official currency of China where it acts as a medium of exchange. The current President of china is Xi Jinping.
Recently, China has decided to join the UN Arms Trade Treaty (UN-ATT) to regulate arms sales saying it is committed to efforts to "enhance peace and stability" in the world. The Communist Party leadership's top legislative body of China voted to adopt a decision on joining the UN-ATT that is designed to control the flow of weapons into conflict zones. The decision comes after U.S. President Donald Trump announced plans last year to pull the U.S. out of the agreement.
ATT: It refers to Arms Trade Treaty. ATT is a multilateral treaty that regulates the international trade in conventional weapons, from small arms to battle tanks, combat aircraft and warships, and controls the flow of weapons into conflict zones. The treaty was adopted at the United Nations General Assembly on 2nd April 2013. It entered into force on 24 December 2014. The treaty was launched with the aim of maintaining international and regional peace.
Under this treaty, member countries are required to keep records of international transfers of weapons and to prohibit cross-border shipments that can be used in human rights violations or attacks on civilians.
The treaty is an attempt to regulate the international trade of conventional weapons for the purpose of contributing to international and regional peace; reducing human suffering; and promoting cooperation, transparency, and responsible action by and among states.
AT present 130 countries have originally signed the treaty but only 104 have joined it. India has not signed the treaty.
Serbia: Serbia, officially the Republic of Serbia, is a landlocked country situated at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe in the southern Pannonian Plain and the central Balkans. It borders Hungary to the north, Romania to the northeast, Bulgaria to the southeast, North Macedonia to the south, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west, and Montenegro to the southwest. Its capital is Belgrade which ranks among the largest and oldest cities in southeastern Europe. The currency used here is Serbian dinar.
Recently, the Serbian Progressive Party (SNS) coalition, under the leadership of the President of Serbia, Aleksandar Vucic registered a landslide win in 2020 parliamentary election. Serbia became the first country to conduct National Elections in Europe since the COVID-19 pandemic outbreak in March 2020.
Ana Brnabic who is the first female Prime Minister of Serbia) is the incumbent Prime Minister of Serbia. She became the Prime Minister in 2017 after President Aleksandar Vucic proposed her name.
The National Assembly of Serbia has a unicameral legislature. The Prime Minister of Serbia is elected and and appointed by the 250 elected members of the National Assembly. The President of Serbia has the power to propose the name of an individual to the National Assembly for the post of the Prime Minister.
Senkaku Islands: The Senkaku Islands are a group of uninhabited islands in the East China Sea. They are located east of Mainland China, northeast of Taiwan, west of Okinawa Island, and north of the southwestern end of the Ryukyu Islands. They are known as the Diaoyu Islands in Mainland China, the Diaoyutai Islands in Taiwan and the Pinnacle Islands by other observers. Japan annexed the archipelago following China’s defeat in the first Sino-Japanese war from 1894 to 1895. Japan administers and controls the Senkaku islands as part of the city of Ishigaki in Okinawa Prefecture.
Recently, Japan has approved a plan to change the name of the area covering the Tokyo-controlled Senkaku Islands from Tonoshiro to Tonoshiro Senkaku. It was approved by the local council in southern Japan.
China said the move is illegal and a serious provocation. The islands are the focus of a territorial dispute between Japan and China and between Japan and Taiwan.
United Nations Public Service Day: It is observed on June 23 every year globally. The General Assembly, on 0 decembe 2002 designated 23 June as Public Service Day by adopting resolution 57/277. This day highlights the contribution of public service in the development process and recognizes the work of public servants.
The prestigious UN Public Service Awards (UNPSA) are also awarded on this day by the United Nations Economic and Social Council for contributions made to the cause of enhancing the role, prestige, and visibility of public service.
The day also marks the anniversary of the date when the International Labour Organization adopted the Convention on Labour Relations (Public Service), 1978 (No. 151). This Convention is a framework for determining working conditions of all civil servants across the world.
Recently, UN Public Service Day 2020 was observed on June 23 to honour public servants in the COVID-19 pandemic response.
This year the UN held a virtual event to engage public servants from across the world and discuss the stiff challenges the pandemic is throwing at frontline workers and citizens virtually every day.
Los Angeles (LA): Los Angeles often known by its initials L.A., is the largest city in California, United States. The city is known for its Mediterranean climate, ethnic diversity, Hollywood entertainment industry, and its sprawling metropolis.
Recently, the world's first yoga university outside India has been launched in Los Angeles, United States as a part of the 6th International Yoga Day commemorations. The virtual launch event was organized at New York City’s Consulate General of India. The university was jointly launched by Chairperson of the Standing Committee on External Affairs P P Chaudhary and Minister of State for External Affairs V Muraleedharan on June 23 during a virtual meeting in New York.
The Yoga University has been named after Swami Vivekananda and it will be known as Vivekananda Yoga University (VaYU). VaYU will offer programmes that combine scientific principles and modern research approach to the ancient Indian practice.
The chancellor of SVYASA- Swami Vivekananda Yoga Anusandhana Samsthana (Deemed University at Bengaluru for the study of yoga), Dr H R Nagendra will be the first Chairman of the Vivekananda Yoga University.
The first day of classes for the fall 2020 semester of the University will commence on 24th August 2020. Online Master’s Program in Yoga (M.S Yoga) will also be offered by the University.
Myanmar: Myanmar officially the Republic of the Union of Myanma was formerly known as Burma,. It is a Southeast Asian nation of more than 100 ethnic groups. It is bordered by Bangladesh and India to its northwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. Myanmar has been a member of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) since 1997. The Capital of Myanmar is Naypyitaw. The currency used here Burmese kyat. The current President of Myanmar is Win Myint.
Recently, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi approved the additional investment of US$ 121.27 million (about Rs.909 crore) by ONGC Videsh Ltd (OVL) towards further development of blocks A-1 and A-3 Blocks of Shwe oil & gas project in Myanmar.
OVL has been associated with exploration and development of Shwe project in Myanmar since 2002, as part of consortium of companies from South Korea, India and Myanmar. The Indian PSU, GAIL, is also an investor in this project. OVL has invested US$ 722 million till 31st March 2019 in this project.
The first gas from the Shwe Project was received in July 2013 and plateau production was reached in December 2014. The Project has been generating positive cash flows since FY 2014-15.
The participation of Indian PSUs in oil & gas exploration and development projects in neighbouring countries is aligned with India's Act East Policy, and also part of India's efforts to develop Energy Bridges with its immediate neighbours.
National
MOFPI: It is an acronym for the Ministry of Food Processing Industries. MOFPI is a ministry of the Government of India (GoI) responsible for formulation and administration of the rules and regulations and laws relating to food processing in India. The ministry was founded in 1947 with a view to develop a strong and vibrant food processing industry, to create increased employment in rural sector and enable farmers to reap the benefits of modern technology and to create a surplus for exports and stimulating demand for processed food. The current Union Minister of MOFPI Harsimrat Kaur Badal and Minister of State (MoS) of MOFPI is Rameswar Teli.
The Union Minister for Food Processing Industries (FPI) recently launched the Food Processing Edition of the Exclusive Investment Forum by Invest India, the National Investment Promotion & Facilitation Agency of the Government of India. It is the webinar hosted by Invest in India.
It has been designed by the Invest India, the National Investment Promotion & Facilitation Agency of the Government of India.
The forum witnessed participation from the senior-most policymakers from Union Government and 6 State Governments – Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Telangana and Uttar Pradesh. 180 companies from 18 countries also participated in the forum.
At the forum, the critical aspects for investment ranging from policy incentives, industrial zones, infrastructure capabilities and special investor facilitation services were discussed so as to make India the next Global Investments hub.
Investment Facilitation Cell of Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) was also established during the forum to handhold both domestic and foreign investors for doing business in India.
Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers: The Ministery of Chemicals and Fertilizers in India is the federal ministry with administrative purview over three departments which are Department of Chemicals and Petrochemicals, Department of Fertilizers and Department of Pharmaceuticals. The Department of Chemicals and Petrochemicals was under the Ministry of Industry until December 1989, when it was brought under the Ministry of Petroleum and Chemicals. On June 5, 1991, the Department of Chemicals and Petrochemicals was transferred to the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers. The current Union Minister and Minister of State of Chemicals and fertilisers are D. V. Sadananda Gowda and Mansukh Mandaviya respectively.
Recently, The Minister of State for Shipping (Independent charge) and Chemicals & Fertilisers Mansukh Mandaviya introduced India’s largest first Virtual Healthcare & Hygiene EXPO 2020. The event was inaugurated virtually and it will be made live daily from 22nd to 26th June, 2020.
The Expo has been organised by Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry (FICCI).
The aim behind this unique expo is to boost Healthcare and Hygiene sector and create awareness about Healthcare and Hygiene in people. This expo seeks to create businesses which will happen virtually giving importance to Digital India movement. The Indian government is also giving incentives for setting up of Bulk Drug Parks and Medical Device Parks in the country which will uplift the Atmanirbharat Abhiyan.
FICCI: It refers to the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry. FCCI is an association of business organizations in India. It was established in 1927, on the advice of Mahatma Gandhi by GD Birla and Purshottamdas Thakurdas. It is the largest, oldest and the apex business organization in India. It provides a platform for networking and consensus building within and across sectors and is the first port of call for Indian industry, policy makers and the international business community. It is headquartered in New Delhi. The current President of FCCI is Sangita Reddy.
GoI: The Government of India (GoI) recently announced historic reforms in space, banking and animal husbandry sector. The reforms were approved at the Cabinet meeting chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi. The decisions were taken in order to boost Infrastructure projects across all the sectors at a time of a global pandemic.
Union Atomic Energy and Space Minister, Dr. Jitendra Singh informed that government government has decided to constitute Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACE) for effective socio-economic usage of space technology. It has also decided that the Urban Cooperative and Multi State Cooperative banks will be brought under the direct supervision of Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and a desision to develop an International Airport in Kushinagar district in Uttar Pradesh too has been taken.
NITI Aayog: NITI (National Institution for Transforming India) Aayog is the premier policy 'Think Tank' of the Government of India (GoI). It was established with the aim to achieve sustainable development goals with cooperative federalism by fostering the involvement of State Governments of India in the economic policy-making process using a bottom-up approach. It was founded on 1 January 2015 to replace the Planning Commission instituted in 1950. It is headquartered in New Delhi. The Governing Council of NITI includes the Prime Minister as its Chairman. It comprises of Chief Ministers of all States and Lt. Governors of Union Territories (UTs). The current Chief Executive Officer(CEO) is Amitabh Kant.
Recently, NITI Aayog, in partnership with Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF), Centre for Social and Behavioural Change (CSBC), Ashoka University, and the Ministries of Health and WCD launched a behaviour change campaign called ‘Navigating the New Normal’, and its website. The campaign focuses on safety behaviours to be taken during COVID-19 pandemic situation and to combat it.
This campaign has been developed under the guidance of Empowered Group 6, constituted by the Government of India and chaired by CEO, NITI Aayog. The campaign has two parts. The first part is a web portal and the 2nd part is a media campaign.
The first is a web portal, http://www.covidthenewnormal.com/, containing resources informed by behavioral science and the use of nudge and social norms theory, related to Covid-safe behavioral norms during the ongoing Unlock phase. The web portal emphasizes on the easy implementation of key behaviours namely: mask-wearing, social distancing, hand hygiene, and not spitting in public.
The second is a media campaign focused on the wearing of masks as it is a simple measure which has made a big difference in the fight against COVID-19.
Ministry of Rural Development: The Ministry of Rural Development is a branch of the Government of India. It was founded in June 2011. It is entrusted with the task of accelerating the socio-economic development of rural India. Its focus is on health, education, drinking water, housing and roads. The ministry has two departments which are Department of Rural Development and Department of Land Resources. The current Union Minister for Rural Development is Narendra singh Tomar and for the State is Sadhvi Niranjan Jyoti.
Recently, Minister for Rural Development Narendra Singh Tomar launched the web portal of the Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan (GKRA) through video conferencing from New Delhi. It was launched on 26 June 2020. This web portal will moniter implementation of GKRA and provide scheme related information to the people.
GKRA: It refers to the Garib Kalyan Rojgar Abhiyaan. GKRA is an initiative of government of India to tackle the impact of COVID-19 on migrant workers in India. This initiative was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on 20 June 2020 in six states through video conferencing. The Abhiyaan was launched from Village Telihar of Khagaria District of Bihar. The scheme covers 116 districts in Bihar, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Odisha and Uttar Pradesh. The Finance Minister N Sitharaman and Labor and Employment Minister Santosh Gangwar announced the launch of the scheme in a press conference. The outlay of this campaign is Rs 50,000 Crores and Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD) is the nodal Ministry for its implementation.
This campaign aims to help migrant laborers who have returned home by providing employment to them at their native places for next 4 months, because of the situation arising out of the Covid-19 pandemic.
People In News
Nikhil Rathi: He is the chief executive of London stock exchange. He has been appointed as the new chief executive of the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). He has been appointed for a five-year term. He has been closely involved in the listing of ‘masala bonds’ by Indian institutions on the London stock market in recent years. Rathi will succeed Christopher Woolard.
FCA: It refers to the Financial Conduct Authority. FCA is the conduct regulator for the UK’s financial markets, over 59,000 financial services firms, and the prudential supervisor for 49,000 firms, setting specific standards for 19,000 firms.
T. Rabi Sankar: He has recently been appointed as the Chairman of Indian Financial Technology & Allied Services (IFTAS). IFTAS is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Reserve Bank of India. At present, he is serving as the Executive Director of Payment Systems, Information Technology(IT), Risk Management and Fintech in the Reserve Bank of India(RBI).
Along with him, the agency has also appoints Dr N Rajendran as the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of the organization. Dr N Rajendran is a leading expert in the field of Payments & Banking Systems and holds a PhD in computer science.
Sankar’s appointement is effective from May 15, 2020 while Dr N Rajendran’s appointment is effective from May 27, 2020.
IFTAS: It refers to the Indian Financial Technology & Allied Services. IFTAS is established under Section 8 of Indian Companies Act, 2013. Its task is to provide essential IT-related services, required by the Reserve Bank of India, banks, and financial institutions, effectively and efficiently. It is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra.
Dr. Nirakar Pradhan: Dr Nirakar Pradhan has recently been appointed as new as the Chief Executive Officer of the Professional Risk Managers’ International Association (PRMIA) of its new India office. He has led teams at State Bank of India and Generali Group in India and Europe.
PRMIA: It refers to the Professional Risk Managers’ International Association. PRIMA is a non-profit led by top professionals dedicated to promoting best practices in risk management. Its main aim is to focus on training and certification has been recognised by the Government, Reserve Bank of India, State Bank of India, Punjab National Bank and HSBC, among others. It was founded in 2002. It is Headquartered in Wilmington,Delaware, United States
Vijay Khanduja: He has recently been appointed as the next Ambassador of India to the Republic of Zimbabwe. He is currently serving as Director in the Ministry of External Affairs(MEA). He is expected to take up the assignment shortly. He will be replacing R. Masakui.
Zimbabwe, officially the Republic of Zimbabwe is a landlocked country located in Southern Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa, Botswana, Zambia and Mozambique. Zimbabwe was formerly known as Southern Rhodesia (1898), Rhodesia (1965), and Zimbabwe Rhodesia (1979). It is known for its known for its dramatic landscape and diverse wildlife. The capital of Zimbabwe is Harare. The currency used here is United States Dollar.The current President of Zimbabwe is Emmerson Mnangagwa.
Sethuraman Panchanath: He is an Indian-American scientist who has recently been appointed as the Director of the National Science Foundation (NSF) by the US Senate. He will be replacing France Cordova, whose six-year term ended in March, as the 15th director of the NSF. He is expected to take office on the 6th of July 2020.
He is the second Indian-American ever to be nominated to the prestigious science position. Dr Subra Suresh was the first Indian who served from October 2010 to March 2013. National Science Foundation (NSF) is a top American body supporting fundamental research in non-medical fields of science and engineering.
NSF: It refers to the National Science Foundation. NSF is an independent federal agency of the United States government. It was founded on 10 May 1950. It was created by Congress to promote the progress of science, to advance the national health, prosperity, and welfare, to secure the national defense. It also supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health. It is headquartered in Alexandria, Virginia, U.S.
Amartya Sen: Amartya Kumar Sen, born on 3rd November 1933 to a Hindu family in Bengal, British India. Rabindranath Tagore gave Amartya Sen his name. He is an Indian economist and philosopher, who since 1972 has taught and worked in the United Kingdom and the United States. He has made contributions to welfare economics, social choice theory, economic and social justice, economic theories of famines, decision theory, development economics, public health, and measures of well-being of countries.
He is currently Thomas W. Lamont University Professor, and Professor of Economics and Philosophy at Harvard University. Amartya Sen’s awards include Bharat Ratna (India); Commandeur de la Legion d'Honneur (France); the National Humanities Medal (USA); Ordem do Merito Cientifico (Brazil); Honorary Companion of Honour (UK); the Aztec Eagle (Mexico); the Edinburgh Medal (UK); the George Marshall Award (USA); the Eisenhower Medal (USA); and the Nobel Prize in Economics.
Recently, Amartya Sen won the prestigious Peace Prize of the German Book Trade 2020 by the German Publishers and Booksellers Association. The 86-year-old Harvard professor was granted the 2020 Peace Prize of the German Book Trade for his "decades-long work on the question "as a questions of global justice". The award will be bestowed to him in a ceremony at the Frankfurt Book Fair in October.
Since 1950, the Börsenverein des Deutschen Buchhandels, the professional organisation of publishers and booksellers in the Federal Republic of Germany, is awarding the Peace Prize annually. The prize comes with a cash prize of €25,000 euros ($28,000). It reflects the German Publishers and Booksellers Association’s commitment to “peace, humanity and understanding among all peoples and nations of the world”:
The Peace Prize promotes international tolerance by honouring individuals who have made outstanding contributions to the idea of peace primarily through their exceptional activities in the fields of literature, science and art. Prize winners are chosen without any reference to their national or religious background.
KK Shailaja: KK Shailaja is the Health Minister of Kerala. she was recently, one among those who were recognised and honoured for its fight against the COVID-19 pandemic by the United Nations on its Public Service Day. She was also hailed by the international organisation for the state's low Covid mortality rates.
The event was held on a virtual platform and saw the participation of UN Secretary General Antonio Guterres and other top UN dignitaries. Kerala Health Minister KK Shailaja was the only speaker from the country to speak about the strategies adopted by the state to contain and curb the transmission of COVID-19.
The UN observed Public Service Day on 23rd June to honour those who are risking their lives and health to deliver essential public services amid the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
During the event, the health minister spoke on how the state's experience gained from tackling Nipah outbreak and the two floods in 2018 and 2019, helped her in tackling Covid-19 effectively. She also said that right from the time when COVID cases got reported in Wuhan, Kerala had started preparing to deal with the pandemic following the directions of the World Health Organization (WHO). The idea of One World One Health, of the United Nations was implemented. In addition, the state followed three strategies to tackle the pandemic which included "Trace, Quarantine, Test, Isolate and Treat", "Break the Chain" and "Reverse Quarantine."
Places In News
Rajasthan: Rajasthan is a state in northern India. It comprises most of the wide and inhospitable Thar Desert (also known as the "Great Indian Desert") and shares a border with the Pakistani provinces of Punjab to the northwest and Sindh to the west, along the Sutlej-Indus river valley.It became a State after 1947 when the princely states and chiefships were integrated into India in stages, and the state took the name Rajasthan. It assumed its present form on November 1, 1956, when the States Reorganization Act came into force.The Capital of Rajasthan is Jaipur. The current Chief Minister and Governor of Rajasthan is Ashok Gehlot and Kalraj Mishra respectively.
Recently, the Government of Rajasthan launched “Indira Rasoi Yojana”. The aim of this a new kitchen scheme is to feed the poor people of the state with food.
Under this scheme, pure and nutritious food will be provided to the needy twice a day at concessional rates. Rajasthan Government will spend Rs 100 crore every year on this sheme.
The state government will line up local NGOs’ and will take the help of IT to effectively run and monitor this scheme.
Jammu & Kashmir: Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) is a region administered by India as a Union Territory. It was a region formerly administered by India as a state from 1954 to 2019. Provisions for the formation of the union territory of Jammu and Kashmir were contained within the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019, which was passed by both houses of the Parliament of India in August 2019. The current Lieutenant Governor of J&K is GC Murmu.
Recently, Lieutenant Governor, GC Murmu accorded approval to appointment of 6 persons as member of the Public Service Commission for the Union territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
The six appointed members are:-
1. S. Ahfadul Mujtaba, IPS, Director General, Prosecution, J&K;
2. Syed Iqbal Aga, retired Development Commissioner (Works);
3. Subash Gupta, retired District and Session Judge;
4. Des Raj, Chief Engineer, Public Works (R&B), Jammu;
5. Sameer Bharti, IFS (retired)
6. Showkat Ahmad Zargar, retired Associate Professor (Mathematics), Higher Education Department.
Their appointment shall take effect from the date they assume the office and as per the notification, they shall hold the position of Member, Public Service Commission, till they attain the age of 62 years.
Devika and Puneja Bridges: These are the two bridges that were e-inaugurated Union Minister of State PMO, Personnel, Public Grievances & Pensions, Dr Jitendra Singh in Udhampur and Doda districts respectively in Jammu and Kashmir.
Devika Bridge: The Bridge on River Devika in Udhampur has been completed by Border Roads Organisation 9BRO) within 15 months time. The bridge will not only take care of traffic congestion and developmental needs of the Udhampur town area but will also help in smooth passage of Army convoys and vehicles.
Puneja Bridge: The 50-meter-long Puneja Bridge was constructed by BRO at Bhaderwah in Doda District. The Puneja Bridge was constructed in 36 months. Puneja Bridge is strategically very important from defence point of view. Basoli-Bani-Bhaderwah road is a vital alternate link to the Doda, Kishtwar, Bhaderwah and Kashmir valley from Pathankot (Punjab) region without passing Jammu and Udhampur. Doda is the only district in the country where 3 big tunnels are being built.
Kushinagar: It is a place which is located in the north-eastern part of Uttar Pradesh about 50 km east of Gorakhpur. It is one of the important Buddhist pilgrimage sites.
Recently, the Union Cabinet chaired by the prime minister Narendra Modi gave its approval for declaration of Kushinagar Airport in Uttar Pradesh as an International Airport.
Kushinagar Airport is also located in the vicinity of several Buddhist Cultural Sites like Sravasti, Kapilvastu and Lumbini. The transformation of Kushinagar Airport into an international airport will also give a boost to domestic and international tourism as well as economic development of the regions.
Uttar Pradesh: Uttar Pradesh is a state in northern India. It was created on 1 April 1937 as the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh during British rule, and was renamed Uttar Pradesh in 1950. Its Capital city is Lucknow. The Chief Minister and the Governor of Uttar Pradesh are Yogi Adityanath and Anandiben Patel respectively.
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi virtually launched a path-breaking scheme “Atma Nirbhar Uttar Pradesh Rojgar Abhiyan” in Uttar Pradesh.
The scheme has been launched in 31 districts of Uttar Pradesh constituting more than 25,000 returnee migrant workers. Nearly 30 lakh migrant workers have returned home due to the ongoing pandemic.
Atma Nirbhar Uttar Pradesh Rojgar Abhiyan initiative of the Uttar Pradesh government aims to generate employment, promote local entrepreneurship and create partnership with Industrial associations and other organizations employment opportunities to the returnee migrant workers.
Karnataka: It is a state in the south western region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as the State of Mysore, it was renamed Karnataka in 1973. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, Goa to the northwest, Maharashtra to the north, Telangana to the northeast, Andhra Pradesh to the east, Tamil Nadu to the southeast, and Kerala to the south. It is the only southern state to have land borders with all of the other 4 southern Indian sister states. Its capital city is Bangalore. The current Chief Minister and Governor of Karnataka are B. S. Yediyurappa and Vajubhai Rudabhai Vala respectively.
Recently, Karnataka Government chaired by Chief Minister B S Yediyurappa has amended the ‘The Karnataka Industries Facilitation Act, 2002. The amendment was done at the state cabinet meeting with an aim to facilitate and attract investment in the state. It has become the first state to amend the act for Small, Medium, and large-Scale Industries.
As per the amendments, an industry does not need statutory permissions for the first 3 years to set up operations in the state. These permissions include getting approvals under multiple state laws, including trade license and building-plan approval which will promote ease of doing business and facilitate investors to invest in the state.
Science and Technology
BDS: It refers to the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System. The BDS is named after the Chinese term for Big Dipper. It is a Chinese satellite navigation system. The BDS has been designed to reach accuracy levels similar to those of GPS and Galileo Open Service by positioning accuracy within 10 meters, timing accuracy within 50 ns and velocity accuracy within 0.2 meters per second. China started developing the Beidou satellite system in the 1990s with the aim of being self-sufficient in navigation technology and having an alternative system to GPS.
Recently, China successfully launched the final member in its Beidou satellite system (BDS) for global coverage constellation. It was launched from the Xichang Satellite Launch center in Sichuan Province on 23 June 2020 by a Long March 3B rocket into the orbit. The satellite launched is a part of the third generation of the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS-3) and the 55th satellite of the whole Beidou system.
The launch marked the completion of the country's domestically developed BeiDou constellation, one of four global navigation networks alongside with the United States Global Positioning System GPS, Russia's GLONASS and the European Union's Galileo. BDS is being projected by Beijing as a rival to the American Global Positioning System (GPS).
BDS-1 also known as the first generation was a constellation of 3 satellites was launched with 3 working and one backup satellite between 2000 to 2003. The first satellite under this system was launched on 30th October 2000. The BDS started providing independent services over China in 2000.
BeiDou-2 also known as the second generation of the system became operational in China in 2011 with a partial constellation of 10 satellites in orbit. This system provides coverage in the Asia-Pacific Region. The first satellite under this system was launched on 13th April 2007.
BDS-3 also known as the third generation of the system was launched on 30 March 2015. The BDS-3 System satellite has a higher bandwidth, enabling enhanced communication. This system consists of 35 satellites. They are 3 Geosynchronous satellite, 3 Inclined Geosynchronous Satellite and 24 Medium Earth Orbits Satellite. Fifteen BDS-3 satellites were launched till October 2018. BDS-3 started providing global navigation services from December 2018 to countries that had signed the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) of China.
ISRO: It is an abbreviation for the Indian Space Research Organizatin. ISRO is the space agency of the Government of India (GoI) and was formed in 15 august 1969. It superseded the erstwhile “Indian National Committee For Space Research” (INCOSPAR) which was established in 1962 by the efforts of Independent India's first prime minister‚ Jawaharlal Nehru‚ and his close aide and scientist Vikram Sarabhai. In 1972, the Government of India had set up a Space Commission and the Department of Space (DOS), bringing ISRO under the DOS. ISRO then embarked on its mission to provide the Nation space based services and to develop the technologies to achieve the same independently. Its vision is to “harness space technology for natural development while pursuing space science research & planetary exploration”. ISRO built India’s first Satellite Aryabhata. It is headquartered in Bangalore, India. The current Chairman of ISRO is K sivan.
Recently, ISRO received a patent for its Liquid Cooling and Heating Garment (LCHG) that is suitable for space applications.
LCHG are made of biocompatible fabrics and components to provide a comfortable temperature and removal of sweat for astronauts, for use in space for protection from hot and cold environments. The patent garment has an outer layer that is made of polymeric fabric net and the inner layer of polymeric fabric tricoting that comes in contact with the wearer. The outer and inner layers are separated by tubes configured to circulate heat transfer through inlet and outlet valves. The garment permits the long term use without any impact on the wearer in terms of skin irritation or infection.
LCGH was invented by Srirangam Siripothu, Reshmi Balachandran, Saraswathi Kesava Pillai Manu, and Gurumurthy Chandrasekaran.
LCGH would provide a comfortable temperature to the astronauts wearing it in space. It can also be used in military applications, fire fighting as well as for personal cooling and heating purposes for protection from extreme hot and cold environments of industrial areas.
ISRO has initiated the Human Space Flight Programme, Gaganyaan, to take humans to space by 2022. Under the programme, three astronauts are to orbit the earth at an altitude of 400 kilometres for 7 days. They are undergoing training in Russia.
Space Sector Reforms: The Union Cabinet recently has approved far reaching reforms in the Space sector. It was approved in the Cabinet meeting held under the chairmanship of Prime Minister Narendra Modi with an aim to boostprivate sector participation in the entire range of space activities.
The Cabinet decision comes weeks after Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced the opening up of the space sector for private entities.
Union Atomic Energy and Space Minister, Dr. Jitendra Singh informed that that government will constitute Indian National Space Promotion and Authorization Centre (IN-SPACE) for effective socio-economic usage of space technology.
The Public Sector Enterprise, New Space India Limited (NSIL) will endeavour to re-orient space activities from a supply driven model to a demand driven model, thereby ensuring optimum utilization of our space assets.
IN-SPACe will not only provide a level playing field for private companies to use Indian space infrastructure but will also guide them through encouraging policies and a friendly regulatory environment.
IN-SPACe will not be a separate institution but work as an extension into ISRO and these reforms will allow ISRO to focus more on research and development activities, new technologies, exploration missions and human spaceflight programme. The Department of Space comes under the PMO.
IISc Bangalore: It is the Indian Institute of Science located in Bangaluru city, in the Indian state of Karnataka. It is a public, deemed, research university for higher education and research in science, engineering, design, and management. The institute was established in 1909 with active support from Jamsetji Tata and Krishna Raja Wadiyar IV and thus is also locally known as the "Tata Institute". It was granted the deemed to be university status in 1958 and the Institute of Eminence status in 2018.
Recently, a research team at IISc Bangaluru developed nanozymes that destroy the cell membrane of bacteria by directly targeting its phospholipids. According to the former PhD students Kapudeep Karmakar and Kritika Khulbe, who conducted the research, the nanozymes developed by them can replace the antibiotics that have become ineffective as several bacteria have developed resistance to them by producing their own enzymes.
The study conducted by the Department of Inorganic and Physical Chemistry and the Department of Microbiology and Cell Biology was published in ACS Applied BioMaterials journal.
Nanozymes are nanomaterials that can behave like human enzymes. It can disintegrate the cell membranes of a range of diseases causing bacteria. This nanomaterial has been tested on several potentially pathogenic bacteria causing typhoid, gastroenteritis, dysentery, cholera and pneumonia. It was found that the nanozyme stopped growth and killed the microbes.
Sports
International Olympic Day: The day is celebrated globally on the 23rd of June every year. The proposal for the celebration of World Olympic Day was made by Doctor Gruss in the 41st Session of the International Olympic Committee (IOC) in Stockholm in 1947 to promote the idea of the Olympics. This day was introduced in 1948 to commemorate the birth of the modern Olympic Games and the foundation of IOC on 23 June 1894 at the Sorbonne in Paris. The first Olympic Day was celebrated on 23 June 1948 by 9 National Olympic Committees (NOC). The goal was to promote participation in sport across the globe regardless of age, gender or athletic ability. Athletes from every nation participate in sports activities, such as runs, exhibitions, music, and educational seminars on this day.
Recently, International Olympic Day 2020 was celebrated on the 23rd of June by creating the world’s largest 24 hour digital-first Olympic workout. The events of 2020 Olympic day was conducted as an online event due to the pandemic crisis.
IOC: It is an acronym for International Olympic Committee. IOC is a non-governmental sports organisation. It was established on 23 June 1894. It was founded by Pierre de Coubertin and Demetrios Vikelas. It is headquartered in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is responsible to organize the modern Summer and Winter Olympic Games. The Olympic motto is made up of three Latin words: CITIUS – ALTIUS – FORTIUS (Faster, Higher, and Stronger) adopted in 1894.
The current President of IOC is Thomas Bach.
Wasim Jaffer: He is the former Indian cricketer. He is a right-handed opening batsman and an occasional right arm off-break bowler. He is currently the highest run-scorer in Ranji Trophy cricket, surpassing Amol Muzumdar. He had reported retirement in March this year.
He has recently been appointed head coach of the Uttarakhand cricket team. This will be his first spell as a lead trainer with a Team.
Ranji Trophy: The Ranji Trophy is a domestic first-class cricket championship played in India. it is played between multiple teams representing regional and state cricket associations. The competition is named after the first Indian cricketer who played international cricket, Ranjitsinhji, who was also known as 'Ranji'
ITF: It is the acronym for the International Tennis Federation. ITF is the governing body of world tennis, wheelchair tennis, and beach tennis. It was founded in 1913 as the International Lawn Tennis Federation by twelve national associations, and as of 2016, is affiliated with 211 national tennis associations and six regional associations. It is headquartered in London, United Kingdom (UK). The current President of ITF is David Haggerty.
Recently, the ITF announced the players who have been elected to the ITF World Tennis Tour Player Panels.
National Champion of India, Niki Poonacha has been elected as a player member to ITF World Tennis Tour Player Men’s panels representing the Asia-Oceania zone with Ti Chen of Chinese Taipei. Alongwith Niki and Ti chen the members of the Men’s tennis panel includes Juan Pablo Paz & Jose Bendeck representing South America, Aldin Sektic & Francesco Vilardo representing Europe.
The Women’s panel includes, Akgul Amanmuradova of Uzbekistan and Olivia Tjandramulia of Australia representing Asia-Oceania, Ines Ibbou of Algeria representing Africa, Petra Januskova of Canada representing North and Central America – Caribbean,Yuliana Lizarazo of Colombia representing South America and Tara Moore of Great Britain and Conny Perrin of Switzerland representing Europe.
The Men’s and Women’s Panel will be headed by Mark Woodforde and Mary Pierce respectively who are the athlete representatives on the ITF board of directors.
The ITF World Tennis Tour Player Panel will provide a forum for players to provide their input on various matters related to how the ITF Tour is run.
World Athletics: World Athletics, formerly known as the International Amateur Athletic Federation (IAAF) and International Association of Athletics Federations, is the international governing body for the sport of athletics, covering track and field, cross country running, road running, racewalking, mountain running and ultra running. It was founded on 17 July 1912 in Stockholm, Sweden. It is headquartered in Monaco. The current President of World Athletics is Sebastian Coe.
Recently, World Athletics on 22nd June announced that Laurent Boquillet has been appointed as the Head of Global Development. World Athletics mentioned that the global search to fill out the new position was conducted in January 2020.
The new position of Head of Global Development supports the body’s vision which is ‘to use the power and accessibility of athletics and our athletes to create a healthier and fitter world.
Laurent Boquillet: He spent his entire career in athletics, in a diverse range of roles and most recently as the CEO of the European Athletics Championships Paris 2020. Laurent started out in a sport as a professional triathlete between 1984-1990. It also included being crowned European Champion in 1986. He had worked in the marketing and commercial side of athletics managing elite athletes.
Arts
Aditya Vikram Birla Kalashikhar Puraskar: The Aditya Vikram Birla Kalashikhar and Kalakiran Puraskar awards, were instituted in 1996 by the Sangeet Kala Kendra (SKK). It was founded in 1973 by Aditya Vikram Birla (former Chairman of Aditya Birla Group), to honor excellence in theatre and performing arts.
Recently, veteran actor Naseeruddin Shah was honoured with the 2020 Aditya Vikram Birla Kalashikhar Puraskar at annual Sangit Kala Kendra Awards.
Alongside, two emerging stars, in the firmament of theatrics – Neel Choudhary and Irawati Karnik were awarded the Aditya Vikram Birla Kalakiran Puraskars.
The central theme for 2020 awards is “Theatre.”
Shaheedi Divas: The Day is observed as the Martyrdom Day of Guru Tegh Bahadur every year on the 24th of November. It was on 24th November in 1675, Guru Tegh Bahadur sacrificed his life to protect religion, human values, ideals and principles.
He was the ninth Guru of Sikhs and he is called “Hind di Chaadar” which means 'Shield of India' with love and respect. He is regarded as the most selfless martyr of the country.
Recently, President Ram Nath Kovind paid tribute to Guru Teg Bahadur on his Martyrdom Day.
In a message, Mr Kovind said, Guru Tegh Bahadur made supreme sacrifice to protect the faith, belief and rights of the people. He said that his sacrifice inspires all of us to unite for the true service of humanity and his teachings and his work will continue to spread the spirit of love and patriotism among all of us.
History: Guru Tegh Bahadur was born in Amritsar in 1621. He was also the youngest son of Guru Hargobind.
He was beheaded publicly in 1675 by Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb in Delhi's Chandni Chowk. Aurangzeb wanted to convert India into an Islamic country and forced Hindus to convert to Islam, or else be ready for execution. To save their lives, a delegation of 500 Kashmiri Pundits went to meet the Sikh Guru at Anandpur Sahib and sought his help.
Guru Tegh Bahadur asked the Kashmiri Pundits to tell Aurangzeb that if he can convert him into Islam, everybody will follow the suit.
When Aurangzeb got to know about the challenge, he arrested Guru Tegh Bahadur. When Guru Tegh Bahadur refused to accept Islam, he and his followers were tortured brutally for five days. The Mughal ruler even burnt Guru Tegh Bahadur's followers alive in front of him, however, Guruji refused to bow down to Aurangzeb. When Aurangzeb could not bring Guruji to submission, he beheaded him in broad daylight at the Chandni Chowk.
Gurudwara Sis Ganj Sahib and Gurudwara Rakab Ganj Sahib mark the places of cremation and execution of his body.
Sir Chhotu Ram: Sir Chhotu Ram (1881 – 1945) was a prominent politician in British India's Punjab Province. His birthname was Ram Richpal and was popularly known as Deen Bandhu (in Urdu as Rahbare Azam, which translates as messiah of the poor).
He belonged to the Jat community and championed the interest of oppressed communities of the Indian subcontinent. For this feat, he was knighted in 1937.
On the political front, he was a co-founder of the National Unionist Party which ruled the United Punjab Province in pre-independent India and kept Congress and Muslim League at bay.
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi paid tribute to prominent leader Sir Chhotu Ram on his birth anniversary i.e. the 24 November 1881.
Lachit Borphukan: Lachit Borphukan (1622 - 1672) was a commander and Borphukan (Phu-Kon-Lung) in the Ahom kingdom, located in present-day Assam. He is known for his leadership in the 1671 Battle of Saraighat that thwarted a drawn-out attempt by Mughal forces under the command of Ramsingh I to take over Ahom kingdom.
On November 24th, to commemorate the heroism of Lachit Borphukan and the victory of the Assamese army at the Battle of Saraighat, every year Lachit Divas (Lachit Day) is clelebrated.
The Prime Minister, Narendra Modi has paid tribute to Lachit Borphukan on Lachit Diwas is celebrated state-wide in Assam.
The best passing out cadet of National Defence Academy is conferred the Lachit Borphukan gold medal every year from 1999.
Lok Virasat: It is a festival of films on folk art and painting organized by the Films Division (FD).
As part of ‘art-outreach’ initiative, FD has been presenting select package of films on Indian art and heritage as curated online festivals during the last few months.
An exclusive bouquet of documentary films on folk art and paintings - Lok Virasat - is being showcased, between November 27–29, 2020 on FD website and You Tube channel.
The films being streamed include:
- The Kingdom of God: It is a film on the great Indian heritage of art and culture with focus on various folk art traditions.
- Naman – Khele: A film on the ancient folk art performed in Ratnagiri, Maharashtra.
- Bhavai – Fading Memories: A film on Bhavai which is a folk art of Gujarat.
- Sahi Jata – The Fusion Cult: A film on the unique fusion of muscle and music in the form of folk art on the back-drop of the ancient Orissa town of Puri.
- Therukoothu – Dancing For Life: A film depicting the age old Tamil folk art.
Economics
UDIN: It refers to Unique Document Identification Number. UDIN is a unique number given to documents attested by Chartered Accountants in Practice. It is an 18 digits system generated unique number which shall generated separately for each document.
Recently, the Finance Ministry said that CBDT (Central Board of Direct Taxes) will validate Unique Document Identification Number (UDIN) generated from ICAI portal at the time of upload of Tax Audit Reports.
Earlier, the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI), in its gazette notification dated 2nd August, 2019, had made generation of UDIN from ICAI website mandatory for every kind of certificate/tax audit report and other attests made by their members as required by various regulators.
This was introduced to curb fake certifications by non-CAs misrepresenting themselves as Chartered Accountants.
PMJJBY: It refers to Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana. The PMJJBY is a low-cost insurance scheme recently launched by India Post Payments Bank (IPPB) in partnership with PNB MetLife India Insurance Company Limited.
The PMJJBY offers protection and financial security to the underprivileged and poor who are living in unbanked and remote areas of the country, in the unforeseen and unfortunate event of the loss of a family member who is primarily the breadwinner.
- Anyone who has a savings account with IPPB.
- Minimum age 18 years and a maximum age 50 years
- The insurance scheme is for anyone who is having a saving account in IPPB.
- It offers maximum coverage of Rs 2 lakhs. The annual premium amount for this scheme is Rs 330.
IPPB: It is the abbreviation for India Post Payments Bank. The IPPB was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2018. It is headquartered in New Delhi. The Tagline of IPPB is Aapka Bank, Aapke Dwar. The current Managing Director & CEO of IPPB is J Venkatramu.
SDGs Investor Map: It refers to the Sustainable Development Goals(SDG) Investor Map launched by United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) India and Invest India. It has laid out 18 Investment Opportunities Areas (IOAs) in six critical SDG (Sustainable Development Goals) enabling sectors that can help India push its Sustainable Development efforts.
Highlights:
This initiative which is an instrumental stride in India’s development trajectory has been developed six SDG enabling sector such as:
- Financial sector
- Education sector
- Healthcare sector
- Agriculture sector
- Allied activities sector,
- Renewable energy and alternative and sustainable environment sector
Among the identified 18 investment opportunities areas (IOAs), 10 out of them are identified Investment Opportunity Areas (IOAs) and have strong venture capital activity and private equity. The remaining 8 IOAs are emerging opportunities, which have received attention from early-stage investors.
Investor Map comes at a critical time for India, as the SDG financing gap in India has only widened further with the emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic. This data-backed research and insights will provide a better understanding as to how the SDG financing gap can be reduced in India.
The map which is crucial to ‘Building Back Better’ will help private and public sector stake-holders direct capital towards IOAs, and White Spaces (Areas of Potential) that can contribute to the sustainable development needs of the country by making the economy and societies more resilient and sustainable.
SDGs: It refers to the sustainable development goals. SDGs also known as the Global Goals, were adopted by all United Nations (UN) Member States in 2015 as a universal call to action to end poverty, protect the planet and ensure that all people enjoy peace and prosperity by 2030. It was launched in order to address the urgent political, environment and economic challenges faced by the world.
UNDP: It is the acronym for United Nations Development Programme. UNDP was founded on 22 November 1965. It is headquartered in New York, USA. It promotes technical and investment cooperation among nations and advocates for change and connects countries to knowledge, experience and resources to help people build a better life for themselves. The current head of UNDP is Achim Steiner.
Invest India: It is a non-profit venture under the Department of Industry and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry. It was founded in 2006 and is headquartered in New Delhi. The current MD & CEO is Deepak Bagla.
Merchant Shipping Bill, 2020: The Government of India (GoI) has recently issued a draft of the Merchant Shipping Bill, 2020 for public consultation.
It has been issued by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways with an aim to repeal and replace the Merchant Shipping Act, 1958 and the Coasting Vessels Act, 1838.
The main objective of drafting the Merchant Shipping Bill, 2020 is promoting the growth of the Indian shipping industry by incorporating the best practices adopted by other advanced countries like the United States, United Kingdom, Japan, Singapore and Australia.
Adequate provisions are incorporated to ensure the safety and security of vessels, safety of life at sea, prevent marine pollution, provide for maritime liabilities and compensations, and ensure comprehensive adoption of India’s obligations under International Conventions, promote ease of doing business.
Defence
SITMEX-20: It is the 2nd edition of India, Singapore and Thailand Trilateral Maritime Exercise conducted from 21st to 22nd November 2020 in Andaman Sea.
The Indian Navy deployed indigenous Anti-Submarine Warfare corvette INS Kamorta and missile corvette INS Karmuk for the exercise and Singapore deployed a ‘Formidable’ Class frigate ‘Intrepid’ and ‘Endurance’ Class Landing Ship Tank ‘Endeavour’ and the Royal Thai Navy deployed a ‘Chao Phraya’ Class frigate ‘Kraburi’ for the exercise.
The 2020 edition of the exercise was hosted by Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN).
SITMEX: The SITMEX series of exercises are conducted to enhance mutual inter-operability and imbibing best practices between IN, Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN) and Royal Thai Navy (RTN). The main objective of the exercise is also to strengthen mutual confidence and develop common understanding and procedures towards enhancing the overall maritime security in the region.
The first edition of SITMEX was hosted by Indian Navy in September 2019 off Port Blair.
SIMBEX: The SIMBEX series of exercises between Indian Navy and Republic of Singapore Navy are being conducted annually since 1994. These exercises are aimed at enhancing mutual inter-operability and imbibing best practices from each other.
Indian Navy is scheduled to host The 27th edition of India - Singapore Bilateral Maritime Exercise SIMBEX-20 is scheduled to be hosted by the Indian Navy from November 23 in Andaman Sea. It will continue till 25th of this month.
The 2020 edition of SIMBEX will witness participation by Indian Navy ships including destroyer Rana with integral Chetak helicopter and indigenously built corvettes Kamorta and Karmuk.
Varunastra: Varunastra is a ship-launched, heavyweight, electrically-propelled anti-submarine torpedo. It is capable of targeting quiet submarines, both in deep and shallow waters in an intense countermeasures environment. It is powered by an electric propulsion system with multiple 250 Kilowatts Silver Oxide Zinc (AgOZn) batteries.
The first Production unit of Heavy Weight Torpedo (HWT), Varunastra was recently flagged off by the Defence Research and Development (DRDO) Chairman G Satheesh Reddy.
In a major boost to Atma Nirbhar Bharat, the Varunastra has been designed and developed by Naval Science & Technological Laboratory (NSTL) of DRDO while Bharat Dynamics Limited (BDL), Vishakhapatnam has manufactured the torpedo for the Indian Navy.
This anti-submarine torpedo weighing more than one ton can carry a warhead of up to 250 kg. This indigenous torpedo will equip Indian warships and Indus class submarines. The torpedo can be launched both from Ship and Submarine.
It was inducted by Indian Navy in 2016 and is named after a legendary weapon created by the Hindu God of the Oceans-- Varunastra.
BDL: It refers to the Bharat Dynamics Limited. BDL is an enterprise of Government of India under the Ministry of Defence. It is the Lead Integrator for the Akash Weapon System of Indian army. It was founded in 1970 as a manufacturing base for guided missiles and allied defence equipment. It is headquartered in Hyderabad, Telangana, India. It is associated with DRDO for various missile programmes and is the production agency for Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile (QRSAM), for which, trials were conducted successfully. It is also the production agency for Astra Air- to- Air Missile System which is indigenously developed by the DRDO for the Indian Air Force (IAF). The current Chairman and Managing Director of BDL is Siddharth Mishra.
Lt Gen Harpal Singh: He has appointed new Engineer-in-Chief of Indian Army. He is presently the Director-General of Border Roads Organization and would take over his new appointment on 1 December.
Lt Gen Harpal Singh is an alumnus of National Defence Academy, Khadakwasla. He was commissioned into the Corps of Engineers on 24 December 1982. He later commanded a Border Roads, Task Force, in Jammu and Kashmir valley. He has also been the Chief Engineer of Project Dantak (BRO) at Bhutan, Chief Engineer (Navy), Mumbai and Chief Engineer HQ Eastern Command. He is a graduate of the Defence Services Staff College, Wellington, the Higher Command and National Defence College courses.
Major Gen Rajeev Chaudhary has been appointed as the new Director-General of the Border Roads Organization (BRO).
BRO: It refers to the Border Roads Organization. In order to ensure coordination and expeditious execution of projects, the Government of India (GoI) set up the Border Roads Development Board (BRDB) with the Prime Minister as Chairman of the Board and Defence Minister as Deputy Chairman. The BRO was formed on 7 May 1960 to secure India's borders and develop infrastructure in remote areas of the north and north-east states of the country. It is responsible for the construction and maintenance of roads along the borders with China and Pakistan. It develops and maintains road networks in India's border areas and friendly neighboring countries. BRO has been entirely brought under the Ministry of Defence.
Environment
DOM: It refers to Deep Ocean Mission. According to the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MMoES), India’s ambitious DOM is all set to be launched in 3-4 months.
The mission envisages the exploration of minerals, energy and maritime diversity of the underground water world which is a vast part that still remains unexplored. The mission is also set to enhance India's presence in the Indian Ocean.
The mission at the expected cost of Rs 4,000 crore, will give a boost to efforts to explore India's vast Exclusive Economic Zone and Continental Shelf.
It will lead to the designing, development and demonstration of human submersibles. It will also help in exploring the possibility of deep-sea mining and also developing necessary technologies.
The ministry's secretary, M Rajeevan, said required approvals are being obtained for the "futuristic and game-changing" mission, and it is likely to be launched in the next 3-4 months.
The stake holders in this mission will be MOS along with other government departments like the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO), Department of Biotechnology, Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) Some of the technologies involved will be developed by organizations such as the ISRO and DRDO.
Note: In September 2016, India signed a 15-year contract with the International Seabed Authority (ISA) for exploration of Poly-Metallic Sulphides (PMS) in the Indian Ocean. The 15-year contract formalised India's exclusive rights for exploration of PMS in the allotted area in the Indian Ocean.
ISA: It is an acronym for International Seabed Authority. ISA is an autonomous international organization body headquartered in Kingston, Jamaica. It was established on 16 November 1994 to regulate mining and related activities in the international seabed beyond national jurisdiction, an area that includes most of the world's oceans. It was established under the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) and the 1994 Agreement relating to the Implementation of Part XI of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (1994 Agreement).
India-Finland: India and Finland recently signed an MoU to develop cooperation in the field of environmental protection and biodiversity conservation.
The MoU was signed virtually by Environment Minister Prakash Javadekar from the Indian side and his Finnish counterpart Krista Mikkonen.
The MoU is a platform to further advance Indian and Finnish partnership and support, exchange best practices in areas like prevention of air and water pollution, waste management,promotion of circular economy and sustainable management of natural resources including forests, Climate change, etc.
Under the MoU, both the countries will work together towards the fulfillment of commitments made under the Paris Agreement.
The MoU seeks to strengthen scientific, technological, and management capabilities. It also aims to develop bilateral cooperation in the field of environmental protection and biodiversity conservation on the basis of equality, reciprocity, and mutual benefit with due respect to the promotion of sustainable development.
PTR: It refers to the Pilibhit Tiger Reserve. PTR and the Uttar Pradesh Forest department have bagged the first-ever international award, TX2 (Tigers times two), for doubling the number of tigers in 4 years against a target of 10 years. PTR was the first to receive the award among 13 tiger range countries.
The 13 tiger range countries are Russia, India, Bangladesh, China, Bhutan, Malaysia, Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Indonesia, Thailand, Myanmar and Nepal
The partners of the award had targeted doubling of population in ten years, but the Pilibhit Tiger Reserve achieved this in 4 years only. The partners are Global Tiger Forum, United Nations Development Programme, Conservation Tiger Standards and Lion’s Share.
The award was virtually presented to the principal chief conservator of forest (wildlife) of the state, Sunil Pandey, by UNDP’s (United Nations Development Program) head of ecosystems and biodiversity, Mindori Paxton.
About PTR: PTR is situated in Uttar Pradesh’s Pilibhit and Shahjahanpur District. It was established in June 2014 as the 46th Tiger Reserve of India under: Project Tiger." It forms the part of the Terai Arc Landscape. It is situated in the upper Gangetic Plain Biogeographic Province. Rivers like Sharda, Mala, Chuka,and Khannot originates from the tiger reserve. The Tiger reserve is home to sal forests, tall grasslands and swamp. These are maintained by periodic floods from rivers.
The tiger population has increased from 25 in 2014 to 64 in 2018.
Climate Change knowledge portal: Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change Prakash Javadekar recently launched the India Climate Change Knowledge Portal.
The portal will have all the major steps the Government is taking at both national and international levels to address the climate change issues.
It will act as a single-point information resource that provides information on the different climate initiatives of the Government. It will enable users to access updated status on these initiatives.
The eight major components of the portal are climate profile of India, NDC goals of India, National Policy Framework, adaptation action, bilateral and multilateral cooperation, report and Publication, mitigation actions, International climate negotiations.
During the launching event, Javadekar said that India has practically achieved its pre-2020 climate action targets.
Indian Policy
CCIM: It refers to the Central Council of Indian Medicine. CCIM, the statutory body that regulates the Indian Medical systems of Ayurveda, Siddha, Sowa-Rigpa and Unani Medicine has issued a notification to streamline some of the provisions of the regulations concerning Post Graduate Ayurveda Education by adding clarity and definition to the same.
The notification relates to the Shalya and Shalakya streams of Post Graduate Education in Ayurveda. Ministry of AYUSH issued clarifications over Indian Medicine Central Council (Post Graduate Ayurveda Education) Amendment Regulations 2020.
As per the notification, it specifies a total of 58 surgical procedures that PG scholars of these streams need to be practically trained in so as to enable them to independently perform the said activities after completion of their PG Degree.
Shalya and Shalakya are independent Departments in Ayurveda colleges, performing such surgical procedures.
The question of mixing Ayurveda with Conventional (Modern) Medicine does not arise here as CCIM is deeply committed to maintaining the authenticity of Indian systems of medicine.
Union Minister for Social Justice and Empowerment: The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment is a ministry of Government of India (GoI). It is responsible for welfare, social justice and empowerment of disadvantaged and marginalized sections of society, including scheduled castes, Other Backward Classes, the disabled, the elderly, and the victims of drug abuse. The current Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment is Thawar Chand Gehlot, who is assisted by a Minister of State, Rattan Lal Kataria, Krishan Pal Gujjar and Ramdas Athavale.
Recently, the Union Minister for Social Justice and Empowerment Shri Thaawarchand Gehlot e-Launched ‘National Portal for Transgender Persons’ and also e-inaugurated 'Garima Greh' which is a Shelter Home for Transgender Persons in Vadodara, Gujarat.
The National Portal for Transgender Persons has been developed as per the Notification of Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Rules, 2020.
Under the Scheme of ‘Shelter Home for Transgender Persons’, the ministry has decided to set up shelter homes for transgender persons who have been forced to leave their homes or abandoned by the family. This is the first such home that has been inaugurated in Vadodara in Gujarat.
The main aim of this portal is to help a transgender person in applying for a Certificate and Identity card digitally from anywhere in the country.
The portal will help the transgender person to get the I-Card without any physical interface and without having to visit any office. Once the Certificate and I-card are issued, the applicant can download them from the Portal itself.
The Portal will monitor the status of their application that ensures transparency in the process.
The issuing authorities are under strict timelines to process the applications and issue certificates and identity cards without any necessary delays and if there are any delays then the applicant has the option to submit grievances through the Portal which are forwarded to the concerned person and will be resolved at the earliest.
This portal will help a lot of people from the community to come forward and get Transgender Certificate and Identity Cards due to The Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019.
Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019: The Act came into effect on 10th January 2020. It is the first concrete step towards ensuring welfare of Transgender persons.
According to the act, the transgender persons are defined as someone whose gender does not match with their gender assigned during birth.
It enforces minor right of residence. This compels the transgenders below 18 years to cohabit with their family.
The act prevents discrimination against transgenders in education, employment, healthcare, housing and other services.
It mandates that the persons will be recognised as transgenders based on the identity cards. The identity cards are issued by the District Magistrates.
According to the act, it is the right of the transgenders to undergo sex reassignment surgeries. Also, it is their right to claim other health facilities.
This Act aims to help them come into the mainstream of the Society.
Garima Greh: A Shelter Home for Transgender Persons: This scheme which was e-inaugurated along with the National Portal for Transgender Persons will be run in association with Lakshya Trust, a Community based organisation entirely run by the Transgenders.
The purpose of the Shelter Home is to provide shelter to Transgender persons, with basic amenities like shelter, food, medical care, and recreational facilities. In addition, Garima Grih will also includes shelter facility, food, clothing, recreational facilities, skill development opportunities, yoga, meditation/prayers, physical fitness, library facilities, legal support, technical advice for gender transition and surgeries, capacity building of trans-friendly organizations, employment and skill-building support, etc.It will enable them to lead a life of dignity and respect.
The Nodal Ministry has identified 10 cities to set up the 13 Shelter Homes and extend the facilities to Transgender persons. It will be in association with selected 13 CBOs in the country on pilot basis. The cities include Vadodara, New Delhi, Kolkata, Manipur, Patna, Bhubaneswar, Jaipur, Chennai, Raipur, Mumbai, etc.
The scheme will rehabilitate a minimum of 25 transgender persons in each homes identified by the Ministry.
This is a pilot project, and on its successful completion, similar schemes will be extended to other parts of the country.
NCTP: It refers to the National Council for Transgender Persons. The council was established in August by the Centre in exercise of the powers conferred by the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019. The NCTP was constituted to formulate policies, programmes, draft legislation and projects regarding members of the community for achieving equality and full participation by them.
The other functions of the council are:
- To review and coordinate the activities of all the departments of government and other governmental and non-governmental organisations dealing with matters relating to transgender persons.
- To redress the grievances of transgender persons.
- To perform such other functions as may be prescribed by the Centre.
The chairperson of the council is the Minister of Social and Justice Empowerment. The council will include 5 members from transgender community, a member from NITI Aayog, National commission for Women, National Human Rights Commission. It will also include representatives from Union Territories and states on rotational basis.
GoI: It refers to the Government of India. The GoI recently, approved 7 proposals of Food Processing Projects worth over 234 crore rupees under the Scheme for Creation of Infrastructure for Agro-Processing Cluster.
The scheme was approved virtually at the Inter-Ministerial Approval Committee meeting chaired by Minister of Food Processing Industries Narendra Singh Tomar.
The scheme for Creation of Infrastructure for Agro-Processing Cluster was approved in 2017 under the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana (PMJSY) to incentivize the setting up of agro processing clusters in the country.
The main aim of this scheme is the development of modern infrastructure to encourage entrepreneurs to set up food processing units based on cluster approach.
JJM: It refers to Jal Jeevan Mission. JJM is a central government initiative under the Ministry of Jal Shakti. This mission aims to ensure access of piped water for every household in India. The Union Cabinet on 13 August 2019 had approved JJM to provide Functional Household Tap Connection (FHTC) to every rural household by 2024. JJM has been launched in partnership with States, to enable every household in villages to have a FHTC within the premises by 2024.
Recently, a multi-disciplinary Technical Committee set up under the Jal Jeevan Mission has recommended 5 technologies to provide field level solutions to the states. These technologies are:
- Presto Online Chlorinator: It disinfects water and removes bacterial contamination using a non-electricity dependent online chlorinator.
- Grundfos AQpure: It is a solar energy-based ultra-filtration water treatment plant.
- Johkasou Technology:It uses advanced anaerobic-aerobic configuration for inbuilt water treatment
- Janajal Water on Wheel: It is an Internet on Things-based, GPS-enabled technology for doorstep delivery of safe water.
- FBTec: It is a decentralized sewage treatment system.
FDPs: It refers to the online Faculty Development Programmes. The Union Education Minister Ramesh Pokhriyal 'Nishank' recently inaugurated 46 online AICTE Training and Learning (ATAL) Academy Faculty Development Programmes (FDPs).
The programmes aim to train teachers of higher education institutions associated with the All India Council of Technical Education (AICTE) in emerging areas in technology.
ATAL Academy is conducting FDPs in online mode, including the process of registration till certificate disbursal mechanism. In the year 2020-21, new thrust areas in the field of Engineering, Management, Life Skills, and Design & Media have been incorporated. The FDPs will be conducted in 22 Indian states according to the new National Education Policy (2020).
The main objective of ATAL Academy is to provide quality technical education in the country and to promote research and entrepreneurship through training in various emerging fields. IITs, IIITs, NITs CU and research labs are organizing these ATAL FDPs. This year the online FDP programme will cost 10 crore rupees.
The FDPs has been recognized by the London-based organization, Book of World Records, as a world record, under which 1,000 online FDPs in over 100 emerging areas will benefit one lakh faculty members across premier institutions like IITs, NITs, and IIITs.
Indian polity
NGT: It refers to the National Green Tribunal. The NGT was established in 2010. It was established by an act of Parliament of India. The Act is known as the National Green Tribunal Act, 2010. The Principal Bench of the NGT is in New Delhi apart from its regional benches in Chennai , Pune, Kolkata and Bhopal. The Chairperson of the NGT is a retired Judge of the Supreme Court Justice Lokeshwar Singh Panta. The NGT has been created after inspirations from the article 21 (Right to life and personal liberty) of the Constitution of India. NGT Act, 2010 of the Indian Parliament enables the creation of a special tribunal to handle the environmental cases.
Recently, the NGT has recently directed all the states and union territories to designate a nodal agency to protect the water bodies in their regions.
As per the directions of NGT:
- The Nodal Agencies shall hold meetings under the guidance of chief secretaries of the state and that the meetings should not be held later than 31 January, 2021.
- The meeting must be held on time to take stock of the situation and plan further.
- The central monitoring committee is also required to monitor the steps taken for restoration of water bodies by all states at least thrice in a year. The committee has to adopt a mechanism to monitor and address related grievances.
Note: The central monitoring committee was formed to monitor the remediation of 351 polluted river stretches.
Polluted river stretches in India:
During 2018, around 351 polluted river stretches on 323 rivers has been identified by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) of India. According to CPCB, these river stretches are located in the states of Gujarat, Assam and Maharashtra. The river stretches in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar are less polluted than these three states.
The Prohibition of Unlawful Religious Conversion Ordinance, 2020: The UP Cabinet recently cleared an ordinance to ban religious conversion for marriage. The new law will put the onus on the defendant to prove that conversion was not for marriage.
The Ordinance makes forced religious conversion a non-bailable offence. It recommends 1-5 years imprisonment if an accused fails to prove that the conversion of the woman was not for marriage or by use of force, allurement etc. Such marriages would lead to imprisonment of a maximum of ten years and a penalty of Rupees 50,000.
The jail sentence for the offence would be 3-10 years if the woman is from the SC/ST community or is seen as part of mass conversion.
The ordinance would declare marriage for the sake of conversion null and void.
Furthermore, the proposed law does not include any restriction on interfaith marriage. If someone willingly wants to convert for marriage then, he or she will have to give two months notice in advance to the concerned district magistrate.
The Ordinance was cleared by the UP Cabinet after CM Yogi Adityanath promised to bring an “effective law” against unlawful marriages. It was done in the light of popularization of a politically motivated legally unrecognized term “Love Jihad”. However, the law itself contains no mention of love jihad.
Constitution Day: The Constitution Day also called the Samvidhaan Divas or National Law Day or National Constitution Day is celebrated on 26 November every year.
The day is observed to mark the anniversary of the adoption of Indian Constitution on November 26, 1949 by the Constituent Assembly of India, which came into effect on 26 January 1950.
The Government of India (GoI) declared 26 November as Constitution Day in 2015 by a gazette notification to mark the 125th birth anniversary of Dr Ambedkar, which was in 2015. The announcement was made by PM Modi while he laid the stone to the Statue of Equality in Mumbai.
Ambedkar who is also called the father of the Indian Constitution played a key role in the drafting of the constitution.
Previously this day was celebrated as National Law Day.
A number of activities aimed at highlighting and reiterating the values and principles enshrined in the Constitution are organized.
Constitution of India: It is the longest written Constitution in the world. It took 2 years, 11 months and 17 days for the drafting committee of the constituent assembly to frame the constitution. The Indian Constitution describes the fundamental political code, structure, procedures, powers, and duties of the government institutions. It also explains fundamental rights, directive principles, and the duties of citizens.
Note: The Constitution of India was adopted on November 26, 1949 but the Constitution came into effect on January 26, 1950 and hence India celebrates its Republic Day on 26th January every year. And the Constitutional head of India, the President hoists the national flag on this day.
The year 2020 marked the 70th anniversary of adoption of the Constitution in 1949 by the Constituent Assembly. Number of events was organized where people read the Preamble of the Constitution.
International
15th G20 Summit: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi recently participated in the 15th G20 Summit which was hosted by Saudi Arabia. The summit was chaired by King Salman bin Abdulaziz Al Saud of Saudi Arabia through video-conferencing, due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Along with the Indian PM, the respective Heads of State and Government of 19 member countries, EU, other invited countries and international organizations also participated in the Summit.
The two-day Summit was held under the theme “Realising the Opportunities of the 21st Century for All”.
During the Summit, the main focus was on resilient, inclusive and sustainable recovery from covid-19 crisis. The leaders discussed on the preparedness of the countries in response to the pandemic. They also shared their vision on building a resilient future.
The subsequent G20 summits are to be held in Italy in 2021, Indonesia in 2022, India in 2023 and Brazil in 2024.
Italy will take over the Presidency of the 16th G20 on 1st December 2020.
At the end of the Summit, a G20 Leaders’ Declaration was issued which called for coordinated global action, solidarity, and multilateral cooperation to overcome the current challenges and realize opportunities of the 21st century for all by empowering people, safeguarding the planet, and shaping new frontiers.
India and Afghanistan: The External Affairs Minister of India, Dr Subrahmanium Jaishankar recently led the Indian delegation at the 2020 Afghanistan Conference which was organized in Geneva from 23-24 November 2020 virtually. The Conference was co-hosted by the United Nations, the Government of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, and the Government of Finland.
The focus of the conference was Self-Reliance, Peace and Prosperity. It aimed at reaffirming the commitment of the international community towards the Afghanistan government to determine shared development objectives for 2021.
At the conference, India emphasizing on its long term commitment for the development of Afghanistan through reconstruction and rehabilitation, announced a new phase of over 100 high-impact community projects worth USD 80 million (Rs 592 crore) in Afghanistan.
The projects include construction of the Shatoot Dam, which would provide safe drinking water to 2 million residents of Kabul city. This dam will be built on the 202-kilometre Phul-e-Khumri transmission line, which was built by India in 2019 to provide electricity to Kabul city. India had earlier built the 202-km Phul-e-Khumri transmission line that provided electricity to Kabul city.
Dr Jaishankar said that as an important stakeholder, India looks forward to walk hand in hand with the people of Afghanistan and world community in working towards a peaceful, prosperous, sovereign, democratic and united Afghanistan.
APEC: It refers to the Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation. The 2020 Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Economic Leaders’ Meeting was recently held under the Chairmanship of Malaysian Prime Minister Tan Sri Muhyiddin Yassin.
Several leaders of the cooperation joined the summit. The Summit was attended by the US President Donald Trump as well.
The theme of the APEC Malaysia 2020 was “Optimising Human Potential Towards a Resilient Future of Shared Prosperity: Pivot. Prioritise. Progress”.
At the summit, the APEC 2020 ended with the adoption of the APEC Putrajaya Vision 2040 and the 2020 Kuala Lumpur Declaration.
The 1994 Bogor Goals were replaced with post 2020 vision.
Putrajaya Vision 2040: It is a new 20-year growth vision, which will replace the existing Bogor Goals, which was agreed by leaders in 1994 for free and open trade and investment in APEC.
The APEC Summit 2021 will be hosted by New Zealand.
This is the second time Malaysia hosted an APEC meeting, having hosted one in 1998.
About APEC: APEC is an inter-governmental forum for 21 member economies in the Pacific Rim that promotes free trade throughout the Asia-Pacific region. It was founded in November 1989 Bob Hawke and is headquartered in Singapore. It operates on the basis of non-binding commitments and open dialogue. It is recognized as one of the highest-level multilateral blocs and oldest forums in the Asia-Pacific region. It exerts a significant global influence.
The members of the grouping are Australia, Brunei, Canada, China, Indonesia, South Korea, Malaysia, Mexico, Hongkong, Chile, Japan, Peru, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea ah, Philippines, Russia, Thailand, Singapore, Taiwan and United States of America.
Note: India is not a full-time member of APEC because the members of the grouping had decided not to allow India as the country as India does not border Pacific Ocean, However, India has an observer status.
4TH Global Conference On Criminal Finances and Cryptocurrencies: The virtual 4th Global Conference on Criminal Finances and Cryptocurrencies was recently attended by more than 2,000 representatives from 132 countries. The representatives from Judiciary, Financial Intelligence Units (FIUs), and international organizations met virtually to shape international cross-sector solutions against the criminal use of cryptocurrencies.
The conference’s agenda included:
- Trends and investigations on cryptocurrency related offences
- Exploring criminal flows and operations in the dark markets.
- Ransomware and sextortion case studies
- Money laundering involving virtual assets
- The transfer of drug proceeds using cryptocurrencies.
The Global conference was organized by the Interpol, Europol (European Police Office) and the Basel Institute on Governance.
About: The conference is an initiative of the Working Group on Cryptocurrencies and Money Laundering. It was established in 2016 by the three organisations. They are:
- Basel Institute on Governance
- Interpol
- Europol
The main objective of launching the conference was to strengthen the knowledge, expertise and best practices for investigations into financial crimes and intelligence on virtual assets and cryptocurrencies.
The conference underlined the need to expand capabilities and regulate virtual asset service providers to prevent money laundering.
Ultimately, the main aim of the conference is to organize an annual global conference for a collective approach against cryptocurrency which will increase the understanding, knowledge and capacity to successfully investigate crimes in which cryptocurrencies are involved.
Scotland: Scotland is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. The name Scotland derives from the Latin Scotia, land of the Scots, a Celtic people from Ireland who settled on the west coast of Great Britain about the 5th century CE. The Capital of Scotland is Edinburg. The currency used here is Pound sterling.
Recently, The Scottish parliament passed a landmark legislation unanimously that has made period products such as sanitary pads and tampons free of cost to those people who need them. Scotland has become the first in the world to make sanitary products free.
Earlier, in 2018, Scotland became the first country to provide free sanitary products in schools, colleges and universities.
The main objective of passing the bill was to tackle “period poverty”, which is when some people who need period products struggle to afford them.
Period Poverty: Certain circumstances make access to sanitary products difficult for women and trans people including homelessness, coercive, controlling and violent relationships and health conditions such as endometriosis.
National
India and Myanmar: The 7th Joint Trade Committee Meeting between India and Myanmar was recently held through virtual mode. The Meeting was co-chaired by Union Minister for Ministry of Commerce and Industry Minister Piyush Goyal and Union Minister for Ministry of Commerce, Myanmar Dr. Than Myint.
At the meeting, various bilateral issues ranging from banking, trade, investment, connectivity, capacity building and upgradation of border infrastructure were reviewed by both the sides.
During the meeting, the strong cultural and commercial ties between India and Myanmar and the priority India attaches to its partnership with Myanmar in accordance with India’s ‘Neighborhood First’ and ‘Act East’ policies were highlighted.
India reiterated its commitment in enhancing its multifaceted cooperation with Myanmar, in several areas including trade and investment and Oil and Gas.
All India Presiding Officers Conference: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently addressed the concluding session of the 80th All India Presiding Officers Conference.
The two day conference which began at Kevadia in Gujarat on the 25th November 2020 was inaugurated by the President Ram Nath Kovind. The conference was attended by Vice President and Rajya Sabha Chairman M Venkaiah Naidu, Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla, Gujarat Governor Acharya Devvrat, the state's Chief Minister Vijay Rupani among others. The chairperson of the conference is Speaker Om Birla.
He addressed the conference via video conferencing at Kevadia in Gujarat. PM Modi paid tributes to many foreign citizens and policemen lost their live in the 26/11 terror attack by terrorist from Pakistan in 2008.
The theme for this year's conference is Harmonious Coordination between Legislature, Executive and Judiciary - Key to a Vibrant Democracy.
The All India Presiding Officers Conference began in 1921 and this conference in Gujarat marks its centenary year.
HRMS: It is an abbreviation for Human Resource Management System. The Inidan Railways (IR) recently launched a completely digitized online Human Resource Management System (HRMS).
HRMS is a high thrust project for Indian Railways to leverage improved productivity and employee satisfaction.
This move by IR aims to improve efficiency and productivity of the Railway system. The system is expected to create a big impact on the functioning of all the employees and will make them more tech savvy.
HRMS is a step towards realizing the vision of Prime Minister Narendra Modi to transform India into a digitally empowered society and knowledge economy.
Under HRMS, Vinod Kumar Yadav, Chairman and CEO of Railway Board launched:
- Employee Self Service (ESS) which enables the railway employees to interact with various modules of HRMS including communication regarding change of data.
- Provident Fund (PF) Advance module which enables Railway employees to check their PF balance and apply for PF advance online.
- Settlement module which digitizes the entire settlement process of retiring employees.
The modules seek to benefit over 27 lakh families of both serving and retired Railway employees.
Several other modules of HRMS are already operational in the Indian Railways.
National Organ Donation Day: This day is celebrated as Indian Organ Donation Day (IODD) on the 27th of November since last 10 years.
The 11th Indian Organ Donation Day was organized and celebrated by the Union Health Ministry in New Delhi.
Tamil Nadu has been adjudged the best in organ donation in the country for the sixth consecutive year.
NOTTO: It refers to the National Organ & Tissue Transplant Organization. NOTTO is mandated under the Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act 2011 to carry out activities for promotion of organ donation from deceased persons.
AAI: It refers to the Airports Authority of India. AAI is a statutory body created through the Airports Authority of India Act, 1994. It was founded on 1 April 1995. It works under the Ministry of Civil Aviation, Government of India (GoI) and is responsible for creating, upgrading, maintaining and managing civil aviation infrastructure in India. The current Chairman of AAI is Arvind Singh.
Recently, AAI observed the Aviation Safety Awareness Week 2020 from 23rd to 27th November 2020.
The week-long celebration was observed at all airports and ANS locations managed by AAI across India.
The Airport Directors organized awareness programme in schools and colleges on role of local residents in aviation safety to make people of surrounding community aware about their role in ensuring safety of aircraft operation in local airport.
The main aim of the Ministry of Civil Aviation is to achieve long term objective of Zero fatality by the year 2030 as envisaged by ICAO in its Global Aviation Safety Plan (GASP-2020-22) through better managed safety systems of stakeholders.
ICAO: It refers to the International Civil Aviation Organization. ICAO is International Civil Aviation organization. It was formed in 1947 as a specialized agency of the United Nations. It is responsible for developing international air transport. It also defines the protocols for air accident investigation
The headquarters of ICAO is located in Quebec Province in Canada.
NCAP 2016: It refers to the National Civil Aviation Policy 2016. NCAP 2016 is government policy approved by Union Cabinet on 15 June, 2016. The proposed new civil aviation policy was first presented in November 2014. After months of debates and inter-ministerial consultations, the Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA) cleared the civil aviation policy for Cabinet approval.
This is for the first time; an integrated Civil Aviation Policy has been brought out by the Ministry of Civil Aviation after independence.
The NCAP 2016 covers the broad policy areas, such as Regional connectivity, Safety, Air Transport Operations, 5/20 Requirement for International Operations, Bilateral traffic rights, Fiscal Support, Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul, Air-cargo, Aeronautical 'Make in India'.
NCAP 2016 aims to make flying affordable to every Indian citizen. The regional connectivity scheme UDAN (Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik) is a key component of the National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP).UDAN is being implemented s to enhance air travel in the unconnected and underserved regions of the country.
People In News
Girish Chandra Murmu: He is the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India who has been elected External Auditor of Inter Parliamentary Union, Geneva, for a three-year term.
He will take charge of this position from the Supreme Audit Institution of Switzerland.
Mala Adiga: She is an Indian-American who has been appointed by Joe Biden as the policy director of his wife Jill Biden, who will be the first lady.
Adiga has served as a senior advisor to Jill and a senior policy advisor on the Biden-Kamala Harris campaign.He, previously was the director for Higher Education and Military Families at the Biden Foundation.
She even served as the deputy assistant secretary of state for Academic Programs at the Bureau of Educational and Cultural Affairs during former President Barack Obama's administration.
Other appointments:
Louisa Terrell, who currently oversees legislative affairs for the Biden-Harris transition team, will serve as the director of the White House Office of Legislative Affairs in Biden administration.
Cathy Russell, Vice-Chair of the Biden-Harris campaign, has been named as the director of the White House Office of Presidential Personnel.
Places In News
Meghalaya: It is a state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed by carving out two districts from the state of Assam: the United Khasi Hills and Jaintia Hills, and the Garo Hills on 21 January 1972. Its capital is Shillong. The current Governor and Chief Minister of Meghalaya are satya Pal Malik and Conrad Sangama respectively.
Recently, the cherry blossom festival was cancelled due to covid-19. It is the only Cherry festival being conducted in India.
Every year the India International cherry blossom festival is hosted by Meghalaya in the starting of November. It is organized by the Government of Meghalaya. The festival is held in Shillong to celebrate the unique autumn flowering of the Himalayan cherry blossoms and mark the beginning of India’s version of autumn. The festival hosts live music, stalls showcasing the cuisine, beauty pageants, etc.
Note: Meghalaya is not only the home to a large variety of fruits, vegetables, spices, and medicinal plants but is also famous for its large variety of orchids — nearly 325 of them. Of these, the largest variety is found in the Mawsmai, Mawmluh and Sohrarim forests in the Khasi hills.
Cherry blossom festival is a national festival of Michigan. It is celebrated in Japan as well.
Himachal Pradesh: Himachal Pradesh is a northern Indian state in the Himalayas. It is situated in the Western Himalayas; it is one of the eleven mountain states of India. Himachal Pradesh shares borders with the union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh to the north, and the states of Punjab to the west, Haryana to the southwest, and Uttarakhand and Uttar Pradesh to the south. The state also has a border with the autonomous region of Tibet to the east. Its summer capital is shimla and winter capital is Dharamshala. The current Governor and Chief Minister of Himachal Pradesh are Bandaru Dattatreya and Jai Ram Thakur respectively.
Recently, the Himachal Pradesh Government launched “Snow Safety Campaign” to make people aware of the Covid-19 Pandemic as well as to collect information about diseases like TB, sugar, blood pressure and leprosy, across the state.
Under this campaign, a door to door campaign has also been started. Health, Ayurveda, Women and Child Development, Panchayati Raj department, district administration and almost 8000 teams of NGOs will work in this campaign. This will ensure door-to-door data collection of people’s health parameters.
Katchal Island: It is one of the Nicobar Islands, India. Katchal Island was previously known as Tihanyu. Katchal is inhabited by Nicobari Tribes and Migrated Tamilians (For Rubber plantation workers under Sastri-Srimao Bandaranayaka Pact of 1964).
Recently, Katchal Island was in news because a fuel tanker was dangerously drifting towards the pristine Katchal Island in Nicobar due to power failure. The Indian Coast Guard (ICG) averted mishap off the Nicobar Islands towed the fuel tanker back to safe waters.
Ladakh: Ladakh is a region administered by India as a union territory, and constituting a part of the larger region of Kashmir, which has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947. Until 2019, Ladakh was a region of the state of Jammu and Kashmir. In August 2019, the Parliament of India passed an act by which Ladakh became a union territory on 31 October 2019. The capital of Ladakh is Leh, Kargil. The current Lieutenant Governor of Ladakh is Radha Krishna Mathur.
Recently, Ladakh has got the largest solar power project set up under the Centre’s ‘Make In India’ initiative at Leh IAF station to provide sustainable energy alternative to fossil fuel and traditional methods of energy generation. The project worth Rs 122 crore was inaugurated by Air Marshal V R Chaudhari, Commander-in-chief, Western Air Command.
The project namely ‘Provision of Solar Photo Voltaic Powerplant 1.5 MW’ has been completed within 12 months well before the completion deadline of March 31, 2021.
It is the largest solar project at a high altitude in the entire Leh in the Union Territory of Ladakh. It has been established at IAF Station Leh. The project was conceptualized under Make In India. It is executed to provide sustainable energy alternative to fossil fuel and traditional methods.
It is the largest installed solar project till date out of the target of 300 MW in three phases for defence sectors and 14 MW for Leh region as set by the Union Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
Maryada Purushottam Sri Ram Airport: It is the new name of Ayodhya airport. The Uttar Pradesh (UP) Cabinet recently cleared the proposal to rename the Ayodhya airport. The proposal for the same will be sent to the Ministry of Civil Aviation after it is passed by the state Assembly.
The announcement was made by UP Chief Minister Adityanat on the occasion of Deepotsav on Diwali eve in November 2018 that Ayodhya will have both international and domestic terminals and could potentially be one of the largest airports of UP.
Uttar Pradesh: Uttar Pradesh is a state in northern India. It was created on 1 April 1937 as the United Provinces of Agra and Oudh during British rule, and was renamed Uttar Pradesh in 1950. Its Capital city is Lucknow. The Chief Minister and the Governor of Uttar Pradesh are Yogi Adityanath and Anandiben Patel respectively.
Har Ghar Nal Yojana: It is a rural drinking water supply project that was recently launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi. An initiative by the Modi government was launched was the residents of Sonbhadra and Mirzapur district in Uttar Pradesh. The project aims to provide tap water connections to around 2,995 villages which will benefit 42 lakh people.
These regions were chosen for this project because, despite having many rivers like Ganga, Ghaghara, Yamuna and Sarayu, water scarcity prevails in the region. In addition, the river water and the underground water in the region is also getting polluted rapidly. Therefore, it is important to provide clean drinking water to the region.
About: The scheme was launched with an objective to provide tap water to every Household. Under the Har Ghar Nal Yojana, water of lakes and river will be purified and supplied to the families in Sonbhadra. Under this scheme, all households are eligible to claim the benefits of the Har Ghar Nal Yojana.
Science and Technology
Copernicus Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite: NASA (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) recently launched opernicus Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich satellite on 21 November 2020 from SpaceX reusable Falcon 9 rocket. It was launched to monitor oceans for 30 years. The mission of this launch is to Measure the height of the ocean as it is one of the key components in understanding the climate change.
The satellite launch was a part of the Mission Jason Continuity of Service. The spacecraft consists of two components. The other component of the spacecraft is to be launched in 2025.
The satellite was jointly developed by National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), European Space Agency (ESA) and European Organization for the Exploration of Meteorological satellite (EUMETSAT) and French National Centre for Space Studies (CNES).
The main objective of the satellite is:
- To make sea level observations and will provide measurements on global sea level rise.
- To measure the sea surface height, the satellite will send pulses to the Earth’s surface and will measure the returning signals.
- To measure water vapour in the earth’s atmosphere.
- It will also collect data supporting oceanography.
Note: The satellite has been named after Michael Freilich, an Earth scientist who retired from NASA in 2019. He was a pioneer in advancing ocean observations from space. He passed away in August 2020 due to Cancer.
NOAA: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) is an American scientific agency within the US Department of Commerce that focuses on the conditions of the oceans, major waterways, and the atmosphere.
National Science Film Festival: The tenth edition of prestigious National science film festival was recently held from 24th to 27th November 2020 in a virtual mode amidst the ongoing pandemic. The festival was inaugurated by Deputy Chief Minister of Tripura Jishnu DevVerma.
The four-day long film festival has been jointly organized by Vigyan Prasar, an autonomous agency under the Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India and the Tripura State Council of Science and Technology, Govt. of Tripura.
A total of 372 films in different languages ​​were received for participation, of which 115 films were shortlisted by the ten-member jury to be screened during the festival.
These films are in Hindi, English, Urdu, Marathi, Punjabi, Malayalam, Kashmiri, Bengali, and Tamil languages.
These films were based on various themes like Science and technology, environment, agriculture, renewable energy, water management, health and drugs and technological innovations.
The science film festival offers a unique platform to showcase the science films made by professionals, amateur and student filmmakers under various themes, to promote science films in India.
IRNSS: It refers to the Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System. IRNSS has recently been recognized as a part of the World Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS) for operation in the Indian Ocean Region by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO). With this recognition India’s reputation has increased in the Indian Ocean Region.
India has become the fourth country in the world to have its independent regional navigation satellite system recognized by the International Maritime Organisation (IMO).
The other three countries that have its navigation systems recognised by the IMO are the US, Russia and China.
Note: The GPS (Global Positioning System) is owned by the United States of America. GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System) is owned by Russia (GLONASS satellite was completed in 1995) and BeiDou is china’s navigational system.
The IRNSS will now be officially used to provide accurate position information services to assist in the navigation of ships in Indian Ocean waters within the area of approximately 1,500 km from the Indian boundary. This will enable merchant vessels to use IRNSS for obtaining position information similar to GPS and GLONASS.
The Maritime Safety Committee (MSC) of IMO approved IRNSS as a World Wide Radio Navigation System (WWRNS) during its 102nd session held virtually on the 4th to 11th November 2020. The process of getting the said recognition took two years.
This is a significant achievement of the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW), Directorate General of Shipping (DGS) and Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) towards Atmannirbhar Bharat.
About IRNSS: The Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (IRNSS), with an operational name of NavIC, is an autonomous regional satellite navigation system that provides accurate real-time positioning and timing services. IRNSS was developed by ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization. The project was approved by GoI in May 2006. It was designed to provide accurate position information services to assist in the navigation of ships in Indian Ocean waters.
NavIC is certified by 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project), responsible for coordinating mobile telephony standards globally. It covers India and 1500 km of region covering India. It consists of 8 constellations in its orbit and a supporting ground segment.
WWRNS: It is World-Wide Radio Navigation System
IMO: It refers to the International Maritime Organisation. IMO is the UN specialized agency with responsibility for the safety and security of shipping and the prevention of marine pollution by ships. It is headquartered in London, United Kingdom. Its main function is to develop and maintain a comprehensive regulatory framework for shipping and its remit today includes safety, environmental concerns, legal matters, technical co-operation, maritime security and the efficiency of shipping. Its current Secretary General is Kitak Lim.
RE-Invest 2020: It is the 3rd Global Renewable Energy Investment Meeting and Expo that was inaugurated by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi through video conferencing. The first two editions of RE-Invest were held in 2015 and 2018.
The summit was organized by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy.
The theme for RE-Invest 2020 is ‘Innovations for Sustainable Energy Transition’.
The main features of this conference were on renewable and future energy choices, and an exhibition of manufacturers, developers, investors and innovators.
This programme aimed at providing an international forum for investment promotion in renewable energy sector and an opportunity to various countries, states, business houses & organizations to showcase their strategies, achievements and expectations.
Sports
Rodchenkov Act: It an Anti-Doping Act that was passed by the US (United States) Senate. This act will become a law once the President of US signs it. This act will become a law once the President of US (United States) signs it.
The Act allows USA to initiate legal proceedings against those involved in running doping rings, including coaches, officials, managers or suppliers even if they are not residents of the United States or if the act of doping took place outside the United States.
The main objective of the Rodchenkov Act is to bring to book facilitators who otherwise got away when athletes who tested positive for performance-enhancing substances were banned under the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) code.
The Act seeks to criminalise ‘major international dope fraud conspiracies’, which is mentioned in Section 4 of the Act. The Act "will provide the tools needed to protect clean athletes and hold accountable international doping conspiracies that defraud sport, sponsors and that harm athletes.
The bill is named after Grigory Rodchenkov. He was a former director of Russia’s anti-doping lab. He had moved to the USA and turned whistle-blower after the 2014 Sochi Winter Games.Rodchenkov’s testimony and an independent report by Professor Richard McLaren, which concluded that at least 1,000 Russian athletes benefitted from doping, resulted in the nation being banned from the 2018 Winter Olympics in South Korea.
ATP Finals 2020: Russian professional tennis player Daniil Medvedev won the ATP (Association of Tennis Professionals) tournament which was held in London. He defeated the Spanish tennis player Rafael Nadal.
Medvedev at rank number 4 under ATP ranking, has won 9 ATP singles titles, including 3 Masters 1000 titles and one year end finals title.
In the doubles final, Dutch-Croatian duo Wesley Koolhof and Nikola Mektic claimed their first title together after surpassing Jurgen Melzer and Edouard Roger-Vasselin.
The ATP tournament is the second highest tier of men’s Tennis Tournament after the Grand Slam. The tournament was first held in 1970.
The participation of a player in the ATP tournament is determined by their ranking. The major qualifications are as follows:
- Top 7 players of ATP ranking
- Two Grand Slam winners ranked between 8 and 20
- The rest of the players in the ATP ranking till the court of 8 is reached.
ICC: It refers to the International Cricket Committee. ICC is the world governing body of cricket. It was founded as the Imperial Cricket Conference in 15 June 1909 by representatives from Australia, England and South Africa. It was renamed as the International Cricket Conference in 1965, and took up its current name in 1989. The ICC, currently, has 104 member nations. It organises world championship events such as Cricket World Cup, Women's Cricket World Cup, ICC T20 World Cup, ICC Women's T20 World Cup, ICC Champions Trophy and Under-19 Cricket World Cup. The current CEO is Manu Sahney.
Recently, Greg Barclay has been elected as the new chairman of the International Cricket Council (ICC). Barclay beat Imran Khwaja in the second round of voting.
He succeeds India’s Shashank Manohar who stepped down in July 2020 and will replace Imran Khwaja, who is currently the interim chairman.
Auckland-based commercial lawyer and director of New Zealand Cricket (NZC) since 2012, was serving as NZC’s representative on the board of the International Cricket Council and had also served as the director of ICC Men’s Cricket World Cup 2015. He is also an experienced company director holding board positions with various New Zealand and Australian companies.
Diego Maradona: He is a Legendary Argentine footballer who was widely regarded among the greatest football players of all time passed away following a heart attack.
Diego Armando Maradona (1960 – 2020) was an Argentine professional football player and manager. He was one of the two joint winners of the FIFA Player of the 20th Century award.
Maradona played in four FIFA World Cups, including the 1986 World Cup in Mexico. He was captain when Argentina won the 1986 World Cup. He was largely responsible for Argentina’s World Cup victory when he led them to victory over West Germany in the final, and won the Golden Ball as the tournament's best player.
He scored two famous goals in one game against England in the quarter-finals. Both the goals in a 2–1 victory over England entered football history for two different reasons.
First, the first goal was an unpenalized handling foul known as the "Hand of God".
The second goal followed a 60 m (66 yd) dribble past five England players, voted "Goal of the Century" by FIFA.com voters in 2002.
He played for Barcelona and Napoli during his club career, winning two Serie A titles with the Italian side.
Maradona was given the nickname "El Pibe de Oro" ("The Golden Kid").
AAI: It refers to the Archery Association of India. AAI is a non-profit, government funded organisation affiliated by World Archery Federation (IAF), Asian Archery Federation (AAF) and Indian Olympic Association (IOA) and recognized by Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports of India. It was founded on 8 August 1973 after archery was reintroduced to the Olympic Games in 1972. It is responsible for organising, promoting and controlling the sport of archery in India. The current President of AAI is Shri Arjun Munda.
Recently, the Youth Affairs and Sports Ministry restored the government recognition to Archery Association of India as a Nation Sports Federation for promotion and regulation of Archery Sport in the country.
The Government recognition of AAI was withdrawn eight years back on account of failure to conduct its elections in accordance with the National Sports Development Code of India, 2011. Government recognition of AAI will be valid for one year.
This decision was welcomed by Tribal Affairs Minister and President of Archery Association of India, Arjun Munda by terming the move as ‘historic',. He said that it heralds the beginning of a new era for Indian Archery.
Current Affairs October 13 to October 19
National
Kartarpur Corridor : It is the corridor which connects Pakistan's Sikh pilgrimage Kartarpur Sahib to Punjab's Gurdaspur. It is located in the Narowal district of Pakistan across the Ravi river. It is about 4 km from the Dera Baba Nanak shrine in India. Kartarpur Sahib was established by Sikh faith founder Guru Nanak Dev in 1522. A gurdwara was built to commemorate the site where Guru Nanak lived for 18 years until his death in 1539. It is the second holiest site of the Sikh religion after Gurdwara Janam Asthan- the birth place of Guru Nanak Dev Ji located at Nankana Sahib, Pakistan.
As a major initiative India and Pakistan agreed to set up the much awaited Kartarpur corridor that will connect the holy shrines of Dera Baba Nanak Shrine in Gurdaspur district to Punjab and Darbar Sahib in Kartarpur. Prime Minister Narendra Modi will be inaugurating Kartarpur corridor from the integrated check post on the Indian side on the 8th of November 2019.
Vajra Prahar: It is a Special Forces joint training exercise conducted alternately in India and the US. Last year the joint training exercise took place in Jaipur, Rajasthan. This year 45-member Special Forces team from the Indian Army will train alongside US Special Forces. The training will enable sharing of best practices and experience in areas such as operational tactics and joint mission planning capabilities.
The 10th edition of the joint military exercise will be Conducted In at Joint Base McChord (JBLM),Seattle between 13 October 2019 and 28 October 2019. The primary goal of these bilateral military exercises and defence exchanges is to achieve a political or military objective between India and the US where a conventional force might affect the overall outcome.
DHARMA GUARDIAN – 2019: It is an annual training event which is being conducted in India since 2018. India undertakes series of military exercises wih various countries. Dharma Guardian, the joint military exercise between India and Japan, will be held at the Counter-Insurgency and Jungle Warfare School Vairengte in Mizoram from 19th October 2019 to 2nd November 2019. It is very crucial and significant in terms of security challenges faced by both the nations in the backdrop of global terrorism. Indian Army and Japanese Ground Self Defence Forces (JGSDF) comprising 25 soldiers each, will participate in exercise. The main aim of the training is to share experience gained during various Counter-Terrorism Operations in respective Countries. The exercisr also aims to cover platoon-level joint training on counter-terrorism operations in jungle and urban scenario. The joint military exercise between Indian Army and Japanese Grouond Self Defence Forces will not only enhance the level of defence co-operation but will furthur encourage the bilateral relations between the two nations.
World Standards Day : World Standards Day is an international day which is celebrated globally each year on 14 October since 1946. The aim of World Standards Day is to raise awareness among regulators, industry and consumers as to the importance of standardization to the global economy. It is celebrated every year by the members of IEC (the International Electrotechnical Commission), ISO (The International Organization for Standardization) and ITU (The International Telecommunication Union). The day honours the efforts of the thousands of experts who develop voluntary standards within standards development organizations such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), International Organization for Standardization (ISO), International Telecommunication Union (ITU), Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
BIS : The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) which is the national Standards Body of India working under the aegis of Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution, Government of India celebrated Worlds Standard Day. It is established by the Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 1986 which came into effect on 23 December 1986.
OASIS: It refers to Officers Automated & Structured Information System. It has been launched by AG/MP 5&6 on the Army Intranet. Indian Army has started digitisation of its official records. Under the programme the records of the Army officers are digitized. OASIS will facilitate officers to view their service records, raise observations, also view & download monthly Statements of Accounts, Form-16 and yearly DSOP Fund statements. When the officer retires, the whole data will migrate from Oasis to Retired Officers Digital Records Archive (RODRA). The RODRA holds the pension details of the officers.
Earlier, the roll out of the Oasis the records were manually preserved by Manpower Planning Directorate and the whole process of collecting the records, keeping a track and checking the records was very cumbersome. With the new system things are expected to become smooth.
GOAL: It refers to Going Online as Leaders. It is a digital skill training programme for tribal Women of India. The program goal aims to inspire, encourage and guide tribal girls across India to become village level digital literate leaders for their community. The first phase of the program was launched in March 2019. The GOAL initiative has been taken by the social networking company - Facebook to empower women by providing digital literacy, leadership, life skills and entrepreneurship skills
Union Minister of Tribal Affairs Arjun Munda announced the second phase of programme GOAL which will mentor 5000 young women from tribal dominated districts of India. The program will provide technical support to the socially and economically marginalized women for their needs to succeed, using the technology they may otherwise have not had access to.
IN-BN Bilateral Exercise : It refers to Indian Navy and Bangladesh Navy bilaeral exercise. Indian navy and the navy of Bangladesh for the first time will participate in a bilateral exercise at Visakhapatnam from October 12 to 16. The exercise will give furthur rise to development of mutual communication and sharing of best practices by adding a new dimension to India- Bangladesh maritime relations.
The exercise would also include air familiarisation of Bangladesh Navy aircrew and a 10-day training exercise between Indian Navy Marine Commandos and BN SWADS. The first edition of IN-BN Bilateral Exercise will be held after the second edition of Indian Navy (IN) and Bangladesh Navy (BN) Coordinated Patrol (CORPAT). The first edition of CORPAT commenced in 2018 in the northern part of the Bay of Bengal.
The IN-BN CORPAT, which commenced last year, is aimed at upgrading to a bilateral exercise with the navies engaging in seamanship evolutions, flying exercises with integral helicopters and maritime patrol aircraft at sea.
INS Ranvijaya a guided-missile destroyer and INS Kuthar, an ingeniously built missile Corvette are participating in the CORPAT along with BNS Ali Haider, a Type 053 frigate and BNS Shadinota, a Type 056 stealth guided missile corvette.
As India and Bangladesh share a common territorial boundary of over 4,000 kilometres and a maritime boundary, the navies of both the countries aim to practice and hone their mutual cooperation whilst patrolling near the International Maritime Boundary Line (IMBL) during the current edition of CORPAT. The sea phase would be followed by harbour phase that would include professional interaction between the navies, visits to the Indian Naval training and maintenance facilities at Visakhapatnam
EX-EASTERN BRIDGE-IV : It is a name given to the joint exercise between Indian Air Force (IAF) and Royal Air Force Oman (RAFO). EX EASTERN BRIDGE-V kickstarted at Air Force Base Masirah, Oman. The exercise will be held till October 26. The last exercise, EX-EASTERN BRIDGE-IV was held in 2017 at Jamnagar.
The IAF contingent comprises of MiG-29 and C-17 aircraft. MiG-29 for the first time participating outside India will be exercising with Royal Air Force Oman’s Eurofighter Typhoon, F-16 and Hawk. The participation of the Indian Air Force in the exercise will promote professional interaction, exchange of experience and operational knowledge.
International
Nobel prize for Economics : The Sveriges Riksbank Prize in Economic Sciences in Memory of Alfred Nobel (Swedish: Sveriges riksbanks pris i ekonomisk vetenskap till Alfred Nobels minne)., informally known as The Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences, is an award for outstanding contributions mainly to the field of economics.
The Nobel prize for economics 2019 was jointly awarded to Esther Duflo and her two co-researchers Abhijit Banerjee and Michael Kremer "for their experimental approach to alleviating global poverty". Duflo is the youngest person and the second woman to win this award. The prize includes 9 million-kronor (USD 918,000) cash, a gold medal and a diploma.
India and Sierra Leone : India and Sierra Leone sign six agreements for cooperation in various fields in the presence of Vice President Venkaiah Naidu and the president of the host nation Julius Mada Bio. The agreement includes the extending of a credit line of $30 million for rice cultivation and credit line of $123 million in various sectors such as agriculture, water, and transmission line.
Both the countries agreed to push for UNSC reforms so that one-third of mankind residing in Africa and India occupy their rightful place in decision making bodies of the UN. India also announced the decision to establish a High Commission in Sierra Leone. Both the countries have agreed to enhance cooperation in agriculture, food processing, Information Technology, infrastructure development and capacity building. Both the countries showed further commitment towards strengthening bilateral relations. MoU has been Signed for Sierra Leone to participate in India’s Pan-African tele-Education, tele-Medicine initiatives, e-Arogya Bharati and e-VidyaBharati and also to encourage a cultural exchange program between the governments of both the countries for the years 2019-23.
India maintains an Honorary Consulate General in Freetown, which functions under the jurisdiction of the High Commission of India in Accra, Ghana. Sierra Leone does not have a diplomatic mission in India.
UNAMSIL: It refers to United Nation Mission in Sierra Leone. India was among the first countries to send deployment of 4000 strong Indian Military contingent who served form january 2000 to january 2001. India has assissted Sierra Leone in the various sectors such as water resources, agriculture, energy and telecommunication. for its development.
Sierra Leone : it is a country in West Africa, on the Atlantic Ocean. It’s known for the white-sand beaches lining the Freetown Peninsula. The capital city, Freetown, commemorates the nation’s slave-trade history with the Cotton Tree landmark and King’s Yard Gate. Both were known as places of refuge for returned slaves in the 18th and 19th centuries. Nearby Bunce Island was a key departure point during the slave trade.
G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance : The World Economic Forum (WEF) formed the G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance. G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance on Technology Governance was established in June 2019,parellel to the G20 Summit held in Osaka, Japan. The alliance includes 15 city networks and technology governance organizations from all over the world. The main oim of the alliance is to promote the responsible and ethical use of smart city technologies by establishing global norms and policy standards for the use of connected devices in public spaces. The Global Smart Cities Alliance’s founding set of institutional partners include the presidents and host nations of the Group of 20 (G20) in 2019 and 2020; Japan and the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia; the Smart City Mission of India; Cities for All; Cities Today Institute; Commonwealth Local Government Forum; Commonwealth Sustainable Cities Network among others.
Smart city technologies can help decrease traffic congestion, combat crime, improve resilience during natural disasters and reduce greenhouse emissions.
India has taken a critical first step towards accelerating global best practices, fostering greater openness and public trust as well as mitigating risks regarding the collection of data in public spaces by joining the World Economic Forum’s (WEF) G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance on Technology Governance. It will work towards advancing the responsible and ethical use of smart city technologies.
The new global policy standards for privacy, security and sustainability of smart technologies will be rolled out in advance of 2020 G20 Summit in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. The first policy design workshops with city leaders will be held in November 2019 in conjunction with the Smart City Expo World Congress in Barcelona, Spain.
Smart cities : A smart city is a designation given to a city that incorporates information and communication technologies (ICT) to enhance the quality and performance of urban services such as energy, transportation and utilities in order to reduce resource consumption, wastage and overall costs.
Comoros : The Comoros is a volcanic archipelago off Africa’s east coast, in the warm Indian Ocean waters of the Mozambique Channel. The nation state’s largest island, Grande Comore (Ngazidja) is ringed by beaches and old lava from active Mt. Karthala volcano. Around the port and medina in the capital, Moroni, are carved doors and a white colonnaded mosque, the Ancienne Mosquée du Vendredi, recalling the islands’ Arab heritage.
Even though political stability and peaceful transition takes place in Comoros,cross border terrorism has, time and again, threatened to derail this process. Piracy and maritime threats as well as cross border transnational crimes, including cybercrimes, have added new dimensions to the problem. India on its part is willing and ready to partner with it, and supplement its efforts to neutralise these threats, particularly in the maritime domain. To expand bilateral relations Vice President M Venkaiah Naidu of India has signed 6 Memrandum of Understanding (MoU) with the island nation Comoros for Cooperation in the fields of- Defence Health and Medicine Arts and Culture Tele-education (or e-Vidya Bharati) Tele-medicine (or e-Arogya Bharati) Exemption of Visa for Diplomatic and Official Passport holders for short visits and protocol on foreign office consultation.
The Order of the Green Crescent Award : It is the highest Civilian Honour of Comoros. Comoros President Azali Assoumani, in Moroni conferred The Vice President of India with 'The Order of the Green Crescent'.
India and China : India has announced significant relaxations in its e-visa policy or rules for Chinese nationals. The announcement comes at a time when the leaders of the two nations Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Chinese Premier Xi Jinping had met for the second informal summit, in Mamallapuram, Tamil Nadu. The decision to offer multiple-entry 5-year visas is offered for a much longer duration than offered till now and meets a long-standing demand from China.
The significance of this unilateral liberalisation of e-TV for Chinese nationalsis that it will not only enhance people-to-people exchanges between the two countries but also encourage more Chinese tourists to choose India as a destination for tourism purposes. In addition to this the existing e-medical visa, e-conference visa, and the one-year multiple-entry e-business visa will continue to be issued from the online platform of Indian visas.
BRICS : BRICS is a group of emerging economies consisting of Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa. (BRICS) Headquartered in Shanghai, China. It main objectives are to cooperate between the member nations for development, provide financial assistance, support various projects, infrastructure etc. It was founded in 2006. Originally acronym BRIC became BRICS when South Africa in 2011, at the Saya Summit became a part of the association. BRICS is a valuable forum for coordination, consultation and cooperation on contemporary global issues of mutual interest for India.
Union Minister of State for Culture and Tourism (Independent charge) Prahlad Singh Patel participated in BRICS Culture Ministers’ meeting held in Curitiba, Brazil. At the meet the minister reaffirmed India’s commitment to contribute towards strengthening bonds between member countries. He proposed to add literature as another field of cooperation between the countries to enhance cooperation in the field of literary works.
World Food Day : It is celebrated every year around the world on 16 October to commemorate the founding of the United Nations' (UN) Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations in 1945. Each year has a different theme. World Food Day helps raise people's awareness of problems in food supply and distribution. The day is celebrated widely by many other organizations concerned with food security, including the World Food Programme and the International Fund for Agricultural Development. The day has since habitually observed in more than 150 countries world-wide and raises different issues for discussion for the global misery of hunger and poverty.
The World Food Day theme for 2019 is “Our Actions Are Our Future. Healthy Diets for A #ZeroHunger World". The theme is designed to urge people from all the walks of society to take action for the prevention of hunger, saving food and understanding nutritional values. It focuses on tackling global hunger. This day is celebrated in India too.
FAO : It refers to Food and Agriculture Organisation. It is a specialised agency of the United Nations. Its headquaters is in Rome, Italy where the programme is organised on a large scale. It works towards defeating hunger via international efforts. FAO aims to achieve food security for all and to make sure that people have regular access to enough high-quality food to lead active healthy lives. It has 194 member states and it works in over 130 countries in the whole world. Some UN Organisations and universities organise symposia, conferences, workshops, presentations on topics like food production, distribution and security.
International Day of Rural Women : The United Nations' (UN) International Day of Rural Women celebrates and honors the role of rural women. The United Nations has dedicated October 15 as the International Day of Rural Women. It recognizes rural women's importance in enhancing agricultural and rural development worldwide. It is observed on the 15th of October every year. The day was first passed under a resolution in 2007.
On International Rural Women's Day, United Nations Women, along with the United Nations community, is drawing attention to the implementation of commitments to gender equality. The theme for this years celebration is "Rural Women and Girls Building Climate Resistance."
The significance of this day is that from agriculture to food security, nutrition, land and natural resource management, domestic care and work, rural women are at the forefront and are taking charge by being in the driver's seat. They collect biomass fuels, process foodstuffs, pump and collect water; 80 per cent of households without piped water rely on women and girls for water collection. As rural women are at the front of the battle lines where natural resources and agriculture are threatened.
This year's theme for International Day of Rural Women have been kept keeping the climate change in mind. On this day the UN Women Community along with other organizations are drawing attention towards implementation of following commitments of UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, that is, Gender Action Plan Call for actions to support capacities of rural women towards climate change through agricultural production and food security. The empowerment of women and girls, ending of poverty and hunger and achieving food security can be achieved only by improving the role of rural women in every aspect of global development.
US sanctions on Turkey : The United States has imposed sanctions on Turkish officials over their invasion into Northeast Syria once again. It is the areas that are held by Kurdish allies of the US. Earlier on October 14, 2019 US Treasury Secretary Steve Mnuchin and Vice President Mike Pence made an announcement regarding the same. Action was taken against Turkey's defence and energy ministries, as well as the ministers of defence, energy and interior. The move freezes their assets in the US and bans transactions with them that involve the US financial system. The sanctions call for an immediate ceasefire with Turkey’s further invasion into Syria. US President Donald Trump has signed an executive order directing Vice President Mike Pence to lead a delegation to Turkey for negotiations between the Turks and Kurds.
Apart from imposing sanctions and calling for a ceasefire, the President also increased steel tariffs and cancelled the negotiations over a trade deal with Turkey which is worth USD 100 billion.
The Turkish invasion of Kurdish-held territory in northern Syria has complicated an already chaotic war. What began eight years ago as a series of nonviolent protests against the Syrian government morphed into an international conflict, between dozens of local factions, the Islamic State and several foreign countries.
UNESCO Asia-Pacific Awards : UNESCO Asia Pacific Heritage Awards are given with as the strategic purpose of UNESCO with in the region Asia Pacific. The objective is to motivate the protection of Cultural Heritage sites, which are initiated by any individual organization under private sector or institutional organization.
The Awards for Cultural Heritage Conservation were declared at a function held in Malaysia.
Award of Distinction :
• Vikram Sarabhai Library, Indian Institute of Management, (Ahmedabad) India
• Keyuan Garden (Suzhou) China
• Nelson School of Music, (Nelson) New Zealand
Award of Merit
• Our Lady of Glory Church (Mumbai) India
• Keneseth Eliyahoo Synagogue (Mumbai) India
• Tseto Goenpa (Paro) Bhutan
• Guyue Bridge (Zhejiang) China
• Lyttelton Timeball Station (Christchurch) New Zealand
Honourable Mention
• Flora Fountain (Mumbai) India
• Westpac Long Gallery (Sydney) Australia
• The 5s Classroom (Kew) Australia
• Liddell Bros. Packing Plant (Wuhan) China
International Poverty Eradication Day 2019: It is celebrated across the globe every year on 17 October to raise awareness and highlight the problems faced by the poverty-stricken people or families and work towards eradicating poverty globally in all its forms. The theme of International for the Eradication of Poverty 2019 is “Acting together to empower children, their families and communities to end poverty”.
The first commemoration of the event took place in Paris, France, in 1987. Over 100,000 people gathered on the Human Rights and Liberties Plaza at the Trocadéro to honour victims of poverty, hunger, violence and fear at the unveiling of a commemorative stone by Father Joseph Wresinski, founder of the International Movement ATD Fourth World. On the 22nd of December 1992, four years after Wresinski's death, a resolution 47/196 was adopted by the General Assembly the United Nations where it officially designated October 17 as The International Day for the Eradication of Poverty. All the States and people are invited to promote the day and do various activities to eradicate poverty and destitution.
People In News
Priyadarshan : He is a noted Indian director and producer. He has made several blockbuster Malayalam and Hindi films. He has been conferred the Madhya Pradesh government’s National Kishore Kumar Samman for 2018-19 at a function held in Khandwa on 13th October 2019.
National Kishore Kumar Samman for 2018-19 : The National Kishore Kumar Award has been instituted by MP Department of Culture in memory of eminent playback singer and all-rounder, Kishore Kumar. He was born in Khandwa, Madhya Pradesh and he died on the 14th of October 1987. It is awarded for excellence in cinematic achievements. It carries a citation and a cash prize of Rs.2 lakh. The first recipient of this award was Hrishikesh Mukherjee (1997–98).
Kais Saied : He is a 61 year old Tunisian politician and former professor of constitutional law. He is an independent candidate with no political experience. He ran as an Independent in the 2019 Tunisian presidential election and was elected the 6th President of Tunisia on 13 October 2019. He won a landslide victory in recently concluded Presidential runoff and is all set to become the President of Tunisia. The Independent law professor won with 72.71% of votes against his rival, Nabil Karoui. The election was brought forward after the death in July of Tunisia's first democratically elected president, Beji Caid Essebsi. The poll was the second free Presidential elections in Tunisia since 2010-11 uprising that toppled long-standing ruler Zine El Abidine Ben Ali. The poll was the second free Presidential elections in Tunisia since 2010-11 uprising that led to the overthrow of long-serving ruler Zine al-Abidine Ben Ali and sparked the Arab Spring.
Booker prize award : 79 year old Margaret Atwood is the oldest ever Booker winner, while Evaristo is the first black woman to win the 2019 Booker Prize. Atwood's The Testaments, the Canadian writer's follow-up to The Handmaid's Tale, was recognised alongside Londoner Evaristo's novel Girl, Woman, Other.
Booker Prize : The Booker Prize for Fiction, formerly known as the Booker–McConnell Prize and the Man Booker Prize, is a literary prize awarded each year for the best original novel written in the English language and published in the United Kingdom.
Sajjan Jindal : He is an Indian entrepreneur. He is the chair and managing director of JSW Group of companies diversified in steel, mining, energy, sports, infrastructure and software business. JSW Steel is India's largest private steel producer. He has been elected as the Vice-Chairman of World Steel Association (Worldsteel) for a period of 1 year. The association alongwith Tata Steel CEO and MD T V Narendran and ArcelorMittal Chief L N Mittal elected HBIS Group Co-Chairman Yu Yong as its chairman, Andre Johannpeter, executive vice-chairman, Gerdau to the post of vice-chairman. Apart from this, the board also elected a 14-member Executive Committeeas its members. RL Steels and Energy Limited (India) too were elected as regular members and Steel Ministry’s Joint Plant Committee (JPC) as an affiliated member.
World Steel Association (worldsteel) : It is international trade body for iron and steel industry. It is one of the largest industry representations in world with members that represent approximately 85 percent of the world's steel production, including over 160 steel producers, national and regional steel industry associations, and steel research. It was established on 10 July 1967. It's headquarts is in Brussels, Belgium.
Justice SA Bobde : Sharad Arvind Bobde is a judge of the Supreme Court of India. He is a former Chief Justice of Madhya Pradesh High Court. He is also serving as the Chancellor of Maharashtra National Law University, Mumbai and Maharashtra National Law University, Nagpur.
His name was recommended by the Chief Justice of India(CJI) Ranjan Gogoi for appointment as the next Chief Justice of India. If he is appointed then he will take the oath of Office on November 18, 2019, a day after the retirement of incumbent CJI Gogoi. Justice Bobde will serve as the 47th Chief Justice of India (CJI) for a period of one year and five months till April 23, 2021.
IPS Anup Kumar Singh : He is a 1985-batch Gujarat-Cadre IPS officer. He has been appointed as the new Director-General (DG) of National Security Guard (NSG) by the Appointments Committee of the Cabinet led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi. NSG is also known as the Black Cat Commando Force.
NSG : It means the National Security Guard or the Black Cat Commando Force. It is a counter terrorism unit under the Indian Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA). It was raised in 15th October1984, following Operation Blue Star, Akshardham Temple attack and the assassination of Indira Gandhi, "for combating terrorist activities with a view to protect states against internal disturbances". NSG commandos are based in five hubs across country.They also render personal security to some of most high-profile VVIPs such as Defence Minister Rajnath Singh and some chief ministers.
Places In News
Madhya Pradesh : To celebrate the idea of unity in diversity of India’s Heritage, the flagship and premier festival of Ministry of Culture, the Rashtriya Sanskriti Mahotsav is to be conducted in Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh on 14th October, 2019. The festival which began in 2015 is a part of the celebrating the plural traditions under the Ek Bharat Shreshta Bharat initiative. It is being organized between the 14th October, 2019 and 21st October 2019. It will be a seven day Mahotsav which will showcase rich Indian cultural heritage.It will cover a profusion of art forms from classical and folk music and dance, theatre to literature and the visual arts and would offer the chance to experience the best in established and emerging virtuosity.
Rajasthan : The two-day Rozgar Mela concluded in Bikaner which was organized on the 12th and 13th of October2019. It was conducted by the National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) under Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship. The Rozgar Mela witnessed overwhelming participation from over 100 companies across more than ten high economic growth sectors. It provided a platform to the youth to interact and engage with the corporate India and explore employment opportunities with them in the areas of their interest. The two-day Skill India Rozgar Mela concluded with more than 7500 visitors and job aspirants. More than 2000 youth were shortlisted over the last two days getting offered for myriad job roles across industry.
Rojgaar Mela : It is an event where a number of employers and job seekers come together for the purpose of applying and interviewing for jobs. Rozgar Melas are typically held in large assembly halls with a booth for each employer. It is one of the largest job fairs that is organized by NSDC with an intention of providing vocational training and job opportunities to the youth through the program. The Rojgaaar fair also included Kaushal mela where councelling is provided for candidates and parents. Here the aspirants have opportunities to register with PMKVY – Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana and PMKKY – Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Kendra Yojana.
PMKVY : It refers to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana which is an initiative of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship. It is implemented by the NSDC. The scheme was launched in 2016 and is planned to operate till 2020. The main objective of the program is to increase productivity and align training and certifications according to the requirement of the country.
Jammu and Kashmir : The Jammu and Kashmir Government will soon start telemedicine services in Srinagar to improve medical facilities in the state capital. Under the proposed service, all medical institutions in Srinagar district will be connected with each other through a trusted and round-the-clock satellite-based networking channels. The project includes upgrading of existing facilities at SKIMS and GMC, Srinagar, where it is available and setting up of these facilities at all other hospitals and health centres in the district and then connecting all of them together. Consultations with concerned agencies to introduce telemedicine services are currently underway.The service will be started in Srinagar as a pilot project.
Sri Lanka : Sri Lanka unveiled South Asia’s tallest tower in Colombo city. The tower stands 350-metre-tall and is 17-storeyed, called the Lotus Tower. It is located in the heart of Colombo city. It is a 17 storeyed tower and comprises a hotel, a television tower, a telecommunications museum, restaurants, a shopping mall, auditorium, an observation deck and a conference centre. The tower is spread over an area of 30,600 sq metres. The tower is built with fibre optic cables and is fully equipped with necessary telecommunication equipment. The construction of the tower cost over $100 of which 80% of the cost was funded by China under the controversial Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). Sri Lanka and China signed the Lotus Tower agreement in 2012 to build the tower. As per the agreement China National Electronics Import and Export Corporation (CEIEC)was the general contractor. It foreseen to be one of the significant landmarks and an epitome of island country’s culture, economy and development.
Manipur : Shirui Lily festival is being celebrated in Manipur. The festival was sponsored by the Department of Tourism, Manipur and organized by the Shirui Lily Festival Organizing Committee. It is celebrated to spread awareness about the endangered Shirui Lily and promoted the district of Ukhrul as a must-visit tourist destination in Manipur.
The Shirui Hills is known for a unique species of land-lily, the Shirui Lily which grows at a height of about 8,500 ft above sea level was declared as the State Flower of Manipur in 1989. Shirui Lily or Siroi lily and Botanical name Lilium Mackliniae Sealy, is known worldwide for its rare and modest beauty. It was discovered in 1946. The flower is today considered an endangered species.
Punjab : The National Highway starting from Kapurthala connecting Gobindwal Sahib and terminating near Taran Taran in the State of Punjab has been declared as new National Highway No. 703AA. Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways Nitin Gadkari has announced that it will be named
‘Shri Guru Nanak Dev Ji Marg’, after the first Sikh guru. This decision has been taken to mark 550th Birth Anniversary of Guru Nanak Dev. The name Shri Guru Nanak Dev Ji Marg will be effectve from November 2019.
Science and Technology
India Mobile Congress : It is the largest mobile technology event in South Asia. It is organized by Department of Telecommunications along with Cellular Operation Association of India (COAI). This year the event is being conducted between October 14, 2019 and October 16, 2019. The Congress brings together Government entities, industries and other ecosystem players. It acts as a common platform to discuss and display the latest technology in the world. Apart from being the largest digital technology event, it is also the largest networking event in India. Highlights of the event During the event exhibition and conferences are organized. It also presents most recognized awards in the technology industry, especially in digital technology. Objectives of the event The event is organized to promote start-ups, innovators and enterprises It also promotes local manufacturing It drives in investments The event acts as a platform to spread knowledge about the ongoing research and development in the field It enhances international regional cooperation in the South and South east region
ISRO : It refers to Indian Space Research Organization. It has achieved numerous milestones since its establishment starting from the first Indian Satellite, Aryabhata to Rohini, the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV).
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) will soon carry out another major test for its reusable launch vehicle (RLV) in which the vehicle will be flown to a height of 3 km by a helicopter and let free to land autonomously at an airstrip in Challakere in Chitradurga district in Karnataks. It will function as a space shuttle that will carry a payload to space and glide back to the earth. It is a second launch by ISRO. The Reusable Launch Vehicle Program was first launched in 2016.
The objective of it is to cut down the launch cost by reusing the spacecraft. The RLV (Reusable Launch Vehicle) has been tested over water butfor the first time,it will be tested on land.
The launch vehicle is critical to India's Human Space Flight initiative – Gaganyaan. The four aspects of the RLV which are to tested are - hypersonic flight experiment (HEX), return flight experiment (REX), autonomous landing experiment (LEX) and scramjet propulsion experiment (SPEX). There are two stages in the recovery process. The first stage is similar to that of SpaceX’s Falcon 9 booster. The second stage is an advanced version of RLV testing done in 20.
The Aeronautical Test Range (ATR) has 2.2 km runway and the RLV will be dropped from a helicopter at an altitude of 3 km. An onboard computer will help the RLV glide for some distance before touching down on the runway like an aircraft.
Space Walk: Two NASA American Astronauts Christina Koch and Jessica Meir created history on Friday, October 18 when they left the International Space Station (ISS) for a spacewalk. It was first all-female space walk ever in space history. The historic extravehicular activity (EVA) began at 7:38 EDT (1138 GMT), which was ahead of schedule as the spacewalk was slated to begin at 7:50 EDT (1150 GMT). The were guided by veteran NASA astronaut and capsule communicator (CAPCOM) Stephanie Wilson on the ground and fellow astronauts Luca Parmitano and Andrew Morgan located on the International Space Station. Both astronauts will replace a power unit on the ISS which failed last week.
Russian Cosmonaut Svetlana Savitskaya was the first woman to do a spacewalk in 1984 followed by NASA astronaut Kathryn Sullivan became the first American woman to do so later the same year. 15 Women have participated in 42 spacewalks over the past 35 years. Out the 15 women who have done spacewalks, 14 have been NASA astronauts. Koch is on track to make history again in December as she gets closer to setting a new record for the longest amount of time continuously spent in space by a U.S. woman, beating former NASA astronaut Peggy Whitson's former record of 288 days.
Sports
World Youth Chess Championship : It is a chess competition for girls and boys under the age of 8, 10, 12, 14, 16 and 18. Twelve world champions are crowned every year. The first predecessor of the youth championship was the Cadet Championship. It started off unofficially in 1974 in France for players under 18.
The World Youth Chess Championship event held in Mumbai concluded With a happy note for India on 12 October 2019. India's 14 year old chess prodigy R Praggnanandhaa shone bright as he claimed the coveted gold in the the World Youth Chess Championship in Mumbai. The Grand Master from Chennai won a Gold in the Under-18 Open category. In this event India bagged 7 medals including 1 gold and 3 silver and 3 bronze medals.
The winners of the World Youth Chess Championship 2019 -
U18 Open: Praggnanandhaa R. (INDIA) 9.0; Shant Sargsyan (ARMENIA) 8.5; Artur Davtyan (ARM)
8.0 U18 Girls: Polina Shuvalova (RUSSIA) 8.5; Vantika Agrawal (INDIA) 8.0; Alexandra Obolentseva (RUSSIA) 7.5
U16 Open: Rudik Makarian (RUSSIA) 8.5; Stefan Pogosyan (RUSSIA) 8.0; Aronyak Ghosh (INDIA) 8.0
U16 Girls: Leya Garifullina (RUSSIA) 8.5; Nurgali Nazerke (Kazakhstan) 8.5; Anousha Mahdian (IRI)8.0
U14 Open: Aydin Suleymanli (Azerbaijan) 9.0; Srihari L R (INDIA) 8.0; Sreeshwan Maralakshikari (INDIA) 8.0
U14 Girls: Meruert Kamalidenova (Kazakhstan) 8.5; Divya Deshmukh (INDIA) 8.0; Rakshitta Ravi (INDIA) 8.0
Cori "Coco" Gauff : She is an American former world No. 1 junior tennis player. She won one junior Grand Slam singles title and another in doubles. She was the runner-up in the girls' singles event at the 2017 US Open, making her the youngest finalist at the event in the tournament's history.
Coco Gauff has won her first WTA title by beating Jelena Ostapenko 6-3, 1-6, 6-2 to capture the Upper Austria Ladies on Sunday. She defeated Jelena Ostapenko. She has became the youngest American woman to win a tour singles title since 1991. Gauff as a result of this win is set to be ranked as world's number 71.
AIBA Women's World Boxing Championships: AIBA Women's World Boxing Championships is a biennial amateur boxing competitions organised by the International Boxing Association (AIBA), which is the sport governing body. Alongside the Olympic boxing programme, it is the highest level of competition for the sport. The mega event was hosted by Ulan-Ude, Russia from 3rd to 13th of October 2019. Around 224 competitors from 57 nations participated in the event. Mary Kom, Manju Rani, Lovlina and Jamuna Boro from India played their semifinal bouts.
The 19 year old Debutant Manju Rani(48kg) from Haryana, India scripted history as she became the first Indian woman boxer in 18 years to enter the finals of Women’s World Boxing Championship. She defeated her opponent Chuthamat Rakshat of Thailand. she won silver medal in the finals after going down 1-4 against the host nation’s second-seeded boxer Ekaterinal Paltceva.
M C Mary Kom (51 kg), Debutante Jamuna Boro (54kg) and Lovlina Borgohain(69kg) won bronze medal.
Japanese Grand Prix 2019: The 2019 Japanese Grand Prix was a Formula One racing event held on 13 October 2019 at the Suzuka International Racing Course in Suzuka in the Mie Prefecture, Japan. The race was the seventeenth round of the 2019 Formula One World Championship and marked the 45th running of the Japanese Grand Prix.
Valtteri Bottas Won the Japanese GP, Mercedes Clinch Record Constructors' Title. He is a Finnish racing driver currently the winner in Formula One with Mercedes. He has previously driven for Williams from 2013 to 2016. Since joining Mercedes, Bottas has won 6 races, 3 in 2017 and 3 in 2019.
BCCI : It refers to The Board of Control for Cricket in India. It is the national governing body for cricket in India. The board was formed in December 1928 as a society, registered under the Tamil Nadu Societies Registration Act.
Former 47 year old Indian cricket captain and Cricket Association of Bengal (CAB) President Sourav Ganguly has been unanimously nominated as the new President of the Board of Control for Cricket in India. BCCI has also selected Jay Shah as Secretary and Arun Dhumal as Treasurer. Jay Shah is the son of Union Home Minister Amit Shah while Dhumal is the younger brother of MoS Finance and former BCCI president Anurag Thakur. All these candidates are expected to be elected unopposed at the Board's Annual General Meeting to be held on 23rd of this month.
Chicago Marathon : The Chicago Marathon is a marathon held every October in Chicago, Illinois. Alongside the Boston, New York, London, Berlin, and Tokyo Marathons, it is one of the six World Marathon Majors. Thus, it is also an IAAF Gold Label race. The Chicago Marathon is the fourth-largest race by number of finishers worldwide
The 25 year old Runner Brigid Kosgei of Kenya smashed women's world record in Chicago Marathon. She broke Radcliff's previous record of 2:15:25 which the Briton set in London in April 2003 by 2:14:04
Dutch Open: The Dutch Open is an annual badminton tournament held in the Netherlands since 1932 and currently organized by Nederlandse Badminton Bond. It is a part of the European Badminton Circuit.
Rising 18 year old Indian shuttler Lakshya Sen on Sunday clinched his maiden BWF World Tour title by winning the Dutch Open men's singles title after beating Yusuke Onodera of Japan in the summit clash.
Sports Ministry : Ministry of sports on Sunday decided to allow national and state sports federations, leagues and clubs to organise sports events in all sporting facilities owned by the government, free of cost. Making sporting infrastructure accessible to all.
Non-Sports Authority of India coaches will also be allowed to train their athletes at the stadiums without any charge. Stadiums in Delhi including Jawaharlal Nehru Stadium, Indira Gandhi Stadium, Major Dhyanchand Stadium and Karni Singh Shooting Range (KSSR) will be opened in the first phase for the state and national federations to host competitions, tournaments and league of all sporting disciplines. The decision has been made in to provide impetus to the Fit India Movement.
SAFF U-15 Women’s Championship : It is an international football competition for women's under-15 national teams organized by SAFF.
The tournament was hosted by Thimpu, Bhutan from 9 October to 15 October 2019. Four teams from the region i.e. india, Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal took part in the tournament. India beat Bangladesh 5-3 via a penalty shoot-out to win the SAFF U-15 Women’s Championship title after the summit clash ended goalless in regulation time.
Golden Shoe Award : The European Golden Shoe is an award that is presented each season to the leading goalscorer in league matches from the top division of every European national league. The trophy is a sculpture of a football boot.
Lionel Messi, star striker of FC Barcelona, has won the 2018/19 European Golden Shoe award. It is the sixth of his illustrious career and the third consecutively. He scored a total of 36 goals in 34 games last season in the league and helped Barca to successfully defend the La Liga title.
Economics
Air India: Air India is the flag carrier airline of India, headquartered at New Delhi. It is owned by Air India Limited, a government-owned enterprise, and operates a fleet of Airbus and Boeing aircraft serving 94 domestic and international destinations.
It has become the 1st airline in world to use Taxibot on A-320 aircraft with passengers on board. Chairman and MD of Air India Ashwani Lohani flagged off the flight AI665 (Delhi – to Mumbai). The use of taxi-boat is a giant step forward towards a cleaner environment. It will bring down the consumption of fuel by 85 per cent and reduce engine wear and tear. The ignition will be turned on only when the aircraft reaches the runway.
Taxiboat : It is a robot-used aircraft tractor for taxiing an aircraft from parking bay to runway and vice-versa. It is a pilot-controlled semi-robotic towbar-less aircraft tractor used as alternate taxiing equipment. The taxibots will be used for departing flights only. It will be significantly used during taxiing of an aircraft.
One Nation One Tag – FASTag : It is the name given to a conference that was inaugurated by the Union Road Transport & Highways Minister Nitin Gadkari
held in New Delhi. The objective of the conference is to roll out the process for having a unified electronic system across the country. Under this system the same FASTag affixed on the windscreen of a vehicle can be used to pay toll across all toll plazas in the country. It aims to integrate the collection of toll digitally and ensure seamless mobility of vehicles across India.
At the conference a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between Indian Highways Management Company Ltd (IHMCL) and Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) for integration of FASTag with GST e-way bill system.
IHMCL also exchanged MoUs with several state departments/other agencies/ authorities for integrating with FASTag.
FASTag : It is a simple to use, reloadable tag or device that employs Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology which enables automatic deduction of toll charges and lets vehicle pass through toll plaza without stopping for cash transaction.
CERAWeek : CERA refers to Cambridge Energy Research Associates. CERAWeek by IHS Markit founded in Cambridge in 1983 has become the world’s premier energy event. Each year, CERA clients gathered for a few days in Houston, Texas to attend the executive conference where they gained insight into the energy future while connecting with their peers. Over time, the program was expanded to five days of informative sessions and networking opportunities—and named CERAWeek.
The 3rd India Energy Forum by CERAWeek was conducted in New Delhi. Hundreds of delegates from Indian as well as regional energy companies, institutions, and governments, and also a number of international speakers gathered at 3rd India Energy Forum by CERAWeek under the patronage Union Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas & Steel and Union Minister Dharmendra Pradhan.
The Key topics explored in the conference includes India's energy transition Low-carbon & sustainable energy solutions asIndia is the third-largest energy consumer in the world after the US and China. The provision of heat, light, and mobility Game-changing industry technologies. Outlook for global oil and gas markets & investment Growing domestic oil and gas production and expanding use of natural gas across the economy. Ethanol blending percentage has risen from 0.67% in 2012-13 to 6%. The government is pushing to achieve 10% blending percentage of ethanol in petrol by 2022, which in turn will boost farm economy. More than 95% of households have become smoke-free because of the use of LPG( Liquid Petrolium Gas) and as well as Natural Gas that is playing an important role in the energy basket.
Team Cashless India: The initiative dubbed as 'Team Cashless India' aims to bring consumers and merchants to the “forefront of the digital payments dialogue”. The campaign will encourage Indian citizens to nominate one or more merchants who currently do not accept digital payments to go digital.
Mastercard and it's brand ambassador MS Dhoni have launched Team Cashless India campaign. It aims to bring more merchants and customers on board to boost digital payments in India. The move is in line with Mastercard's endeavor to create an ecosystem that encourages users to use digital payments for their day-to-day purchases.
Environment & Climate
Typhoon Hagibis : It is a large and powerful typhoon which was has been named Hagibis to name four tropical cyclones in the western north Pacific Ocean. The name Hagibis contributed by the Philippines means "rapidity" or "swiftness." Thphoon Hagibis was a large and powerful tropical cyclone that was considered to be the most devastating typhoon to hit the Kanto region of Japan since Typhoon Ida in 1958. Hagibis caused additional impacts in Japan, after Faxai struck the same region one month prior.It has been used to name four tropical cyclones in the western north Pacific Ocean. The name was contributed by the Philippines and means "rapidity" or "swiftness."
Recently,Japan was Hit by the ferocious Typhoon Hagibis which caused fight floods. Some of the worst damage hit Nagano city, central Japan, where the Chikuma River burst its banks, inundating large swaths of land in brown water and forcing military helicopters to airlift stranded people from homes.
Paris Zoo : A strange and mysterious new yellowish organism has been unveiled at Paris zoo. It has no has no mouth, no stomach and no eyes, but can somehow detect and digest food. This strange organism has been dubbed as "blob". The "blob" has almost 720 sexes, can move without legs or wings and heals itself in two minutes if it gets cut in half.
As per the director of the Paris Museum of Natural History Bruno David, it is a living being which belongs to one of nature’s mysteries. It is still a mystery whether the organism is an animal or a fungus as it behaviour is very strange.
The blob was named after a 1958 science-fiction horror B-movie, starring a young Steve McQueen, in which an alien life form - The Blob - consumes everything in its path in a small Pennsylvania town.
Switzerland Glaciers : All glaciers are located within the Swiss Alps. Most of them are situated in the Pennine and Bernese Alps. The Jungfrau-Aletsch protected area includes the largest glaciers of the Alps. There are glaciers in the four major drainage basins of Switzerland. There are more than 500 glaciers in the country.
Due to climate change glaciers in Switzerland have shrunk by 10% in the last five years. A record melting rate that has never been seen before in over a century of observations. According to the annual study published by the Cryospheric commission at the Swiss Academy of Sciences around 20 glaciers have shown melt rates that have reached record levels. The summer 2019 heatwave saw glacier melt rates break records, leading to huge losses in ice volume. As per the report most glaciers in Central Europe, Western Canada and the United States will vanish in the second half of this century if current rates of ice loss continue.
According to the letter published in the National Journal glaciers have lost over 9,000 billion tons of ice between 1961 and 2016. More than 4,000 glaciers are to disappear from the Alps at the end of this century if green house gas emissions are not controlled
Storm quakes : Scientists have discovered a phenomenon in which a strong storm causes seismic events in the seafloor. Some of which are as strong as a magnitude 3.5 earthquake. The quakes are fairly common, but they weren't noticed before because they were considered seismic background noise. However, they aren't dangerous.
Indian Policy
Sewa Service Trains : The Indian railways today started 10 Sewa Service trains. It launched a website and mobile app that allows passengers to register their complaints online.
These Sewa Service trains will not only ease the hassle of travelling for daily passengers but will also help divert short distance traffic from roads to the railways.These trains will connect small towns with their closest major cities and ease the hassle of travelling for daily passengers. The trains will run between Delhi and Shamli, Bhubaneswar and Nayagarh Town, Murkongselek and Dibrugarh, Kota and Jhalawar City and Coimbatore and Palani as a daily passenger train from today.
Minister of Railways Piyush Goyal flagged off the Sewa Service train between Delhi and Shamli at New Delhi and other trains through video conferencing along with health minister Harsh Vardhan , oil minister Dharmendra Pradhan and Minister of state for railways Suresh C. Angadi. These trains will provide better rail connectivity between smaller and satellite towns and important cities.
The 10 ‘Sewa service’ Trains are - Vadnagar to Mahesana DEMU train, Asarva (Ahmedabad) to Himmatnagar DEMU, Karur to Salem DEMU, Murkongselek to Dibrugarh passenger train, Yesvantpur to Tumkur DEMU, Delhi to Shamli daily passenger train, Bhubaneswar to Nayagarh Town Express, Kota to Jhalawar City Passenger train, Palani to Coimbatore Passenger train, Coimbatore to Pollachi Passenger train.
5G Spectrum Auction : It is a process where a government uses an auction system to sell the rights to transmit electromagnetic signals overs specific bands. Union telecom minister Ravi Shankar Prasad on Friday said the 5G spectrum auction will be conducted this year-end or early next year. Under the scheme, the government plans to auction around 8,293.95 MHz of airwaves at an estimated total base price of Rs 5.86 lakh crore. The last spectrum sale, 4G spectrum was conducted in 2016.
The High-band 5G spectrum will clearly provide the anticipated leap in data speed, capacity, quality and low latency as compared to 4G spectrum.It will lead to much higher data speeds and propel Internet of Things, which will transform sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, healthcare, and education.
World Skills India Training Centres Union Skill Development and Entrepreneurship Minister Mahendra Pandey unveiled plans to set up 14 Authorized World Skills India Training Centres across 9 cities for media and entertainment sector. The new institutes will be set up for advanced skill training of candidates in media and entertainment sector and also to develop skilling eco-system for training candidates for the international market. These cities are Chandigarh, Chennai, Delhi, Hyderabad, Indore, Mumbai, Pune, Shillong and Trivandrum. The main objective of the new institutes by the government is to encourage more youth to get skilled and not just participate. Certification courses of 9 months to 36 months duration on graphic design technology, 3D digital game and print media technology will be offered by the centre.
Indian polity
NCERT: It refers to The National Council of Educational Research and Training. The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) is an autonomous organisation of the Government of India which was established in 1961 as a literary, scientific and charitable Society under the Societies' Registration Act (Act XXI of 1860).
The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) is planning to review the 14-year-old National Curriculum Framework (NCF) in accordance with a new national education policy (NEP) and set up a committee for the purpose. The NCF has been revised four times so far in 1975, 1988, 2000 and 2005. The recently proposed revision is the fifth framework. A committee will be set up for this purpose.
RTI Act : It refers to Right to Information. It is act of the Parliament of India to provide for setting out the practical regime of the right to information for citizens and replaces the erstwhile Freedom of information Act, 2002.The authorities under RTI Act 2005 are called quasi-judicial authorities.
As defined in the Right to Information Act, 2005, the Chief Information Commissioner (CIC) and Information Commissioner(IC) currently hold tenure of 5 years and their perks are similar to that of the Chief Election Commissioners.
In July 2019, the Government of India amended the act Section 13 and Section 16 of the RTI Act to lay down terms and conditions of services to the officials. According to the new draft rules from Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT), the terms and perks of the CICs and ICs are to be fixed as that of Cabinet Secretary and Secretary to the GoI level. This may also mean that they will likely be downgraded in the ‘Table of Precedence’ several notches down from 9A where the CEC, Comptroller and Auditor General and Chairman, UPSC are placed, to position 23 occupied by the Secretary to the Government of India.
Table of Precedence : It is a protocol list prepared by the Ministry of Home Affairs and is based on the hierarchy and rank of government functionaries.
Jammu & Kashmir Legislative Council : The Government of Jammu and Kashmir abolished the 62 year old Legislative Council of Jammu and Kashmir under Section 57 of J&K Reorganization Act, 2019. The State Legislative Council has come to an end with the State Administration issuing orders for its abolition with immediate effect. This order has been issued ahead of the bifurcation of Jammu and Kashmir into two Union Territories of Ladakh and Jammu and Kashmir - on the midnight of October 31. J&K and Ladakh will now be Union Territories from November 1, 2019. The J&K Reorganisation Bill, 2019 was passed by the Parliament in August 2019. For the transition of Ladakh region as the youngest Union Territory that will be done on 31 October 2019, Jammu and Kashmir Government has shifted Ladakh Affairs Department along with its Administrative Secretary Rigzin Samphel to Leh. Mr Rigzin who hails from Ladakh region is a 2003 Uttar Pradesh cadre IAS officer. Jammu and Kashmir government has also issued formal orders for opening of new administrative secretariat in Ladakh under the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Bill which was passed in August 2019.
According to the order the State Administration has asked the 116-member staff of Legislative Council to report to the General Administration Department (GAD) by 22nd of October. As per the government order, all the vehicles purchased for council were transferred to state motor garages.
J&K legislative council : It was established in 1957 following adoption of a new constitution by state constituent assembly and passing of Legislative Councils Act in Parliament.. The council was created with a strength of 36 members. The council functioned as an upper house. The members of the legislative council members remained in office for a period of six years. The council comprised of 22 members elected by state assembly, 2 members from local authorities, 2 from panchayat constituency and 8 members nominated by Jammu and Kashmir Governor from eminent persons from various fields.
Economics
SBI: It refers to the State Bank of India. SBI is an Indian multinational, public sector banking and financial services statutory body. It is a government corporation statutory body. It is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. It was established in 1 July 1955. SBI is ranked as 236th in the Fortune Global 500 list of the world's biggest corporations of 2019. The current Chairperson is Rajnish Kumar
The South Central Zone (SCR) of Indian Railways has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with SBI for door step banking. Under the MoU, the bank will enables to collect earnings generated from all 585 stations of the zone. The traffic earnings will be collected by SBI and transferred to the Government account. The direct pick up of cash from all the railway stations on SCR by SBI will save the tiring and complex activity of movement of cash earnings through ‘cash safes’ by trains and it will also speed up the pace of financial transactions and digitize the remittance of cash earnings of the Railways. Furthermore, railway stations will have uniform cash remittance mechanism, unnecessary accumulation of cash at the railway stations can be avoided with the above facility and there will be better supervision and accountability of the cash deposited by different stations.
Gold Hallmarking: The process of certifying the purity of gold is called hallmarking. The BIS system of hallmarking of gold jewellery began in April 2000 and around 40% of gold jewellery is being hallmarked currently. BIS is the National Standards Body of India established under the Bureau of Indian Standards Act 2016. It has provisions under Sections 14 and 16 for making hallmarking of mandatory by the Central Government. It certifies that the piece of jewellery conforms to a set of standards laid by the Bureau of Indian Standards, the national standards organization of India. India is the second biggest market for gold and its jewellery.
On January 14, 2020, The Union Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution Ram Vilas Paswan announced that Indian jewellers will be allowed to sell hallmarked gold artifacts made of 14, 18 and 22-carat gold only. It has now become mandatory for all the Indian Jewellers to get the hallmarking of Gold jewellery and artefacts with Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) to sell only hallmarked Gold jewellery & artefacts. The mandatory rule is to be implemented from 15 January 2021. Any violation in the new rule will result in one year imprisonment and a fine under the provisions of the Bureau of Indian Standards Act, 2016.
The purpose of making hallmarking mandatory is not only to curb frauds and fake gold but also to ensure that consumers are not cheated while buying gold ornaments and get the purity as marked on the ornaments.
GEFCO: It is an acronym for Griqualand Exploration and Finance Company Ltd. GEFCO Group is a world wxpert in supply chain solutions and the European leader in automotive logistics. It was founded in 1949 by the French car manufacturer Groupe PSA. It is headquartered in France. Its parent organization is the Russian Railways.
Global software major Infosys has signed a 5-year deal with leading European automotive logistics firm Gefco to digitize its worldwide operations. Infosys has partnered with GEFCO to strengthen its Digital Transformation. Infosys will help GEFCO to transform GEFCO’s next-generation business application management services. It will also help GEFCO to evolve into a ‘Digital Native’ organization. The main aim of the partnership is to support GEFCO to create new sustainable sources of competitive advantage and to constantly improve value for its customers.
Infosys: Infosys Limited is an Indian multinational corporation that provides business consulting, information technology and outsourcing services. It is headquartered in Bangalore, Karnataka, India. The Chief Executive Officer and Managing Director of Infosys is Salil Parekh.
RBI: It refers to the Reserve Bank of India. RBI is India's central bank, which controls the issue and supply of the Indian rupee.The RBI carries out India's monetary policy and exercises supervision and control over banks and non-banking finance companies in India. It was founded in 1st April 1935 under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 in Kolkata, west Bengal. Its headquarters is in Mumbai. The current Governor isShaktikanta Das and the Deputy Governors are N S Vishwanathan, B P Kanungo and M K Jain.
Recently, the Appointments committee of the Cabinet approved the appointment of Michael Debabrata Patra as Deputy Governor of Reserve Bank of India (RBI). He has been appointed for the period of three years. He will be the fourth Deputy Governor of the RBI. The post fell vacant after Viral Acharya resigned on July 23 last year. Dr. Patra was Executive Director of the Reserve Bank before being elevated to the post of Deputy Governor. Mr. Patra is likely to retain the monetary policy department (MPC), which was handled by Mr. Acharya, as the deputy governor.
The RBI, headed by Governor Shaktikanta Das, can have a maximum of four deputy governors. N S Vishwanathan, B P Kanungo and M K Jain are the other deputy governors working at the central bank.
MPC: It refers to Monetary Policy Committee. It ia a panel of six members with 3 members from RBI and other 3 members are elected by the Government of India(GoI). MPC was constituted on 27 June 2016. Its aim is to determine interest rates in a more useful and transparent manner.
Defence
Armed Forces Veterans Day: The day is observed every year on 14th January since 2017. The Armed Forces Veterans Day is celebrated as a mark of respect and recognition to the services rendered by the first Commander-in-Chief of Indian Army, Field Marshal KM Cariappa who retired on 14 Jan 1953. Cariappa had led the Indian forces to victory in the 1948 war. The day was initially called Armistice Day. The current chief of Army staff is Manoj Mukund Narvane.
Recently, the 4th Armed Forces Veterans Day was celebrated at Chandimandir Cantonment located in the Panchkula district, Haryana.
Veterans Day: The day was initially known as Armistice Day. Armistice Day was renamed Veterans Day in 1954. The day is observed annually on November 11 to honor the living legends of all wars.
Armistice Day and Remembrance Day are celebrated in other countries that mark the anniversary of the end of World War I. Major hostilities of World War I were formally ended at the 11th hour of the 11th day of the 11th month of 1918, when the Armistice with Germany went into effect.
LCA Tejas: It refers to light Combat Aircraft. LCA Tejas is an Indian single-engine, delta wing, multirole light fighter designed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) for the Indian Air Force and Indian Navy. It was built under the Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) programme, which began in the 1980s to replace India's ageing MiG-21 fighters. In 2003, the LCA was officially named "Tejas. The LCA Tejas is the second supersonic fighter developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) after the HAL HF-24 Marut.
Recently, the naval variant of the indigenous LCA Tejas fighter achieved an important milestone with the successful Arrested Landing on the INS Vikramaditya, India’s only aircraft carrier. With this, the LCA has become the first aircraft to make an arrested landing on a naval ship.
ICGS: It refers to Indian Coast Guard Ships- Annie Besant and Amrit Kaur. The ships are built indigenously by the Garden Reach Shipbuilders & Engineers (GRSE) Ltd, Kolkata. The ships are fitted with state-of-the-art technology, and navigation equipment. They are equipped with Bofors 40/60 guns and 12.7 mm Stabilized Remote Controlled Gun (SRCGs) for enhanced fighting efficiency.
Recently, the two Indian Coast Guard Ships (ICGS), Annie Besant and Amrit Kaur were commissioned by Defence Secretary Ajay Kumar at Khidderpore park, Kolkata, West Bengal. Indian Coast Guard Ship Annie Besant and Amrit Kaur are second and third in the series of five Fast Patrol Vessels.
ICGS Annie Besant ship commanded by Commandant (JG) Sunny Deo will be based at Chennai. she was named Annie Besant in honor of Annie Besant, philanthropist, theosophist, prolific author and supporter of the Indian freedom struggle. While ICGS Amrit Kaur commanded by Commandant (JG) Himanshu Mishra will be based at haldia. She got her name Rajkumari Amrit Kaur, who belonged to the ruling family of Kapurthala, Punjab. She took an active part in the ‘Salt Satyagraha’ and ‘Quit India Movement’ during the freedom struggle of India and she also served as the first Health Minister of Independent India.
IAF: It refers to Indian Air Force. IAF is the air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its complement of personnel and aircraft assets ranks fourth amongst the air forces of the world. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial warfare during armed conflict. IAF was officially established on 8 October 1932. Its first ac flight came into being on 01 Apr 1933. It is headquartered in New Delhi. President Ram Nath Kovind is its Commander-in-chief. Air Chief Marshal Rakesh Kumar Singh Bhadauria and Air Marshal Harjit Singh Arora are the Chief of the Air Staff and Vice Chief of the Air Staff respectively.
Recently, Defense Secretary Ajay Kumar announced that The Government of India (GoI) is in the process of acquiring 200 aircrafts to cope with the depleting aerial inventories of the Indian Air Force.
The Air Force has Sukhoi 30 MKIs, Mirage 2000s, Mig 29s and the ageing Jaguars and Mig 21 Bisons in its inventory of fighter jets at present.
The last fleet of seven swing-wing MiG-27 fighters, which played an important role during the 1999 Kargil war, was decommissioned on 27 December 2019.
Indian Army Day: The Day is celebrated on 15 January every year in India, in recognition of Field Marshal Kodandera M. Cariappa. He took over as the first Commander-in-Chief of the Indian Army from General Sir Francis Butcher, the last British Commander-in-Chief of India, on 15 January 1949. General Manoj Mukund Naravane is the current 28th Chief of Army Staff.
Captain Tanya Shergill became the first woman officer to lead an all-men contigent at Army Day Parade in New Delhi, India. The 26 year old Shergil, an officer with Army’s Corps of Signals, will be the first woman parade adjutant for the Republic Day parade. A parade adjutant is responsible for the parade.
Tanya Shergill: Hoshiarpur-born Shergill who holds a B.Tech. in electronics and telecommunications from Nagpur University is the fourth generation woman army officer. Both her father and grandfather have served in the Army. Her father was in 101 Medium Regiment (Artillery) while her grandfather was in the 14th Armed Regiment (Scinde Horse). Interestingly, her great grandfather was in the Sikh Regiment. She was commissioned in March 2017 from the Officer Training Academy, Chennai.
51st K9 Vajra-T guns: It is a self-propelled Howitzer gun made by L&T’s Armoured System Complex at Hazira in Gujarat. The gun weighs 50 tonnes. It can not only fire 47-kilogram bombs at targets up to a distance of 43 kilometres but also turn around at zero radii.
Recently, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh deducated the 51st K9 Vajra-T guns to the nation. The future-ready combat vehicles meet the requirement of 21st-century warfare including deep fire support to the longer firing range.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi in January Last year had dedicated L&T’s Armoured System Complex at Hazira in Surat to the nation. The aim is that the participation of the private sector in defence manufacturing is toward fulfilling the government's commitment to make India an arms manufacturing hub and net defence exporter.
Environment
Kaziranga: It is a National Park which was established in 1908. The park was declared as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1985. It is a protected area in the northeast Indian state of Assam. It is spread across the floodplains of the Brahmaputra River. Its forests, wetlands and grasslands are home to tigers, elephants and the world’s largest population of Indian one-horned rhinoceroses. Ganges River dolphins swim in the park’s waters. It’s visited by many rare migratory birds, and gray pelicans roost near Kaziranga village. Kaziranga was declared a Tiger Reserve in 2006.The park is governed by the Government of Assam and Government of India.
According to the officials of the Kaziranga National Park and avian specialists who conducted the second wetland bird count on January 9-10 counted a total of 19,225 birds belonging to 96 species under 80 families. Kaziranga, home of the world's most one-horned rhinos, has 96 species of wetland birds which is one of the highest for wildlife preserves in India. The first waterfowl census in 2018 had yielded 10,412 birds covering 80 families from 21 families.
WFES: It is an acronym for The World Future Energy Summit. WFES is an annual event started in 2011. It is dedicated to advancing future energy, energy efficiency and clean technologies. It is held under the patronage of Sheikh Mohammed Bin Zayed Al Nahyan, Crown Prince of Abu Dhabi and Deputy Supreme Commander of the UAE Armed Forces. WFES includes a summit, an exhibition, the Project Village, Round Table Discussions, the Young Future Energy Leaders program, corporate meetings and social events.
The Summit attracts world leaders, international policy makers, industry leaders, investors, experts, academia, intellectuals and journalists to discuss practical and sustainable solutions to future energy challenges.
The World Future Energy Summit will begin in Abu Dhabi. Around 33,500 participants from 170 countries and 800 specialist exhibitors are expected to attend the four-day annual event on 13 January 2020. The four day Summit is the Middle East’s largest future energy and sustainability event. It is dedicated to advancing future energy, clean technologies, and energy efficiency.
The theme for this year's summit is "Rethinking Global Consumption, Production, and Investment."
The event will showcase 42 of the world’s most disruptive innovations which was selected from 1,402 global submissions from 128 countries, related to the future of energy, agriculture, food, and sustainability in space.
CLIX: It is a short form for Climate Innovations Exchange. CLIX and Future Sustainability Summit will also be held alongside the WFES.
Australian Koalas: The koala (Phascolarctos cinereus, or, inaccurately, koala bear) is an arboreal herbivorous marsupial native to Australia. It is the only extant representative of the family Phascolarctidae and its closest living relatives are the wombats, which comprise the family Vombatidae. Koalas live in the tall eucalypt forests and low eucalypt woodlands of mainland eastern Australia, and on some islands off the southern and eastern coasts. Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria and South Australia are the only states where Koalas are found naturally in the wild.
The Australian government is set to declare koalas as an endangered species after the bushfire crisis as the calamity has destroyed 30% of the habitat of koalas across the country.
The bushfires, one of its worst in the history of Australia which has been raging since September 2019 has killed 26 people, destroyed over 2,000 homes, burned more than 10 million hectares of land and pushed many species towards extinction. It has been recorded that over 1.25 billion animals were dead in the wake of bushfires. According to the experts, around hundreds of billions of insects may have also been wiped out.
Talle Valley Wildlife Sanctuary: It is in Arunachal Pradesh’s Lower Subansiri district. Three new tiny species of frogs has been discovered by scientists of Zoological Survey of India, according to a recently published journal in Talle Valley Wildlife Sanctuary. The size of the frogs are so small that they can sit on a coin. The specimens of the new frog species were collected by Bikramjit Sinha, another scientist of ZSI in Itanagar during 2015-16 as part of the documentation of faunal diversity in the protected area.
Environment
IDA: It stands for the Island Development Agency. It was constituted in 2017 under the aegis of Ministry of Home Affairs to look into the holistic development of islands. The chairman of IDA is Home Minister of India and CEO of NITI Aayog acts as its convener. The IDA members include secretary of Environment, Forests and climate change, Tourism, Tribal affairs, the Home Secretary, S and Cabinet secretary. NITI Aayog has been mandated with the task to steer the holistic development of the islands in sustainable manner.
The Government of India (GoI), on 13th of January 2020 held the 6th Island Development Agency (IDA) meeting in New Delhi. The meeting was chaired by the Union Home Minister, Shri Amit Shah.
The Meeting of the Island Development Agency focused on Green Development in the Islands to reach a new Height. The progress made towards the Holistic development of islands programme was reviewed at the meeting. GoI, for the first time, carried out an initiative of sustainable development in the identified Islands within scientifically-assessed carrying capacity under the guidance of IDA.
The scientific development plans include creating jobs through tourism promotion and increasing export of sea food and coconut based products that are prepared in the islands itself.
The plan is to be implemented in four islands of Andaman and Nicobar Islands and five islands of Lakshadweep Islands. The second phase will cover 12 more islands of Andaman and Nicobar Islands and 5 Islands of Lakshadweep islands.
The decisions taken at the meeting were:-
To improve and implement those infrastructure projects that connects the islands through sea and air.
Port Blair and another 7 islands in Andaman & Nicobar would get digitally connected through submarine optical fiber cable by June, 2020.
Bids for already planned model tourism projects both on Land-based and Water Villas have been invited for private sector participation.
To formulate separate policy for maintaining a clean, green and healthy environment in the islands, Information Technology based micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) are to be set up under the Lakshadweep and Andaman and Nicobar Islands Industrial Development (LANIDS) Scheme.
NEAT AI scheme: It is a National Educational Alliance for Technology (NEAT) Artificial Intelligence (AI) scheme which was launched by the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD), recently. The scheme was launched to customize learning process using Artificial Intelligence (AI). NEAT AI Scheme aims to recognize the development of emerging technologies in Adaptive Learning and bring them under a common platform so that learners can access it easily. NEAT program will be implemented by All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE).
The National Institute of Information Technology (NIIT) has been selected as one of the EdTech companies for the NEAT initiative. NIIT was established with a vision to bring about innovation in higher education and learning in emerging areas of the knowledge society.
AICTE: All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) was founded in November 1945 as a national-level apex advisory body to conduct a survey on the facilities available for technical education and to promote development in the country in a coordinated and integrated manner. It is headquartered in New Delhi.
AS per the National Policy of Education (1986) defines AICTE as the Statutory authority for planning, formulation and maintenance of norms & standards, quality assurance through accreditation, funding in priority areas, monitoring, and evaluation, maintaining parity of certification & awards, and the management of technical education in the country.
ICAR: It refers to Indian Council of Agricultural Research. It is an autonomous organization under the Department of Agricultural Research and Education (DARE), Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Government of India. It is responsible for co-coordinating agricultural education and research in India. The ICAR is responsible for coordinating, guiding and managing research and education in agriculture including horticulture, fisheries and animal sciences in the entire country. It was founded in 16 July 1929 as a registered society under the Societies Registration Act, 1860 in pursuance of the report of the Royal Commission on Agriculture. It is headquartered in New Delhi. It is the largest network of agricultural research and education institutes in the world and it has played a pioneering role in ushering Green Revolution and subsequent developments in agriculture in India. The Union Minister of Agriculture serves as its president.
The Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) is all set to start a Farmers” Innovation Fund (FIF). It was announced by the Director General Trilochan Mohapatraat at the 1st ever Farmers' Science Congress, a part of the ongoing 107th Indian Science Congress. ICAR will start operating the FIF in fiscal 2020-21.
The main aim of FIF is to scientifically validate, scale-up and propagate the innovations of progressive farmers. The scientific farming based activities will not only link farmers and farming with science but also encourage them to continue their innovations. As part of this system, an innovation centre will be established in New Delhi where the innovations will be scientifically validated and farmers will be allowed to pursue research work. At present, the innovations of farmers are being documented by the Krishi Vigyan Kendras.
KVK: It refers to Krishi Vigyan Kendra. KVK was founded by the by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR). It is an integral part of the National Agricultural Research System (NARS). It is a district level Farm Science Centre responsible for speedy transfer of technology to the farmer’s fields. The KVK aims to reduce the time period between generation of technology at the research institution and its transfer to the farmer’s field. The KVKs are 100% funded by the Government of India. The first KVK was established in 1974 at Puducherry under the administrative control of Tamil Nadu Agricultural University, Coimbatore.
PCRA: It refers to Petroleum Conservation Research Association. PCRA is a registered society set up under the aegis of Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas, Government of India. It is a non-profit organization. PCRA undertake studies to identify the potential and to make recommendations for achieving conservation of petroleum products in various sectors of the economy. It helps the government in proposing policies and strategies for petroleum conservation, aimed at reducing excessive dependence of the country on oil requirement. The present Chairman of PCRA is M.M. Kutty.
A month long fuel conservation campaign of Petroleum Conservation Research Association (PCRA), Saksham 2020, was launched by the Chairman of Petroleum Conservation Research Association (PCRA). It was launched in New Delhi recently. The objective of the campaign is creating mass awareness among public about conventional fuel conservation. To create this awareness in the public, PCRA, carries out various activities like ‘Saksham’ cycle Day, cyclotrons, seminars for housewives on adopting the simple fuel-saving measure.
Blue Flag tag: The Blue Flag is a certification by the Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE) that a beach, marina, or sustainable boating tourism operator meets its stringent standards. It is a trademark owned by FEE which is a not-for-profit non-governmental organization. It consists of 65 organizations in 60 member countries. Certificates, which FEE refers to as awards, are issued on an annual basis to beaches and marinas of FEE member countries. This concept started in France in 1985. Europe adopted the ‘Blue Flag’ program in 1987 and South Africa was the first outside European country that joined the program in 2001.
Recently, The Ministry of Environment and Forest (MoEF) issued an Extraordinary Gazette Notification declaring a list of activities and facilities that would be allowed in the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) areas of certain beaches, which have been identified for obtaining the ‘Blue Flag’ certification. In July 2019, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has identified 13 beaches across the country for the Blue Flag certification. CRZ rules restrict the construction work around sea beaches.
Chandrabhaga beach located on the Konark coast of Odisha is the first beach in the country to receive 'Blue Flag Certification'.
IIFPT: It is an acronym for Indian Institute of Food Processing Technology.IIFPT is a pioneer Educational and R&D Institution under the Ministry of Food Processing Industries. IIFPT has a 15-acre campus. It was established in 1967 in Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu.
Recently,IIFPT, Bathinda signed Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with 8 different reputed institutes of the region in the states of Punjab and Haryana for facilitating a collaborative research, skill development and students's in-plant training.
IIFPT signed and exchanged the MoU's with the VC's and Directors of these Universities, Colleges, and Institutes. The MoU was signed with an aim to not only increase the income of the farmers but also open new opportunities for the benefit of farmers.
The 8 institutes include Maharaja Ranjit Singh Punjab Technical University (MRSPTU) from Bathinda, Central Institute of Post-Harvest Engg. & Technology (CIPHET) and Punjab Agricultural University (PAU) both from Ludhiana, National Dairy Research Institute (NDRI) and Indian Institute of Wheat & Barley Research (IIWBR) both from Karnal, Sant Longowal Institute of Engg. & Tech. (SLIET), Sangrur, Guru Nanak College, Budhlada and National Agri-Food Biotechnology Institute (NABI) from Mohali.
Indian polity
The Union Cabinet: The Union Council of Ministers exercises executive authority in the Republic of India. It consists of senior ministers, called 'cabinet ministers', junior ministers, called 'ministers of state' and, rarely, deputy ministers. It is led by the Prime Minister. A smaller executive body called the Union Cabinet is the supreme decision-making body in India. Only the prime minister and ministers of the rank of cabinet minister are members of Union Cabinet in accordance with Article 75.
Recently, on 11 January 2019, the Union Cabinet approved the promulgation of the ordinance for amendment in the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) (MMDR) Act, 1957 and the Coal Mines (Special Provisions) Act, 2015. Amendments to these two Acts approved by the Cabinet aims to ease the auction of coal mines allow Foreign direct investment (FDI) and enhance ease of doing business.
The amendments in the laws will not only open up new areas of growth in the coal and mining sector but also offer unexplored and partially explored coal blocks for mining through prospecting license-cum-mining lease (PL-cum-ML).
The ordinance democratizes the coal industry and makes it attractive for merchant mining companies, including multinationals to look at India.
It will allow Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the coal mining sector by removing the restriction and eligibility criteria for participation.
Section 11A of the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act provides that the central government can auction coal and lignite mining licenses only to companies engaged in iron and steel, power and coal washing sectors. It will enable any India-registered company to invest in the coal mining sector and develop coal blocks provided that the companies must have prior experience of mining in India to bid for the blocks.
Large investment in mining is expected to create jobs and set off demand in critical sectors such as mining equipment and heavy commercial vehicles.
It will allow successful bidder/allottee to utilize mined coal in any of the plant of its subsidiary or holding company as restrictions of end use has been dropped.
ECI: It stands for the Election Commission of India. The ECI is an autonomous constitutional authority responsible for administering Union and State election processes in India. The body administers elections to the Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies in India, and the offices of the President and Vice President in the country. It was founded in 25 January 1950. The current Election Commissioner is Shri Ashok Lavasa and the Chief Election Commissioner is Sh. Sunil Arora.
Recently, on 14th January 2020, the Election Commission of India organized a Briefing Meeting for Observers to be deployed for the forthcoming NCT of Delhi Legislative Assembly Elections, for which schedule was announced on 6th January, 2020. Poll date for the single phased election for Delhi's 70 constituencies is February 8, 2020 and Counting will be held on February 11, 2020. More than 150 officers drawn from IAS, IPS and also from Indian Revenue Service and other Central Services were called for the General, Police and Expenditure Observers briefing today. Adequate number of officers would be deployed on actual duty.
ECI Observers: They are appointed under the powers conferred on it by Section 20B of the Representation of the People Act, 1951 and the plenary powers available to the Commission under the Constitution of India. They work under the superintendence, control and discipline of the Commission for the period from their appointment till the completion of the process of election. Statutory powers were provided to the Observers to watch the conduct of elections and especially in respect of counting of votes after the amendment of the Representation of the People Act, 1951 in August 1996 under which new Section 20B was added.
International
Statue of Unity: The Statue of Unity is a colossal statue of Indian statesman and independence activist Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel (1875–1950), who was the first Deputy Prime Minister and Home minister of independent India and the chief adherent of Mahatma Gandhi during the non-violent Indian Independence movement. It was designed by Indian sculptor Ram Vanji Sutar. The statue stands 182 metres high, making it the tallest monument in the world. It is at Sadhu Bet Island. The Statue of Unity which is a tribute to the Indian leader Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel, was unveiled on 31 October 2018 by the Prime Minister of India Narendra Modi. It was unveiled on the 143rd birth anniversary of Sardar Vallabhai Patel.
Recently, External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar announced that the World’s tallest statue on Narmada river, the Statue of Unity in Gujart, has been included in the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation’s ‘8 Wonders of SCO’ list. Apart from the Statue of Unity the others incluided in the 8 wonders of the SCO list are Navruz Palace in Tajikistan, the Tamgaly Gorge in Kazakhstan, the Daming Palace in China, Po-i-Kalan complex in Uzbekistan, Lahore – the Mughals Heritage in Pakistan and the Golden Ring of Russia.
SCO: It is an acronum for Shanghai Cooperation Organization. It was founded by the presidents of Russia, China, Kyrgyz Republic, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan at the summit in Shanghai in 2001. The supreme decision-making body in the SCO are the Heads of STate Council(HCO) who meet once a year and adopt decisions and guidelines on all improtant matters of the organisation. Military exercises are also regularly conducted among members to promote cooperation and coordination against terrorism and other external threats, and to maintain regional peace and stability. It is the largest regional organisation in the world in terms of geographical coverage and population, covering three-fifths of the Eurasian continent and nearly half of the human population and is also regarded as the "alliance of the Ease".
India became a member of the SCO at the SCO summit held Nur-sultan previously known in Astana, Kazakhstan in the year 2017 along with Pakistan. Before becoming a member of SCO, India was granted with the observer status from 2005.
World Future Energy Summit: World Future Energy Summit is an annual event dedicated to advancing future energy, energy efficiency and clean technologies. It was first held in 2011 in UAE. The summit invites innovators, academicians, political leaders and industry leaders to create new business and investment.
The World Future Energy Summit began at the Abu Dhabi, National Exhibition Centre (ADNEC), on 13 January 2020. The 2020 theme of the summit is Rethinking Global Consumption, Production, and Investment. About 33,500 participants from 170 countries participated in the event. The 4 day event included exhibition and forum programs that address energy, solar, water, waste and smart cities. It also focused on clean energy generation, water sustainability and discussions on the ways in which digital innovation can help to improve the quality of life in an urban environment was held. Along with the summit, the Climate Innovations Exchange (CLIX) was also held.
Abu Dhabi: It is the capital of the United Arab Emirates. The city of Abu Dhabi is located on an island in the Persian Gulf, off the Central West Coast.
Corona Virus: Coronaviruses are species of virus belonging to the subfamily Coronavirinae in the family Coronaviridae, in the order Nidovirales. Coronaviruses are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and with a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. Coronaviruses are types of viruses that typically affect the respiratory tract of mammals, including humans. They are associated with the common cold, pneumonia, and severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) and can also affect the gut.
In 2002-03, around 700 people died due to Corona virus in the world. The virus originated in China. There is no specific vaccine for the virus as of 2019. The virus was first identified in Saudi Arabia, in 2012. Most cases were found in the Arabian Peninsula.
Recently, a new stain of virus which has been identified as Corona virus by the researchers has been found in China. Chinese health authorities reported that a new virus implicated in a pneumonia outbreak was identified in the city of Wuhan, China.
Hormuz Peace Initiative: The initiative is led by Iran. The initiative reviewed the developments in the Persian Gulf region and evaluated the regional cooperation plans under the ‘Hormuz Peace Endeavor’ (HOPE). The HOPE was proposed by Iranian President at UN General Assembly meeting in September, 2019. The initiative aims at enhancing solidarity, peace, mutual understanding and friendly relations among countries in the region in order to guarantee the territorial integrity and political independence of regional states.
India along with other leading trade partners of Iran namely China, Oman and Afghanistan attended the meeting of Hormuz Peace Initiative which was recently held in Tehran, Iran. The developments in the Persian Gulf region and evaluation of the regional cooperation plans under the ‘Hormuz Peace Endeavor’ (HOPE) were reviewed at the initiative. The initiative aimed at stabilizing one of the world’s busiest shipping lanes, the Strait of Hormuz in the backdrop of US-Iran tensions.
Strait of Hormuz: It is the waterway that separates Iran and Oman. It is a strait between the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman. It provides the only sea passage from the Persian Gulf to the open ocean and is one of the world's most strategically important choke points. Iran lies on the North Coast while UAE and Musandam, an enclave of Oman lies in the south coast. The Strait is 21 miles (33 km) wide at its narrowest point, but the shipping lane is just two miles (three km) wide in either direction. A third of the world’s liquefied natural gas and almost 25% of total global oil consumption passes through the strait, making it a highly important strategic location for international trade. Two-thirds of the oil and half the liquefied natural gas India imports come through the strait between Iran and Oman.
Taiwan: Taiwan, officially the Republic of China, is a state in East Asia. Neighboring states include the People's Republic of China to the north-west, Japan to the north-east, and the Philippines to the south. Its capital is Taipei. The official language of Taiwan is Mandarin Chinese. The currency used here is New Taiwan dollar.
Tsai Ing-wen an opponent of Beijing, has won the Taiwan presidential election for the second time. Her Democratic Progressive party retained control of the legislature, according to final results. She defeated Han Kuo-yu with 57.1% of the vote.
National
National Youth Day: The day is celebrated on the 12 January every year. The Government of India declared 12th January as the National Youth Day in 1984 to commemorate the birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda who was one of the greatest social reformers, thinkers, and philosophers of India. Since then it is celebrated all over the country every year. The main aim of the celebration of the Youth day is to motivate the students across the country to apply the ideas and philosophy of Swami Vivekananda in their lives so as to make a better future for India.
Recently, on 12 January 2020 India celebrated National Youth Day. The theme of the National Youth Day 2020 is "Channelizing Youth Power for Nation Building". It aims to inspire the youth generations and to educate them to behave properly in society.
Swami Vivekanand: He was a great social reformer, philosopher, thinker and a patriotic saint of India. He was born in 12 January 1863 in Kolkata as Narendra Nath Datta and came to be known as Swami Vivekanand after he became a monk and a chief disciple of Ramakrishna Paramhansa. His father was a successful attorney. He used to practice meditation even from his boyhood, and was associated with Brahmo Movement for some time.
He represented India in the first Parliament of Religion held in Chicago in 1893. He is especially remembered around the world for his speech at the Parliament of the World’s Religions in Chicago in 1893. The speech covered topics including universal acceptance, tolerance and religion and got him a standing ovation. For three years he spread the Vedanta and Yoga philosophy and religion in America and England and then returned to India. He is also credited with raising interfaith awareness. He is perhaps best known for his speech which began with the words, "Sisters and brothers of America ..," in which he introduced Hinduism at the Parliament of the World's Religions in Chicago in 1893.
He found the Ramakrishna Math and Mission on 1 May 1897. In 1898, he established Belur Math. He died on 4 July 1902. The spent the rest of his life inspiring and guiding the people of India. The mission has been doing extensive educational and philanthropic work in India.
Some of Swami Vivekanand's quotes:
*Arise, awake and do not stop until the goal is reached.
*You cannot believe in God until you believe in yourself.
*You have to grow from the inside out. None can teach you, none can make you spiritual. There is no other teacher but your own soul.
CPA: It is an acronym for Commonwealth Parliamentary Association. The CPA previously known as the Empire Parliamentary Association was founded in 1911, with its first branches being Australia, Canada, Newfoundland, New Zealand, South Africa and the United Kingdom, the latter branch administering the Association as a whole. In 1948 the Association changed its name to the current Commonwealth Parliamentary Association, and invited all branches to participate in the organization’s administration. It is an organization which works to support good governance, democracy and human rights.
Recently, the 7th Conference of CPA India Region was inaugurated by Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla in Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh.
The main theme of the conference is the ROLE OF LEGISLATORS. In the Conference, the Capacity Building of Legislators for Scrutinizing Budgetary Proposals and Enhancing Focus of Legislators on Legislative Business will be discussed by the delegates. State Governor, Anandiben Patel will also address the Valedictory Session.
CoD: It refers to Content on Demand. CoD are the services that will be provided by RailTel unit of Government of India (GoI) Under the project, the provision of content such as movies, shows, educational programs, etc. will be made available both in paid and unpaid formats.
With an aim to generate more non fare revenue, recently, the Indian Railways entrusted RailTel a Miniratna Public sector undertaking (PSU) under Ministry of Railways with providing CoD service to passengers in trains. Margo Network, a subsidiary of Zee Entertainment has been selected by RailTel as the digital entertainment service provider (DESP) for providing CoD service in trains and stations. The contract period is for 10 years including the two year s which is the time period for implementing the project. The project will be implemented in several languages. The aim is to cover all the 17 zones of the Railways.
RailTel: It is a Miniratna Public sector undertaking (PSU) enterprise of the Government of India focusing on providing broadband and VPN services. It was founded in September 2000. It is headquartered in Gurugram, UP. It works under the Ministry of Railways.
Indian Railways: Indian Railways (IR) is India's national railway system operated by the Ministry of Railways. It was founded in 16 April 1853. The first railway on Indian sub-continent ran over a stretch of 21 miles from Bombay to Thane. It is headquartered in New Delhi. It manages the fourth largest railway network in the world by size, with a route length of 67,368-kilometre (41,861 mi) as of March 2017. The present Railway Minsiter is Piyush Goyal and the Chairman of the Railway Board is Vinod Kumar Yadav.
On January 13, 2020, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed by the Indian Railways with RailTel, a miniratna Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) under the Ministry of Railways for Phase 2 project of e-office execution. The MoU was signed after the successful completion of the Phase 1 execution of National informatics Centre (NIC) e-office for 50,000 users in 58 units which was completed ahead of the deadline.
Under Phase 2 project, RailTel will have to register 39,000 users over 34 Railway divisions in NIC e-office platform by 30th June 2020.
E-Office is an integrated file management system that will help employees manage data, content electronically thereby fostering paper-less culture which saves operational cost and also reduces the carbon footprint which is one of the most urgent needs of the world and directly impacting every citizen of the country.
NIC: It refers to National information Centre. NIC is an attached office under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY), Government of India. NIC provides infrastructure to help support delivery of Government IT services and delivery of some of the initiatives of Digital India. It was founded in 1976.
NIC e-Office: It is a cloud enabled software developed by NIC. It is deployed from RailTel Tier III certified data centre at Secundrabad and Gurgaon. It is based on Central Secretariat Manual of e-Office Procedure (CSMeOP). Presently, 4 modules (File Management System (eFile), Knowledge Management System (KMS) Collaboration & Messaging Services (CAMS) & Personnel Information Management System (PIMS) are the part of the e-office system being implemented.
HURL: It stands for Hindustan Urvarak and Rasayan Ltd. HURL is a joint venture firm promoted by three PSUs namely - Coal India Limited (CIL), NTPC Ltd and Indian Oil Corporation Ltd (IOCL). The three units of HURL are expected to be commissioned in February 2021, while Ramagundam (Telangana) and Talcher (Odisha) units are also likely to commence operations next year. The company’s aim is not only to focus on single brand urea, but to diversify its product portfolio to include agrochemicals, compost, and nano-fertilizers. It is headquartered in New Delhi.
Recently, Union Chemicals and Fertilizers Minister D.V. Sadananda Gowda unveiled the logo and brand ‘Apna Urea Sona Ugle‘ of Hindustan Urvarak and Rasayan Ltd (HURL). HURL is in the process of reviving three sick urea units. The sick urea units are located at Gorakhpur (Uttar Pradesh), Barauni (Bihar) and Sindri (Jharkhand).
People In News
Prof M S Swaminathan: He is an Indian geneticist and administrator. M. S. Swaminathan was born in Kumbakonam, Tamilnadu on 7 August 1925. He is known for his role in India's Green Revolution, a program under which high-yield varieties of wheat and rice were planted. He has been called the "Father of Green Revolution in India" for his role in introducing and further developing high-yielding varieties of wheat in India. He also founded the MS Swaminathan Research Foundation. From 1972 to 1979 he was director general of the Indian Council of Agricultural Research. He was Principal Secretary, Ministry of Agriculture from 1979 to 1980. He served as Director General of the International Rice Research Institute (1982–88) and became president of the International Union for the Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources in 1988. He was a follower of Mahatma Gandhi. Prestigious awards like Padma Shri, Padma Vibhushan, Padma Bhushan are among the other awards that he has been conferred with.
On January 14, 2020, eminent Agricultural Scientist Dr M S Swaminathan was presented the ‘MuppavarapuVenkaiah Naidu National Award for Excellence’ for his distinguished contribution to the field of agriculture. The prestigious award instituted by the Muppavarapu Foundation was presented to him by the Vice President of India, Shri M Venkaiah Naidu presented him the award during the Pongal Celebrations held at Raj Bhavan in Chennai. The Award carries a cash prize of Rs. 5 lakhs and a citation.
The National Award for Excellence was instituted by the Muppavarapu Foundation. The award for Social Service was launched by the Swarna Bharat Trust, in Hyderabad.
Ishwar Sharma: He is a 10 year old British Indian boy. He is originally from Mysore. He has the skill to chant up to 50 shlokas from the Vedas and ‘Bhagavad Gita’ and practices yoga. He has participated in over 100 yoga events across the UK and worldwide.
The British Indian yoga boy Ishwar Sharma won the ‘Global Child Prodigy Award’. He was chosen from the UK for the awards which honor child prodigies from across 45 countries and 30 different categories such as palaeontology, biking, choreography, fitness and martial arts etc.
Harish Salve: Harish Salve is an Indian senior advocate who practices at the Supreme Court of India. He was designated as a Senior Advocate by the Delhi High Court in 1992 and he also served as the Solicitor General of India from 1 November 1999 to 3 November 2002. He did his LLB from Nagpur University and began his legal career in 1980 with JB Dadachandji & Co. He has represented India in several important matters in India as well as abroad. He fought the case of kulbhushan jadhav at International Court of Justice (ICJ). He even played a key role in the Hyderabad Nizam funds case, in which India had won decades-old legal dispute with Pakistan at the UK Court over £35m-worth funds belonging to the 7th Nizam of Hyderabad.
Noted Senior Indian Advocate Harish Salve has been appointed as Queen's Counsel (QC) for the courts of England and Wales, 'Bar and Bench'. His appointment was announced when the UK’s Ministry of Justice released the new list of silk appointments on January 13, 2020. Salve and other appointees will be formally appointed as QC on March 16, where the Lord Chancellor will preside over the appointment ceremony at Westminster Hall.
The title of Queen's Counsel (QC) is awarded to those who have demonstrated particular skill and expertise in the conduct of advocacy.
Kaifi Azmi: Kaifi Azmi originally named Athar Hussein Rizvi. He was an Indian Urdu poet born on January 14, 1919, in Mizwan village of Azamgarh. He was fond of writing poems since childhood. He started taking part in poetry reciting events during his teenage. He is remembered as the one who brought Urdu literature to Indian motion pictures. He grew up to be inspired by Mahatma Gandhi's Quit India freedom movement of 1942 and later left for Mumbai to write for an Urdu newspaper. His first collection of poems 'Jhankar' was published in 1943. He was a member of the Progressive Writers' Association who used to write to bring socio-economic reforms. Kaifi Azmi's legendary works such as Pakeezah's Chalte Chalte, Koi Yeh Kaise Bataye from Arth and Yeh Duniya Yeh Mehfil have gone down as notable contributions in Urdu and Hindi language.
On 14 January 2020, Google honored India’s famous poet, lyricist, and activist Kaifi Azmi by preparing a special doodle on his 101st birth anniversary. Kaifi Azmi has won numerous awards for his work, including the prestigious Padma Shri Award for Literature and Education and the Sahitya Akademi Fellowship, one of India's highest literary honors and 3 Filmfare Awards. He is the father of Bollywood's famous actress Shabana Azmi.
Places In News
Kolkata: Kolkata (formerly Calcutta) is the capital of India's West Bengal state. Founded as an East India Company trading post, it was India's capital under the British Raj from 1773–1911. Today it’s known for its grand colonial architecture, art galleries and cultural festivals. Chief Minister and Governor of West Bengal is Mamta Banerjee and Jagdeep Dhankhar respectively.
Recently Prime Minister Narendra Modi attended the 150th celebrations of Kolkata Port Trust. The Kolkata Port was also renamed as Shyama Prasad Mukherjee Port at the event. A commemorative Stamps of the port trust was launched and dedicated to the nation by PM Modi during the celebration. He also inaugurated the Kaushal Vikas Kendra and Pritilata Chhatri Avas for 200 tribal girl students from Sundarbans during the event.
At the event, two oldest pensioners of the Port Mr. Naresh Chandra Chakraborty (100 years old) and Smt. Nagina Bhagat (105 years old) were honored too.
Puri: Puri is a city and a Municipality in the state of Odisha in eastern India.It is one of the original Char Dham pilgrimage sites for Hindus. Puri is known by several names since the ancient times, and was locally known as "Sri Kshetra" and Lord Jagannatha temple is known as "Badadeula".
Puri district of Odisha has been awarded the Swachhata Darpan Awards 2019 for its initiatives for plastic waste management. The award ceremony was held during the Open Defecation Free Sustainability Workshop held in New Delhi which was organised by the Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS) and Ministry of Jal Shakti. The award was presented by Indian Bollywood actor Aamir Khan who is also the Founder of Paani Foundation, to Puri Municipality Additional Executive Officer Saroj Kumar Swain.
Swachhata Darpan Award has been instituted under Swacha Bharat Mission to encourage the states and districts to focus on Open Defecation Free (ODF) sustainability and social and liquid waste management.
Delhi: The fourth edition of Raisina Dialogue was held recently, in New Delhi. It was held between January 14, 2020 and January 16, 2020. The dialogue which is held annually since 2016 is organized by the Ministry of External Affairs and Observer Research Foundation.
The 2020 Theme of the Dialogue was 'A World Reorder: New Geometries; Fluid Partnerships'.
Foreign Ministers from 13 countries participated in the dialogue including Iran, Australia and Russia.
During the Resina dialogue, a defense agreement was signed by India and Finland and Russia announced that it supports India for the latter’s permanent membership at the UNSC (United Nations Security Council).
Ministry of External Affairs in partnership with Observer Research Foundation has organized the flagship annual geopolitical and geostrategic conference.
The dialogue is named after Raisina Hill, which is the seat of the Government of India, as well as the Rashtrapati Bhavan. Since its inception in 2016, the conference has emerged as India’s flagship conference on geopolitics and geo-economics.
Sufal Bangla scheme: It is an initiative of the Government of West Bengal which was initiated in 2014. The scheme is being run with the assistance of Safal (National Diary Development Board, New Delhi). It is financially supported by Rashtriya Krishi Vikash Yojana. The implementing agency is Paschimbanga Agri Marketing Corporation Ltd.
The scheme aims to help the farmer’s get premium price and have rational share in consumer’s price, to supply quality produce at less retail price to the consumers and to make fruit and vegetable producer’s retail market competitive.
Recently, the Government of West Bengal implemented the Sufal Bangla Scheme which have protected consumers from the spike in food inflation.
Gandhinagar: Gandhinagar is a planned city in the western Indian state of Gujarat. It is the capital of the state of Gujarat in India. It lies on the west bank of the Sabarmati River.
Recently, Union Home Minister Amit Shah inaugurated various people centric projects of Gujarat Police and Indian Postal Department at Mahatma Mandir in Gandhinagar. The project includes‘Netrang’ project to establish Command and Control Room in 33 districts, online portal to pay E Challan and Cyber Crime Prevention Unit-AASHVAST and Video Integration and State Wide Advance Security-VISWAS project, which will have a dedicated service helpline for victims of cyber crimes.
Six different postal memory cards depicting various folk dances of Gujarat was also inaugurated by him.
Goa: Goa is a state in western India with coastlines stretching along the Arabian Sea. It is surrounded by the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the east and south, with the Arabian Sea forming its western coast. It is India's smallest state by area and the fourth-smallest by population. Its capital city is Panaji.Its long history as a Portuguese colony prior to 1961 is evident in its preserved 17th-century churches and the area’s tropical spice plantations. The Chief Minister of Goa is Pramod Sawant and the Governor is Satya Pal Malik.
Recently, the Union minister for women and child development Smriti Irani launched 3 welfare schemes for women in Goa. The event was held at Dr Shyama Prasad Mukherjee Stadium at Taleigao near Panaji. The schemes are Yashaswini Scheme for Women Entrepreneurship, Swasthya Sahayak Project and breast cancer screening initiative handheld device facilitating detection of cancer.
Yashaswini Scheme: Under the Yashaswini scheme, women self-help groups (SHGs) will be given interest-free loans of up to Rs.5 lakh for business. The scheme aims to strengthen the socio-economic empowerment of women in Goa. SHGs including Umang Self-Help Group, Adarsha Satari Mahila Mandal Guleli –Sattari, Salcete and Phoenix Womens Wing Self-Help Group Valpoi –Sattari were given loans under the newly launched scheme.
Swasthya Sahayak Project: Under the Swasthya Sahayak scheme, primary healthcare workers and Anganwadi workers will be given a diagnostic kit developed by the Public Health Foundation of India, in association with Procter and Gamble to manufacture and supply the kits using corporate social responsibility (CSR) fund. It will help them to conduct basic diagnostic tests at people's doorstep so that every individual will be given basic health care.
Breast cancer screening initiative: Under the breast cancer screening initiative, the Anganwadi and healthcare workers will screen women for breast cancer using handheld devices. The initiative aims to reach out to the women in rural parts of the state. It is expected that the delivery of health services will become more accessible and affordable.
Ladakh: Ladakh is a region administered by India as a union territory, and constituting a part of the larger region of Kashmir. It is located between the Kunlun mountain range in the north and the main Himalayas to the south. The capital of Ladakh is Leh, Kargil.
On 17 January 2020, NITI Aayog and Union Territory of Ladakh sign MoU to promote the development of key infrastructure sectors in the region. It was signed between NITI Aayog Senior Adviser Dr Yogesh Suri and Adviser to the Lieutenant Governor of Ladakh Umang Narula. The agreement was executed in the presence of NITI Aayog CEO Amitabh Kant.
Under this agreement, NITI Aayog will provide support to the UT’s administration through its key initiative ‘Development Support Services to States for Infrastructure Projects (D3S-i)’.
The MoU will help towards identification of high-impact priority projects, expedited project implementation, addressing structural-level issues and creating unique models of development for the Union Territory of Ladakh, especially in tourism, solar energy and basic infrastructure.
The main purpose of D3S-i projects is creating PPP (Public Private Partnership) projects. In 2018, phase I of the project was completed. In phase I, 10 projects were selected from 400 projects that were submitted by the states. In phase II, that was completed in the year 2018-19, the selected projects entered transaction stage.
Science and Technology
China: China has launched the world's largest and most sensitive single-dish radio telescope.
The Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST) is a single-dish telescope with a diameter of half a kilometer and a receiving area equivalent to about 30 football fields and has double the collecting power of the Arecibo. It is located in a naturally deep and round karst depression in southwest China's Guizhou Province. It is also known by the name “Sky Eye” in China.
The telescope will gradually open to astronomers around the globe, providing them with a powerful tool to uncover the mysteries surrounding the genesis and evolutions of the universe.
After its commissioning, FAST can now be used for observation at full capacity, and is expected to make a number of major scientific discoveries in the coming two or three years.
NASA: It is an acronym for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. NASA is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research.
NASA’s Artemis mission: Under the Artemis program, NASA wants to land the first woman and next man on the Moon by 2024, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
ARTEMIS: It is an acronym for Acceleration, Reconnection, Turbulence and Electrodynamics of the Moon’s Interaction with the Sun. The mission is named Artemis after the Greek goddess of the Moon Artiemis. With this mission NASA aims to establish a lunar outpost, investigate the Moon’s resources and how they might be exploited, inspire a new generation and encourage careers in STEM and broaden commercial and international partnerships
GSAT-30 satellite: GSAT-30 is a communication satellite of India which is configured on ISRO’s enhanced I-3K Bus structure to provide communication services from Geostationary orbit in C and Ku bands. The satellite derives its heritage from ISRO’s earlier INSAT/GSAT satellite series and is equipped with 12 C and 12 Ku band transponders. GSAT-30 is to serve as replacement to the “aging” INSAT-4A spacecraft services with enhanced coverage. It was recently launched onboard Arianne 5 rocket from French Guiana successfully. The satellite aims to provide high- quality television, telecommunications and broadcasting services. The satellite provides Indian mainland and islands coverage in Ku-band and extended coverage in C-band covering Gulf countries, a large number of Asian countries and Australia.
Seismic Hazard Microzonation: In most general terms, seismic microzonation is the process of estimating the response of soil layers under earthquake excitations and thus the variation of earthquake characteristics on the ground surface. This necessitates the development of microzonation maps for big cities for detailed seismic hazard analysis.
The Ministry of Earth Science under the Government of India (GoI) has launched “Seismic Hazard Microzonation” to minimize the hazards of seismic activities by putting in adequate measures.
So far, microzonation has been done in the state of Sikkim and in the cities of Delhi, Kolkata, Bengaluru, Guwahati, Jabalpur, Dehradun, Ahmedabad and Gandhidham.
Japan is the best example where microzonation techniques are well implemented.
Sports
Polly Umrigar Award: Polly Umrigar award is presented to the best male International cricketer and it carries a citation, trophy and cheque for Rs. 15 lakh.
India’s fast bowling sensation Jasprit Bumrah and Poonam Yadav will receive the prestigious Polly Umrigar Award for the best international cricketer (2018-19) at the BCCI Annual Awards (Naman) to be held today in Mumbai.
Jasprit Bumrah is the world's No. 1 ODI bowler. HE made his Test debut during India's tour of South Africa in January 2018.
Poonam Yadav has claimed the top prize in women's section. The award will be another feather in the leg-spinner's cap who recently received the Arjuna Award.
Mayank Agarwal and Shafali Verma bagged the awards for best international debut in men's and women's category.
WTA doubles Title: India's Sania Mirza and Ukraine's Nadiia Kichenok have won the women’s doubles title of the Women's Tennis Association (WTA) International trophy at Hobart, Australia. They beat Shuai Peng and Shuai Zhang from China 6-4,6-4. It’s Sania’s 42nd WTA doubles title and first since Brisbane International trophy in 2007 with American partner Bethanie Mattek-Sands.
Wrestling: Star women wrestler Vinesh Phogat won her first gold medal of the 2020 season at the Rome Ranking Series event after teen sensation Anshu Malik settled for a silver in 57kg competition, recently,in Rome. She overcame two tough Chinese rivals on her way to the 53kg gold medal bout ultimately to overpower Valverde comprehensively. Earlier, Vinesh won her bouts against Khrystyna Bereza (10-0) and Lannuan Luo (15-5) by technical superiority.
Khelo India Youth Games: In the third Khelo India youth games in Guwahati, Devanshi Dhama and Shravan Kumar representing Uttar Pradesh won gold in mix team event under 21 category in 10-meter air pistol. Delhi settled for silver in this event. In Lawn Bowls, Assam boys team secured a bronze in Triples event while girls team entered into the final in Four categories.
Currently, Maharastra is leading the medal tally with 42 gold followed by Haryana with 36 gold.
ODI: It refers to One Day International cricket. India defeated Australia in the second One Day International by 36 runs at Saurashtra Cricket Association Stadium in Rajkot, Gujarat. With this win India has now leveled the three-match series 1-1 after losing the first game by 10 wickets in Mumbai. K L Rahul was declared Player of the Match.
Arts
Tangams: The Tangams are a lesser known community within the Adi tribe of Arunachal Pradesh. The community resides in the hamlet of Kugging in Upper Siang district’s Paindem circle. Solung (harvesting festival) and Aran (a hunting festival) are two major festivals of the Adi tribes. For long, the only account of the Tangams could be found in a book, “Tangams” (1975) where the community’s population was pegged at 2,000 spread across 25 villages. Their original language is Tangam which is an oral language that belongs to the Tani group, under the greater Tibeto-Burman language family. This language is marked ‘critically endangered’ by the UNESCO World Atlas of Endangered Languages (2009).
According to the extensive field research and documentation the community which was carried out by the Centre for Endangered Languages (CFEL) of Rajiv Gandhi University (RGU), at present the Tangams are concentrated in only one village (Kugging), with only 253 reported speakers.
Recently, the Chief Minister of Arunachal Pradesh Pema Khandu released a book titled Tangams: An Ethnolinguistic Study Of The Critically Endangered Group of Arunachal Pradesh. The book aims to help the future generations of the Tangam community. The book is published by Centre for Endangered Languages, Rajiv Gandhi University and Himalayan Publishers, New Delhi. The Centre for Endangered Languages is a University Grant Commission sponsored centre.
The languages of Arunachal Pradesh have been classified under the Sino-Tibetan language family, and more specifically under the Tibeto-Burman and Tai group of languages, such as Lolo-Burmish, Bodhic, Sal, Tani, Mishmi, Hruissh and Tai.
Arunachal Pradesh: Arunachal Pradesh is the northeasternmost state of India. It is the largest of the Seven Sister States of Northeast India. Arunachal Pradesh means Land of the Dawn-Lit Mountains, which is the sobriquet for the state in Sanskrit. The state is known as the Orchid State of India or the Paradise of the Botanists. This state is also known as” Land of Rising Sun”. The Tawang Monastery in Arunachal Pradesh, is the largest monastery in India and second largest in the world after the Potala Palace in Lhasa, Tibet. It is one of the few monasteries of Tibetan Buddhism that have remained protected from Mao's Cultural Revolution without any damage. It has among the highest diversity of mammals and birds in India. There are around 750 species of birdsand more than 200 species of mammals in the state. The current Governor and Chief Minister of Arunachal Pradesh are B. D. Mishra governor and prema khandu respectively.
Bastille Day: Bastille Day is the common name given in English-speaking countries to the national day of France, which is celebrated on 14 July each year. It is also called the French National Day. This day is the anniversary of Storming of the Bastille on 14 July 1789, a turning point of the French Revolution as well as the Fête de la Fédération that celebrated the unity of the French people on 14 July 1790. The celebrations are held throughout France.
History: Jacques Necker, the Finance Minister of Louis XVI, who was sympathetic to the Third Estate, was dismissed by the king on 11 July 1789. These third estate people who were made up 90% of the French population were peasants and wage labourers.
Upon the dismissal of the minister, people of Paris stormed the Bastille fearing that they might be attacked by the royal army. People rushed to Bastille to get gunpowder and ammunition.
Bastille was the fortress prison in Paris that had often held people jailed on the basis of lettres de cachet (literally "signet letters"), arbitrary royal indictments that could not be appealed and did not indicate the reason for the imprisonment.
This day is marked in the French history as the beginning of French Revolution. The revolution overthrew the monarchy and established a republic and finally ended in a dictatorship under Napoleon. A year after the Storming of the Bastille, the French began celebrating the Fête de la Federation.
The day was meant to symbolise peace and brotherhood during the revolution and today, the founding message still remains prominent. It is commonplace for the words “liberty, equality and fraternity” to be heard during the celebrations.
If It Bleeds: This is the name of the new book authored by Stephen King. The new book titled “If It Bleeds” is a collection of four stories. The book is published by Hachette India. The story in the book centres around a bomb at Albert Macready Middle School. It is a sequel to his bestselling work, “The Outsider”.
Stephen King: Stephen Edwin King is an American author of horror, supernatural fiction, suspense, crime, science-fiction, and fantasy novels. He is one of the most distinguished contemporary authors. He has been the recipient of the 2014 National Medal of Arts. He was also awarded the 2003 National Book Foundation Medal for Distinguished Contribution to American Letters. He was in the news recently for voicing his support for the transgender community.
PRASHAD Scheme: It refers to the Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive scheme. The ‘National Mission PRASHAD was launched by the Ministry of Tourism in the year 2014-15 with the objective of integrated development of identified pilgrimage and heritage destinations.
The scheme is aimed at infrastructure development such as entry points (Road, Rail and Water Transport), last mile connectivity, basic tourism facilities like Information Centers, eco-friendly modes of transport, ATM and Money exchange, area Lighting and illumination with renewable sources of energy, parking, drinking water, toilets etc.
Recently, the Union Minister for Tourism inaugurated the project of “Development of Pilgrimage Amenities at Somnath, Gujarat.” This project which was sanctioned under the PRASHAD scheme in March 2017 has been successfully completed with the cost of Rs. 45 crores.
Economics
CBDT: It refers to the Central Board of Direct Taxes. CBDT is a statutory authority functioning under the Central Board of Revenue Act, 1963. The officials of the Board in their ex-officio capacity also function as a Division of the Ministry dealing with matters relating to levy and collection of direct taxes. It functions as a division of the Ministry of Finance under the Department of Revenue. Its functions include formulation of policies, dealing with natters relating to levy and collection of direct taxes, and supervision of the functioning of the entire Income Tax Department. The current Chairperson of CBDT is Pramod Chandra Mody.
Recently, CBDT announced that a new Utility Tool has been launched that will facilitate the Banks and Post Offices across the country with the accurate TDS rate (Tax Deduction at Source) applicable on cash withdrawals.
The utility tool can be accessed by the Banks and Post Offices by visiting the web portal- ‘incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in’ and is available under the name’ Verification of Applicability u/s 194N’ on the portal.
The Utility Tool was developed based on the Data of Cash Withdrawal from across the country that has suggested that large amounts of cash were withdrawn by Individuals who had never filed income tax returns.
Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry: The Minister of Commerce and Industry is the head of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry and one of the cabinet ministers of the Government of India. The first Minister of Commerce and Industry of independent India was Syama Prasad Mukherjee. The current Minister is Piyush Goyal of the Bharatiya Janata Party.
Recently, according to the data released by the commerce ministry, in 2019-20, the bilateral trade between the US and India stood at USD 88.75 billion as against USD 87.96 billion in 2018-19. Latest data also revealed that the bilateral trade between India and China has dipped from $87.08 billion in 2018-19 to $81.87 billion in 2019-20.
The reason behind increasing Indo-US bilateral ties, as per Biswajit Dhar, professor of economics at Jawaharlal Nehru University is, the presence of Indian diaspora in the US is one of the main reasons for increasing bilateral trade. Both nations are negotiating a limited trade pact with a view to remove differences at trade front and boost commercial ties.
India and Bangladesh Trade Relations: The Indian Railways for the first time has loaded special Parcel train beyond the country borders to Benapole (in Bangladesh) with Dry Chillies from Reddipalem (in Guntur District of Andhra Pradesh).
The cost per tonne for carrying by Special Parcel Express train is Rs. 4,608 and which is very cheap and economical as compared to Road transport. Earlier, the farmers and merchants in and around Guntur area have been transporting Dry Chillies by road to Bangladesh in small quantities and that was costing around Rs 7000 per tonne.
Guntur and its surrounding areas in the state of Andhra Pradesh are well known for Chillies cultivation.
Defence
NATGRID: It refers to the National Intelligence Grid. NATGRID is an ambitious counter terrorism programme, which will utilise technologies like Big Data and analytics to study and analyse the huge amounts of data from various intelligence and enforcement agencies to help track suspected terrorists and prevent terrorist attacks. It was setup with approval from the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS), as an attached office of the Ministry of Home Affairs on 1st December 2009. It was first proposed after the Mumbai terror attacks in 2008.
It will be a medium for at least 10 Central agencies such as the Intelligence Bureau and the Research and Analysis Wing to access data on a secured platform. The data will be procured by NATGRID from 21 organisations such as the telecom, tax records, bank, immigration etc. It aims to become the one-stop destination for security and intelligence agencies to access database related to immigration entry and exit, banking and telephone details of a suspect on a “secured platform”.
Recently, NATGRID signed an MoU with the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) to access the centralised online database on FIRs and stolen vehicles.
The MoU will allow NATGRID to access the Crime and Criminal Tracking Network and Systems (CCTNS) database, a platform that links around 14,000 police stations. All State police are mandated to file FIRs in the CCTNS.
DAC: It refers to the Defence Acquisition Council. The DAC is the highest decision-making body in the Defence Ministry for deciding on new policies and capital acquisitions for the three services (Army, Navy and Air Force) and the Indian Coast Guard. The Minister of Defence is the Chairman of the Council. The current Minister of DAC is Rajnath singh. It was formed, after the Group of Ministers recommendations on 'Reforming the National Security System', in 2001, post Kargil War (1999). The main objective of the DAC is to ensure expeditious procurement of the approved requirements of the Armed Forces in terms of capabilities sought, and time frame prescribed, by optimally utilizing the allocated budgetary resources.
Recently, the DAC entrusted capital procurement powers to Armed Forces. The decision was taken during the Special Meeting of the Defence Acquisition Council held under the chairmanship of Raksha Mantri Rajnath Singh. With this, the Armed Forces will now be able to progress urgent Capital Acquisition Cases upto Rs 300 crores to fulfil their emergent operational requirements.
The new powers to the Armed Forces will not only decrease the procurement timelines but will also ensure the placement of orders within 6 months and the delivery within one year. The decision has been taken after considering the security environment caused by prevailing situation along the Northern Borders.
Environment
Himalayan Viagara: It is the world’s costliest fungus. Its scientific name is Ophiocordyceps sinensis. It is known as Catterpillar Fungus in English. It is known as keeda jadi in Uttarakhand, Yartsagunbu (in Tibet) and Yarsagumba (in Nepal) because of its caterpillar-like appearance. It is an entomopathogenic fungus (a fungus that grows on insects) in the family Ophiocordycipitaceae. It is mainly found in the meadows above 3,500 meters (11,483 feet) in the Himalayan regions of Nepal, Bhutan, India, Myanmar and Tibet. In India, it is primarily found in Uttarakhand in the higher reaches of districts like Pithoragarh and Chamoli. It is also known as Himalayan Viagra, which sells in international markets for upwards of Rs 20 lakh per kg. It is used as a tonic and a therapeutic medicine in Tibet and China. In recent times, it has also been widely traded as an aphrodisiac.
Recently, this caterpillar fungus has entered the International Union for Conservation of Nature’s (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species.
Citing the reason for placing the fungus in the vulnerable category, IUCN said that its spread has declined by at least 30% over the past 15 years as a result of overharvesting.
Indian Policy
NABARD: It refers to the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development. NABARD is an apex development finance institution in India. It was founded on 12 July 1982. The bank has been entrusted with "matters concerning policy, planning, and operations in the field of credit for agriculture and other economic activities in rural areas in India". It is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. The current Chairman is G R Chintala.
Recently, NABARD celebrated its 39th Foundation day i.e., on the 13th of July. It organized its first digital conference named “digital choupal”. The video conference brought together farmers from across the country who have been associated with NABARD in 7 development projects in rural India viz. Rural Livelihoods Matter Immensely, Empowering Tribal Communities, Soil Health is Real Health, Direct Marketing to Urban Consumers, Climate Resilience, Climate Proofing of Koutuguda and Collectivisation of Weavers.
On this occasion, a refinance scheme for financial institutions and banks was launched. An amount of Rs 5,000 crores was allocated for the scheme.
Under the scheme, the Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS) are to be turned into multi-service centres. The fund allocated under the scheme is to be made available to financial institutions and banks to lend to the beneficiaries in 2,150 water shed development projects. The scheme will mainly focus on watershed development projects. These projects are spread over 2.3 million hectares of watershed, tribal development and rainfed areas.
NABARD has also launched the scheme to computerise PACS which will enable these ground-level entities to provide seamless credit services to their farmer members. Under this scheme, 5,000 PACS are to be upgraded in the initial phases, 15,000 by 2022 and another 15,000 by 2023.
MHRD: It refers to the Ministry of Human Resources and Development. The Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) was formerly known as the Ministry of Education. It was founded on 26 septenber 1985. It is headquartered in New Delhi, India. It is responsible for the development of human resources in India. The current Minister of MHRD is Ramesh Pokhriyal.
Recently, the Union HRD (Human Resource Development) Minister Ramesh Pokhriyal Nishank and Minister of State (MoS) for HRD Sanjay Dhotre jointly launched the first on-line NISHTHA programme for 1,200 Key Resources Persons of Andhra Pradesh.
NISHTHA Programme: It refers to a National Initiative for School Heads and Teachers Holistic Advancement programme. NISHTHA is organised at the elementary stage under Samagra Shiksha, a centrally sponsored flagship programme of Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD) to improve learning outcomes and holistic development of children.
It is a capacity building programme that was launched by the government of India on 21st August, 2019 to improve the quality of school education through Integrated Teacher Training. Following which 33 states and UTs have launched this programme in collaboration under Samagra Shiksha. In 29 States and UTs, the NISHTHA training programme has been completed by the NCERT at the state level.
Around 23 thousand Key Resource Persons and more than 17 lakh teachers and school heads have been covered under NISHTHA face to face mode till date. However, COVID-19 pandemic situation has affected the conduct of this programme in face-to-face mode. For providing training to remaining 24 lakh teachers and school heads, NISHTHA has been customized for online mode to be conducted through DIKSHA and NISHTHA portals by the NCERT.
Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying: The Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying is a newly formed ministry in India. It was formed in May 2019 by Modi government from the department of same name under Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare. The current Union Minister of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying is Giriraj Singh and the Minister of State for the same is Pratap Chandra Sarangi.
Recently, Union Minister of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying Minister Giriraj Singh launched the Implementation Guidelines for Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AHIDF) worth Rs. 15,000. It is a first type of scheme for private sector.
The scheme was approved by the Union Cabinet on 24.06.2020 under the Atma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyaan stimulus package for ensuring growth in several sectors.
AHIDF: It refers to the Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund. AIHDF was established as MSMEs and Private companies are to be promoted and incentivized for their involvement in processing and value addition infrastructure.
GoI has implemented several schemes for incentivizing the investment made by dairy cooperative sector for development of dairy infrastructure and AHIDF is a first-of-its-kind type of scheme for private sector.
Its main aim is to benefit millions of farmers by creating infrastructure and more milk will be processed. This will also increase export of dairy products which is presently negligible.
The eligible beneficiaries under the Scheme would be Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs), MSMEs, Section 8 Companies, Private Companies and individual entrepreneurs with minimum 10% margin money contribution by them. The balance 90% would be the loan component to be made available by scheduled banks.
Indian polity
The Supreme Court of India is the highest judicial forum and final court of appeal under the Constitution of India, the highest constitutional court, with the power of constitutional review. It consists of the Chief Justice of India and a maximum of 34 judges, it has extensive powers in the form of original, appellate and advisory jurisdictions. It is regarded as the most powerful public institution in India. It was established on 26 January 1950. It is headquartered in New Delhi. The current CJI of the Supreme Court is Sharad Arvind Bobde.
Recently, in a significant decision, the Supreme Court confirmed that persons suffering from disabilities are also socially backward and entitled to the same benefits of relaxation as Scheduled Caste/Scheduled Tribe candidates in public employment and education. A three-judge Bench led by Justice Rohinton Nariman upheld a 2012 judgment of the Delhi High Court in Anamol Bhandari (minor) through his father/Natural Guardian v. Delhi Technological University in a significant decision.
High Court’s judgment in Anamol Bhandari case of 2012 held that people suffering from disabilities are also socially backward, and are therefore, at the very least, entitled to the same benefits as given to the Scheduled Caste/ Scheduled Tribe candidates.
The present decision came on a petition filed by Aryan Raj, a special needs person, against a Punjab and Haryana High Court order. Raj was denied relaxation in minimum qualifying marks in the Painting and Applied Art course in the Government College of Arts, Chandigarh. The college insisted that disabled persons too need to meet the general qualifying standard of 40% in the aptitude test, whereas SC/ST candidates were given a relaxation to 35%.
International
Poland: Poland officially the Republic of Poland is a country located in Central Europe. It is bordered by Germany to the west, the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south, Lithuania, Belarus and Ukraine to the east and Russia and the Baltic Sea to the north. Poland's national emblem is a white eagle with a golden crown on a red background. The national flag is white and red. The Currency used in Poland is Polish złoty. Its capital is Warsaw.
Recently, Andrzej Duda, backed by the ruling conservative-nationalist Law and Justice party (PiS), was re-elected as the President of Poland. He won the presidential elections that was held in Poland. He won 51.21% of the votes, defeating the opposition candidate, liberal Warsaw Mayor Rafal Trzaskowski who got 48.79% votes.
Mr Duda, a 48-year-old devout Catholic, is only the second president in modern Poland to win re-election. His victory means that Law and Justice will maintain its grip on power until at least the 2023 parliamentary election.
He had won the Poland’s presidential election in year 2015, when he defeated the incumbent Bronislaw Komorowski.
Singapore: Singapore: Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is a sovereign island city-state in maritime Southeast Asia. This sovereign island nation is located just off the southern tip of Peninsular Malaysia in Southeast Asia bordering the Straits of Malacca to the west, the Riau Islands to the south, and the South China Sea to the east. Singapore has no capital. It is an island city state. The currency used here is Singapore dollar. The current Prime minister of Singapore is Lee Hsien Loong.
Recently, Lee Hsien Loong has been re-elected as the Prime Minister of Singapore after the ruling People’s Action Party (PAP) won the General Elections held in the country. In the elections held amidst the Covid-19 pandemic, PAP won 83 of the 93 seats contested in General Election. With this, Lee Hsien Loong has won a fourth term as the Prime Minister of Singapore. The People’s Action Party is the ruling party in Singapore since independence in 1965.
The General Elections held in Singapore are the only elections in South-East Asia, undertaken amid the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
Suriname: Suriname officially known as the Republic of Suriname is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America with Guyana to the west, French Guiana to the east, and Brazil to the south. It was once known as Dutch Guiana. It is one of South America's smallest countries and also is one of the most ethnically diverse countries in the Americas. Most of its people are descended from African slaves and Indian and Javanese indentured labourers brought over by the Dutch to work in agriculture. Most political parties are ethnically based. Since independence from the Netherlands in 1975 Suriname has endured coups and a civil war. The currency used here is Suriname Dollar. The capital of Suriname is Paramaribo.
Recenlty, an Indian-origin, Chandrikapersad ‘Chan’ Santokhi was elected the president of Suriname. A former Justice Minister, Santokhi of the Progressive Reform Party (PRP) was elected unopposed. He will succeed Desi Bouterse, a former military strongman, whose National Party of Suriname (NPS) lost the election in May as he sent the country to an economic precipice.
Chandrikapersad Santokhi: Chandrikapersad Santokhi was trained in a police academy in the Netherlands. He rose to be the chief police commissioner of Suriname. He later served as the justice minister in an earlier administration in 2005.
Gabon: Gabon officially the Gabonese Republic (French: République gabonaise), is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. It shares borders with Cameroon to the north, the Republic of the Congo to the east and south, and Equatorial Guinea to the northwest. To the west is the Gulf of Guinea. The currency used here is Central African CFA franc and Libreville is its capital.
There have been three presidents since the country’s independence from France on August 17, 1960. Gabon introduced a new constitution in the early 1990s with a more transparent multi-party system. Gabon’s small population and natural resources has made it one of the regions most prosperous countries.
Recently, Rose Christiane Ossouka Raponda has been appointed as the first woman prime minister of Gabon. She is the 12th PM of the country and succeeds Julien Nkoghe Bekale.
Prior to becoming appointed as the Prime Minister, she served as Defence Minister since February 2019. Her appointment is the fourth cabinet reshuffle by the President of Gabon, Ali Bongo Ondimba since January 2019.
HLPF: It refers to the United Nations High-level Political Forum. The HLPF is the foremost international platform for follow-up and review of progress on the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). HLPF meets every year in July for 8 days under the auspices of the Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) of the UN.
Recently, India's second Voluntary National Review (VNR) was presented at the HLFP on Sustainable Development, 2020 by NITI Aayog. HLPF 2020, was hosted virtually amid the COVID-19. The title of India’s 2nd Voluntary National Review is “Decade of Action: Taking SDGs from Global to Local”. The presentation also included a short film which encapsulated the processual aspects of the second VNR and captured some of India’s major progress areas on the SDGs.
The 2nd VNR report highlighted the features and responses of India under the Aatma Nirbhar Bharat Campaign that will help in accelerating progress on the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The first VNR of India was prepared and presented by NITI Aayog in 2017.
The VNRs presented by the Member States at the HLPF are a critical component of the review of progress and implementation of the 2030 Agenda and the SDGs. The reviews are voluntary and state-led and are aimed at facilitating the sharing of experiences, including successes, challenges and lessons learned.
NITI Aayog has the mandate of overseeing the adoption and monitoring of SDGs at the national and sub-national level.
VNRs: It refers to Voluntary National Review reports. VNRs are reports that the member countries are required to present to HELP about the review of the implementation and progress of SDGs. Its main purpose is to present a report of where the country stands in SDG implementation, with a view to help accelerate progress through experience sharing, peer-learning, identifying gaps and good practices, and mobilizing partnerships. In 2020, 51 countries signed up to conduct a VNR review.
APTTA: It refers to the Afganistan–Pakistan Transit Trade Agreement. APTTA is a bilateral trade agreement signed in 2010 by Pakistan and Afghanistan that calls for greater facilitation in the movement of goods amongst the two countries.
Recently, Pakistan decided to allow Afghanistan to send goods to India via the Wagah border from July 15. The decision is a part of Islamabad’s commitment under the Pakistan-Afghanistan Transit Trade Agreement. It is expected to boost Afghanistan’s exports to India.
The 2010 APTTA allows both the countries to use each other's airports, railways, roads, and ports for transit trade along designated transit corridors. The 2010 agreement supersedes the 1965 Afghanistan Transit Trade Agreement, which granted Afghanistan the right to import duty-free goods through Pakistani seaports.
WYSD: It refers to the World Youth Skills Day. WSYD is observed on the 15th of July every year globally. The United Nations, at its General Assembly in November 2014, declared 15 July as World Youth Skills Day. This day is observed with an aim to raise awareness about the importance of technical, vocational education training and the development of other skills relevant to both local and global economies. The World Youth Skills Day is an opportunity for technical and vocational education and training (TVET) institutions to acknowledge the importance of equipping young people with skills for employment.
Recently, World Youth Skills Day 2020 was held on July 15. The theme this year was “Skills for a Resilient Youth in the Era of COVID-19 and Beyond”.
This year World Youth Skills Day took place in a challenging context due to COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown measures that have led to the worldwide closure of technical and vocational training education and training (TVET) institutions, alarming the vitality of skills development.
In India, the Skill India Mission was launched 5 years ago on this day. This year marked the 5th anniversary of the launch of Skill India Mission. On this occasion a digital conclave to mark the occasion was organized by the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship.
National
CAPF: It is an acronym for the Central Armed Police Forces. CAPF refers to uniform nomenclature of security forces in India under the authority of Ministry of Home Affairs. Their role is to defend the national interest mainly against the internal threats. They are the Border Security Force (BSF), Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), Central Industrial Security Force (CISF), Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP) and National Security Guard (NSG) and Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB). The CAPF forces battle terrorists, insurgents and naxalites and even play a role in the smooth conduct of elections. CAPF which are tasked with doing the job of both the army and the police in guarding the borders as well as battling terrorists and insurgents are 365 days swinging Machine. The current Minister responsible for CAPF is Union Home Minister Amit Shah.
Recently, Union Home Minister, Amit Shah launched the Central Armed Police Force’s (CAPFs) nationwide tree plantation drive by planting a sapling of the peepal tree at the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) campus in Gurugram.
Under this drive, saplings have been planted by the jawans of the CAPF in Chhattisgarh. The personnel of CRPF, BSF, CISF, and ITBP who have been deployed in Chhattisgarh for anti-Naxals operations, have been planting saplings in their respective campuses.
All the CAPFs will undertake a drive in their respective organisations to achieve the collective target of planting more than 1.35 crore saplings by this month.
The tree plantation drive is a CAPF’s initiative towards Green India. The planting of saplings by paramilitary forces are also contributing their role in preserving and promoting the environment as well as to check the pollution and save the Earth.
IEMF: It refers to the India Energy Modeling Forum. IEMF was recently launched in the joint working group meeting of the Sustainable Growth Pillar (SG Pillar) of the India-US partnership. The activities of the forum and finalization of its governing structure is to be initially coordinated by NITI Aayog. The forum would include knowledge partners, data agencies and concerned government ministries.
The IEMF seeks to provide a platform for policy makers to study important energy and environmental issues and ensure induction of modeling and analysis in informed decision making process. The Forum aims to improve cooperation and coordination between modeling teams.
IEMF has been created in India as there was no formalized and systematic process of having a modeling forum.
Sustainable Growth Pillar: It is an important pillar of India–US Strategic Energy Partnership co-chaired by NITI Aayog and USAID. The SG pillar entails energy data management, energy modelling and collaboration on low carbon technologies as three key activities.
EMF: It refers to the Energy Modeling Forum. The EMF in USA was established in 1976 at Stanford University to connect leading modeling experts and decision makers from government, industry, universities, and other research organizations. The forum provides an unbiased platform to discuss the contemporary issues revolving around energy and environment.
15th India-EU Summit: The 15th Summit between India and the European Union was recently held in virtual format. India was represented by Prime Minister Narendra Modi. The EU was represented by President of the European Council and President of the European Commission.
On the back of the coronavirus-led economic crisis, the leaders in the India-EU summit discussed the global cooperation and solidarity to protect lives, in order to mitigate the socio-economic risks.
During the summit, the leaders adopted the “India-EU Strategic Partnership: A Roadmap to 2025” to guide cooperation between India and the EU over the next 5 years.
They welcomed, the signing of the India-EURATOM Agreement on research and development cooperation in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy, the upcoming renewal of the India-EU Science and Technology Agreement for another five years and also the ongoing activity in India of the European Investment Bank and the upcoming planned investments of Euros 550 million in the Pune and Bhopal Metro Rail Projects.
They also adopted a Joint Declaration on Resource Efficiency and Circular Economy.
People In News
Rudrendra Tandon: He is an Indian Foreign Service officer who is currently serving as Indian envoy to ASEAN at Jakarta. He has recently been appointed as the next Ambassador of India to Afghanistan. He has served in Indian missions in Paris, Algiers, Kabul and Moscow. He had also served as India’s Consul General in Jalalabad in Afghanistan.
He will be replacing Vinay Kumar who performed admirably with the withdrawal of US forces from Afghanistan after striking a deal with Taliban insurgents.
The government's decision to appoint Tandon as India's ambassador to Afghanistan comes at a time when the long-pending peace and reconciliation process in the war-ravaged country is gaining momentum.
Afganistan: Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country in Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the east and south; Iran to the west; Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan to the north; and China to the northeast. Its Capital is Kabul and the currency used here is Afghan afghani. The President of Afganistan is Ashraf Ghani.
Vikram Doraiswami: He is a 1992 batch Indian Foreign Service officer who is currently serving as additional secretary in-charge of international organisations and summits at the headquarters of the external affairs ministry in Delhi. He has recently been appointed as the next Ambassador of India to Bangladesh. He will succeed Riva Ganguly Das in Dhaka.
Bangladesh: It is a country which is bordered by the Indian states of West Bengal to the west and north, Assam to the north, Meghalaya to the north and northeast, and Tripura and Mizoram to the east. To the southeast, it shares a boundary with Myanmar (Burma). The southern part of Bangladesh opens into the Bay of Bengal. Its Capital is Dhaka. The currency used her is Bangladeshi Taka. The Prime Minister of Bangladesh is Sheikh Hasina.
Vidhu P Nair: He a 2002-batch IFS officer, is presently serving as director in the ministry. He has recently been appointed as the next ambassador of India to Turkmenistan by the Government.
The government has also appointed Hemant Harishchandra Kotalwar, a 1996-batch IFS officer, as India's next envoy to the Czech Republic.
Turkmenistan: Turkmenistan also known as Turkmenia, is a sovereign country in Central Asia. It is bordered by the Caspian Sea and largely covered by the Karakum Desert. Its Capital is Ashgabat and its official language is Turkmen. The currency used here is Turkmenistan manat. The current President of Turkmenistan is Gurbanguly Berdimuhamedow.
Czech Republic: The Czech Republic is a landlocked country in Central Europe bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast and Slovakia to the southeast. Along with Slovakia, the Czech Republic was established when Czechoslovakia broke in two in 1993. It comprises the historical provinces of Bohemia and Moravia along with the southern tip of Silesia, collectively often called the Czech Lands. In 2016 the country adopted the name “Czechia” as a shortened, informal name for the Czech Republic. The Capital of Czechia is Prague. The currency used here is Czech Koruna. The current president is Miloš Zeman.
Madeline Swegle: She is the "first known Black female Tactical Aircraft (TACAIR) pilot" in the U.S. Navy's 110 history of aviation.
The US Navy recently announced that Lt. j.g. Madeline Swegle had completed naval flight school and would later this month receive the flight officer insignia known as the "Wings of Gold."
Swegle's milestone comes more than 45 years after Rosemary Mariner in 1974 became the first woman to fly a tactical fighter jet in the Navy.
Bhanu Bhakta: Bhanubhakta Acharya was a Nepali poet, translator and writer. He was the first writer to translate the great epic Ramayana from Sanskrit to Nepali breaking the Brahmin hegemony of having only Sanskrit, thus besides having many contemporary great poets in the country during his times Bhanubhakta is honoured with the title of Adikavi of Nepal. He has made great contributions in the field of poetry and Khas literature. His birthday is celebrated every year on the 13th of July as Bhanu Jayanti (Asar 29). Literary festivals are organized to honour him through programs of recitations, art, academic and poetic importance.
Recently, the 206th Birth Anniversary of Bhanubhakta Acharya was celebrated in Sikkim. Bhanu Jayanti is also celebrated across the state of Nepal on 13th July every year.
Ved Parkash Dudeja: He is the vice chairman of Rail Land Development Authority (RLDA). He has recently been awarded with the coveted ‘Infra Business Leader of the Year’ award for 2020.
He was conferred this award by the Rail Infra and Mobility Business Digital Awards (RIMBDA) for his contribution towards the infrastructure development. Under his leadership, RLDA has launched various commercial projects, multifunctional complex, colony redevelopment and station redevelopment projects.
RLDA: It refers to the Rail Land Development Authority. RLDA is a statutory authority under the Ministry of Railways. The statutory body is responsible for the development of vacant railway land for commercial use in order to generate revenue with the help of non-tariff measures and creating assets for Indian Railways.
Sachin Awasthi: He has recently been honoured with the “Top Publicist” award in the Global Humanitarian Awards 2020, through webinar took place in London.
He organised a 5-day long clean Ganga awareness journey which was begun from Haridwar to Varanasi. It is called as Vande Gange Swachhata Jan Jagran Yatra.
Global Humanitarian Award: The Global Humanitarian Award is known as a part of the honouring the honourable initiative of the World Humanitarian Drive(WHD). The main aim of this award is to honour the popular men and women who are paying contributions to the betterment of society and the world.
WHD: It is an acronym for the World Humanitarian Drive. The founder & chairman of WHD is Abdul Basit Syed. It is headquartered in London, United Kingdom.
Places In News
Chhattisgarh: Chhattisgarh is a heavily forested state in central India. It is one of the fastest-developing states in India. The state was formed on 1st November 2000 by partitioning ten Chhattisgarhi and six Gondi-speaking southeastern districts of Madhya Pradesh. The capital city of Chattisgarh is Raipur. The current Chief Minister and Governor of Chhattisgarh are Bhupesh Baghel and Anusuiya Uikey respectively.
Recently, the Chhattisgarh government organised e-Lok Adalat amid the COVID-19 pandemic. It is the first e-Lok Adalat of India. The “e-Lok Adalat” was organized by the High Court and Chhattisgarh State Legal Services Authority and was inaugurated by P R Ramchandra Menon, the Chief Justice of Chhattisgarh High Court. The virtual hearings were conducted through video conferencing along with its live streaming.
It was organized in order to bring relief to people and to reduce the pendency of cases amid the COVID-19 pandemic. During the “e-Lok Adalat”, more than 3,000 cases were heard in around 200 benches of 23 districts across the state.
STRR: It refers to the Satellite Town Ring Road between Tamil Nadu and Karnataka. The Expert Appraisal Committee of the Environment Ministry recently recommended the grant of Environmental Clearance for the development of an economic corridor which is the Satellite Town Ring Road (STRR).
The greenfield highway is part of Bharatmala Pariyojna and will be implemented by the National Highways Authority of India. The project will start in Dabaspet in Karnataka and end near Devarapalli village on the Tamil Nadu-Karnataka border. The new road seeks tp provide better, fast, safe and smooth connectivity for commuters between the two States as well as in the region.
Bharatmala Pariyojana: Bharatmala Pariyojana is a centrally-sponsored and funded Road and Highways project of the Government of India (GoI). It is a new umbrella program for the highways sector that focuses on optimizing efficiency of freight and passenger movement across the country by bridging critical infrastructure gaps through effective interventions like development of Economic Corridors, Inter Corridors and Feeder Routes, National Corridor Efficiency Improvement, Border and International connectivity roads, Coastal and Port connectivity roads and Green-field expressways. This mammoth scheme was announced by the Minister of Road Transport and Highways Shri Nitin Gadkari, in the presence of the Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi. It was established on 31 July 2015. All key aspects of the scheme is managed by the Road Transport and Highways Ministry of the country.
Science and Technology
TRAIL: It refers to the TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology-Madras have recently shown that the active compound from the common household spice turmeric — curcumin — can enhance cancer cell death.
TRAIL is an agent with the ability to programme cell death (apoptosis) and has triggered many preclinical studies the world over.
Curcumin was chosen by the IIT-M research team as it is known to inhibit carcinogenesis and induce apoptosis in various cancer cells.
The researchers isolated leukaemia cells from cancer patients and found that non-toxic concentrations of curcumin can significantly increase the efficiency of TRAIL-induced cell death.
SHUDH: It is the name of an Ultraviolet (UV) sanitizing device named Smartphone operated Handy Ultraviolet Disinfection Helper. Shudh has been developed by IIT Kanpur.
SHUDH device has aix UV lights of fifteen Watts each that can be individually monitored from a distance. The device at its full operation can disinfect a 10x10 squared feet room in about 15 minutes.
It can assist in killing the spread of coronavirus at the highly prone places such as hospitals, hotels, malls, offices and schools. The on and off, speed, and location of the product can be controlled remotely using your available smartphone while installing an android application.
APSTAR-6D: It is a telecommunication satellite recently launched successfully by China. It was launched via a Long March 3B carrier rocket from Xichang Satellite Launch Center.
This commercial satellite ‘APSTAR-6D’ has been developed by China Academy of Space Technology Corp.(CASC). APSTAR-6D marked the 18th Rocket Launched by China in the year 2020. The satellite was purchased by APT Mobile SatCom Limited in 2016.
The satellite aims to provide high-speed communications with a capacity of almost 50 gigabytes/sec. APSTAR-6D is a part of Chin’s First Global High-Throughput Broadband Satellite Communication System. It is expected to last about 15 years in space in geostationary orbit, as part of a broadband satellite communications system serving the Asia-Pacific region.
CASC: It refers to the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corp. CASC is a subsidiary of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corp. It is headquartered Beijing, China. The current President of China Aerospace Science and Technology Corp is Xu Qiang.
DCGI: It refers to the Drug Controller General of India. DGGI has recently given its approval to the first fully indigenously developed Pneumococcal Polysaccharide Conjugate Vaccine. The vaccine has been developed by Serum Institute of India, Pune. This is the first indigenously developed vaccine in the field of pneumonia.
This vaccine is used for active immunization against invasive disease and pneumonia caused by “Streptococcus pneumonia” in infants. It is administered in an intramuscular manner.
Streptococcus pneumonia: Streptococcus pneumonia (pneumococcus) is a Gram-positive bacterium that is responsible for the majority of community-acquired pneumonia. It is a commensal organism in the human respiratory tract which means that it benefits from the human body, without harming it. However, infection by pneumococcus may be dangerous, causing not only pneumonia, but also bronchitis, otitis media, septicemia, and meningitis.
COROSURE: It is the world’s most affordable COVID-19 test Kit which has recently been launched by the Union Human Resource Development (HRD) Minister Ramesh Pokhriyal.
COROSURE kit has been developed by IIT Delhi. It will be now available for use by the authorized testing labs. This launch will significantly bring down the cost of COVID-19 RT-PCR testing.
The base price of the RT-PCR assay is Rs 399. Even after adding the RNA isolation and laboratory charges, the cost per test will be considerably cheaper compared to currently available kits in the market.
5G: 5G or the fifth generation is the latest upgrade in the long term evolution (LTE) mobile broadband networks. All 5G networks chiefly operate on three spectrum bands. They are:-
1. The low-band spectrum has been proven to have great coverage but the maximum speed limit on this band is 100 Mbps (Megabits per second).
2. In the mid-band spectrum, though the speeds are higher, but has limitations related to coverage area and penetration of telephone signals into buildings.
3. The high-band spectrum offers the highest speed but has extremely limited network coverage area and penetration capabilities.
Recently, Reliance Industries CMD Mukesh Ambani announced that the company’s telecom venture Jio has designed and developed from scratch, a complete indigenous 5G solution ready for deployment. This will enable Jio to export 5G solutions to other telecom players globally.
The benefit of 5G networks is that it will have even faster speeds with latency down to between 1-10 milliseconds.
Latency is the time a device takes to communicate with the network, which stands at an average of up to 50 milliseconds for 4G networks across the world.
It uses beam tracking to follow all devices on the network to ensure consistent connection in real-time for the device.
5G networks are also designed to multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) efficient which improves signal throughput for all devices on the network.
Sports
Mohun Bagan Ratna: Mohun Bagan Ratna is an award presented each year on Mohun Bagan Day to outstanding former players. The first recipient was former captain Sailen Manna.
Recently, ATK-Mohun Bagan club announced that Hockey legend Gurbux Singh and former first-class cricketer Palash Nandi will receive this year’s Mohun Bagan Ratna. The club has decided not to hold the customary ‘Mohun Bagan Day’ function on July 29 this year due to the ongoing pandemic. July 29 was the date of Bagan’s IFA Shield triumph in 1911 when they defeated East Yorkshire Regiment 2-1.
The other recepients are:
Lifetime Achievement Award will be awarded to Ashok Kumar, a member of India’s 1975 World Cup-winning hockey team along with Pranab Ganguly (football) and Monoranjan Porel (athletics).
Best footballer (senior) prize to Joseba Beitia.
Best youth player to Sajal Bag (U-18).
Mohun Bagan Athletic Club: Mohun Bagan Athletic Club, commonly known as Mohun Bagan, is a major Indian multi-sport club based in the Kolkata, India. Founded 15 August 1889, is an Indian sports club best known for its association football team, one of the oldest football clubs in Asia. Mohun Bagan was established by three famous aristocratic Bengali families of North Kolkata. Bhupendra Nath Bose was the first president of the club. In 1911, Mohun Bagan created history by becoming the first Indian club to win the IFA Shield after defeating East Yorkshire Regiment 2–1 on 29 July. This win was considered a landmark victory in the Indian freedom struggle.
They have won the top-flight league a record 5 times, the National Football League three times and the I-League twice. They are the most successful team of India in the history of the Federation Cup, having won the championship a record 14 times. The club has also won several other trophies, including the Durand Cup (16 times), IFA Shield (22 times), and the Calcutta Football League (30 times). In total, the club has won 253 trophies. The club contests the Kolkata Derby with long-time rivals East Bengal.
BCCI: It is an acronym of the Board of Control for Cricket in India. BCCI is the national governing body for cricket in India. The board was formed in December 1928 as a society, registered under the Tamil Nadu Societies Registration Act. Its headquarters are in Wankhede Stadium, Mumbai. Grant Govan was its first president and Anthony De Mello its first secretary. The current President of BCCI is Sourav Ganguly.
Recently, Hemang Amin has been appointed by BCCI as its interim chief executive officer (CEO). He will replace Rahul Johri who recently resigned as the chief executive officer (CEO) of BCCI and his resignation was accepted by the BCCI office-bearers.
Hemang Amin is the Chief Operating Officer (COO) of the Indian Premier League. He joined the IPL operations team in June 2010 and was appointed as the COO of IPL in 2015.
FIFA: It is an acronym for International Federation of Association Football. FIFA is a non-profit organization and the highest governing body of Football. It was founded on 21 May 1904. It is headquartered in Zurich, Switzerland. The current President of FIFA is Gianni Infantino.
Recently, the Federation Internationale de Football Association announced that the 2022 World Cup is to be held in Qatar. The schedule of matches was also released by the governing body. The matches will take place between November 21 and December 18 in 2022. The final match of the tournament has been scheduled on December 18, 2020, which is also Qatar National Day.
The 2022 FIFA World Cup will be the first world cup to be held in Arab World and also the first in a muslim-majority country.
La Liga Champion: Real Madrid was recently crowned La Liga champions for the 34th time after Karim Benzema scored twice in a 2-1 victory over Villarreal which clinched the title with one game to spare. Barcelona lost to 10-man Osasuna at the Camp Nou Stadium.
A total of 62 teams have competed in La Liga since its inception. Nine teams have been crowned champions, with Real Madrid winning the title a record 34 times and FC Barcelona 26 times. During the 1940s, Valencia, Atlético Madrid and Barcelona emerged as the strongest clubs winning several titles.
Arts
Museum on Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose: The Government of India (GoI) has recently announced that a museum on Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose is set on 23 January 2022. The museum will be established in Kolkata. The museum will be inaugurated on the 125th birth anniversary of Netaji.
The Central Government is also planning to reprint some of the books written by Netaji Bose. The Netaji museum in New Delhi is also to be expanded.
About New Delhi Museum:
The museums in New Delhi are digital and are distributed over three floors.It depicts the contributions of the legend since his childhood.
The museum has also documented the role of Indian National Army (INA), battles fought, awakening it created and its popularity in India. It highlights the role of the people of Indian origin, especially in South East Asia and their contributions to the INA.
It also depicts the secret operation of Col Amrik Singh Gill and 4 others who landed by submarine at Konark temple to establish their Indian National Army (INA) secret centres in India.
The museum has been established in Red Fort as it is from this place; the soldiers of the INA were court martialled by the British Government. All the four barracks of the Red Fort have been converted into museums.
Apart from the museum on Subhash Chandra Bose, 3 more museums will be established. They will be on Jallianwala Bagh Massacre (1857) revolt and contemporary paintings.
INA: It refers to the Indian National Army. INA was established in 1942 by the Indian National Party and the Japanese Empire. The main aim of the INA was to secure Indian independence from the Britishers. It was originally formed by Mohan Singh. He was later captured and eventually the first INA collapsed. Later it was revived under the leadership of Netaji.
Management of Red Fort: The Red Fort is managed by the Bureau of Archaeological Survey of India (ASI). The ASI is responsible for the protection of Indian cultural properties and national heritage sites.
ASI: The ASI is an Indian government agency attached to the Ministry of Culture that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural monuments in the country. ASI was founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham- the first Director-General of ASI. Alexander Cunningham is also known as the “Father of Indian Archaeology”. It administers more than 3650 ancient monuments, archaeological sites and remains of national importance. Its activities include carrying out surveys of antiquarian remains, exploration and excavation of archaeological sites, conservation and maintenance of protected monuments etc.
Yours Truly Margazhi: It is the name of the festival that Vice President M. Venkaiah Naidu virtually inaugurated in Chennai from Hyderabad recently.
‘Yours Truly Margazhi’ festival is an initiative to uphold Chennai’s famed tradition of the December dance and music festival. The event witnessed the participation for around 500 artists from across 100 events.
The Vice President, at the event, called upon the practitioners, patrons, and organizers to showcase the Indian culture, thought, and way of life. He said that through the dance and music, ideals like non-violence, peace, and harmony around the world, in line with India`s philosophy of `Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam," can be spread.
Losar: Losar is a festival in Tibetan Buddhism. The holiday is celebrated on various dates depending on location. The Losar Festival is celebrated in India in the north-eastern region. Places like Nepal, Tibet, Sikkim, and Bhutan are major contributors of this Losar Festival. Losar customs in Bhutan are similar to, but distinct from, customs in neighbouring Tibet. Losar is celebrated on the first day of the lunisolar Tibetan calendar, which corresponds to a date in February or March in the Gregorian calendar.
The festival came into existence much before Buddhism was celebrated as a gesture of thanks to the Gods. Initially celebrated mostly among farmers, Losar went on to become a predominantly Buddhist festival celebrating the commencement of the New Year.
Losar is mainly celebrated for 15 days, with important celebrations on the first three days. The festival mostly starts with the commemoration of eight symbols like the parasol, conch shell, vase, and victory banner.
The first day of the festival begins with cleaning the house and preparing special Tibetan dishes. On the second day, many religious ceremonies take place in various monasteries. The firecrackers keep the evil spirits away. The third day of the festival is the New Year's Day where people wear new clothes, visit monasteries to be a part of this cultural festival.
The families organize a reunion dinner which includes a special kind of cake which is known as 'kapse'. Along with this, an alcoholic drink is also a part of this dinner which is known as 'Chang'.
In 2020, the New Year commenced on the 24th of February and celebrations ran until the 26th of the same month. It also commenced the Year of the Male Iron Rat.
Recently, People in Ladakh region are celebrating Ladakhi New Year, Losar from the 15th of December this year.
Symbolic Losar celebrations and special prayers are held at Chokanga Vihara in Leh where Traditional Flag ‘Tarchen’ was hoisted to mark the beginning of New Year.
Ladakh Buddhist Association’s Youth Wing and Ladakh Autonomous Hill Development Council (LADHC), Leh jointly organized symbolic events at Chokanga Vihara.
Note: Jamyang Tsering Namgyal is the youngest and 8th consecutive Chief Executive Councillor of LAHDC, Leh.
Economics
India Workplace Equality Index (IWEI): It is the name of India's own workplace equality Index launched by the Government of India for the first time. India Workplace Equality Index (IWEI) has been launched virtually by the Keshav Suri Foundation (KSF), Pride Circle and FICCI (Federation for Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry).
It is the country’s first comprehensive benchmarking tool for employers to measure their progress on LGBT+ (Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Trans +) inclusion at the workplace in the Indian corporate world.
IWEI also identifies the employers who have successfully upheld the rights of LGBT+ in their organizations. In its first report it virtually announced winners from among 65 companies which shared data on their diversity and inclusion practices.
The IWEI measures nine areas namely policies and benefits, employee lifecycle, employee network group, allies and role models, senior leadership, monitoring, procurement, community engagement and additional work.
The IWEI comes two years after the Supreme Court’s landmark reading down of Section 377. It has been inspired from the WEI by Stonewall, UK which is in use since 15 years in Britain.
Section 377 of the IPC: Section 377 of the Indian Penal Code is a section of the Indian Penal Code introduced in 1861 during the British rule of India. Modelled on the Buggery Act of 1533, it makes sexual activities "against the order of nature" illegal.
Two years back, on 6 September 2018, the Supreme Court of India (SCI) ruled that the application of Section 377 to consensual homosexual sex between adults was unconstitutional, "irrational, indefensible and manifestly arbitrary".
However, section 377 remains in force with respect to sex with minors, non-consensual sexual acts, and bestiality.
DakPay: It is a new digital payment app named DaKPay. The Department of Posts and India Post Payments Bank (IPPB) recently unveiled DakPay to provide Digital Financial inclusion PAN-India.
DakPay is a suite of digital payment apps and assisted banking services provided by India Post and IPPB.
DakPay UPI app allows users to create UPI ID and link multiple accounts across banks in a single mobile app. The app facilitates instant money transfers, QR based payments in merchant stores and online shopping on e-commerce websites.
RBI: It refers to the Reserve Bank of India. The RBI is India's central bank, which controls the issue and supply of the Indian rupee. It carries out India's monetary policy and exercises supervision and control over banks and non-banking finance companies in India. RBI was set up in 1935 under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. It is headquartered in Mumbai. RBI plays an important part in the Development Strategy of the Government of India. The current Governor of RBI is Shaktikanta Das.
Recently, the RBI approved the re-appointment of Uday Kotak as Managing Director of Kotak Mahindra Bank for a further period of three years, with effect from January 1, 2021. Kotak is founder managing director and promoter of the bank.
RBI has also approved the appointment of part-time chairman Prakash Apte and Dipak Gupta as Joint MD of the bank for a period of three years.
Kotak Mahindra Bank: Kotak Mahindra Bank Limited is an Indian private sector bank established in 2003 by Uday Kotak. The bank is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. The tagline for Kotak Mahindra Bank Tagline is "Let’s make money simple." the current Ceo of this bank is Uday Kotak.
Defence
Vijay Diwas: India celebrates Vijay Diwas on the 16th of December every year to commemorate its victory over Pakistan during the 1971 war.
The year 2021 marks 50 years of India’s victory over Pakistan in the 1971 war and India has planned to celebrate the 50th anniversary of its victory as Golden victory your, that is, Swarnim Vijay Varsh.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi lit up the Swarnim Vijay Mashaal on the occassion of Vijay Divas to kickstart the 50th anniversary celebrations, Swarnim Vijay Varsh. It was lit up from the Eternal Flame at the National War Memorial in New Delhi.
Four victory flaming torches will be carried to various parts of India. This includes the villages of Param Vir Chakra and Mahavir Chakra awardees of 1971 war. The soil from the major areas where the 1971 war was fought and from the villages of the awardees of 1971 war are also to be brought to National war Memorial.
A wreath-laying ceremony was also held at Vijay Smarak at Fort William the Head Quarters of Eastern Command in Kolkata, West Bengal. A delegation of Mukti Joddhas from Bangladesh and Indian war veterans also took part in the celebrations. The day is also a remembrance of the brave soldiers of India and Mukti Joddhas from Bangladesh who sacrificed their lives for a noble cause.
National war Memorial: It is an Indian National monument built to honour the soldiers of Indian armed forces who sacrificed their lives in armed conflicts of independent India. The walls of the memorial carry names of armed forces personnel who sacrificed their lives in conflict with China and Pakistan and as well as in the 1961 war in Goa, Operation Rakshak, Operation Pawan. Their names are inscribed in Golden letters.
The monument which is spread over 40 acres of land was built by Government of India (GoI) near India Gate. The construction of the memorial was completed in 2019.
The eternal flame at the national war Memorial is called “Amar Jawan Jyoti” which means Flames of eternal soldiers.
History: In December 1971, the Indian Armed Forces secured a decisive and historic Victory over Pakistan Army, which led to creation of a Nation- Bangladesh and also resulted in the largest Military Surrender after the World War-II. The chief of the Pakistani forces, General AA Khan Niazi, along with 93 thousand troops, surrendered to the allied forces consisting of the Indian Army and Mukti Bahini. The war culminated with the subsequent secession of East Pakistan into Bangladesh.
S-400 Air Defence Missile System: The United States (US) recently imposed sanctions on Turkey over Ankara’s acquisition of Russian S-400 air defence systems.
According to US, the acquisition of the weapons will ‘risk’ NATO’s security.
The S-400 Triumf, (NATO calls it SA-21 Growler), is a mobile, surface-to-air missile system (SAM) designed by Russia. It is the most dangerous operationally deployed modern long-range SAM (MLR SAM) in the world, considered much ahead of the US-developed Terminal High Altitude Area Defense system (THAAD).
The system has the capacity to engage all types of aerial targets including aircraft, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV and ballistic and cruise missiles within the range of 400km, at an altitude of up to 30km. The system can track 100 airborne targets and engage six of them simultaneously.
The S-400 Triumf air defence system integrates multifunction radar, autonomous detection and targeting systems, anti-aircraft missile systems, launchers, and command and control centre.
It is capable of firing three types of missiles to create a layered defence.
Note: India is set to get the consignment of the S-400 air defence system early next year as it's acqisition is crucial to counter attacks in a two-front war, including even high-end F-35 US fighter aircraft. From India’s point of view, China is also buying the system. In 2015, Beijing signed an agreement with Russia to purchase six battalions of the system. Its delivery began in January 2018.
India has got a waiver from the outgoing Trump administration but hopes that the incoming Biden administration would not work towards reversing the decision.
ICG: It refers to Indian Coast Guard. ICG is an armed force that protects India's maritime interests and enforces maritime law, with jurisdiction over the territorial waters of India, including its contiguous zone and exclusive economic zone. IGC was founded in 18 August 1978 by the Coast Guard Act, 1978 of Parliament of India an independent Armed force of India. The moto of IGC is Vayam “Vayam Rakshamah” meaning “We Protect”. The Coast Guard works in close cooperation with the Indian Navy, the Department of Fisheries, the Department of Revenue (Customs) and the Central and State police forces. The Director General of IGC is Krishnaswamy Natrajan, PTM, TM, and Additional Director General is Krupa Ram Nautiyal, PTM, TM.
Recently, the Indian Coast Guard Interceptor Boat got commissioned at Hazira in Gujarat. It was commissioned by Surat Police Commissioner Ajay Tomar.
The Interceptor boat has been built indigenously by M/s L&T Jetty, Hazira. It is capable of a high speed of 45 knots having capability to operate in shallow waters.
The Vessel is fitted with latest state-of-the-art navigation and communication equipment designed for high speed interception, close coast patrol, low intensity maritime operations, Search and Rescue and maritime surveillance.
Furthermore, It will also augment patrolling and prevent illicit activities such as infiltration, smuggling and illegal fishing activities along the international maritime borders.
This Interceptor Boat will operate from Gujarat under the control of the Commander Coast Guard Region North-West of the Indian Coast Guard.
Offshore Patrol Vessel (OPV) ‘Sujeet’: The Offshore Patrol Vessel (OPV) ‘Sujeet’, of the Indian Coast Guard (ICG) was commissioned at the Goa Shipyard Limited (GSL) in Vasco Town, Goa by Raj Kumar, Secretary (Defence Production).
Sujeet is second in the series of 5 OPVs. The vessel has been designed and built indigenously by GSL.
The 1st ship in series – ICGS (ICG Ship) Sachet was commissioned by Union Defence Minister Rajnath Singh in May 2020 in the presence of K Natarajan, Director General of Indian Coast Guard and others.
About: Sujeet is equipped with features like Integrated Bridge System, Integrated platform management system, power management system and high power external fire-fighting.
It is capable of carrying 1 twin-engine helicopter, 4 high-speed boats, 2 inflatable boats for boarding operations, search and rescue, law enforcement and maritime patrol.
The ship will be 105 metres long and weigh 2400 tonnes.
The ship will be based at Goa and will be deployed extensively for EEZ (Exclusive Economic Zone) surveillance and other duties.
AS per the statement by ICG, at present, it has 155 ships and 62 Aircraft at its disposal with 35 more ships in various stages of construction at shipyards across India.
Himgiri: Himgiri is the name of Indian Navy's second Project 17A Frigate. It was launched on December 14, 2020 at the Garden Reach Shipbuilders and Engineers Limited (GRSE) in Kolkata. Himgiri made her first contact with the waters of Hoogly River on 14th December 2020.
P17A ships have been indigenously designed by Directorate of Naval Design (Surface Ship Design Group) – DND (SSG). The ships are being built at indigenous yards namely MDL and GRSE.
The Indian Naval Ship has taken its name and crest from the second frigate of the Leander-class of ships, which was incidentally launched 50 years ago in 1970.
The launch of ‘Himgiri’ has showcased GRSE’s commitment towards the building of 3 state-of-the-art warships of P17A for Indian Navy.
Since its inception, Project 17A has upheld India’s vision for Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Under the Project 17A program, a total of 7 ships, 4 at Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Limited (MDL) and 3 ships at GRSE are being built with enhanced stealth features, advanced indigenous weapon and sensor fit along with several other improvements.
P17A ships are the first gas turbine propulsion and largest combat platforms ever built at GRSE.
Environment
Indian Gaur: The gaur, also known as Indian bison, is native to South and Southeast Asia. It's scientific name is Bos Gaurus. It is one of the largest extant bovines. It is one of the largest species among the wild cattle, reaching a shoulder height of up to 220 cm. Gaurs are found on the forested hills and grassy areas of south to south east Asia. They are found in India, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, Malaysia, Nepal and Thailand.
In India: The Western Ghats in southern India constitute one of the most extensive extant strongholds of gaur, in particular in the Wayanad – Nagarhole – Mudumalai – Bandipur complex. The gaur is the State Animal of Goa and Bihar.
It is listed as Vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature(IUCN) Red List since 1986. The Indian Government has included it in the Schedule I of the Wild Life Protection Act, 1972. It is listed in CITES Appendix I.
Recently, the images of the Gaur, in Pune’s urban landscape, the frenzy among people, the capture of the injured animal that ran around in panic, and the sad news of its death has put the spotlight on human-Gaur conflict in the country.
Actually, a male Gaur aged between three to four years, was spotted in the residential area of Mahatma Society in Kothrud area of Pune. The Forest Department officials were informed by local residents and subsequently police, Municipal Corporation and Fire Brigade personnel rushed to the area.
After initial attempts by Forest department staff to tranquilise it, the Gaur ran towards an adjacent locality, where it had to face an unruly crowd, which, according to forest officials, added to its panic. After running in panic for over 3 km, the animal was tranquilised with a dart and captured.But it died after being taken to a transit treatment centre.
Himalayan Serow: The Himalayan serow is a subspecies of the mainland serow native to the Himalayas. Its scientific name is Capricornis thar. Taxonomically, it is a subspecies of the mainland serow (Capricornis sumatraensis).
It resembles a cross between a goat, a donkey, a cow, and a pig. It’s a medium-sized mammal with a large head, thick neck, short limbs, long, mule-like ears, and a coat of dark hair. Himalayan serows are herbivores.
There are several species of Serows, and all of them are found in Asia. They are typically found at altitudes between 2,000 metres and 4,000 metres (6,500 to 13,000 feet). They are known to be found in eastern, central, and western Himalayas, but not in the Trans Himalayan region.
Previously assessed as ‘near threatened’, the Himalayan serow is now been categorised as ‘vulnerable’ in the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
It is listed under Schedule I of The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, which provides absolute protection.
Recently, a Himalayan serow was sighted for the first time in the Himalayan cold desert region. The animal was spotted near Hurling village in Spiti, Himachal Pradesh.
Serows are generally not found at this altitude, and never before has a serow been seen in the Himalayan cold desert.
Wildlife officials believe this particular animal may have strayed into the Spiti valley from the Rupi Bhaba Wildlife Sanctuary in adjoining Kinnaur.
India Water Impact Summit 2020: India Water Impact 2020 is a five-day long summit. The summit hosts experts and academicians from all over the world to discuss and debate issues related to water conservation, water security and river rejuvenation. The event is co-organized by National Mission for Clean Ganga and Centre for Ganga River Basin Management and Studies.
Recently, the Norwegian Institute of Bioeconomy Research (NIBIO) signed an MoU with cGanga, a think-tank of National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) for development of sludge management framework in India.
Norway, through this initiative, intends to deepen the relationship with India especially in the prevention of climate change and conservation of the environment.
Miyawaki: Miyawaki is a technique pioneered by Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki. Miyawaki Akira, born 29 January 1928 is a Japanese botanist and expert in plant ecology, specializing in seeds and the study of natural forests.
Miyawaki afforestation method is also called Potted Seedling Method.The Miyaki technique helps to build dense, native forests. This afforestation technique uses native species to create dense, multilayered forests. A central tenet in creating these forests is its use of indigenous species for plantations. It involves planting dozens of native species in the same area, and becomes maintenance-free after the first three years.
The approach is supposed to ensure that plant growth is 10 times faster and the resulting plantation is 30 times denser than usual.
Recently, the Mansa unit of Punjab state Police has started developing Miyawaki forests. The Bengaluru Hennagara Lake is also set to get a new life with Miyawaki Forests.
The Kerala Forest Department has adopted Miyawaki Afforestation Method to be used in government schools, offices and in waste lands.
Indian Policy
RKA: It stands for Rashtriya Kamdhenu Aayog. The RKA is a high powered permanent body to formulate policy and to provide direction to the implementation of schemes related to cattle so as to give more emphasis on livelihood generation of small and marginal farmers. It has been constituted by the Government of India (GoI) under the ministry of animal husbandry to organize animal husbandry on modern and scientific lines and to take steps for preserving and improving breeds, and prohibiting the slaughter, of cows and calves and other milch and draught cattle. It was constituted by the resolution dated 21st February, 2019.
Recently, the RKA organized an open house national webinar titled ‘Kamdhenu chair in universities and colleges’ The event witnessed the participation of more than 500 vice-chancellors and officials of universities from across the country.
At the event, around 10 universities from across the country have announced that they will set up Kamdhenu Chairs in their respective institutions of higher learning.
This virtual event was organized by the Rashtriya Kamdhenu Aayog (RKA) in association with the University Grants Commission (UGC), All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) and Association of Indian Universities (AIU).
The Kamdhenu Chairs aim to educate students about indigenous cow breeds. The RKA has also proposed diploma and certificate courses on cow-based entrepreneurship.
In additon, RKA has also proposed setting up of certificate and diploma courses on cow-based entrepreneurship and sensitizing students about the environmental, scientific, economic and spiritual importance and impact of cow.
UNESCO New Delhi: The UNESCO New Delhi recently launched the 2nd edition of ‘State of the Education Report for India 2020: Technical and Vocational Education and Training (TVET). The virtual event was attended by over 400 attendees, including representatives from the government, civil society, academia, partners and youth.
The second edition of the State of Education Report focuses on technical and vocational education and training (TVET).
With an in-depth analysis of the current state of TVET in India highlighting next practices and recommendations, the Report aims to serve as a reference tool for enhancing and influencing the policies and programs related to skills development in India.
It can be used by TVET practitioners, policy makers, private sector and donor agencies for planning future engagements in the TVET sector in India.
The Report outlines 10 recommendations to achieve the stated vision for TVET in India. They are as follows:
- Place learners and their aspirations at the centre of vocational education and training programmes
- Create an appropriate ecosystem for teachers, trainers and assessors
- Focus on upskilling, re-skilling and lifelong learning
- Ensure inclusive access to TVET for women, differently abled and disadvantaged learners
- Massively expand the digitalization of vocational education and training
- Support local communities to generate livelihoods by engaging in the preservation of tangible and intangible cultural heritage
- Align better with the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development
- Deploy innovative models of financing TVET
- Expand evidence-based research for better planning and monitoring
- Establish a robust coordinating mechanism for inter-ministerial cooperation
The substance of the Report has been developed by an experienced team of researchers from the Tata Institute of Social Sciences, Mumbai, under the guidance of UNESCO New Delhi. Its technical partner was the technical and financial partner — American India Foundation (AIF).
American India Foundation (AIF) is a leading not-for-profit organization committed to improving the lives of India’s underprivileged, with a special focus on women, children, and youth.
Note: As stated in the National Policy of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (NPSDE), released in 2015, India has made considerable progress towards its goal of creating a skilled workforce of 110 million people by 2022. It is currently training 10 million youth every year through the many ongoing schemes.
BEAM: The full form of BEAM is “BSE E-Agricultural Markets Ltd. BEAM is an e-agricultural spot market platform recently launched by Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) Ltd. for agricultural commodities through its subsidiary BSE Investments Ltd.
The platform functions as a "national level, institutionalised, electronic, transparent commodity spot trading platform in line with the Prime Minister's vision to create a "single market". It aims to boost the competitiveness of the Indian agricultural market by enhancing the strength of the BSE in financial markets, market technology and its vibrant ecosystem.
The features of BEAM Platform are as follows:
- The state of the art technology used by BEAM will offer the customized solutions to traders, farmers and stakeholder.
- It will help farmers in one state will be able to reach out to markets in other states and auction their produce. The farmers will be able to discover the best prices for their products based on the quality, as well as build capacity to help intermediaries; processors and exporters procure from states.
- It will help to reduce the cost of intermediation, to enhance producers’ realization, competitive consumer prices and improved procurement efficiency.
- It will help to eliminate the obstructions related to procurement and trading.
BSE: It is an acronym for Bombay Stock Exchange. BSE was established in 1987. It is one of India’s leading exchange groups and also Asia’s first & world’s fastest Stock Exchange with a speed of 6 microseconds. It is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. The current MD and CEO of BSE is Ashish Kumar Chauhan.
NERPSIP: It refers to the north eastern region power system improvement project. NERPSIP is a central scheme under the Ministry of Power.
Recently, the Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi has approved the Revised Cost Estimate (RCE) of the NERPSIP. The revised estimated cost is Rs 6,700 crores.
The scheme is being implemented through POWERGRID, a Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) under Ministry of Power in association with 6 beneficiary North Eastern States namely, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, and Tripura. The scheme is targeted to be commissioned by December 2021. After commissioning, the project will be owned and maintained by the respective North Eastern State Utilities.
The main objective of the project is the economic development of the northeast through the strengthening of intra-state transmission and distribution infrastructure.
North Eastern Council: The North Eastern Council is a statutory advisory body constituted under the NEC Act 1971. The council came into being on 7 November 1972 at Shillong. It functions under the Ministry of Development of North Eastern Region (DONER) of the Government of India. The council is responsible for the social and economic development of the North Eastern region of India. The members of the council are the Governors, chief ministers of the eight states. The eight states are Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Mizoram, Sikkim. (Sikkim was added to the council in the year 2002)
Indian polity
Breach of Privilege Motion: Questioning the boundaries of the judiciary's powers, the State Legislature of Maharashtra recently passed proposals stating that they will not reply to any notice sent by Supreme Court or High Court in the breach of privilege motion against the Republic TV editor Arnab Goswami.
In the State Assembly, the proposal was declared as “passed unanimously” by Speaker Nana Patole. It stated that Speaker Patole and Deputy Speaker Narhari Zirwal would not respond to any notice or summons issued by the Supreme Court.
In the Legislative Council, too, the proposal was passed unanimously, said Chairman Ramraje Naik Nimbalkar. It stated that no cognizance will be taken of any notice or summons issued by the High Court or Supreme Court if Goswami challenges Breach of Privilege proceedings.
The proposal cites two articles of the constitution as the basis of its argument. They are articles 194 and Article 212.
- Article 194 of the Constitution lays down the powers and privileges of the Houses of Legislatures. It states that there shall be freedom of speech in the Legislature of every State and no member of the Legislature of a State shall be liable to any proceedings in any court in respect of anything said or any vote given by him in the Legislature or any committee thereof, and no person shall be so liable in respect of the publication by or under the authority of a House of such a Legislature of any report, paper, votes or proceedings.
- Article 212 states that the validity of any proceedings in the Legislature of a State shall not be called in question on the ground of any alleged irregularity of procedure and no officer or member of the Legislature of a State in whom powers are vested by or under this Constitution for regulating procedure or the conduct of business, or for maintaining order, in the Legislature shall be subject to the jurisdiction of any court in respect of the exercise by him of those powers.
Note: The parliamentary privileges refer to the rights and immunities enjoyed by the parliamentarians. Without these they cannot discharge their functions as and out upon them by the constitution. The scrutiny of breach of privilege motion is managed by speaker in Lok Sabha and by the chairperson in Rajya Sabha. Both chairperson and the speaker have the authority to consider the occupations and call upon the members to explain themselves. After the motion is passed, the Parliament (or Legislative Assembly) Speaker or Rajya Sabha (or Legislative Council) Chairman constitutes a Privileges Committee, which will look into the motion and recommend the punishment.
Under Parliamentary privilege, the legislators are granted protection against civil or criminal liability for actions done or statements made in the course of their legislative duties. The special privileges are granted to maintain the dignity and authority of the Houses. But there are no clear notified rules to decide the breach of privilege.
Cases of privilege motion:
- In 1976 Subramanian Swamy a BJP MP was expelled from Rajya Sabha for disgracing Indian government through his interview to foreign journals.
- In 1978 the most significant privilege motion was passed against Indira Gandhi. It was introduced by the then home minister Charan Singh. Under the motion she was found guilty and was expelled from the house.
- Recently, breach of privilege motion was passed against the Defence Minister and the Prime Minister of the country claiming that the ministers have misled the country on Rafale fighter jet deal.
Shakti Act: The Government of Maharashtra recently launched the Maharashtra Shakti Criminal Law (Maharashtra Amendment) Act of 2020 and the Special Court and Machinery for the implementation of the Maharashtra Shakti Criminal Law of 2020.
The state cabinet, in a bid to curb crimes against women and children in Maharashtra, approved a draft bill called the Shakti act that has provisions for stern punishment, including the death penalty, life sentence, and hefty fines against perpetrators.
Key Features of the Bill are:
- Maharashtra Shakti Bill has been framed in lines with the Andhra Pradesh Disha Act, 2019.
- The bill seeks to amend the Code of Criminal Procedure, Indian Penal Code and the Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act.
- The bill seeks to add third explanation in Section 375 of Indian Penal Code. It deals with rape. It talks about “Presumption of Consent”.
- The acid attack victims shall be provided with a compensation of ten lakhs of rupees for plastic surgery and facial reconstruction.
- The court can sentence to death penalty if the accused is charged of gang rape, rape or penetrative assault against children.
- The bill seeks to complete the trial process within 30 days. Currently it is 60 days.
- The bill suggests creation of “Women and Children Offenders Registry”, a separate registry. This registry will be linked to the National Registry of Sexual Offenders.
- The bill also includes provisions to punish persons filing false rape cases to threaten, extort or defame the accused.
Justice Verma Committee: The Indian Penal Code had made several stringent provisions after Nirbhaya case in 2013 based on the recommendations of Justice Verma Committee.
Note: According to the National Crime Record Bureau (NCRB), the crimes against women had increased by 7.3% in 2019 as compared to 2018. Around 88 cases of crimes against women are being registered in the country according to NCRB.
International
International Year of Creative Economy for Sustainable Development: The year 2021 was recently declared by UNESCO as ‘International Year of Creative Economy for Sustainable Development’. The decision was taken during the 74th session of the UN General Assembly in November 2019.
The day aims to raise awareness, promote cooperation and networking, encourage sharing best practices and experiences, enhance human resource capacity, promote an enabling environment at all levels as well as tackle the challenges of creative economy.
International Migrations Day: The International Migrants Day is observed on 18 December across the globe every year. In December 2000, the UN General Assembly proclaimed 18 December as International Migrants Day after considering the large and increasing number of migrants in the world.
The theme of International Migrants Day 2020 is ‘Reimagining Human Mobility’.
The day marks the anniversary of the adoption of the International Convention on the Protection of the Rights of All Migrant Workers and Members of Their Families, which was adopted by the United Nations (UN) on 18 December 1990.
Morocco: Morocco is a mountainous country of western North Africa that lies directly across the Strait of Gibraltar from Spain. It a North African country bordering the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea, is distinguished by its Berber, Arabian and European cultural influences. The capital of Morocco is Rabat. The currency used here is Moroccan dirham.
Recently, Morocco agreed to become the fourth Arab nation to normalise relations with Israel in as many months, as part of a deal in which the US agreed to recognize its claim over the disputed Western Sahara region.
As part of the agreement, U.S. President Donald Trump changed longstanding U.S. policy and recognized Morocco's sovereignty over the Western Sahara.
The Western Sahara is a desert region where a decades-old territorial dispute has pitted Morocco against the Algeria-backed Polisario Front, a breakaway movement that seeks to establish an independent state in the territory.
Western Sahara dispute: A former Spanish colony, Western Sahara is a vast, arid region in northwest Africa. It is mineral rich home to abundant reserves of phosphate, a key ingredient in the manufacturing of synthetic fertilizers. It has also lucrative fish resources and is believed to have off-shore oil.
The region first came under Spanish control in 1884, and was made a province called ‘Spanish Sahara’ by the European country in 1934. Then in 1957, its northern neighbour Morocco, which had become independent from French rule just a year before, staked its claim over the entire territory, reasserting a centuries-old position.
Then in 1975, ten years after the UN called for its decolonization, Spain withdrew from Western Sahara, partitioning the region between Morocco, which received the region’s northern two-thirds, and Mauritania the remaining third in the south.
Since then, Morocco has controlled around 80 per cent of Western Sahara, including its phosphate reserves.
Note: Combined with its own deposits of the mineral, Morocco currently holds over 72 per cent of the world’s phosphate reserves. China, which has the second-most reserves, has less than 6 per cent.
Kazakhstan: Kazakhstan, also spelled Kazakstan, officially Republic of Kazakhstan is a country of Central Asia. It is bounded on the northwest and north by Russia, on the east by China, and on the south by Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, the Aral Sea, and Turkmenistan; the Caspian Sea bounds Kazakhstan to the southwest. It is the world's largest landlocked country, and the eighth-largest country in the world. The capital of Kazakhstan is Nur-Sultan, formerly known as Astana. The currency used here is Kazakhstani tenge (KZT). The current president of Kazakhstan is Kassym-Jomart Tokayev.
Recently, Kazakhstan celebrated its 29th anniversary as a sovereign independent nation on the 16th of December 2020.
December 16, 1991, was a prominent day in Kazakh history, as the country’s Supreme Council passed the Constitutional Independence Law, which, together with the Declaration of Sovereignty established what is now considered Central Asia’s wealthiest country.
The document ushered in the era of Nursultan Nazarbayev, who was elected the first president of Kazakhstan in 1991. The country’s new two-house parliamentary system and national Armed Forces were subsequently established to meet the needs of defense. The capital city, which is now the country’s landmark, was moved from Almaty to Astana (Nur-Sultan) in 1997.
Holder of a “City of Peace” UNESCO award, through all the international events it successfully hosted so far in its young history of 23 years, this vibrant metropolis proves that it fully deserves this brand.
The city has already had a successful track record over the last years of hosting major global gathering events: the Congress of leaders of world and traditional religions or the Astana Economic Forum. The historic OSCE summit was held in Nur-Sultan, the anniversary summits of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) and the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC) were also hosted by the capital city. In addition, in the beginning of 2011, the capital of the Republic hosted the participants and guests of the VII Asian Winter Games.
A new era marked significant changes in Kazakhstan’s status as a nuclear power, as the country’s authorities renounced nuclear defense capabilities and closed down the former Soviet Semipalatinsk nuclear test site.
India-Kazhak relations: Relations between India and Kazakhstan are ancient and historical going back to more than 2000 years. Both the countries actively cooperate under the aegis of Multilateral Fora including CICA, SCO and the UN organizations.
India was one of the first countries to recognize the independence of Kazakhstan. Diplomatic relations were established in Feb 1992. The Embassy of India was opened in Almaty in May 1992 and the Embassy of Kazakhstan in New Delhi in 1993.
India is one of the key political, trade, economic and investment partners of Kazakhstan.
UNEP: It is an abbreviation for United Nations Environment Programme. UNEP was founded on 5 June 1972 by a Canadian businessman and philanthropist Maurice Strong. It is responsible for coordinating the UN's environmental activities and assisting developing countries in implementing environmentally sound policies and practices. It is the global champion for the environment with programmes focusing on sustainable development, climate, biodiversity and more. It is headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya. The current Executive Director of UNEP is Inger Andersen and the current Regional Director and Representative for Asia and the Pacific, UNEP is Dechen Tsering.
Recently, UNEP announced six laureates of the 2020 Champions of the Earth Award, UN’s highest environmental honour.
The six laureates are Nemonte Nenquimo, Dr. Fabian Leendertz, Frank Bainimarama, Yacouba Sawadogo, Mindy Lubber, and Professor Robert D. Bullard. The Champions were chosen for their transformative impact on the environment and their leadership in urging bold and decisive action on behalf of the planet and its inhabitants.
The Champions of the Earth Award is presented in 5 categories:
- Lifetime Achievement,
- Policy Leadership,
- Entrepreneur Vision,
- Inspiration and Action,
- Science and Innovation.
The award for Lifetime Achievement Award was awarded to Professor Robert D. Bullard (USA) for his commitment and service to environmental justice.
The award for Policy Leadership was awarded to
Prime Minister Frank Bainimarama of Fiji was honoured for his global climate action work and his commitment to climate-responsive national development.
The award for Entrepreneur Vision was awarded to Mindy Lubber (USA) was awarded for her commitment to turning capital markets green by mobilizing top investors and companies and making the business case for climate action and sustainability.
The award for Inspiration and Action was awarded to Yacouba Sawadogo (Burkina Faso) for teaching farmers his traditional nature-based solution to regenerate their soil and turn barren land into arable land and forest across Africa.
The award for Inspiration and Action was awarded to Nemonte Nenquimo (Ecuador) for her leadership and unifying work with indigenous communities that halted drilling in Ecuador’s Amazon rainforest.
The award for Science and Innovation was awarded to Dr Fabian Leendertz (Germany) for his discoveries in zoonotic and his work in One Health.
The award recognizes outstanding environmental leaders from the public & private sectors for their efforts to heal the planet amid natural & human-made threats.
UNEP first presented The Champions of the Earth Award was presented for the first time in 2005.
ABU: It refers to the Asia Pacific Broadcasting Union. ABU was formed in 1964 as a professional association of broadcasting organizations with over 286 members in 57 countries and regions. It is headquartered in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. One of the ABU's activities is Asiavision. It is a daily exchange of news feeds by satellite among television stations in 20 countries in Asia.
Recently, Prasar Bharati CEO Shashi Sekhar Vempati has been elected as Vice President of Asia-Pacific Broadcasting Union for 3 years with immediate effect.
National
India and UK: India and UK recently held delegation level talks on strengthen cooperation in different areas including trade and prosperity, defence and security, climate and health.
External Affairs Minister S Jaishankar met the visiting UK Foreign Secretary Dominic Raab in New Delhi.
At the meeting, the two leaders discussed how to give policy directions to broaden bilateral cooperation and encourage more activities and collaborations. They also discussed the situation in Afghanistan, the evolution of the Indo-Pacific and developments in the Middle East.
The concern for the challenges posed by terrorism and radicalism were shared too.
Mr. Jaishankar said that as India enters the UN Security Council next month, it will look forward to working together with the UK on a range of global issues.
TWG: It stands for Trilateral Working Group. The first TWG Meeting between India, Iran and Uzbekistan on the joint use of Chabahar Port was recently held.
The Meeting was jointly chaired by Secretary (Shipping), Government of India (GoI), Deputy Minister of Transport, Uzbekistan and Deputy Transport Minister of Iran.
During the meeting, the participants discussed joint use of Chabahar Port for trade and transit purposes and enhanced regional connectivity.
India’s proposal to hold "Chabahar Day” on the side-lines of the International Maritime Summit scheduled to be hosted by India in January 2021 was welcomed by all sides.
The meeting was held as a follow up of decisions taken during the virtual summit held between Prime Minister Narendra Modi and President of Uzbekistan on 11th December 2020.
Chabahar Port: The Chabahar Port is a seaport in Chabahar located in south-eastern Iran, on the Gulf of Oman. It serves as Iran's only oceanic port, and consists of two separate ports named Shahid Beheshti and Shahid Kalantari. It is a significant transit route to connect South Asia with Central Asia while bypassing Pakistan which has consistently impeded land access from India to Afghanistan and beyond. The port is being developed by India, Iran and Afghanistan to boost trade ties among the three countries.
India and Bangladesh: The ‘Swadhinata Sarak’ between Bangladesh and India will be opened on 26th March 2021.This was announced by Bangladesh Foreign Minister Dr. Momen.
The road remains functional on the Indian side. It will be connected through Mujibnagar, Meherpur district in Bangladesh.
Chilahati-Haldirbari rail link which was active till 1965 will be inaugurated during the summit meeting between the two Prime Ministers on the 17th of December 2020.
India and Myanmar: The fifth India- Myanmar Bilateral Meeting on Drug Control Cooperationon Drug Control Cooperation was recently conducted by the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB), India and the Central Committee on Drug Abuse Control.
The Indian delegation was led by the Director-General Narcotics Control Bureau, Shri Rakesh Asthana. The Myanmar delegation was led by Pol. Brig. Gen. Win Naing. the Commander of the Drug Enforcement Division (DED) cum Joint Secretary of the Central Committee for Drug Abuse Control.
Key Highlights of the Meeting:
Both countries agreed on the exchange of intelligence information in a timely manner to conduct follow-up investigations in drug seizure cases, new psychotropic substances and their precursors.
They also agreed to conduct Border Level Officers and Field Level Officers meetings on regular basis between frontline officers to strengthen the existing cooperation on drug law enforcement.
The decision to exchange information on illegal entry and exit points of illicit drug trafficking on the Myanmar-India borders and information on the technology being used to interdict drug trafficking was also taken.
The 6th India – Myanmar Bilateral Meeting on Drug Control Cooperation will be held in India in 2021.
FICCI’s 93rd Annual General Meeting: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently delivered the inaugural address at FICCI’s 93rd Annual General Meeting (AGM) and Annual Convention via video conferencing.
Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI) had organised the convention from December 11 to 14, 2020.
The theme for the FICCI 93rd AGM was ‘Inspired India’.
The Prime Minister also inaugurated the virtual FICCI Annual Expo 2020. It started from 11 December 2020 and will continue for a period of a whole year. More than 10000 delegates are virtually participating in this mega event from across the globe.
FICCI Annual General Meeting (AGM): FICCI AGM is the annual high-powered flagship event where Cabinet Ministers, Secretaries to Government of India (GoI), Global Industry Captains, Diplomats, Political party leaders, and other thought leaders participate.
FICCI Annual Expo, 2020: The Expo is a one-of-its-kind virtual event in the country. It is focused on the manufacturing and services sectors. It aims to provide an opportunity to exhibitors from across the globe to showcase their products and advance their business prospects.
People In News
Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman: Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, shortened as Sheikh Mujib or just Mujib, was a Bangladeshi politician and statesman. He was born on 17 March 1920. He is called the "Father of the Nation" in Bangladesh. He served as the first President of Bangladesh and later as the Prime Minister of Bangladesh from 17 April 1971 until his assassination on 15 August 1975.
Recently, UNESCO launched an international award named after Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman following Bangladesh’s proposal.
The UN agency’s executive board unanimously adopted the proposal on UNESCO-Bangladesh Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman International Prize for the “Creative Economy” in its 210th session. Bangladesh had proposed the award in August 2019.
Starting November 2021, the $50,000 prize money award will be given away once in two years for global economic initiatives of the youth.
The award will recognize exceptional initiatives taken by cultural workers and organizations in the development of the creative economy.
The UNESCO launches awards in recognition of the contribution of leaders in several fields, such as education, culture, science and technology, with the financial help of the member states. It had launched 22 awards named after noted individuals or organizations. This is the first time that UNESCO has decided to introduce an award in the name of someone from Bangladesh.
Currently, there are 23 UNESCO International Awards in the name of international celebrities and organizations.
Ambrose Mandvulo Dlamini: He was a Swazi business executive who served as the 10th Prime Minister of Eswatini. Following the death of Prime Minister Barnabas Sibusiso Dlamini in 2018, Dlamini was selected by King Mswati III to succeed him. He was the youngest PM in the country's history. He held the office from October 2018 until his death on 13 December 2020. He passed away after contracting COVID-19.
Eswatini: Eswatini is officially known as the Kingdom of Eswatini, sometimes written in English as eSwatini, and formerly and still commonly known in English as Swaziland. It is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its north, west, and south
The government is an absolute monarchy, ruled by King Mswati III since 1986. Elections are held every five years to determine the House of Assembly and the Senate majority.
Paul Sein Twa: Myanmar’s Paul Sein Twa is the co-founder of the Karen Environmental and Social Action Network (KESAN), established in 2001. He has recently been awarded the Goldman Environmental Prize 2020 for Asia.
He was awarded by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Asia Regional Office for his efforts in promoting the self-determination of the Karen people in managing their natural resources.
The Salween Basin is home to vast stretches of teak forests, teeming with tigers, sun bears, and clouded leopards. Paul and his team at KESAN supported Karen indigenous communities in establishing the Salween Peace Park in Myanmar and on the border of Thailand. The Peace Park represents a unique community-based approach to conservation in one of Asia’s biodiversity hotspots.
Goldman Environmental Prize: The Goldman Environmental Prize is one of the most prestigious environmental prizes awarded annually to grassroots environmental activists, one from each of the world’s six geographic regions: Africa, Asia, Europe, Islands and Island Nations, North America, and South and Central America.
Ashraf Patel: She is the founder member and Board member of Pravah and ComMutiny – The Youth Collective (CYC). She was recently declared as the winner of the Social Entrepreneur of the Year (SEOY) Award – India 2020. The award was presented to her by the Union Minister of Women & Child Development & Textiles, Smriti Zubin Irani.
Social Entrepreneur of the Year (SEOY) Award: The SEOY award “recognizes entrepreneurs who implement innovative, sustainable and scalable solutions to solve India’s social problems. It was instituted by the Schwab Foundation and Jubilant Bhartia Foundation in 2010. This award for 2020 was the 11th edition of the annual award.
Places In News
Gujarat: Gujarat is a state on the western coast of India most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. The state is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west. Its capital city is Gandhinagar. The Governor and Chief Minister of Gujarat are Acharya Devvrat and Vijay Rupani respectively.
Recently, Prime Minister Narendra Modi laid the foundation stone of the 30,000 megawatt (MW) capacity hybrid renewable energy park in Kutch district of Gujarat. It will be the largest renewable energy park of its kind in the world.
This renewable park aims to play a major role in fulfilling India’s vision of generating 450 GW (4,50,000 mw) of power by 2030.
The park is being constructed between Khawda and Vighakhot villages near India-Pakistan border. It will have two dedicated zones, one each for the wind energy and solar energy.
It will be spread over 72,600 hectares of waste land, including 49,600 hectares for solar project and 23,000 hectares of land for wind power.
Gujarat Land Grabbing (Prohibition) Bill, 2020: The Gujarat Land Grabbing (Prohibition) Act,2020 passed in the last session of the state Assembly has come into force in the state on 16 December 2020.
The Bill seeks to curb land grabbing in the state by setting up special courts. It has provisions for stringent action with a jail term of upto 14 years and a fine extending to the (Jantri) value of the land.This Act will be strictly implemented in the state to take legal action against the land mafias in the state, who have illegally occupied the state government's land as well as the land that belongs to common farmers and privately-owned public trusts and monasteries.
Under the provisions of the new Act, a special committee will be formed to ensure comprehensive scrutiny of complaints received. The committee will comprise of seven officials, headed by the district collector concerned has been set up in each district. It will also have other members such as district development officer, district superintendent of police, municipal commissioner, police commissioner, chief executive officer of urban development authority, while the resident additional collector of each district will be the member secretary of the committee.
Key Highlights of the Act:
- The rules and regulations of the Gujarat Land Grabbing Prohibition Act will be strictly implemented in the state.
- Under the Act, the committee has been mandated to meet at least once in 15 days.
- A decision will have to be taken within 21 days on the investigation report submitted before the committee.
- Besides a special committee, special courts will be set up to dispose off cases within six months.
- The special court will be empowered to conduct civil and criminal court proceedings.
- Under the Act, not only a district collector can take suo motu cognizance of any act of grabbing government land but a special court can also take suo motu cognizance of any matter related to land grabbing.
- In each special court, one public prosecutor will be appointed and disposal of such cases will be ensured within six months.
- The Act will cover the government as well as privately-owned land, properties and properties of trusts and religious organizations.
- The main objective behind the enforcement of the act is not only to enable the common man to get speedy justice but also punish the guilty land mafia severely.
Maharashtra: Maharashtra is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau. It was formed on 1 May 1960. It was formed by merging the western and south-western parts of the Bombay State, Berar and Vidarbha, and the north-western parts of the Hyderabad State and splitting Saurashtra (in present-day Gujarat) by the States Reorganisation Act. Its capital is Mumbai. The Chief Minister and the Governor of Maharashtra are Uddhav Thackeray and Bhagat Singh Koshyari respectively.
Recently, the Maharashtra Government approved the Unified Development Control and Promotion Regulations (UDCPR), to strengthen and bring uniformity in the real estate construction laws of the state.
The new Regulations will be implemented on municipal corporations, councils and Nagar panchayats in the entire state except Mumbai and some neighbouring areas like hill stations, eco-sensitive zones and specified corporation areas.
These new regulations aim to help in defining everything from the height of structures to the width of roads and the size of amenity spaces. It will also help in increasing the stock of affordable housing projects and improving ease of doing business as well as to help the developers to improve their resource management.
Science and Technology
NETRA: It is a dedicated Space Situational Awareness (SSA) Control Centre named “NETRA”. The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) has set up NETRA at its ISTRAC campus at Peenya, Bengaluru. It was formally inaugurated by ISRO Chairman K Sivan.
The full form of NETRA is NEtwork for space object TRacking and Analysis. The main objective of NETRA is to monitor, track and protect Indian Space Assets. It will conduct concurrent processing of data from the upcoming observational facilities for space objects’ orbit determination, catalogue generation and correlation.
It will act as the hub for all SSA activities.It has been set up as a ‘Directorate of Space Situational Awareness and Management (DSSAM).’ The state-of-the-art facility, dedicated to SSA activities, will also help to coordinate between Indian agencies, their foreign counterparts and international bodies.
The main elements of NETRA would be radar, an optical telescope facility, and a control centre.
The core activities of NETRA include timely dissemination of advance alerts on collision avoidance of space assets, approach analysis between ISRO satellite and launch vehicles and prediction of atmospheric re-entry of rocket bodies or derelict satellites. Derelict Satellites are the satellites that are in poor condition due to disuse or neglect.
SSA: The Space Situational Awareness (SSA) is the science of tracking objects (man-made and natural) that are in orbit and also predicting what they would be at a given point in time. SSA is important for safe and sustainable operations.
Only the US, Russia and Europe have similar facility in place to track space objects and share collision warnings.
Note: As of January 2020, there are more than 2000 active satellites orbiting the earth. Also, there are more than 23,000 pieces of space debris. These larger space debris are larger than ten centi-metres.
Project Loon: It is a subsidiary of Google which comprises of helium-filled balloons that aim to deliver internet access to remote parts of the world. These high-altitude balloons are found in the stratosphere and create aerial wireless networks. The project has collaborated with several countries and their technology partners to provide internet connectivity.
Recently, Project Loon, announced that its balloons have successfully stayed in the stratosphere for almost a year. Loon has created a new record for the longest stratospheric flight by staying in air for 312 days.
Last year, the company announced that its balloons reached over one million hours of stratospheric flight.
Currently, the internet connectivity system consists of only two basic methods to deliver a connection. They are - Signal from Space and Signal from Ground. Lately, the Project Loon balloons are also being used as weather monitors.
Helium Balloons: Helium Balloons are balloons that are filled with helium and rises up into the air if not held. The balloons are 15 metres wide and 12 metres tall. They are launched at an altitude of 20 km above the earth, which is above the zone where the airplanes fly. These balloons act as cell towers receiving and transmitting signals. The balloons are powered by solar panels.
Changing altitudes control the path of the balloons. Wind speed and direction is used to move the balloons up or down.
The altitude is changed by pumping or releasing air. The next balloon moves in when one station moves off to a pre-determined position.
The users need special antenna to receive and transmit signals from and to the balloon. The inflatable part of the balloon is called “Balloon Envelope”.
The panels in the balloon produce 100 watts of power when completely exposed to the sun.
ISRO: It is an abbreviation for the Indian Space Research Organizatin. ISRO is the space agency of the Government of India (GoI) and was formed in 15 august 1969. It superseded the erstwhile “Indian National Committe For Space Research” (INCOSPAR) which was established in 1962 by the efforts of Independent India's first prime minister‚ Jawaharlal Nehru‚ and his close aide and scientist Vikram Sarabhai. In 1972, the Government of India had set up a Space Commission and the Department of Space (DOS), bringing ISRO under the DOS. ISRO then embarked on its mission to provide the Nation space based services and to develop the technologies to achieve the same independently. Its vision is to “harness space technology for natural development while pursuing space science research & planetary exploration”. ISRO built India’s first Satellite Aryabhata. It is headquartered in Bangalore, India. The current Chairman of ISRO is K sivan.
Recently, ISRO successfully launched the country’s new communication satellite CMS-01 into the Geostationary Transfer Orbit. The satellite was launched on a PSLV-C50 launch vehicle.
CMS-01 Satellite: It was earlier called the GSAT-12R. It is the 42nd communication satellite of India. The weight of this satellite is 1,410 kilograms and it is a replacement of GSAT-12. It has a mission life of 7 years.
The GSAT-12 was launched in 2011 to provide services such as disaster management support, tele-medicine, satellite internet access and tele-education. These functions are now to be replaced by CMS-01. The satellite will provide telecom services in the extended C-Band of the frequency spectrum. It will include Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep Islands.
ISRO will launch a series of satellites and probes in the days to come. They include the PSLV-C51 and the Small Satellites Launch Vehicle SSLV.
Preparations for the prestigious missions like Chandrayaan-3, the Gaganyaan and the probe to study the sun called Aditya L-1 are also in full swing.
SpaceCom Policy of India:
The Government of India (GoI) has given permission for space reforms by allowing the participation of private players. The draft Spacecom was released by ISRO. The SpaceCom Policy, 2020 aims on the following
- To adopt measures to monitor and authorize use of space assets
- To promote increased participation of commercial Indian industry.
- To ensure protection of space assets.
- To concentrate on realization of space-based communication systems.
- To provide timely and responsive regulatory environment.
NASA: It is an acronym for National Aeronautics and Space Administration. NASA is an independent agency of the United States Federal Government responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). It is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States. The Administrator of NASA is Jim Bridenstine and the Deputy Administrator of NASA is James Morhard.
Recently, NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) have selected Indian-American Raja Chari to be the Commander of the SpaceX Crew-3 mission to the International Space Station.
Raja Chari is currently a colonel in the US Air Force. He will be the commander of SpaceX Crew-3 mission, while Nasa’s Tom Marshburn will be pilot and ESA’s Matthias Maurer will serve as a mission specialist. This mission is expected to be launched next year. This will be the first spaceflight for Raja Chari. He became a Nasa astronaut in 2017.
When Chari, Marshburn, and Maurer arrive at the orbiting laboratory, they will become expedition crew members for the duration of their six-month stay. The crew will have a slight overlap with the Crew-2 astronauts, who are expected to launch in the spring of 2021.
Sports
Ankita Raina: She is an Indian Tennis player who clinched her third doubles title of the season after she won the 2020 Al Habtoor Tennis Challenge jointly with her Georgian partner Ekaterine Gorgodze in Dubai.
The unseeded Indo-Georgian pair defeated the pair of Spain’s Aliona Bolsova Zadoinov and Slovakian Kaja Juvan by 6-4 3-6 10-6 to win the final of the USD 1,00,000 event.
It was the fourth doubles final of the season for Ankita but the biggest trophy of the calender since her earlier two titles were at the USD 25,000 level.
Al Habtoor Tennis Challenge: It is a professional female tennis tournament and part of the ITF Women’s World Tennis Tour, held annually in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, since 1998.
Abu Dhabi Grand Prix: Max Verstappen (Red Bull – Netherlands) won the season-ending Abu Dhabi Grand Prix 2020. The race was held in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates.
This was his second victory of the season and 10th victory of his career. The race was the 17th and final round of the 2020 Formula One World Championship.
Valtteri Bottas (Mercedes-Finland) stood second, followed by world champion Lewis Hamilton (Mercedes-Great Britain) at third place.
AIFF: It stands for the All India Football Federation. AIFF has formally announced its candidature to host the AFC Asian Cup 2027 and deliver a brighter future in India & across Asia.
A logo epitomized by the royal bengal tiger representing ambition, focus and spirit of the bid was revealed for India's 2027 campaign.
The slogan for the campaign is “Bright Future Together”.
Note: Qatar is the winner of the Asian Football Confederation (AFC) Asian Cup 2019.
Yogasana: The term "yoga" comes from a Sanskrit word meaning "union." Yoga combines physical exercises, mental meditation, and breathing techniques to strengthen the muscles and relieve stress. Asana is a body posture. Yogasana is an integral and important component of Yoga, which is psycho-physical in nature and popular across the globe for its efficacy in fitness and general wellness.
The origins of Yogasana competitions can be traced to the Indian Yoga tradition, where such competitions have been held for centuries.
Recently, the Ministry of AYUSH (Ayurveda Yoga and Naturopathy Unani Sidda Homoeopathy) and Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports formally recognized Yogasana as a competitive sport.
The announcement was made at a joint press conference held in New Delhi by the Union Minister of State for AYUSH Shripad Naik and Sports Minister Kiren Rijiju.
Competitions that will arise out of the recognition of Yogasana as a sport will enhance interest in Yoga among people around the globe.
The sports discipline of Yogasana is likely to have 51 medals in 4 events and 7 categories.
The proposed events for both men and women include Traditional Yogasana, Artistic Yogasana (Single), Artistic Yogasana (Pair), Rhythmic Yogasana (Pair), Free Flow/Group Yogasana, Individual All Round - Championship and Team Championship.
Government of India (GoI) is planning to include Yogasana as a Sport discipline in National Games, Khelo India and international sports events.
Arts
 Raja Prabha: Raja Parba the famous festival of Odisha has started being celebrated in Odisha on June 14, 2021.
Raja Prabha: Raja Parba the famous festival of Odisha has started being celebrated in Odisha on June 14, 2021.
It is a 3-day festival that celebrates womanhood.
About Raja Parba:
- Raja Parba is also known as Mithuna Sankranti.
- This festival falls in mid-June.
- It is a three-day-long festival of celebrating womanhood in Odisha.
- First day is called Pahili Raja; second day is Mithuna Sankranti while the third day is Bhudaaha or Basi Raja.
- Day before first day is called Sajabaja, during which house, kitchen including grinding stones are cleaned and spices are ground for three days. Women and girls take rest from work.
- The very first day of this long festival is considered to be the last day of the month Jestha (summers).
- Second day of the festival marks the beginning of solar month of Mithuna, on which season of rains starts.
- Fourth day is called Vasumati Snana or ceremonial bath of Bhudevi.
- This festival became more popular in medieval time as an agricultural holiday marking worship of Bhudevi.
- During 3 days, women don’t work.
Mythology:
- It is believed that the mother Goddess Earth or the divine wife of Lord Vishnu undergoes menstruation during the first three days.
- Mother Earth menstruates and prepares herself for future agricultural activities as the monsoon arrives.
Meaning:
- Name Raja came from Sanskrit word ‘Rajas’ which means menstruation.
- When a woman menstruates, she is called ‘Rajaswala’ or a menstruating woman.
Note: This festival is synonymous with varieties of cakes (pithas). Thus, Odisha Tourism Development Corporation (OTDC) has also launched a special programme named ‘Pitha on Wheels’.
Odisha:
- Odisha also formerly Orissa, is an Indian state located on the eastern coast of India.
- It neighbors the states of West Bengal and Jharkhand to the north, Chhattisgarh to the west and Andhra Pradesh to the south.
- It is an eastern Indian state on the Bay of Bengal.
- It is known for its tribal cultures and its many ancient Hindu temples. The Jagannath Temple in Puri is a very sacred and religious temple of Hindus.
- The capital of Odisha is Bhubaneswar.
- The Governor and the Chief Minister of Odisha are Ganeshi Lal and Naveen Patnaik respectively.
 Pulitzer Prizes 2021: The 105th class of Pulitzer Prize 2021 winners in Journalism, Books, Drama and Music were announced recently recognizing the best work in a year in which people isolated themselves because of a deadly pandemic and took to the streets over racial injustice.
Pulitzer Prizes 2021: The 105th class of Pulitzer Prize 2021 winners in Journalism, Books, Drama and Music were announced recently recognizing the best work in a year in which people isolated themselves because of a deadly pandemic and took to the streets over racial injustice.
Highlights:
- The Pulitzer Prizes in journalism were first awarded in 1917 and are considered the field’s most prestigious honour in the United States.
- Pulitzer Prizes awarded special citation to Darnella Frazier, the teenager who recorded the killing of George Floyd.
- The Star Tribune, of Minneapolis, won a Pulitzer Prize for breaking news for its coverage of the May 25, 2020, killing of Floyd and the resulting civil unrest that tore through the city.
Complete List of Winners:
| Sl. No. | Winner | Category |
|---|---|---|
| JOURNALISM | ||
| 1 | The New York Times | Public service |
| 2 | Wesley Morris of The New York Times | Criticism |
| 3 | Robert Greene of the Los Angeles Times | Editorial writing |
| 4 | Megha Rajagopalan, Alison Killing and Christo Buschek of BuzzFeed News | International Reporting |
| 5 | Staff of the Star Tribune, Minneapolis, Minn. | Breaking News Reporting |
| 6 | Matt Rocheleau, Vernal Coleman, Laura Crimaldi, Evan Allen and Brendan McCarthy of The Boston Globe | Investigative Reporting |
| 7 | Andrew Chung, Lawrence Hurley, Andrea Januta, Jaimi Dowdell and Jackie Botts of Reuters | Explanatory Reporting |
| 8 | Kathleen McGrory and Neil Bedi of the Tampa Bay Times | Local Reporting |
| 9 | Staffs of The Marshall Project; AL.com, Birmingham; IndyStar, Indianapolis; and the Invisible Institute, Chicago | National Reporting |
| 10 | Mitchell S. Jackson, freelance contributor, Runner’s World | Feature Writing |
| 11 | Michael Paul Williams of the Richmond (Va.) Times-Dispatch | Commentary |
| 12 | Photography Staff of Associated Press | Breaking News Photography |
| 13 | Emilio Morenatti of Associated Press | Feature Photography |
| 14 | Lisa Hagen, Chris Haxel, Graham Smith and Robert Little of National Public Radio | Audio Reporting |
| BOOKS, DRAMA, AND MUSIC | ||
| 15 | The Night Watchman by Louise Erdrich | Fiction |
| 16 | The Hot Wing King, by Katori Hall | Drama |
| 17 | Franchise: The Golden Arches in Black America, by Marcia Chatelain (Liveright/Norton) | History |
| 18 | The Dead Are Arising: The Life of Malcolm X by Les Payne and Tamara Payne | Biography or autobiography |
| 19 | Postcolonial Love Poem by Natalie Diaz | Poetry |
| 20 | Wilmington’s Lie: The Murderous Coup of 1898 and the Rise of White Supremacy by David Zucchino | General nonfiction |
| 21 | Stride, by Tania León (Peermusic Classical) | Music |
| 22 | Darnella Frazier, The teenager who recorded the killing of George Floyd | Special Citation |
About Pulitzer Prize:
- The Pulitzer Prize is an award for achievements in newspaper, magazine and online journalism, literature, and musical composition in the United States.
- It was established in 1917 by provisions in the will of American (Hungarian-born) Joseph Pulitzer who had made his fortune as a newspaper publisher and is administered by Columbia University in New York City.
- In twenty-two of the categories, each winner receives a certificate and a US $15,000 cash award (raised from $10,000 in 2017).
- The winner in the public service category is awarded a gold medal.
 Declassification of War Histories: The Minister of Defence Shri Rajnath Singh has recently approved a policy on declassification of War histories by the Ministry of Defence (MoD).
Declassification of War Histories: The Minister of Defence Shri Rajnath Singh has recently approved a policy on declassification of War histories by the Ministry of Defence (MoD).
Key Features of the Policy:
- The policy requires MoD organizations, such as the army, navy, air force, coast guard, Integrated Defence Staff and Assam Rifles, to transfer their records -- including war diaries, letters of proceedings and operational record books – to the ministry’s History Division for proper upkeep, archival and recording of history.
- The responsibility for declassification of records rests with the respective organisations as specified in the Public Record Act 1993 and Public Record Rules 1997, as amended from time to time.
- Under this policy, Ministry of Defence (MoD) will archive, declassify, compile and publish war and operations histories.
- However, declassification of older wars like of 1962 war is not automatic.
- Declassification will be taken up on case-by-case basis by a committee which will be constituted under the new policy.
- As per policy, records should ordinarily be declassified in 25 years.
- Records which are older than 25 years should be appraised by archival experts and transferred to National Archives of India after histories of war or operations have been compiled.
Constitution of a Committee:
- The policy mandates constitution of a committee.
- As per policy, a committee will be constituted which will be headed by Joint Secretary of MoD.
- It will comprise of representatives of Services, Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) and prominent military historians for compilation of war & operations histories.
- The History Division of the committee will be responsible to coordinate with various departments while compiling, for approval & publishing of war and operations histories.
- War/operations histories are to be compiled within 5 years.
- The above-mentioned Committee should be formed within two years of completion of war/operations.
- Thereafter, collection of records and compilation should be completed in three years and disseminated to all concerned.
Will all reports on wars be public?
- Committee will take a view on earlier wars and operations.
- Compiled history on wars and operations will be consumed internally first, within five years.
- After that, the committee may decide to publicly release whole or parts of it based on the sensitivity of subject.
Background:
- The Proposal of having war histories written with clear cut policy on declassification was recommended by Kargil Review Committee headed by K Subrahmanyam and N.N. Vohra Committee with a purpose to analyse lessons learnt and prevent future mistakes.
 Fakir Mohan Senapati: He was an Indian writer, poet, philosopher and social reformer. June 14, 2021 was his 103rd death anniversary.
Fakir Mohan Senapati: He was an Indian writer, poet, philosopher and social reformer. June 14, 2021 was his 103rd death anniversary.
He passed away on June 14, 1918.
About Fakir Mohan Senapati:
- Fakir Mohan Senapati (13 January 1843 – 14 June 1918) often referred to as Utkala Byasa Kabi (Odisha's Vyasa).
- He is regarded as the father of Odia nationalism and modern Odia literature.
- He played a leading role in establishing the distinct identity of Odia language.
- He is known to have introduced novel writing, short story, and autobiography genres in Odia literature.
Key works by him:
- Chha Maana Atha Guntha is the first Indian novel to deal with the exploitations of landless peasants by the feudal Lord.
- It was written much before the October revolution of Russia or much before the emerging of Marxist ideas in India.
- His "Rebati" (1898) is widely recognized as the first Odia short story.
- He wrote a long poem, Utkala Bhramanam, that first appeared in 1892.
Economics
 44th meeting of GST Council: On June 12, 2021, the 44th meeting of Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council was chaired by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman where several changes in GST rate have been made which would be applicable till September 30, 2021.
44th meeting of GST Council: On June 12, 2021, the 44th meeting of Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council was chaired by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman where several changes in GST rate have been made which would be applicable till September 30, 2021.
Key Highlights:
- The following decisions were taken at the meeting:
- GST Council has accepted recommendations of Group of Ministers (GoM) which was set up to look on tax relief on Covid-19 medical supplies.
- It decided to waive the tax levied on two critical drugs against COVID-19 and mucormycosis — tocilizumab and amphotericin B — and reset the tax rate to 5% for 14 major pandemic relief items, till September 30.
- The 5% GST levied on vaccines was left unchanged.
- GST rates on anticoagulants such as Heparin and Remdesivir have been cut from 12% to 5%.
- Ambulances, which are currently taxed at 28%, will attract a GST levy of 12%.
- GST rates on gas or electric or other furnaces used in crematorium including the installation charges have been reduced to 5% from 18%.
- For oxygen concentrators, medical grade oxygen and related devices such as ventilators, BiPAP machines, the GST rate has also been brought down to 5% from 12%.
- The same reduction has been approved in the levies on COVID-testing kits and pulse oximeters.
- The 5% rate will apply to personal imports of oxygen concentrators as well as pulse oximeters.
- The 18% GST payable on hand sanitizers has been reduced to 5%.
- 5% tax would be applied on ventilator masks or cannula or helmets.
Background:
- Last meeting of GST Council was held on May 28, 2021 which had recommended full exemption from IGST on several specified COVID-19 related goods like medical oxygen, oxygen concentrators etc.
- Following the meeting, Council decided to constitute a Group of Ministers (GoM) to recommend on rates for individual items.
.jpg) Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS): The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently announced that the scope of Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS) will be expanded by August 31 2021.
Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS): The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently announced that the scope of Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS) will be expanded by August 31 2021.
Highlights:
Scope of BBPS has been expanded by adding ‘mobile prepaid recharges’ as a biller category.
This move aims to help millions of prepaid phone subscribers across India.
Background:
- The scope and coverage of BBPS were expanded in September 2019.
- It then included all categories of billers raising recurring bills as eligible participants voluntarily.
- It did not included billers of mobile prepaid recharges.
- Before 2019, facility of payment of recurring bills through BBPS was available only to five sectors viz, direct to home (DTH), gas, electricity, water and telecom.
About BBPS:
- BBPS refers to Bharat Bill Payment System.
- BBPS functions under the aegis of the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- It is an integrated bill payment system offering interoperable bill payment service to customers online and through a network of agents on ground.
- It provides for multiple payment modes and instant confirmation of payment.
About NCPI:
- NCPI refers to the National Payment Corporation of India.
- NPCI is an umbrella organization for all retail payments in India.
- It was founded in 2008.
- It has been incorporated as a Not for Profit Company under the provisions of Section 25 of Companies Act 1956 (now Section 8 of Companies Act 2013).
- It is an initiative of Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Indian Banks Association (IBA) under the provisions of the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 for creating a robust Payment & Settlement Infrastructure in India.
- It is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra.
- The current MD & CEO is Dilip Asbe.
 Inland Vessel Bill 2021: The Union Cabinet on recently gave the nod to the Inland Vessels Bill, 2021, which will replace the Inland Vessels Act, 1917.
Inland Vessel Bill 2021: The Union Cabinet on recently gave the nod to the Inland Vessels Bill, 2021, which will replace the Inland Vessels Act, 1917.
- The Bill will regulate safety, security and registration of inland vessels.
Key Features of the Bill:
- A key feature of the Bill is a unified law for the entire country, instead of separate rules framed by the States.
- The certificate of registration granted under the proposed law will be deemed to be valid in all States and Union Territories, and there will be no need to seek separate permissions from the States.
- The Bill provides for a central database for recording the details of vessel, vessel registration, crew on an electronic portal.
- Non-mechanically propelled vessels will also require to be enrolled at district, taluk or panchayat or village level.
- It enlarges the definition of ‘inland waters’, by including tidal water limit and national waterways declared by the Central Government.
- It also deals with pollution control measures of Inland Vessels.
- This Bill directs the Central Government to designate a list of chemicals, substances, etc. as pollutants.
- As of now, total 4,000 km inland waterways have been operationalized.
Inland Water Transport (IWT) in India:
- India has about 14,500 km of navigable waterways which comprise of rivers, canals, backwaters, creeks, etc.
- It is a fuel-efficient and environment-friendly mode of transportation.
- Under National Waterways Act 2016, 111 waterways have been declared as National Waterways.
- The Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) is implementing the Jal Marg Vikas Project (JMVP) at an estimated cost of ₹5369.18 crores for capacity augmentation of navigation on the Haldia-Varanasi stretch of Ganga (part of NW-1) with the technical and financial assistance of the World Bank.
About Inland Waterways Authority (IWT) of India:
- It came into existence on 27th October 1986 for development and regulation of inland waterways for shipping and navigation.
- It primarily undertakes projects for development and maintenance of IWT (Inland Water Transport) infrastructure on national waterways through grants received from the Ministry of Shipping.
- It is headquartered at Noida (Uttar Pradesh).
 FAME II Amendment: Ministry of Heavy Industry recently announced major amendments in ongoing FAME-II (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles in India) scheme.
FAME II Amendment: Ministry of Heavy Industry recently announced major amendments in ongoing FAME-II (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles in India) scheme.
The Ministry has fixed incentives for India-made electric two-wheelers.
Highlights:
- With the recent amendments on price side and subsidies government aims to promote electric two-wheeler usage across India.
- The second phase of FAME India Scheme focuses on supporting electrification of public and shared transportation and aims to support electrification through subsidies for electric vehicles, including buses, passenger cars and two-wheelers.
- Out of total budgetary support, about 86 percent of fund has been allocated for Demand Incentive so as to create demand for xEVs in the country.
- Reduction is price will help in EV adoption and strengthen government’s plans of making India an electric vehicle nation by 2030.
What are the recent amendments?
- The subsidy rate for electric two-wheelers has been increased to Rs 15,000/kWh, which is nearly 40 percent of vehicle cost.
- Earlier, subsidy rate for electric two-wheelers was Rs 10,000/kWh
Procurement of EVs:
- Central government will procure electric buses and three-wheelers on large scale.
- EESL will be directed to procure three lakh electric rickshaws and has been told to aggregate demand for electric buses across nine major cities namely, Surat, Pune, Mumbai, Hyderabad, Chennai, Ahmedabad, Kolkata, Delhi and Bengaluru.
FAME India Scheme:
- This scheme was launched in 2015 with the aim of incentivising vehicle segments including 2-Wheeler, Passenger 4-Wheeler Vehicle, 3-Wheeler Auto, Light Commercial Vehicles and Buses.
- It also covers Hybrid & Electric technologies such as Mild Hybrid, plug in Hybrid, Strong Hybrid and Battery Electric Vehicles.
- This scheme is monitored by Department of Heavy Industries.
- It has four focus areas viz., Technology development, Demand Creation, Charging Infrastructure and Pilot Projects.
 Simplified Registration Process for MSMEs: The Government of India (GoI) has simplified the process of registration for the Micro, Medium and Small Enterprises, MSMEs.
Simplified Registration Process for MSMEs: The Government of India (GoI) has simplified the process of registration for the Micro, Medium and Small Enterprises, MSMEs.
Key Points:
- MSMEs will only require PAN and Aadhaar for registration.
- Once the MSMEs are registered, they will be getting priority and finance.
- No new training will be required to small units in fields of entrepreneurship and other related aspects.
- In order to boost the economic activities of MSMEs, the Government had announced a special incentive package of 20 lakh crore rupees under Aatmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
About MSME:
- MSMEs are considered as engine of economic growth which are involved in promoting equitable development.
- They comprise of 90% of total enterprises and generate highest rates of employment growth.
- They require low investment and have operational flexibility & capacity to develop appropriate indigenous technology.
- MSME is second largest employment generating sector after agriculture, providing employment to 120 million persons in country.
- It contributes about 6.11% of manufacturing GDP and 24.63% of GDP from service activities.
- It also contributes 45% of overall exports from India.
- Inclusive growth is promoted by MSMEs as it provides employment opportunities in rural areas.
Growth of MSMEs in India:
- Campaigns such as Start-up India, Skill India, Digital India and Make in India were launched with the aim of providing MSME players a level playing field in a bid to enhance productivity.
- Increasing internet penetration and tie-ups with non-banking finance companies are also facilitating growth in MSME sector.
44th GST Council: The 44th GST Council recently met under the Chairmanship of Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman.
Key highlights:
- The Council in its meeting has decided to reduce the GST rates on various items being used in Covid-19 relief and management till 30th September, 2021.
- It was decided to waive the tax levied on two critical drugs against COVID-19 and mucormycosis — tocilizumab and amphotericin B — and reset the tax rate to 5% for 14 major pandemic relief items.
- The 5% GST levied on vaccines was left unchanged.
- The GST rate on Remdesivir and anti-coagulants like Heparin has been reduced from 12% to 5%.
- Ambulances, which are currently taxed at 28%, will attract a GST levy of 12%, while temperature checking equipment and electric furnaces used in crematoriums will attract a 5% GST instead of 18%.
- For oxygen concentrators, medical grade oxygen and related devices such as ventilators, BiPAP machines, the GST rate has also been brought down to 5% from 12%.
- The same reduction has been approved in the levies on COVID-testing kits and pulse oximeters.
- The 5% rate will apply to personal imports of oxygen concentrators as well as pulse oximeters, while the 18% GST payable on hand sanitizers has been reduced to 5%.
Defence
.jpg) Ordnance Factory Board (OFB): The Union Cabinet has approved the corporatization of the British-era Ordnance Factory Board (OFB) located in Kolkata which has 41 factories.
Ordnance Factory Board (OFB): The Union Cabinet has approved the corporatization of the British-era Ordnance Factory Board (OFB) located in Kolkata which has 41 factories.
Key Points:
- The 246-year old OFB will be dissolved, and replaced seven new fully government-owned corporate entities on the lines of Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSU).
- The corporatization process by the cabinet would be supervised by the Empowered Group of Ministers (EGM) chaired by Rajnath Singh and this EGM would address any issue that may arise during the course of the implementation.
- The creation of the entities will be 100 percent owned by the government.
- There would be no change in the service conditions of the OFB employees.
- All IFB employees (Group A, B, and C) from different production units will be transferred to the corporate entities on deemed deputation for an initial period of 2 years.
- The transformation is likely to take place by the end of the year.
Purpose of Restructuring OFB:
- This decision was taken from the perspective of becoming Atmanirbhar in terms of national security.
- The move to replace the OFB with the seven corporate entities will allow these companies autonomy as well as help improve accountability and efficiency.
- The restructuring is aimed at the following:
- Transforming the ordnance factories into productive and profitable assets
- Deepening their specialization in product range
- Enhancing competitiveness
- Improving quality
- Cost-efficiency
- Seven entities will be responsible for different verticals of products that are being produced by 41 ordnance factories.
- Ammunition and Explosives group will be engaged in production of ammunition.
- Vehicles group will engage in production of defence mobility and combat vehicles.
About Ordnance Factory Board (OFB):
- Ordnance Factory Board (OFB) consisting of the Indian Ordnance Factories is a Government agency under the control of department of defence production (DDP) Ministry of Defence (MoD), Government of India (GoI).
- OFB is a conglomerate of 41 Factories, 9 Training Institutes, 3 Regional Marketing Centres and 4 Regional Controller of Safety.
- It is headquartered at Kolkata.
- It is the world's largest government-operated production organisation and the oldest organization in India.
- It is often called the "Fourth Arm of Defence" and the "Force Behind the Armed Forces" of India.
- It is the 35th largest defence equipment manufacturer in the world, 2nd largest in Asia, and the largest in India.
- It is engaged in research, development, testing, production, marketing and logistics of the product range across air, land and sea systems.
- Under the ‘Make-In-India’ initiative, Ordnance Factories have made considerable progress with the development of the 155 mm 45 calibre ‘Dhanush’ and the upgrading of existing 130 mm M-46 artillery guns to 155 mm 45 calibre ‘Sharang’ gun systems.
Origin:
- The first Indian ordnance factory can trace its origins back to the year 1712 when the Dutch Ostend Company established a Gun Powder Factory in Ichhapur.
- In 1787, another gunpowder factory was established at Ichapore; it began production in 1791, and the site was later used as a rifle factory, beginning in 1904.
- On 18th March 1801, the first Ordnance Factory, now known as the ‘Gun and Shell Factory’ at Cossipore was established under the aegis of its corporate headquarters Ordnance Factory Board (OFB) in Kolkata and production began on 18 March 1802.
- This is the oldest ordnance factory in India still in existence.
Now, OFB will be replaced by 7 new Defence PSU.
Note: Every year, 18 March is celebrated as the Ordnance Factory Day in India.
 ADMM-Plus: The Defence Minister Rajnath Singh recently addressed the ADMM-Plus through video conferencing; says terrorism & radicalization gravest threats to peace and security in world.
ADMM-Plus: The Defence Minister Rajnath Singh recently addressed the ADMM-Plus through video conferencing; says terrorism & radicalization gravest threats to peace and security in world.
Note: ADMM-Plusrefers to The ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting Plus.
Highlights:
- Addressing the ADMM-Plus, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh hailed the Indian values of ‘Vasudhaive Kutumbakam’ and ‘Sarve Bhavantu Sukhinah’ and urged every country to develop an outlook envisaging world as one family to encourage shared approach.
- He highlighted India’s views on dealing with major security challenges in the region. He said, terrorism and radicalization are the gravest threats to peace and security in the world.
- He underlined the importance of need based respect for sovereignty and territorial integrity of nations, peaceful resolutions of disputes through dialogue and adherence to International rules and laws.
- He also reiterated India’s support to freedom of navigation and over-flight for all in International waters in accordance with the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS).
- He called for a multi-stakeholder approach, guided by democratic values for safe digital connectivity with due respect to sovereignty of countries.
- He said that as a founding member of the Heads of Asian Coast Guard Agencies Meeting, India seeks to enhance capacity building through collaboration in the areas of Maritime Search and Rescue.
About ADMM-Plus:
- The ADMM-Plus is a forum comprising 10 ASEAN member countries and 8 dialogue partner nations including India, China, Australia, Japan, New Zealand, South Korea, Russia and the United States.
- The 15th ASEAN Defence Ministers’ Meeting is being hosted by Brunei as it is the chair of the ASEAN grouping this year.
- The ADMM-Plus forum aims to strengthen security and defence cooperation for peace, stability and development in the region.
- The inaugural ADMM-Plus was convened in Hanoi, Vietnam in 2010.
 SIPRI Yearbook 2021: The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) recently launched the findings of SIPRI Yearbook 2021.
SIPRI Yearbook 2021: The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) recently launched the findings of SIPRI Yearbook 2021.
Highlights:
The SIPRI Yearbook 2021 assesses the current state of armaments, disarmament and international security.
The 51st edition of the Yearbook reveals an unbroken deterioration within the conditions for international stability.
Findings:
- In accordance with the “SIPRI Yearbook 2020-Armaments, Disarmament and International Security” from 2019 there’s a rise within the nuclear weapons stockpile of India and China.
- However India’s overall possession of nuclear weapons is a smaller amount than half Beijing’s and also slightly less than what Pakistan possesses.
- The nine nuclear armed states — the U.S., Russia, the U.K., France, China, India, Pakistan, Israel and North Korea — together possessed an estimated 13,080 nuclear weapons at the start of 2021.
- Russia and the U.S. together possessed over 90% of global nuclear weapons.
- India possessed an estimated 156 nuclear warheads at the start of 2021, compared with 150 at the start of last year, while Pakistan had 165 warheads, up from 160 in 2020.
- China’s nuclear arsenal consisted of 350 warheads, up from 320 at the start of 2020.
About the decrease in nuclear arsenals:
- The nine nuclear-armed states together possessed an estimated 13,080 nuclear weapons at the start of 2021.
- This marked a decrease from the 13,400 possessed at the beginning of 2020.
- Despite this overall decrease, the estimated number of nuclear weapons currently deployed with operational forces increased to 3825, from 3720 last year.
- Around 2000 of these—nearly all of which belonged to Russia or the USA—were kept in a state of high operational alert.
What is SIPRI?
- The full form of SIPRI is Stockholm International Peace Research Institute.
- SIPRI was established in 1966.
- It is an independent international institute dedicated to research into conflict, armaments, arms control and disarmament.
- SIPRI provides data, analysis and recommendations, based on open sources, to policymakers, researchers, media and the interested public.
.jpg) Indian Navy & EUNAVFOR Joint Exercise: The Indian Navy and European Union Naval Force (EUNAVFOR) recently conducted their first ever exercise in Gulf of Aden.
Indian Navy & EUNAVFOR Joint Exercise: The Indian Navy and European Union Naval Force (EUNAVFOR) recently conducted their first ever exercise in Gulf of Aden.
This two-day exercise ended on June 19, 2021.
Key Points:
- Indian Naval Ship Trikand participated in the exercise, which is currently deployed for anti-piracy operations.
- Total of five warships from four navies participated in the exercise held on 18th & 19th
- Other warships that participated in exercise include Italian Navy Ship ITS Carabinere, two French Navy Ship FS Tonnerre & FS Surcouf and Spanish Navy Ship ESPS Navarra.
- A virtual “Information Sharing Exercise” is also being conducted between Indian Navy Information Fusion Centre in Indian Ocean Region and Maritime Security Centre in Horn of Africa
About the exercise:
- The two-day exercise witnessed high tempo-naval operations at sea such as advanced air defence & anti-submarine exercises, cross deck helicopter operations, boarding operations, tactical manoeuvres, underway replenishment, search & rescue etc. Ships of four navies endeavour to enhance their war-fighting skills and their ability to promote peace, security and stability in maritime domain.
- EUNAVFOR and Indian Navy also saw eye-to-eye on multiple issues such as counter piracy operations and protection of vessels which were deployed under charter of World Food Programme (UN WFP).
Indian Navy and EUNAVFOR:
- Both the navies conduct regular interaction through SHADE (Shared Awareness and Deconfliction) meetings which is held annually at Bahrain.
- It highlights their shared values of ensuring freedom of seas.
Arts
Hindi Diwas 2021:
India celebrates Hindi Diwas, also known as Hindi Day, on September 14 every year to commemorate the adoption of Hindi in the Devanagari script as one of the official languages of the nation.
Key Highlights:
-
One of the reasons behind celebrating this day is to prevent the increasing trend of the English language in the nation and to promote the Hindi language.
-
Hindi is the 3rd most spoken language in the world.
Note: India has two official languages. Besides Hindi, English is also considered an official language in India.
History of Hindi Diwas:
-
The Constituent Assembly of India accepted Hindi, written in Devanagari script, as the official language of India on September 14, 1949.
-
Hindi language along with English was adopted out of the 22 recognized Indian languages under Article 343 (1).
-
Out of the 22 languages of the 8th Schedule of the Constitution of India, Hindi is used at the Union level.
-
Officially, the first Hindi Day was celebrated on September 14, 1953.
-
The main reason behind adopting Hindi as one of the official languages was to simplify administration in a nation with multiple languages.
-
This day also marks the birth anniversary of Beohar Rajendra Simha who contributed largely towards making Hindi the official language of India.
-
Several activists, poets, and writers made huge efforts to make Hindi as the official language. Among these are Maithili Sharan, Kaka Kalelkar, Beohar Rajendra Simha, Hazari Prasad Dwivedi and Seth Govind Das.
Key Points Hindi:
-
Hindi belongs to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European family of languages.
-
The word Hindi derives its name from the Persian word Hind.
-
In the 11th century, Turkish invaders named the language Hindi, meaning ‘land of the Indus River’.
-
Literary Hindi, written in the Devanagari script, has been strongly influenced by Sanskrit.
-
Its standard form is based on the Khari Boli dialect, found to the north and east of Delhi.
-
Hindi is the lingua franca of the Hindi belt.
-
Braj Bhasha, which was an important literary medium from the 15th to the 19th century, is often treated as a dialect of Hindi, as are Awadhi, Bagheli, Bhojpuri, Bundeli, Chhattisgarhi, Garhwali, Haryanawi, Kanauji, Kumayuni, Magahi, and Marwari.
-
In India, Hindi is spoken as a first language by nearly 425 million people and as a second language by some 120 million more.
-
Significant Hindi speech communities are also found in South Africa, Mauritius, Bangladesh, Yemen, and Uganda.
Significance:
-
Hindi day not only marks the celebration of the adoption of Hindi as an official language but also aims to honor and promote the language with several cultural festivals and awards such as Rajbhasha Gaurav Puraskar and Rajbhasha Kirti Puraskar across the country.
Difference between Hindi Divas and World Hindi Day:
-
World Hindi Day, also called Vishwa Hindi Divas it is not similar to the Hindi Diwas.
-
The National Hindi Day or Hindi Diwas is celebrated every year on September 14 to commemorate the day of adoption of Hindi as an official language in India on September 14, 1949.
-
While the World Hindi Day is observed on January 10 to mark the anniversary of the first World Hindi Conference that took place in 1975 in Nagpur, Maharashtra.
-
However, both the days aim at the promotion and celebration of Hindi as a language of India even if they have different histories and significance.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Battle of Saragarhi: September 12, 2021 marks the 124th anniversary of the Battle of Saragarhi that has inspired a host of armies, books and films, both at home and abroad.
Note: The Indian Army's 4th battalion of the Sikh Regiment commemorates the battle every year on 12 September, as Saragarhi Day.
What makes this battle unique?
-
It considered one of the finest last stands in the military history of the world.
About Battle of Saragarhi:
-
The Battle of Saragarhi was fought on 12 September 1897.
-
This battle was a last-stand battle fought before the Tirah Campaign between the British Raj and Afghan tribesmen.
-
Twenty-one soldiers from British Army were pitted against over 8,000 Afridi and Orakzai tribals but they managed to hold the fort for seven hours.
-
Though heavily outnumbered the soldiers of 36th Sikhs (now 4 Sikh), led by Havildar Ishar Singh, fought till their last breath, killing 200 tribals and injuring 600.
Importance of Saragarhi:
-
Saragarhi was the communication tower between Fort Lockhart and Fort Gulistan.
-
The two forts in the rugged North West Frontier Province (NWFP), now in Pakistan, were built by Maharaja Ranjit Singh but renamed by the British.
-
Saragarhi helped to link up the two important forts which housed a large number of British troops in the rugged terrain of NWFP.
The legacy:
-
Making a departure from the tradition of not giving gallantry medals posthumously, Queen Victoria awarded the 21 dead soldiers — leaving out the non-combatant — of the 36th Sikh the Indian Order of Merit (comparable with the Victoria Cross) along with two ‘marabas’ (50 acres) and Rs 500 each.
-
The British, who regained control over the fort after a few days, used burnt bricks of Saragarhi to build an obelisk for the martyrs.
-
They also commissioned gurdwaras at Amritsar and Ferozepur in their honour.
Books ad Authors:
Human Rights and Terrorism in India: A book titled 'Human Rights and Terrorism in India' is authored by BJP MP Subramanian Swamy.
About the Book:
-
His book traces how the combating of terrorism can be harmonised with human and fundamental rights within reasonable restrictions that are permitted by the Constitution and upheld by the Supreme Court.
-
It is the theses of this study that to deter terror, India as a nation must foster a concept of identity.
-
The release of three dreaded terrorists in exchange for hijacked Indian Airlines passengers in Afghanistan’s Kandahar in 1999 is the “worst capitulation” to terrorists in India”s modern history.
Vishwakarma Jayanti: Vishwakarma Jayanti was celebrated on September 17, 2021.
Highlights:
It is an important festival celebrated by the Hindu community.
On this occasion, workers of factories and industrial areas worship their tools and offer prayers to Lord Vishwakarma to keep their livelihoods secure.
About Lord Vishwakarma:
-
According to legends, Lord Vishwakarma is the son of Vastu Dev and Goddess Angisri.
-
Vishwakarma, the Hindu god, is a craftsman diety and is considered as the divine engineer, craftsman of the whole universe.
-
As per Hindu religious belief, he is believed to be the creator of the world, the Swayambhu.
-
Vishwakarma Jayanti, the auspicious day dedicated to him falls on Kanya Sankranti or Bhadra Sankranti, which comes when Sun transits from zodiac sign Leo to Virgo. As per the Gregorian calendar, the date of Vishwakarma Puja almost remains the same every year in mid-September.
Significance:
-
Vishwakarma Puja is celebrated in honor of Lord Vishwakarma.
-
He was the divine architect who constructed the kingdom of Lord Krishna, in the holy city Dwarka.
-
He also constructed Indraprastha, the Maya Sabha for the Pandavas and many more palaces.
-
Lord Vishwakarma was known to be the creator of many fabulous weapons for the gods such as Lord Shiva's Trishul, Indra's Vajra (thunderbolt) and Lord Vishnu's Sudarshana Chakra.
-
He is also credited with Sthapatya Veda, the science of architecture and mechanics.
-
He is represented as being the source of all prosperity and is considered both the divine engineer and the divine architect of the universe.
-
The famous Jagannath temple in Puri is also believed to be his creation.
The day is mainly celebrated in the Eastern part of the country in states such as West Bengal, Assam, Odisha, Tripura, Bihar, and Jharkhand. India's neighbour, Nepal also celebrates Vishwakarma Puja.
Economics
T+1 settlement system:
Capital markets regulator Securities and Exchange Board of India (Sebi) recently introduced ‘T+1' (trade day plus one) cycle of settlements for equities.
This system has been introduced for completion of share transactions on optional basis in a move to enhance market liquidity.
What is T+1 Settlement System?
In the new system, due to come into force from January 1, 2022, once a trade is executed, the settlement will be carried out within one day as against the current system of T+2, wherein it takes two days.
Presently, trades on the Indian stock exchanges are settled in two working days after the transaction is done (T+2).
If stock Markus exchanges agree to the proposal for the T+1 settlement system made by the Sebi, investors will get money for shares they sold or bought in their accounts faster, and in a safer and risk free environment.
In April 2002, stock exchanges had introduced a T+3 rolling settlement cycle.
This was shortened to T+2 from April 1, 2003.
What has Sebi allowed?
Sebi has allowed stock exchanges to start the T+1 system as an option in place of T+2.
If it opts for the T+1 settlement cycle for a scrip, the stock exchange will have to mandatorily continue with it for a minimum 6 months.
Thereafter, if it intends to switch back to T+2, it will do so by giving one month’s advance notice to the market.
Any subsequent switch (from T+1 to T+2 or vice versa) will be subject to a minimum period.
A stock exchange may choose to offer the T+1 settlement cycle on any of the scrips, after giving at least one month’s advance notice to all stakeholders, including the public at large.
Why T+1 settlement?
According to a Sebi paper, a shortened cycle not only reduces settlement time but also reduces and frees up the capital required to collateralize that risk.
T+1 also reduces the number of outstanding unsettled trades at any instant, and thus decreases the unsettled exposure to Clearing Corporation by 50%.
The narrower the settlement cycle, the narrower the time window for a counterparty insolvency/bankruptcy to impact the settlement of a trade.
Systemic risk depends on the number of outstanding trades and concentration of risk at critical institutions such as clearing corporations, and becomes critical when the magnitude of outstanding transactions increases.
How does it work?
If an investor sells shares, say on Wednesday then settlement of the trade takes place in two working days (T+2).
The broker who handles the trade will get the money on Friday, but will credit the amount in the investor’s account only by Saturday. In effect, the investor will get the money only after three days.
However, in T+1, settlement of the trade takes place in one working day and the investor will get the money on the following day.
The move to T+1 will not require large operational or technical changes by market participants, nor will it cause fragmentation and risk to the core clearance and settlement ecosystem.
GI Tag for Sirarakhong Chilli and Tamenglong Orange: The famous Sirarakhong Chilli and Tamenglong Orange have now received the Geographical Index (GI) tag.
Note: The GI status is an indication that identifies goods as produced from a particular area which has special quality attributable to its geographical origin.
Highlights:
This was announced by Manipur Chief Minister, N. Biren Singh while speaking at the inaugural function of the Van Dhan Vikas Kendra (VDVK) Mela, 2021, organized by the State Forest Department.
Key Points
- Hathei chilli, one of the best varieties of chillies with a distinct flavour and colour, grows in Sirarakhong village in Ukhrul district.
- This chilli is considered to be God’s gift and the pride of the region.
- It flourishes only in the hills of Mahadev surrounding the remote Tangkhul Naga.
- On the other hand, Tamenglong orange, a species of the mandarin family, is a unique fruit crop found mostly in Tamenglong district.
- It contributes over 50% of the state’s annual production.
- It is famous especially for its well blended sweetness and acidic taste.
Background:
- Manipur Organic Mission Agency (MOMA) applied for GI tags for Tamenglong orange and Sirarakhong Hathei chilli in 2019.
- Manipur has been promoting these two produce by celebrating the Orange Festival every December and Sirarakhong Hathei festival every August for over a decade now.
GI Tags for Manipur produce:
- Manipur black rice, scented glutinous rice which has been cultivated in the state over centuries and it is characterised by its special aroma, bagged GI tag in May 2020.
- Earlier Kachai Lemon, a unique lemon variety which grows at Kachai village in Ukhrul district, was also accorded GI registration tag.
Additional News:
- Prior to the inauguration of the fair, the Chief Minister also inaugurated a VDVK Outlet and Extension Centre at Forest Department Head Office, Sanjenthong, where products manufactured by different Vandhan Kendras of the State are showcased and sold.
Achievements:
- Manipur has emerged as a model State for the scheme in the whole country.
- Manipur was conferred with five national awards during the first Van Dhan Annual Awards, 2020 21 at 34th Foundation Day celebration of TRIFED, Ministry of Tribal Affairs on August 8, 2021.
- About 41,908 women of 3320 SHGs had been benefited under the scheme in Manipur so far.
About Manipur:
- Manipur is a state in northeastern India.
- It is bounded by the Indian states of Nagaland to the north, Mizoram to the south, and Assam to the west; Myanmar lies to its east.
- Manipur literally means, “the jeweled land”.
- The exquisite state is known for its traditions, dance forms, music and sumptuous cuisine.
- Most of the state is covered in forests, which houses some of the rarest species of plants and animals.
- It was formed on 21 January 1972.
- Its Capital is Imphal.
- The current Governor and the Chief minister of Manipur are Najma Heptulla and Biren Singh respectively.
What is a geographical indication?
- A geographical indication (GI) is a name or sign used on certain products which corresponds to a specific geographical location or origin (e.g., a town, region, or country).
- Geographical indications are typically used for agricultural products, foodstuffs, wine and spirit drinks, handicrafts, and industrial products.
Who accords and regulates Geographical Indications?
- GI is part of the intellectual property rights (IPRs) that comes under the Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property.
- At the International level, GI is governed by the World Trade Organisation’s (WTO’s) Agreement on Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS).
- GIs have been defined under Article 22 (1) of the WTO Agreement on Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) Agreement as: "Indications which identify a good as originating in the territory of a member, or a region or a locality in that territory, where a given quality, reputation or characteristic of the good is essentially attributable to its geographic origin."
- In India, as a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO), Geographical Indications registration is administered by the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 which came into force with effect from 15 September 2003.
Note: The first product in India to be accorded with GI tag was Darjeeling tea in the year 2004 05.
Benefits of GI Registrations:
The following are the benefits of Geographical Indication registration:
- Prevents unauthorized use of GI tag products by others.
- Legal protection to the products.
- Promotes the economic prosperity of producers of GI tag goods by enhancing their demand in national and international markets.
- It helps consumers to get quality products of desired traits and is assured of authenticity
45th GST Council Meeting: The 45th Goods and Services Tax (GST) Council meeting was recently held in Lucknow.
Highlights:
- It was held under the chairmanship of the Union Finance & Corporate Affairs Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman.
- Finance Ministers from all states will attend the meeting.
- At the meet, discussions over bringing petrol & diesel under the GST regime were discussed and several key decisions were also taken.
Key Points of the Meeting:
- The issue of Petrol & Diesel was discussed about which the Kerala High Court had questioned.
- However, The GST Council has decided not to put petrol and diesel under GST.
- The consumers will have to keep paying the Compensation Cess levied on products like automobiles till March 2026 instead of July 2022 as originally envisaged at the time of rolling out the indirect tax regime.
- Concessional GST rates on Covid 19 related medicines were also announced, which are applicable till September 30. Now, the date has been extended till December 31, 2021
Key Decisions:
- Concessional GST rates on drugs used in COVID 19 treatment extended till Dec 31.
- Tax rates on medicines used in cancer treatment was cut from 12 pc to 5 pc.
- GST rate on biodiesel for blending it with diesel was reduced from 12 pc to 5 pc.
- Inverted duty structure on footwear and textiles will be corrected from January 1, 2022.
- It is not the correct time to bring petroleum products under GST regime.
- E commerce operators like Zomato and Swiggy will come under GST regime.
- They are now required to pay GST on restaurant service supplied through them, since tax is charged at point of delivery. Earlier, restaurants used to pay the tax.
- A Group of state ministers (GoM) will be established to look after the rate rationalization related issues.
- GoM will be making recommendations in 2 months.
- Another GoMs will be set up in order to look after issues of e way bills, plugging of loopholes, FASTAGs, compliances, technology, composition schemes etc.
UPI & PayNow: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) recently announced a project to link their respective fast payment systems — Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and PayNow.
Key Points:
- The linkage is targeted to be operationalised by July 2022.
- The UPI PayNow linkage will enable users of each of the two fast payment systems to make instant, low cost fund transfers on a reciprocal basis without a need to get onboarded onto the other payment system.
- India uses Unified Payments Interface (UPI) as a fast payment method while Singapore uses the PayNow system.
About UPI:
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI) is India’s mobile based, ‘fast payment’ system.
- It facilitates customers to make round the clock payments instantly using a Virtual Payment Address (VPA) created by the customer.
- This eliminates the risk of sharing bank account details by the remitter.
- UPI supports both Person to Person (P2P) and Person to Merchant (P2M) payments as also it enables a user to send or receive money.
About PayNow:
- PayNow is the fast payment system of Singapore that enables peer to peer fund transfer service.
- PayNow supports nine participating banks and three Non Bank Financial Institutions (NFIs).
Digital Agriculture Mission: The Agriculture Ministry recently signed agreements with Reliance's Jio Platforms, ITC, Cisco, NCDEX e Markets and Ninjacart.
- The agreements were signed to develop agritech solutions using its National Farmers Database, which includes information of 5.5 crore farmers.
Key Details:
- This is part of an effort to modernize the agriculture sector by infusing new technologies so that farmers can increase their income.
- The pilot projects including one to monitor soil conditions and another to help on post harvest linkages are part of the Digital Agriculture Mission and will draw on the National Farmers Database.
- The Centre has asked States to attach land records to the database, to grow it to 8 crore farmers.
Benefits:
The benefits are as follows:
- Improved management and decision making processes
- Improved efficiency through more target applications
- Real time information
- Advancements in record keeping
- Management of risks and uncertainties
- A reduction in regulatory burden
- An increase in productivity and profit
- Improved marketing
About NCDEX:
- National Commodity & Derivatives Exchange Limited (NCDEX) is an Indian online commodity and derivative exchange based in Mumbai.
- It is under the ownership of Ministry of Finance, Government of India (GoI).
- It was incorporated on 23 April 2003 under the Companies Act, 1956.
- It obtained its Certificate for Commencement of Business on 9 May 2003.
- It commenced operations on 15 December 2003.
Decks for NARCL: The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, has recently approved the decks for National Asset reconstruction Company Limited (NARCL)
Key Highlights:
- This proposal requires the government to guarantee Security Receipts (SR) issued by NARCL, while buying non performing assets (NPAs) from banks.
Note: The Security Receipts (SR) are issued by Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) when NPAs of the commercial banks (CB) or financial institutions (FI) are acquired by the ARCs for recovery.
- This move will clear the path for the launch of National Asset Reconstruction Company (NARCL).
About NARCL:
- National Asset Reconstruction Company Ltd (NARCL) is a type of Bad Bank that has to be set up to resolve the problem of bad loans impacting the public sector banks.
Note: bad bank refers to an entity that houses the bad loans (non performing assets) of banks and resolves or liquidates them to recover as much money as it can.
- They take over the stressed assets of lenders.
- It is having a public sector character because e idea is mooted by the government and majority ownership is likely to rest with state owned banks.
- The NARCL is sponsored primarily by Canara Bank (likely to take a 12% equity stake) and has equity participation by other nationalized banks.
Background:
- Proposal to create NARCL was announced in the Budget for 2021 22.
Functions of NARCL:
- NARCL will buy bad loans from banks and issue security receipts (SR) to them for up to 85%. Remaining 25% will be provided in cash.
- These receipts can be redeemed as and when the ARC recovers a particular loan
Defence
Baijayant Panda Committee:
The Ministry of Defence (MoD) has recently constituted a High Level Expert Committee, under the chairmanship of former Member of Parliament Shri Baijayant Panda.
- This committee has been constituted for a comprehensive review of National Cadet Corps (NCC) in order to make it more relevant in changed times.
Key Points:
The Terms of Reference of the Committee, interalia, broadly provide for the following:
- To suggest measures which can empower NCC cadets to contribute more effectively towards nation building and national developmental efforts in various sectors;
- To propose measures for gainful engagement of its Alumni for betterment of the organization as a whole and
- To recommend best practices of similar international youth organizations for the inclusion in NCC curriculum.
Members of the Committee:
The Chairperson of the committee is Shri Baijayant Panda, former Member of Parliament.
Other member includes:
- Col. (Retd) Rajyavardhan Singh Rathore
- Vinay Sahasrabuddhe
- Anand Mahindra
- Mahendra Singh Dhoni
- Sanjeev Sanyal
- Prof. Najma Akhtar
- Prof. Vasudha Kamat
- Mukul Kanitkar
- Maj. Gen. Alok Raj (Retd)
- Milind Kamble
- Rituraj Sinha
- Vedika Bhandarkar
- Anand Shah
- Mayank Tewari
About NCC:
- It is an acronym for National Cadet Corps.
- The NCC is the youth wing of Armed Forces of India.
- It is the largest uniformed organization which aims at developing character, discipline, a secular outlook and ideals of selfless service amongst young citizens.
- It is a TriServices Organization, comprising the Army, Navy and Air Wing, engaged in creating a pool of organized, trained and motivated youth with leadership qualities in all walks of life.
- It operates under the Ministry of Defence (MoD).
- It is also the largest uniformed youth organization of the country.
- It was formed on 16 April 1948.
- Since its inception the NCC cadets have been contributing to the national cause during natural calamities like cyclone, floods etc.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- The motto of NCC is "Unity and discipline".
- The current DirectorGeneral of NCC is Lt Gen Tarun Kumar Aich.
SCO PEACEFUL MISSION 2021: The Indian military contingent consisting of an all arms combined force of 200 personnel, including 38 personnel from the Indian Air Force, participated in the Joint Counter Terrorism Exercise PEACEFUL MISSION 2021.
Key Highlights:
- The 6th edition of Exercise Peaceful Mission is being hosted by Russia in the Orenburg Region of South West Russia from 13th to 25th September 2021.
- The exercise has been organized under the aegis of the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO).
Aim:
The aims of the exercise are as follows:
- To foster close relations between SCO member states.
- To enhance the abilities of the military leaders to command multinational military contingents.
- To increase global cooperation to counterterrorism.
- To share best practices between the armed forces of SCO nations.
Indian Contingent:
- Indian contingent was inducted to exercise area by two IL76 aircrafts.
- Before their departure, contingent underwent training and preparation under the aegis of South Western Command.
Significance of the exercise:
- This exercise will enable the sharing of best practices between the Armed Forces of SCO nations.
- It will also provide an opportunity to the Armed Forces of SCO Nations to train in CounterTerrorism Operations in an urban scenario in a multinational and joint environment.
- The key scope of the exercise includes professional interaction, mutual understanding of drills & procedures, the establishment of joint command & control structures, and the elimination of terrorist threats.
- It is a landmark event in the military interactions and the global cooperation to counterterrorism.
About SCO Peaceful Mission:
- SCO Peaceful Mission or Joint Counter Terrorism Exercise PEACEFUL MISSION is a Multilateral Exercise.
- It is conducted biennially as part of military diplomacy between Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) member states.
- India, for the first time, participated in the 5th edition of the Exercise (2018).
About SCO:
- The Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) is an eightmember economic and security bloc that has also emerged as one of the largest transregional international organization.
- It was founded in Shanghai in 2001 by the Presidents of China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, and the Kyrgyz Republic.
- Both India and Pakistan became a permanent member of SCO in 2017.
Surya Kiran – 15: The 15th Edition of Indo Nepal Joint Military Training Exercise "Surya Kiran" between Indian Army and Nepali Army is commencing from 20 September 2021 at Pithoragarh in Uttarakhand.
Key Points:
- During this exercise, an Infantry Battalion from Indian Army and an equivalent strength from Nepali Army would be sharing their experiences gained during the conduct of various counterinsurgency operations over a prolonged period in their respective countries.
- The joint military training would culminate with a gruelling 48hour exercise to validate the performance of both armies in counterinsurgency operations.
- The aim of the exercise is as follows:
- To share their experiences of various counterinsurgency operations.
- To familiarize themselves with each other’s weapons, equipment, tactics, techniques, and procedures of operating in a counterinsurgency environment in mountainous terrain.
- It will also boost the bilateral relations and further strengthen the traditional friendship between India and Nepal.
- Last edition of Exercise Surya Kiran was conducted in Nepal in 2019.
INS Dhruv: India’s first nuclearmissile tracking ship, named INS (Indian Naval Ship) Dhruv, has recently been commissioned from Visakhapatnam in Andhra Pradesh.
Highlights:
- INS Dhruv was launched by the National Security Advisor Ajit Doval in the presence of Chief of Naval Staff Admiral Karambir Sings.
- It will be under the controll of the SC (Strategic Forces Command).
- It will advance India's presence in the IndoPacific regiion.
- The 10,000tonne ship has the ability to track nuclear ballistic missiles at a longrange and is at the heart of India’s antiballistic missile capability.
- With the induction of INS Dhruv, India joins a select group of countries like the US, the UK, Russia, China and France to have such specialized vessels.
About INS Dhruv:
- This nuclear missile tracking ship is built by the Hindustan Shipyard Limited (HSL) in collaboration with the Defence Research and Development Organization (DRDO) and the National Technical Research Organization (NTRO).
- It has been designed in India by Vik Sandvik Design India Pvt. Ltd. (VSDI) which is headquartered in New Delhi.
- INS Dhruv is capable of tracking nuclear missiles at a long range.
- The INS Dhruv could provide early warning of attacks by ballistic missiles launched from Pakistan and China.
- It is also equipped with the capability to map ocean beds for research and detection of enemy submarines.
- The ship is equipped with the DRDO developed stateoftheart active scanned array radar or AESA that can scan monitor spy satellites watching over India as well as monitor missile tests in the entire region.
Environment
World Ozone Day 2021:
World Ozone Day, also known as International Day is observed every year on September 16 to commemorate the signing of the Montreal Protocol.
- It is celebrated to spread awareness among people about the depletion of the Ozone Layer and search for possible solutions to preserve it.
Theme of World Ozone Day 2021:
- The theme for International Day for the Preservation of the Ozone Layer fot the year 2021 is Montreal Protocol 'Keeping us, our food and vaccines cool.'
History:
- In order to keep in check on substances that deplete the Ozone layer, a deal named Montreal Protocol was signed by almost every country on September 16, 1987 and subsequently, in 1994, the UN General Assembly proclaimed this day as the World Ozone Day.
World Ozone Day 2021 in India:
- India observed the 27th Global Ozone Day this year.
- The Ozone Cell, Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC), Government of India (GoI) has been celebrating the World Ozone Day since 1995 at the National and State levels.
About the Montreal Protocol:
- The Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer (the Montreal Protocol) is an international agreement made on 16th September, 1987, where countries from across the globe decided to curb substances such as:
- Chlorofluorocarbon
- Aerosols
- Halons
- It was designed to stop the production and import of ozone depleting substances and reduce their concentration in the atmosphere to help protect the earth's ozone layer.
- These substances are widely used for cooling and refrigerating purposes.
- As a result of the usage of these harmful substances, a hole in the ozone layers in Antarctica was discovered back in 1970.
- This ultimately led to acute global warming in the past 20 years.
- According to the World Meteorological Organization, the Antarctic hole caused by Ozonedepletion was finally closed as a result of the collaborative efforts by these countries.
About Ozone Layer:
- The ozone layer or ozone shield is a region of Earth's stratosphere that absorbs most of the Sun's ultraviolet radiation.
- Life is not possible on Earth without the ozone layer.
- It contains a high concentration of ozone in relation to other parts of the atmosphere, although still small in relation to other gases in the stratosphere.
- Sunlight makes life, but the ozone layer creates life as we know it today.
- It protects life on Earth by absorbing Sun's harmful ultraviolet radiation and so is also known as Ozone Shield.
- Ultraviolet rays can cause several skin diseases.
Permafrost: The latest Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) report has warned that increasing global warming will result in reductions in Arctic permafrost and the thawing of the ground is expected to release greenhouse gases like methane and carbon dioxide.
- The IPCC report titled ‘Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis’ which was recently released said that heatwaves and humid heat stress will be more intense and frequent during the 21st century over South Asia.
What is Permafrost?
- Permafrost or permanently frozen ground is defined as ground (soil, rock and any included ice or organic material) that remains at or below zero degree Celsius for at least two consecutive years.
- Permafrost is spread across an area of over 23 million square kilometers, covering about 15% of the land area of the globe.
- Permafrost is mainly found near the poles, covering parts of Greenland, Alaska, Northern Canada, Siberia and Scandinavia.
- The Arctic region is a vast ocean, covered by thick ice on the surface (called sea ice), surrounded by land masses that are also covered with snow and ice.
Effects of permafrost melting due to increasing global temperatures:
- The Arctic is in the process of disintegrating as we know it, and the permafrost is one major component with some pretty grave implications.
- The warming Arctic tundra will make it harder for the world to curb climate change, as thawing permafrost and wildfires release greenhouse gases that are not fully accounted for in global emissions agreements.
- As temperatures rise and permafrost thaws, carbon dioxide and methane trapped within the longfrozen soil are released.
- The deeper the thaw, the more gas is released.
- This threatens to create a feedback loop which contributes more and more warming of the atmosphere.
- Scientists have warned in a study published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Why a matter of concern?
- The first impacts that are very rapid will affect countries where roads or buildings were constructed on permafrost.
- For example, the Russian railways.
- But the biggest international problem is to do with the potential for organic material, which is now entombed and frozen in the ground.
- If the ground begins to thaw, this material will become available for microbiota to break down.
- In some environments, the biota will release carbon dioxide, and in others release methane which is about 25 to 30 times more potent as a greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide.
- The total quantity of carbon that is now buried in the permafrost is estimated at about 1,700 billion tonnes and the top three meters of the ground has about 1000 billion tonnes.
- Even if half of it were to be released to the atmosphere, it would be game over for the climate.
Impact in India:
- The IPCC has indicated that the glacial retreat in the Hindu Kush Himalayas, compounding effects of sealevel rise and intense tropical cyclones leading to flooding, an erratic monsoon; and intense heat stress are likely to impact India in recent years.
- The Indian Ocean, which includes the Arabian Sea and Bay of Bengal, has warmed faster than the global average.
- The oceans factsheet released by IPCC indicates that sea surface temperature over Indian ocean is likely to increase by 1 to 2 degrees C (°C) when there is 1.5°C to 2°C global warming.
About IPCC:
- The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is an intergovernmental body of the United Nations.
- It is responsible for advancing knowledge on humaninduced climate change.
- It was established in 1988 by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), and later endorsed by United Nations General Assembly.
- It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It is comprised of 195 member states.
Objectives:
- The main objective of the IPCC is to provide governments at all levels with scientific information that they can use to develop climate policies.
- IPCC reports are also a key input into international climate change negotiations.
Note: The IPCC shared the 2007 Nobel Peace Prize with Al Gore for contributions to the human understanding of climate change.
International Coastal Cleanup Day 2021: The International Coastal Cleanup Day is traditionally held on the third Saturday in September.
Highlights:
- In 2021, the day is being held on 18 September.
Theme of the day for 2021:
- International Coastal CleanUp Day 2021 is being celebrated under the theme: “Keep trash in the bin and not in the ocean”.
- Coastal Cleanup Day was established by the Ocean Conservancy, an organization that works to help protect the ocean from the challenges it faces every year.
International Coastal Cleanup Day 2021 in India:
- The 36th International Coastal Cleanup Day was celebrated for the tenth consecutive year by the Eastern Naval Command (ENC).
- As part of the day, ENC carried the Coastal Cleanup Drive at Yarada Beach, Bheemili Beach and other sea fronts in the premises of Naval units of Visakhapatnam.
- About 500 Naval personnel, Defence Civilians and their families overtook the cleanup drive by complying with the COVID19 protocols.
Aim of the drive:
- The main aim of launching a cleanup drive was to create awareness among people to keep beaches clean, safeguarding our environment and inculcating the habit of respecting the coastlines which ultimately nurtures the marine biodiversity.
History of the day:
- The International Coastal Cleanup was started by the Ocean Conservancy, in 1986.
- During that time, communities rallied together with a common goal of collecting and documenting the trash lying on their coastline.
- Since then, International Coastal Cleanup Community encourages people across the world to remove trash and debris from waterways, beaches & other water bodies, on the third Saturday of September, each year.
- The day aims to increase public awareness about the accumulation and negative impacts of litter in oceans, on coastlines and on beaches.
EV Chargers: The British government has recently announced that it will introduce legislation in 2021.
Key Points about the legislation:
- Under this new Legislation, all the newly built homes and offices would require to feature Electric Vehicle (EV) chargers in England.
- This law will make England the first country to mandate new homes to install EV chargers.
- According to this new legislation, new office blocks will require to install a charging point for every five parking spaces.
- The legislation is part of the movement that seeks to rapidly boost the number of chargers in England ahead of UK’s 2030 ban of new fossilfuel vehicles.
- Home and office EV charger proposal is expected to start in 2022.
Significance of the legislation:
- It will also boost confidence in helping those who transition from gas cars to overcome range anxiety, as so many homes in England don't have offstreet parking or garages.
Background:
- The British government had originally announced a proposal to mandate that all new homes have a charge point with a parking space in 2019.
UK’s 2030 ban of new fossilfuel vehicles:
- United Kingdom (UK) Prime Minister, Boris Johnson, had recently announced to ban the sale of gasolinepowered vehicles from 2030, nothing the future of personal mobility on electric vehicles.
- The ban on gasoline vehicles had initially been proposed for 2040.
- But it has been brought forward by ten years under the tenpoint plan of UK of achieving net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.
- Hybrid vehicles would be phased out by 2035.
International Red Panda Day 2021: The International Red Panda Day (IRPD) is celebrated every year on ‘Third Saturday of September’.
Key points:
- This day is celebrated to raise public awareness and support for red panda conservation issues.
- In 2021, the IRPD is being observed on 18 September.
- International Red Panda Day is dedicated to the red pandas—a mammal species native to the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China.
History:
- The day was launched by the Red Panda Network (RPN) in 2010.
- The first international Red Panda day was celebrated on 18th September 2010.
Facts about Red Panda:
- Discovered about 50 years before giant pandas, red pandas are the only species left in the Ailuridae family.
- Red Panda and the Gaint Panda, though having similar names, are not closely related.
- There are two distinct species of red pandas. They are:
- Ailurus fulgens is commonly known as Himalayan Red Panda.
- Ailurus fulgens styani commonly known as Chinese Red Panda.
- Red panda is also known as lesser panda, panda, red catbear, or red bearcat.
- It is a reddishbrown, longtailed, raccoonlike mammal and has soft thick fur, above is rich reddishbrown and black underneath.
- The face of the red panda is white, consisting of a stripe of redbrown, and from each eye to the corners of the mouth. Also, the bushy tail is faintly ringed.
- Its size is about the size of a large domestic cat.
- These are mostly found in the Eastern Himalayan region and southwestern China.
- They live high within the mountains among rocks, and trees and climb with agility.
- They are nocturnal and may live alone, in pairs, or in family groups.
- Genetically the red pandas belong to the order of Carnivora, but mostly eat bamboo shoots, mushrooms etc and also eat birds, eggs, and insects.
- The average lifespan of these red pandas is 23 years and the female pandas stop breeding after the age of 12.
Indian Policy
Reforms in the Telecom Sector:
The Union Cabinet, chaired by the Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi, recently approved a number of structural and process reforms in the Telecom sector.
Key Points:
- The Cabinet Committee has approved 9 structural reforms and 5 process reforms for the telecom sector.
- These new reforms are expected to protect and generate employment opportunities, protect the interests of consumers, promote healthy competition, infuse liquidity, encourage investment and reduce the regulatory burden on Telecom Service Providers (TSPs).
- For all the TSPs, the cabinet has approved moratorium/deferment of upto 4 years in annual payments of dues arising out of the AGR judgment, by protecting the Net Present Value (NPV) of the due amounts being protected.
- The definition of Adjusted Gross Revenue (AGR) has been rationalized to exclude nontelecom revenues prospectively.
- Four year moratorium on telecom dues was also approved as well.
- A 100% foreign direct investment (FDI) under automatic route has been permitted in telecom sector to encourage investment.
- Spectrum user charges have been rationalized.
- There will be now an annual compounding of rates.
- Spectrum can now be surrendered and it can also be shared.
- No Spectrum Usage Charge (SUC) for spectrum acquired in future spectrum auctions.
- In future auctions, tenure of spectrum will be increased from 20 to 30 years.
- The KYC process for shifting to postpaid from prepaid has been done away with.
Reason for these reforms:
- The Government of India (GoI)initiated these reforms in the backdrop of outstanding performance of the Telecom Sector in meeting COVID19 challenges, with a huge surge in data consumption, online education, work from home, interpersonal connect through social media, virtual meeting.
PLI Scheme for Automobile & Drone Industries: The Union Cabinet has recently approved production linked incentive (PLI) schemes for auto industry, auto component industry, and drone industry to enhance India's manufacturing capabilities.
Key Highlights:
- A provision of Rs 26,058 crore for PLI schemes for auto, auto component industry and drone industry was announced by the Government.
- Rs. 25,938 crores for the auto sector and Rs. 120 crores for the drone industry.
- The PLI scheme for the automotive sector along with the already launched PLI for Faster Adoption of Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) Scheme (Rs 10,000 crore) and Advanced Chemistry Cell (Rs 18,100 crore) will give a big boost to the manufacturing of electric vehicles in the country.
Background:
- The PLI Scheme for Automobile Industry and Drone Industry is part of the overall announcement of PLI Schemes for 13 sectors made earlier during the Union Budget 202122, with an outlay of ₹ 1.97 lakh crore.
PLI for Auto Sector:
- The PLI scheme for the auto sector has been modified to focus on advanced automotive technologies.
- The makers of the diesel, petrol, and CNG vehicle makers will not be covered under the scheme.
- The PLI scheme for the auto sector will incentivize high value Advanced Automotive Technology vehicles and products.
- It will encourage industry to make fresh investments for indigenous global supply chain of Advanced Automotive Technology products.
- It is estimated that over a period of five years, the PLI Scheme for Automobile and Auto Components Industry will lead to fresh investment of over ₹42,500 crore, incremental production of over ₹2.3 lakh crore and will create additional employment opportunities of over 7.5 lakh jobs.
- In addition, it will further increase India’s share in global automotive trade.
- The PLI Scheme for auto sector is open to:
- The existing automotive companies and
- The new investors who are currently not in automobile or auto component manufacturing business.
Components of the scheme:
- The scheme has two components viz Champion OEM Incentive Scheme and Component Champion Incentive Scheme.
- The Champion OEM Incentive scheme is a ‘sales value linked’ scheme, applicable on Battery Electric Vehicles and Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles of all segments.
- The Component Champion Incentive scheme is a ‘sales value linked’ scheme, applicable on Advanced Automotive Technology components of vehicles, Completely Knocked Down (CKD)/ Semi Knocked Down (SKD) kits, Vehicle aggregates of 2Wheelers, 3Wheelers, passenger vehicles, commercial vehicles and tractors etc.
PLI for Drones Sector:
- The PLI Scheme for the Drones and Drone components industry addresses the strategic, tactical and operational uses of this revolutionary technology.
- The incentive for a manufacturer of drones and drone components shall be as high as 20% of the value addition made by her.
- The Government has agreed to keep the PLI rate constant at 20% for all three years, an exceptional treatment given only to the drone industry.
Note: In PLI schemes for other sectors, the PLI rate reduces every year.
- The Government has agreed to widen the coverage of the incentive scheme to include developers of dronerelated IT products also.
- The PLI for Drones and Drone components industry, will over a period of three years, lead to investments worth ₹ 5,000 Crore, increase in eligible sales of ₹ 1500 crore and create additional employment of about 10,000 jobs.
What do you mean by performancelinked incentive (PLI)?
- A performancelinked incentive (PLI) is a form of incentive from one entity to another, such as from the government to industries or from an employer to an employee, which is directly related to the performance or output of the recipient and which may be specified in a government scheme or a contract.
- PLI may either be openended or closeended.
- Openended does not have a fixed ceiling for the quantum of incentive granted.
- The openended incentives are normally applicable to revenuegenerating activities (e.g., sales, production, efficiency, competitiveness, etc)
- Closeended has an upper ceiling as stipulated in the scheme or the contract.
- The closeended incentives are associated with quality improvement or support functions (e.g., operations, human resources, administration, etc.)
Method of calculation:
- In calculating PLI, only the performance and not the potential of the recipient are considered.
- Potential of the recipient is normally subjective and can be contested.
- PLI is based on metrics which are absolutely objective and clearly perceived as fair by both the PLI provider and the recipient.
NDEAR: Recognizing the transitions happening in the Education sector, where Digital Technology has come to dominate the face of most remote learnings, the Government of India (GoI) has announced a National Digital Educational Architecture, or in short, NDEAR.
Note: The NDEAR 2021 outlines the framework to energize and catalyze the digital education ecosystem to create and deliver diverse, relevant, contextual, innovative solutions that benefit the student, parent, teacher and educational communities.
About NDEAR:
NDEAR is
- An architectural blueprint for the education ecosystem and not a system.
- That defines a set of
- Principles e.g. technology and ecosystem
- Standards and Specifications e.g. technology and data
- Guidelines e.g. data process, ecosystem engagement
- Policies e.g. data, openness, inclusion, accessibility
- And identifies the key building blocks needed to make the architecture blueprint a reality for an ecosystem of
- Actors to build, develop, innovate interoperable building blocks
- Applications/Innovations in the form of Solutions, platforms, tools, assets to be developed and used
- To enable the achievement of policy goals through programmes such as SSA, FLN Mission etc
- It identifies the key building blocks needed to make the architecture blueprint a reality
- NDEAR is under the aegis of the Ministry of Education in collaboration with MeitY.
How does NDEAR differ from any technology project of the government?
- NDEAR is not a project where the Government will be building technology solutions for the use of the education ecosystem.
- Through NDEAR, the Government will play the role of an enabler, providing a framework where technology can be built by anyone.
- Further, solutions that use NDEAR frameworks, standards and specifications, would be considered NDEAR compliant.
- Any technology solution which is NDEAR compatible will be able to connect with other solutions that are NDEAR compliant.
- State Governments would be free to embark on building solutions to suit their needs.
- NDEAR, by identifying needs and curating the building blocks needed for the education ecosystem, would be able to help with enabling the States with a leg up by providing technology components that can be configured for different solutions.
- This is much like selecting good quality bricks, which could be used to make any building of choice by the builder.
Phase II of Visvesvaraya PhD Scheme: The Union Minister of Electronics & Information Technology Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw, launched Phase II of Visvesvaraya PhD Scheme.
Highlights:
- This scheme has been launched to promote research in 42 emerging technologies in Electronics System Design & Manufacturing (ESDM) and Information Technology (IT)/ Information Technology Enabled Services (ITES).
- The scheme is manifestation of Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s vision of providing world class education and opportunities for research and development to the students at the bottom of the pyramid in society.
- This scheme supports the talent that India has.
Key Points:
- The main aim of the Phase II of the scheme is to support 1000 Full Time PhD Candidates, 150 Part Time PhD Candidates, 50 Young Faculty Research Fellowships and 225 PostDoctoral Fellowships.
- Currently, 492 Fulltime & 268 Parttime PhD Fellows are pursuing while 422 Full Time & 43 Part Time PhD have submitted thesis or completed PhD.
- During the event achievements of Phase I of the Visvesvaraya PhD scheme were also celebrated.
Background:
- Visvesvaraya PhD Scheme was initiated by Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) in 2014.
- It was initiated with the approval of Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA).
- The main objective of the scheme is to enhance number of PhDs in ESDM & IT/ITES sectors. PhD seats were allocated to 97 institutions (IITs, NITs, Central & State Universities etc.) in 25 states and 4 Union Territories.
Shoonya Campaign: NITI Aayog, in association with the Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) and RMI India, recently launched Shoonya campaign.
Note: RMI is an independent nonprofit organization founded in 1982.
Key highlights:
- Shoonya Campaign was launched on 15 September 2021.
- It is an initiative to promote zeropollution delivery vehicles by working with consumers and industry.
- This campaign was launched with the aim to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in urban delivery segment and raise consumer awareness regarding the benefits of pollutionfree delivery.
- As part of the campaign, a corporate branding and certification programme is being launched to recognize and promote industry’s efforts towards transitioning to EVs for finalmile deliveries.
- An online tracking platform will share the campaign’s impact through data such as vehicle kilometres electrified, carbon savings, criteria pollutant savings and other benefits from clean delivery vehicles.
Objective:
- The main objective of the campaign is to eliminate pollution from urban freight sector.
- For this purpose, ecommerce companies, automakers, and logistics fleet operators have been asked to recognize the opportunity.
Urban freight vehicles in India:
- Urban freight vehicles account for 10% of freight transportationrelated CO2 emissions in India.
- These emissions are expected to grow by 114 percent by 2030.
- Since, EVs emit no tailpipe emissions; they can contribute immensely to an improved air quality.
- As far as manufacturing is concerned, they emit 1540 percent less CO2 and they also have lower operational cost compared to their internal combustion engine counterparts.
- The central and the state governments have introduced policies to provide upfront incentives for EVs, which will lower the capital cost by a high margin.
- The names of some initiatives taken by the Indian Government are:
- The National Electric Mobility Mission Plan 2020.
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles in India (FAME India Scheme).
- Implementation of smart cities
About NITI Aayog:
- The National Istitution For Transforming India (NITI) Aayog is the premier policy 'Think Tank' of the Government of India (GoI).
- It was established on 1 January 2015.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi,India.
- The current CEO of NITI Aayog is Amitabh Kant.
About RMI India:
- Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) India is an independent non profit organization that works towards accelerating India's transition to a clean, prosperous, and inclusive energy future.
- It was established in 2019.
- RMI India takes inspiration from and collaborates with Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI), USA.
About RMI:
- Rocky Mountain Institute (RMI) is an organization in the United States (US) dedicated to research, publication, consulting, and lecturing in the general field of sustainability, with a special focus on profitable innovations for energy and resource efficiency.
- It was established in 1982.
- It is headquartered in Basalt, Colorado.
- Its current CEO is Jules Kortenhorst
Indian polity
Bhupendra Patel:
Ghatlodia BJP MLA Bhupendra Patel was sworn in as the new Chief Minister of Gujarat on September 13, 2021.
Key Highlights:
- He was sworn in by the State Governor Acharya Devvrat at the Raj Bhavan, Gandhinagar.
- He will be the 17th Chief Minister of Gujarat.
- Cabinet members will be sworn in later after party will decide the names.
- 59 year old first time MLA, Patel was unanimously elected leader of BJP Legislature Party.
- He met the governor and staked the claim to form a new government in the state after the resignation of Vijay Rupani as Chief Minister of Gujarat.
About Bhupendra Rajnikant Patel:
- Mr Patel has previously served as president of Memnagar Municipality in Ahmedabad, and the standing committee chairman of Ahmedabad Municipal Corporation and Ahmedabad Urban Development Authority.
- Patel became the MLA from the Ghatlodiya seat of Ahmedabad city in 2017.
- He is the chairman of the standing committee of Vishwa Umiya Foundation.
- He has also been associated with Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh.
- He is believed to be close to Anandiben Patel Governor of Uttar Pradesh and former Chief Minister of Gujarat.
Reforms in Urban Planning Capacity in India: NITI Aayog, 16 SEP 2021, launched a report on measures to ramp up urban planning capacity in India.
Highlights:
- The report is titled ‘Reforms in Urban Planning Capacity in India’.
- It was released by NITI Aayog Vice Chairman Dr Rajiv Kumar, CEO Shri Amitabh Kant and Special Secretary Dr K. RajeswaraRao.
- The event was attended by the Secretaries of the ministries of housing and urban affairs, higher education, and panchayati raj, and chairpersons of AICTE and TCPO, Director of NIUA and President of ITPI.
About the report:
- The report has been developed by NITI Aayog, in consultation with concerned ministries and eminent experts in the domain of urban and regional planning.
- The report presents a condensed outcome of the extensive deliberations and consultations conducted over a period of nine months.
- The report has made several recommendations that can unblock bottlenecks in the value chain of urban planning capacity in India.
- Some of them are as follows:
Programmatic Intervention for Planning of Healthy Cities:
- Every city must aspire to become a ‘Healthy City for All’ by 2030.
- The report recommends a Central Sector Scheme ‘500 Healthy Cities Programme’, for a period of 5 years, wherein priority cities and towns would be selected jointly by the states and local bodies.
Re engineering of Urban Governance:
- The report recommends the constitution of a high powered committee to re engineer the present urban planning governance structure. The key aspects that would need to be addressed in this effort are:
- Clear division of the roles and responsibilities of various authorities, appropriate revision of rules and regulations, etc.,
- Creation of a more dynamic organizational structure, standardisation of the job descriptions of town planners and other experts, and
- Extensive adoption of technology for enabling public participation and inter agency coordination.
Revision of Town and Country Planning Acts:
- Formation of an apex committee at the state level is recommended to undertake a regular review of planning legislations (including town and country planning or urban and regional development acts or other relevant acts).
Demystifying Planning and Involving Citizens:
- The committee strongly recommends a ‘Citizen Outreach Campaign’ for demystifying urban planning.
Steps for Strengthening Urban Planning Education System:
- The Central universities and technical institutions in all the other States/UTs are encouraged to offer postgraduate degree programmes (MTech Planning) to cater to the requirement of planners in the country in a phased manner.
Measures for Strengthening Human Resource and Match Demand–Supply:
- The report recommends the constitution of a ‘National Council of Town and Country Planners’ as a statutory body of the Government of India.
- Also, a ‘National Digital Platform of Town and Country Planners’ is suggested to be created within the National Urban Innovation Stack of MoHUA.
- This portal will enable self registration of all planners and evolve as a marketplace for potential employers and urban planners.
About NITI Aayog:
- NITI (National Institution for Transforming India) Aayog is the premier policy 'Think Tank' of the Government of India (GoI).
- It was established with the aim to achieve sustainable development goals with cooperative federalism by fostering the involvement of State Governments of India in the economic policy making process using a bottom up approach.
- It was founded on 1 January 2015 to replace the Planning Commission instituted in 1950. It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- The Governing Council of NITI includes the Prime Minister as its Chairman.
- It comprises of Chief Ministers of all States and Lt. Governors of Union Territories (UTs). The current Vice Chairman of NITI Aayog is Rajiv Kumar the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) is Amitabh Kant.
Sansad TV: Vice President and Rajya Sabha Chairman, Shri M. Venkaiah Naidu, Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi and Lok Sabha Speaker Shri Om Birla jointly launched Sansad TV.
Highlight:
- Sansad TV was launched on the occasion of International Day of Democracy at the Main Committee Room, Parliament House Annexe.
- The launch of Sansad TV is a new chapter in the story of Indian democracy as the country is getting a medium of communication and dialogue which will become a new voice of the nation’s democracy and people’s representative.
- Sansad TV programming will primarily be in 4 categories –
- Parliament and democratic institutions
- Governance and Implementation of schemes and policies
- History and culture of India
- Issues of interest to the common man
Background:
In February, 2021, the decision to merge Lok Sabha TV and Rajya Sabha TV was taken and the CEO of Sansad TV was appointed in March, 2021.
International
Najib Mikati:
Billionaire businessman Najib Mikati has been appointed as Lebanon’s new prime ministerdesignate following binding parliamentary consultations with President Michel Aoun.
Key Highlights:
- Mikati ran virtually unopposed, receiving 72 votes, with former ambassador Nawaf Salam receiving just one vote.
- He faced opposition from the country's two Christian parties, the Free Patriotic Movement and the Lebanese Forces.
- His appointment comes just 11 days after Saad Hariri resigned as prime ministerdesignate, following nine months of political deadlock and dispute with President Aoun and his soninlaw MP Gebran Bassil.
Lebanon Crisis:
- Lebanon’s economy is still crumbling with half the population living below the poverty line and a spiralling local currency that lost more than 90% of its value.
- The country has also been without a fullfledged government for almost one year.
- It is struggling to reform its economy to unlock international aid.
About Lebanon:
- Lebanon, officially known as the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in Western Asia.
- It is bordered by Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lies west across the Mediterranean Sea.
- It is situated by the Lebanon Mountains and has taken on a triangular shape.
- It is largely influenced by its situation between and atop two hills: AlMusaytibah and AlAshrafieh.
- The capital of Lebanon is Beirut.
- The currency used here is Lebanese pound.
- The current President of Lebanon is Michel Aoun.
CAFMD: India and the United States jointly launched the Climate Action and Finance Mobilization Dialogue (CAFMD) of the Agenda 2030 Partnership recently.
Key Highlights:
- The dialogue was formally launched by Union Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Bhupender Yadav and US Special Presidential Envoy for Climate (SPEC) John Kerry at an event held in New Delhi.
- The CAFMD is one of the two main tracks of the USIndia Climate and Clean Energy Agenda 2030 Partnership.
- This Partnership will provide both countries with an opportunity to renew collaborations on climate change.
- It will provide both countries an opportunity to renew collaborations on climate change and also address the financing aspects.
- It will deliver climate finance primarily as grants and concessional finance, as envisaged under Paris Agreement to strengthen climate action,
- The dialogue will not only strengthen IndiaUS bilateral cooperation on climate and environment but will also help to demonstrate how the world can align swift climate action with inclusive and resilient economic development.
Significance:
- This partnership would serve as a “powerful avenue for IndiaU.S. collaboration
- It would have three pillars:
- The first pillar would be a “climate action pillar” which would have joint proposals looking at ways in emissions could be reduced in the next decade.
- The second pillar would be setting out a roadmap to achieving the 450GW in transportation, buildings and industry.
- The final pillar or the ''Finance Pillar” would involve collaborating on attracting finance to deploy 450 GW of renewable energy and demonstrate at scale clean energy technologies.
Objective:
This initiative was started with the objective:
- To mobilize investments
- To demonstrate clean technologies
- To enable green collaborations in India in order to create templates of sustainable development for other developing countries.
Background:
This was one of the main tracks of the U.S.India Agenda 2030 Partnership that President Biden and Prime Minister Modi announced at the Leaders Summit on Climate in April 2021.
Additional Info:
- The launch was preceded by a bilateral meet where both sides discussed at length a wide range of climate issues relating to COP26, Climate Ambition, Climate Finance, Global Climate Initiatives including International Solar Alliance (ISA), Agriculture Innovation Mission for Climate (AIM4C).
- The special envoy's travel will also bolster the US bilateral and multilateral climate efforts ahead of the 26th Conference of the Parties (COP26) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- The 26th Conference of COP26 will be held from October 31 to November 12, 2021, in Glasgow (United Kingdom).
AUKUS: Australia, the U.K. and the U.S. announced a new trilateral security partnership, AUKUS.
Highlights:
- It is a new trilateral security partnership for IndoPacific region.
- This security grouping was announced in a joint address by British Prime Minister Boris Johnson, his Australian counterpart Scott Morrison and US President Joe Biden with a vision for a safer and more secure IndoPacific.
- The three countries are forming a new security alliance that will help equip Australia with nuclearpowered submarines.
- These three heads of state reaffirmed their intention to continue to work with their allies and groupings in tandem with AUKUS, with the Quad being mentioned by Morrison and Biden.
Key Points about AUKUS:
- Under the arrangement, Australia will acquire nuclearpowered submarines with help from the U.K. and the U.S.
- Within 18 months, the first fleet of nuclearpowered submarines will be delivered.
- The pact will help Australia to acquire submarines that are quieter, more capable as compared to their conventional counterparts.
- These submarines are capable of being deployed for longer periods and remain submerged for longer periods than conventional submarines.
- However, these nuclear powered submarines and not armed with nuclear weapons.
- AUKUS will not only involve a new architecture of meeting and engagements between three countries but it also involves the cooperation across emerging technologies like AI (Artificial Intellegence), quantum technologies as well as undersea capabilities.
- With this, Australia will join the league of nations that operate nuclearpowered submarines. These are the U.S., the U.K., France, India, China, and Russia.
What is the purpose of forming AUKUS?
- This initiative was launched in response of Australia wanting to strengthen its feet with regard to maritime security in the IndoPacific region.
- Furthermore, tensions between Australia and an increasingly assertive China have grown, so, Australia has sought to strengthen its partnerships with India, the U.S., the U.K. and Japan as well as through other plurilateral forums.
Significance:
- The AUKUS will advance strategic interests, uphold the international rulesbased order, promote peace and stability in the IndoPacific region, along with generating hundreds of highskilled jobs.
- As per the analysts, this alliance is the most significant security arrangement between the three nations since World War II, as per the analysts.
- The AUKUS is different from, but complementary to other groupings such as Quad and Five Eyes Network.
- In addition, the US is sharing its submarine technology for the first time in 50 years and had shared it previously only with the UK.
About Australia:
- Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia is a sovereign country and the smallest continent and one of the largest countries on Earth.
- It lies between the Pacific and Indian oceans in the Southern Hemisphere. Australia's capital is Canberra.
- The currency used there is Australian dollar (AUD).
- The current Prime Minister of Australia is Scott Morrison.
About U.K. (United Kingdom):
- The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK or U.K.) or Britain,is a sovereign country located off the northwestern coast of the European mainland.
- The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the northeastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands.
- It consists of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland.
- It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean, The North Sea, and the Irish Sea.
- The United Kingdom is a unitary parliamentary democracy and constitutional monarchy.
- The monarch is Queen Elizabeth II, who has reigned since 1952, making her the world's longestserving current head of state.
- The capital of the United Kingdom is London.
- The currency used here is Pound sterling.
- The current Prime Minister of UK is Boris Johnson.
About U.S. (United States):
- The United States of America (USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country consisting of 50 states, a federal district, five major selfgoverning territories, and various possessions.
- The 50 states covers a vast swath of North America, with Alaska in the northwest and Hawaii extending the nation’s presence into the Pacific Ocean.
- The currency used in USA is United States dollar USD also abbreviated US$.
- The capital of US is Washington, D.C.
- The current President of US is Joe Biden
International Day of Democracy: International Day of Democracy is observed globally on 15th September every year.
Highlights:
- The day is observed for promoting and upholding the principles of democracy.
- It provides an opportunity to review the state of democracy in the world.
International Day of Democracy 2021:
- International Day of Democracy was observed on September 15, 2021, in order to review the state of democracy across the globe.
- The theme for 2021 International Day of Democracy is “Strengthening democratic resilience in the face of future crises”.
- The aim of the day is to make the ideal of democracy “into a reality to be enjoyed by everyone, everywhere.”
History of the day:
- The Day was proclaimed by the UN General Assembly (UNGA) through a resolution in 2007 to strengthen national programmes devoted to the promotion and consolidation of democracy.
- The day is largely based on the Universal Declaration on Democracy, which was adopted on September 15, 1997, by the InterParliamentary Union (IPU).
Note: The IPU is an international organization of national parliaments.
- However, the seeds of International Day of Democracy were sown in the year 1988.
- That year, President Corazon C. Aquino of the Philippines started the International Conferences on the New and Restored Democracies (ICNRD) process.
- In 2006, ICNRD6, held in Qatar, decided on a declaration that reestablished the basic principles of democracy.
- Thereafter, Qatar took the lead to promote a resolution for the International Day of Democracy in the UN General Assembly.
- Finally, on November 8, 2007, the day was established as the UNGA adopted by consensus the resolution titled “Support by United Nations system of efforts of governments to promote and consolidate a new or restored democracy.
- The day was observed for the first time in 2008.
Significance:
- According to the United Nations (UN), the International Day of Democracy provides an opportunity to review the state of democracy in the world.
- Democracy is a process as a goal which can be made into a reality only with the full participation of international community.
- It is essentially a government that empowers its people to make decisions concerning national interests.
- Essential elements of democracy include:
- Values of freedom,
- Respect for human rights
- Holding periodic & genuine elections by universal suffrage.
CSTO: A Russialed security bloc Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO) is planning to hold large military drills in Tajikistan.
Highlights:
CSTO has planned to hold this drill amid a deteriorating situation in neighbouring Afghanistan.
What is the rationale behind this military exercise in Tajikistan?
The rationale behind this drill is that:
Tajikistan is the only country out of the sixmember bloc led by Russia that shares a border with Afghanistan.
The group has taken “collective measures” to ensure Tajikistan’s security in case of an “aggravation” on its border with Afghanistan.
The series of drills will include the largest exercise this year among CSTO nations.
Moscow has moved to cement its position as a key player in the region after the United States’ hasty retreat from Afghanistan and the Taliban’s takeover of the country.
About Collective Security Treaty Organization (CSTO):
The CSTO is an intergovernmental military alliance in Eurasia that consists of selected postSoviet states.
On 15 May 1992, the Collective Security Treaty was signed by the heads of Armenia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan.
This treaty is also referred to as the “Tashkent Pact” or “Tashkent Treaty”.
Three other postSoviet states—Azerbaijan, Belarus, and Georgia—signed the next year and the treaty took effect in 1994.
Five years later, six of the nine—all but Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Uzbekistan—agreed to renew the treaty for five more years.
Then in 2002 those six agreed to create the Collective Security Treaty Organization as a military alliance.
It is headquartered in the Russian capital of Moscow.
Note: Afghanistan and Serbia hold observer status in the CSTO.
What are the objectives of CSTO?
- The objectives of the CSTO is to strengthen peace, international and regional security including cybersecurity and stability, the protection on a collective basis of the independence, territorial integrity and sovereignty of the member states.
Quad Summit 2021: The US President Joe Biden recently announced that it will be hosting the firstever inperson Quad Summit on September 24, 2021, in Washington.
Highlights:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi, Australian PM Scott Morrison and Japanese PM Yoshihide Suga will be present at the meeting.
- PM Modi will travel to the US to attend the Quad Leaders summit and address the UN General Assembly in New York on September 25, 2021.
- According to the White House statement, at the meeting, the Quad leaders will focus on issues related to the Covid19 crisis, climate change, cyberspace and security in the IndoPacific.
- The firstever Quad leaders’ summit will also be the first inperson meeting of PM Modi and US President Biden.
- The two leaders have interacted virtually three times during the Quad summit in March 2021, the Climate Change summit in April 2021, and the G7 summit in June 2021 amid the COVID19 pandemic.
Agenda:
- The White House statement stated that the “Biden administration has made elevating the Quad summit a priority of engaging in the IndoPacific, including through new multilateral configurations to meet the challenges of the 21st century.”
- The Quad leaders will ‘review the progress made since their first virtual Quad summit held on March 12, 2021, and deliberate on regional issues of shared interest.
- The leaders will also review the Quad Vaccine initiative that was announced in the Quad Summit held in March 2021 as part of their ongoing efforts to contain the COVID19 pandemic.
- The leaders will deliberate on contemporary global issues such as humanitarian assistance, disaster relief, connectivity and infrastructure, critical and emerging technologies, cyber security, education, and climate change.
About Quad:
- The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue, also known as the Quad, is a strategic dialogue between the United States (US), India, Australia, and Japan.
- The representatives for the fourmember nations have met periodically since its establishment in 2007.
- Following the Indian Ocean tsunami, India, Japan, Australia, and the US created an informal alliance to collaborate on disaster relief efforts.
- The Quad was formed in 2007 by Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe along with support from the then US Vice President Dick Cheney, Indian PM Manmohan Singh, and Australian PM John Howard.
- In December 2012, Shinzo Abe again floated the concept of Asia’s “Democratic Security Diamond” involving Australia, India, Japan and the US to safeguard the maritime commons from the Indian Ocean to the western Pacific.
- In 2017, faced again with the rising threat of China, the four countries revived the Quad, broadening its objectives and creating a mechanism that aimed to slowly establish a rulesbased international order.
- In 2020, the trilateral IndiaUSJapan Malabar naval exercises expanded to include Australia, marking the first official grouping of the Quad since its resurgence in 2017 and the first joint military exercises among the four countries in over a decade.
- In March 2021, the Quad leaders met virtually and later released a joint statement titled ‘The Spirit of the Quad,’ which outlined the group’s approach and objectives.
How was Quad formed?
- The beginning of the Quad group can be traced to the evolution of Exercise Malabar.
- The military exercise was widely viewed as a response to the increasing economic and military power of China.
- The Chinese government therefore issued formal diplomatic protests to the members of the Quad. The US, Japan, and India continue to hold joint naval exercises through Malabar.
- The Quad however ceased due to the withdrawal of Australia in the wake of the growing tension between the US and China in the AsiaPacific region.
- In 2010, Julia Gillard replaced Australian PM Rudd following which enhanced military cooperation between Australia and the US was resumed.
- During the 2017 ASEAN Summits in Manila, all four member countries namely the US, India, Australia, and Japan led by Donald Trump, Narendra Modi, Malcolm Turnbull, and Shinzo Abe came together to revive the Quad alliance in order to curb the growing military power of China in the South China Sea.
The objectives of the Quad are:
- To advance the security and the economic interests of all countries.
- To develop a free and open IndoPacific free of any Chinese influence,
- To develop a rulesbased maritime order in the South and East China seas to counter the Chinese military power
Aziz Akhannouch: Aziz Akhannouch has recently been appointed as the new Prime Minister of Morocco.
Key Highlights:
- He was appointed by the country’s King Mohammed VI.
- Akhannouch’s National Rally of Independents (RNI) party secured 102 out of the 395 seats in the parliament election, held on September 10, 2021.
- He defeated the moderate Islamist Justice and Development Party (PJD), which won a paltry 13 seats.
About Aziz Akhannouch:
- Prior to this appointment, the 60yearold was the Minister of Agriculture from 2007 to 2021.
- He is one of the wealthiest people in Morocco with an estimated fortune of around $2 billion.
- He is the CEO of the Akwa Group. It is a Moroccon conglomerate that operates mainly in the gas and the oil sector.
About Morocco:
- Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco is the northwesternmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa.
- It lies directly across the Strait of Gibraltar from Spain.
- It is bordered by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea.
- Algeria and Western Sahara are the land borders to the south and east.
- The high Atlas Mountains separate the mild coastline from the harsh Sahara.
- Moroccan identity and culture is a vibrant mix of Berber, Arab, and European cultures.
- Its capital is Rabat.
- The currency used here is Moroccan dirham.
- The current King of Morocco is Mohammed VI.
National
Operation Blue Freedom Triple World Records:
A team of eight persons with disabilities created a new world record for the “largest number of people with disabilities” to scale the world’s highest battlefield, Siachen Glacier.
Key Highlights:
- They scaled up to the Kumar Post at an altitude of 15,632 ft.
- The team with disabilities was trained and led by CLAW Global, a team of Special Forces veterans who had left the service due to disabilities.
- This is the land world record expedition part of “Operation Blue Freedom Triple World Records” being undertaken by CLAW Global.
- The expedition team climbed a total distance of 60 km atop the spine of the Siachen Glacier over a period of five days from September 7 to finally reach Kumar Post on September 11, 2021.
About Team CLAW:
- Team CLAW (full form of CLAW is Conquer Land Air Water) is a team of exIndian Special Forces commandos.
- In general, all the team members are either from Indian Army Para Commandos or the Naval Marine Commandos, also known as the MARCOS.
- Each team member had been a crack soldier in the Army / Navy Special Forces and was highly trained with multiple specializations in Mountaineering, Skydiving, SCUBA diving, Unarmed combat, Multi – terrain survival tech, Emergency Med Response, etc.
- Each team member had undergone some of the toughest selection, training and operational environments anywhere on the globe.
- The Team united their energy and skills to teach their life skills to people having disabilities.
- Their focus is to design and implement sustainable largescale employment solutions for people with disabilities and the underprivileged, especially in the Environment conservation and Sustainability space.
- The initiative was taken by Major Vivek Jacob, a Para (Special Forces) officer.
About Maj Vivek Jacob:
- Team CLAW’s founder Major Vivek Jacob served 14 years as a Special Forces operator.
- Post his training in the National Defence Academy and the Indian Military Academy, he volunteered for and successfully completed one of the harshest Special Forces selections in the world.
- In January 2019, Major Vivek Jacob, a Para SF officer with 14 years of experience in the Indian Army who had to hang up his boots following a combat skydive injury, founded CLAW Global (Conquer Land Air and Water), to teach life skills to adventurers and people with disabilities (PWD).
About the Operation Blue Freedom:
- Operation Blue Freedom was launched in 2019 by CLAW Global, a team of former Special Forces Operatives of the Indian Army and the Indian Navy.
- Its main aim is to shatter the common perception of pity, charity and inability associated with people with disabilities and recreates it to one of dignity, freedom and ability.
- Further, their focus is to ‘design and implement sustainable largescale employment solutions’ for people with disabilities, especially in the ‘Environment conservation and Sustainability’ space.
About Siachen Glacier:
- The Siachen Glacier is located in the Eastern Karakoram range in the Himalayas, just northeast of Point NJ9842 where the Line of Control between India and Pakistan ends.
- It is the SecondLongest glacier in the World's NonPolar areas.
- Fedchenko Glacier, located in Yazgulem Range, Tajikistan is the longest glacier in the World's NonPolar areas.
- The Siachen Glacier lies immediately south of the great drainage divide that separates the Eurasian Plate from the Indian subcontinent in the extensively glaciated portion of the Karakoram sometimes called the "Third Pole".
- The Siachen Glacier is part of Ladakh which has now been converted into a Union Territory.
- The Siachen Glacier is the world's highest battlefield.
- The entire Siachen Glacier has been under the administration of India since 1984 (Operation Meghdoot).
What is the importance of Siachen Glacier?
- The Siachen glacier demarcates central Asia from the Indian subcontinent, and separates Pakistan from China in the region.
- The Saltoro Ridge of the Siachin glacier serves as a divide that prevents direct linking of PoK with China, stopping them to develop geographical military linkages in the area.
Engineer's Day 2021: September 15 is observed as Engineer's Day every year in India to mark the birth anniversary of Mokshagundam Visvesvaraya who is considered a pioneer in the field of engineering in India.
Highlights:
The day is observed to commemorate the great work of engineers and to encourage them for improvement and innovation.
The year 2021 marks the 160th birth anniversary of M Visvesvaraya.
His contributions to the field of engineering and education are significant.
Visvesvaraya was regarded as the "Father of Modern Mysore".
History of Engineers Day:
Since 1968, India has celebrated Engineers day on this day every year.
His birthday is celebrated as Engineers’ Day in India, Sri Lanka and Tanzania.
Note: Every country celebrates its engineers on different days.
UNESCO has marked March 4 as the annual World Engineer's Day to honour the contribution of various engineers in a variety of field.
About Sir MV:
Popularly known as Sir MV, Mokshagundam Visvesvaraya was born on September 15, 1861, in the Muddenahalli village of Karnataka.
He completed his school education in his hometown and later went to study Bachelor of Arts (BA) from the University of Madras. However, he changed his career path after graduating and pursued civil engineering at the College of Science in Pune.
He undertook many complex projects and delivered remarkable infrastructural results during his career.
Mokshagundam Visvesvaraya passed away in 1962 but his achievements and contributions are celebrated till date.
Contributions of Sir Visvesvaraya:
Sir MV was the founder of Block System to prevent the wasteful flow of water in dams, which was first installed at the Khadakvasla reservoir in Pune.
He patented and designed the 'automatic barrier water floodgates' installed in Pune in 1903 at the Khadakvasla reservoir.
In 1917, he established the Government Engineering College at Bangalore which was later renamed after him as University Visvesvaraya College of Engineering (UVCE).
He was the Chief Engineer for the Krishna Raja Sagar dam project in Karnataka.
He was one among the committee members who had planned the Indian Economy in 1934.
An expert in irrigation techniques and flood disaster management, Sir MV was not just a great civil engineer but also served as the 19th Diwan of Mysore from 1912 to 1919.
While serving as the Diwan of Mysore, in 1915 he was awarded ‘Knight’ as a commander of the British Indian Empire by King George V.
In 1955, Sir Mokshagundam Visvesvaraya received India's highest honour, the Bharat Ratna for his contribution to the building of India.
India's Top Six Engineers:
The milkman of India Verghese Kurien
The Indian king of communication Satish Dhawan
The missile man of India Dr APJ Abdul Kalam
Magic maker at Microsoft Satya Nadella
Google's Sundar Pichai
India and Italy: Union Cabinet chaired by the Prime Minister Narendra Modi recentlyapproved the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Italy on Cooperation in the field of Disaster Risk Reduction and Management.
- MoU was signed between National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) of India and Department of Civil Protection of the Presidency of Council of Ministers of Italy.
Benefits of the MoU:
- The MoU seeks to put in place a system, whereby both India and Italy will benefit from the Disaster Management mechanisms of each other.
- It will help in strengthening the areas of preparedness, response and capacity building in the field of Disaster Management.
Background:
- This MoU on cooperation in the Field of Disaster Risk Reduction and management between the NDMA of the Republic of India and the Department of Civil Protection of the Presidency of the Council of Ministers of the Italian Republic was signed in June, 2021.
Economic, Political and Cultural and Historical Relations with India:
Economic Relations:
- India fifth largest trading partner among the European Union in Italy whereas Italy is the fifth largest investor in India.
Political Relations:
- India and Italy established political relations in 1947 after India's independence.
Cultural Relations:
- India and Italy, both signed cultural cooperation in 1976.
- It comprises of Cultural Exchange Programme (CEP) between both the nations, that provides for exchange of students in language programmes and other academic courses.
- However, culturally both the countries share relation since ancient time.
Historical Relations:
- Classical languages namely Sanskrit and Latin belong to IndoEuropean language family.
- For more than 2000 years, peoples of these two ancient civilizations have interacted and traded with each other.
- Italian port cities acted as important trading posts on the spice route to carry spices from India to European nations. Indian troops were also active in Italy during World War II.
About Italy:
- Italy, officially the Italian Republic is a country consisting of a peninsula delimited by the Alps and several islands surrounding it.
- Italy is located in the center of the Mediterranean Sea, in Southern Europe and is also often considered part of Western Europe.
- It shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia, and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino.
- Its capital is Rome which is home to the Vatican as well as landmark art and ancient ruins.
- The currency used here is Euro.
- The current President and Prime Minister of Italy are Sergio Mattarella and Mario Draghi.
15th EAS of Energy Ministers: The Union Minister of State for Power Shri Krishan Pal Gurja recently attended the 15th East Asia Summit Energy Ministers Meeting virtually.
Key Highlights:
- The Theme of the meeting was “We Care, We Prepare, We Prosper”.
- The meeting was aimed at coordinating efforts of Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) countries in pursuing the goal of energy security and energy transition that will benefit the people of the region.
Key points about the meeting:
- India established that ASEAN is a region of great importance and engagement with ASEAN has been, and will remain, a critical element of India’s ‘Act East’ policy and strategy.
- Acting East is now a central element in India’s IndoPacific vision.
- India also provided a brief status of the Indian energy transition plans, policies, challenges and efforts towards decarbonization.
- Some of India’s towards decarbonization initiatives include the following:
- National Solar Mission (NSM)
- Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY)
- Unnat Jyoti by Affordable LEDs for All (UJALA)
- Smart City Mission (SCM)
- FAME India Scheme
- National Hydrogen Mission
- Waste to Energy Projects
- International Solar Alliance (ISA), which has more than 70 member countries.
- As of now, India is among the world’s top five countries in terms of renewable power capacity.
About East Asia Summit:
- The East Asia Summit, established in 2005, is a premier forum in the AsiaPacific region dealing with issues relating to security and defence.
- It is a forum of 18 regional leaders for strategic dialogue and cooperation on the key political, security, and economic challenges facing the IndoPacific region.
- The concept of East Asia Grouping was first promoted in 1991 by the then Malaysian Prime Minister, Mahathir bin Mohamad.
Membership:
- It comprises the ten member states of the ASEAN which are Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand, and Vietnam, along with 8 other countries namely Australia, China, Japan, India, New Zealand, the Republic of Korea, Russia and the USA.
- ASEAN leads the forum, and the chair position rotates between the ASEAN Member States annually.
- India is one of the founding members of the East Asia Summit.
Note: Brunei Darussalam is the chair for 2021.
ASEAN:
- It refers to the Association of Southeast Asian Nations.
- ASEAN is a regional intergovernmental organisation and it comprises of 10 countries in Southeast Asia.
- It was created on 8 August 1967 by 5 countries namely Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Philippines and Thailand.
- The ASEAN Secretariat is located at Jakarta, Indonesia.
- The Summit is held twice annually.
- The First ASEAN Summit was held in Bali, Indonesia in 1976.
- It was created with an aim to promote intergovernmental cooperation.
- The organization also facilitates political, economic, military, educational, security, and sociocultural integration among its members as well as in other countries in Asia.
- ASEAN has been India’s utmost priority under its Act East Policy.
- The 10 member countries are Indonesia, Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia, Philippines, Vietnam, Brunei, Cambodia, Myanmar (Burma), Laos
Act East Asia Policy:
- It was announced in November 2014 as a diplomatic initiative to promote economic, strategic and cultural relations with the vast AsiaPacific region at different levels.
- It involves intensive engagement with Southeast Asian countries in the field of connectivity, trade, culture, defence and peopletopeoplecontact at bilateral, regional and multilateral levels.
Ek Pahal Drive: A PanIndia Special Campaign called “Ek Pahal / à¤à¤• पहल” drive for Justice Delivery at doorstep was recently launched by the Ministry of Law and Justice.
Key Points about EK Pahal Campaign:
- This campaign was launched by Department of Justice and National Legal Services Authority (NALSA).
- It was launched on 17 September 2021 in a bid to encourage mass registration under TeleLaw.
Note: TeleLaw means the use of communications and information technology for the delivery of legal information and advice.
- Department of Justice has partnered with NALSA and CSC eGovernance Service India Limited for mainstreaming legal aid to the marginalized communities through Common Services Center (CSC).
- The Ek Pahal campaign will run across the India from 17th September till 2nd October.
Justice in Preamble:
- The Preamble to the Constitution of India has recognised Justice as the first deliverable for the Indian citizens.
- A successful and vibrant democracy is where every citizen not only get guaranteed justice, but where justice is equitable.
- This principal mandates for State to create an environment where justicedelivery is looked as a citizencentric service rather than a sovereign function.
What is the significance of Tele law?
- The significance of Tele law is that provides prelitigation advice or consultation to beneficiaries by Panel Lawyers.
- This medium uses a huge network by covering 51,434 Common Service Centres across 50,000 Gram Panchayats in 633 districts of 34 States & UTs.
- It will also be holding 4100 Legal Aid Clinics to give prelitigation or legal advice to common citizens with the help of Panel Lawyers and ParaLegal Volunteers.
- Awareness programmes will also be launched at village level on legal aid in 672 districts.
About NALSA:
- The National Legal Services Authority (NALSA) has been constituted under the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987.
- It was established on 9 November 1995.
- The principal objective of NALSA is to provide free and competent legal services to the weaker sections of the society and to ensure that opportunities for securing justice are not denied to any citizen by reason of economic or other disabilities, and to organize Lok Adalats for amicable settlement of disputes.
- The current Executive of NALSA is Hon'ble Mr. Justice Uday Umesh Lalit.
Planetarium Innovation Challenge: MyGov India, under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has recently launched the Planetarium Innovation Challenge for Indian startups and tech entrepreneurs.
Key Highlights:
- This Planetarium challenge was launched with the main aim to bring together the tech firms and Startups, which are based out of India, with the potential to build indigenous planetariums system software.
- This system software must be built by using latest technologies such as Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR) and Merged Reality (MR).
- Planetarium Innovation Challenge Registration is open till 10th October 2021.
- The Innovation Challenge can be joined at https://innovateindia.mygov.in/.
- This challenge perfectly aligns with the objective of India’s progressive digital transformation under the Aatmanirbhar Bharat initiative.
Significance:
- This challenge provides an opportunity for Planetariums in India to deploy indigenously built new technologies for smaller cities and rural areas.
- It invites applications from startups and tech entrepreneurs in order to develop stateoftheart technology for Planetariums.
Background:
- This challenge has been inspired by the Chandrayaan launches.
- Prior to the launch, Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) had conducted the ISRO Quiz Competition2019 in collaboration with MyGov.
- In that quiz, several schools, parents and enthusiastic mentors had actively participated.
Planetarium Innovation Challenge Prizes:
- The 1st Winner will get five lakh.
- The 2nd Winner will get three lakh.
- The 3rd Winner will get two lakh.
About MyGov:
- MyGov has been established as Government of India's Citizen Engagement Platform.
- This platform collaborates with multiple Government bodies/ Ministries to engage with citizens for policy formulation and seeks the opinion of people on issues/ topics of public interest and welfare.
- It was established on 26th July 2014.
- Its main aim is to promote the active participation of Indian citizens in the governance and development of India.
- It also aims to create common platform for Indian citizens in a bid to “crowdsource governance ideas from citizens”.
People In News
Appointments:
Justice M. Venugopal: Justice M. Venugopal has been named as the new Acting Chairperson of the appellate tribunal, National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT).
Highlights:
- This is the third time in a row that an Acting Chairperson is at the helm of the NCLAT, after the retirement of permanent Chairperson Justice S J. Mukhopadhaya on March 14, 2020.
- Previously, Justice Bansi Lal Bhat was the first Acting Chairperson from March 15, 2020 and then Justice AIS Cheema from April 19, 2021, and now Justice M. Venugopal with effect from September 11, 2021.
Note: The Government of India (GoI) has appointed thirty one members to the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) and the Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT).
About Justice M. Venugopal:
- He is a former judge of the High Court of Madras.
- He had joined as a SubJudge in Tamil Nadu State Judicial Service on June 5, 1997.
- Later was elevated to Madras High Court in November 2007, where he had served for elevenandahalf years.
- He has also served as the Judicial Member of BCLAT, Principal Bench from October 2019 and then later moved to Chennai Bench of NCLAT in January 2021.
About the NCLAT:
- The NCLAT (National Company Law Appellate Tribunal) was constituted by the Central Government of India under Section 410 of the Companies Act, 2013.
- The tribunal is responsible for hearing appeals from the orders of National Company Law Tribunal(s) (NCLT), starting on 1 June 2016.
- It is also an appellate tribunal for hearing appeals against the orders passed by NCLT under the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), and by the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India (IBBI) under Section 202 and Section 211 of IBC.
- It is also the appellate tribunal to hear and dispose of appeals against any direction issued or decision made or order passed by the Competition Commission of India (CCI).
About the NCLT and ITAT:
The National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) deals with matters mainly related to companies law and the insolvency law, while the Income Tax Appellate Tribunal (ITAT) deals with income tax matters.
Alka Nangia Arora: Alka Nangia Arora has recently been appointed as the Chairman cum Managing Director (CMD) of the National Small Industries Corporation Ltd. (NSIC).
Highlights:
- Ms Alka Arora took the additional charge of the post on September 14, 2021.
- She is a Joint Secretary in Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises.
About NSIC:
- The National Small Industries Corporation Limited (NSIC) is an ISO 9001:2015 certified Government of India (GoI) Enterprise.
- It falls under Ministry of Micro, Small & Medium Enterprises of India.
- It is a Mini Ratna company established in 1955.
- It serves as a nodal agency for several schemes of Ministry of MSME.
PM Modi: Prime Minister Narendra Modi has recently been named among 100 most influential people of 2021 by the Time Magazine.
Highlights:
Time magazine unveiled its annual list of ‘The 100 Most Influential People of 2021’ on September 15, 2021.
Apart from PM Modi, Mamata Banerjee who is the chief minister of West Bengal and CEO of Serum Institute of India, Adar Poonawalla have also been named among the world’s 100 most influential people.
This annual list is a global list comprising of US President Joe Biden, VicePresident Kamala Harris, Duke & Duchess of Sussex Prince Harry & Meghan, former US president Donald Trump, Chinese President Xi Jinping, and cofounder of the Taliban, Mullah Abdul Ghani Baradar.
Time’s profile of PM Modi:
- According to Time’s profile of PM Modi, India has had three pivotal leaders namely Jawaharlal Nehru, Indira Gandhi and Modi.
- He is the third who has been dominating the India’s politics like no one since them.
Time’s profile of Mamata Banerjee:
- Mamata Banerjee has been described as the face of fierceness in Indian politics on the time’s profile.
- The profile mentions that the streetfighter spirit and selfmade life in the patriarchal culture sets her apart.
Time’s profile of Poonawalla:
- According to Time profile of Poonawalla, the 40yearold head of world’s largest vaccine maker “sought to meet the moment, from the beginning of Covid19 pandemic.
About Time:
- Time is an American news magazine and news website.
- It is published and is based in New York City.
- It was published weekly earlier, but by March 2020 it had switched to biweekly.
- First edition of the magazine was published on March 3, 1923.
Pawan Goenka: He is a former managing director of Mahindra & Mahindra who has been appointed as the chairperson of the Indian National Space Promotion Authorization Centre (InSPACe).
About InSPACe:
- INSPACe functions as an independent nodal agency under the Department of Space, Government of India (GoI).
- This centre acts as a facilitator and regulator of space activities in India.
About Pawan Goenka:
- Goenka, an IIT alumnus, had been associated with two major automobile companies – General Motors and Mahindra & Mahindra in his professional career that spanned over four decades.
- He retired as the MD of the company on April 1, 2021, after spending 27 years with the Mahindra Group.
- During his R&D tenure in M&M, he led the development of the Scorpio SUV.
Awards:
Women’s Prize for Fiction 2021: Author Susanna Clarke recently won the Women’s Prize for Fiction 2021 for her novel ‘Piranesi’.
Highlights:
- Susanna Clarke is an English author known for her debut novel Jonathan Strange & Mr Norrell.
- Novelist and Bookerwinner Bernardine Evaristo chaired the Women’s Prize judging panel for the year 2021.
About Piranesi:
‘Piranesi’ is narrated by a man living in a labyrinthine, statuefilled house — alone except for a visitor known as the Other — that comprises his whole universe.
Prof. S.K. Joshi Laboratory Excellence Award: Quality Council of India (QCI) recently launched India's firstofits kind Laboratory Excellence Award the Prof. S.K. Joshi Laboratory Excellence Award.
Key Points:
- This Award has been instituted to promote Laboratory Quality and performance improvement in the country.
- The award has been incepted to ensure the laboratory’s commitment to achieve excellence in providing high precision testing and calibration services in line with the prevalent national/international quality systems legislations, including Health, Safety & Environment.
- This award will be open to all currently operational Laboratories.
- The award has been categorized into 3 categories which are Testing, Calibration & Medical including their Proficiency Testing Providers & Reference Material Producers located in India.
- Each category includes a cash award as well.
- The award was named after Padma Bhushan awardee, late Prof. S.K. Joshi, a luminary in the discipline of science and academia.
About Prof. S.K. Joshi:
- Late Prof. S.K. Joshi was a luminary in the field of Science and Academica.
- He made a significant contribution in improving scientific research in India by serving as PresidentINSA, DGCSIR, DirectorNPL and ChairmanNABL.
- He was felicitated with Padma Bhushan, Padma Shri, CV Raman Medal of INSA and several other prestigious awards.
Places In News
Forest Rights Act, 2006:
The Jammu and Kashmir government, after a long delay, has decided to implement the Forest Rights Act, 2006 which was not enforced in the Union Territory for the past 14 years.
Key Points:
- It became applicable to J&K only after 31st October, 2019, hence, recognising the rights of forest dwelling communities for the first time in the Union Territory.
- The Forest Rights Act, 2006, will elevate the socioeconomic status of a sizeable section of the 14 lakh population of tribals and nomadic communities, including GujjarBakerwals and GaddiSippis in the Union Territory.
- In the past few years, there were growing cases of eviction of tribals from forest land in parts of the Kashmir Valley and Jammu region.
- The government termed them “illegal encroachers” but the regional parties accused the Forest Department of acting above the law in these cases.
- The Union Territory saw the arbitrary demolition of Gujjar and Bakerwal houses during a forest reclamation drive in contravention of the Forest Rights Act of 2006.
About Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006:
- The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006, is a key piece of forest legislation passed in India on 18 December 2006.
- It has also been called the Forest Rights Act, the Tribal Rights Act, the Tribal Bill, and the Tribal Land Act.
- The Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006 recognizes the rights of the forest dwelling tribal communities and other traditional forest dwellers to forest resources, on which these communities were dependent for a variety of needs, including livelihood, habitation and other sociocultural needs.
About Jammu and Kashmir:
- Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) is a region administered by India as a Union Territory.
- It was a region formerly administered by India as a state from 1954 to 2019.
- Provisions for the formation of the union territory of Jammu and Kashmir were contained within the Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019, which was passed by both houses of the Parliament of India in August 2019.
- The region of Jammu and Kashmir is separated by the Line of Control from the Pakistaniadministered territories of Azad Kashmir and GilgitBaltistan in the west and north respectively.
- It lies to the north of the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Punjab and to the west of Ladakh, which is also subject to the dispute as a part of Kashmir, and administered by India as a union territory.
- The current Lieutenant Governor of J&K is Former Union minister and BJP leader Manoj Sinha
Swachhata Pakhwada 2021: Swachhata Pakhwada 2021 was recently launched in Cochin Port Trust by administering the Swachhata pledge in all departments.
Highlights:
- On this occasion, the Shramdaan cleaning activities have also been started in the Port areas.
- Activities that were proposed during the Pakhwada includes the cleaning of work places, crafts & public spaces and office premises within the Port area.
- Various programmes during the period will be led by all the heads of the department.
- All the activities are being carried out in compliance of the social distancing/safety instructions issued by the Government to contain Covid19 pandemic.
About Swachhta Pakhwada:
- Swachhata Pakhwada started in April 2016.
- This initiative was started with the objective of bringing a fortnight of intense focus on the issues and practices of Swachhata by engaging GOI Ministries/Departments in their jurisdictions.
- In order to plan the Pakhwada activities, an annual calendar is circulated among the Ministries in advanced.
- The Ministries observing Swachhata Pakhwada are monitored closely using online monitoring system of Swachhata Samiksha where action plans, images, videos related to Swachhata activities are uploaded and shared.
- After observing Swachhata Pakhwada, Ministries/ Departments announce their achievements through a press conference and other communication tools.
- For the Pakhwada fortnight, observing ministries are considered as Swachhata Ministries and are expected to bring qualitative Swachhata improvements in their jurisdictions.
About Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM):
- The Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) is a countrywide campaign that was initiated by central government in 2014.
- The SBM was started with the objective of eliminating open defecation and improving solid waste management.
- This mission is a restructured version of Nirmal Bharat Abhiyan which was launched in 2009.
- Nirmal Bharat Abhiyan failed to achieve its intended targets.
- Phase 1 of the Swachh Bharat mission ended in October 2019 while Phase 2 of the mission has been implemented between 2020–21 & 202425.
About Cochin Port Trust:
- Kochi, formerly known in English as Cochin is a major port city on the Malabar Coast of India bordering the Laccadive Sea, which is a part of the Arabian Sea.
- It is part of the district of Ernakulam in the state of Kerala and is often referred to as Ernakulam.
- Kochi is known as the financial, commercial and industrial capital of Kerala.
NIELIT Centres: The Union Minister of State in the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, Skill Development and Entrepreneurship Rajeev Chandrasekhar inaugurated five NIELIT Centres in North East Region.
Highlights:
- He inaugurated one of the NIELIT centres in Manipur’s Churachandpur district physically and two other centres at Aizawl of Mizoram and Kokrajhar and Tejpur of Assam through video conferencing.
- On the occasion, two existing centres at Imphal & at Aizawl districts of Mizoram were upgraded.
- The Minister noted that these NIELIT centres would be soon be acting as job creation centres with the collaboration of Centre and States.
- These centres will not just be training centres for students but will get them into the runway of opportunity and jobs.
About National Institute of Electronics & Information Technology (NIELIT):
- NIELIT is an autonomous scientific body under the administrative control of the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MoE&IT), Government of India (GoI).
- NIELIT was formerly known as the DOEACC Society.
- It was set up to carry out Human Resource Development and related activities in the area of Information, Electronics & Communications Technology (IECT).
- It offers Information Technology & Electronics training at different levels.
- IT enjoys the power similar to Organizations like CBSE, UGC etc.
About Northeast India:
- Northeast India is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political administrative division of the country.
- The North Eastern Region (NER) comprises eight states – Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura and Sikkim.
- Previously known as the Seven Sisters, northeast India became richer with the addition of an eighth, Sikkim in 1975.
Medicine from the Sky: Civil aviation minister Jyotiradtiya Scindia has recenlty launched a first of its kind project named “Medicine from the Sky” in Telangana.
Key points about the project:
- The project has aimed at transporting vaccines and other essential products to remote areas using drones.
- The Medicine from the Sky project will be taken up on a pilot basis in 16 green zones in Telangana and later scaled up on the national level based on data.
- Medicines from the Sky project will be taken up in 16 green zones and the data will be analysed for three months.
- Along with the health ministry, IT ministry, state government and the Centre will together analyze the data and make a model for the whole country.
About Telangana:
- It is a state in India situated on the centresouth stretch of the Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau.
- It was founded on 2 June 2014.
- Its Capital city is Hyderabad.
- The current Governor and Chief Minister of Telangana are Tamilisai Soundararajan and K. Chandrashekar Rao respectively.
Rajbhasha Keerthi Puraskar: Recently, on September 14, 2021, the highest and the most prestigious ‘Rajbhasha Keerthi Puraskar’ award was given to National Mineral Development Ltd. (NMDC) under the Ministry of Steel during the Rajbhasha Diwas Samaroh in New Delhi.
Highlights:
- Minister of State for Home Affairs Nityanand Rai presented the awards during the National Hindi Day celebrations.
- The Hindi Diwas Samaroh was presided over by Home Minister Shri Amit Shah.
Winners:
- NMDC got the 3rd prize in the category of Undertakings situated in the ‘C’ region during 201920.
- NMDC has been winning the Rajbhasha Keerthi Puraskar award for the past three years in a row.
- The award is presented to recognize the efforts towards the implementation of Hindi as the official language.
- Dr. Sailesh Shukla, Assistant Manager (Rajbhasha), NMDC Donimalai Iron Ore Project was also awarded Rajbhasha Gourav Puraskar for his article.
- Vishakhapatnam Steel Plant was also presented with the Rajbhasha Keerthi Puraskar (first prize) for the effective implementation of Hindi as the official language during 202021.
About National Mineral Development Ltd. (NMDC):
- NMDC Limited is a government owned mineral producer.
- It is under the administrative control of Ministry of Steel, Government of India (GoI).
- It was founded on 15 November 1958.
- It is involved in the exploration of iron ore, copper, rock phosphate, limestone, dolomite, gypsum, bentonite, magnesite, diamond, tin, tungsten, graphite, etc.
- It is India's largest iron ore producer and exporter, producing more than 35 million tonnes of iron ore from three mechanized mines in Chhattisgarh and Karnataka.
- It also operates the only mechanized diamond mine in the country at Panna in Madhya Pradesh.
Kushinagar Airport: The Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) has recently declared Kushinagar Airport in Uttar Pradesh as a Customs notified airport.
Highlights:
- This would also facilitate international passenger movements including that of Buddhist pilgrims.
About the airport:
- Kushinagar airport is an international airport spread across an area of 600 acres.
- It had been granted the licence to operate international flights by Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) last February.
About Kushinagar:
- Kushinagar is a town in the Kushinagar district of Uttar Pradesh.
- It is an important Buddhist pilgrimage site, where Buddhists believe Gautama Buddha attained Mahaparinirvana after his death.
About CBIC:
- Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) (erstwhile Central Board of Excise & Customs) is the nodal national agency responsible for administering Customs, GST, Central Excise, Service Tax and Narcotics in India.
- It comes under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance.
- It was founded on 1 January 1964.
- Shri M. Ajit Kumar is the Chairman of Central Board of Excise & Customs.
MeghEA: IT Minister Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw and CM Meghalaya Shri Conrad Sangma recently launched Meghalaya Enterprise Architecture Project (MeghEA).
Key points:
- The MeghEA initiative is spread across 6 pillars which are as follows:
- Governance
- Human Resources
- Entrepreneurship
- Primary Sector
- Infrastructure
- Environment
- The project envisions making Meghalaya a high income state by 2030.
- The project aims to improve service delivery and governance for the people using power of Digital technologies.
- The initiative is in line with Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi’s vision of Digital India that focuses on transforming the lives of common people.
- With the notification of India Enterprise Architecture (IndEA) in 2018, design and implementation of integrated, nationally portable and scalable digital platforms have gained a new momentum.
Background:
- During the launch of the North East vision document in Aug 2018, Meghalaya was selected as the pilot first pilot State for preparation of Meghalaya Enterprise Architecture (MeghEA) and design and implementation of MeghEA integrated Finance Solution Architecture.
About Meghalaya:
- It is a state in northeastern India.
- Meghalaya was formed by carving out two districts from the state of Assam: the United Khasi Hills and Jaintia Hills, and the Garo Hills on 21 January 1972.
- Its capital is Shillong.
- The current Governor and Chief Minister of Meghalaya are satya Pal Malik and Conrad Sangama respectively.
Science and Technology
pgSIT:
Using Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)based genetic engineering, the scientists at the University of California San Diego have recently created a new technology for controlling mosquitoes.
Highlights:
- pgSIT stands for precisionguided Sterile Insect Technique”.
- Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) is an environmentally safe and proven technology to suppress wild populations.
- Details of the pgSIT have been described in Nature Communications.
Note: Mosquitoes infect millions each year with debilitating diseases such as malaria and dengue.
Key Details:
- To advance its utility, a novel CRISPRbased technology is termed as precisionguided sterile insect technique (pgSIT).
- The pgSIT is a new scalable genetic control system that uses a CRISPRbased approach to engineer deployable mosquitoes that can suppress populations.
- Males don't transmit diseases so the idea is to release more and more sterile males.
- Therefore, the population can be suppressed without relying on harmful chemicals and insecticides.
- It alters genes linked to male fertility—creating sterile offspring—and female flight in Aedes aegypti, the mosquito species responsible for spreading diseases including dengue fever, chikungunya and Zika.
- The pgSIT uses CRISPR to sterilize male mosquitoes and render female mosquitoes (which spread disease) flightless.
- According to the release, the system is selflimiting and is not predicted to persist or spread in the environment, two safety features that should enable acceptance for this technology.
- The scientists have stated that the pgSIT eggs can be shipped to a location threatened by mosquitoborne disease or developed at an onsite facility that could produce the eggs for nearby deployment.
- Once the pgSIT eggs are released in the wild, sterile pgSIT males will emerge and eventually mate with females, driving down the wild population as needed.
About CRISPR:
- Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) is a gene editing technology.
- It replicates natural defence mechanisms in bacteria to fight virus attacks, using a special protein called Cas9.
- CRISPRCas9 technology behaves like a cutandpaste mechanism on DNA strands that contain genetic information.
- The specific location of the genetic codes that need to be changed, or edited, is identified on the DNA strand, and then, using the Cas9 protein, which acts like a pair of scissors, that location is cut off from the strand.
- A DNA strand, when broken, has a natural tendency to repair itself.
- Scientists intervene during this autorepair process, supplying the desired sequence of genetic codes that binds itself with the broken DNA strand.
- CRISPRCas9 is a simple, effective, and incredibly precise technology with potential to revolutionize human existence in future.
Imp Info: Emmanuelle Charpentier of France and Jennifer A Doudna of the USA were awarded the 2020 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing CRISPR/Cas9 genetic scissors.
Source: IE & SD
Transparent Ceramics: Indian researchers, for the first time in India, have recently developed transparent ceramics, reaching theoretical transparency through a technique called colloidal processing followed by simultaneous application of temperature and pressure.
Key Details:
- The material can be used for thermal imaging applications, especially in harsh service conditions and personal protection systems such as face shields, goggles and helmets.
- These transparent ceramics is a new class of advanced materials with unique transparency and excellent mechanical properties.
- The materials can be designed not only for transparent to visible light but also for ultraviolet (UV), Infrared (IR), and Radiofrequency (RF), giving opportunity for diverse applications.
- Though produced by different countries globally, transparent ceramics are restricted in supply as they can be used for strategic applications.
- This research has been published in the journal ‘Materials Chemistry and Physics’ recently.
- With potential applications in infantry personal protection systems involving thermal imaging such as helmets, face shields, and goggles, these transparent ceramics developed in India is a step towards Atmanirbhar Bharat.
Strophodus jaisalmerensis: In a rare discovery, teeth of new species of hybodontshark of Jurassic age have been reported for the first time from Jaisalmer in Rajasthan.
Highlights:
- As per a statement released on September 15, 2021 by the mines ministry of India, the "rare" and newly discovered crushing teeth represent a new species named by the research team as Strophodusjaisalmerensis.
- The discovery was made by a team of officers from the Geological Survey of India (GSI), Western Region, Jaipur.
- This finding has been published in Historical Biology, Journal of Palaeontology of International repute
- Hybodont sharks have been reported for the first time from the Jurassic rocks (approximately, between 160 and 168 millionyearsold) of the Jaisalmer region of Rajasthan.
Key Points about Hybodonts:
- Hybodonts, an extinct group of sharks, was a dominant group of fishes in both marine and fluvial environments during the Triassic and early Jurassic time.
- However, hybodont sharks started to decline in marine environments from the Middle Jurassic onwards until they formed a relatively minor component of openmarine shark assemblages.
- Hybodonts finally became extinct at the end of the Cretaceous time 65 million years ago.
- Significantly, the newly discovered crushing teeth from Jaisalmer represent a new species named by the research team as Strophodus jaisalmerensis.
- The genus Strophodus has been identified for the first time from the Indian subcontinent and is only the third such record from Asia, the other two being from Japan and Thailand.
- The new species has recently been included in the Shark references.com, an international platform operating in association with International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), Species Survival Commission (SSC), and Germany.
Significance:
- This discovery marks an important milestone in the study of Jurassic vertebrate fossils in the Jaisalmer region of Rajasthan, and it opens a new window for further research in the domain of vertebrate fossils.
About Geological Survey of India (GSI):
- The Geological Survey of India (GSI) is a scientific agency of India.
- The GSI was set up on 4 March 1851 primarily to find coal deposits for the Railways.
- Over the years, GSI has not only grown into a repository of geoscience information required in various fields in the country but has also attained the status of a geoscientific organisation of international repute.
- Its main functions relate to creating and updating of national geoscientific information and mineral resource assessment.
BRICS Young Scientists Forum: The 6th BRICS Young Scientist Forum was conducted on September 17, 2021 in India by Science and Technology (DST), in collaboration with National institute of Advanced Studies, Bengaluru (NIAS).
Highlights:
- The Secretary Department of Science and Technology Dr Renu Swarup, highlighted the importance of cooperation, collaboration and connections for science to move forward, at the BRICS Young Scientists Forum.
Background:
- India at the 6th BRICS Summit in Fortaleza Brazil (July 2014) had came up with the idea of creation of BRICS Young Scientists Forum.
- The proposal was put forward to develop an engaging and innovative mechanism to network and connect the BRICS youth.
About BRICSYSF:
- The BRICSYSF summits were first hosted by India in Bengaluru in 2016, followed by China in 2017, South Africa in 2018, Brazil in 2019, and Russia in 2020.
- This year the fourday conclave started on 13 September 2021 would end on 16 September.
- The best young scientist with an idea on innovation would be awarded at the BRICSYSF 2021.
- Young innovator prize has been one of the focuses of the BRICSYSF and the award is supported by the DST, Government of India (GoI).
- The next conclave would be organized by China in 2022.
BRICSYoung Innovator Prize:
- India's first BRICSYoung Innovator Prize was started in 2016.
- It was aimed at recognizing and rewarding the best innovation projects representing technological innovation and a potential contribution to the science and technology sector for the benefit of the BRICS countries.
- In this the winner gets award money of USD 25000. China hosted the 2nd BRICS YSF in 2017.
Private EarthCircling Trip: SpaceX recently launched four amateurs on its first ever private flight.
Key Highlights:
- It was for the first time that a spacecraft circled Earth with an allamateur crew and no professional astronauts.
- Earthcircling trip was started onboarding two contest winners, a health care worker as well as their rich sponsor.
- The four amateur astronauts are travelling to an altitude of 357 miles (575 kilometres) above the surface of the Earth.
- They will be encircling the Earth in the private flight which is much further and deeper into space than the International Space Station (ISS), for three days.
- Their flight will splash down off the Florida coast by September 19th.
Who is leading the flight?
- The trip is being sponsored by Jared Isaacman, a 38yearold billionaire and philanthropist with pilot training. He is the founder and chief executive officer (CEO) of payment processor Shift4 Payments Inc, and also the mission commander of the spaceflight, having chosen the rest of the crew himself through a competition.
- Isaacman is the third billionaire to launch so far, following the brief spaceskimming flights of Virgin Galactic’s Richard Branson and Blue Origin’s Jeff Bezos in July 2021.
- Apart from this, Arceneaux is flying who is set to become the youngest American in space as well as the first person with prosthesis, a titanium rod in her left leg, to travel space.
- Chris Sembroski, a US Air Force veteran who now works as an aerospace data engineer for Lockheed Martin in Seattle is also part of the crew.
- The other member is Sian Proctor, a 51yearold geoscientist in Phoenix who was almost selected to become an astronaut for NASA in 2009.
Space Tourism:
- This flight is the first entry in the competition for space tourism dollars by SpaceX founder Elon Musk.
About Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX):
- Space Exploration Technologies Corp., trading as SpaceX, is an American aerospace manufacturer and space transportation services company.
- It was founded on 6 May 2002 by Elon Musk with the goal of reducing space transportation costs to enable the colonization of Mars.
- This privately held company is headquartered in Hawthorne, California, United States.
- SpaceX manufactures Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy launch vehicles, rocket engines, crew spacecraft, Dragon cargo, and Starlink communications satellites.
Sports
US Open 2021:
Daniil Medvedev recently won the U.S. Open as Novak Djokovic fell short of a Grand Slam.
Highlights:
In the men's category, he defeated world number one Novak Djokovic 64 64 64 in the U.S. Open final on 12 September 2021 to win his first Grand Slam title at the Arthur Ashe Stadium in New York.
In the women’s category, Great Britain’s tennis player Emma Raducanu defeated Canada’s Leylah Annie Fernandez to win the 2021 US Open women’s singles final title.
Complete List of Winners in Different Categories:
Men’s Singles category:
Daniil Medvedev and runners up was Novak Djokovic
Women’s Singles category:
Emma Raducanu and runners up was Leylah Annie Fernandez
Men’s Doubles category:
Ram/Salisbury and runners up were Jamie Murray/Bruno Soares
Women’s Doubles category:
Stosur/Zhang runners up were Coco Gauff/ McNally
Mixed Doubles category:
Krawczyk/Salisbury runners up were Giuliana Olmos/Marcelo Arevalo
About US Open Tennis Tournament:
The United States Open (US Open) Tennis Championships is a hard court tennis tournament.
The tournament is the modern version of one of the oldest tennis championships in the world, the US National Championship, for which men's singles and men's doubles were first played in August 1881.
This tournament was founded in 1881.
Since 1987, the US Open has been chronologically the fourth and final Grand Slam tournament of the year.
The other three, in chronological order are:
The Australian Open,
French Open
Wimbledon
The US Open starts on the last Monday of August and continues for two weeks, with the middle weekend coinciding with the US Labor Day holiday.
Italian Grand Prix 2021: Daniel Ricciardo (McLaren, AustralianItalian) has won the Formula One Italian Grand Prix 2021 title held at Autodromo Nazionale Monza track, Italy.
Highlights:
It is his first victory in 9 years.
Lando Norris came second while Valtteri Bottas came third in the F1 race.
Lewis Hamilton and Max Verstappen crash out of Italian Grand Prix 2021 due to collision.
Current Affairs October 06 to October 12
Indian polity
AOEI : It means Automatic exchange of information. It is a framework which provides cooperation between tax authorities across countries. It also provides information about the OECD and Global Forum on Transparency and Exchange of Information for Tax Purposes in the area of the automatic exchange of information.
India achieved success against black money hoarding by Indians in Switzerland Banks. Switzerland shared the details under the automatic information exchange framework (AOEI) between the two countries. India received the first tranche of information. The information given by Switzerland authorities includes tax identification numbers and also names, addresses, details concerning the financial institution, account balance and capital income. The account detail information was exchanged by the Federal Tax Administration (FTA) of Switzerland under AOEI with India and 75 countries. This is for the first time under the pressure of the whole world Switzerland shared financial details of accounts that is currently active as well as those accounts that were closed during 2018.
Previously, in December 2017 India and Switzerland had signed an agreement that allowed automatic sharing of tax-related information from January 2018. The agreement marked an important milestone to fight against black money deposited abroad.
Draft Arms (Amendment) Bill : According to the draft Arms (Amendment) Bill, anyone possessing more than two licensed guns will have to deposit the third one with authorities as the Government of India (GoI) is planning to ban the practice of multiple licenses to individual by making amendment in Section 25 (1AA) of Arms act 1959. The Union Home Ministry proposed an amendment to convict makers and users of illegal arms.
As per the draft of the proposed law - the offence invites imprisonment not be less than seven years but may extend to life imprisonment that is up to 14 years that person's life" for manufacturing, selling, repairing and possessing "prohibited" arms. The amendment also categorizes illegal import of guns and their sales as “illicit trade”. The makers of “prohibited” arms and those carrying or buying such arms will have to spend remainder of their life in prison if convicted. The bill is to be introduced in the winter session of the parliament.
Arms Act 1878 : The Indian Arms Act of 1878 was enacted by legislated during Lord Lytton's time. By this act, no Indians could manufacture, sell, possess, and carry firearms. At that time Lord Lytton was the Viceroy of India in 1858.
Arms Act, 1959 : The Arms Act was passed in 1959 .It is an Act of the Parliament of India to consolidate and amend the law relating to arms and ammunition in order to curb illegal weapons and violence stemming from them. It replaced the Indian Arms Act, 1878. However many changes have been made in the Arm Act since 1959. Most recently in 2010 amendment was made in The Arms Act. The changes made in the draft were rules and regulations about acquisition, possession, manufacture, sale, and import and export ammunition in India. It also provided provisions relating to licenses. The act listed the punishments associated with breaking rules related to the act. IT also provided details on powers that the officials possessed to enact it.
Indian Policy
E – Dant Seva : Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare, Dr Harsh Vardhan launched eDant Seva website & Mobile application. A Braille Booklet which focuses on oral health for visually impaired which constitutes in the National Oral Health Program was also launched by the minister. It is an initiative launched under Oral Health Program. Its objective is to sensitize the importance of maintaining oral health. It provides information about nearest oral health service facility and also oral health information collected from authentic scientific sources. It aims to promote Public Private Partnership (PPP) to achieve public health goods.
The first National Oral Health Policy that was launched in 1986 was drafted by the Indian Dental Association. The first National Oral Health Care Program was launched in 1999. In the 11th five-year plan, between 2007 and 2012, a token amount was allocated for research in oral health under National Rural Health Mission. In 2014, The National Oral Health Program was launched in 2014 by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare National Oral Health Program.
PMJAY : It refers to Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana. The scheme was launched in September 2018 with cancer care as its top priority. The National Cancer Grid alongwith the National Health Authority collaborated to battle cancer under the scheme. The main objective was to develop uniform standards of patient care of prevention, diagnosis and treatment for cancer.
The Union Health Ministry released its data on PMJAY – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana. The aim of the scheme is to help economically vulnerable persons. It's aim is to cover more than 10 crore families.
GEMINI : It means Gagan Enabled Mariner’s Instrument for Navigation and Information. It provides information about emergency situations, communication on disaster warnings, potential fishing zones and ocean states forecasts to the fishermen.
GAGAN : It means GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation.It provides a navigation system. There are 10Gagan payloads in the satellites GSAT – 8 and GSAT – 10. The entire area from Australia to Africa is covered by GAGAN. It studies the ionospheric behavior over the Indian region too.
The Government of India (GOI) launched GEMINI so as to provide information relating to warning of disasters to fishermen. It is a step towards satellite – based navigation services taken by the Government of India for the country.
DHRUV : It is a Pradhan Mantri Innovative Learning Program (PMILP). It is named after the pole star Dhruv Tara. It will be launched by The Human Resource Development Minister Shri Ramesh Pokhriyal from Indian Space Research Organization Headquarter Bangalore (ISRO) on 10 ocotber 2019. The programmes will cover Science and Performing Arts. About 60 students from class 9 to 12 coming from private and public schools all over the country will be selected on the basis of their performance in the National Talent Search Examinations and competitions.
The main objective of the program is to sharpen the innovative imagination skills of the students and allow them to realize their complete potential and contribute to the society by bringing solutions to socio-economic, environmental and political issues faced by the country. The purpose of the program is also to help the nation achieve 5 trillion Dollar economy target.
SUMAN Scheme : It refers to Surakshit Matritva Aashwasan scheme.It is a scheme launched by the Union Minister Dr Harsha Vardhan at the conference of Central Council of Health and Family Welfare for pregnant women. The initiative was launched during the 13th Conference of Central Council of Health and Family Welfare. Its aims to lower maternity mortality rate (MMR)and Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) in the country. The scheme focuses on providing dignified, respectful, healthy life care and medicines free of cost to them and zero tolerance for denial of services for every woman and new-born visiting the public health facility in order to end all preventable maternal and new-born deaths. The scheme aims at providing pregnant women ante-natal services and required treatment for free at government health centres and hospitals on 9th of every month. It also aims to make pregnant women aware of their health issues and diseases and to ensure a healthy and safe delivery of the baby. The check-ups will be done at the medical centres, government and private hospitals and private clinics across the country.
National
India Air Force Day : This day is celebrated at the Hindon base in Ghaziabad, Uttar Pradesh in presence of the Indian Air Force or IAF chief and senior officials of the three armed forces every year. The IAF was founded on October 8, 1932. It has participated in several crucial wars and landmark missions.
The Indian Air Force (IAF) is celebrating its 87th anniversary with a spectacular air display that included the vintage and modern transport aircraft and frontline fighters. The air display commenced with flag-bearing sky divers of the famous Akash Ganga team dropping out of an AN-32 aircraft in their colourful canopies. During the event, three Mirage 2000 aircraft and two Su-30 MKI fighter aircraft in ‘Avenger formation was flown by Indian Air Force officers who participated in the Balakot strike. Wing Commander Abhinandan Varthaman who downed Pak F16, lead MiG-21 Bison formation in flypast with heroes of Balakot airstrike. The ceremony concluded with a spell-bound aerobatic display. The President Ram Nath Kovind, the Vice President M Venkaiah Naidu and the Prime Minister Narendra Modi greeted air warriors on the occasion.
Rafale Jet : It is a French twin-engine, canard delta wing, multirole fighter aircraft capable of carrying out a wide range of short and long-range missions, including ground and sea attacks, reconnaissance, high-accuracy strikes and nuclear strike deterrence. The fighter aircraft were developed and designed by Dassault Aviation.The countries that are currently using aircraft include Egypt, Qatar, Libya, Mali, Afghanistan, Iraq and Syria.
India's Defence Minister Rajnath Singh formally received the first of the 36 long-awaited Rafale fighter jets on behalf of the Indian Air Force (IAF). The Rafale handover ceremony took place at Merignac in Bordeaux, France, in a facility of Dassault Aviation. However, the first batch of four jets wills arrive in India in May 2020. All 36 jets are expected to arrive in India by September 2022.
Rafale deal worth Rs 59000 crores was signed by India and France in September 2016.
President's Colour Award: It is a prestigious award presented for the acknowledgment of the meritorious service rendered by the Army Aviation Corps over the years. It is a visible symbol of excellence earned through dedication and worthy contribution during war and peace. The President of India, who is also the supreme commander of the armed forces presents this prestigious award.
President Ram Nath Kovind on Thursday presented the prestigious award to the Army Aviation Corps at a grand ceremonial parade held at the Combat Army Aviation Training School at Nashik Road and lauded the wing for serving the nation with dedication.
International
India and Bangladesh : Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Bangladesh Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina met for bilateral talks on the 6th of October at Hyderabad House in New Delhi. The two leaders will jointly inaugurate three projects to strengthen ties in diverse areas including defence and security, trade and connectivity. The two countries signed 7 pacts in core areas such as transport, connectivity, capacity building and culture. Three projects involving the import of LPG from Bangladesh were also launched during the meeting.
The issue of implementation of the National Register of Citizens (NRC) in Assam was also discussed by the two leaders.
China : China state oil firm withdraws from USD 5 billion deal to develop of Iran's massive offshore natural gas field. Iran holds the second-largest reserves of natural gas and the world's fourth-largest oil reserves. The pulling out of China comes at a time when Washington and Beijing are engaged in their trade war with levying tariffs and counter-tariffs on each other. The South Pars field deal between China National Petroleum Company (CNPC), Iranian PetroPars and France's Total SA was signed in 2017. Notably, Total SA earlier withdrew in light of US President Donald Trump sanctions in 2018.
South Pars field is the world's second-largest known reserves of natural gas to build 20 wells and two wellhead platforms, a project that would have a capacity of 2 billion cubic feet of natural gas a day.
UNICEF : It refers to United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund. The United Nations Children's Fund, originally known as the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, was created by the United Nations General Assembly on 11 December 1946, to provide emergency food and healthcare to children and mothers in countries that had been devastated by World War II. It's headquarters is in New York City, U.S. Henrietta H. Fore is the Executive Director of the United Nations Children’s Fund. It functions under the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) and the United Nations Economic and Social Council (UNSC).
UNICEF launched the Cryptocurrency Fund making it the first UN agency that can receive donations and make disbursements in bitcoin and ether without having to convert the cryptocurrencies into fiat currency. The main aim of the UNICEF's Cryptocurrency Fund is to fund open source technology benefiting children and young people around the world. The first contributions to the fund will be made by the Ethereum Foundation which will benifit three grantees of the UNICEF Innovation Fund and also a project coordinated by the Global Imaging Genetics of Adolescents (GIGA) initiative. The grantees are organizations dedicated to connecting schools around the world to the internet.
Cryptocurrency : It is a digital asset designed to work as a medium of exchange that uses strong cryptography to secure financial transactions, control the creation of additional units, and verify the transfer of assets.
Bitcoin : It is a cryptocurrency. It is a decentralized digital currency without a central bank or single administrator that can be sent from user to user on the peer-to-peer bitcoin network without the need for intermediaries.
India and France: India and France agreed to deepen defence ties. Defence minister Rajnath Singh visited France where he held the second India-France Ministerial level Annual Defence Dialogue with his French counterpart, the Minister for the Armed Forces Ms. Florence Parly on October 8th in Paris. The two ministers comprehensively reviewed the entire gamut of the bilateral defence cooperation, which is a key pillar of the India-France strategic partnership. Views on contemporary regional and international developments of mutual interest was also exchanged between both the sides. Ways to further deepen defence-related official as well as operational level interactions was also discussed. The two nations agreed to expand the scope and complexity of the existing regular bilateral joint exercises (SHAKTI, VARUNA and GARUDA). Shri Rajnath Singh attended a ceremony for the Handing over of the first of the 36 Rafale aircrafts being acquired by India from France on the 7th of October 2019.
As early as the 1980s France wished to give greater scope to its relations with India. This closer bilateral relationship was concretized with the establishment of a strategic partnership in 1998, and a strategic dialogue a year later. This dialogue is based on annual high-level meetings and consultations conducted twice a year by the Diplomatic Advisor to the French President and the National Security Advisor to the Prime Minister of India.
Nobel Peace Prize : It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Swedish industrialist, inventor, and armaments manufacturer Alfred Nobel, along with the prizes in Chemistry, Physics, Physiology or Medicine, and Literature. Since March 1901, it has been awarded annually (with some exceptions) to those who have "done the most or the best work for fraternity between nations, for the abolition or reduction of standing armies and for the holding and promotion of peace congresses".
The 2019 Nobel Peace Prize has been awarded to The Ethiopian Prime Minister, Abiy Ahmed Ali. He in close cooperation with the President of Eritrea, Isaias Afwerki secured a peace agreement to end the long-drawn standoff between Ethiopia and Eritrea.
The 2018 Nobel Peace Prize was awarded jointly to Denis Mukwege and Nadia Murad to recognize their efforts to end the use of sexual violence as a weapon of war
Places In News
Bihar : Bihar Chief Minister Nitish Kumar was re-elected unopposed as the President of Janata Dal (United) for another term of three years. He was the only candidate from his party who filed the nomination for this post. He will again lead his party during the upcoming state assembly by-polls and the state assembly elections in 2020. His certificate of re-election was officially handed over at the party office in New Delhi to Kumar’s representative Sanjay Kumar Singh, who is a Member of the Legislative Council (MLC) in Bihar.
Assam : Justice Lamba was administered the oath of secrecy to the office by Governor Professor Jagdish Mukhi at the Raj Bhawan in Guwahati.
Several ministers including the Assam Chief Minister Sarbanand Sonowal attended the oath-taking ceremony.
Uttar Pradesh : UP Chief Minister Yogi Adityanath introduces Mukhya Mantri Kanya Sumangala Yojana. This program aims at empowering the girl child for which an amount of 15 thousand rupees will be provided to every family in which a girl child takes birth.
Kerala : Kerala will soon get its own Kerala Bank. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) on Tuesday gave the nod to the Kerala government to set up a bank of its own by merging the district cooperative banks to form a state cooperative bank. With its formation, the proposed "Kerala Bank" will be largest banking network in the state. Its formation is one of the major promises made by the Left Democratic Front (LDF) in the elections. The district cooperative banks of all the 14 districts in the state, except the Malappuram District Cooperative Bank, had approved the government's amalgamation scheme.
Pompeii : it was an ancient Roman city located in the modern comune of Pompei near Naples in the Campania region of Italy. Pompeii, along with Herculaneum and many villas in the surrounding area, was buried under 4 to 6 m of volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79.
Cultural ministry of Italy revealed that a vivid fresco depicting an armour-clad gladiator standing victorious as his wounded opponent stumbles gushing blood has been discovered in the ancient Roman city of Pompeii. As per the experts, the stiking scene painted in gold, blue and red was a tavern frequented by gladiators, who fought each other, prisoners and wild animals for the public's entertainment.
The ruined city Pompeii that lies in southern Italy is the second most visited tourist site in the country, after the Coliseum in Rome.
People In News
Ramesh Pandey : He is the Senior Indian Forest Service officer. The 1996-batch IFS officer currently posted as Chief Conservator Forests in Lucknow and Secretary, UP State Bio-diversity Board, is known for his investigation and intelligence gathering on poachers has been selected for the prestigious Asia Environmental Enforcement Award 2019 by the United Nations Environment Programme. He will receive the award on November 13 at the United Nations Conference Centre in Bangkok. Mr Panday has been recognised by the selection panel for his excellent work in combating trans-boundary environmental crime.
The purpose of the Asia Environmental Enforcement Awards is to publicly recognise outstanding achievements by public organisations and individuals in Asia to combat trans boundary environmental crime.
Asha Bhosle : She is an Indian playback singer. She is best known for her playback singing in Hindi cinema, although she has a wider repertoire. Bhosle's career started in 1943 and has spanned over six decades. She has done playback singing for over a thousand Bollywood movies. Singer Asha Bhosle on Monday was conferred an honorary doctorate by the University of Salford in Greater Manchester, England. She has also been the recipient of Padma Vibhushan and she also holds the Guinness World Record for the most single studio recordings.
IAF Marshal late Arjan Singh : He was the Marshal of the Indian Air Force DFC and was the senior most Indian Air Force officer who served at various Key positions, namely; Chief of the Air Staff from 1964 to 1969. After retiring from the IAF, he served as a diplomat, politician and advisor to the Indian government. He was the first and only officer of the Indian Air Force (IAF) to be promoted to 5-star rank as Marshal of IAF. Many prestigious awards conferred to him. The awards included General Service Medal 1947, Samar Seva Star, Raksha Medal, Sainya Seva Medal, Indian Independence Medal, Distinguished Flying Cross, 1939–1945 Star, Burma Star, War Medal 1939–1945, India Service Medal and the highest civilian award the Padma Vibhushan the highest civilian award, in 1965.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi released a commemorative stamp to honour the birth centenary of Marshal of the Air Force Late Arjan Singh. It was released at the home programme of the Indian Air Force (IAF) on its 87th raising day. The stamp was released as a tribute to his exemplary service to the nation.
Ashleigh Barty : Ashleigh Barty is an Australian professional tennis player and former cricketer. She is ranked No. 1 in the world in singles by the Women's Tennis Association and is the second Australian WTA singles No. 1 after Evonne Goolagong Cawley. She has been awarded Australian sport's highest individual honour "The Don" Award at the annual Sport Australia Hall of Fame Awards in Melbourne. She has joined legends like Cathy Freeman and Ian Thorpe in lifting the prestigious prize. She is the first female tennis player to claim the honour, named after the great Donald Bradman. Barty won her maiden Grand Slam title at the French Open 2019 and become the first female Australian world-number-one since 1976.
Sports
Japan Open Title : Novak Djokovic, the Serbian world number one won the Japan Open Title. He claimed his 76th tournament win. He defeated his opponent Australian John Millman in the final in Tokyo by 6-3, 6-2 win in straight sets at the Ariake Coliseum at Tokyo. The win marks Novak Djokovic’s tenth win in a tournament main draw debut in his entire tennis career, which includes 16 Grand Slam wins.
Cricket : Rohit Sharma is an Indian international cricketer who plays for Mumbai in domestic cricket and captains Mumbai Indians in the Indian Premier League as a right-handed batsman and an occasional right-arm off break bowler. He is the vice-captain of the Indian national team in limited-overs formats. He broke multiple records as he smashed the South Africa bowling attacks to all parts in Vizag.
He set the record of hitting most number of sixes in a single test. He hit 13 sixes in India’s first test against South Africa. He has become the 6th Indian to score a century in each innings of a test after legendary Indian cricketers including Sunil Gavaskar (thrice), Rahul Dravid (twice), Vijay Hazare and Indian skipper Virat Kohli and teammate Ajinkya Rahane. He also became the first player to score a century in each innings of his maiden Test as an opener and the second Indian cricketer to hit 600 runs in the World Cup record..
Cricket : Harmanpreet Kaur who is the Indian women's cricket captain has becomes the first Indian cricketer to reach 100 T20 International matches. She has become the first Indian cricketer to achieve this feat in both the female and male categories in October 2019 during the series against South Africa. Rohit Sharma and Mahendra Singh Dhoni both, who have the same 98 matches registered in their names, appear second after her. She plays as an all-rounder for the Indian women's cricket team and was awarded the prestigious Arjuna Award for Cricket in the year 2017 by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports.
World Boxing Championship: The Manipuri Indian boxer M C Mary Kom has become the most successful boxer in the history of Women’s World Championships by winning her sixth gold medal by defeating Ukraine’s Hanna Okhota at Labuan Bajo, Indonesia. Mary Kom also became the first boxer in the history of World Championships to win 8 world meet medals. She was tied on 7 with Cuban men's legend Felix Savon after winning the gold in the 48kg category in New Delhi last year. She now has an incredible six gold and one silver in the tournament and is the most successful boxer in both male and female category in history of World Championships.
Gymnastic championship : American star gymnast Simone Biles won the 15th world title as US women claim team gold in Gymnastic championship in Stuttgart, Germany. She has become the most decorated women's gymnast after clinching the 21st medal at the championships, taking her ahead of Russia's Svetlana Khorkina for the most medals won by a woman at the world championships.
Cricket : Indian skipper Virat Kohli has become the 12th fastest batsman in the world to make 20,000 international runs and the third Indian batsman after Sachin Tendulkar (34,357 runs), Brian Lara and Rahul Dravid (24,208 runs). After getting out early against South Africa in the India's World Cup opener, Kohli scored 82 runs against Australia and 77 runs against Pakistan. Kohli had also become the fastest batsman to score 11,000 ODI runs during India vs Pakistan at the same venue, Old Trafford in Manchester. He is currently the top-ranked ODI and test batsman in the world.
World Athletics Championship, 2019 : It is organized by IAAF – International Association of Athletics Federations. This year it was held between September 27 and October 6, 2019 in Doha, Qatar. Athletes from 209 countries from all over the world participated in more than 49 athletic events. The competition was previously known as World Championship in Athletics. It is the first time it is being conducted in its new name.
Several record were broken this year. India ranked 7th in 100 metres, 6th in 400 meters, 8th in 200 meters and 1500 meters respectively. The 200m winner Noah Lyles and Niklas Kaul of Germany in Decthlon victor were the youngest gold medallists in their respective events. Ukraine athlete Yaroslava Mahuchikh broke her own record twice winning silver medal. USA bagged maximum gold in the event.
Economics
SEBI : It refers to Securities and Exchange Board of India. It announced a new rule to impact foreign funds. It notified that only Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPI) located in FATF countries or managed by an enterprise based under FATF jurisdiction can deal in Participatory Notes(PNs). PNs are financial instruments with Indian stocks, futures and options as underlies. Financial centres like Mauritius, Cayman Islands and Cyprus will have a severe impact as they are not FATF members.
Participatory Notes : These are financial instruments required by investors to invest in Indian stock markets without being registered with SEBI.
FATF : It means Financial Action Task Force. It is an inter-governmental policymaking body that monitors money laundering and terrorism funding all over the world. It also develops policies to curb money laundering and terror financing. It was established in 1989 G7 summit that was held in Paris.
The reason for taking this step was because of the economic scenario taking place around different parts of the world had great effect over the Indian economy. Since 2016, rupee value has depreciated over 16% causing a risk of increased inflation. The concern of the rising prices of the crude oil because of the trade war between US and china and also the fear of US sanctions over India importing oil from Iran is also the main reason.
Global Competitive Index, 2019 : According to the report, released by the Geneva-based World Economic Forum (WEF), India slips down 10 places to 68th rank on global competitiveness index. This is because India has not done well in most parameters such as infrastructure, the adoption of information, communications and technology (ICT), financial markets, skills, and innovation capability, compared to last year. As many as 141 countries were surveyed for the index.
The Global Competitiveness reports is a yearly report published by the World Economic Forum. Since 2004, the Global Competitiveness Report ranks countries based on the Global Competitiveness Index, developed by Xavier Sala-i-Martin and Elsa
GeM: It refers to Government e-Marketplace. It is an initiative of the Government of India launched by the commerce ministry offering one stop platform facilitating online procurement of common use goods and services required by various government departments, organisations, Public Sector Units. GeM provides tools for Direct Purchase, bidding and reverse auction in a transparent manner for government departments. GeM has signed MoU with 14 Public Sector and private banks to enable this.
Government e-Marketplace (GeM) signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with Union Bank of India (UBI)in New Delhi. Through this partnership the bank will offer several services including the transfer of funds through GeM Pool Accounts (GPA). According to the MoU, It will help in advising the registered users on the GeM portal for Performance Bank Guarantees (e-PBG) and Earnest Money Deposit (EMD), it will facilitate a cashless, paperless and transparent payment system on the portal.The MoU will create an efficient procurement system for government entities. It will also facilitate the online integration for payments and various banking services to GeM.
Science and Technology
Nobel Prize : The Nobel Prize is a set of annual international awards bestowed in several categories by Swedish and Norwegian institutions in recognition of academic, cultural, or scientific advances. The will of the Swedish chemist, engineer and industrialist Alfred Nobel established the five Nobel prizes in 1895.
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine: The Nobel Assembly announced the Nobel prize at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm for Physiology or Medicine. It was jointly awarded to two Americans and a British scientist-Drs. William G Kaelin Jr of Harvard University, Gregg L Semenza of Johns Hopkins University and Peter J Ratcliffe at the Francis Crick Institute in Britain and Oxford University for physiology or medicine for discovering how the body’s cells sense , react and adapt to oxygen levels. Their work established the genetic mechanisms that allow cells to respond to changes in oxygen levels. Their work has paved way the way for new strategies to treat a variety of diseases, including cancer, anaemia, heart attacks and strokes.
Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2019 jointly awarded to John B. Goodenough, M. Stanley Whittingham and Akira Yoshino for the development of lightweight, powerful and rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. These batteries are lightweight, powerful and rechargable used it almost all kinds of wireless electronics. It can also store vast energy from solar and wind power paving the way for a wireless and fossil energy-free society.
The Nobel Prize in Physics 2019 was jointly awarded to three scientists for their work in understanding how the universe has evolved, and the Earth’s place in it. James Peebles was awarded the prize for ‘theoretical discoveries in physical cosmology’ and Swiss astronomers Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz won it for ‘the discovery of an exoplanet orbiting a solar-type star.’ An exoplanet is a planet outside the solar system. The Nobel Prize announcement was done by the Secretary-General of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences, Goran K. Hansson. The award recognises the work in understanding the structure and history of the universe and the first discovery of an exo-planet. The discoveries of of the exo-planet had changed the conception of the world completely.
Saturn : It is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius about nine times that of Earth. At least 82 moons are known to orbit Saturn, of which 53 are officially named. This does not include the hundreds of moonlets in the rings.
A team of scientists led by Scott Shepherd of the Carnegie Institution for Science spotted Saturn’s new moons using a Subaru telescope in Maunakea, Hawaii at the International Astronomical Union's Minor Planet Center.It announced that 20 new moons have been discovered around the ringed planet, Saturn bringing its total to 82. Earlier Jupiter was the planet with most moons but now after the discovery of the new moon Saturn overtakes Jupiter as planet with most moons.
The moons are tiny and measure just 5 kilometres (3 miles) in diameter and orbit around Saturn, 17 of them orbit backwards. This is known as a retrograde direction. The other three moons orbit in a prograde direction - the same direction as Saturn rotates. Two of the prograde moons take about two years to travel once around the ringed planet
Virus : It is a small infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses can infect all types of life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
For the first time, researchers of USA have captured images of the formation of individual viruses using a viewing technique known as interferometry scattering microscopy, in which the light scattered by an object created a dark spot in a larger field of light. The research provides new insights into how to fight viruses and engineer self-assembling particles. However, the virus structure is not yet known.
Mission of MEV-1 : It is a first of its kind satellite service spacecraft. It was built by Virginia-based company Northrop Grumman. It is designed for 15-year useful life, and can dock and undock multiple times. Its mission is to provide service to the Intelsat 901. MEV-1 will lend Intelsat 901, to make use of its orientation thrusters to put it back into an ideal target orbit. It can provide extension to orbital geosynchronous satellites l running low on its own propellant supply. It is designed to dock with aging spacecraft more than 22,000 miles above Earth.
The US-based Northrop Grumman Corporation launched the first satellite-servicing spacecraft robotic Mission Extension Vehicle-1 (MEV-1) successfully. It was launched aboard a Russian Proton rocket from Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. It was launched along with the Eutelsat 5 West B communications satellite. Its successful launch marks beginning of era of commercial satellite servicing in the space.
Environment & Climate
BS-VI emission norms : It refers to emission standards which sets quantitative limits on the permissible amount of specific air pollutants that may be released from specific sources over specific timeframes. They are generally designed to achieve air quality standards and to protect human life.
Union Environment Minister Prakash Javadekar recently announced that India will be adopting the BS-VI emission norms by April 2022. In 13 major cities, Bharat Stage IV emission norms have been in place since April 2010 and it has been enforced for entire country since April 2017. In 2016, but from now Bharat Stage Six (BS-VI) is expected to bring transformation in fuels. About Rs 60,000 crores have been spent by the government to switch from BS-IV fuel to BS-VI fuel. The main objective is to tackle the alarming pollution level.
Ganga Aamantran Abhiyan : It is a month long exploratory open water rafting expedition launched by the newly constituted Jal Shakti Ministry Gajendra Singh Shekhawat to connect with the stakeholders of the river. The Jal Shakti Ministry is a newly constituted ministry. The pioneering exploratory open- water rafting and kayaking expedition on the Ganga river will begin on Thursday and will continue till 11th of next month. It will start at Devaprayag and culminate at Ganga Sagar covering the entire stretch of over 25,000 kilometres of the River. This is the first ever effort by National Mission for Clean Ganga to raft across the entire stretch of the river. It is the longest ever social adventure sporting activity campaign undertaken. The main objective of this expedition is to spread the message of River Rejuvenation and Water Conservation on a massive scale. It is also expected tp highlight the ecological challenges faced by the Ganga River.
Mexican Tropical Forest : A new antibiotic has been discovered in the Mexian tropical forest by the scientists of Rutgers University that may help lead to a 'plant probiotic,' more robust plants and other antibiotics. Probiotics provide friendlier bacteria which is beneficial for humans health, can also be beneficial to plants, keeping them healthy and more robust. It is produced by a soil bacterium and is known as phazolicin. It prevents harmful bacteria from getting into the root systems of bean plants. It is found in the root nodules of wild beans. They have their application both in medicine and agriculture. It is a peptide. The bacterium that produces phazolicin, is an unidentified species of Rhizobium. It was found in a tropical forest in Los Tuxtlas, Mexico, in the soil and roots of wild beans called Phaseolus vulgaris that is why the antibiotic is named phazolicin.
Wildlife Week India, 2019 : The event is organized by National Board of Wildlife since its establishment in 1972. A Wild Life Week celebration was planned to arouse the general awakening of the normal people in the country towards the protection of wildlife and to preserve animal life in India. It is celebrated all over the country between 2nd October and 8th October every year. Events and campaigns are organized throughout the week to teach people about animal life and encourage them save large number of animals by not killing them for food and other purposes.
According to The Science Magazine, about 5,500 species of birds, reptiles and amphibians are being sold in world markets. It is a multi – dollar business and is considered as the most severe threats of biodiversity.
Varieties of sanctuaries and national parks have been already launched in the appropriate localities all across the country by the Government of India. .
Government launches Green Crackers : The Indian Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) has launched environment-friendly firecrackers called 'Green Crackers'. These firecrackers have 30 per cent less emissions and are eco-friendly that have been developed keeping in mind the pollution danger and health risks, which the regular firecrackers pose. The of green crackers were developed with an aim of reducing pollution. The environmental-friendly crackers will help keep the traditional Indian festivities and celebrations intact and also provide a livelihood to the millions of homes, which are dependent on the sale and manufacture of fireworks. In 2018, just before Diwali, the Supreme Court had banned manufacturing of polluting firecrackers and ruled that only green crackers with reduced emission will be allowed to be sold in the country.
Pangio Bhujia: It is a new species of miniature well-dwelling subterranean fish known as Eel-loach. Eel-loaches are generally found in fast-flowing streams in the south and the south-east Asia.
Scientists from the Kerala University of Fisheries and Ocean Studies (KUFOS) have identified a new species of eel-loach. It belongs to genus Pangio.
The latest discovery has been named ‘Pangio bhujia’, due to its resemblance to the North Indian snack, bhujia.
The Pangio bhujia, is approximately 3 centimetres long and pinkish-red in colour. It resides in the purest waters of deep subterranean aquifers. The absence of the dorsal fin and pelvic fins on its body makes it very unique, and its long nasal barbels distinguish it from other species of the Pangio genus.
World Migratory Bird Day : It is celebrated to raise awareness for the protection of the migratory birds and their habitats.It is organized by CMS (Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of wild animals) and AEWA (Agreement on the Conservation of African – Eurasian Migratory water birds) to highlight the conservation of migratory birds, threats faced by them, their ecological importance the need for international cooperation to conserve them. Different Countries organize different activities based on the theme to mark the WMBD all around the world. This year theme is - Protect birds – Be the solution to plastic pollution.
Dolphins : It is an endangered freshwater or river dolphin that are found in the region of Indian Subcontinent which is split into two subspecies, the Ganges river dolphin and the Indus river dolphin.It is one of the oldest creatures in the world along with some species of turtles, crocodiles and sharks. The Ganges river dolphin was officially discovered in 1801. Ganges river dolphins once lived in the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna and Karnaphuli-Sangu river systems of Nepal, India, and Bangladesh. But the species is extinct from most of its early distribution ranges. The Ganges river dolphin live in freshwater and are essentially blind. They hunt by emitting ultrasonic sounds, which bounces off of fish and other prey, enabling them to “see” an image in their mind. They are frequently found alone or in small groups, and generally a mother and calf travel together. Calves are chocolate brown at birth and then have grey-brown smooth, hairless skin as adults. Females are larger than males and give birth once every two to three years to only one calf.
The Forest department and World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF India) launched the annual dolphin census — part of the ‘My Ganga, My Dolphin campaign.The survey is being conducted in the stretch of Ganges from Bijnore to Narora, which is also a Ramsar site (as per the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands in 1971). The Ganga dolphin sencus is launched to create awareness among the inhabitants along the banks of the Ganges.
Economics
NSIC & Saudi Aramco: It refers to National Small Industries Corporation and Saudi Aramco is also known as Soudi Arabian Oil Company. A Memorandum of understanding (MoU) was signed between National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC) and Aramco Asia. for the development of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) Ecosystem in India in Oil & Gas Sector. The MoU will pave a way for accredited Indian MSMEs to carve out a space as vendors in Global space. The MoU is also aimed for the development of Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME) Ecosystem in India in Oil & Gas Sector.
The MoU was signed by Sh. P. Udayakumar, Director (P&M) from NSIC and Mr. Mohammed Al Mughirah, President, Aramco Asia for the development of Ministry of MSME.
NSIC: The National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC) was founded on 1955 as a Government of India agency and was later made into a fully owned government corporation. Its headquartered in New Delhi, India. It is a flagship Mini Ratna public sector undertaking (PSU) under Union Ministry of MSME in the business of facilitating MSMEs in India.
Suadi Aramco: It is a Saudi Arabian national petroleum and natural gas company based in Dhahran, Saudi Arabia. It is world’s largest Oil & Gas Company and is one of the largest companies in world by revenue.
Indian Economic Census: It is the census of the Indian economy which counts all entrepreneurial units in the country involved in any economic activities of either agricultural or non-agricultural sector which is engaged in production and/or distribution of goods and/or services and not for the sole purpose of own consumption. The economic census provides information on operational and other characteristics such as number of establishments, number of persons employed, type of ownership,source of finance, etc. These information which the census provides is used for micro level/ decentralized planning and to assess contribution of various sectors of the economy in the gross domestic product (GDP). It was first launched in 1977. So far 6 census have been conducted in the years 1977, 1980, 1990, 1998, 2005, 2013. The economic census 1980 and 1990 were integrated with population census.
7th Economic Census: On December 13, 2019, 7th Economic Census was launched in the National Capital Territory of Delhi. Delhi is the 26th state where the survey has been launched. It is being carried out by the Ministry of Statistics and Program Implementation (MoSPI) in collaboration with Common Service Centre (CSC), a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) under Ministry of Electronics and IT.
It is for the first time the census is being conducted on digital platform named ICT (Information and Communication Technology). Digital platform has reduced time of survey to 6 months from 2 years earlier. It is expected to be completed by March 2020. About 1.5 lakh trained enumerators who have been employed in the census will visit 35 crore households and establishments to carry out the census.
NHAI: It refers to the National Highways Authority of India. It was constituted under National Highways Authority of India Act, 1988. It is a nodal agency of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
It is responsible for the development, Management and maintenance of National Highways entrusted to it and for matters connected or incidental there.
Union Cabinet has given its approval to the proposal of Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, authorizing National Highways Authority of India, NHAI to set up Infrastructure Investment Trust (InvITs), as per Guidelines issued by Securities and Exchange Board of India, SEBI. This will enable NHAI to monetize completed National Highways that have a toll collection track record of at least one year and NHAI reserves the right to levy a toll on the identified highway.
NHAI's InvITs: InvIT Trust will be a trust formed under Indian Trust Act, 1882 and Securities and Exchange Board of India (Infrastructure Investment Trusts) Regulations, 2014. It will be formed with an objective of investment primarily in infrastructure projects. It may hold assets either directly or through a Special Purpose Vehicles (SPV) or a holding.
The trust will provides greater flexibility to investors and it is expected to create opportunities like the generation of specialized Operation and Maintenance (O&M) Concessionaires, attract long-term capital to the Indian highway market and retail domestic savings and corpus of special institutions such as mutual funds, Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA), among others is expected to be invested in the infrastructure sector.
Environment
IUCN: It refers to International Union for the Conservation of Nature. IT is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. It is involved in data gathering and analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education. Its headquartered in Gland, Switzerland. It was founded by Julian Huxley on 5 October 1948.
According to the biggest study of its kind, undertaken by conservation group IUCN, there is a continuous decrease in the amount of oxygen in the oceans due to climate change. As per the report, Oxygen level has decreased by 2% in oceans. This deoxygenation in the oceans is having a negative effect on marine organisms that require more oxygen and one million animals are on the verge of extinction due to human activities.
Around 700 ocean sites are now suffering from low oxygen, compared with 45 in the 1960s. The threat to oceans are from nutrient run-off of chemicals such as nitrogen and phosphorus from farms and industry has long been known to impact the levels of oxygen in the sea waters and still remains the primary factor, especially closer to coasts. As more carbon dioxide is released enhancing the greenhouse effect, much of the heat is absorbed by the oceans. In turn, this warmer water can hold less oxygen. The scientists estimate that between 1960 and 2010, the amount of the gas dissolved in the oceans declined by 2%.
In recent years the threat from climate change has increased. According to the paper was published in the journal Ecology Letters. In 2014, researchers found that alpine goats appeared to be shrinking due to warming temperatures. The same year, another study found salamanders had shrunk rapidly in response to climate change. Even the size of the birds has shrunk due to climate change. It builds on a growing body of evidence that suggests animals are shrinking as the climate warms.
Volcano: A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. Earth's volcanoes occur because its crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter, softer layer in its mantle.
New Zealand has been the site of many large explosive eruptions during the last two million years, including several of super volcano size. These include eruptions from Macauley Island and the Taupo, Whakamaru, Mangakino, Reporoa, Rotorua, and Haroharo calderas.
White Island: It is also known as Whakaari located 48 kilometers off the coast of New Zealand’s North Island.It is the summit of a large volcano around 16 km wide and 18 km long. Most of the volcano is below water, and only a 2-kilometre-wide section of the cone is visible. The Maori name for the island is “Te Puia o Whakaari”, which means “The Dramatic Volcano”. The largest and longest series of eruptions ever recorded on White Island happened between 1976 and 1982. Molten rock rose up near the surface and ejected lava bombs and blocks of rock, and huge clouds of ash.
Deadly eruption hit New Zealand volcano tourist town White Island and transformed tourist destination to disaster zone as the volcanic activity drew thousands of tourists annually escalated with deadly consequences.
4th India Water Impact Summit, 2019: The Ministry of Jal Shakti and the Centre for Ganga River Basin Management and Studies (cGanga) led by IIT Kanpur organized the 4th India Water Impact Summit, 2019. The summit was held from 5-7 December 2019 at the Vigyan Bhawan, New Delhi. The summit seeks to focus on integrated management of water resources in rural and urban areas and discuss the biggest problems associated with water. The theme of the 2019 summit is Valuing Water, transforming Ganga. The theme also focuses on the Financing of High Impact Projects in the water sector.
The Government of India has launched several initiatives namely, Environment Flow and Urban River Management Plan, Ganga River Basin Management Plan, Jal Jeevan Mission, National Mission for Clean Ganga in order to the impact of human activities on water and to reduce water scarcity. Addressing 4th India Water Impact Summit, 2019 in New Delhi,Jalshakti Minister Gajendra Singh Shekhawat said that river Ganga has become one of the 10 cleanest rivers in the world among the major rivers category because of the efforts made by the government towards that direction.
River Ganga: The Ganges, or Ganga, is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The 2,525 km river rises in the western Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand, and flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain of India and Bangladesh, eventually emptying into the Bay of Bengal. Ganga and it's tributaries (Yamuna, Gomati, ghagara and many more smaller ones) are the main source of water for domestic as well as irrigation purposes for the North Indian states. Ganga is considered to be a sacred river for the Hindus.
Due to the increase in the population density and various human activities such as bathing, washing clothes, the bathing of animals, and dumping of various harmful industrial waste into the rivers Ganga had become much polluted. The Centre approved the establishment of the Clean Ganga Fund (CGF). A massive river rafting expedition, Ganga Aamantran Abhiyan, was launched on 10 October 2019. Centre also launched the NamamiGange Mission as an integrated mission. The mission aimed at the conservation and rejuvenation of Ganga and its tributaries with a comprehensive basin based approach. SabkaSaath, SabkaVikas, SabkaVishwas is the motto of the mission.
CAA: It refers to Climate Ambition Alliance. About 73 Countries join Climate Ambition Alliance at COP25. Chile has led this alliance after a request of United Nations Secretary General Antonio Guterres in the context of the 2019 Climate Summit. It was launched at the Climate Action Summit, New York in 2019. They will also work towards COP26 that is to be held in November 2020 at Glasgow, UK. The CAA seeks to focus Nationally Determined Contributions in order to achieve Net Zero by 2050. The focus will be mainly on the resilience in infrastructure, management of water and sustainability of cities. This alliance demonstrates the urgent need to take ambitious action to address the climate change emergency.
Indian Policy
MoCA: It refers to the Ministry of Civil Aviation. It has recently announced that it is kicking off the fourth phase of the UDAN (Ude Desh ka Aam Naagrik) scheme. It aims to improve connectivity to remote and regional areas (like North East regions, hilly states, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh) besides giving flexibility to airlines in designing their network, promoting short-haul routes, and revising the parameters of VGF (viability gap funding).The scheme is a part of the government's vision to operationalize over 100 airports in smaller towns and cities over the next five years.
UDAN: It is a Regional Connectivity Scheme. UDAN refers to Ude Desh ka Aam Naagrik. It was launched in 2017. Under this scheme the airlines compete to win subsidies to operate flights that link small airports with bigger airports in the country. In its 4th phase the operation of the helicopter and seaplane would also be allowed. The 4th phase scheme will not only promotes short-haul routes but the government will develop airports and operationalize the routes that were auctioned during the previous phase of the RCS scheme.
National award: Department of Social Justice and Empowerment has started the scheme of National award for outstanding service in the field of Prevention of Alcoholism and Drug abuse. The scheme is applicable to institutions and individuals working in the field of prevention of alcoholism and drug abuse. The national award will be presented to the awardees on the occasion of International Day against Drug Abuse and Illicit Trafficking on 26th of June 2020. Thaawar Chand Gehlot is the Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment.
GoI: It refers to the Government of India. On 13 December 2019, the Ministry of Coal initiated the auction process of coal mines. It initiated the auction process for 27 coal mines. It includes mines at Bikram, Brahmapuri, Bhaskarpara, Jagannathpur and Jamkhani. This move came after the poor participation of investors in the previous rounds of coal auctions. The purpose of these auctions is to reduce the dependency on coal and its imports. Coal India seeks to raise its annual output to 880 million tons by 2024. This will not only help in reducing imports but eventually stop the country’s energy dependence on coal. This will also aid in India’s plan to expand the economy to 5 trillion USD by 2024. The Government of India is also using Clean Coal Technology to reduce air pollution caused due to usage of coal.
Clean Coal Technology: Clean technology, sometimes referred to as Cleantech, is a term generally used to define a set of technologies that either reduces or optimises the use of natural resources, whilst at the same time reducing the negative effect that technology has on the planet and its ecosystems. Some of the Clean Coal Technology procedure that are used in the country at present includes pre-combustion capture, oxy-fuel combustion and post-combustion capture. Pre-combustion capture includes production of heat through gasification of feedstock. In this process, a mix of hydrogen and Carbon dioxide rich gas is produced which can be separated easily. In Oxy-fuel combustion, fossil fuel such as coal is burnt in recirculated flue gas and oxygen rather than air. This eliminates nitrogen largely.
FASTag: It is an electronic toll collection system in India, operated by the National Highway Authority of India (NHAI). It employs Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology for making toll payments directly from the prepaid or savings account linked to it or directly toll owner. It is affixed on the windscreen of the vehicle and enables to drive through toll plazas without stopping for transactions.
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways had announced that FASTags will become mandatory for all vehicles, private and commercial from 15 December. Earlier the deadline was set to 1 December 2019. If the vehicle owners do not have a FASTag, they should pay twice the regular amount if you pass a toll booth and your vehicle. The government has made it mandatory for all vehicle owners to adopt electronic toll payment using FASTags and not cash payment which will attract penalties. FASTags can be bought through e-tailers, banks, payment apps, fuel bunks, and toll plazas.
The National Electronic Toll Collection (NETC) programme, the flagship initiative of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, has been implemented on a pan-India basis in order to remove bottlenecks and ensure seamless movement of traffic and collection of user fee as per the notified rates, using passive radio frequency identification (RFID) technology.
Indian Culture web portal: Its a portal that will host images, documents, audio-video files and other data from archives, museums, academies and libraries across India. It was developed by a team from the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Bombay and the curation of the data was done by Indira Gandhi National Open University (IGNOU), New Delhi.
Ministry of Culture Prahlad Singh Patel launched the Indian Culture web portal in New Delhi. The knowledge and cultural resources of various organizations of the Ministry of Culture are now available in the public domain on a single platform. It will showcase information about the rich cultural heritage of India. The portal also has a collection of rare books, manuscripts, e-books, virtual galleries, artifacts from the museum, photo archives, archives, gazetteers, Indian National Bibliography, videos, cuisine, images, UNESCO, Musical Instruments of India and many more. The content will be available both in Hindi and English language.
Indian polity
The Arms (Amendment) Bill, 2019: It is a Bill that has been introduced to control the use and possession of weapons in the country so as to reduce the illegal usage that endangers another human being. Strict punishment has been provided in the Bill against those who are found to be involved in the manufacturing, transportation and use of illegal arms.
The Parliament has passed the Arms (Amendment) Bill, 2019. The Bill seeks to amend the Arms ACt, 1959. The Bill was introduced in the Lok Sabha by Union Home Minister Amit Shah on November 29, 2019. It was passed by the Lok Sabha on December 9, 2019 and by the Rajya Sabha on December 10.
Important features of the Bill:-
*The Bill intends to decrease the number of licensed arms allowed per person and increase the alloted penalties for violations of the law. The excess firearms will be delicensed within 90 days from expiry of 1-year period including licenses given on inheritance basis. The new bill allows only 2 guns for the license holders.
*The Bill increases the duration of the validity of arms license from three years to five years.
*Strict punishment has been provided in the Bill against those who are found to be involved in the dealing in un-licensed firearms, including their manufacture, procurement, sale, transfer, conversion, shortening or conversion of a firearm without a license, and import and export of banned firearms with the intention of curbing the illegal trafficking of arms.
* The bill also introduces new categories of offences for forcefully taking a firearm from police or armed forces which is punishable with imprisonment between 10 years and life imprisonment along with fine, using firearms in a celebratory gunfire which endangers human life or personal safety of others. It is punishable with imprisonment of up to 2 years, or fine of up to Rs.1 lakh rupees, or both.
*The bill also proposes maximum punishment of life in jail for the makers of illegal arms if convicted.
*Shortening or conversion of a firearm without a license is also punishable by law.
*The Bill, however, accords special status to a sportsperson who need firearms and ammunition for practice and participating in tournaments. The bill allows members of rifle clubs or associations to use any firearm for target practice instead of only point 22 bore rifles or air rifles.
ANTI-MARITIME PIRACY BILL: The Bill seeks to provide for stringent punishment, including death penalty or life imprisonment, to those involved in piracy at sea. It was introduced with an aim to promote the safety and security of India's maritime trade, and the safety of the crew members. The government is bringing the law as part of commitment made by India while signing the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) in 1982. The UNCLOS was ratified by India in 1995.
External Affairs Minister Jaishankar introduced the Anti-Maritime bill in parliament. It was introduced on the 10th of December, 2019 after the kidnapping of 18 Indians aboard in Nigeria.
The Bill includes death penalty to those involved in piracy at sea. Under Section 3 of the Bill, persons involved in the act of piracy shall be punished with life imprisonment or death penalty.
It enables the Central Government, in consultation with the Chief Justice of the concerned High Court to specify certain courts as Designated Courts for speedy trial of offences of piracy under the proposed legislation.
UNCLOS: It refers to United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea. It is also called the Law of the Sea Convention or the Law of the Sea treaty. It is an International Agreement that resulted from the third United Nations Conference on the Law of the Sea, which took place between 1973 and 1982. As of June 2016, 167 countries and the European Union have joined in the Convention. The Convention, concluded in 1982. It replaced the quad-treaty 1958 Convention on the High Seas. It came into force in 1994, a year after Guyana became the 60th nation to ratify the treaty.
The Law of the Sea Convention defines the rights and responsibilities of nations with respect to their use of the world's oceans, establishing guidelines for businesses, the environment, and the management of marine natural resources.
Constitution (126th Amendment) Bill, 2019: The Bill seeks to extend reservation of seats in Lok Sabha and State Assemblies for SCs and STs by another ten years. The Bill was passed in the Lok Sabha with 352 members voting in favor and none against it and passed in the Rajya Sabha on December 12, 2019 with 163 votes in favor and none against. The voting had taken place through division, as it was a constitution amendment bill.
The Bill seeks to extend the reservation for SCs and STs by another 10 years till January 25, 2030. The reservation has been included in Article 334 and therefore the bill seeks to amend the article.
The Bill does not propose an extension of reservation quota for the Anglo-Indian community, which is also set to expire on January 25. As per the Government, there are only 296 Anglo-Indians in the country.
Article 334: Under this Article, the Constitution provides for reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) and representation of the Anglo-Indian community by nomination, in Lok Sabha and Legislative Assemblies of states. This has been provided for a period of 70 years since the enactment of the Constitution and will expire on January 25, 2020.
The Recycling of Ships Bill, 2019: It is a Bill passed by the Parliament for safe and environmentally sound recycling of ships in India. It was passed On December 9, 2019 with Rajya Sabha approving it after its clearance in the Lok Sabha. Shipping Minister, Mansukh Mandaviya moved the bill. Once the Bill receives President’s assent and becomes an Act, it will ensure environment friendly recycling process of Ships and adequate safety of the yard workers.
Key features:-
*The bill restricts the use of hazardous materials on ships and regulates recycling of ships.
*It defines ship recycling as dismantling it at a facility to recover the components and materials for reuse and taking care of the hazardous material so produced.
*Under the legislation, every ship recycler must ensure safe and environmentally sound removal and management of hazardous materials from a ship.
*On violating these provisions, the ship recycler will be liable to pay environmental damages and cleanup operation compensation as prescribed.
*The Bill joins together the existing Ship breaking Code (revised), 2013 and the provisions of the Hong Kong Convention, 2009. So, now, ships to be recycled in India will need to obtain a ‘Ready for Recycling Certificate’ in accordance with Hong Kong Convention.
* The Bill will help the ship recycling industry and generate more jobs in the country.
*The Bill will raise brand value of India’s Ships Recycling Yards located at Mumbai Port, Kolkata Port, Azhikkal (Kerela) and Alang (Gujarat).
*10% of country’s Secondary steel needs, which is an outcome of Recycling of Ships, will be met in an eco-friendly manner.
*The National Authority will be the nodal agency to supervise, monitor and administer the recycling operations.
*The Bill will be applicable to any new or existing ship which is registered in India, the ships entering a port or terminal in India or the territorial waters of India​​​​​​​, ships owned and operated by an administration or any warships that are used on government non-commercial service, ship recycling facilities operating in India.
Aircraft (Amendment) bill, 2019: It is a bill approved by the Union Cabinet on December 11, 2019 to amend the Aircraft Act, 1934. The Bill will now be introduced in the Parliament.
Key Features:-
*The Bill is intended to carry out amendments to the Aircraft Act, 1934 (XXII of 1934).
*The Bill enhances the maximum limit of fine from the existing ten lakhs rupees to one crore rupees failing to comply norms of Government of India.
*It will increase the safety and security of aircraft operations in the country.
* It aims to fulfill the safety requirements of International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO).
* It will bring the regulations of all areas for air navigation within the ambit of the Act.
*It will enable three regulatory bodies namely Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS), Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) and Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB) to become more effective in the level of safety and security of aircraft operations in the country.
ICAO: It refers to International Civil Aviation Organization. It is a specialized agency of the United Nations charged with coordinating and regulating international air travel. It was established in 1944 by Convention on International Civil Aviation (Chicago Convention).It's headquarters is in Quebec, Canada. Its council is composed of 36 states which are elected for a three-year term. It changes the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth.
CAB: It refers to Citizenship (Amendment) Bill, 2019. CAB is a bill amending the Citizenship Act of 1955 to grant Indian citizenship to illegal migrants who are Hindus, Sikhs, Buddhists, Jains, Parsis and Christians from Afghanistan, Bangladesh and Pakistan, who entered India on or before 31 December 2014. It also seeks to relax the requirement of residence in India for citizenship by naturalization from 11 years to 5 years for these migrants.
President Ram Nath Kovind has given his assent to the Citizenship (Amendment) Bill, 2019, turning it into an Act. The Act has comes into effect with its publication in the official gazette. The Act was passed by both Houses of Parliament earlier this week with a clear majority.
The amendment is not applicable to the tribal areas of Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram or Tripura as included in the Sixth Schedule to the Constitution and in the areas covered under the Inner Line Permit. The Inner Line Permit regime is applicable in Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland and Mizoram.
It also proposes to incorporate a sub-section (d) to Section 7, providing for cancellation of Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) registration where the OCI card-holder has violated any provision of the Citizenship Act or any other law in force.
Citizenship Act, 1955: According to the provisions of the Citizenship Act, 1955, illegal migrants can either be kept in jail or sent back to their country under the Foreigners Act, 1946 and the Passports (Entry into India) Act, 1920. These two Acts empower the central government to check the entry, exit and residence of foreigners within India. A person is labeled an “illegal immigrant" if he or she has entered India without travel documents or has overstayed the date specified in the documents.
International Financial Services Centres Authority Bill, 2019: It is the Bill that seeks to set up a unified authority to regulate all financial activities in international financial services centres (IFSCs) in India. The Lok Sabha passed the International Financial Services Centers Authority Bill, 2019 on the 11th of December, 2019. The bill was earlier withdrawn from the Rajya Sabha.The first IFSC was set up at Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT) in Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
Provisions of the Bill:-
*The Bill will apply to all IFSCs set up under the Special Economic Zones Act, 2005.
*The bill will amend fourteen Acts, including the SEBI Act, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA) Act and the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) Act.
*The bill seeks to establish a unified Authority that will regulate various financial activities in the IFSC in India. At pressent, multiple agencies are entrusted with regulating the specific market including the SEBI, RBI, IRDA and PFRDA.
*The authority will follow all that processes that are applicable to such financial services, financial products, and financial institutions
*An International Financial Services Centres (IFSC) provides jurisdiction for carrying out international financial services domestically.
*The IFSC’s are not necessarily restricted to the Gujarat International Finance Tech-City, known as the GIFT city in Gujarat alone. Other states can also seek nod for similar centres.
*All the laws of the land and the unified authority will be subject to audit by the Central Vigilance Commission (CVC) and the Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG). The Central agencies like the CBI, the ED and the Prevention of Money Laundering Act-PMLA will have jurisdiction over the proposed authority.
*According to the bill, there will be a tax holiday only for 10 years in the IFSC.
*The bill defines various financial products including IT-enabled services in the financial sector.
*The Bill sets up the International Financial Services Centres Authority. It will consist of 9 members, appointed by the central government. Members will have a term of 3 years, subject to reappointment.
Social Security Code Bill: It is a Bill that paves way for universalization of social security of 50 crore workers in the country. The Code on Social Security, 2019 was introduced in the Lok Sabha on the 11th of December, 2019 by the Minister for Labour and Employment Santosh Kumar Gangwar.
Key Features:-
*It has an enabling provision to empower the Centre to set up funds for providing social security such as medical cover, pension, death and disablement benefits to gig, platform, and unorganised workers.
*The Bill seeks to enable the central government to fix provident fund contributions to be made by employees in different sectors and provides for payment of gratuity to fix-term employees.
*The code makes Aadhaar mandatory for availing benefits under various social security schemes.
*The bill will provide options of reducing the provident fund contribution of the employees thereby increasing their take-home payment.
*The Code on Social Security will subsume 9 Central Labour Acts namely Employees' Compensation Act, 1923; Employees State Insurance Act, 1948, Employees Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Provisions Act, 1952; Maternity Benefit Act, 1961, Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972, Cine Workers Welfare Fund Act, 1981, Building and Other Construction Workers Cess Act, 1996 and Unorganized Workers Social Security Act, 2008 and Employment Exchanges (Compulsory Notification of Vacancies) Act 1959.
*The bill also makes the fixed-term contract workers eligible for gratuity. Currently under the Payment of Gratuity Act, 1972, workers are not entitled to gratuity only after the completion of 5 years.
Aircraft Amendment Bill, 2019: The Cabinet on Wednesday approved the introduction of the Aircraft (Amendment) Bill, 2019 in the Parliament. The Bill is intended to carry out amendments to the Aircraft Act, 1934 (XXII of 1934).
The Bill enhances the maximum limit of fine from the existing ₹10 lakhs to ₹one crore. It will also include the regulation of all areas of air navigation to the Aircraft Act, 1934. The proposed amendments would fulfill the safety requirements of International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO) enabling the three regulatory bodies in the civil aviation sector in India, namely Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB) and Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS) to become more effective, thereby, enhancing the level of safety and security of aircraft operations in the country.
Sanskrit Central Universities Bill, 2019: The Central Sanskrit Universities Bill, 2019, was passed by the Lok Sabha on December 12. The bill was initiated by Union Human Resource Development (HRD) Minister Ramesh Pokhriyal ‘Nishank’.
The Bill seeks to The Bill seeks to convert three deemed Sanskrit universities into Central universities, which are-Sri Lal Bahadur Shastri Rashtriya Sanskrit Vidyapeeth in New Delhi, Rashtriya Sanskrit Sansthan in Bhopal and Rashtriya Sanskrit Vidyapeeth in Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh.
The Sansthan dates back to 1970, Lal Bahadur Shastri Rashtriya Sanskrit Vidyapeeth was established in 1962 while the Rashtriya Sanskrit Vidyapeeth in Tirupati was set up in 1961. All three were granted deemed university status by the UGC later. The purpose of these universities will not only to impart Sanskrit knowledge to students but also to attract more students from India and abroad.
International
Diwali-Power of One Awards: Its the awards that have now come to be known as ‘Oscars of Diplomacy’ It is the “Power of One” award, established in 2017 by the Diwali Foundation USA. Currently it is chaired by Ranju Batra. The New York-based Batra is credited with the seven-year-long efforts towards the release of a Diwali stamp by the US Postal Service.
The awards seek to promote a peaceful and consensus-based process to achieve societal good, as befitting high hopes and ideals of humanity enshrined in the UN Charter. They are awarded to former Permanent Representatives or high-level UN diplomats or those diplomats who will soon finish their tenure at the world organization for working selflessly to help form a more perfect, peaceful and secure world for all." Six top diplomats, including an Indian woman, have been felicitated with the inaugural Diwali "Power of One" award at the UN headquarters here for their contribution to help form a more "perfect, peaceful and secure world". It was presented on the occasion of the first anniversary of the US Postal Service's issuing of a forever Diwali stamp last year.
The awardees were :-
*Former foreign minister and Permanent Representative of Kazakhstan to UN: Kairat Abdrakhmanov.
*Former Permanent Representative of Cyprus to UN: Nicholas Emiliou.
*Former Chef de Cabinet to President of 72nd Session of the UN General Assembly (UNGA)
*Permanent Representative of Slovakia to UN: Frantisek Ruzicka.
*Permanent Representative of Ukraine to the UN: Volodymyr Yelchenko.
*Indian head of the UN Women: Lakshmi Puri.
December 9: It is observed as the International Day of Commemoration and Dignity of the Victims of the Crime of Genocide and of the Prevention of this Crime. It is a day established by the U.N. General Assembly to raise awareness of genocide and the role the U.N. Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide. Since, in 1948, on the 9th of December, the U.N. General Assembly adopted the Genocide Convention. The Genocide Convention was the first document that defined genocide and imposed obligations on states to prevent genocide and punish the perpetrators.
This year marked the 70th anniversary of the Convention. The purpose of the day is to raise awareness of the Genocide Convention and its role in combating and preventing the crime of genocide, as defined in the Convention, and to commemorate and honor its victims. In adopting the resolution, without a vote, the 193-member Assembly reiterated the responsibility of each individual State to protect its populations from genocide, which entails the prevention of such a crime, including incitement to it.
Exercise Iron Union 12: It is a joint militry exercise between the ground forces of the UAE and the United States. Exercise Iron Union 12 commenced on 10 December 2019 in the presence of Lieutenant General Terry Ferrell, commander of US Army Central, USARCENT and Major General Saleh Mohamed Saleh Al Amiri, UAE Commander of Land Forces. The exercise showcases the determination of the UAE Armed Forces that has proved to stand firm against all threats and challenges facing the region.
HUMAN RIGHTS DAY 2019: It is celebrated annually across the world on 10 December every year. This day is celebrated internationally to honor 10th Dec 1948, when the United Nations adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights(UDHR) at Palais de Challoit, Paris after the experience of the Second World War.
The theme of 2019 is – ‘Youth Standing Up for Human Rights’. UN believes that the participation of youth is an essential element to achieve sustainable development for everyone. Also, young people are always taken as major drivers of social, economic and political transformation.
NHRC: It refers to the National Human Rights Commission. Human Rights law came into existence in September 1993, 28 in India. The government of India constituted the National Human Rights Commission on October 12, 1993. This day is celebrated annually to recognize and empower human rights. It mainly includes economic, social, cultural rights and international commitments on civil and political rights.
United Kingdom: Prime Minister Boris Johnson's Conservative party won the UN's General election with a majority vote. 15 Indian-origin politicians have entered the House of Commons in the historic general election held on 12 December 2019. Indian-origin candidates in both the ruling Conservative and opposition Labour parties have registered equally strong results of seven wins on each side.
The Indian origin candidates are:-
The former UK Home Secretary Priti Patel who is likely to remain in Johnson's top team in the new Cabinet after her comfortable win. Gagan Mohindra and Claire Coutinho won for the Conservative Party where as Navendru Mishra for Labour Party and Munira Wilson for the Liberal Democrats are among the first-timers. Former International Development Minister Alok Sharma, Shailesh Vara, Tanmanjeet Singh Dhesi, Goan-origin Suella Braverman, Preet Kaur Gill, Virendra Sharma are among others.
USMCA: It refers to United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement. The representatives from the United States, Mexico and Canada have finalized a trade deal that will replace the 25-year-old North American Free Trade Agreement (Nafta). The three countries signed the pact in Mexico. The deal aims to improve enforcement of worker rights and hold down prices for biologic drugs by eliminating a patent provision. The United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) will now go to the countries’ legislatures for final approval.
National
Exercise Hand-in-Hand-2019: It is a military exercise of India and China called ‘Hand-in-Hand’. The joint military exercise commenced at Umroi, Meghalaya on 7 December 2019. It is a 14-day long event which is being conducted at the company level. Its the 8th edition of the exercise which is being held under the United Nations mandate. The main aim of the exercise is to enrich both Indian and Chinese contingents from each other's experience to combat counter-terrorism. The theme of this training exercise is Counter-terrorism. Under the theme, both the countries will practice joint planning and conduct of counter-terrorist operations in semi-urban terrain.
The Tibet Military command comprising of 130 personal from the Chinese side and 100 personnel from the Indian side will be participating in the event. The events includes discussions on Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) operations. The tactical exercises will include, one on counter-terrorism scenario and the other on HADR operations. It will also include lectures and drills on handling on weapons and fire arms, special helicopter-borne operations, battle obstacle courses and case studies of operations done in the counter terrorism field.
INDRA 2019: Its a joint navy exercise which will be conducted by Russia and India. The aim of exercise INDRA 2019 is to enhance interoperability between the two countries and also to develop an understanding among the countries in order to effectively tackle common security challenges.
The Russian Federation Navy (RuFN) Ships Yaroslav Mudry, Viktor Konetsky and Elyna arrived at Goa on December 10 to participate in INDRA 2019, the second edition of the tri-services exercise between the Indian and the Russian armed forces. The first Joint Tri-Services of the INDRA exercise was conducted in 2017.
MEA: It refers to Union Ministry of External Affairs. MEA will host 6th Indian Ocean Dialogue and Delhi Dialogue XI at Pravasi Bharatiya Kendra in New Delhi on 13 December 2019. For the first time, these two events will be held consecutively and on similar Indo-Pacific themes. The theme for Indian Ocean Dialogue is "Indo-Pacific: Re-imagining the Indian Ocean through an Expanded Geography”. The theme for the Delhi Dialogue is “Advancing Partnership in Indo-Pacific”. The themes are intended to build on the ‘growing recognition of the Indo-Pacific concept in strategic and academic circles within the region and beyond. The 6th IOD is being organized with assistance of the Indian Council for World Affairs (ICWA). The theme for this year’s Delhi Dialogue is "Advancing Partnership in Indo-Pacific”.
Through these processes, India intends to emphasise its open and inclusive approach to fostering a cooperative, free, and rules-based Indo-Pacific domain, in which all nations and their aspirations for development have equal space to find expression.
Ministry of Tourism: The ministry has identified 17 sites in 12 clusters in the country under the Iconic Tourist Sites Development Project. The 17 sites are TajMahal and Fatehpur Sikri in Uttar Pradesh, Ajanta and Ellora in Maharashtra, Humayun's Tomb, Red Fort and Qutub Minar in Delhi, Colva beach in Goa, Amer Fort in Rajasthan, Somnath and Dholavira in Gujarat, Khajuraho in Madhya Pradesh, Hampi in Karnataka, Mahabalipuram in Tamil Nadu, Kaziranga in Assam, Kumarakom in Kerala and Mahabodhi in Bihar. The monuments taken up for development under the Iconic Tourist Sites Development Project fall under the jurisdiction of Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and State Archaeology Departments.
India and Maldives: India and Maldives will review bilateral cooperation at Joint Commission Meeting in New Delhi. Maldivian Foreign Minister Abdulla Shahid will co-chair the India-Maldives 6th Joint Commission Meeting. The aim of the meeting is to enhance cooperation for peace and mutual security in the Indian Ocean Region.
India and Myanmar: The 18th India-Myanmar Foreign Office Consultations was held in New Delhi on 6 December 2019. The Indian delegation was led by Foreign Secretary, Shri Vijay Gokhale, and the Myanmar delegation was led by Permanent Secretary, U Soe Han. The two sides reviewed the entire details of bilateral relations. The status of India's ongoing projects in Myanmar, capacity building initiatives, bilateral trade relations, border cooperation was also discussed.India reiterated its priority for the partnership with Myanmar which is at the intersection of Neighbourhood First and Act East policies. The Myanmar Permanent Secretary equally reaffirmed the high priority his Government attaches to relations with India, which are based on historic and civilizational contact.
Places In News
Nagaland: The State of Nagaland was formally inaugurated on December 1st, 1963, as the 16th State of the Indian Union. It is bounded by Assam in the West, Myanmar (Burma) on the east, Arunachal Pradesh and part of Assam on the North and Manipur in the South. The State consists of seven Administrative Districts, inhabited by 16 major tribes along with other sub-tribes. Each tribe is distinct in character from the other in terms of customs, language and dress. It is a land of folklore passed down the generations through word of mouth. Here, music is an integral part of life. Its home to diverse indigenous tribes, with festivals and markets celebrating the different tribes' culture. The capital city of Kohima suffered heavy fighting in World War II, commemorated by memorials at the Kohima War Cemetery.
Hornbill Festival : Every year the “Hornbill Festival” is celebrated in the Kisama village near Kohima, the state capital between December 1 and December 10. The festival is organized by the State Tourism and art and culture department in Kohima. The art and culture, paintings and lifestyles of the Morung tribes is exhibited at the festival. The aim of the festival is to protect and revive the rich culture of Nagaland. All the tribes of Nagaland take part in the festival. Traditional arts of the state such as wood carvings, paintings and sculptures are displayed in the festival.
Naga Morungs: The Naga Morung is a self-governing body that aims to protect the village men. Morungs were the community spaces in Nagaland where the young boys were trained. The boys are taught history and culture of the tribes in the land. They also learnt folk songs and tales during their stay. The boys were made Naga warriors in these Morungs.
Hornbill: It is a revered bird that is featured widely in the songs of Nagaland tribes. Hence the name horn bill is given to the festival. Hornbills are birds that are found in tropical and sub-tropical Asia, Africa and Melanesia.
Nagaland,ILP regime: Nagaland Government Brings Dimapur under Inner Line Permit Regime. Dimapur is the commercial hub of the state and it was the only district that was not under the ILP regime unlike the rest of Nagaland, which came into being in 1963. The state Cabinet had approved the proposal to extend the ILP to Dimapur. The ILP regime was also extended to neighboring Manipur with President Ram Nath Kovind signing the order in this effect. Besides Nagaland and Manipur, the ILP regime is also applicable to Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram.
ILP regime: It refers to Inner line permit regime. It aims to prevent settlement of other Indian nationals in these states to protect indigenous population. There are also protections for locals with regards to lands, jobs and other facilities. Under these regime outsiders, including people from other states of country need to take permission to visit the ILP-regime states. The ILP regime is applicable under the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulation, 1873. In terms of Section 2 of the Bengal Eastern Frontier Regulations, 1873, citizens of other states require ILP for visiting these three states.
Jammu and Kashmir: Lt Governor of Jammu and Kashmir Girish Chandra Murmu, inaugurated Draj Bridge in Rajouri, J&K.This bridge will facilitate all-weather and speedy movement of Army troops and locals.
Draj Bridge: The bridge which is a 72-metre-long Multi Cell Box Type Load Class 70 bridge spans over Draj nallah connects Draj Area with Tehsil Kotranka area under District Rajouri. The important Draj Bridge has been constructed by 110 Road Construction Company of 31 Task Force under Project Sampark of Border Roads Organisation (BRO). It is responsible for infrastructure development and war preparedness through construction of roads, bridge and tunnels. It also plays an important role in field of surface transport by connecting far-flung inaccessible remote areas along borders. It is involved with more projects in area to strengthen road network.
Punjab: The Union Government has formulated a special action plan for the development of tourism in Sri Anandpur Sahib parliamentary constituency under the Swadesh Darshan Scheme. The Ministry of Tourism under its Swadesh Darshan scheme had sanctioned a project Development of Heritage Circuit: Anandpur Sahib, Fatehgarh Sahib – Chamkaur Sahib – Ferozpur –Amritsar – Khatkar Kalan – Kalanour – Patiala in Punjab for Rs.99.95 crore in the year 2018-19.
Karnataka: The first event of the Human Library was held in the City of Palaces, Mysuru, Karnataka. Human Library event is a concept which seeks to replace books with humans. The main aim of the Human Library event is to break past long-standing prejudices and stereotypes by creating a safe framework for conservation by using a library analogy of lending people rather than books. It intends to generate greater human cohesion across various social, religious and ethnic diversities. It was organized by international non-profit organization.
Human Library: It is also known as Human Library Organization. The notion of Human Library was initially launched in the year 2000 and currently exists in more than 85 countries. It is a registered non-profit international organization which is headquartered in Copenhagen, Denmark. Its aim is to ensure a global implementation of the Human Library as a learning platform. In India, Human Library is spread across various metropolitan cities including Hyderabad, Mumbai, Delhi, Bengaluru.
Madhya Pradesh: It is a large state in central India nicknamed the "Heart of India", retains landmarks from eras throughout Indian history. Begun in the 10th century, it’s Hindu and Jain temples at Khajuraho are renowned for their carvings of erotic scenes, most prominently Kandariya Mahadeva, a temple with more than 800 sculptures. The eastern Bandhavgarh and Kanha national parks, noted Bengal tiger sanctuaries, offer guided safaris.
The State government of Madhya Pradesh has sanctioned a sum of Rs.156 crore for the development of Omkareshwar. It was approved in a meeting chaired by Chief Minister Kamal Nath.
Omkareshwar: It is a famous pilgrimage centre which houses one of the twelve jyotirlinga shrines of Lord Shiva. It is located about 80km from Indore.
Andhra Pradesh: It is a state bordering India’s southeastern coast. Major cultural landmarks include Tirumala Venkateswara Temple, an ornate hilltop shrine to Hindu’s Vishnu, in the southern part of the state. The largest city in Andhra Pradesh is Visakhapatnam. Telugu is one of the classical and major and official language of Andhra Pradesh.
Andhra Pradesh Government decided to table a Bill in the Assembly to punish perpetrators of heinous crimes against women and children within 21 days. This was decided after the gang-rape and murder of a woman veterinarian in Hyderabad. The state Cabinet, chaired by Chief Minister Y. S. Jaganmohan Reddy has approved to enact the new law, Andhra Pradesh Disha Act, Andhra Pradesh Criminal Law (Amendment) Act, 2019 and Andhra Pradesh Special Court for Specified Offences against Women and Children Act- 2019. The Act would cover sexual offences against women and children, acid attacks and harassment of women and provide for harsher punishments which will including death sentence to those guilty. Andhra Pradesh is to set up a virtual police station (VPS) in the Andhra University (AU) which will be the first of its kind. It will help the students to report violence or any other crime online.
New Delhi: The 37th National Symposium of Heads of Police Training Institutions held in New Delhi. It was organized by the Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPR&D), Ministry of Home Affairs. The theme of the Symposium was ‘Optimal Utilization of Resources-Through Sharing and Networking’. A Directory of Indian Police Training Institutions (DIPTI) which has information on the resources of around 300 Police training institutions all over the country, was released during the event. The symposium includes discussions on topics including Optimizing Capacity Building: Through Partnership and Collaboration, Skill Development: the Role of Co-ordination and Networking, Understanding the Learner's Psychology, and Optimal Utilization of Resources- through Sharing and Networking.
Bureau of Police Research and Development: The Bureau of Police Research and Development, was established on 28 August 1970 in furtherance of the objective of the Government of India for the modernization of police forces.
Odisha: President Ram Nath Kovind laid the foundation stone to the memorial being built in memory of the Paika rebellion, a 200-year-old armed revolt in 1817 against the British East India Company in Odisha which is often termed as the First War of Independence.The proposed project will come up at the foothills of Barunei hills in Khurda district, Odisha.
The memorial is seen as an epitome of Odisha’s valour and will serve as an inspiration for the youth. To mark the two hundred years of the event, a chair in the name of Buxi Jagabandhu who led this revolt has been established with a Rs 5 crore grant and memorial coin and a stamp has been issued.
Science and Technology
ISRO: It refers to the Indian Space Research Organization. It is the space agency of the Government of India headquartered in the city of Bengaluru. It was founded in 15 August 1969 by Vikram Sarabhai. it's parent organization is Department of Space. Its vision is to "harness space technology for national development while pursuing space science research & planetary exploration".
RISAT-2BR1: It is a radar imaging earth observation satellite weighing about 628 kg. The satellite will provide services in the field of Agriculture, Forestry and Disaster Management. The mission life of RISAT-2BR1 is 5 years.
ISRO launched RISAT-2BR1 and 9 Commercial satellites on-board PSLV-C48 in its 50th flight into designated orbit successfully. It was launched from Satish Dhawan Space Centre at Sriharikota, a rocket port in Andhra Pradesh. As per ISRO, in the coming days, the satellite would be brought to its final operational configuration.
(PSLV)-C48: It refers to Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle. IT is an expendable medium-lift launch vehicle which is designed and operated by ISRO.
The Duchifat 3: It is a small remote sensing satellite weighing 2.3 kilogram, built by students from Sha'ar HaNegev High School and few other schools in collaboration with Herzliya Space Center (HSC) in Israel. It is designed to serve children from across the country to carry experiment through Earth observation. It was part of the nine commercial satellites launched by ISRO along with its own earth observation satellite. The other 8 foreign satellites are Italy's (search and rescue Tyvak-0092), Japan's (QPS-SAR – a radar imaging earth observation satellite) and USA's (multi-mission Lemur-4 satellites, earth imaging 1HOPSAT, technology demonstration Tyvak-0129). These international customer satellites are being launched under a commercial arrangement with NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) under Department of Space.
Electric Aircraft: It is an aircraft powered by electric motors. Electricity may be supplied by a variety of methods including batteries, ground power cables, solar cells, ultracapacitors, fuel cells and power beaming
The world’s first fully-electric commercial aircraft took its inaugural test flight. It took off from the Canadian city of Vancouver. It flying for 15 minutes. This 62-year-old six-passenger DHC-2 de Havilland Beaver seaplane was re-fitted with a fully electric 750 horsepower motor. It was piloted by Greg McDougall. He is the founder and chief executive of Harbor Air, a British Columbia-based charter airline that transport passengers between Vancouver. MagniX designed the motor and worked in partnership with Harbor Air which ferries thousands of people a year between Vancouver, Whistler ski resort and nearby islands.
Airtel Wi-Fi Calling: It is service designed to enhance voice calling experience for Airtel smartphone customers, especially when they are indoors. With 'Airtel Wi-Fi Calling', customers with Wi-Fi at home or office will get excellent signal quality indoors.
Telecom major Bharti Airtel on Tuesday launched the Wi-Fi calling service for its subscribers. The service is currently rolling out in Delhi-NCR and will be gradually implemented in other cities as well. This service is presently compatible with Airtel Xstream Fiber home broadband and will soon be compatible with all broadband services and Wi-Fi hotspots.
Bharati Airtel: It is an Indian global telecommunications services company based in Delhi which operates in 18 countries across South Asia and Africa.
BEE: It refers to Bureau of Energy Efficiency. It is an agency of the Government of India, under the Ministry of Power created in March 2002 under the provisions of the nation's 2001 Energy Conservation Act. The agency's function is to develop programs which will increase the conservation and efficient use of energy in India. It was founded on 1st March 2002. Its headquarters is in SEWA Bhavan, R. K. Puram, New Delhi.
The BEE is celebrating 'National Energy Conservation Week' from 9 to 14 December 2019 to raise awareness among the general public about the importance of energy efficiency and conservation. BEE in association with the International Energy Agency (IEA) under the SEAD initiative of Clean Energy Ministerial (CEM) conducted the International Workshop on Energy Efficient Cooling at Scope Convention Centre, New Delhi. It was organized as a part of the Energy Conservation Week that was observed from 9-14 December 2019. It served as a platform for global experts, industries, and policymakers to explore opportunities to accelerate deployment of energy-efficient cooling, across different sectors and establishments. Various delegates involving regulatory bodies, policymakers, Government officials, Public sector undertakings (PSUs), etc. from across the world participated in the workshop.
National Energy Conservation Day 2019: This day is observed every year on December 14 in India. National Energy Conservation Day is organized by the Energy Efficiency Bureau (BEE), a subordinate Ministry of Power. It aims to showcase India's achievements in energy efficiency and conservation.
TRAKEA: It is unique barcoding software that is used to ensure that 1000s of digital forensic reports are stored safe and secure. It ensures foolproof security of the samples collected from the scene of crime, and the forensic analysis reports, and is different from traditional methods that the state police force has been following for decades. The software was originally designed by a prisoner who was a software engineer by profession. He was lodged in Bhondsi jail for 13 months.
The Haryana Police Department has adopted this unique barcoding software (TRAKEA).
Sports
WADA: It refers to World Anti-Doping Agency. It is a foundation initiated by the International Olympic Committee based in Canada to promote, coordinate and monitor the fight against drugs in sports. It was founded on the 10th of November 1999. It’s Headquartered in Montreal, Canada.
World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) has banned Russia for 4 years, from participation in global sporting events, including the 2020 Tokyo Olympics and the 2022 Beijing Winter Olympics for falsifying data from an anti-doping laboratory.
SAG: It refers to the South Asian Games championship. It was formerly known as South Asian Federation Games. It is a biennial multi-sport event held among the athletes from South Asia. The governing body of these games is South Asia Olympic Council (SAOC), formed in 1983. It is held every two years. The first South Asian Games were hosted by Kathmandu, Nepal in 1984. The motto of SAG is Peace, Prosperity and Progress.
South Asian Games championship, 2019 was held in Nepal. The official mascot for the SAG,2019 was a pair of blackbucks (Krishnashar). The opening and closing ceremonies were hosted at the Dasarath Stadium. India won the 13th edition of the 2019 South Asian Games championship which started from the 1st to 10th December 2019 in Kathmandu and Pokhara, Nepal. India collected 174 gold, 93 silver and 45 bronze after ten days of competitions.
GS Lakshmi: She is an Indian cricket match referee and a former domestic cricket player and coach. 51 year old Laxmi was a right handed batswoman and right-arm fast-medium outswing bowler. She is from Andra Pradesh. Earlier on May 2019, she became the first woman to get appointed onto the ICC International Panel of Match Referees. She has the experience of officiating in three women’s ODI matches, 16 men’s T20Is and seven women’s T20Is.
The former Indian cricketer has again set to become the first woman to be appointed to the International Cricket Council's International Panel of Match Referees on 14 May 2019. She will oversee the third series of the ICC Men’s Cricket World Cup League 2. The opening match of the competition will take place between the United Arab Emirates and the United States of America at Sharjah Cricket Stadium.
UEFA Europa League: It is an annual football club competition organized by UEFA since 1971 for eligible European football clubs. Clubs qualify for the competition based on their performance in their national leagues and cup competitions. It is the second-tier competition of European club football, ranking below the UEFA Champions League. It was founded in 1971 and known as UEFA Cup. The name was rebranded in 2009 as UEFA Europa League.
Four-star Manchester United wins Europa League group. Teenager Mason Greenwood Stars As Manchester United Top Group, Arsenal Draw 2-2 In Europa League. He scored twice in a 4-0 thrashing of AZ Alkmaar in the Europa League while Arsenal came back from two goals down to draw 2-2 vs Standard Liege.
BWF World Tour Finals: The BWF Super Series Finals (named as BWF Super Series Masters Finals until 2009) was an annual badminton tournament held at the end of the year where the players with the most points from that calendar year's twelve events of the BWF Super Series competed for total prize money of at least US$ 1,000,000. It was replaced by BWF World Tour Finals in 2018.
2019 BWF World Tour was held from 11 to 15 December 2019 in Tianhe Gymnasium in Tianhe, Guangzhou, China.
The defending world champian PV Sindhu knocked out of the BWF World Tour Finals after her second straight defeat. The world champion lost to China’s Chen Yufei 22-20, 16-21, 12-21 in 72 minutes in Guangzhou. Chen Yufei has won all six of her finals, including the All England Championships.
However, India's P V Sindhu recorded a consolation win over China's He Bingjiao in the third Group A match to end her campaign on a positive note at the year-ending BWF World Tour Finals in Guangzhou.
FICCI : It refers to Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry. FICCI confers the India Sports Awards to acknowledge and recognize contribution of sports persons and various stakeholders who deliver excellent results during the year.
The coveted FICCI India Sports Awards 2019 were were presented to the winners on 11 December 2019 at New Delhi. The jury for the awards included Justice (Retd) Mukul Mudgal.
The awardees were:-
Sports Person of the Year(Female): Rani Rampal for hockey
ports Person (Male): Saurabh Chaudhary for shooting
Para-Athlete: Sandeep Chaudhary for javelin
Special Recognition Para-Athlete: Manasi Joshi for badminton
Special Recognition Breakthrough Sports Person: Esow Alben for cycling
Breakthrough Sports Person: Amit Panghal
Coach or Support Staff: Satyanarayana
Lifetime Achievement (administrator): Govindaraj Kempareddy
Lifetime Achievement: Pankaj Advani for cue sport
Best State promoting sports: Odisha
Best Sports Journalist: Kamesh Srinivasan
Best National Sports Federation: National Rifle Association of India
Best Company Promoting Sports (Public Sector): Railway Sports Promotion Board
WTA Finals: WTA refers to Women's Tennis Association. WTA Finals is a tournament of the Women's Tennis Association played annually at the end of the season for the top-ranked professional players. The tournament predates WTA and started in 1972 as the Championship tournament of WTA Tour's predecessor: the Virginia Slims Circuit.
The current champion for Women's singles is Ashleigh Barty from Australia and Women's doubles is Timea Babos from Hungary and Kristina Mladenovi from France.
WTA Player Of The Year Award: World No. 1 Ashleigh Barty Wons WTA Player Of The Year Award. She won four titles in 2019 including the prestigious WTA Finals and finished the year on top of the WTA rankings. She is the first Australian to top the women’s tennis rankings since Evonne Goolagong Cawley in 1976.
People In News
Dr. Padmeswar Gogoi: He is a noted educationist, Botanist and folklore researcher. He was conferred the Siu-Ka-Pha Award, instituted by the central committee of different ethnic groups and organisations of Golaghat district at a programme held at Siu-Ka-Pha Samannay Kshetra in Golaghat, Assam. He was presented with the award for his effort and contribution in the field of botany and science. The award was presented to him by Golaghat Deputy Commissioner Dhiren Hazarika. The cash prize was donated by Gogoi to the organizing committee to spend on activities that are done in order to promote the ideals of Chaolung Siu-Ka-Pha.
Siu-Ka-Pha Award: It is an award that was instituted by the central committee of different ethnic groups and organizations of Golaghat district, Assam. The inaugural edition of the award carries a citation, a memento, a cheleng chador and Rs 10,000. The award is named after the great King Sui-Ka-Pha. He was an able administrator. He laid the foundation of modern-day Assam. He was a strong believer of integration and oneness among his subjects and was instrumental in unifying various ethnic tribes.
Sanna Marin: She is a 34 year old Finnish politician. She is a Social Democrat and she has also been a member of the Parliament of Finland since 2015. She was the Minister of Transport and Communications between 6 June 2019 and 10 December 2019.
Sanna Marin becomes World’s Youngest-Serving Prime Minister. She was selected by her Social Democratic party of Finland. She took over after the resignation of outgoing leader Antti Rinne. She is expected to be sworn in as the new Prime Minister of Finland at the Parliament of Finland.
Before her The Prime Minister of Ukraine (aged 35) was the youngest Prime Minister in the world.
Zozibini Tunzi : She is a South African model. She has been crowned Miss Universe for the year 2019, beating more than 90 contestants on 8 December 2019 in Atlanta, Georgia, United States. She is the third woman from South Africa to win the title, and the first black woman since Leila Lopes was crowned Miss Universe 2011. She was presented the crown by Philippines’ Catriona Gray, who was the Miss Universe winner in 2018.
Miss Universe: It is an annual international beauty pageant that is run by the United States-based Miss Universe Organization. The contest is the largest pageant in the world in terms of live TV coverage, airing yearly in more than 190 countries worldwide to an audience of over 500 million people. Along with Miss World, Miss International, and Miss Earth, Miss Universe is one of the Big Four international beauty pageants. It was formed on June 28, 1952. It is headquartered in New York City, New York.
Girish Chandra Chaturvedi: He is a retired IAS officer and former Secretary, Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas. He is currently on board of ICICI Bank and member of government appointed board of Infrastructure Leasing and Financial Services Ltd (IL&FS). He also served as Director (Government Nominee) on Boards of Canara Bank, Bank of Baroda, IDBI Bank Ltd, GIC Re of India, IDFC Ltd, United India Insurance Co. Ltd, Agriculture Insurance Co. of India, New India Assurance Co. Ltd, National Insurance Academy and Institute of Banking Personnel Selection (IBPS).
He has been appointed as the new chairman of the National Stock Exchange (NSE) by NSE with the approval of markets regulator Securities and Exchange Board of India (Sebi).
Greta Thunberg: Greta Thunberg born on 3 January 2003 is a Swedish environmental activist on climate change whose campaigning has gained international recognition. She started protesting on 20 August 2018, outside of the Swedish parliament in Stockholm to reduce carbon emissions according to the Paris Agreement. Nearly about 20,000 schools in 270 cities in the world went on strike on her call. She also gave a speech at the United Nations Climate Action Summit this year which was widely appreciated worldwide.
She has been selected as 'Person of the Year' by 2019 magazine for the year 2019. She was awarded as she managed to attract worldwide attention and changed millions of vague ideas. She called for immediate change and turned an idea into a global movement.
Person of the Year (called Man of the Year or Woman of the Year until 1999) is an annual issue of the United States news magazine Time that features and profiles a person, a group, an idea, or an object that "for better or for worse... has done the most to influence the events of the year".
Vishwanath Prasad Tiwari: He is an Eminent Hindi poet. He was a former president of Sahitya Academy and has authored several anthologies. Notable among his creations are 'Rachana ki sarokar', 'Kavita kya hai', 'Saath chalte hue' and Bistar duniya le liye'. He would be honored with the prestigious Gangadhar National Award during the 53rd Foundation Day celebrations of the Sambalpur University.
Gangadhar National Award: The award was instituted in memory of legendary Odha poet Gangadhar Meher. It is being conferred on a bard of national repute every year since 1991. The award carrying a cash prize of Rs 50,000, a shawl and a citation.
Arts
ONLINE NAIMISHA 2020: It is a Summer Art Program announced by National Gallery of Modern Art (NGMA), New Delhi. The month-long ONLINE summer program by NGMA will be held from the 8th of June 2020 to 3rd of July 2020.
This initiative by NGMA aims to provide a chance to its participants to create and learn from practicing artists without compromising their health. Under this programme, 4 workshops will be organized entitled Painting workshop, Sculpture workshop, Printmaking and Indrajaal - The Magic of Art. The exhibition of selected artworks from NAIMISHA 2020 Summer Art Program will be displayed virtually on SO-HAM platform. The title of the program NAIMISHA-represents a sacred place where people offer their shraddha or devotion.
NGMA: It is an acronym for National Gallery of Modern Art. NGMA was established in 1954, at the Jaipur House, New Delhi. It is run and administered as a subordinate office to the Department of Culture, Government of India (GoI). It has two branches, one at Mumbai and the other at Bengaluru. The most important task of NGMA is to ensure quality and to set and maintain standards of excellence. The gallery is an archive of the cultural ethos of the country and showcases the changing art forms through the passage of the last hundred and fifty years starting from about 1857 in the field of Visual and Plastic arts.
So’ham: It is the first cultural media platform of India. So’ham is an intiative of National Gallery of Modern Art (NGMA). The platform seeks to develop a dialogue between NGMA, artists and art enthusiasts. It is inspired by the Vedic philosophy of So’ham, which means identifying oneself with the universe or ultimate reality.
Aguada Fénix: It is a site near the Guatemalan border where an enormous 3,000-year-old earthen platform topped with a series of structures, including a 13-foot-high pyramid has been discovered in the Maya region. The discovery took place in Mexico’s Tabasco State at the site of Aguada Fénix, about 850 miles east of Mexico City. It is in a region known as the Maya lowlands, from which the Maya civilization began to emerge. Archeologists discovered the old Mayan temple through laser mapping technique, making it the ancient civilisation's oldest and largest monument.
The temple site is 4,600 feet long and up to 50 feet high, making it larger than the Mayan pyramids and palaces of later periods. The structure, unlike the soaring Maya pyramids at cities like Tikal in Guatemala and Palenque in Mexico erected some 1,500 years later, was not built of stone but rather of clay and earth. It was built between 800 BC and 1,000 BC. One of the most remarkable revelations from the find was the complete lack of stone sculptures related to rulers and elites, such as colossal heads and thrones, that are commonly seen in other Mayan temples. This suggests that the people who built it were more egalitarian than later generations of Mayans.
Economics
RBI: It refers to the Reserve Bank of India. The RBI is India's central bank, which controls the issue and supply of the Indian rupee. It carries out India's monetary policy and exercises supervision and control over banks and non-banking finance companies in India. RBI was set up in 1935 under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. It is headquartered in Mumbai. RBI plays an important part in the Development Strategy of the Government of India. The current Governor of RBI is Shaktikanta Das.
Recently, The RBI has created a Payments Infrastructure Development Fund (PIDF) with an outlay of Rs. 500 Cr. The main objective of PIDF is to encourage acquirers to deploy Points of Sale (PoS) infrastructure — both physical and digital modes in tier-3 to tier-6 centres and north eastern states.
The setting of PIDF is in line with the measures proposed by the vision document on payment and settlement systems in India 2019-2021. It is also in line with the RBI’s proposal to set up an Acceptance Development Fund which will be used to develop card acceptance infrastructure across small towns and cities. It will be governed through an Advisory Council and managed and administered by RBI.
RBI will make an initial contribution of Rs 250 crore to the PIDF, covering half of the fund and the remaining contribution of the fund will come from card-issuing banks and card networks operating in the country. It will also receive recurring contributions to cover operational expenses from card-issuing banks and card networks. RBI will also contribute to its yearly shortfalls, if necessary.
According to RBI, the need for PIDF was felt, as for over the years, the payments ecosystem in the country has evolved with a wide range of options such as bank accounts, mobile phones, cards, etc., so, to provide further fillip to digitization of payment systems, it is necessary to give impetus to acceptance infrastructure across the country, more so in under-served areas.
CBIC: It is an acronym for the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs. CBIC is the nodal national agency responsible for administering Customs, GST, Central Excise, Service Tax and Narcotics in India. It comes under the Department of Revenue, Ministry of Finance. It was founded on 1 January 1964. The current CBIC is M. Ajit Kumar.
Recently, the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs (CBIC) launched its flagship programme Turant Customs at Bengaluru and Chennai which is a mega reform for the ease of doing business. The programme has been launched to take a leap forward to take advantage of the technology for faster Customs clearance of imported goods. With the initiation of programme at Bengaluru and Chennai it will be the first phase of the All India roll out which would get completed by 31st December this year. The first phase will cover imports of Mechanical, Electrical and Electronics machineries at the ports, airports and ICDs of Bengaluru and Chennai.
Under this programme the Customs officers located outside the port of import will clear the goods from Customs after doing faceless assessment remotely. Now, the goods imported at Chennai may be assessed by the Customs officers located at Bengaluru and vice versa, as assigned by the Customs’ automated system. Turant Customs will not only benefit the importers by eliminating routine interface with the Customs officers but also provide uniformity in assessment across the country.
NHAI: It refers to the National Highway Authority of India. NHAI is an autonomous agency of the Government of India. It was set up under the provisions of National Highway Authority of India Act, 1988. It is responsible for management of a network of over 50,000 km of National Highways out of 1,15,000 km in India. It is a nodal agency of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways. The current Chairman of NHAI is Sukhbir Singh Sandhu (IAS).
Recently, NHAI has become the first of its kind organisation in the construction sector to go fully digital with the launch of unique cloud based and Artificial Intelligence (AI) powered Big Data Analytics platform. It has integrated Data Lake and Project Management Software to ensure transparency, speed and quick decision making in the process.
With social distancing being one of the key methods to prevent COVID-19 infection, the online portal will help the NHAI employees in continuing their work without any physical contact.
Under the fully digitalised set up, entire project management work flow of NHAI is transformed from manual to online portal. All the project execution operations including workflow with time lines and mechanism have been configured digitally. All project documentation, contractual decisions and approvals are now being done only through the portal.
The whole correspondences and Project Management will be stored in Digital format in the cloud-based ‘Data Lake’ linked with GIS tagging and Unique Project ID, so that the project data can be easily retrieved as and when required from any location.
The Data Lake software, with advanced analytics, will not only forecast the delays, disputes and advance alerts but will also predict the financial impacts based on the historical data which will help in taking correct and timely decisions.
Data Lake: It is a repository of data. It allows storing all structured and unstructured data at any scale.
Defence
ARPIT: It refers to the Airborne Rescue Pod for Isolated Transportation. ARPIT has recently been indigenously designed, developed and manufactured by the Indian Air Force (IAF). This pod will help in the evacuation of critical patients with infectious diseases including COVID-19, from isolated, high altitude, and remote areas.
In support of the ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat Initiative’, only indigenous materials have been used to fabricate this pod.
The system is a lightweight isolation system made from aviation certified material. It not only has a transparent and durable cast Perspex for enhanced patient visibility but is also larger, higher, and wider than the existing models.
The isolation system caters for suitable number of air exchanges, integration of medical monitoring instruments, and ventilation to an intubated patient. In addition, it generates high constant negative pressure in the isolation chamber for prevention of infection risk to aircrew, ground crew and health care workers involved in air transportation.
ARPIT utilises High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) H-13 class filters. It also supports invasive ventilation using a Transport ventilator.
The design requirements have based on the guidelines issued by National Accreditation Board of Hospitals and Healthcare Providers (NABH), Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW), and Centre for Disease Control (CDC), USA.
The Indian Air Force is inducting a total of 7 ARPITS as of now.
IAF: It is an acronym for Indian Air Force. IAF is the air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. It was officially established on 8 October 1932 as an auxiliary air force of the British Empire which honoured India's aviation service during World War II with the prefix Royal. With the government's transition to a Republic in 1950, the prefix Royal was removed. The present Commander-in-Chief of IAF is Ram Nath Kovind. The Chief of Air Staff, an air chief marshal, is a four-star officer and is responsible for the bulk of operational command of the Air Force. The present Chief of the Air Staff (CAS) is Air Chief Marshal Rakesh Kumar Singh Bhadauria, PVSM, AVSM, VM, ADC and the Vice Chief of the Air Staff (VCAS) is Air Marshal Harjit Singh Arora, AVSM, ADC.
DSRV: It refers to the Deep Submergence Rescue Vehicle Complex. The DSRV Complex was recently inaugurated at Eastern Naval Command (ENC) in Visakhapatnam, Andhra Pradesh. It was inaugurated by Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief of Eastern Naval Command (ENC) Vice-admiral Atul Kumar Jain.
The complex has been designed to accommodate the newly inducted submarine rescue system and store the DSRV assets in the rescue-ready state. It consists of a submarine rescue vessel, a remote operations vehicle (ROV) and side-scan sonar and associated equipment. It not only also has diver decompression chambers but also a hyperbaric medical equipment to decompress submariners after being rescued from sunken submarines.
The system can help recover submarine crew from depths of up to 650m. To facilitate submarine rescue operations even at distant locations, the DSRV can be mobilised by air or road.
The Indian Navy has inducted two such systems which will provide rescue cover to submarines on the east and west coast of India. At present, there are about 40 nations that operate submarines, of which only a few have submarine rescue capability in any form.
The third generation submarine rescue capability of Indian Navy can be sought by the other navies for assistance during contingencies in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
Indian Navy: The Indian Navy is the naval branch of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Navy. The Chief of Naval Staff, a four-star admiral, commands the navy. It was founded in 5 September 1612. The current Chief of Navy Staff (CNS) is Karambir singh. The main objective of the Indian Navy is to protect the country’s maritime borders and help in the expansion of its forces.
There are 3 commands under the Navy which are:
1. The Western Naval Command (Headquarters at Mumbai).
2. The Eastern Naval Command (Headquarters at Visakhapatnam)
3. The Southern Naval Command (Headquarters at Kochi)
Environment
World oceans day: World Oceans Day is an international day which is celebrated annually on 8 June. The concept was originally proposed in 1992 by Canada's International Centre for Ocean Development and the Ocean Institute of Canada at the Earth Summit – UN Conference on Environment and Development in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. In 2008, the United Nations General Assembly decided that, as of 2009, 8 June would be designated by the United Nations as “World Oceans Day”.
Recently, World oceans day 2020 was celebrated on 8 June across the world. The theme this year is "Innovation for a Sustainable Ocean." World Ocean Day is a reminder to the people about the importance of the role played by oceans in the lives of human beings. The oceans are facing unprecedented pressures from factors ranging from pollution to climate change which are projected to rise more in the future. The need to balance the preservation of a healthy ocean and ever-increasing economic activities requires a fresh approach and rethinking in many areas.
This year's celebrations were held online due to coronavirus COVID-19 pandemic.
Ocean: An ocean is a body of water that composes much of a planet's hydrosphere. On Earth, an ocean is one of the major conventional divisions of the World Ocean. These are, in descending order by area, the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans. Oceans are areas of continuous body of salt water that covers more than 70 percent of the Earth's surface. The scientists and geographers divide it into five different sections. From biggest to smallest, they are the Pacific, the Atlantic, the Indian, the Antarctic (sometimes called the Southern), and the Arctic Oceans.
Importance of Oceans: As the world ocean is the principal component of Earth's hydrosphere, it is integral to life. It forms part of the carbon cycle where a vast amount of greenhouse gas that is carbon dioxide (CO2) is absorbed by ocean water and help human in tackling the problem of global warming and climate change.
Oceans play a key role in regulating the weather and climate. Ocean controls temperature and weather by absorbing over half the heat reaching the Earth from the sun.
Water evaporating from the oceans which falls in land as rain is used as drinking water and for growing crops.
A variety of life-saving medicinal compounds, including anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer drugs have also been discovered in the oceans.
The oceans not only provide us with abundant opportunities for recreation and inspiration but the ocean is vital to the world’s economy, with more than 90% of trade using sea routes and as a source of jobs for millions of people.
The ocean is also the stage for a growing range of new ocean-related economic activities and constant innovations.
The ocean is home to the greatest abundance of life on our planet. It is a home to millions and millions of marine species that are discovered nd ye to be discovered. The origin of Earth's oceans is unknown.
Threats to Oceans: The major threats to oceans include pollution, overfishing, invasive species, and rising ocean acidity due to the extensive use of fossil fuels. Above all global warming is causing sea levels to rise, threatening coastal population centers. Many pesticides and nutrients used in agriculture and even plastic waste end up in the coastal waters, resulting in oxygen depletion that kills marine plants and shellfish. Factories and industrial plants discharge sewage, oil spills into the oceans are endangering marine habitats around the world.
EESL: It refers to Energy Efficiency Services Limited. EESl is an energy service company which works under the administration of the Ministry of Power, Government of India (GoI). It is the world's largest public ESCO. It is 100% government owned a joint venture of state-owned NTPC Limited, Power Finance Corporation, Rural Electrification Corporation and POWERGRID. It works towards mainstreaming energy efficiency and is implementing the world’s largest energy efficiency portfolio in the country. It main objective of EESL is to create market access for efficient and future-ready transformative solutions that create a win-win situation for every stakeholder. It also helps in implementing programmes such as UnnatJyoti by Affordable LED for All (UJALA), Smart Meters, etc. It is headquartered in New Delhi. The current Chairman of EESL is Rajeev Sharma.
Recently, on the occasion of World Environment Day, EESL in partnership with the U.S. Agency for International Development’s (USAID) MAITREE programme, launched the “Healthy and Energy Efficient Buildings” initiative.
The reason behind this initiative is that poor air quality has been a concern in India for quite some time and has become more important in light of the COVID 19 pandemic. Most of the buildings in India are not equipped to establish and maintain healthy indoor air quality and there is a need to upgrade them. The initiative aims to pave ways to make workplaces healthier and greener.
Under this initiative the challenges of retrofitting existing buildings and air conditioning systems will be addressed so that they are both healthy and energy efficient.
MAITREE: It refers to the Market Integration and Transformation Program for Energy Efficiency. MAITREE is a part of the US-India bilateral Partnership between the Ministry of Power and USAID. It is aimed at accelerating the adoption of cost-effective energy efficiency as a standard practice within buildings, and specifically focuses on cooling.
USAID: It refers to the US Agency for International Development. USAID is an independent agency of the United States federal government. It is primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and development assistance. It was founded on 3rd November 1961. It is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States. The current Administrator of USAID is Mark Green.
CSE: It is an acronym for The Centre for Science and Environment. CSI is a not-for-profit public interest research and advocacy organisation. It is headquartered in New Delhi, India. It was founded in 1980 by Anil Agarwal. It works as a think tank on environment-development issues in India, poor planning, climate shifts devastating India's Sundarbans. It advocates for policy changes and better implementation of the already existing policies. CSE researches into, lobbies for and communicates the urgency of development that is both sustainable and equitable. The CSE also publishes the environment magazine called Down to Earth.
Recently, the State of India’s Environment (SoE), 2020 report was released by CSE. According to the report:
19 major extreme weather events claimed thousands of lives last year.
More than 50 lakh internal displacements have occurred in India in 2019 which is supposed to be the highest in the world. The major factors being the floods, cyclones like Fani, Vayu and Bulbul and droughts.
The report also broke down 2011 census data on migrant populations. There were more than 45 crore migrants in the country at the time, with the vast majority migrating within their own State. In 2011, over 1.7 crore new migrants had moved for employment purposes, mostly from rural to urban areas.
The report observed that India’s ranking in terms of Sustainable Development Goals has slipped to 114 in 2019 as compared to 115 in 2018.
Indian Policy
Agriculture Ministry: The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare is a branch of the Government of India (GoI). It is the apex body for formulation and administration of the rules and regulations and laws related to agriculture in India. The three broad areas of scope for the Ministry are agriculture, food processing and co-operation. It was formed in 1947 and is headquartered in New Delhi. Currently the agriculture ministry is headed by Minister of Agriculture Narendra Singh Tomar and the Minister of State in the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare is Parshottam Rupala.
Recently, the Union Minister for Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare, Narendra Singh Tomar launched Sahakar Mitra which is a Scheme on Internship Programme (SIP). It is an initiative by National Cooperative Development Cooperation (NCDC).
The initiative was launched with an objective to help cooperative institutions access innovative ideas of young professionals while the interns will gain experience of working in the field to be self-reliant. Sahakar Mitra would also provide an opportunity for professionals from academic institutions to develop leadership and entrepreneurial roles through cooperatives as Farmers Producers Organizations (FPO).
Professional graduates in disciplines such as Agriculture and allied areas, IT etc. and also Professionals who are pursuing or have completed their MBA degrees in Agri-business, International Trade, Cooperation, Finance, Forestry, Rural Development, Project Management etc. are eligible for the internship.
NCDC: It refers to the National Cooperative Development Cooperation. NCDC is a statutory Corporation set up under an Act of Indian Parliament on 13 March 1963. The main objectives of NCDC are planning and promoting programmes for production, processing, marketing, storage, export and import of agricultural produce, foodstuffs, industrial goods, livestock and certain other notified commodities and services on cooperative principles and for matters concerned therewith or incidental thereto. The Minister currently responsible for NCDC is the Minister of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare Narendra Singh Tomar.
IFLOWS-Mumbai: IFLOWS-Mumbai which is a state of art Integrated Flood Warning system was recently inaugurated by the Chief Minister of Maharashtra Uddhav Thackeray and Union Minister for Health and Family Welfare, Science and Technology, Dr Harsh Vardhan in Mumbai. Mumbai is only the second city in the country after Chennai to get this system. Similar systems are being developed for Bengaluru and Kolkata.
The system is expected to enhance Mumbai’s resilience by providing early warning for flooding specially during high rainfall events and cyclones. It has provisions to capture the urban drainage within the city and predict the areas of flooding, which will be incorporated in the final system.
About IFLOWS-Mumbai: It is a state of art Integrated Flood Warning system for Mumbai. It is a monitoring and flood warning system that will be able to relay alerts of possible flood-prone areas anywhere between six to 72 hours in advance. The system can provide all information regarding possible flood-prone areas, likely height the floodwater could attain, location-wise problem areas across all 24 wards and calculate the vulnerability and risk of elements exposed to flood.
The system incorporates weather models from the National Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasting (NCMRWF), India Meteorological Department (IMD), field data from the rain gauge network of 165 stations set up by Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), BMC and IMD. It comprises of various modules namely Data Assimilation, Flood, Inundation, Vulnerability, Risk, Dissemination and Decision Support System.
This system is a joint initiative between the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) and Brihanmumbai Municipal Corporation (BMC).
DST: It refers to the Department of Science & Technology. DST is a department within the Ministry of Science and Technology in India. It was founded in May 1971. It's responsibility is to promote new areas of science and technology and to play the role of a nodal department for organising, coordinating and promoting Scientific and Technological activities in the country. It gives funds to various approved scientific projects in India. It also supports various researchers in India to attend conferences abroad and to go for experimental works. Minister of State Dr. Harsh Vardhan is the current head of the department, while Ashutosh Sharma is its present secretary.
Recently, the Department of Science & Technology (DST) has constituted a joint Science Communication Forum. It has been constituted to facilitate interaction, cooperation, and coordination amongst various public sector science communication institutions and agencies.
The Forum would be served by a Secretariat at the National Council for Science & Technology Communication (NCSTC), Department of Science & Technology. It will be represented by senior officials from various central ministries including Science & Technology, Agriculture, Health, Culture, Defense, Space, Atomic Energy and Information & Broadcasting.
The forum will integrate the science communication efforts spread across various institutions and It can also help adoption of a common policy and best practices at a wider scale, ultimately aiming towards a national science communication framework.
The Forum too would be responsible to work upon strategies for effective planning and implementation of science communication programmes at macro and micro level in the country Hence, it will spread scientific awareness and result into an innovation-driven society.
Ministry of Women and Child Development: The Ministry of Women and Child Development is a branch of the Government of India (GoI). It is an apex body for formulation and administration of the rules and regulations and laws relating to women and child development in India, a branch of the Government of India, is an apex body for formulation and administration of the rules and regulations and laws relating to women and child development in India. It was founded on 30 January 2006. The current minister for the Ministry of Women and Child Development is Smriti Irani and the Minister of State is Sushri Debasree Chaudhuri.
Recently, the Central Government of India has formulated a task force to examine matters pertaining to age of motherhood, imperatives of lowering Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR), improvement of nutritional levels and related issues. The task force has been set up by the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
The task force will be headed by Ms. Jaya Jaitly. It will be responsible for reviewing the correlation of age of marriage and motherhood along with health, medical well being, and nutritional status of mother and child, during pregnancy & birth. It will also examine the key parameters like Infant Mortality Rate (IMR), Maternal Mortality Rate (MMR), Total Fertility Rate (TFR), Sex Ratio at Birth (SRB), Child Sex Ratio (CSR) etc., any other relevant points pertaining to health and nutrition in this context.
It will not only suggest measures to promote higher education among women but also suggest suitable legislative instruments and amendments in existing laws to support the recommendations of the Task Force. It will chalk out a detailed roll-out plan with timelines to implement these recommendations too.
Indian polity
Ministry of Personnel & Public Grievances: The Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions is a ministry of the Government of India (GoI) in personnel matters specially issues concerning recruitment, training, career development, staff welfare as well as the post-retirement dispensation. The Ministry is also concerned with the process of responsive people-oriented modern administration. Allocation of Business Rules defines the work allotted for the Ministry. It was formed on 1 August 1970. The Ministry comprises of the following three Departments.
1. Department of Personnel and Training
2. Department of Pension and Pensioners' Welfare
3. Department of Administrative Reforms & Public Grievances
Narendra Modi, the Prime Minister of India is the current Minister of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions and Deputy Minister responsible is Jitendra Singh, Minister of State for Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
Recently, the Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) Development of North Eastern Region (DoNER), MoS PMO, Personnel, Public Grievances, Pensions, Atomic Energy and Space, Dr Jitendra Singh today inaugurated the 18th Bench of Central Administrative Tribunal (CAT) for the Union Territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh. It was inaugurated through a video conference due to the ongoing pandemic.
The CAT Bench of Jammu is set up exclusively to deal with service matters of government employees which would reduce the burden of various Courts. Earlier, in a notification issued under section 5(7) of the Administrative Tribunals Act, 1985, the Central Government has specified Jammu and Srinagar as the places at which the benches of the CAT shall ordinarily sit for the UT of Jammu and Kashmir and UT of Ladakh.
CAT: It refers to the Central Administrative Tribunal. CAT is a Statutory Body established on 1 November 1985 under The Administrative Tribunals Act, 1985 and is directly under the Supervision of the Department of Personnel and Training. It was established under Article 323A of the Constitution (inserted by the 42nd Constitutional Amendment, 1976).
In pursuance of Article 323-A, the Parliament has passed the Administrative Tribunals of the Administrative Tribunals Act, 1985. This act aimed in providing speedy and inexpensive justice to the aggrieved public servants. The act authorizes the Central government to establish one Central Administrative Tribunal and the state administrative tribunals.
It was established to adjudicate disputes and complaints with respect to recruitment and conditions of service of persons appointed to public services and posts in connection with the affairs of the Union or other authorities under the control of the Government.
The tribunal will adjudicate complaints regarding conditions of service of public servants and also recruitment of posts associated with the affairs of the UTs.
Under Section 17 of the Administrative Tribunal Act, 1985, the Tribunal has been conferred with the power to exercise the same jurisdiction and authority in respect of contempt of itself as a High Court.
The Tribunal is guided by the principles of natural justice in deciding cases and is not bound by the procedure, prescribed by the Civil Procedure Code.
Salaries and Allowances and Conditions of Service of the officers and other employees of the Tribunal are specified by the Central Government.
The CAT is a specialist body consisting of Administrative Members and Judicial Members. The CAT comprises of a chairman, vice- chairman and other members who are appointed by the President.
There are 17 Benches and 21 Circuit Benches in the Central Administrative Tribunal all over India.
Uttarakhand Government: The Government of Uttarakhand also known as the State Government of Uttarakhand is the supreme governing authority of the Indian state of Uttarakhand and its 13 Districts. The Chief Minister is the head of government and is vested with most of the executive powers. The current Chief Minister and Governor of Uttarakhand are Trivendra Singh Rawat and Baby Rani Maurya respectively.
Recently, Gairsain in Chamoli district has been formally declared as the summer capital of Uttarakhand. A notification was issued after State Governor Baby Rani Maurya gave her assent to the move.
Earlier in March 2020, during the budget session of Uttarakhand, Chief Minister Trivendra Singh Rawat had announced making Gairsain the summer capital. He dedicated the summer capital status to Gairsain to thousands of men and women of Uttarakhand who fought for its statehood.
Gairsain: It is a town and Nagar Panchayat in Chamoli district, Uttarakhand and is situated at the eastern edge of the Dudhatoli mountain range. Chief Minister Trivendra Singh Rawat dedicated the summer capital status to Gairsain to thousands of men and women of Uttarakhand who fought for its statehood. Statehood activists had long contended that Gairsain, a tehsil in Chamoli district, was best suited to be the capital of the mountainous state as it was a hilly region falling on the border of Kumaon and Garhwal regions. However, after the formation of the state, Dehradun was made the temporary capital of the state. The state Assembly is located in Dehradun, but sessions are held in Gairsain as well.
Uttarakhand was formed on 9th November 2000 as the 27th State of India, when it was carved out of northern Uttar Pradesh.
International
WFSD: It refers to the World Food Safety Day. WFSD is celebrated every year on June 7 to draw global attention to the health consequences of contaminated food and water. The United Nations General Assembly declared June 7 as the World Food Safety Day in 2018. WFSD was first celebrated in 2019 to strengthen commitment to scale up food safety made by the Addis Ababa Conference and the Geneva Forum in 2019 under the umbrella of “The Future of Food Safety”. World Health Organization (WHO) in collaboration with the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) pursues its efforts to mainstream food safety in the public agenda and reduce the burden of foodborne diseases globally.
WFSD 2020 was celebrated on 7 June 2020 under the theme “Food safety, everyone’s business”. According to WHO, under this year's theme 'Food safety, everyone's business', the action-oriented campaign aims to promote global food safety awareness and call upon countries and decision-makers, the private sector, civil society, UN organizations and the general public to take action. As food safety is a shared responsibility in which everybody has a role to play so it is the duty of all to ensure that the food which is consumed is safe and will not cause damages to our health. Food safety is the key to achieving several of the Sustainable Development Goals and WFSD brings it into the spotlight, to help prevent, detect and manage foodborne risks. Safe food contributes to economic prosperity, boosting agriculture, market access, tourism and sustainable development.
IPAC: It refers to the Inter-Parliamentary Alliance. IPAC is an international cross-party group of legislators working towards reforms to help counter the threat China’s growing influence poses to global trade, security and human rights.
Recently, a group of senior lawmakers from 8 democracies including the US have launched the Inter-Parliamentary Alliance (IPAC) on China to counter China. IPAC was launched on 5 June 2020 to help counter what the threat posed by China’s growing influence to global trade, security and human rights.
The main aim of the IPAC is to construct appropriate and coordinated responses, and to help craft a proactive and strategic approach on issues related to China. The 8 participating Nations of IPAC are US, Germany, UK, Japan, Australia, Canada, Sweden, Norway as well as members of the European parliament.
India-Denmark: India and Denmark have recently signed an Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with an aim to develop a strong, deep and long-term co-operation between two nations in the power sector. The Indian electricity market would benefit from cooperation with Denmark in all the aspects of power.
The memorandum was signed between Denmark’s Ministry of Energy, Utilities and Climate, and India’s Power Ministry. The MOU was signed by the Secretary (Power), Sanjiv Nandan Sahai and Ambassador of Denmark to India, Freddy Svane.
Under the MoU, both the countries have agreed to collaborate in areas such as long- term energy planning, forecasting, offshore wind, flexibility in the grid, consolidation of grid codes to integrate and operate efficiently variable generation options, incentivize power plant flexibility, flexibility in the power purchase agreements and variability in renewable energy production.
As per the MOU, to implement the agreement of the identified areas, a Joint Working Group (JWG) will be established and co-chaired by joint Secretary-level officials who will report to a Steering Committee jointly chaired by the Secretary level officers from both the sides.
The approval for this Cooperation agreement between the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy of India and Ministry for Energy, Utilities and Climate of the Kingdom of Denmark on the strategic sector of power were approved by the Union Cabinet chaired by the PM Modi in June last year. A Letter of Intent to establish an Indo-Danish Centre of Excellence for Renewable Energy in India was also signed in this respect.
Denmark: Denmark officially the Kingdom of Denmark, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is a Scandinavian country comprising the Jutland Peninsula and around 406 islands. It is bordered to the west by the North Sea, and its islands are located on the sea lane from the Baltic to the main oceans of the world, as well as the trade route from the Nordic countries to Central Europe. It is an independent country since the late 10th century and is also one of the oldest states of Europe. The capital of Denmark is Copenhagen. The currency used here is Danish Krone. The current prime minister of Denmark is Mette Frederiksen.
ASEAN: It refers to the Association of Southeast Asian Nations. ASEAN is a regional intergovernmental organisation and it comprises of 10 countries in Southeast Asia. It was created on 8 August 1967 by 5 countries namely Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia, Philippines and Thailand. The ASEAN Secretariat is located at Jakarta, Indonesia. It was created with an aim to promote intergovernmental cooperation. The organisation also facilitates political, economic, military, educational, security, and socio-cultural integration among its members as well as in other countries in Asia. ASEAN has been India’s utmost priority under its Act East Policy. The 10 member countries are Indonesia, Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia, Philippines, Vietnam, Brunei, Cambodia, Myanmar (Burma), Laos
Recently, the third India-ASEAN Youth Dialogue as held between June 8, 2020 and June 10, 2020. The dialogue took place in virtual mode. The dialogue primarily revolved around the fight against the ongoing Coronavirus Pandemic.
During the dialogue, India and ASEAN pledged to enhance cooperation in ways to effectively and constructively in skill development, youthful energy, and education. These areas were identified as a strategic partnership between the two countries. The leaders also acknowledged the re-establishment and revival of Nalanda University in Bihar. Nalanda University has been offering several scholarship programs for ASEAN students.
National
WCL: It refers to the Western Coalfields Ltd. WCL is one of the 8 Subsidiary Companies of Coal India Limited (CIL) which is under administrative control of Ministry of Coal. The Company incorporated under the Companies Act, 1956 has its registered office at Coal Estate, Civil Lines, Nagpur–440001. WCL has been conferred "Miniratna" status on 15 March 2008. The Company has contributed about 7.02% of the national coal production during 2015-16. Mr. Rajiv Ranjan Mishra is the present Chairman-cum-Managing Director of Western Coalfields.
Recently, the Coal India Subsidiary WCL opened 3 new coal mines in Madhya Pradesh and Maharashtra having combined annual production capacity of 2.9 million tonnes (MT). The three mines are Sharda underground Mine in Kanhan Area and Dhankasa underground mine in Pench Area of Madhya Pradesh and Adasa Mine, an underground to open cast mine, in Nagpur Area of Maharashtra and.
WLC has launched a surveillance System named ‘WCL EYE’. This surveillance System will monitor operations of fifteen major mines of the company round the clock. It will also help monitor coal stocks. An App named SAMVAAD to connect with its employees and stakeholders on this occasion has also been launched by the company.
IR: It refers to the Indian Railways. IR is India's national railway system operated by the Ministry of Railways. It is among the world's largest rail networks. It was founded on 8 May 1845. The first railway on Indian sub-continent ran over a stretch of 21 miles from Bombay to Thane. The idea of a railway to connect Bombay with Thane, Kalyan and with the Thal and Bhore Ghats inclines first occurred to Mr. George Clark, the Chief Engineer of the Bombay Government, during a visit to Bhandup in 1843. The current Minister of Railways is Piyush Goyal.
Recently, the Indian Railways (IR) created history by successfully running first Double-Stack Container Train in OHE electrified territory on Western Railway. With this remarkable development, IR has become the first to run Double-Stack Container train with high reach pantograph in high rise Over Head Equipment territory, which has contact wire height of 7.57 metre. The Operations successfully commenced on 10th June from Palanpur and Botad stations in Gujarat.
This achievement will boost India's latest ambitious mission of Green India. This initiative is expected to bring innovation, speed and customization in freight operations.
MHA: It is an acronym for Ministry of Home Affairs. MHA is the head of the Ministry of Home Affairs of the Government of India (GoI). It is one of the senior-most officers in the Union Cabinet. The chief responsibility of the Home Minister is the maintenance of India's internal security. The country's large police force comes under its jurisdiction. It is also mainly responsible for the maintenance of internal security and domestic policy. The Home Ministry is currently headed by Union Minister of Home Affairs Amit Shah.
Recently, MHA reconstituted a new committee for the welfare of the freedom fighters with the Minister of State for Home Affairs G Kishan Reddy as the chairman and nine “eminent freedom fighters” from across the country as its members. Along with Reddy, former Congress MLA from Gujarat, Dinakar Bhai Desai, who took part in 1942 Quit India Movement is one among the 9 member panel.
The task of this new committee is to look into the welfare and grievances of freedom fighters and their families.
The ministry has a separate division to serve freedom fighters who are alive and their families. It disburses pension to about 30,000 freedom fighters and their families.
People In News
Javed Akhtar: Javed Akhtar (born 17 January 1945) is an Indian political activist, poet, lyricist and screenwriter, originally from Gwalior area. He is a recipient of the Padma Shri (1999), Padma Bhushan (2007), the Sahitya Akademi Award as well as five National Film Awards.
Recently, the leading figure in Indian cinema Javed Akhter has won the prestigious Richard Dawkins Award. He was honoured with the award for his “critical thinking, holding religious dogma up to scrutiny, advancing human progress and humanist values”. He is the only Indian to have won this award.
Javed Akhtar has lent his support to various social causes. He has also never shied away from expressing his views on issues like CAA, Islamophobia among more.
Richard Dawkins Award: The Richard Dawkins Award is named after an English evolutionary biologist who was named the world's top thinker in a 2013 reader's poll of the Prospect Magazine. It is an annual award that is bestowed upon individuals who “publicly proclaim the values of secularism, rationalism, upholding scientific truth”, since 2003. Previous famous awardees include Ricky Gervais, Stephen Fry and Bill Maher.
RAJEEV TOPNO: He is a 1996 batch IAS from Gujarat cadre. He has been recently appointed as Senior Advisor to the Executive Director of the World Bank in Washington DC. He has been appointed for a period of three years. Topno has been the Prime Minister’s private secretary since 2014.
World Bank: The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of poorer countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. It comprises two institutions which are the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, and the International Development Association. It is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States. It was founded on July 1944 by John Maynard Keynes and Harry Dexter White. Its main aim is providing financing, advice, and research to developing nations to aid their economic advancement. The bank predominantly acts as an organization that attempts to fight poverty by offering developmental assistance to middle- and low-income countries. The current President of World Bank is David Malpass.
Brajendra Navnit: He a 1999 batch Tamil Nadu cadre IAS officer, another officer who served in the Prime Minister's Office (PMO) as Joint Secretary, has been sent to the World Trade Organisation (WTO) as Ambassador and Permanent Representative of India (PRI). He has been appointed for a period of three years. He will be based in Geneva.
The Appointments Committee of the Cabinet, which approved Navnit’s foreign post, also gave a nod to the appointment of Anwar Hussain Shaik for the post of Counselor, at the PMI to WTO, Geneva. He is a 2000 batch IRTS officer.
WTO: It is an acronym of World Trade Organization. WTO is largest international economic organization that is concerned with the regulation of international trade between nations. It is the only global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations. It was founded 1 January 1995 under the Marrakesh Agreement, signed by 123 nations on 15 April 1994, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), which commenced in 1948. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. The WTO has over 160 members representing 98 per cent of world trade. Over 20 countries are seeking to join the WTO.
Monika Kapil Mohta: Monika Kapil Mohta an IFS officer of 1985 batch, has been, recently, appointed as the next Ambassador of India to Switzerland. She is currently serving as the Ambassador of India to Sweden. She will replace Sibi George as the next Ambassador of India to Switzerland. Sibi George has been appointed as the next Ambassador of India to the State of Kuwait.
Switzerland: Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a country situated in the confluence of Western, Central, and Southern Europe. It is a landlocked country bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. It is geographically divided among the Swiss Plateau, the Alps, and the Jura. It's official language is German, Romansh, French, Italian. The Capital of Switzerland is Bern City. The currency used here is Swiss franc. Simonetta Sommaruga is the current President of the Swiss Confederation.
Rahul Shrivastava: Rahul Shrivastava an IFS officer of 1999 batch, has been recently, appointed as the next Ambassador of India to Romania. He is currently serving as Joint Secretary in the Ministry of External Affairs. He will replace Thanglura Darlong as the next Ambassador of India to Romania.
Romania: Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders with Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, and Moldova to the east and has its opening to the Black Sea. It has a predominantly temperate-continental climate. The Capital of Romania is Bucharest. The current President and Prime Minister of Romania are Klaus Iohannis and Ludovic Orban respectively.
Javed Iqbal Wani: He is a senior Kashmiri lawyer who also served as additional advocate general of Jammu and Kashmir High Court for nearly 11 months in 2019. He has been recently appointed by President Ram Nath Kovind as a Judge of the Jammu and Kashmir High Court. His appointment was recommended on January 22 by the Supreme Court Collegium headed by Chief Justice of India S A Bobde. With his appointment, the strength of the HC will increase to 13 against the total strength of 17. This is for the first time, after a gap of seven years, that a Kashmiri lawyer has been elevated as judge of the High Court from Bar quota. The last such appointment was made in 2013 when Justice Ali Muhammad Magrey was appointed as judge of the High Court.
Places In News
Faridkot: Faridkot district is one of the 22 districts in the state of Punjab, India. It is a royal and historic city in the state of Punjab, India. It is the headquarters of the Faridkot district. The city is named in the honor of Baba Farid, a revered 13th century Sufi saint whose shrine is located in Pakpattan, Pakistan. The town of Faridkot was founded during this century as Mokalhar by Raja Mokalsi, the grandson of Rai Munj, a Bhatti Chief of Bhatnair, Rajasthan. Prior to independence, a large part of the Faridkot district was under the rule of the Maharaja of Faridkot and later it became a part of the Patiala & East Punjab States Union (PEPSU) in 1948.
Recently, the Punjab and Haryana High Court passed a judgment in a three-decade-old case upholding the property rights of women in the family of Harinder Singh Brar, the last Maharaja of Faridkot, who died in 1989. The Punjab and Haryana High Court not only upheld the rights of the daughters but also gave Brar’s mother, who was alive when her son died, her share in the property. Amrit Kaur had laid claim to the whole property on the basis of Section 4(3) of the 1948 Act, which states that in absence of the male descendant or his legitimate descendants, the property would go to the nearest agnate (descendant from a male ancestor). The HC held that the 1948 Act was not an existing enactment at the time the Constitution came in force, and the matter would not be covered under Section 5 (ii) of The Hindu Succession Act, 1956, which says the Act will not apply to any estate which descends to a single heir by the terms of any agreement entered into by the Ruler of any Indian State with the Government of India or by terms of any law passed before commencement of the 1956 law.
When the Faridkot state surrendered sovereignty and joined the Patiala and East Punjab States Union in 1948, the Maharaja was allowed to retain certain personal properties, spread over Faridkot, Chandigarh, Shimla and Delhi. When he died, his daughters had no inheritance rights as was the norm under the feudal system.
Himachal Pradesh: Himachal Pradesh is a northern Indian state in the Himalayas. It is situated in the Western Himalayas. It is one of the eleven mountain states of India. Its summer capital is Shimla and winter capital is Dharamshala. The current Governor and Chief Minister of Himachal Pradesh are Bandaru Dattatreya and Jai Ram Thakur respectively.
Recently, the Chief Minister of Himachal Pradesh Jai Ram Thakur launched “Panchvati Yojana” for the senior citizens of rural areas of the state. Under this initiative, the state government of Himachal Pradesh will set up parks and gardens in every development block with all the necessary amenities. State government aims to develop 100 such parks in the state in the current financial year.
The main objective of Panchvati Yojana is not only to provide an opportunity for elderly people to spend their leisure time while strolling in these parks and gardens but also to improve the life expectancy of the elder people by keeping in view their health requirements. This will be executed under the MNREGA scheme of rural development.
Tamil Nadu: It is located in the extreme south of the subcontinent. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the east and south and by the states of Kerala to the west, Karnataka (formerly Mysore) to the northwest, and Andhra Pradesh to the north. It was formerly the Madras Presidency of British India but was renamed Madras (State) after independence in 1947. Madras (State) was again renamed Tamil Nadu in 1968. Its Capital is Chennai. The Governor and Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu are Banwarilal Purohit and Edappadi K. Palaniswami respectively.
Recently, the Tamil Nadu government issued a notification for changing the English names of 1,018 places to match their exact Tamil pronunciation.
For instance Coimbatore will be called Koyampuththoor, Vellore will be written Veeloor and Madurai will be Mathurai. Places in Chennai whose names have been changed include Egmore (now Ezhumboor), Mylapore (Mayilaappoor), Saidapet (Saithaappettai) and Adyar (Adaiyaaru).
Andra Pradesh: Andhra Pradesh is situated in the south-eastern part of India. It came into existence in its present form in 1956 as a result of the demand of the Andhras for a separate state. Its Capital is Amaravati. The current Governor and the Chief Minister of Andra Pradesh is Biswabhusan Harichandan and Y. S. Jaganmohan Reddy respectively.
Recently, the Chief Minister of Andra Pradesh Y S Jagan Mohan Reddy launched country’s first online Waste Exchange Platform for industrial waste. The digital online waste exchange programme was launched on the occasion of World Environment day. During the launch of the programme, it was announced that the AP Environment Improvement Act, 2020 is to be enacted soon.
The platform is to track, audit, scrutinize the waste and encourage proper utilization of the waste. The platform will also encourage proper utilisation of waste and promote 6Rs — reduce, reuse, recycle, refurbish, redesign and re-manufacturing of waste items.
The platform is to be managed by the Andhra Pradesh Environment Management Corporation (APEMC). It will work in close coordination with the Andhra Pradesh Pollution Control Board (APPCB).
According to environment Rules and Regulations, the Andhra Pradesh Pollution Control Board is to make necessary changes in order to hand over the waste to the APEMC.
Science and Technology
Coro-bot: It is an ‘Internet-controlled’ robot developed by a 23 year old engineer Pratik Tirodkar from Thane. Coro-bot which is designed and created by him is the first of its kind that addresses the needs of the hospitals treating COVID-19 patients.
This robot can be operated from any part of the world through internet. It can deliver food, water, medicines and interact with the patients through a camera. Through a speaker, it can also advise patients on various precautions like sanitizing their hands before picking up anything from the robotic tray. It eliminates the need of physical presence or contact of nurses or ward boys with the patient.
The Coro-bot has three nozzles. The first nozzle is used to provide disinfectant bath for the robot himself, the second is used to spray sanitizers on both sides of the path and the third is used to disinfect the ground with UV light as the robot moves. It also has dispensers for water, tea and coffee.
The robot becomes the first in world to be operated using Internet of Things (IoT) technology in medical field.
Pratik Tirodkar: He is designer and creator of the first of its kind robot named Coro-bot. He is also the founder of a start up ‘PNT solutions’. He has developed other unique creations when he had barely stepped to college. This includes world’s first ‘Humanoid’ with 47 body (axis) movements, a robotic bird ornithopter for various outdoor applications, a mini packaging robot and several others.
This young genius has even given over a 100 guest lecturers to the brain students of IITs and NITs in the country.
DIAT: It refers to the Defence Institute of Advanced Technology. DIAT is the Premier Deemed University under the Department of Defence Research & Development, Ministry of Defence, Government of India (GoI). It was established in 1952. Earlier it was called the Institute of Armament Studies (1952–1967) and Institute of Armament Technology (1967–2006). Ministry of Human Resource Development, GoI has placed DIAT in Category 'A' Deemed University & accredited by National Assessment and Accreditation Council and National Board of Accreditation. The institute trains officers of Indian Ordnance Factories, Coast Guards, Indian Armed Forces (Air Force, army and Navy). The Defence Minister of India Rajnath Singh is the current Chancellor of the Institute.
Recently, DIAT, Pune developed a Nano-technology based disinfectant spray to combat COVID-19 by disinfecting all types of surfaces. It has been named “ANANYA”.
This can be used by anyone, from a common man to a healthcare worker and individual. It can also be used for large scale use. This spray can be used on masks, PPEs, hospital linens, as well as other likely contaminated surfaces such as medical instruments, door knobs, corridors elevator buttons and rooms.
The spray which has been prepared based on Nano-Technology assisted formulation will not only stop the novel coronavirus from entering human body, but it will also kill the virus when the virus comes in contact with this formulation layer on masks and PPEs.
This is a water based spray and will be effective for more than 24 hours after spray. It adheres very effectively to fabric, plastic and metallic objects and it's toxicity of the spray is negligible to humans. The shelf life of the spray is said to be more than 6 months.
Ananya has been tested by the Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy and Infrared Spectroscopy methods.
Gussies Electric Boat Awards: Gussies Electric Boat Awards were instituted in memory of Gustave Trouvé, a French electrical engineer and pioneer in electric cars and boats. Trouvé was a prolific inventor with over 75 patents. Back in 1881, he developed a 5-m-long prototype electric boat. There are 3 award categories:-
1. Electric boats up to 8m in length,
2. Electric boats more than 8 m long and
3. Electric ferry boats (passenger boats)
Recently, India’s first solar-powered ferry, Aditya has been shortlisted for the Gustave Trouvé Award as the sole entrant from Asia. It has been shortlisted for Electric ferry boats (passenger boats) category award.
Aditya: Aditya is a solar-powered ferry operating between Vaikkom and Thavanakkadavu in the Indian state of Kerala. It is not only the first solar-powered ferryand but also the largest solar-powered boat in India. The boat was inaugurated by Kerala Chief Minister Sri. Pinarayi Vijayan and Central Cabinet Minister for Power, Renewable Energy, Sri. Piyush Goyal on 12 January 2017. The vessel was designed and built by NavAlt Solar and Electric Boats in Kochi, India. It is operated by the Kerala State Water Transport Department (KSWTD).
It is powered by a motor that can source energy from solar panels, batteries, and generators so the per km energy cost of Aditya is low and it does not create air and noise pollution. It operates 22 trips a day, covering a total of 66 km, carrying 75 passengers per trip. It covers a total distance of 66 km with just ₹180 per day energy cost. Till now the ferry has transported 11 lakh passengers, covering a distance of 70,000 with a zero carbon footprint.
Sports
FIFA: It is an acronym for Federation Internationale de Football Association. FIFA is a non-profit organization and the highest governing body of Football. It was founded on 21 May 1904. It is headquartered in Zurich, Switzerland. The current President of FIFA is Gianni Infantino.
Recently, the FIFA ranking was released. The rankings are based on points awarded to the teams. The points are awarded based on the results of international matches that were played by a country.
In its latest rankings, India football team has retained its 108th spot. Belgium has retained the first position while France has retained the second positions with Brazil at the third position followed by England at the 4th position.
India football team is set to host Asian champions Qatar on October 8 in its next 2022 Fifa World Cup qualifying round game, which would be India's first international fixture amid the coronavirus pandemic. India will then take on Bangladesh in an away game on November 12 and play against Afghanistan in the home condition on November 17.
Arts
Purushottam Laxman Deshpande: Purushottam Laxman Deshpande (1919 –2000), was a Marathi writer and humorist. He was popularly known by his initials ("Pu. La.") or as P. L. Deshpande.
He was not only an accomplished film and stage actor, script writer, author but also a composer, musician (he played the harmonium), singer and orator. He was often referred to as "Maharashtra's beloved personality".
He was a recipient of Padma Bhushan (1990), Sangeet Natak Akademi Award (1967) and Sangeet Natak Akademi Fellowship (1979).
Recently, he has been marked by Google Doodle on his 101st birth anniversary.
Sarnath: Sarnath is a famous place in Varanasi and it is the destination for cultures like Hindu, Buddha and Jain. It is a small village which is a located 10 kilometres north-east of the holy city of Varanasi city near the confluence of the Ganges and the Varuna rivers in Uttar Pradesh, India.
Formerly known as Isipatana, it is famous as the site where Gautama Buddha first taught the Dharma, or where Buddha preached his first sermon. It is also the place where the original Sangha was formed.
This city is mentioned by the Buddha as one of the four places of pilgrimage to which his devout followers should visit.
It was also the site of the Buddha's Dhammacakkappavattana Sutta, which was his first teaching after attaining enlightenment, in which he taught the four noble truths and the teachings associated with it.
Note: The birthplace of Shreyansanath, the Eleventh Tirthankara of Jainism lies in Singhpur, a village approximately 1km away from the site.
In News: Prime Minister Narendra Modi will inaugurate various development projects in Varanasi including Sarnath Light and Sound show.
Ganga Utsav 2020: It was a three-day-long Ganga Utsav-2020 which was organized from 2nd November to 4th November 2020. It was organized jointly by the National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) jointly with the Ministry of Jal Shakti. This annual event was organized virtually due to the ongoing pandemic.
The 2020 edition marks the 12th anniversary of Ganga being accorded the status of National River.
Ganga Utsav is a cultural and educational festival to celebrate the glory of holy river Ganga. On 4th November 2008, Ganga was declared “National River”. Since 2016, every year the NMCG has been celebrating Ganga Utsav on November 4.
The event is organized every year with an aim to spread awareness about river Ganga and the need to keep the river clean and rejuvenated.
Ganges: The Ganges or the Ganga is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The Ganges is the national and the longest river of India. The river originates in Gangotri Glacier as River Bhagirathi. Later it joins the Alaknanda at Devprayag.
Ganga is considered a central part of Indian tradition, life and culture. She is a lifeline to millions who live along its course. It is a sacred river and worshipped as the goddess Ganga in Hinduism. The major tributaries of Ganga river are Yamuna, Kali, Son, Gandak, Ghagra,and RamGanga. The river drains in 11 states namely Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Uttarakhand, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan, Haryana, Bihar, West Bengal. The Ganges joins River Brahmaputra and flows into the Bay of Bengal as River Padma in Bangladesh. The mouth of River Ganga forms the world’s largest delta, known as Sunderbans, and was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1997.
Economics
NPCI: It refers to the National Payment Corporation of India. NPCI is an umbrella organization for all retail payments in India. It was founded in 2008. It has been incorporated as a Not for Profit Company under the provisions of Section 25 of Companies Act 1956 (now Section 8 of Companies Act 2013). It is an initiative of Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Indian Banks Association (IBA) under the provisions of the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 for creating a robust Payment & Settlement Infrastructure in India. It is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. The current MD & CEO is Dilip Asbe.
Recently, NCPI which manages Unified Payment Interface (UPI), has approved the Facebook backed messaging service WhatsApp to go live on UPI in the multi-bank model. This is to be achieved through new feature of WhatsApp called “WhatsApp Pay”.
WhatsApp, in order to achieve this, has partnered with five banks namely ICICI Bank, Axis Bank, Indian Bank, HDFC Bank, and State Bank of India. Apart from these five banks, Jio Payment Bank has also been included.
The messaging app is just a platform that will help transfer the money to other people. The payment feature is being powered by UPI. Now, anyone can send money on WhatsApp to any other user using the UPI supported application.
IREDA: It refers to the Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency Limited. IREDA was set up in 1987 and is the leading financial institution dedicated to clean energy expansion in India. It is a non-banking financial institution.
Recently, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed by IREDA with the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India (GoI). The MoU was signed for for setting key targets for the year 2020-21.
The MoU was signed by Indu Shekhar Chaturvedi, Secretary, MNRE and Pradip Kumar Das, CMD, IREDA
Under this MoU, the GoI has set a new revenue target of Rs 2,406 crore from the renewable energy industry.
IREDA, until now, has financed more than 2700 renewable energy projects in India by offering a loan of Rs 57,000 crores. It has also supported green power capacity addition of 17,259 MW in India.
MNRE: It is an acronym for the Ministry of Power & Ministry of New and Renewable Energy. MNRE is the nodal Ministry of the Government of India in New Delhi, for all matters relating to new and renewable energy. The ministry was established as the Ministry of Non-Conventional Energy Sources in 1992. It started functioning independently with effect from 2nd July, 1992. Earlier it was known as the Ministry of Energy sources. Electricity is a concurrent subject at Entry 38 in List III of the seventh Schedule of the Constitution of India. It is mainly responsible for research and development, intellectual property protection, and international cooperation, promotion, and coordination in renewable energy sources such as wind power, small hydro, biogas, and solar power. The current Minister of MNRE R. K. Singh, a Minister of State (Independent Charge).
Defence
Enhanced PINAKA Rocket: The enhanced version of Pinaka multi-barrel rocket system (MRLS) was successfully flight tested by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO). The test-flight was carried out from Integrated Test Range (ITR) in Chandipur, off the coast of Odisha.
This enhanced version of the Pinaka rocket would replace the existing Pinaka Mk-I rockets. The new variant can hit a target 45 to 60 km away while Mk-1 had a range of 40 km.
The enhanced Pinaka along with guidance Pinaka will cover the range between 60 to 90 kilometres and will be deployed by the Indian Army.
It has been indigenously developed by DRDO. The design and development has been carried out by Pune based DRDO laboratories, namely Armament Research and Development Establishment, ARDE and High Energy Materials Research Laboratory, HEMRL.
Malabar Naval Exercise: It is a four-day-long phase first of the Malabar naval exercise. The Navies of India, the US, Japan and Australia took part in the exercise which began on the 3rd of November 2020 in the Bay of Bengal.
From the Indian side, destroyer Ranvijay, frigate Shivalik, off-shore patrol vessel Sukanya, fleet support ship Shakti and submarine Sindhuraj was the part of the drill.
US Navy Ship USS John S McCain (Guided-missile destroyer) , Australian Navy Ship HMAS Ballarat (long-range frigate) and Japan Maritime Self Defence Ship (JMSDF) Ship JS Onami (destroyer) participated along with Indian Navy units.
In first phase of the exercise, navies witnessed complex and advanced naval drills like anti-submarine and anti-air warfare operations, cross deck flying, seamanship evolutions and weapon firings.
Phase-II is scheduled to be held from November 17 to 20 in the Arabian sea.
This is the first time that the member nations of the Quad or Quadrilateral Coalition is participating in the exercise together after 2007 (Quad member nations are India, the US, Japan and Australia).
The Malabar exercise started in 1992 as a bilateral drill between the Indian Navy and the US Navy in the Indian Ocean. Japan became a permanent member of the exercise in 2015.
Environment
NGP: It refers to the Namami Gange Project. The NGP is an Integrated Conservation Mission, approved as 'Flagship Programme' by the Union Government in June 2014 with budget outlay of Rs. 20,000 Crore. It's primary twin objectives is to accomplish the effective abatement of pollution, conservation and rejuvenation of National River Ganga.
The programme is being implemented by National Mission on Clean Ganga (NMGC) along with its State Programme Management Groups (SPMGs). It is being operated under the Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation, Ministry of Jal Shakti.
The main pillars of the programme are - Sewage Treatment Infrastructure & Industrial Effluent Monitoring, River-Front Development & River-Surface Cleaning, Bio-Diversity & Afforestation and Public Awareness.
Recently, Chacha Chaudhary, the iconic Indian superhero, whose brain works faster than a computer, has been selected as the brand ambassador for the centrally-sponsored NamamiGangeProgramme.
This new ‘Talking Comics’ will be conceptualized and published by Diomand Toons which launches the comic books of Chacha Chaudhary.
Chacha Chaudhary's character will spread awareness on the cultural and spiritual significance of River Ganga and deploy best available knowledge across the masses for Ganga rejuvenation.
The teaser was released during Ganga Utsav 2020.
Great Barrier Reef: The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system. The reef is is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, Australia and can be seen from outer space. It is the world's biggest single structure made by living organisms. The structure is composed of and built by billions of tiny organisms, known as coral polyps. It supports a wide diversity of life. It was selected as a World Heritage Site in 1981. It was also labeled as one of the seven natural wonders of the world by CNN. It was named as a state icon of Queensland by the Queensland National Trust.
Recently, a massive detached reef has been discovered by the Australian Scientists from the Schmidt Ocean Institute. It is the first to be discovered in 12 decades. The reef is taller than the Empire State Building (1,224 ft (373.1 m)) of the United States of America and Eiffel Tower in Paris.
It was discovered while the team was conducting underwater mapping of the Great Barrier Reef Seafloor. They were on an exploration in the Falkor vessel around Australia.
The team used an underwater robot named SuBastian to explore the reef and the footage of the exploration was live streamed.
About the Reef: The “blade like” reef is nearly 500 metres tall and 1.5 kilometres wide. It lies 40 metres below the ocean surface and about 6kilometres from the edge of Great Barrier Reef. The newly discovered reef adds to the seven other tall detached reefs in the world making the total to eight detached reefs.
Detached reefs: A "detached" reef refers to a reef bedded to the ocean floor and not part of the main body of the Great Barrier Reef.
SuBastian: It is an underwater robot that is being deployed by the team in the newly discovered reef. The robot has a remotely controlled arm to collect samples for identification.
Panna National Reserve: Panna National Park is located in Panna and Chhatarpur districts of Madhya Pradesh in India. Panna is spread over an area of 542.67 km square. In 1993, Panna National Park was declared as the 22nd Tiger reserve of India and 5th in Madhya Pradesh.
Recently, UNESCO has included Panna Biosphere region as one of its Biosphere Reserve. The Panna National Reserve was included under UNESCO's Man and Biosphere programme. The Park was included as biosphere reserve in the country by the Union Ministry of Environment and Forest on 25 August 2011.
Biosphere Reserve:Biosphere reserves are areas of terrestrial and coastal or marine ecosystems or its amalgamation. The criterion for designation of Biosphere Reserve includes focus on the following three things:
1. Conservation of cultural diversity and biodiversity.
2. Economic development that is environmentally and socio-culturally sustainable.
3. Development through research, education, monitoring and training.
The biosphere reserve network was launched in 1971 by UNESCO, two years after the initiation of MAB- Man and the biosphere program.
The government of India has established 18 biospheres in the country (categories generally relating to IUCN Category V Protected areas).
Indian Policy
Prasar Bharati: It is the public broadcaster of India. Recently, in landmark step the broadcasting agency entered into a MoU with Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-Informatics, Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
Under the Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), Fifty one DTH education TV channels will be available as DD co-branded channels to all DD FreeDish viewers.
This main aim of this move is to bring quality educational programmes to every household, including those in rural and remote areas.
The services will be available free of cost for all the viewers 24x7. It is in line with Government’s commitment towards skill development and providing quality education to the last person in the country.
Arbitration and Conciliation (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020: The President of India Ram Nath Kovind recently promulgated the Arbitration and Conciliation (Amendment) Ordinance, 2020 to further amend Arbitration and Conciliation Act 1996.
The Ordinance aims to ensure that all the stakeholders get an opportunity to seek unconditional stay of enforcement of arbitral awards where the underlying arbitration agreement or contract or making of the arbitral award are induced by fraud or corruption.
The ordinance seeks to ensure that stakeholder parties can seek an unconditional stay on enforcement of arbitral awards in cases where the “arbitration agreement or contract is induced by fraud or corruption.”
It also does away with the 8th Schedule of the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 which contained the necessary qualifications for accreditation of arbitrators.
Furthermore, through the Ordinance, a provision has been added to Section 36 whereby if the Court is satisfied that a prima facie case is made out that the arbitration agreement or contract which is the basis of the award was induced or effected by fraud or corruption, it will stay the award unconditionally pending disposal of the challenge made to the award under Section 34.
Arbitration: Arbitration, a form of alternative dispute resolution, is a way to resolve disputes outside the courts. The dispute will be decided by one or more persons, which renders the 'arbitration award'. An arbitration award is legally binding on both sides and enforceable in the courts.
Arbitration award: Arbitration award refers to the decision of an arbitrator. This award can be in the form of money that one party has to pay to the other party or it can be a non-financial award, such as adding an employment incentive or stopping a certain business.
UMI: It refers to the Urban Mobility India. The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Government of India issued the National Urban Transport Policy, 2006 (NUTP). As part of the NUTP enunciations, the Ministry has taken the initiative to organize an annual international Conference-cum-Exhibition on Urban Mobility India popularly known as UMI.
Recently, the 13th Urban Mobility India Conference 2020 organized by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) on 9th November 2020. It was held virtually on the theme " Emerging Trends in Urban Mobility." The UMI Confereance 2020 was inaugurated by Minister of State-MoS (Independent Charge-IC) Hardeep Singh Puri.
The primary objective of the conference was to disseminate information to the cities, whose officials attend the conference.
This year's theme focuses on innovative measures taken at national and international level to address the challenges posed by Covid-19 pandemic to provide accessible and convenient transport to the people.
Indian polity
ECI: It refers to Election Commission of India. The ECI is an autonomous constitutional authority responsible for administering Union and State election processes in India. The body administers elections to the Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha, State Legislative Assemblies in India, and the offices of the President and Vice President in the country. It was formed on 25 January 1950. It’s headquartered in New Delhi.It functions under the jurisdiction of Government of India.
Recently, the ECI decided to organize a three-day International Virtual Election Visitors Programme 2020 (IEVP) in the context of the ongoing Bihar Legislative Assembly Elections. The IEVP programme is meant for Foreign Election Management Bodies and Organizations.
More than 40 countries participated in the programme. The delegates included from Afghanistan, Australia, Bangladesh, Cambodia, Indonesia, Malawi, Maldives, Moldova, Mongolia, Mauritius, Nepal, Philippines, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago, Ukraine, Uzbekistan and Zambia. Along with these countries 3 international organizations such as International IDEA,
International Foundation of Electoral Systems (IFES) and Association of World Election Bodies (A-WEB) also participated in the programme.
The main objective of conducting this programme is to provide unique overview of SVEEP (Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation) programme.
The ECI not only provided a virtual tour to the polling stations in Bihar to the participating countries but also shared its knowledge and technology being implemented in conducting elections.
Earlier, the ECI had launched this prgramme during the 2014 Lok Sabha elections, elections for a few State Assemblies in February-March 2017 and Lok Sabha Elections last year. This time ECI chose Bihar as the state has one of the largest electorates in the world. There are above 72 million electorates. Therefore, the ongoing election process, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic will provide an opportunity to share the best practices and experience with the world.
SWEEP: The full form of SWEEP is Systematic Voters’ Education and Electoral Participation. SWEEP is a flagship programme of ECI that focuses on voter education and spreads awareness about voter literacy. The main objective of this programme is to build a truly participative democracy in the nation by encouraging all eligible citizens to vote and make an informed decision during the elections.
It is based on the socio-economic, cultural and demographic profile of the state as well as the history of electoral participation.
International
UNGA: It refers to the United Nations General Assembly. UNGA is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations. It is the main deliberative, policymaking and representative organ of the United Nations. Comprising all 193 Member States of the UN, it provides a unique forum for multilateral discussion of international issues including peace and security. It was formed in 1985. It is headquartered in New York, New York, United States. The current President of UNGA is Tijjani Muhammad-Bande.
Recently, the First Committee of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) adopted two resolutions sponsored by India which call for the prohibition of nuclear weapons and reduce the risks of accidental use of nuclear weapons in the world.
The two resolutions were named:
1. Convention on the Prohibition of the use of Nuclear Weapons
2. Reducing Nuclear Danger'', under the ''Nuclear Weapons'' cluster.
These resolutions manifest India's commitment towards the goal of nuclear disarmament.
Convention on the Prohibition of the use of Nuclear Weapons: The resolution was tabled by India since 1982 in the General Assembly, which requests the Conference on Disarmament in Geneva to commence negotiations on an international convention prohibiting the use or threat of use of nuclear weapons under any circumstances.
The resolution is supported by a majority of UN members. The adoption of resolutions shows India’s conviction that such a multilateral, universal and legally binding agreement would generate the necessary political will among States possessing nuclear weapons to engage in negotiations leading to the total elimination of nuclear weapons.
Reducing Nuclear Danger: The resolution was tabled since 1998. It draws global attention to the risks of unintentional or accidental use of nuclear weapons and underscores the need for a review of nuclear doctrines. It calls for concrete steps to reduce such risks, including through de-alerting and de-targeting of nuclear weapons.
UNGA First Committee: The UNGA first committee deals with the issue of disarmament and works in close cooperation with the United Nations Disarmament Commission and the Geneva-based Conference on Disarmament, the other two bodies to deal with the nuclear issue.
CD: It refers to the Conference on Disarmament. CD was formed in 1979 as the single multilateral disarmament negotiation forum of the international community. The agreement was reached among Member states during the first special session of UNGA devoted to disarmament (1978). It is the successor to the TNDC (Ten-Nation Committee on Disarmament), Geneva, 1960, the ENDC ( Eighteen-Nation Committee on Disarmament, Geneva, 1962-68 and the CCD ( Conference of the Committee on Disarmament, Geneva 1969-78.
India-GCC Troika Dialogue: India and the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council)Troika held their annual Political Dialogue. It was held recently on 3 November 2020 in virtual mode.
The Indian Delegation was led by the Foreign Affairs Minister Subrahmanyam Jaishankar while, the GCC was represented at the Troika-level by Secretary General of GCC, Minister of External Affairs, Bahrain and Minister of State for Foreign Affairs, United Arab Emirates. Representatives from Quatar, Kuwait and Saudi Arabia also participated in the dialogue.
During the dialogue:
- The leaders undertook detailed review of India-GCC ties and appreciated the upward trajectory in ties witnessed in the last few years.
- GCC expressed its gratitude for India's inclusion in the UNSC as a non-permanent member from January 2021.
- India ensured that the supply chains from India to the Gulf countries are not disrupted amid the nationwide lockdowns during the COVID-19 and India also requested the members of GCC to ease the return of Indian professionals and workers to the Gulf countries.
GCC: It refers to the Gulf Cooperation Council. GCC is an intergovernmental economic and political union. It comprises of Arab states such as Bahrain, Saudi Arabia, Oman, Kuwait, Qatar and UAE. The Charter to establish the Gulf Cooperation Council was signed on 25 May 1981. The structure of GCC consists of the Supreme Council, the Ministerial Council and the Secretariat general. The secretariat is headquartered at Riyadh.
The main objectives of the council are to formulate regulations in trade, tourism, administration and customs. It establishes scientific research centres.
Mississippi: It is a state in the Deep South region of the United States. It is bordered to the north by Tennessee, to the east by Alabama, to the south by the Gulf of Mexico, to the southwest by Louisiana, and to the northwest by Arkansas. Mississippi's western boundary is largely defined by the Mississippi River. The capital of Mississippi is Jackson.
Recently, the voters in Mississippi approved a new flag, “The New Magnolia”, featuring a magnolia flower. The new flag is designed by Rocky Vaughan and features a white magnolia on a blue banner with red and gold bars on each end. The flower is encircled in 20 five-point stars and the words “In God We Trust”. An additional star on the flag represents the indigenous Native Americans.
Mississippi is nicknamed the “Magnolia State”, a reference to the magnolia trees that grow there.
The new flag will replace the old one that has been in use for 126 years. The old flag carries the Confederate battle emblem on it. Mississippi was the last state in the US to have a flag that featured the Confederate battle emblem.
India-Nordic-Baltic Conclave: The first India-Nordic-Baltic Conclave was held virtually on 5 November 2020. India was represented by Subrahmanyam Jaishankar Minister of External Affairs (MEA).
The Tri Conclave was jointly hosted by Foreign Affairs Ministry and Confederation of Indian Industry (CII). The theme for the conclave was: ‘An Innovation-Driven Partnership for Growth in New World’.
At the conclave, dignitaries focused on clean technologies and renewable energies, AI, supply chain logistics and block chain led transformation.
In 2018, the first Summit of India and Nordic was held in Sweden during which Prime Minister Narendra Modi and all the five leaders were present.
NB8: Nordic-Baltic Eight (NB8) is a regional co-operation format that includes Estonia, Denmark, Finland, Latvia, Lithuania, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden. The Baltic States are Latvia, Lithuania and Estonia. These three countries are located in the Baltic Sea and are fast growing economies.
Nordic Council: It was established in 1952. The headquarters of the council is located in Copenhagen, Denmark. It provides a link between governments, parliaments of Nordic states. The members of Nordic council are Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Finland and Iceland. Finland joined in 1955.
National
India and Israel: The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, recently approved the signing of Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between India and Israel for cooperation in the field of health and medicine.
The areas covered under the MoU are as follows:
- Promotion of mutual research.
- Sharing of expertise against public health actions and climate risks.
- Exchange and training of medical doctors and other professionals.
- Assistance in setting up of health care facilities.
- Exchanging information related to medical devices, pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
The representatives of both India and Israel will be encouraged to participate in seminars, workshops, symposia and conferences.
Earlier, in April 2020, Israel supplied advanced medical equipment to help India fight COVID-19. India in return sent five tonnes of medicines including Hydroxychloroquine. A special team of defence experts, researchers also arrived from Israel to join hands with Indian researchers in developing rapid testing solution of CORONAVIRUS.
Under this agreement, the researchers are now developing a CORONAVIRUS testing kit that will produce results in less than 30 seconds.
Fortification of Rice Scheme: Fifteen State Governments have recently identified districts for implementing Centrally Sponsored Pilot Scheme on Fortification of Rice & its distribution through Public Distribution System.
The Government of India"s (GoI) Department of Food and Public Distribution, has been implementing the “Centrally Sponsored Pilot Scheme on Fortification of Rice and its distribution through Public Distribution System”.
The scheme is to be implemented for a period of three years between 2019-20 and 2022-23.
The Pilot Scheme has been approved for a period of three years beginning 2019-2020 with a total budget outlay of Rs.174.6 Crore.
This scheme was launched to take the country towards nutritional security. FCI has been asked to come up with a comprehensive plan for procurement and distribution of fortified rice in all the Districts of the country under Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) & Mid-Day Meal (MDM) Scheme from 2021-2022.
The distribution of fortified rice is already being implemented by 5 states namely Andhra Pradesh,Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Chhattisgarh.
Need for Fortification: According to the National Family Health Survey (NFHS-4), India has has been ranked at 94 among 107 countries in the Global Hunger Index (GHI) 2020. This is because 58.4 percent of children (6-59 months) are anaemic, 53.1 percent of women in the reproductive age group are anaemic and 35.7 percent of children under 5 are underweight. As per the experts, the deficiency of micronutrients is known as hidden hunger and is a serious health risk, these nutrients help in curbing malnutrition. The fortification initiative seeks to combat high malnutrition, promote food processing industry and also improve customer satisfaction.
Fortification of Rice: According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), fortification of rice is done by adding micronutrient powder to the rice. This powder adheres to rice grains. Fortifying rice involves grinding broken rice into powder, mixing it with nutrients, and then shaping it into rice-like kernels using an extrusion process. These fortified kernels are then mixed with normal rice in a ratio ranging from 1:50 to 1:200.
FSSAI: It is an acronym for Food Safety and Standards Authority of India. FASSAI has been established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006. The Ministry of Health & Family Welfare is the administrative Ministry for the implementation of FSSAI. Its main objective is to establish a single reference point for all matters relating to food safety and standards.
People In News
Dr Susanta Kar: He is a Senior Scientist, Molecular Parasitology and Immunology, CSIR-CDRI, Lucknow. He has been chosen by the Society of Biological Chemists, (India) for this year's Prof.A N Bhaduri Memorial Lecture Award for his contributions towards defining the survival tactics of Leishmania donovani.
About Leishmania Donovani: It is a protozoan parasite that infects macrophages and is a causative agent of visceral leishmaniasis (Kala Azar), a lethal infectious disease affecting millions worldwide.
The research team of Susanta Kar studied the interaction of Leishmania with immune cells like macrophages, dendritic cells and T cells and the fate of these interactions on modulation of various intracellular signaling cascades that ultimately affect immune response and infection progression.
SBC(I): Society of Biological Chemists (India) or SBC(I) was founded in 1930. Its headquarters is at the Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru. This prestigious society was registered under the Societies Act in the then Princely State of Mysore.
A N Bhaduri Memorial Lecture Award: The Prestigious award is conferred in every 2 years. The recipient of the award should be below 50 years of age. The Award is given for Biological Chemistry and Allied sciences, preferably related to parasitic infections.
Yashvardhan K Sinha: He is a former diplomat, who has served as high commissioner of India to the United Kingdom and Sri Lanka. He was appointed as the Information commissioner in 2019. He was recently appointed as the new Chief Information Commissioner (CIC) of India. He was administered the oath by the President Ram Nath Kovind.
The post of CIC was lying vacant since the retirement of Bimal Julka on August 26, 2020.
Apart from Sinha, three new Information Commissioners were also administered the oath of office, by the newly appointed CIC. They are:
1. Shri Heeralal Samariya who is a former IAS officer, who served as Secretary in Ministry of Labour & Employment
2. Ms. Saroj Punhani who is an IA&AS officer, who was holding the post of Deputy Comptroller & Auditor General (HR & Training)
3. Shri Uday Mahurkar who is a veteran journalist, was functioning as Senior Deputy Editor with a leading media house.
CIC: It refers to the Chief Information Commissioner. Eligibility of CIC under Section 12(6) of the Right to Information Ac, 2005 says that the CIC and the Information Commissioners shall not be a Member of Parliament. Section 12(5) of the Act states that he should a person of eminence in public life, experience in law, science and technology.
The CIC will hold office for three years. Earlier it was five years
The roles and functions of the CIC are defined by the right to Information Act, 2005. The act also defines the tenure, terms of service and salaries of the commissioner.
Central Information Commission: It was constituted in 2005. It acts upon complaints from individuals those who are not able to submit information to a Central Public Information Officer or a State Public Information Officer.
Rajiv Jalota: He is a 1988 batch Maharashtra cadre IAS officer. He is currently serving as the additional chief secretary in the higher and technical education department of the state government. He first served as sales tax commissioner and then as GST commissioner from January 2015 to January 2020.
He has recently been appointed as chairperson of Mumbai Port Trust (MbPT) by the Appointments Committee of the Cabinet on the proposal of the Shipping Ministry.
The post of Mumbai Port Trust chairman was vacant after former chairman Sanjay Bhatia retired on 31st July and was appointed as Lokayukta of Maharashtra (Established in 1971).
Places In News
DMC: It refers to the Dehradun Municipal Corporation. DMC of Uttarakhand recently launched an initiative named "Plastic Lao MASK LE JAO" to fight against the menace of plastic waste and contain the spread of Covid-19. Under this initiative, it has distributed five thousand face masks in exchange for plastic waste.
Municipal commissioner of Dehradun, Vinay Shankar Pandey by being the first to bring plastic waste from his house and get a face mask created awareness in the public against plastic waste and also the importance of masks.
Uttarakhand: It is a state in northern India crossed by the Himalayas. It is known for the natural environment of the Himalayas, the Bhabar and the Terai and also for for its Hindu pilgrimage sites. It is often referred to as the "Devabhumi" (literally "Land of the Gods"). Uttarakhand became the 27th state of the Republic of India On 9 November 2000. it was carved from the Himalayan districts of Uttar Pradesh. Its winter Capital is Dehradun and summer capital is Gairsain. The Chief Minister and the Governor of Uttarakhand are Trivendra Singh Rawat and Baby Rani Maurya respectively.
Assam: Assam is a state in northeastern India known for its wildlife, archeological sites and tea plantations. It is situated south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. The state was the first site for oil drilling in Asia. Its capital is Dispur. The current Governor and the Chief Minister of Assam are Professor Jagdish Mukhi and Sarbananda Sonowal respectively.
Recently, the Chief Minister of Assam, Sarbananda Sonowal laid the foundation stone of Indo-Israeli Centre of Excellence (CoE) for Vegetables Protected Cultivation at Khetri on the outskirts of Guwahati.
The Indo-Israeli Centre of Excellence for Vegetables Protected Cultivation will be built under the Agricultural Project of India and is estimated to be set up at an investment of Rs 10.33 Crore.
The CoE aims to provide exposure to the latest Israeli technologies to the farmers of Assam which will help them in maximizing their production and income. Furthermore the facility will boost agricultural and horticultural production in Assam leading to greater economic rewards to state’s farmers.
Kerala: It is a state on the southwestern Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganization Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile states of Travancore-Cochin and Madras. It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Lakshadweep Sea to the west. Its capital is Thiruvananthapuram. The current Governor and Chief Minister of Kerala are Arif Mohammad Khan and Pinarayi Vijayan respectively.
Recently, Kerala's Chief Minister Pinarayi Vijayan inaugurated India’s first of its kind solar energy-driven miniature train. It was inaugurated at the Veli Tourist Village.
The train, developed with an outlay of Rs 10 crore was a part of a string of projects totally worth Rs 60 crore taken up to elevate the facilities at the panoramic destination to international standards. The train will be an attraction for children especially.
The Chief Minister also dedicated an “Urban Park” and a swimming pool at the eco-friendly tourist village, located on the outskirts of the state capital where the Veli Lake meets the Arabian Sea.
Features of the Train: The miniature rail has all the features of a fully- equipped rail system. It includes a tunnel, station and a ticket office. It covers a distance of 2.5 km with three bogies that can accommodate around 45 people at a time.
The eco-friendly solar-powered 2.5 km miniature railway will enable visitors to enjoy the beauty of nature.
The surplus energy generated by the system will be routed to the Kerala State Electricity Board Limite (KSEBl) grid.
Formation Day: The Prime Minister of India Narendra Modi, President Ram Nath Kovind and Vice President M Venkaiah Naidu greeted people of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Haryana, Punjab, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Anadman and Nicobar, Lakshadweep and Puducherry on their formation day.
All the above mentioned states observe their foundation day or Statehood day respectively.
Andhra Pradesh Governor Biswa Bhusan Harichandan paid rich tributes to Sri Potti Sriramulu and paid homage to freedom fighters on the occasion of AndhraPradesh Formation Day at a programme held in Raj Bhavan. Chief Minister YS Jagan Mohan Reddy unfurled the national flag at his official residence at Tadepalli, Guntur District, He paid floral tributes at the statue of freedom fighter, Potti Sriramulu and Telugu Thalli.
Science and Technology
ISRO: It is an abbreviaion for the Indian Space Research Organizatin. ISRO is the space agency of the Government of India (GoI) and was formed in 15 august 1969. It superseded the erstwhile “Indian National Committe For Space Research” (INCOSPAR) which was established in 1962 by the efforts of Independent India's first prime minister‚ Jawaharlal Nehru‚ and his close aide and scientist Vikram Sarabhai. In 1972, the Government of India had set up a Space Commission and the Department of Space (DOS), bringing ISRO under the DOS. ISRO then embarked on its mission to provide the Nation space based services and to develop the technologies to achieve the same independently. Its vision is to “harness space technology for natural development while pursuing space science research & planetary exploration”. ISRO built India’s first Satellite Aryabhata. It is headquartered in Bangalore, India. The current Chairman of ISRO is K sivan.
Recently, ISRO successfully launched the 51st mission of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV). This is the first mission by ISRO in 2020. The carrier vehicle PSLV C49 will deliver 10 satellites in all with EOS-01 as the primary one.
The launch was carried out from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
EOS-01: It is an earth observation satellite launched by ISRO using PSLV-C49 rocket along with nine customer satellites. The satellite is intended to provide agriculture, forestry and disaster management support.
The nine customer satellites are from 1 from Lithuania, 4 from Luxembourg and 4 from USA. The customer satellites were being launched under a commercial agreement with NewSpace India Limited (NSIL), department of space.
NASA: It is an acronym for National Aeronautics and Space Administration. NASA is an independent agency of the United States Federal Government responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). It is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States. The Administrator of NASA is Jim Bridenstine and the Deputy Administrator of NASA is James Morhard.
Recently, NASA reported that on the 28th of April 2020, it observed a mix of X-ray and radio signals. This was detected by the CHIME telescope. This has never been observed earlier in the galaxy. Significantly, the flare-up it observed included the first fast radio burst (FRB) in Milky Way. Though the Fast Radio Bursts were discovered in 2007 during a pulsar survey data but it is for the first time that such phenomenon has occurred in the Milky Way Galaxy. However, the origin of Radio Bursts has not yet been located.
The detection of the phenomenon called FRB was published in the journal Nature on November 4.
Origin: The source of the FRB detected in April in the Milky Way Galaxy was from a very powerful magnetic neutron star, referred to as a magnetar, called SGR 1935+2154 or SGR 1935. It is located in the constellation Vulpecula and is estimated to be between 14,000-41,000 light-years away.
The X-ray bursts lasted for less than a second and the radio burst, on the other hand, lasted for a thousandth of a second and was thousands of times brighter than any other radio emissions from magnetars ever seen in the Milky Way.
This was the brightest of the any other radio transmissions from magnetars. The FRB-associated burst was exceptional maybe because it likely occurred at or close to the magnetar’s magnetic pole.
This flare-up, which lasted for hours, was picked up by NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space telescope and NASA’s Neutron star Interior Composition Explorer (NICER), which is an X-ray telescope mounted on the International Space Station.
Fast Radio Bursts: Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) are bright bursts of radio waves produced by astronomical objects with changing magnetic fields. The duration of these bursts last only for millisecond-scale. Due to this short duration of occurrence, it is highly difficult to detect Fast Radio Bursts and determine their position in the sky.
CHIME Telescope: The full form of CHIME is Canadian Hydrogen Intensity Mapping Experiment. CHIME is a radio telescope located at Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory (DRAO) in Kaleden, British Columbia, Canada. It is used for receiving radio waves.
Magnetar: A magnetar is a type of neutron star believed to have an extremely powerful magnetic field. According to NASA, a magnetar is a neutron star, “the crushed, city-size remains of a star many times more massive than our Sun.”
The magnetic field of such a star is very powerful, which can be over 10 trillion times stronger than a refrigerator magnet and up to a thousand times stronger than a typical neutron star’s. A magnetar's magnetic field gives rise to very strong and characteristic bursts of X-rays and gamma rays. The active life of a magnetar is short.
Sports
F1 Emilia Romagna Grand Prix 2020: Lewis Hamilton (Mercedes-Great Britain) has won the Emilia Romagna Grand Prix 2020. Formula One motor race took place on 1 November 2020 at the Autodromo Internazionale Enzo e Dino Ferrari in Imola, Italy.
This was his 9th win of the season and 93rd F1 win of his career. Mercedes won the seventh consecutive constructors’ title for 2020 breaking the record for the most consecutive World Constructors' Championships.
Valtteri Bottas finished second while Daniel Ricciardo finished third.
Alexis Vastine International: Indian boxers Amit Panghal, Sanjeet and Ashish Kumar have won gold medals at the recently concluded Alexis Valentine International Boxing Tournament held in Nantes, France.
The tournament was the first international event that Indian boxers were a part of since the lockdown.
Amit Panghal won the gold in the 52 kg-weight category, Sanjeet won in the 91 kg final bout while Ashish Kumar won the gold medal in the 75 kg weight category.
Kavinder Singh Bisht won silver in the 57 kg weight category while Shiva Thapa (63 kg), Sumit Sangwan (81 kg) and Satish Kumar (Over 91 kg) secured the bronze medals for India.
Arts
 How the Earth Got Its Beauty: Veteran writer, philanthropist and entrepreneur, Sudha Murty, has recently launched her new book titled ‘How The Earth Got Its Beauty’.
How the Earth Got Its Beauty: Veteran writer, philanthropist and entrepreneur, Sudha Murty, has recently launched her new book titled ‘How The Earth Got Its Beauty’.
Highlights:
-
The book was published by Penguin Random House imprint Puffin.
-
This book features illustrations by Priyanka Pachpande.
About Sudha Murthy:
-
Sudha Murthy is the chairperson of the Infosys Foundation, and wife of the co-founder of Infosys, N. R. Narayana Murthy.
-
She is a prolific writer in English and Kannada.
-
She has written novels, technical books, travelogues, collections of short stories and non-fictional pieces, and four books for children.
-
Her books have been translated into all the major Indian languages.
Awards:
-
Sudha Murty was the recipient of the R.K. Narayan Award for Literature and the Padma Shri in 2006.
-
In 2021, she was awarded the Attimabbe Award from the government of Karnataka for excellence in Kannada literature.
 Quit India Movement: The 78th anniversary of the Quit India Movement was observed on 8 August 2020. Also known as the August Kranti Din, the mass civil disobedience movement is considered to be one of the most significant events in the history of India's freedom struggle.
Quit India Movement: The 78th anniversary of the Quit India Movement was observed on 8 August 2020. Also known as the August Kranti Din, the mass civil disobedience movement is considered to be one of the most significant events in the history of India's freedom struggle.
Highlights:
-
To commemorate the movement, Union Minister of Culture, Tourism, and Development of North Eastern Region (DoNER) Shri G. Kishan Reddy inaugurated an exhibition to mark the 79th anniversary of the 'Quit India Movement' at National Archives of India in New Delhi today in presence of Ministers of State for Culture Shri Arjun Ram Meghwal and Smt Meenakshi Lekhi .
-
The exhibition was put up at the National Archives of India as part of 'Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav' being celebrated to commemorate 75 years of Independence.
-
This exihibiton is an endeavour to portray the significance of the Quit India Movement in the Freedom Struggle of India through public records, private papers, maps, photographs and other allied material.
-
The exhibition will remain open from 9th August onwards from 10 AM to 5:30 PM for the public till 8th November this year.
Note: AzadiKaAmritMahotsav celebrates the sentiment of oneness and freedom.
History:
-
Quit India covers the period from 1939 when the Second World War broke out.
-
On 8 Aug 1942, Mahatma Gandhi gave a clarion call to end the British rule and launched the Quit India Movement at the session of the All-India Congress Committee in Mumbai.
-
On this day in 1942, after the failure of Cripps Mission, Gandhiji gave the call to “Do or Die” in his Quit India speech delivered at the Gowalia Tank Maidan in Mumbai.
-
He launched the Quit India Movement at the session of the All-India Congress Committee in Mumbai.
-
The movement began from Gawalia Tank in Mumbai.
-
It also presents the role of the INA and Subhash Chandra Bose in India’s freedom struggle.
Kakori Train Action: The UP (Uttar Pradesh) government recently renamed a landmark freedom movement called “Kakori Train Conspiracy” as “Kakori Train Action.”
Key Highlights:
-
A programme was held on August 9, 2021 to commemorate the anniversary of the event at Kakori-based Kakori Shaheed Smarak on the outskirts of Lucknow.
-
The event witnessed the attendance of UP Chief Minister Yogi Adityanath and UP Governor Anandiben Patel.
-
On this occasion, the UP Government paid tributes to the revolutionaries who were hanged for robbing a train at Kakori in Uttar Pradesh.
-
The family members of the freedom fighters were also honoured.
Key Points:
-
Revolutionaries had robbed the train in order to buy weapons in 1925.
-
Those revolutionaries were some passionate people who were having a single goal of independence of India from British rule.
-
Their act was a glorious one and using the derogatory word 'kand' (meaning conspiracy) would only malign their image. Hence, a decision was taken to replace 'kand' with 'action'."
-
Freedom fighters Ram Prasad Bismil, Ashfaqulla Khan and Roshan Singh were hanged to death on December 19, 1927 for their involvement in Kakori robbery.
About Kakori Train Action:
-
It was a train robbery that took place on August 9, 1925 in a village called Kakori near Lucknow during Indian Independence Movement against British Raj.
-
Robbery was organized by Hindustan Republican Association (HRA).
-
It was conceived by Ram Prasad Bismil and Ashfaqullah Khan. HRA was established to carry out revolutionary activities against British Empire with the objective of achieving independence.
What was the main purpose of the robbery?
-
The HRA was established to carry out revolutionary activities against the British Empire in India to help India gain independence.
-
Revolutionaries like Bismil and his party needed money to purchase weapons for HRA. So, they decided to plunder a train on a Northern Railway line.
-
Plan for robbery was executed by Ram Prasad Bismil, Ashfaqulla Khan, Rajendra Lahiri, Keshab Chakravarty, Mukundi Lal, Banwari Lal etc.
Hindustan Socialist Republican Association (HSRA):
-
HSRA was a revolutionary organization which was founded by Ram Prasad Bismil, Sachindra Nath Sanyal, Sachindra Nath Bakshi and Jogesh Chandra Chatterjee.
-
Earlier it was known as Hindustan Republican Association (HRA).
 National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC): The National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC) is to be developed as an international tourist destination.
National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC): The National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC) is to be developed as an international tourist destination.
Key Details:
-
It will be dedicated to the legacy of maritime heritage of India, at Lothal in Gujarat.
-
It will comprise of several tourist facilities or amenities like National Maritime Heritage Museum,
-
Maritime Research Institute, Heritage Theme Park,
-
landscaping and recreational venues in order to attract tourists for each coastal states and union territories to showcase the maritime heritage of India.
-
The plans for providing digital tourism includes the following:
-
Virtual reality to offer immersive experience of maritime heritage.
-
Sound and light shows
-
Touch screen kiosks and
-
Short films on important events of Maritime history.
About NMHC:
-
The National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC)which is to be developed in Lothal region of Gujarat as an international tourist destination will showcase maritime heritage of India from ancient to modern times.
-
It seeks to create an edutainment approach for the interest of visitors.
-
Note: Edutainment means education with entertainment.
-
It will cover an area of 400 acres comprising structures like Heritage Theme Park, National Maritime Heritage Museum, Maritime Institute, Lighthouse Museum, eco-resorts etc.
-
It will also comprise pavilions where all coastal states of India and union territories can showcase artifacts and maritime heritage.
-
NMHC will recreate the ancient Lothal city, a prominent city and port of ancient Indus valley civilization.
About Lothal:
-
Lothal was one of the southernmost cities of the ancient Indus Valley Civilization.
-
It was located in the BhÄl region of the modern state of GujarÄt.
-
Construction of the city began around 2200 BCE.
-
Exploration of the Sabarmati Valley in the mid-1950s led to the discovery of Lothal and several other Harappan sites
-
The excavation started from 13 February 1955 to 19 May 1960 by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) to unearth the ancient city.
-
Lothal is a combination of two words; Loth and thal, which in Gujarati means ‘the mound of the dead.’
-
Fun Fact: Mohenjo-daro too means the mound of the dead in Sindhi.
-
The 4,500-year-old city was mathematically planned. It had a grid pattern with proper streets crossing at right angles and drainage systems.
-
The city had world’s earliest known dock, which connected the city to the ancient course of Sabarmati River.
-
The river lied on the trade route of Harappan cities in Sindh and peninsula of Saurashtra.
Economics
 Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (Amendment) Bill, 2021: The Parliament, on 9th August 2021, passed the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (Amendment) Bill, 2021 with the Lok Sabha clearing it amid din.
Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (Amendment) Bill, 2021: The Parliament, on 9th August 2021, passed the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (Amendment) Bill, 2021 with the Lok Sabha clearing it amid din.
The Bill has already been approved by the Rajya Sabha.
Key Points:
-
It seeks to amend the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation Act, 1961.
-
The Bill seeks to provide depositors time-bound access to their insured deposit amount, in case they are restricted from accessing their bank deposits.
-
It provides that the Corporation will be liable to pay the insured deposit amount to depositors on an interim basis.
-
The Bill mandates the Corporation to pay the insured amount to the depositors within 90 days of the date such liability arises.
Benefits:
-
The legislation is aimed at supporting the small depositors.
-
Depositors of Punjab and Maharashtra Cooperative Bank, Sri Guru Raghavendra Sahakara Bank and others will be benefited with this move.
-
The insurance cover limit has been raised from one lakh to five lakh.
-
The legislation was passed by the House without any discussion.
 Seekho Aur Kamao Scheme: Minister of Minority affairs Shri Mukhtar Abbas Naqvi informed Rajya Sabha about the Seekho Aur Kamao scheme.
Seekho Aur Kamao Scheme: Minister of Minority affairs Shri Mukhtar Abbas Naqvi informed Rajya Sabha about the Seekho Aur Kamao scheme.
Key Points about the Scheme:
-
Seekho Aur Kamao is a skill development scheme for youth of 14 - 35 years age group.
-
This scheme aims at providing employment and employment opportunities, improving the employability of existing workers, school dropouts etc.
-
It ensures 75% placement, out of which 50% should be in organized sector.
-
As per scheme guidelines, the implementing organizations will be required to establish linkages with placement services.
-
The candidates interested in self employment after availing the training, the organization shall arrange easy micro finance/ loans for them through financial institutions, National Minority Development Finance Corporation (NMDFC), banks etc.
-
Post placement support of Rs. 2000/- per month is provided to placed trainees for two months as placement assistance.
-
In the last 7 years appx. 3.92 lakh persons have been benefitted under this employment oriented scheme.
Background:
-
“Seekho aur Kamao (Learn & Earn)” is a scheme implemented since 2013-14 for skill development of minorities.
About Ministry of Minority Affairs:
-
It is a ministry of the Government of India (GoI).
-
It was carved out of Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
-
It was created on 29 January 2006 to ensure a more focused approach towards issues relating to the notified minority communities namely Muslim, Christian, Budhist, Sikhs, Parsis and Jain.
-
The minority religious communities in India are notified as minority communities in The Gazette of India under Section 2(c) of the National Commission for Minorities Act, 1992.
-
The mandate of the Ministry includes formulation of overall policy and planning, coordination, evaluation and review of the regulatory framework and development programmes for the benefit of the minority communities.
-
The Union Minister of Minority Affairs is Shri Mukhtar Abbas Naqvi.
 SonChiraiya: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) recently launched a brand and logo called `SonChiraiya’ to market the products of urban self-help groups (SHGs).
SonChiraiya: Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) recently launched a brand and logo called `SonChiraiya’ to market the products of urban self-help groups (SHGs).
Key Points:
-
The brand and logo was launched in line with government’s priority area of helping women to become financially empowered and live a dignified life.
-
The Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Urban Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NULM) under the aegis of MoHUA has focussed on equipping the urban poor women with adequate skills and opportunities to enable them to promote sustainable micro enterprises.
-
It mobilizes women from urban poor households into SHGs and their federations to create a support system for these women.
-
Many of these SHGs are engaged in livelihood activities, producing goods such as handicrafts, textiles, toys, eatables and so on.
-
Over 5.7 lakh SHGs have been formed across various States/ UTs with almost 60 lakh members.
-
This initiative (SonChiraiya) will certainly prove as a step towards increased visibility and global access for the products made by urban SHG women.
Significance of SonChiraiya:
-
This initiative is a significant step towards increased visibility and global access for the products made by urban SHG women.
-
Under the initiative, variety of professionally packaged and hand-crafted ethnic products will reach the doorsteps of the customers worldwide.
Steps Taken by MoHUA:
-
Many of these SHGs are engaged in livelihood activities, producing goods such as handicrafts, textiles, toys, eatables and so on.
-
These were being sold primarily in local neighbourhood markets and often faced barriers in achieving visibility and wide market access.
-
To overcome these challenges, Ministry entered into a Memorandum of Understandings (MoUs) with leading e-Commerce Portals viz. Amazon and Flipkart, with an underlying narrative of women empowerment.
-
This partnership, despite the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic, has on-boarded more than 2000 products of some 5000 SHG members from 25 states and UTs.
About MoHUA:
-
It refers to the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
-
MoHUA is a federal ministry of Government of India with executive authority over the formulation and administration of the rules and regulations and laws relating to the housing and urban development in India.
-
It was founded in 1952.
-
The current Minister responsible for MoHUA is Hardeep Singh Puri (Union Minister).
![]() Semiconductors: Mumbai-based conglomerate Tata Group, which has already forayed into manufacturing of hi-tech electronics, is now planning to get into semiconductor manufacturing.
Semiconductors: Mumbai-based conglomerate Tata Group, which has already forayed into manufacturing of hi-tech electronics, is now planning to get into semiconductor manufacturing.
Key Details:
-
The move comes at a time when the Covid-19 pandemic caused and later exacerbated a global shortage of chips and semiconductors.
-
The world, at present is experiencing a shortage of chips and semiconductors that have become essential not only for new-age technological products like smartphones and computers, but also for traditional sectors like automobiles.
-
Several carmakers in the world have delayed deliveries of their vehicles and even pushed the launch of new vehicles because of the chip shortage.
-
Tata Motors’ UK-based unit Jaguar-Land Rover has also done so.
Why is Tata Group foraying into semiconductor manufacturing?
-
For the Tata Group, while a foray into chip making would mean entering a lucrative business that can find customers not only in India but across the world, it would also be significant for captive use with Tata Motors, Tata Power, etc.
What is the reason behind the global chip shortage?
-
The chips, or semiconductors, which are the brain-centre of any electronic technology has found itself to become a rare commodity in the post-Covid era, with several large factories in places like South Korea and Taiwan being shut down.
-
This has created pent-up demand that these foundries were unable to satisfy after opening up.
-
On the one hand, the pandemic caused a surge in demand for electronic devices such as smartphones, laptop and computers, etc.
-
This shortage that began last year is expected to go on till 2022.
 NMEO-OP: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently announced a new national initiative on palm oil production to help increase farm incomes.
NMEO-OP: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently announced a new national initiative on palm oil production to help increase farm incomes.
Key Points:
-
He has announced a Rs 11,000 crore on this palm oil scheme called the National Edible Oil Mission-Oil Palm (NMEO-OP).
-
This palm oil initiative aims to make India self-sufficient in cooking oils, including palm oil.
-
One of the other key aims of the move is to harness domestic edible oil prices that are dictated by expensive palm oil imports.
-
The government will ensure that farmers get all the facilities, from quality seeds to technology under the mission.
Key features of the scheme:
-
The Centre plans to raise the domestic production of palm oil by three times to 11 lakh MT by 2025-26.
-
This will involve raising the area under oil palm cultivation to 10 lakh hectares by 2025-26 and 16.7 lakh hectares by 2029-30.
-
The special emphasis of the scheme will be in India's north-eastern states and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands due to the conducive weather conditions in the regions
-
Under the scheme, oil palm farmers will be provided financial assistance and will get remuneration under a price and viability formula.
-
The government will ensure that farmers get all the facilities, from quality seeds to technology under the mission.
Consumption of Palm oil:
-
Palm oil is currently the world’s most consumed vegetable oil.
-
Top consumers of the commodity are India, China, and the European Union (EU) with India being the largest consumer of vegetable oil in the world.
-
Palm oil is used extensively in the production of detergents, plastics, cosmetics, and biofuels.
Schemes launched to expand palm oil production:
-
India has been trying to expand its domestic production by investing in domestic oil palm.
-
Government schemes between 2011-14, like the Oil Palm Area Expansion (OPAE) and National Mission on Oilseeds and Oil Palm (NMOOP 2014), were launched to increase domestic cultivation of oil palm.
About Palm Oil:
-
Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil that comes from the fruit of oil palm trees.
-
Its scientific name is Elaeis guineensis.
-
This oil is derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of the oil palms.
-
Two types of oil can be produced fruit of the oil palm tree in two forms i.e.,
-
Crude palm oil comes from squeezing the fleshy fruit, Palm kernel oil which comes from crushing the kernel, or the stone in the middle of the fruit.
-
Oil palm trees are native to Africa but were brought to South-East Asia just over 100 years ago as an ornamental tree crop.
-
Now, Indonesia and Malaysia make up over 85% of global supply but there are 42 other countries that also produce palm oil.
Uses of Palm Oil:
-
Palm oil is in nearly everything.
-
It is in close to 50% of the packaged products that is found in supermarkets, everything from pizza, doughnuts and chocolate, to deodorant, shampoo, toothpaste and lipstick.
-
It’s also used in animal feed and as a biofuel in many parts of the world.
Harmful Effects of Palm Oil:
-
It is the cause of environmental damage & harm to the biodiversity.
-
Palm oil has been and still continues to be a major driver of deforestation of some of the world’s most biodiverse forests, destroying the habitat of already endangered species like the Orangutan, pygmy elephant and Sumatran rhino.
-
Socially, there also remains some exploitation of workers and child labour.
Defence
 Zayed Talwar 2021: The Indian Navy, on 7th August 2021 took part in a bilateral exercise "Zayed Talwar 2021" with the United Arab Emirates (UAE) Navy off the coast of Abu Dhabi.
Zayed Talwar 2021: The Indian Navy, on 7th August 2021 took part in a bilateral exercise "Zayed Talwar 2021" with the United Arab Emirates (UAE) Navy off the coast of Abu Dhabi.
Zayed Talwar 2021 was designed to enhance interoperability and synergy between the two navies.
About Zayed Talwar 2021:
-
The UAE participated in the exercise with Al-Dhafra, a Baynunah class guided missile corvette, and one AS-565B Panther helicopter while the Indian Navy deployed its warship INS Kochi and two integral Sea King MK 42B helicopters.
-
The exercise took place amid rising tension in the Gulf region after a drone attack on a merchant tanker off Oman killed a British national and a Romanian citizen over a week back.
-
As part of the exercise, the ships undertook tactical manoeuvres, over the horizon targeting, search and rescue and electronic warfare.
-
Helicopters were extensively used all through the exercise, ranging from search and rescue series to passing of targeting data to ships for simulated missile engagement drills.
-
The naval exercise came a week after Chief of Air Staff Air Chief Marshal RKS Bhadauria visited the United Arab Emirates.
Background:
In December 2020, Army Chief Gen MM Naravane had visited the UAE and Saudi Arabia in a first-ever visit by a head of the Indian Army to the two important Gulf countries.
 Al-Mohed Al-Hindi 2021: India and Saudi Arabia are all set to conduct their first-ever naval exercise called “AL-MOHED AL-HINDI 2021”.
Al-Mohed Al-Hindi 2021: India and Saudi Arabia are all set to conduct their first-ever naval exercise called “AL-MOHED AL-HINDI 2021”.
Key Highlights:
-
The joint naval exercise showcases the reflection of growing defence and military cooperation between India and Saudi Arabia.
-
Indian Navy's guided-missile destroyer INS Kochi reached Saudi Arabia on 9th August 2021 for the "Al-Mohed Al-Hindi 2021" exercise after conducting the “Zayed Talwar” drill with the United Arab Emirates (UAE) off the coast of Abu Dhabi
-
The harbour phase of the "Al-Mohed Al-Hindi 2021" exercise began on 9th August while the sea-based drills are taking place from 11th August 2021.
-
The joint naval exercise is taking place amid increasing tension in the Gulf region following a drone attack on the merchant tanker off Oman that killed a British national and Romanian citizen.
-
INS Kochi, on its arrival was given a warm welcome by officials of Royal Saudi naval forces.
Al-Mohed Al-Hindi:
-
Al-Mohed Al-Hindi comprises a number of shore and sea-based drills between the two navies.
-
During its stay at Jubail port, the Indian warship will follow all Covid-19 protocols laid down by Saudi authorities.
Note: Planning by India and Saudi Arabia for their first naval exercise had begun in 2019 but the move was impacted by the Covid-19 pandemic.
Significance:
-
The exercise is taking place amid rising tension in the Gulf region after a drone attack on a merchant tanker off Oman killed a British national and a Romanian citizen over a week back.
-
United States and United Kingdom had accused Iran for carrying the attack on MV Mercer Street.
Background:
-
Indian Army Chief General M M Narvane, in December 2020, was the first ever Army Chief to visit Saudi Arabia.
-
The armies of the two nations planned to hold the first ever joint military exercise in the later part of 2021.
About INS Kochi:
-
INS Kochi is an indigenously designed and built Kolkata-class stealth guided missile destroyer.
-
The warship incorporates new design concepts for stealth and has a large component of indigenous combat suites.
-
It was built for Indian Navy under the code name Project 15A.
-
The ship was constructed by Mazagon Dock Limited (MDL) in Mumbai and commissioned to Indian Navy service in September 2015.
-
This ship is classified as a ‘Network of Networks' because it is equipped with sophisticated digital networks, and a unique feature of the warship is the high level of indigenization, with most systems sourced from within India.
-
Some of the major indigenized systems on INS Kochi include the electronic warfare suite and the ship’s stabilizers.
-
It is also equipped sophisticated array of state of art weapons and sensors that can neutralise any threat from air, sea and underwater.
 Honour FIRST: The Indian Navy has inked a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Infrastructure Development Finance Company (IDFC) FIRST Bank
Honour FIRST: The Indian Navy has inked a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with the Infrastructure Development Finance Company (IDFC) FIRST Bank
Highlights:
-
The MoU was signed at the Naval Headquarters in New Delhi to initiate ‘Honour FIRST’, a premium banking solution for serving personnel and veterans of the Indian Navy.
-
The MoU for Honour FIRST has been signed between Commodore Neeraj Malhotra, Commodore – Pay and Allowances, Indian Navy and IDFC FIRST Bank’s senior officials.
About Honour FIRST:
-
‘Honour FIRST’ is a premium banking solution for serving personnel and veterans of the Indian Navy.
-
This Defence Account has been introduced to fill the needs of the Armed Forces and its veterans.
-
It has been especially designed keeping in mind the needs of the Armed Forces and its veterans.
-
It is supported by a dedicated team of defence veterans.
Key features of Honour FIRST Defence Account:
-
The Honour FIRST Defence account offers a range of privileges and features like zero balance salary account, net banking and mobile App.
-
The account holders can take a free enhanced Personal Accident Insurance Cover of Rs 46 lakhs for both on-duty and off-duty incidents.
-
In addition, the insurance not only covers accidental death but also total and partial permanent disability.
-
Personal Accident Insurance Cover includes a Child Education Grant of Rs 4 lakhs, and a marriage cover of Rs 2 lakh.
-
It also comprises a free lost card liability and fraud protection of up to Rs. 6 lakhs, purchase protection against theft and damage up to 90 days.
-
Furthermore, other benefits like free unlimited ATM transactions across all domestic ATMs in the country, free online payment transactions, unlimited cheque books and anywhere banking across the Bank’s network of branches and ATMs are also included.
About IDFC FIRST Bank:
-
IDFC (Infrastructure Development Finance Company) First Bank (formerly IDFC Bank) is a professionally managed new private sector bank in India, promoted by IDFC Limited (Infrastructure Development Finance Company Limited).
-
The bank started operations on 1 October 2015.
-
It received a universal banking license from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in July 2015.
-
It was listed on BSE and NSE.
-
It is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra.
-
The current CEO of IDFC FIRST Bank is V. Vaidhanathan.
About IDFC Limited:
-
Infrastructure Development Finance Company Limited, more commonly known as IDFC, is a finance company based in India.
-
It provides finance and advisory services for infrastructure projects as well as asset management and investment banking.
 International Army Games 2021: A 101-member Indian Army contingent is set to participate in the International Army Games 2021.
International Army Games 2021: A 101-member Indian Army contingent is set to participate in the International Army Games 2021.
-
Highlights:
-
This has officially been confirmed by the Ministry of Defence (MoD).
-
The 7th edition of the International Army Games, 2021, will be held from 22 August to 04 September 2021 in Russia.
-
The competition will be hosted in eleven countries in the 2021 Games.
-
Over 280 teams from 42 countries will compete in the game to show their combat skills, professionalism and determination to win.
Key Points:
-
The International Army Games is organized each year by the Russian Ministry of Defence, since 2015.
-
The International Army Games also referred to as ‘War Olympics’, is an international military sports event, which aims to strengthen military-to-military cooperation between countries and trust between the participating nations.
-
This competition also fosters military to military cooperation while building upon the best practices of participating nations.
About the Indian Contingent:
-
The Indian Army contingent has been selected out of the best from various arms after three levels of screening.
-
The contingent will participate in Army Scout Masters Competition (ASMC), Elbrus Ring, Polar Star, Sniper Frontier and Safe Route games showcasing various drills in High Altitude Area terrain, operations in snow, sniper actions, combat engineering skills in obstacle ridden terrain in the various competitions.
-
It will also contribute two observers (one each) for the Open Water and Falcon Hunting games in which Pontoon Bridge laying and UAV crew skills will be showcased by the participating teams.
-
Participation in these annual games is a reflection of the level of professionalism of the Indian Army amongst the world Armies.
-
Previously India stood first amongst the eight countries that had participated in Army Scouts Master Competition 2019 in Jaisalmer, Rajasthan.
Environment
 World Lion Day 2021: World Lion Day is celebrated annually throughout the world on August 10.
World Lion Day 2021: World Lion Day is celebrated annually throughout the world on August 10.
The day is celebrated to commemorate the existence of the ‘king of the jungle' in the biodiversity and raise awareness about the need for its conservation.
Objectives:
The day is celebrated to fulfill the following three major objectives:
-
To raise awareness about the plight of the lion & other issues that the species faces in the wild
-
To find ways to protect its natural habitat and for creating more such habitats like national parks.
-
To educate people who live near wild cats on the dangers and how to protect themselves. Humans and large species like cats can live in harmony together, but only if they understand how to do so.
History:
-
World Lions Day is celebrated across the world since 2013.
-
The World Lion Day was established by 'Big Cat Rescue' - world’s largest accredited sanctuary for big cats.
-
The day was co-founded by Dereck and Beverly Joubert of the Big Cat Initiative and National Geographic in a partnership.
-
Also known as the National Geographic Big Cats Initiative, the partnership aims to protect these wild cats in their natural habitat.
-
Furthermore, the initiative also works on safety measures with communities that live near wild cats.
Significance:
-
Lions are the top predators of their habitat, and checking browsers and grazing populations can help maintain ecosystem balance.
-
They also target the weakest members of the herd, keeping prey populations healthy and robust and indirectly helping control prey population diseases.
-
Their conservation also helps protect natural forest areas and habitats, which in turn helps manage biodiversity.
-
They have been at the heart of human fascination from time immemorial, beyond national borders and across cultures.
-
From guarding temples to adorning national flags, decorating coins to beautifying ancient Indian pillars, Lions have commanded symbolic importance throughout the ages.
Significance of Lion in Indian History:
-
They have an illustrious place in India’s history and culture, with their earliest known references found in the pillars of the Mauryan Empire.
-
The Indian national emblem too is adorned by the majestic lion on all four sides.
Threat:
-
Among the many other threats that face the mighty animal, today, the most prominent of them are trophy hunting and loss of natural habitat
IUCN List:
-
Currently, they are listed as endangered species by the International Union for Conservation of Nature’s (IUCN) Red List.
-
In West Africa, the species is now classified as “critically endangered.”
-
According to reports, over a century ago there were more than 2,00,000 wild lions living in Africa.
-
Recent surveys estimate that in the last two decades, lion numbers have declined from approximately 30,000 to about 20,000
Asiatic Lions:
-
The Asiatic lions are found in India in the restricted Gir Forest and National Park and its surrounding areas.
-
However, in the past, they roamed across the Indo-Gangetic plains, extending from Sindh in the west to Bihar in the east.
-
Several paintings, literature and the records of lion hunt reveal that the lions were part of Indian mythology, royal emblems and a part of its cultural identity.
-
It was only during the British colonial rule when lions were hunted on a large scale and their numbers depleted from most of their distribution range.
Efforts by India for Conservation of Lions:
-
The Indian government is already making efforts to protect the king of the jungle through various schemes and projects.
-
According to the census of the majestic big cats that was conducted by the Gujarat government in June last year, it showed a rise.
-
India recorded the highest ever increase of 29 per cent in its lion population from 523 in 2015 to 674 in 2020. The report also cited that their distribution expanded from 22,000 sq. km in 2015 to 30,000 sq. km in 2020.
About Lions:
-
Lions, one of the largest animal species on earth are scientifically named ‘Panthera Leo’.
-
The king of the jungle lives in a large group known as pride. It is like the wolves’ pattern of living.
-
Lions live only in grasslands and plains.
-
The male lion weighs more than 500 pounds and grows up to eight feet in length.
-
The male lions have dignified manes; long thick hair around they head, neck and shoulder which makes them appear larger and more intimidating.
-
Unlike the female cubs, the male cubs are responsible for their own living post maturity.
-
The female lions are smaller and faster. The female lions and their sisters live together. Even the female cubs are joined in the pride.
-
The roar of the male lion can be heard from up to 5 miles away. Their roar is the loudest amongst the big cat species.
-
A lion usually lives for maximum 16 years in the wild and 25 years in captivity.
-
Mostly lions hunt at night because of the adaptation skills of their eyes over dark. This gives them huge advantage over the prey.
-
The coloration of these animals varies from light yellow to dark brown.
-
The lion is armed with claws, which can be almost 10 cm each.
Note: The overall intention to celebrate the World Lion Day is to find sustainable solutions to protect and save wild lion populations from extinction globally.
 Greece Wildfires-Evia: Wildfires are continuing to rip through the Greek island of Evia with strong winds driving flames towards villages.
Greece Wildfires-Evia: Wildfires are continuing to rip through the Greek island of Evia with strong winds driving flames towards villages.
Key Details:
-
More than 2,000 people have already been evacuated from the island, many of those by ferry.
-
Greece and neighbouring Turkey is experiencing its most severe heatwave in 30 years in which temperatures have spiked to 45C (113F) in Greece.
-
A number of wildfires have struck the country in recent days.
-
On Evia, two fire fronts have destroyed thousands of hectares of land, along with a number of houses and businesses.
-
One blaze in the northern suburb of Athens is said to have subsided.
Causes:
-
Heatwaves such as this are becoming more likely and more extreme because of human-induced climate change.
-
The subsequent hot, dry weather is likely to fuel wildfires.
About Euboea:
-
Evia or Euboea is the second-largest Greek island in area and population, after Crete.
-
It is located in the Central Greece in the Aegean Sea.
-
The narrow Euripus Strait separates Evia from Boeotia in mainland Greece.
-
Euboea was believed to have originally formed part of the mainland, and to have been separated from it by an earthquake. This is fairly probable, because it lies in the neighbourhood of a fault line.
 AMOC: A study recently published in Nature Climate Change notes that the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is losing its stability.
AMOC: A study recently published in Nature Climate Change notes that the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is losing its stability.
Key Points:
-
According to the IPCC’s Report (AR6) released on August 9, it is very likely that AMOC will decline over the 21st century.
-
Modelling studies have shown that an AMOC shutdown would cool the northern hemisphere and decrease rainfall over Europe.
What is AMOC?
-
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) is a major ocean current system transporting warm surface waters toward the northern Atlantic.
-
It is the Atlantic branch of the ocean conveyor belt or Thermohaline circulation (THC). It distributes heat and nutrients throughout the world’s ocean basins.
-
AMOC carries warm surface waters from the tropics towards the Northern Hemisphere, where it cools and sinks.
-
It then returns to the tropics and then to the South Atlantic as a bottom current.
-
From there it is distributed to all ocean basins via the Antarctic circumpolar current.
What happens if AMOC collapses?
-
A collapse from the currently attained strong to the weak mode would have severe impacts on the global climate system and further multi-stable Earth system components.
-
Modeling studies have shown that an AMOC shutdown would cool the northern hemisphere and decrease rainfall over Europe.
-
It can also have an effect on the El Nino.
-
Gulf Stream which is a part of the AMOC is a warm current responsible for mild climate at the Eastern coast of North America as well as Europe.
-
Without a proper AMOC and Gulf Stream, Europe will be very cold.
 World Elephant Day 2021: The World Elephant Day is observed every year on 12 August across the globe.
World Elephant Day 2021: The World Elephant Day is observed every year on 12 August across the globe.
The day aims to spread awareness about the plight of elephants and to identify their importance in our ecosystem
History:
-
World Elephant Day was co-founded by a Canadian filmmaker Patricia Sims and the Elephant Reintroduction Foundation of Thailand, an initiative of HM Queen Sirikit of Thailand on 12 August 2012.
-
The first World Elephant Day was observed in the year 2012 to bring attention to the urgent plight of Asian and African elephants.
-
Since then, the day is being observed every year on 12 August.
-
This is not just a day but a movement in itself.
-
Since 2012, Ms Sims has been leading World Elephant Day.
Significance:
-
World Elephant Day plays a very important role in raising awareness about problems faced by elephants.
-
According to World Elephant Society various threats including, poaching, habitat loss, mistreatment in captivity hover over elephants, especially Asian and African.
-
On this day, they encourage individuals and organizations around the world to work towards elephant conservation.
IUCN Status:
-
The IUCN Red List of threatened species has listed African elephants as ‘Critically Endangered’ and Asian elephants as ‘Endangered’.
-
An estimated 100 African elephants are killed each day by poachers seeking ivory, meat and body parts, leaving only 400,000 remaining.
Causes for Decline in the Populations of Elephants:
-
Elephants are shot by hunters and they die in extreme pain and agony. Because of this, their tribes are damaged which leads to populations decline.
-
Elephants are killed by poachers for their ivory which is used in making tableware, sculptures, jewellery, and Chinese traditional medicines, and other things.
-
Wild Asian elephants suffer severe habitat loss in some of the most densely human-populated regions on the planet.
-
Many elephants fall prey to electrocution, train accidents and poisoning.
What can be done to save the elephants?
-
Never buy ivory products.
-
Donate to reputed organizations like World Wildlife Fund (WWF), The Elephant Society, Wildlife SOS, and others as these organizations work tirelessly towards the rescue. So, donations will help support their activities better and faster.
-
Protect wild elephant habitat.
-
Provide sanctuaries and alternative habitats for domestic elephants to live freely.
Conservation and protection of Elephants in India:
Project Elephant:
-
In 1992, the Government of India (GoI) had launched Project Elephant as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme to protect elephants and their habitats, address issues of human-elephant conflict, and ensure the welfare of captive elephants.
-
The funding is provided by the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change for the project across the country.
-
The project has been implemented in 16 states across India namely Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Orissa, Tamil Nadu, Tripura, Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal.
-
India has 32 Elephant reserves, as stated by the GoI.
-
The Singhbhum Elephant Reserve of Jharkhand was the first elephant sanctuary in the country.
-
The Ministry of Environment and Forests, in 2011, collaborated with Wildlife Trust of India to launch the campaign ‘Hathi Mere Sathi’.
Indian Policy
 Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules 2021: Keeping in view the adverse impact of littered plastic on both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC), Government of India (GoI), on 13 August, 2021, notified the Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021, prohibiting identified single-use plastic items by 2022.
Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules 2021: Keeping in view the adverse impact of littered plastic on both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems, the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC), Government of India (GoI), on 13 August, 2021, notified the Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021, prohibiting identified single-use plastic items by 2022.
Highlights:
-
The development is in line with the call given by Prime Minister Narendra Modi to phase out single-use plastic by 2022.
-
The amendments prohibit specific single-use plastic items which have “low utility and high littering potential” by 2022.
-
The recent release from the MoEFCC stated that the thickness of plastic carry bags is to increase from 50 to 75 microns from 30 September 2021 and to 120 microns with effect from 31 December 2022.
-
The Gazette notification for the same that was issued on 11th August 2021 also has 'Guidelines for Extended Producer Responsibility given legal force.'
Note: Extended Producer Responsibility is a policy approach in which producers take responsibility for management of the disposal of products they produce once those products are designated as no longer useful by consumers.
Key Details:
-
Plastic packaging waste not covered under the phase-out of identified single-use plastic items should be collected and managed in an environmentally sustainable way through the Extended Producer Responsibility of the producer, importer and brand owner (PIBO) as per Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016.
-
From July 2022, the manufacture, import, stocking, distribution, sale, and use of identified single-use plastic items will be banned from July 1, 2022.
-
These include ear buds with plastic sticks, plastic sticks for balloons, candy sticks, ice-cream sticks, plastic flags, polystyrene (Thermocol) for decoration, plates, cups, glasses, cutlery such as forks, spoons, knives, straws, trays, wrapping or packing films around sweet boxes, invitation cards, and cigarette packets, plastic or PVC banners less than 100 microns, and stirrers.
-
From September 30, 2021, onwards, the thickness of plastic carry bags will be increased from 50 microns to 75 microns, and thereafter from December 31, 2022, it will be increased to 120 microns.
-
The provisions will not apply to commodities made of compostable plastic.
Background:
-
A draft outlining the way forward was issued in March and involved amending the Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016.
-
Currently the Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016, prohibits manufacture, import, stocking, distribution, sale and use of carry bags and plastic sheets less than 50 microns in thickness in the country.
-
There is a ban on sachets using plastic material used for storing, packing or selling tobacco, gutkha, and pan masala.
-
India had adopted a resolution to address single-use plastic products pollution at the 4th United Nations Environment Assembly held in 2019.
-
Under the Swacch Bharat Mission, the Government is taking measures to strengthen the waste management infrastructure in the States and UTs.
-
A National Level Taskforce had also been constituted by the Ministry for taking coordinated efforts to eliminate identified single use plastic items and effective implementation of Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016.
About MoEFCC:
-
It refers to the MoEFCC. It refers to the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change.
-
MoEFCC an Indian government ministry was formed in 1985. It is headquartered in New Delhi.
-
The ministry is responsible for planning, promoting, coordinating, conservation and survey of forest, flora and fauna of India, prevention and control of pollution, afforestation, land degradation mitigation and overseeing the implementation of environmental and forestry programmes in the country.
-
The current Minister of MoEFCC are Ashwini Kumar Choubey (Minister of State), Bhupender Yadav (Union Minister).
 Vehicle Scrappage Policy: Prime Minister Narendra Modi, on August 13, 2021, launched the Voluntary Vehicle Fleet Modernisation Programme, or the automobile scrappage policy.
Vehicle Scrappage Policy: Prime Minister Narendra Modi, on August 13, 2021, launched the Voluntary Vehicle Fleet Modernisation Programme, or the automobile scrappage policy.
He launched the National Automobile Scrappage Policy through video conferencing during the Investor Summit 2021, in Gujarat.
Aim:
-
This policy aims to phase out old and unfit vehicles in an environment-friendly manner.
-
It is in line with India’s goal for 21st century to achieve a clean, congestion-free and convenient mobility.
-
It seeks to create a viable circular economy and bring value for all stakeholders.
Key Details:
-
The National Vehicle Scrappage Policy (VVMP) is also dubbed as “voluntary vehicle-fleet modernisation programme”.
-
Under the policy, vehicles will be scientifically tested through authorised and automated centres before it is finally scrapped.
-
Commercial vehicles that are over 15 years’ old and personal vehicles that are more than 20 years old will be eligible for scrapping.
-
The policy will be first implemented for government-owned vehicles, and then for heavy commercial and personal vehicles.
-
From 2023 onwards, heavy commercial vehicles need to be scrapped if they do not conform to the fitness level prescribed under the rules.
-
For personal vehicles, the Govt. plans to implement this from June 2024 onwards.
Benefits:
-
This Policy has several economic and environmental benefits.
Economic Benefits:
-
The vehicle scrappage policy will bring in investments of around INR 10,000 crore to set up 450-500 Automated Testing Stations (ATS) and 60-70 Registered Vehicle Scrapping Facilities (RVSF) across the country.
-
A single window clearance portal is being developed where the applications for ATS and RVSF will be catered through a single portal within 60 days.
-
The cost of raw material by approx 40 percent as 99 percent of recovery of metal waste can be done with regular scrapping.
-
This in turn, will make the components less expensive and increase competitiveness in the international market.
-
With the increased sales of automobiles, the government will get a profit of Rs 30,000-40,000 cr in GST.
-
The state government will also get a profit of Rs 30,000-40,000 cr in GST.
-
It will also promote self-reliance of India in the auto sector and metal sector.
-
It will generate about 50000 direct and indirect employments.
Environmental Benefits:
-
Currently, India has 10 million cars without valid fitness parameters that add to pollution and fuel costs. Thus, the replacement of old vehicles will positively benefit the environment.
-
The policy will play a big role in modernizing and phasing out the old polluting vehicles in an environment-friendly manner.
Incentives for scrapping old vehicles:
The incentives are as follows:
-
The owners of such vehicles will get a scrap value which will be equivalent to 4 - 6 percent of the ex-showroom price of the new vehicle that they would be purchasing.
-
There will be zero registration fees for new vehicle purchased if the owner shows a certificate of deposit.
-
The state governments have been asked to offer concessions on motor vehicle tax. The concessions include up to 25 percent for non-transport vehicles and up to 15 per cent for transport vehicles.
-
The vehicle manufacturers have been advised to provide 5 per cent discount on purchase of new vehicle against certificate of deposit.
 Ujjwal Abahan: Minister of State (MoS), Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas and Labor & Employment Shri Rameswar Teli launched a programme "Ujjwal Abahan" through virtual platform.
Ujjwal Abahan: Minister of State (MoS), Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas and Labor & Employment Shri Rameswar Teli launched a programme "Ujjwal Abahan" through virtual platform.
Key Points:
-
Ujjwal Abahan is an ONGC-supported Assam Handloom project.
-
The project will support and train over a hundred artisans of Bhatiapar of Sivasagar, Assam in Hathkharga handicraft.
-
This project is in line with the government’s observance of “Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav”.
-
ONGC also has earlier launched two projects supporting the indigenous handicrafts of the country under the above observance.
 PM-DAKSH: Union Minister Virendra Kumar recently launched PM-Daksh portal, PM Daksh mobile app to promote skill development in Nalanda Auditorium at Dr. Ambedkar International Centre, Delhi.
PM-DAKSH: Union Minister Virendra Kumar recently launched PM-Daksh portal, PM Daksh mobile app to promote skill development in Nalanda Auditorium at Dr. Ambedkar International Centre, Delhi.
Note: The ‘PM-DAKSH’ stands for Pradhan Mantri Dakshta Aur Kushalta Sampann Hitgrahi (PM-DAKSH) Yojana.
Key Details:
-
The platform has been developed by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, in collaboration with National E-Governance Division (NeGD), under the Department Of Electronics And Information Technology.
-
The portal can be accessed at: http://pmdaksh.dosje.gov.in.
Aim:
-
The Portal and app aims to make the skill development schemes accessible to the target groups.
-
It ensures availability of all information related to skill development at one place for Scheduled Castes, Backward Classes and Safai Karamcharis.
Background:
-
PM-DAKSH Yojana is being implemented by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment from the year 2020-21.
-
Under this scheme, eligible target group are being provided skill development training programmes on
-
Up-skilling/Re-skilling,
-
Short Term Training Programme,
-
Long Term Training Programme and
-
Entrepreneurship Development Program (EDP).
About National e-Governance Division (NeGD):
-
NeGD was created as an Independent Business Division under Digital India Corporation.
-
It was created in 2009 by Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology.
-
Since its creation, it has been playing a significant role in supporting Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology in management & implementation of Programme.
-
It has been implementing several e-Governance Projects and initiatives at the Central as well as State levels.
Indian polity
-Order-(Amendment)-Bill-2021.jpg) Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2021: The Lok Sabha, on 9th August 2021, passed The Constitution (Schedule Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill 2021.
Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2021: The Lok Sabha, on 9th August 2021, passed The Constitution (Schedule Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill 2021.
Highlights:
-
This Bill was passed after a brief discussion as some Opposition members kept protesting in the House.
-
The Bill was passed by the Rajya Sabha on August 5 with a voice vote amid din.
Key Details:
-
The Bill amends the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950.
-
The Bill seeks to amend the constitutional list of Scheduled Tribes as recommended by Arunachal Pradesh.
Note: The Constitution empowers the President to specify the Scheduled Tribes (STs) in various states and union territories. It also permits Parliament to modify this list of notified STs.
-
The bill was brought in to remove the Abor tribe from the list of STs in the state.
-
The Bill also replaces certain STs with other tribes.
-
Khampti is replaced with Tai Khamti,
-
Momba is replaced with Monpa, Memba, Sartang, and Sajolang (Miji)
-
Mishmi, Idu, and Taroan are replaced with Mishmi-Kaman (Miju Mishmi), Idu (Mishmi), and Taraon (Digaru Mishmi)
-
Any Naga Tribes is replaced with Nocte, Tangsa, Tutsa, and Wancho.
Additional News:
-
The House paid tributes to those who had participated in the Quit India Movement. The country is celebrating the 79th anniversary of the Quit India Movement that was launched in 1942 under the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi.
-
The Lower House also passed The Limited Liability Partnership (Amendment) Bill 2021 and The Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (Amendment) Bill 2021.
-
The bills have already been passed by the Upper House.
 127th Constitution Amendment Bill: The Central Government, on 9th August 2021, introduced the 127th Constitution (amendment) bill, 2021 in Lok Sabha.
127th Constitution Amendment Bill: The Central Government, on 9th August 2021, introduced the 127th Constitution (amendment) bill, 2021 in Lok Sabha.
Key Points:
-
The bill seeks to restore the power of States and Union Territories to make their own OBC lists.
-
The Bill was introduced in the Parliament by Union minister of Social Justice and Empowerment, Virendra Kumar.
-
It was introduced to clarify some provisions of the 102nd Constitutional Amendment Bill, restoring the power of states to identify backward classes.
Constitutional Provisions:
-
As per the Indian Constitution, Articles 15 (4), 15 (5), and 16 (4) confer power on the State Government to declare and identify the list of socially and educationally backward classes.
-
As a practice, separate OBC lists are drawn up by the Central Government and each State concerned.
Why is it 127th Constitution Amendment Bill needed?
-
The amendment was necessitated after the Supreme Court of India (SCI) in its Maratha reservation ruling of May 2021 upheld the 102nd Constitutional Amendment Act.
-
However, SCI also stated that, the President will determine which communities will be included on state OBC list, on the recommendations of the National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC).
-
The 102nd Constitution Amendment Act of 2018 had inserted the Articles 338B and Article 342 A (with two clauses) after Article 342.
-
Articles 338B deals with the structure, powers, and duties of the National Commission for Backward Classes.
-
Article 342A says that the President, in consultation with the Governor, will specify the educationally and socially backward classes.
About 127th Constitution Amendment Bill:
-
The Amendment Bill will amend clauses 1 and 2 of Article 342A.
-
It will also introduce a new clause 3.
-
It will also amend Articles 366 (26c) and 338B (9).
-
The bill is designed to clarify that, State Governments can maintain state list of OBCs, restoring the system prior to SC judgment.
-
Articles 366 (26c) define the socially and educationally backward classes.
-
Under the amendment, the latest ‘State List’ will be taken out of the purview of the President completely and it will be notified by State Assembly.
What is the procedure to get 127th Constitution Amendment Bill passed?
-
An amendment of the Constitution can be initiated only by the introduction of a bill in either House of Parliament.
-
The bill must then be passed in each House by a majority of the total membership of that House and by a special majority of not less than two-thirds of the members present and voting.
-
In case of disagreement between the two Houses, there is no provision for a joint sitting.
-
If the amendment seeks to make any change in any of the provisions mentioned in the provision to Article 368, it must be ratified by the Legislatures of not less than one-half of the states.
-
Although there is no prescribed time limit for ratification, it must be completed before the amending bill is presented to the president for his assent.
International
 International Day of World's Indigenous Peoples 2021: International Day of the World's Indigenous Peoples is observed on August 9 every year across the world.
International Day of World's Indigenous Peoples 2021: International Day of the World's Indigenous Peoples is observed on August 9 every year across the world.
Highlights:
-
This day is also known as World Tribal Day.
-
This day is observed to raise awareness and protect the rights of the world's indigenous population.
-
This event also recognizes the achievements and contributions that indigenous people make to improve world issues such as environmental protection.
History:
-
On December 23, 1994, the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) decided that that the International Day of the World's Indigenous People will be observed every year on August 9.
-
On the same date in 1982, the UN Working Group on Indigenous Populations (WGIP) of the Sub-Commission on the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights had convened its first meeting in Geneva, Switzerland.
Objective:
-
The main objective of the First International Decade was to solidify international cooperation to solve problems in the areas, including human rights, the environment, development, education, health culture, economic and social development, the environment, and human rights.
-
The focus is mostly to strengthen international cooperation on solving problems of the indigenous population globally.
Significance:
-
The day serves as a reminder to all of us that we need to do much more than what we have done so far for indigenous people.
-
On this day, UNESCO considers the multiple challenges indigenous people face for their sustainability.
-
Worldwide, people are encouraged to spread the United Nations' message of protection and promotion of the rights of indigenous people.
Theme of 2021:
-
The theme for this year's International Day of Indigenous Peoples is “Leaving no one behind: Indigenous peoples and the call for a new social contract”.
Events 2021:
-
The United Nations Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues (UNPFII) organized a virtual commemoration for speakers.
-
The event featured an interactive session with two speakers.
-
The discussion focused on the distinct elements which should be considered while building and redesigning a fresh social contract inclusive of indigenous peoples.
Facts About indigenous people:
-
As per an estimate by the United Nations, nearly 476 million indigenous people live in 90 countries across the world.
-
They account for 6.2 per cent of the world's total population.
-
They are spread across 90 countries and representing 5,000 different cultures.
Indigenous Tribes in India:
-
The central tribal belt which comprises the Northeastern states of India claims to have the maximum concentration of indigenous population. Here are a few of them.
Great Andamanese Tribes:
-
This group occupies the regions of Strait Island and some parts of Rutland Island.
-
It consists of Onge, Jarawa, Jangil and Sentinelese, who are the first inhabitants of the island and paint their faces, bodies with clay.
-
These tribes are into chanting while they work and are fond of communicating with big, colourful pigeons in the forest.
The Jarawa Tribe:
-
The Jarava Tribe lives in the pristine islands of Andaman and Nicobar.
-
It is one of the oldest tribes of India. With a scanty population of almost 420, they are almost on the verge of extinction.
-
They live along the western coast of the south and middle Andaman Islands.
-
Mostly hunters and gatherers, they are dependent on terrestrial and aquatic resources.
-
They had inhabited the islands almost 60,000 years ago.
Bhils:
-
Till 2013, Bhils were the largest tribal group in India, known to have a rich, distinctive culture.
-
They are an Indo-Aryan speaking ethnic group in Gujarat, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Maharashtra; the western Deccan region.
Gond Tribes:
-
Mostly spotted in Bastar highland regions of Southern Chhattisgarh, there are three important Gond tribes- Muria, the Bisonhorn Maria, and the Hill Maria.
-
Raj Gond is known to be the most developed in the Gond tribes.
Santhal Tribes:
-
The Santhal tribes are the major tribes of West Bengal and are mostly seen in the districts of Bankura and Purulia.
-
They are also widely seen in parts of Bihar, Jharkhand, Odisha and Assam.
-
The Santhals are largely dependent on agriculture and livestock; further, they are well versed in the art of hunting.
 11th Annual meeting FEMBoSA: The 11th Annual meeting of the Forum of the Election Management Bodies of South Asia (FEMBoSA) was inaugurated by Chief Election Commissioner of India & Chairman of FEMBoSA, Sushil Chandra for the year 2021.
11th Annual meeting FEMBoSA: The 11th Annual meeting of the Forum of the Election Management Bodies of South Asia (FEMBoSA) was inaugurated by Chief Election Commissioner of India & Chairman of FEMBoSA, Sushil Chandra for the year 2021.
Key Points:
The meeting in Virtual mode was hosted by the Election Commission of Bhutan.
FEMBoSA meeting was held under the theme of ‘Use of Technology in Elections’.
The delegations from Bangladesh, Afghanistan, Maldives, Bhutan, Nepal and Sri Lanka along with India participated in the meeting.
The Chairmanship of FEMBoSA was virtually handed over by Sushil Chandra, CEC, as the outgoing Chair of FEMBoSA to Dasho Sonam Topgay, Chief Election Commissioner of Bhutan.
On behalf of Election Commission of Bhutan, H.E. Major General Vetsop Namgyel, Ambassador of Bhutan to India accepted FEMBoSA Logo from Shri Sushil Chandra for Election Commission of Bhutan assuming the role of new Chair of FEMBoSA 2021-22.
Note: Logo of FEMBoSA with golden pearls stands for eternal values of democracy, transparency, impartiality and cooperation.
About 11th Annual meeting of FEMBoSA:
-
The Thimphu Resolution was unanimously adopted by the FEMBoSA members at this meeting to extend the tenure of the chairmanship to two years during the current pandemic situation.
-
At the meet, Sushil Chandra highlighted that the ECI has digitized many processes by keeping pace with rapid strides of Technology.
-
Technology driven processes have become more important during the Covid 19 situation as it is helping in minimizing person-to-person contact.
About FEMBoSA:
-
The full form of FEMBoSA is Forum of the Election Management Bodies of South Asia.
-
FEMBoSA was established at the 3rd Conference of Heads of Election Management Bodies of SAARC Countries held at New Delhi in 2012.
-
The annual FEMBoSA meeting is held by rotation among the members.
-
Besides ECI, the other 7 members are EMBs from Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
-
The objectives of the Forum are as follows:
-
To promote contact among the EMBs of the SAARC countries.
-
To share experiences with a view to learning from each other.
-
To cooperate with one another in enhancing the capabilities of the EMBs towards conducting free and fair elections.
 International Youth Day: The International Youth Day (YID) is observed on August 12 annually across the globe.
International Youth Day: The International Youth Day (YID) is observed on August 12 annually across the globe.
Highlights:
-
The day is observed to draw the attention of governments and others towards youth issues worldwide.
-
This day is also celebrated to recognize the efforts put in by the youth for the betterment of society.
Aim:
-
The Day aims to promote the ways to engage the youth and make them more actively involved in their communities through positive contributions.
Theme of International Youth Day 2021:
-
The theme of International Youth Day 2021, “Transforming Food Systems: Youth Innovation for Human and Planetary Health”.
-
This year's theme highlights the crucial need for "inclusive support mechanisms that ensure youth continue to amplify efforts collectively and individually to restore the planet and protect life while integrating biodiversity in the transformation of food systems."
World Youth Day in India:
-
Health Minister Mansukh Mandaviya, on the occassion of World Youth Day, launched the first phase of the awareness campaign for HIV, TB and Blood Donation.
History of International Youth Day:
-
The International Youth Day (IYD) was instituted by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) by passing resolution 54/120 in December 1999.
-
The General Assembly endorsed the recommendation made by the World Conference of Ministers Responsible for Youth (Lisbon, 8-12 August 1998) that 12 August be declared International Youth Day.
-
This day was observed on August 12, 2000, for the first time.
-
The day is celebrated through various awareness campaigns, community concerts, and events to bring to notice the socio-economic and socio-political issues that the youth in every nation face.
About UNGA:
-
It refers to the United Nations General Assembly. UNGA is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations.
-
It is the main deliberative, policymaking and representative organ of the United Nations. Comprising all 193 Member States of the UN, it provides a unique forum for multilateral discussion of international issues including peace and security.
-
It was formed in 1985.
-
It is headquartered in New York, New York, United States.
-
The current President of UNGA is Abdulla Shahid.
 UN Security Council Open Debate: Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi recently chaired the High-level Open Debate on 'Enhancing Maritime Security – A Case for International Cooperationt' via video conferencing.
UN Security Council Open Debate: Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi recently chaired the High-level Open Debate on 'Enhancing Maritime Security – A Case for International Cooperationt' via video conferencing.
Highlights:
-
With this, Prime Minister Modi, has become the first Indian Prime Minister to preside over a UN Security Council Open Debate.
Note: India had assumed the Presidency of the UNSC for August 2021, taking over from France.
-
The heads of state or government in attendance, included Russian President Vladimir Putin, President of Kenya Uhuru Kenyatta and Premier of Vietnam Pham Minh Chinh.
-
The UNSC adopted a ‘Presidential [India’s] Statement’ which reaffirmed that the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) establishes the legal framework for maritime activities.
Key Points:
-
The Open Debate focused on ways to effectively counter maritime crime and insecurity and strengthened coordination in the maritime domain.
-
India will organize two more meetings during its presidency, on peacekeeping and counterterrorism.
-
During the debate, PM Modi also underlined five principles that need to be followed in terms of maritime trade and security, which included:
Free maritime trade sans barriers:
-
The first was removing barriers to maritime trade.
-
PM Modi put forward the vision of SAGAR - an acronym for ‘Security and Growth for all in the Region’, which provides a framework for a safe and stable maritime domain in the region.
-
“SAGAR” is a 2015 Indian framework for regional maritime security.
Peaceful settlement of maritime disputes:
-
The Second was that maritime disputes should be resolved peacefully and in accordance with international law,” as this was “extremely important for promoting mutual trust and confidence, and ensuring global peace and stability.”
Combating maritime threats:
-
The third principle Mr Modi proposed was that countries jointly tackle maritime threats from non-state actors and natural disasters.
Preserving maritime environment and resources:
-
The Fourth was that the maritime environment and marine resources needed to be conserved, highlighting pollution from plastic waste and oil spills.
Encouraging responsible maritime connectivity:
-
The fifth was that there was a need for responsible maritime connectivity.
-
A structure was required to boost maritime trade, with the development of global norms and standards.
Background:
In 2019, at the East Asia Summit, this initiative was further elaborated through the Indo-Pacific Oceans’ Initiative (IPOI) with a focus on seven pillars of maritime security including
-
Maritime Ecology
-
Maritime Resources
-
Capacity Building and Resource Sharing
-
Disaster Risk Reduction and Management
-
Science, Technology and Academic Cooperation
-
Trade Connectivity and
-
Maritime Transport.
 Mohammad Mokhber: The new President of Iran Ebrahim Raisi recently named Mohammad Mokhber who is the chairman of a powerful state-owned foundation sanctioned by the United States as his first vice-president.
Mohammad Mokhber: The new President of Iran Ebrahim Raisi recently named Mohammad Mokhber who is the chairman of a powerful state-owned foundation sanctioned by the United States as his first vice-president.
Key Points:
-
Mohammad Mokhber has for years headed the foundation known as Setad or the Execution of Imam Khomeini’s order.
-
He was appointed to the position by the supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei in 2007.
-
The Setad was originally founded in the late 1980s to manage confiscated properties following the 1979 Islamic Revolution.
About Iran:
-
Iran also called Persia, and officially the Islamic Republic of Iran is a country in Western Asia.
-
It is bordered to the northwest by Armenia and Azerbaijan,to the north by the Caspian Sea, to the northeast by Turkmenistan, to the east by Afghanistan and Pakistan, to the south by the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, and to the west by Turkey and Iraq.
-
Its central location in Eurasia and Western Asia, and its proximity to the Strait of Hormuz, give it geostrategic importance.
-
The capital of Iran is Tehran.
-
The currency used there is Iranian Rial.
-
The current President of Iran is Ebrahim Raisi.
National
-Bill-2021.jpg) Central Universities (Amendment) Bill, 2021: The Indian Parliament, on 9th August 2021, passed the Central Universities (Amendment) Bill, 2021 amid an opposition walkout.
Central Universities (Amendment) Bill, 2021: The Indian Parliament, on 9th August 2021, passed the Central Universities (Amendment) Bill, 2021 amid an opposition walkout.
Highlights:
-
The Bill in the Upper House was passed with a voice vote.
-
It seeks to establish a central university in the Union Territory of Ladakh.
-
The bill was cleared by Lok Sabha last week.
Key Details:
-
According to the Statement of Objects and Reasons of the Bill, at present there is no Central university in Ladakh and therefore, the government has decided to establish a new one there to ensure increase in accessibility and quality of higher education and research for the people of the Union territory.
-
It also aims to facilitate and promote avenues of higher education and research for the people of the Union territory.
-
As per the to the statement of objects, the Bill seeks to amend the Central Universities Act, 2009, to provide for the establishment of a university named “Sindhu Central University” in Ladakh.
-
The varsity is intended to cater to other areas of the UT including Leh and Kargil.
-
The government had said that the varsity is likely to reduce the imbalance in the Education sector of the region and provide opportunities to the students belonging to the UT of Ladakh to pursue higher educational opportunities.
-
An amount of Rs. 750 crore has been allocated by the government for the establishment of the central varsity in which nearly 2,500 students will get an opportunity to study in their own city.
 India and US: Indian and American bodies, on August 10, 2021, signed an agreement on monsoon data analysis and cooperation.
India and US: Indian and American bodies, on August 10, 2021, signed an agreement on monsoon data analysis and cooperation.
Key Details:
-
The two bodies would enhance technical cooperation for improving weather forecasts.
-
The agreement was signed by India's National Institute of Ocean Technology Director, G.A. Ramadass and the U.S. Assistant Administrator for Research and Acting Chief Scientist, Craig McLean of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
-
The two bodies would enhance technical cooperation in the development of the Research Moored Array for African-Asian-Australian Monsoon Analysis and Prediction (RAMA) and the Ocean Moored buoy Network in the northern Indian Ocean (OMNI) for improving weather and monsoon forecasts between NOAA and India’s Ministry of Earth Sciences.
Background:
-
The agreement is a follow up to the memorandum of understanding (MoU) signed between the Ministry of Earth Sciences and NOAA last October for Technical Cooperation in Earth Observations and Earth Sciences.
-
The MoU had been signed by India’s Ambassador to the US, Taranjit Singh Sandhu and Dr Neil A Jacobs, Assistant Secretary of Commerce and Acting Administrator, NOAA.
About National Oceanic & Atmospheric Administration (NOAA):
-
NOAA is an American scientific agency working under the United States Department of Commerce.
-
It focuses on the conditions of oceans, major waterways, and the atmosphere.
-
It warns about the dangerous weather, charts seas and guides on use & protection of ocean & coastal resources.
-
It also conducts research to provide the understanding and improve stewardship of the environment.
 Nation First, Always First: The theme of India’s 75th Independence Day celebrations will be ‘Nation First, Always First’.
Nation First, Always First: The theme of India’s 75th Independence Day celebrations will be ‘Nation First, Always First’.
Key Highlights:
-
This year, India will celebrate its 75th year of Independence at Red Fort from where Prime Minister Narendra Modi will address the nation on August 15, 2021.
-
All the Olympians who won medals at the 2020 Tokyo Games have been sent special invites for the event.
-
Like 2020, due to the pandemic, the event this year too will be restricted to the public with no cultural performance.
-
Usually, the day is observed with parades and pageants showcasing the scenes of independence struggle to the cultural diversity of India.
-
A group of NCC cadets will attend the event.
-
From paintings to floral arrangements, all aspects of the programme will bear ‘Nation First, Always First’ theme.
Drone alert:
-
The Union Ministry of Home Affairs, after the recent drone attacks in Jammu, has asked the Delhi Police to strictly follow the Standard Operating Procedures for drone operations.
-
Personnel have also been directed to take down the drones or the aerial objects in case anyone sees one approaching the Red Fort.
-
A makeshift wall of containers has also been erected at the periphery of the Red Fort.
-
It will rule out any form of security breach owing to the ongoing farmers’ protest.
Additional Info:
Amrit Mahotsav:
-
Independence Day 2021 will be known as 'Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav'.
-
A 241 mile long march will take place from Ahemdabad to Dandi.
-
The event started on 12th March to mark the anniversary of Dandi March that Mahatma Gandhi did for salt.
About Independence Day:
-
Independence Day is marked as the occasion to celebrate the countless sacrifices and struggles our freedom fighters have made to make India independent from British rule.
-
It is observed as a national holiday with a flag hoisting ceremony, parade, and singing the national anthem with patriotic spirit.
-
It was on August 15, 1947 that India was freed from British colonialism by gaining independence.
History:
-
For a period of almost 200 years, the British ruled India.
-
At the Lahore meeting of the Indian National Assembly in 1929, the Purna Swaraj Declaration or “Indian Declaration of Independence” was promulgated, and it was declared Independence Day on January 26, 1930.
-
Congress called on the people to guarantee civil disobedience and implement the instructions issued by the Congress from time to time until India achieves complete independence.
-
Congress designated January 26 as Independence Day from 1930 to 1946.
-
The British Parliament had authorized Lord Mountbatten to transfer power before June 30, 1948.
-
As per Mountbatten’s inputs, the Indian Independence Bill was introduced in the British House of Commons on July 4, 1947, and passed within a fortnight.
-
It provided for the end of the British rule in India, on August 15, 1947, and the establishment of the Dominions of India and Pakistan.
-
After gaining actual independence on August 15, 1947, the Indian Constitution came into effect on January 26, 1950. Since then, January 26 has been designated as “Republic Day.”
 Partition Horrors Remembrance Day: Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Saturday declared August 14 will be observed as ‘Partition Horrors Remembrance Day’ to acknowledge the pain undergone by Indians due to the partition of India in 1947.
Partition Horrors Remembrance Day: Prime Minister Narendra Modi on Saturday declared August 14 will be observed as ‘Partition Horrors Remembrance Day’ to acknowledge the pain undergone by Indians due to the partition of India in 1947.
Key Points:
-
The day commemorates the victims and sufferings of people during Partition of India.
-
The Union Home Ministry on 14th August 2021 evening issued a notification declaring that August 14 will be observed as Partition Horrors Remembrance Day.
-
Declaration of such a day would remind present and future generations of Indians of the pain and suffering faced by the people during the partition.
Aim:
-
The day was announced with the aim of reminding Indians the need of removing social divisions and disharmony.
-
It also seeks to further strengthen the spirit of oneness, social harmony and human empowerment.
About Partition:
-
The Partition of India was the division of British India[c] into two independent Dominions: India and Pakistan.
-
The Dominion of India is today the Republic of India (since 1950); while the Dominion of Pakistan was composed of what is known today as the Islamic Republic of Pakistan (since 1956) and the People's Republic of Bangladesh (since 1971).
-
The partition involved the division of two provinces, Bengal and Punjab, based on district-wide non-Muslim or Muslim majorities.
-
The partition was outlined in the Indian Independence Act 1947 and resulted in the dissolution of the British Raj, i.e. Crown rule in India.
The horrors of partition:
-
India attained its freedom from British rule on 15th August, 1947.
-
However, with the sweetness of freedom came also the trauma of partition leaving permanent scars on millions of Indians.
-
The partition displaced between 10 and 20 million people along religious lines, creating overwhelming refugee crises in the newly constituted dominions.
-
The partition caused amongst the largest migrations in human history.
-
Millions of families had to abandon their ancestral villages/towns/cities and were forced to find a new life as refugees.
-
The violent nature of the partition created an atmosphere of hostility and suspicion between India and Pakistan that affects their relationship to this day.
People In News
 Baba Saheb Purandare ji: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi paid rich tributes to Baba Saheb Purandare ji on entering the 100th year of his life.
Baba Saheb Purandare ji: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi paid rich tributes to Baba Saheb Purandare ji on entering the 100th year of his life.
About Baba Saheb Purandare ji:
-
Baba Sahib Purandare ji's full name is Balwant Moreshwar Purandare.
-
He was born in 1922.
-
He is a writer and theatre personality from Maharashtra.
-
His works are mostly based on the events related to the life of Shivaji, the 17th-century founder of the Maratha Empire; as a result he is termed as Shiv-Shahir ("Shivaji's bard").
-
He is mostly known for his popular play on Shivaji Jaanta Raja.
-
Baba Saheb Purandare also contributed to the Goa Mukti Sangram to the Dadar Nagar Haveli freedom struggle.
Awards:
-
In 2015, he was awarded with Maharashtra Bhushan Award, Maharashtra's highest civilian award.
-
Shri Purandare has been honored with Padma Vibhushan in 2019.
-
Madhya Pradesh Government also saluted him by awarding him Kalidas award.
Appointments:
 Kamlesh Kumar Pant: He is a 1993-batch IAS officer of Himachal Pradesh cadre, who has recently been appointed as the new chairman of National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA).
Kamlesh Kumar Pant: He is a 1993-batch IAS officer of Himachal Pradesh cadre, who has recently been appointed as the new chairman of National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA).
Highlights:
-
He was appointed by the Appointments Committee of the Union Cabinet.
-
The pharmaceutical pricing agency was currently headed by IAS officer Shubhra Singh, who was appointed to the post in 2018.
-
Singh has been repatriated to her cadre state Rajasthan, according to an order of the personnel ministry.
About Kamlesh Kumar Pant:
-
Pant was formerly the Principal Secretary (Revenue) in the government of Himachal Pradesh.
-
He was also the Financial Commissioner (Appeals) at Himachal Pradesh and the head of the Himachal Pradesh State Pollution Control Board.
About NPPA:
-
National Pharmaceutical Pricing Authority (NPPA) was founded on 29 August 1997.
-
NPPA is headquartered in New Delhi.
Additional News:
-
Meanwhile, the Appointments Committee also announced new additional secretaries in various ministries and departments.
-
Amrit Lal Meena has been appointed as Additional Secretary (Logistics), Department of Commerce, Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
-
Sudhir Garg and Jayant Sinha have been appointed as Additional Secretary, National Disaster Management Authority and Additional Secretary & Financial Advisor, Ministry of Information & Broadcasting, respectively.
Obtiruaries:
 Kasargod Patnashetti Gopal Rao: Commodore Kasargod Patnashetti Gopal Rao, a 1971 war hero and recipient of the Mahavir Chakra, passed away.
Kasargod Patnashetti Gopal Rao: Commodore Kasargod Patnashetti Gopal Rao, a 1971 war hero and recipient of the Mahavir Chakra, passed away.
About:
-
Rao was a recipient of the Veer Seva Medal also.
-
He played a key role in the war with Pakistan to liberate East Pakistan that is now Bangladesh.
-
He led a small task group of the Western Fleet and launched an offensive off the coast of Karachi as part of Operation Cactus Lily.
-
Notwithstanding the threat of air, surface and submarine attack, he led the group into enemy waters on the night of December 4, 1971.
 Neeraj Chopra: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has appoined Neeraj Chopra for banking fraud awareness campaign.
Neeraj Chopra: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has appoined Neeraj Chopra for banking fraud awareness campaign.
Key Points:
-
This campaign has been started by RBI to warn people against digital banking frauds.
-
The central bank has asked people to be a little cautious as doing so can protect them from a lot of troubles.
-
The campaign sees Chopra urging users to not divulge details like OTP, CVV number and ATM PIN in front of anyone.
-
The users should keep changing their online banking passwords and PIN numbers frequently and immediately block ATM card, credit card, debit card and/or prepaid card if one loses it.
-
Block your card if stolen, lost or compromised.
About Neeraj Chopra:
-
He is an Indian track and field athlete, competing in the javelin throw.
-
He is the Junior Commissioned Officer (JCO) in the Indian Army.
-
He is also the first track and field athlete who won IAAF World U20 Championships.
-
In 2016, he achieved under-20 world record of 86.48 m.
-
After Abhinav Bindra, he is the second Indian to win a Gold Medal at the Olympics.
-
He has also become the youngest-ever Indian gold medalist in the individual event and the first to won gold in his Olympic debut.
 Rekha Sharma: The Government of India (GoI) has given a three-year extension to Rekha Sharma as Chairperson of the National Commission for Women (NCW).
Rekha Sharma: The Government of India (GoI) has given a three-year extension to Rekha Sharma as Chairperson of the National Commission for Women (NCW).
She will serve for another three years term with effect from August 07, 2021, or till the age of 65 years or until further orders whichever is the earliest.
About Rekha Sharma:
-
Rekha Sharma first assumed the charge as Chairperson of NCW on August 7, 2018.
-
The 57-year-old Sharma has been associated with the Commission as a member since August 2015 and held the additional charge as the chairperson from September 29, 2017, before becoming its regular chief.
-
She has been a vocal advocate of gender sensitisation of police personnel since they are the first point of contact for victims.
About NCW:
-
The National Commission for Women (NCW) was set up as statutory body in January 1992 under the National Commission for Women Act, 1990 ( Act No. 20 of 1990 of Govt. of India).
-
NCW was established on 31 January 1992 under the provisions of the Indian Constitution, as defined in the 1990 National Commission for Women Act.
-
It is concerned with advising the government on all policy matters affecting women.
-
They have also discussed police abuses against women.
-
The commission regularly publishes a monthly newsletter, Rashtra Mahila, in both Hindi and English.
Objectives:
-
The objective of the NCW is to represent the rights of women in India and to provide a voice for their issues and concerns.
-
The subjects of their campaigns have included dowry, politics, religion, equal representation for women in jobs, and the exploitation of women for labour.
Places In News
.jpg) Rajiv Gandhi Award for Excellence in Information Technology (IT): The Government of Maharashtra on 10th August, 2021, has decided to name an award after former Prime Minister of India Rajiv Gandhi.
Rajiv Gandhi Award for Excellence in Information Technology (IT): The Government of Maharashtra on 10th August, 2021, has decided to name an award after former Prime Minister of India Rajiv Gandhi.
Highlights:
-
It was decided to announce this award at a meeting of IT department on July 7.
-
Creation of the new award was announced days after the central government renamed the Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna Award as Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award.
Key Details:
-
A new award named “Rajiv Gandhi Award for Excellence in Information Technology (IT)” will be given to institutes doing remarkable work in the field of information technology.
-
Minister of State for Information and Technology Satej Patil said that the award would be announced on August 20, birth anniversary of the former Prime Minister.
-
This award is a lasting tribute to Late Shri Rajiv Gandhi for his pioneering work in the technology sector in India.
-
The State government will talk to bodies such as NASSCOM to finalise the modalities of the award.
-
It will be given to the companies or institutions which excel in the field with their new ideas and innovations.
-
The award will be given out to them by Maharashtra Chief Minister Uddhav Thackeray.
Who will propose the award?
-
The Maharashtra IT Corporation Limited (MAHA-IT) which is a state government enterprise has been appointed a nodal agency to propose the newly constituted award.
About Rajiv Gandhi:
-
Rajiv Ratna Gandhi was an Indian politician who served as the sixth prime minister of India from 1984 to 1989.
-
At 40, Mr. Rajiv Gandhi was the youngest Prime Minister of India, perhaps even one of the youngest elected heads of Government in the world.
-
He took over as the PM of India after the assassination of his mother, Prime Minister Indira Gandhi in 1984.
-
He was born on August 20, 1944, in Bombay.
-
He was just three when India became independent and his grandfather Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru became Prime Minister.
-
He died in a tragic bomb blast on 21st May, 1991 at Sriperumbudur in Tamil Nadu.
-
As the PM of India, he began leading in a direction significantly different from his mother's socialism.
-
He improved bilateral relations with the United States — long strained owing to Indira's socialism and close friendship with the USSR .
-
He expanded economic and scientific cooperation.
-
The Indo-Sri Lanka Peace Accord was signed by Rajiv Gandhi and the Sri Lankan President J.R.Jayewardene, in Colombo on 29 July 1987.
-
He increased government support for science and technology and associated industries, and reduced import quotas, taxes and tariffs on technology-based industries, especially computers, airlines, defence and telecommunications.
-
He introduced measures significantly reducing the License Raj, allowing businesses and individuals to purchase capital, consumer goods and import without bureaucratic restrictions.
About Maharashtra:
-
Maharashtra is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau.
-
It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, the Indian states of Karnataka and Goa to the south, Telangana to the southeast and Chhattisgarh to the east, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh to the north, and the Indian union territory of Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the north west.
-
It was formed on 1 May 1960.
-
It was formed by merging the western and south-western parts of the Bombay State, Berar and Vidarbha, and the north-western parts of the Hyderabad State and splitting Saurashtra (in present-day Gujarat) by the States Reorganisation Act.
-
Its capital is Mumbai.
-
The Chief Minister and the Governor of Maharashtra are Uddhav Thackeray and Bhagat Singh Koshyari respectively.
 eNagar Mobile Application and Portal: Gujarat Chief Minister, Vijay Rupani recently launched eNagar mobile application and portal.
eNagar Mobile Application and Portal: Gujarat Chief Minister, Vijay Rupani recently launched eNagar mobile application and portal.
Key Points:
-
The eNagar covers 10 modules with 52 services including property tax, professional tax, water & drainage, Complaints and grievance redressal, building permission, fire and emergency services.
-
Gujarat Urban Development Mission has been appointed as a nodal agency for eNagar project.
-
Total 170 locations including 162 municipalities and 8 Municipal Corporations are covered under the eNagar project.
About Gujarat:
-
Gujarat is a state on the western coast of India most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula.
-
The state is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west.
-
Its capital city is Gandhinagar.
-
The Governor and Chief Minister of Gujarat are Acharya Devvrat and Vijay Rupani respectively.
 Implementation of NEP-2020: Karnataka has become the first state in the country to issue the order with regard to the implementation of the National Education Policy-2020.
Implementation of NEP-2020: Karnataka has become the first state in the country to issue the order with regard to the implementation of the National Education Policy-2020.
Key Points:
-
The state government has issued an order on the implementation of NEP-2020 with effect from the current academic year 2021-2022.
-
The implementation will be done as per the guidelines of the NEP.
Additional Info:
Earlier on July 29, on the first anniversary of NEP, Prime Minister Narendra Modi had launched SAFAL (STRUCTURED Assessment For Analysing Learning), a competency-based assessment for grades 3,5, and 8 introduced by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE).
About the policy:
This policy seeks to entirely overhaul the system through various reforms: A single regulator to oversee higher education; no more MPhil courses before PhD; fixed fees for public and private institutions; students can choose between three and four-year undergraduate courses; multiple entries and exit points in degree courses.
About Karnataka:
-
It is a state in the south western region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganization Act.
-
Originally known as the State of Mysore, it was renamed Karnataka in 1973.
-
It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, Goa to the northwest, Maharashtra to the north, Telangana to the northeast, Andhra Pradesh to the east, Tamil Nadu to the southeast, and Kerala to the south.
-
It is the only southern state to have land borders with all of the other 4 southern Indian sister states.
-
Its capital city is Bangalore.
-
The current Chief Minister and Governor of Karnataka are Basavaraj Bommai and Thawar Chand Gehlot respectively.
 MoU with Walmart Vriddhi: The Haryana government recently signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with ‘Walmart Vriddhi’ and ‘Haqdarshak’.
MoU with Walmart Vriddhi: The Haryana government recently signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with ‘Walmart Vriddhi’ and ‘Haqdarshak’.
Key Details:
-
The MoU was signed by the Haryana Government to create a pathway for Indian MSMEs’ products to move to the international markets.
-
It was signed in the presence of Haryana Deputy Chief Minister Dushyant Chautala, Vikas Gupta, MSME Department Director-General, the Indian government, Nitin Dutt from Walmart Vriddhi, and Aniket Doegar (CEO of Haqdarshak).
-
To promote MSMEs apart from large industries, many important concessions have been given to investors in ‘Haryana Enterprises and Employment Policy-2020’.
-
This move seeks to bring a big opportunity for the MSME sector, as the products of traditional weavers of rural areas, haldlooms and handicrafts will be displayed in 24 countries.
-
These products will be available in 10,500 stores under 48 banners.
About Haryana:
-
Haryana is a North Indian state surrounding New Delhi on 3 sides.
-
It is located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 November 1966 on a linguistic basis.
-
It is bordered by Himachal Pradesh to the north-east, by river Yamuna along its eastern border with Uttar Pradesh, by Rajasthan to the west and south, and Ghaggar-Hakra River flows along its northern border with Punjab. Since Haryana surrounds the country's capital Delhi on three sides (north, west and south), consequently a large area of Haryana is included in the economically-important National Capital Region for the purposes of planning and development.
-
The capital of Haryana is Chandigarh.
-
The current Chief Minister and Governor of Haryana are Manohar Lal Khattar and Bandaru Dattatraya respectively.
 ATC towers in Ladakh: The Indian Air Force (IAF) has constructed one of the world’s highest mobile Air Traffic Control (ATC) towers at the Advanced Landing Ground in the Ladakh region.
ATC towers in Ladakh: The Indian Air Force (IAF) has constructed one of the world’s highest mobile Air Traffic Control (ATC) towers at the Advanced Landing Ground in the Ladakh region.
Key Details:
The ATC towers controls operations of the fixed-wing aircraft and helicopters operating in the eastern Ladakh region.
-
Meanwhile, India is also deliberating into multiple options to develop airfields in eastern Ladakh, including Nyoma, Fukche, and Daulat Beg Oldi (DBO).
-
The IAF has already deployed the Igla man-portable air defence missiles to counter any aerial attack by any opponent aircraft.
-
It has also regularly been deploying fighter aircraft including MiG-29s and Rafale in eastern Ladakh to carry out operations where there has been disengagement of troops at two locations including Pangong Tso and Gogra heights but both sides have not de-escalated.
About Ladakh:
-
Ladakh is a region administered by India as a union territory, and constituting a part of the larger region of Kashmir, which has been the subject of dispute between India, Pakistan, and China since 1947.
-
Until 2019, Ladakh was a region of the state of Jammu and Kashmir.
-
In August 2019, the Parliament of India passed an act by which Ladakh became a union territory on 31 October 2019. The capital of Ladakh is Leh, Kargil.
-
The current Lieutenant Governor of Ladakh is Radha Krishna Mathur.
Science and Technology
 IIGF - 2021: Shri Anil Kumar Jain, the CEO, National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI), Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY) and the Chairman of Coordination Committee, India Internet Governance Forum 2021 (IGF), announced the launch of India Internet Governance Forum (IIGF) - 2021.
IIGF - 2021: Shri Anil Kumar Jain, the CEO, National Internet Exchange of India (NIXI), Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY) and the Chairman of Coordination Committee, India Internet Governance Forum 2021 (IGF), announced the launch of India Internet Governance Forum (IIGF) - 2021.
Highlights:
-
The Ministry of Electronics and Information and Technology (MeitY) informed that India’s first IIGF will be held for three days starting from October 20, 2021.
-
The launch of IIGF - 2021 was announced on 9th August 2021 in a Press Conference, organized at Electronics Niketan, New Delhi.
-
The theme of this year's meeting is “Inclusive Internet for Digital India”.
-
With this announcement, the Indian chapter of the United Nations based forum namely Internet Governance Forum has begun.
-
Pre-IIGF engagement events will also start from August 2021 across colleges and universities.
-
Pre-events will be organized with the aim of engaging students and youth to participate in main event in October.
About IIGF:
-
Full form of IIGF is 'India Internet Governance Forum.'
-
IIGF is an Indian version of Internet Governance Forum under the United Nations.
-
It is an Internet Governance policy discussion platform to bring representatives together from various groups, considering all at par to discuss public policy issues related to the Internet.
-
This mode of engagement is referred to as the multi-stakeholder model of Internet Governance, which has been the key feature for the Internet's success.
-
The multi-stakeholder concept is well adopted by IGF (Internet Governance Forum) under United Nations and by Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN).
IIG Coordination Committee:
-
Among the key members of the India Internet Governance coordination committee include Anil Kumar Jain who is named chairman, TV Ramchandran as Vice-Chairman, Jaijeet Bhattacharya as Vice Chairman, Rajat Moona as Vice-Chairman.
-
There are also about 12 members representing the government, civil society, industries, trusts as members.
About Internet Governance Forum (IGF):
-
The IGF is a multistakeholder governance group for policy dialogue on issues of Internet governance.
-
It brings together all stakeholders in the Internet governance debate, whether they represent governments, the private sector or civil society, including the technical and academic community, on an equal basis and through an open and inclusive process.
-
The establishment of the IGF was formally announced by the United Nations Secretary-General in July 2006.
-
It was first convened in October–November 2006 and has held an annual meeting since then.
 Marburg Disease: The World Health Organization (WHO) recently said that Guinea has confirmd West Africa’s first case of Marburg disease.
Marburg Disease: The World Health Organization (WHO) recently said that Guinea has confirmd West Africa’s first case of Marburg disease.
Key Points:
-
Marburg disease is a lethal virus that’s related to Ebola and, like Covid-19, passed from animal hosts to humans.
-
This virus, which is carried by bats has a fatality rate of up to 88 %.
-
The virus was found in samples taken from a patient who died on August 2 in southern Gueckedou prefecture.
-
The discovery comes just two months after the WHO declared an end to Guinea's second outbreak of Ebola, which started last year and claimed 12 lives.
-
Dr Matshidiso Moeti, WHO Regional Director for Africa said that the potential for the Marburg virus to spread far and wide needed to stop it in its tracks.
-
WHO considers the threat “high” at the national and regional level, but “low” globally.
-
Previous outbreaks and sporadic cases have been reported in South Africa, Angola, Kenya, Uganda, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
-
But this is the first time the virus has been detected in West Africa.
About Marburg Virus:
-
Marburg virus is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the Filoviridae family of viruses.
-
It is a member of the species Marburg marburgvirus, genus Marburgvirus.
-
Marburg virus causes Marburg virus disease in humans and other primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever.
-
The Marburg virus is usually associated with exposure to caves or mines housing colonies of Rousettus bats.
-
The virus is considered to be extremely dangerous.
-
Once caught by a human, it is spread through contact with bodily fluids of infected people, or with contaminated surfaces and materials.
-
The disease begins suddenly, with a high fever, severe headache and discomfort.
-
Although there are no approved vaccines or antiviral treatments, oral or intravenous rehydration and treatment of specific symptoms improve survival rates.
 World Biofuel Day: World Biofuel Day is observed on August 10 every year.
World Biofuel Day: World Biofuel Day is observed on August 10 every year.
Key Points:
-
The day is celebrated to raise awareness about the importance of non-fossil fuels as an alternative to conventional fossil fuels and highlight the various efforts made by Government in the biofuel sector.
-
The development of biofuels is in sync with schemes such as Swach Bharat Abhiyan and Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
-
World Biofuel Day was first observed by the Ministry of Petroleum and Gas in August 2015.
Theme of 2021:
-
The theme of 2021 has been announced to be "promotion of biofuels for a better environment".
-
The focus will be squarely on using biofuels in an optimum manner while ensuring that their adverse effects on the environment are kept at a minimum.
-
Raising awareness of the availability of biofuels as effective replacements for traditional fuels will also be another important objective.
Background:
-
In June 2021, PM Modi joined the World Environment Day event via video conferencing and declared “biofuels for a better environment” as the theme for this year’s World Environment Day.
History:
-
In India, it is being observed by the Ministry of Petroleum & Natural Gas since 2015.
-
The day honours the research experiments by Sir Rudolf Diesel (inventor of the diesel engine).
-
It was just one day before, on August 9 in 1893, he ran an engine with peanut oil.
-
His experiments predicted that vegetable oil would replace fossil fuels in the subsequent century to fuel various mechanical engines.
-
To commemorate this achievement, the date was chosen to observe World Biofuel Day.
What is Biofuel?
-
Biofuels are environmentally friendly fuels whose use would go a long way in reducing carbon emissions.
-
They are created through renewable biomass resources (plant, or algae material, or animal waste) and therefore make a strong case for sustainable development.
-
They are renewable, biodegradable, and sustainable sources of energy.
-
As such biofuels will help meet the energy requirements of the 21st-century world without damaging the environment in the process.
-
Broadly Biofuels are of two types-
-
Primary Biofuels: The organic materials which are used in an unprocessed form such as fuelwood, wood chips and pellets, primarily for heating, cooking, electricity production.
-
Secondary Biofuels: The materials which result from the processing of biomass such as liquid fuels such as ethanol and biodiesel.
-
Biofuels are generally classified into three categories. They are
-
First-generation biofuels – First-generation biofuels are made from sugar, starch, vegetable oil, or animal fats using conventional technology. Common first-generation biofuels include Bioalcohols, Biodiesel, Vegetable oil, Bioethers, Biogas.
-
Second-generation biofuels – These are produced from non-food crops, such as cellulosic biofuels and waste biomass (stalks of wheat and corn, and wood). Examples include advanced biofuels like biohydrogen, bioethanol.
-
Third-generation biofuels – These are produced from microorganisms like algae.
Benefits of Biofuel:
-
Cleaner environment
-
Employment generation
-
Reduction of import dependence
-
Additional income to farmers
 Indo-Bhutan Space odyssey: Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is set to launch a Bhutanese satellite in December 2021.
Indo-Bhutan Space odyssey: Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is set to launch a Bhutanese satellite in December 2021.
Key Details:
-
The development of the INS-2B satellite of Bhutan is being underway by four Bhutanese engineers who are being trained by ISRO.
-
The space engineers from Bhutan’s department of information technology and telecom were trained from December 28 to February 25, 2021 at ISRO’s UR Rao Satellite Centre in Bengaluru.
About the Training:
-
The training covered theoretical and technical aspects and included visits to laboratories and test facilities.
-
With the first phase of the satellite development already done, the second phase of training will focus on finishing touches of the satellite.
About Indo-Bhutan Space odyssey:
-
Space odyssey is an event showcasing India’s achievements in space technology.
-
The event was organized by the Indian embassy in Bhutan as part of India’s 75th year of Independence – ‘Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav’.
-
ISRO’s Scientific Secretary R Umamaheswaran, who was the keynote speaker at the event, said that ISRO plans to fly the satellite by end of this 2021 in the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) mission.
Background:
Indo-Bhutan Space Cooperation:
-
India and Bhutan have been engaged in space cooperation with a ground Earth station for South Asia Satellite (SAS) that was inaugurated in Thimphu, Bhutan during Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s visit in August 2019.
-
The SAS was launched by India in 2017 as a gift to the countries in the South Asia region, including Bhutan.
-
Under the project, New Delhi has offered increased bandwidth on an additional transponder on the satellite for Bhutan as a gift as per the country’s requirement.
About ISRO:
-
ISRO is an abbreviation for the Indian Space Research Organization.
-
It is the space agency of the Government of India (GoI) and was formed in 15 august 1969.
-
It superseded the erstwhile “Indian National Committe For Space Research” (INCOSPAR) which was established in 1962 by the efforts of Independent India's first prime minister‚ Jawaharlal Nehru‚ and his close aide and scientist Vikram Sarabhai. In 1972, the Government of India had set up a Space Commission and the Department of Space (DOS), bringing ISRO under the DOS.
-
ISRO then embarked on its mission to provide the Nation space based services and to develop the technologies to achieve the same independently. Its vision is to “harness space technology for natural development while pursuing space science research & planetary exploration”.
-
ISRO built India’s first Satellite Aryabhata.
-
It is headquartered in Bangalore, India.
-
The current Chairman of ISRO is K Sivan.
ISRO’s Odyssey:
-
Over 342 satellites of foreign countries sent to space by ISRO.
-
India scripted history, as the total number of customer satellites from foreign countries placed in orbit by PSLV reached 342 from more than 34 countries.
-
On 28th February 2021, India’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle PSLV-C51 successfully launched Amazonia-1 along with 18 co-passenger satellites from Satish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR, Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh.
-
After a flight of about 17 minutes, the vehicle injected the Amazonia-1 into its intended orbit, and in the succeeding 1 hour 38 minutes other 18 co-passenger satellites were injected in a predetermined sequence.
Note: The Aryabhata spacecraft, named after the famous Indian astronomer, was India's first satellite. It was completely designed and fabricated in India and launched by a Soviet Kosmos-3M rocket from Kapustin Yar on April 19, 1975.
Sports
 Tokyo Olympics 2020: The 32nd edition of the Olympics has come to an end after a jam-packed action of 15 days.
Tokyo Olympics 2020: The 32nd edition of the Olympics has come to an end after a jam-packed action of 15 days.
Highlights:
-
The Tokyo 2020 Olympics were declared closed on Sunday by IOC chief Thomas Bach, who called the pandemic-delayed Games the "most challenging Olympic journey.
-
The theme of the ceremony was unitedly moving forward despite the challenges thrown at the world.
-
With a moment of silence, the ceremony then remembered all the people who lost their lives during the pandemic, members of the Israeli delegation killed during the 1972 Munich Games massacre, the 2011 earthquake, Tsunami and the nuclear disaster.
-
The next Olympics will be held in Paris, France in 2024.
-
The Olympic flag was passed to Paris mayor Anne Hidalgo.
-
Wrestler Bajrang Punia led the Indian contingent out during the parade of athletes during the closing ceremony of Tokyo 2020.
Background:
-
The Tokyo Olympics 2020 or officially the Games of the XXXII Olympiad was held from July 23 to August 8, 2021, in Tokyo, Japan.
-
The quadrennial event was earlier scheduled to be held from July 24 to August 9 in the year 2020 but was postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
-
Olympic Games for the second time, the first being in 1964, this will be the fourth Olympic event to be conducted in Japan, including two Winter Olympics in 1972 and 1998.
-
The Tokyo 2020 Olympic Games mascot was named Miraitowa.
-
It is a tribute to both the respected tradition and modern innovation of Japanese culture.
-
The Tokyo Olympics 2020 mascot has a personality inspired by the Japanese proverb, “learn from the past and develop new ideas”.
Spirit of the whole Olympic movement:
-
One moment summed up the spirit of the whole Olympic movement that was the men's high jump.
-
Qatar's Mutaz Barshim and Italy's Gianmarco Tamberi, both of whom have returned from the same career-threatening injury, agreed to share the gold medal and both exploded in joy when officials agreed.
Key Highlights of the winners:
-
A record 83 nations reached finals, there were 43 teams on the podium and 23 won gold.
-
There were three world records, 12 Olympic records, 28 area records and 151 national records set.
-
The official rankings and medal tally of top ten countries from the Tokyo Olympics 2020 are as follows:
| Rank | Team/NOC | Gold | Silver | Bronze | Total | Rank by Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States of America | 39 | 41 | 33 | 113 | 1 |
| 2 | People's Republic of China | 38 | 32 | 18 | 88 | 2 |
| 3 | Japan | 27 | 14 | 17 | 58 | 5 |
| 4 | Great Britain | 22 | 21 | 22 | 65 | 4 |
| 5 | ROC | 20 | 28 | 23 | 71 | 3 |
| 6 | Australia | 17 | 7 | 22 | 46 | 6 |
| 7 | Netherlands | 10 | 12 | 14 | 36 | 9 |
| 8 | France | 10 | 12 | 11 | 33 | 10 |
| 9 | Germany | 10 | 11 | 16 | 37 | 8 |
| 10 | Italy | 10 | 10 | 40 | 40 | 7 |
India's Olympics Medals:
With seven medals, including one gold, two silver, and four bronze medals, in the Tokyo Games, India has registered its best-ever performance in the Olympics.
 World Athletics Rankings: The Indian javelin thrower, Neeraj Chopra, has gained 14 places to become world No. 2 in the latest World Athletics Rankings after his sensational performance in the Tokyo Olympics 2020.
World Athletics Rankings: The Indian javelin thrower, Neeraj Chopra, has gained 14 places to become world No. 2 in the latest World Athletics Rankings after his sensational performance in the Tokyo Olympics 2020.
Highlights:
-
Neeraj Chopra has been ranked second with his score of 1315.
-
He is only behind German athlete Johannes Vetter who is having the score of 1396.
-
Neeraj, on August 7, 2021, had scripted history by becoming the first Indian to win gold in track and field in the Olympics.
-
Chopra threw the javelin to a distance of 87.58m and picked the yellow metal at the Tokyo Games.
-
His historic golden throw in the Olympics has also been listed as one of the 10 magical moments of athletics (track and field) in the Tokyo Olympics by the World Athletics.
-
Following his win, Neeraj has also become the most followed track & field athlete in the world with number of followers on Instagram at 3.2 million.
About Neeraj Chopra:
-
He is an Indian track and field athlete, competing in the javelin throw.
-
He is the Junior Commissioned Officer (JCO) in the Indian Army.
-
He is also the first track and field athlete who won IAAF World U20 Championships.
-
In 2016, he achieved under-20 world record of 86.48 m.
-
After Abhinav Bindra, he is the second Indian to win a Gold Medal at the Olympics.
-
He has also become the youngest-ever Indian gold medalist in the individual event and the first to won gold in his Olympic debut.
 Javelin Throw Day: The Athletics Federation of India (AFI) has decided to name the day of 7th August ‘Javelin Throw Day’ in India to honor Neeraj Chopra’s first historic Olympic gold.
Javelin Throw Day: The Athletics Federation of India (AFI) has decided to name the day of 7th August ‘Javelin Throw Day’ in India to honor Neeraj Chopra’s first historic Olympic gold.
Key Points:
-
The 23-year-old, Haryana-based Neeraj Chopra made a history by winning the gold medal in the javelin throw at Tokyo Olympics 2020.
-
No athletics has achieved a medal for over 100 years.
-
Neeraj Chopra threw his javelin a distance of 87.58 metres
-
He is India’s second individual Olympic gold medallist after Abhinav Bindra.
-
AFI’s bid to name August 7 as Javelin Throw Day is an attempt to attract more youth towards the sport.
Note: The AFI started National Open Javelin Throw Championships in 2018 and its third edition is scheduled in October this year.
About AFI:
-
The Athletics Federation of India is the apex body for Athletics in India and affiliated to the IAAF, AAA and Indian Olympic Association.
-
The AFI came into existence in 1946.
-
It was earlier called as Amateur Athletic Federation of India (AAFI).
-
It is headquartered in New Delhi.
-
The current President of AFI is Adille J Sumariwalla and Secretary-General is Ravinder Chaudhry.
 ICC players of the month for July: West Indies skipper Stafanie Taylor and Bangladesh all-rounder Shakib Al Hasan was named the ICC Player of the Month for July in men’s and women’s categories respectively.
ICC players of the month for July: West Indies skipper Stafanie Taylor and Bangladesh all-rounder Shakib Al Hasan was named the ICC Player of the Month for July in men’s and women’s categories respectively.
-
Shakib was nominated alongside West Indies’ Hayden Walsh Jr and Australia’s Mitchell Marsh.
About Stafanie Taylor:
-
Stafanie Taylor was the standout performer for West Indies in the limited-overs series against Pakistan.
-
She was nominated for the award alongside teammate Hayley Matthews and Pakistan’s Fatima Sana, but her all-around performance in the series helped her claim the most votes.
About Shakib Al Hasan:
-
Shakib’s contributions in all three formats of the game helped Bangladesh win their series against Zimbabwe last month.
-
He had scored an unbeaten 96 in Bangladesh’s three-wicket win over Zimbabwe in the second ODI at the Harare Sports Club.
-
In the T20Is, Hasan took three wickets at an economy rate of seven, leading his country to a series win against Zimbabwe.
-
He is also the top all-rounder in the latest ICC men’s T20 Rankings.
 Durand Cup: Durand Cup is Asia’s oldest and world’s third oldest football tournament.
Durand Cup: Durand Cup is Asia’s oldest and world’s third oldest football tournament.
Highlights:
-
It is all set to make a comeback, after a year’s gap. The 130th edition of the Durand Cup is scheduled to be held in and around Kolkata from September 05 to October 03, 2021.
-
Due to the Covid-19 pandemic, the competition was cancelled last season.
History of Durand Cup:
-
The prestigious tournament is named after Mortimer Durand, who was then the Foreign Secretary in charge of India.
-
This tournament was first held in 1888, at Dagshai (Himachal Pradesh).
-
The tournament was a conscious way to initially maintain health and fitness amongst the British troops but was later opened to civilians and currently is one of the leading sports events in the world.
-
Mohun Bagan and East Bengal are the most successful teams in the history of the Durand Cup winning it sixteen times each.
-
The winning team is presented with three trophies ie the President’s Cup (first presented by Dr Rajendra Prasad), the Durand Cup (the original challenge prize – a rolling trophy) and the Shimla Trophy (first presented by citizens of Shimla in 1903 and since 1965, a rolling trophy).
 2020 Summer Paralympics Games: Shri Anurag Thakur, Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports and Nisith Pramanik, Minister of State, Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports on August 12, 2021, addressed virtually and sent a 54-member, largest ever Indian contingent to Tokyo Paralympic Games.
2020 Summer Paralympics Games: Shri Anurag Thakur, Union Minister for Youth Affairs and Sports and Nisith Pramanik, Minister of State, Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports on August 12, 2021, addressed virtually and sent a 54-member, largest ever Indian contingent to Tokyo Paralympic Games.
Highlights:
-
An 88 member Indian contingent including 54 athletes were given a formal send-off at Indira Gandhi International Airport.
-
This is India's largest-ever contingent to the Paralympic Games in Tokyo
-
The 54-member Indian contingent consists of 54 para-sportspersons across 9 sports disciplines.
-
The 2020 Summer Paralympics Games are scheduled to be held in Tokyo, Japan from August 24 to September 05, 2021.
Background:
-
Minister Shri Anurag Singh Thakur, 03 AUG 2021 had launched the Paralympic theme song.
-
The song “Kar De Kamaal Tu” is composed and sung by a Divyang cricket player Sanjeev Singh who is a resident of Lucknow.
-
The idea of Paralympic Committee of India was to get the song composed from the Divyang community as a mark of inclusiveness.
-
The lyrics of the song motivate not only the athletes but all the people with any form of disability to never underestimate themselves and what they have in them to create wonders.
Current Affairs September 29 to October 05
National
Delhi-Meerut PKG-3 : It refers to Delhi-Meerut Package-3. Indian Road Transport and Highways Union Minister Nitin Gadkari inaugurated the 22.27 kilometre Delhi-Meerut PKG-3 which connects Dasna in Ghaziabad to Hapur in Western Uttar Pradesh (UP) state built with cost of RS 1,058 crores.
The significance of this project is that it will help in decongesting National Capital Region (NCR) and bring significant reduction in pollution level. It will also lead to reduction in travel time by more than an hour. The development of this highway will lead to the development of this area.
The Delhi-Meerut PKG-3 has a six-lane NH 24 section with 2+2 lane service roads on both side from Dasna to Hapur and a 4.68km-long six-lane elevated corridor at Pilkhuwa. This 4.68-km long 6-lane elevated corridor at Pilkhuwa has been conferred Gold Medal for innovation in construction technology and Pilkhuwa Viaduct has also been awarded as outstanding concrete structure of western UP. This highway is the country's first 16 lane express-highway. The project involves construction of several underpasses, a bridge across Upper Ganga Canal, seven new minor bridges and a flyover at the Hapur bypass. It features 11 vehicle and two pedestrian underpasses, two pedestrian over bridges and six major and 105 minor junctions respectively.
The President’s Colours Award : It is the highest military honour for an armed forces organisation. It is awarded in recognition of exceptional service rendered by to the nation, both during peace and hostile.
President Ram Nath Kovind on Saturday handed over the prestigious President’s Colours Award to the Corps of Army Air Defence at Gopalpur in Odisha’s Ganjam district.
During World War II, the Air Defence troops participated in various operations like Burma campaign, Siege of Imphal and Kohima, recapture of Rangoon, operations in Arakans, Myitkiyina, Hongkong, Singapore, Malaya, Bahrain, Iraq and Persia and won multiple gallantry awards namely four Military Crosses, one Medal of the British Empire, seven Indian Distinguished Service Medals and two Orders of the British Empire, said sources.
The Air Defence has been in existence since 1940 as a part of Corps of Artillery however, as an independent arm, it got recognition in 1994. The Corps of Army Air Defence has been awarded with two Ashok Chakras, two Kirti Chakras, 20 Vir Chakras, nine Shauryas Chakras, 113 Sena Medals and 55 Mention-in-Despatches in addition to four Honour Titles awarded during 1971 Indo-Pak war.
INS Khanderi : It is India's second Scorpene-class attack submarine It is a diesel-electric attack submarine which was designed by French naval defence and energy company DCNS and manufactured at Mazagon Dock Limited in Mumbai.
India's second Scorpene-class attack submarine INS Khanderi was commissioned by Defence Minister Rajnath Singh on Saturday and is expected to increase the country's maritime combat lethality by several folds. It was induced into Indian Navy only after it successfully cleared all the rigorous sea trials and tests in over last two and a half years. This state-of-the-art submarine has been built with such a technology that reduces its noise when it is under the sea. It can roll-in a crew of 36 members.
Its name and features are inspired by the fish named 'Kanneri'which is found in Arabian Sea. The fish is known for hunting while swimming close to the bottom of the ocean using the barbells to find their prey. The fish uses its long serrated saw to kill and shred their prey before eating it.
INS Khanderi is fully weaponised to attack its enemies. It is equipped with a set of missiles and torpedoes that can be fired upon detecting enemy targets. It has a sonar suite that enables long-range detection and classification of targets. The submarine's warfare capability comprises a cluster of integrated advanced weapons and sensors. It has undertaken multiple torpedo and missile firing trials to validate its fighting capability.
Commerorative Coins : These are coins that are released to mark some special events such as birth anniversaries of popular historical figures. These coins sport a distinct desigh to signify the occasin on which they are issued. The lower denomination coins are used for general circulation whereas higher denomination coins are usually used for collection purposes. They usually contain some gold and silver in them. These are Non-circulating legal tender (NCLT). As per the law, commemorative coins cannot be used legally unless notified.
PM Narendra Modi released commemorative Rs 150 coin on Mahatma Gandhi's 150th birth anniversary. He had also released a commemorative coin of Rs.350 denomination marking birth anniversary of Guru Gobind Singh and a commemorative coin of Rs.100 in honour of the former prime minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee, In 2018.
The first commemorative coin with an image of the first Prime Minister of India Jawaharlal Nehru in India was issued in 1964 to commerorate his birth anniversary.
International
Nizam Funds case : Nizam VII, Mir Osman Ali Khan the last ruler of Hyderabad had filed a case in 1954 to recover the deposited £1 million with Pakistan's high commissioner to the United Kingdom, Habib Ibrahim Rahimtoola, in 1948. The money was transferred to Rahimtoola’s account in UK’s National Westminster Bank from the state of Hyderabad’s bank account. Pakistan refused to give it back. The descendants of Nizam VII- Mukarram Jah (Titular Nizam VIII) and his younger brother Muffakham Jah joined hands with the Indian government and laid claim to the amount. Pakistan disputed the claim by stating that the money was for the payment of supplying weapons to Hyderabad while the Nizam’s descendants said that they were the beneficiary owners of the fund, as it was given to them by their grandfather as a gift in a trust that was set up in April 1963. The Nizam’s descendants had attempted to go for an out-of-court settlement with Pakistan over the dispute in 2008 but there was no response from Pakistan. The case remained dead till 2013.
The dispute started around the time of partition. In 1948, when the Nizam of Hyderabad Asaf Jah sent £1 million and one Ginni to the then Pakistan High Commissioner’s London account as a fund for "trust for safekeeping" of Hyderabad from India if there were an invasion. At that time, the princely state of Hyderabad was not under the Indian government. Hyderabad was annexed in 1948. The Pakistan government had claimed the ownership of the fund and had filed a case against Mukarram Jah in the UK court in 2013. Both India and Pakistan fought a decade-long legal battle.
Finally, on Wednesday, the UK High Court dismissed Pakistan’s claims and granted Mukarram Jah, the titular Nizam of Hyderabad, the ownership of a fund which has been in dispute for over 70 years which now amounts to £35 million. The judgement completely ruled out Pakistan’s claims over the amount and rejected its arguments that the dispute was non-justiciable and that the doctrine of illegality somehow barred recovery or that the claims of other parties were time-barred.
Taliban and U.S. peace envoy meet: US peace envoy Zalmay Khalilzad and the Taliban delegation led by Mullah Abdul Ghani Baradar, a co-founder of the movement that was ousted in 2001 by the US-led coalition met for the first time since "Dead Deal". The meeting is important as the United States seeks an exit from Afghanistan's 18-year war. A high-level Taliban delegation met Qureshi as part of a push to revive the Afghan peace process.
Taliban : It is an organization who refer to themselves as the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. They are a Sunni Islamic fundamentalist political movement and military organization in Afghanistan currently waging war within that country. Since 2016, the Taliban's leader is Mawlawi Hibatullah Akhundzada.
Environment
Typhoon ‘Mitag’ : The name Mitag has been used to name three tropical cyclones in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. It is categorised by Taiwan's weather bureau as at the second-strongest typhoon level. It is bearing down on northern Taiwan, where it is expected to bring high winds and heavy rain. Warnings have been issued for parts of parts of island’s east and north, including the capital, Taipei. As per the Taiwan’s weather bureau reperts were that it was expected to approach the coast of Yilan county with maximum winds about 27 kilometres per hour with winds gusting at up to 162 kilometres per hour (100 mph). After passing over Taiwan, the typhoon is expected to approach China's eastern city of Shanghai, then weakening as it moves toward South Korea and Japan.
Typhoons : A typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere. This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, and is the most active tropical cyclone basin on Earth, accounting for almost one-third of the world's annual tropical cyclones.
Brain-shrinking killer fungus : It is also known as Poison Fire Coral. It is one of the world's deadliest fungus. It is a bright orange fungus. It is rationally found in mountains of Japan and South Korea where it caused a number of deaths. It is the only fungus that can infect people by its toxins absorbing through people's skin. Touching the fungus could lead to organ failure and brain nerve damage. Symptoms of infection can lead to brain shrinking, dermatitis and a fever.
The Poison Fire Coral fungus was found by photographer Ray Palmer while he was exploring rainforest in Redlynch, in Cairns in Queensland. Dr Barrett ran DNA tests to confirm the discovery and according to it was for the first time that this deadly fungus has been discovered in Australia.
Indian Oil Corporation : It is Country's largest PSU oil refiner and retailer. It launches drive to turn plastic waste into bitumen that can be used for construction of roads and highways. The company has taken up various initiatives to support the government's drive to eliminate single use plastic by converting these toxic waste to productive use.
A 850 meters of road outside Indian Oil R&D Centre in Faridabad chosen as the testing area in Faridabad will be monitored in association with the CSIR-CRRI to fine-tune the concentration of single-use plastic to be added.
The company has also announced its other initiatives, that is, the introduction of Soluble Bitumen Poly Bags for bitumen filling which is produced from 100% single-use waste plastic, which solubilise fully in the bitumen at the time of road paving.
Francois' Langur : It is the world's rarest and critically endangered animal in the world. It is also known as the Francois' leaf monkey, Tonkin leaf monkey, or white side-burned black langur. It is a species of lutung and the type species of its species group. It is one of the least studied of the species belonging to the Colobinae subfamily. The animal is found only in Vietnam and China where it is threatened by poachers and loss of habitat from encroaching development. According to the zoo estimates there are only about 3 000 of the species left in the wild.
One of the world's rarest monkeys,the male Francois' langur with its distinctive orange fur was born at Sydney's Taronga Zoo last week and has not yet been named. The baby’s bright orange hair lasts just a few weeks before it begins to darken to the colour of its mother Noel’s hair.
Science and Technology
DRDO : It refers to Defence Research and Development Organization. DRDO sussessfully test-fired land attack version of BRAHMOS Supersonic Cruise Missile, featuring Indian propulsion system, airframe, power supply and other major indigenous components from Integrated Test Range (ITR), Chandipur coast in Odisha’s Balasore district. The missile was test-fired for its full strike range of 290-km during the launch jointly conducted by DRDO and BrahMos Aerospace. The missile, with a strike range of 290km, can be fired from land as well as sea-based platforms. The missile has been fitted with increased indigenous equipment and is a version used by Indian Army. The first extended version of BrahMos missile with a strike range of 450 kilometres was successfully tested on 11 March, 2017. BrahMos is a joint venture between the DRDO and the NPOM of Russia.
BRAHMOS Supersonic Cruise Missile : The multifaceted missile is Jointly developed by India and Russia, it has been operationalised in the Indian Armed Forces with all the three services. It is a "Fire and Forget" missile which is capable of navigating on its own towards a pre-determined and programmed target. It can be fired from submarine, ships, aircraft, or land.It uses a Transport Launch Canister (TLC) for transportation, storage and launch. It is not only the fastest supersonic cruise missile in the world but also the world's fastest anti-ship cruise missile in operation.
With this successful mission, the indigenous content in the formidable weapon has reached a high value, thus strengthening India's defence indigenisation and the flagship 'Make in India' programme.
INS Tarkash : It refers to the ship which is part of the Indian Navy's Western Fleet and under the Operational Command of Flag Officer Commanding-in-Chief, Western Naval Command. It was commisssioned on 9 November 2012. It is equipped with a versatile range of weapons and sensors capable of addressing threats in all the three dimensions. It is a potent frontline frigate and second Talwar-class frigate constructed for the Indian Navy. It is part of the second batch of Teg-class frigates ordered by the Indian Navy. She was built at the Yantar shipyard in Kaliningrad, Russia.
Indian Navy ships are regularly deployed overseas as part of Navy's mission of building 'bridges of friendship' and strengthening international cooperation with friendly countries. As part of Indian Navy's Overseas Deployment to Africa, Europe and Russia, Indian Naval Ship Tarkash commanded by Captain Sathish Vasudev arrived at St Denis, Reunion Island, France today for a three-day visit.
Bridges of Friendship : The Indian Navy hosted its first International Fleet Review in February 2001. This event was termed "Bridges of Friendship" and was attended by 24 warships form 19 countries.
Economics
Forever 21 : It is an Fashion retailer with over 800 stores in 57 countries across the globe. It was founded in Los Angeles in 1984 as a fast-fashion retailer. Since its founding, it has served as a low-price one-time destination for teen shoppers. The fashion brand mainly sells trendy clothing and accessories at cheap rates. The popularity of these brands had grown during the Great Recession.
Forever 21 Inc. has filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection. It announced that it will make its exit from most international locations in Asia and Europe. The move comes as traditional retailers continue to struggle against the rise in competition posed by online retailers.
Linda Chang, the Executive Vice President of Forever 21, said that it was an important and necessary step to secure the company’s future, as it would enable them to reorganize their business and reposition the brand. The brand has now joined other US fashion retailers seeking bankruptcy protection such as Barneys New York and Diesel USA, while they face stiff competition from online retailers. However the company is unlikely to be affected in US so it does not plan to exit from any major market in the US.
Chapter 11 Bankruptcy protection : Chapter 11 Bankruptcy protection provides the US companies with time to reorganize their debts and sell parts of their business, postponing the company’s obligations to its creditors.
DGTR : It refers to Directorate General of Trade Remedies. It functions under the Ministry of Commerce and is the apex National Authority to administer and investigate all trade remedial measures. The directorate deals with anti-dumping duty, safeguard duty, and countervailing duty.
The arm of the Ministry of Commerce, DGTR has launched ARTIS (Applications for Remedies in Trade for Indian Industry and other Stakeholders).It is developed for the presentation of requests, responses and other related presentations regarding various commercial corrective measures.
ARTIS : It is an online system which will be used for the filing of anti-dumping applications by the domestic industry with an aim to facilitate speedy resolution to the injury faced by the Indian domestic industry and to increase the accessibility of directorate to all the stakeholders.The online system is presently functional for filing of applications by domestic industry in original investigation and concluding investigation of anti-dumping cases.
Modules for other types of applications like the review of new-shippers , anti-circumvention, mid-term review and for filing of responses by exporters, importers, users within anti-dumping and modules for anti-subsidy, safeguard and quantitative restriction cases will be launched shortly.
CBDT : It refers to the Central Board of Direct Taxes. Ministry of Finance Ms. Nirmala Sitharaman launched a computer-generated Documentation Identification Number (DIN) system of the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) on 1 October 2019 to ensure greater transparency and accountability in tax administration. On the day of launching, nearly about 17,500 communications with DIN were generated. The introduction of DIN will make every CBDT communication to have a documentation identification number. It will apply to all kind of communications from Income Tax (IT) Department, whether it is related to investigation, assessment, rectification, appeals and penalty among other things.
DIN : It refers to Documentation Identification Number (DIN) system. The system has been created as per the direction of Union Finance Minister Ms. Nirmala Sitharaman.The Provisions of the DIN is that any communication from the Income Tax (IT) Department without a computer-generated DIN, including letter, order, notice and summon or any other correspondence, would treated invalid. Verification on the e-filing portal is a must for all communication with DIN and no communication would be issued manually without the DIN except if it falls under the specified exceptional circumstances. If there is any communication issued manually under exceptional circumstances then in this case it would have to be uploaded and regularised on the system portal within 15 days of its issuance. The benefits of the DIN system are that it is expected to ensure greater accountability and transparency in tax administration. The tax payers would also detect fake notices and letters because of the notices being verified on e-filling portal department.
IRCTC IPO: It refers it the Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation (IRCTC) and IPO refers to initial public offer.
The initial public offer (IPO) of Indian Railway Catering and Tourism Corporation (IRCTC), which closed for subscription on Thursday, has created a record in terms of the highest-ever subscription for a public issue of a government-owned company. It got subscribed more than 112 times than its actual decided numbers.
It has not only become the highest-ever subscribed government-owned company for a public issue but also a first PSU (Public Sector Undertaking) which has been subscribed for more than 100 times.
IPO Price Band : It means that the companies that are allowed to launch IPOs can decide the price of their shares but those companies which are in the field of infrastructure and some other sectors have to get permission from SEBI and the Reserve Bank first. The price band is decided by the company's board of directors, along with Bookrunner. Maximum 20 per cent price band is allowed in India. The price band cannot be more than 20 per cent above the floor price of the share.
Repo rate : Repo rate is the rate at which the central bank of a country (Reserve Bank of India in case of India) lends money to commercial banks in the event of any shortfall of funds. Repo rate is used by monetary authorities to control inflation.
The 4th bi – monthly policy review has been released by Reserve Bank of India (RBI). It has reduced the repo rate by 25 base points to 5.15%. for the fifth consecutive time this year by RBI governor Shaktikanta Das led panel. The current inflation of India is 3.21%. This is below the RBI target of 4%. It is the lowest since 2010.
Sports
SAFF U-15 Championship : It is an international football competition for men's under-15 national teams organized by South Asian Football Federation (SAFF). The championship for the first time was in August 2015 in Nepal.
India lift SAFF U-18 Championship title for first time by beating Bangladesh by 2-1 in the finals held in Kathmandu,Nepal. Vikram Partap Singh and Ravi Bahadur Rana scored a goal each for India. India's Ninthoinganba Meetei was adjudged Most Valuable Player of the tournament.
Wrestling Ranking: World Championship silver medallist wrestler Deepak Punia has been ranked world number one in 86kg category in the World Wrestling Championship issued by the International Wrestling Federation. Bajrang Punia lost the top rank in the 65kg category in the latest rankings.
Deepak Punia : He recently won silver in the World Wrestling Championship, after he pulled out of the final bout due to an ankle injury. He is the current junior world champion. This was his first senior World Championship. He became the only fifth Indian to reach the finals at the senior World Championships. He is from among the four Indian wrestlers to have secured his place at the 2020 Tokyo Olympic Games. He currently has four more than the previously top-ranked wrestler, Hasan Yazdani from Iran with a total of 82 points.
Bajrang Punia : He dropped from the top rank to the second spot after losing his semi-final bout and settling for bronze.He currently has 63 points.
Russian Gadzhimurad Rashidov : He won gold in Nur Sultan and is the new world number one in 65kg category.
Ravi Dahiya entered the top 5 ranking list in the 57 kg category, while Rahul Aware was pushed to the second rank with his bronze in the World Championship.
In women's rankings, Vinesh Phogat, who also won bronze in the World Championship, is ranked second in the 53 kg category. Seema Bisla dropped to rank 3 in the 50kg category, while Pooja Dhanda is ranked five in 59kg category. Manju Kumari is world no.3 in the 40kg category.
Currently, four Indian wrestlers have qualified for the 2020 Tokyo Olympics in their respective weight categories. The wrestlers include Deepak Punia, Bajrang Punia, Vinesh Phogat and Ravi Kumar Dahiya.
Roger Binny : He is a former Indian cricket all-rounder and is best known for his impressive bowling performance in the 1983 Cricket World Cup in which India won the cup. Roger Binny scored 830 runs in test cricket and 629 runs in One Day International matches.
The former cricketer was chosen president by a thumping majority as the Karnataka State Cricket Association elections. He defeated Captain M M Harish, while Abhiram won against Joseph Hoover.
Roger Binny was elected as the president while J Abhiram became the vice-president. Santosh Menon and Shavir Tarapore were elected as secretary and joint secretary, Vinay Mruthyunjaya, who was elected Treasurer.
Ravindra Jadeja : He is a left arm spinner all rounder Indian internatinal cricketer. He has become the second fastest Indian to take 200 wickets in Test cricket during the opening match against South Africa . He achieved the feat when he bowled out Dean Elgar during the Day 3 of India’s first test against South Africa in Visakhapatnam. Jadeja is also the fastest left-arm bowler to achieve the feat ahead of Sri Lanka's Rangana Herath (47 matches) and Australia's Mitchell Johnson (49),Mitchell Starc (50) and Pakistan's Wasim Akram (51).
Places In News
Bengaluru : Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) corporator from Jogupalya, Gowtham Kumar who was their official candidate won the election for the post of mayor of Bruhat Bengaluru Mahanagara Palike (BBMP). He defeated his Congress rival R Sathyanarayana by 17 votes. He won by 17 votes with 129 votes in his favour, while 112 votes went to the Congress candidate. He will replace Congress leader Gangambike Mallikarjun. This is the first time BJP has won the post in four years.
Haryana : Congress releases list of 84 candidates for the upcoming Haryana Assembly polls. The party on Thursday fielded 16 out of the 17 sitting MLAs barring Renuka Vishnoi who represented the Hansi constituency. Former CM Bhupinder Singh Hooda will contest from Garhi Sampla-Kiloi seat, party spokesperson Randeep Surjewala will contest from Kaithal seat while both sons of former CM late Bhajan Lal have been fielded by the party, with Kuldeep Vishnoi from Adampur, in Hisar, and his brother and former deputy chief minister Chander Mohan from the Panchkula seat . Elections to the 90-member Haryana Assembly will be held on 21 October and results will be declared on 24 October.
Rajasthan : Rajasthan Government under the Food Security Act banned certain categories of Pan Masala and flavoured Tobacco products made of magnesium, carbonate, nicotine and mineral oil and flavoured supari on the occasion of the 150th birth anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi. Rajasthan is the third state after Maharashtra and Bihar to announce such a move. State medical and health minister Raghu Sharma, making the announcement stated that the initiative has been taken in accordance to the Food Security Act 2006. All food security offices of the state have been directed to check the sale, distribution and production of such products. Now any kind of sale, production or storage of these products will not be allowed in the Rajasthan. Earlier, the Government has banned e-cigarettes and hookah-bars in the state. The initiative has been taken to prevent youths from getting addicted to such tobacco products.
In India, according to Cancer Society of India. the incidence of cancer is increasing rapidly and chewing tobacco is majorly blamed for mouth cancer in the country. Tobacco can cause various types of cancer like mouth, lung, throat, bladder, kidney, stomach, colon and many other organs of the body can be affected.
Chattisgarh : Government of Chhattisgarh, on October 2, 2019, under the leadership of Chief Minister Bhupesh Baghel launched 5 new schemes namely Mukhyamantri Suposhan Abhiyaan, Mukhyamantri Shahariya Slum Swasthya Yojana, Mukhyamantri Haat Bazaar Clinic Yojana, Universal PDS Scheme and Mukhyamantri Ward Karyalaya.
Mukhyamantri Suposhan Abhiyan : The Chief Minister Nutrition Scheme or the Mukhyamantri Suposhan Abhiyan was started in June 2019. Under the scheme, fresh and nutritious food is provided to malnourished children and anaemic women with the help of panchayats and self-help groups.
Mukhyamantri Haat Bazaar Clinic Yojana : Under the (Chief Minister Market Clinic Scheme) or the Mukhyamantri Haat Bazaar Clinic Yojana, mobile teams of health department along with doctors and necessary equipment will visit local haat-bazaars to provide health facilities in remote tribal and forest areas of the state.
Mukhyamantri Shahariya Slum Swasthya Yojana : Under the Chief Minister Market Clinic Scheme or Mukhyamantri Shahariya Slum Swasthya Yojana, mobile medical team along with available health facilities will cater to health care needs of over 7 lakh 80 thousand people. At the beginning, 3 mobile medical teams will be deployed in Raipur, 2 each in Bhilai and Korba and one each in other municipalities.
Universal PDS Scheme : Under the Public Distribution System or the Universal PDS Scheme the general category families are eligible for food grains. Families with single member will be eligible to get 10 kg of rice per month, family of 2 will receive 20kg rice per month and family with three or more members will receive 35kg of rice per month at a cost of Rs 10 per kg.
Mukhyamantri Ward Karyalayas : Under Chief Minister Ward Offices or Mukhyamantri Ward Karyalayas, citizen services and facilities will be provided immediately to city people.
People In News
Viju Khote: The veteran Hindi and Marathi film-theatre actor passed away due to multiple organ failure on September 30. He was 77. The actor, most famous for playing the dacoit Kalia in 'Sholay' and Robert in 'Andaz Apna Apna', died at his residence. The character of Kalia in the film Sholay potrayed by him left deep impression on the hearts of people even today. Viju Khote was also praised for his outstanding performance in several Marathi films. Viju Khote started his career in the year 1964. He also performed a memorable role in TV Show Zabaan Sambhalke.
Air Chief Marshal RKS Bhadauria : Air Chief Marshal Rakesh Kumar Singh Bhadauria on the 30th of September took charge as the new Chief of the Indian Air Force (IAF). He is now the 26th Chief of the Air Staff of the Indian Air Force. He succeeds Air Chief Marshal BS Dhanoa, who retired after 41 years of service in the IAF.
Bhadauria an alumnus of National Defence Academy (NDA) was the Vice Chief of Air Staff (VCAS). He won the coveted Sword of Honour for standing first in overall order of merit. During his 39-year-long career, he commanded a Jaguar squadron and a premier Air Force Station. He even devised a method for carrying bombing from the Jaguar aircraft using the Global Positioning System (GPS) which played an important bombing role in Operation Safed Sagar in 1999. He also has 4,250 hours of flying experience on 26 types of fighters and transport aircraft. He was among the few air force pilots to fly the Rafale fighter jet. He flew the aircraft in July 2019, during Exercise Garuda between Air Forces of India and France. He played a key role in procuring the 36 multirole Rafale fighter jets for India as the Chairman of the Indian team that negotiated the deal with France. The new IAF chief had served as Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief (AOC-in-C), Southern Air Command from March 2017 to August 2018. He has held several important positions in the IAF such as Commandant at National Defence Academy, Senior Air Staff Officer at the Central Air Command and Vice Chief of Air Staff from January 2016 to February 28, 2017.
RKS Bhadauria has been awarded several medals including the Ati Vishisht Seva Medal, the Vayu Sena Medal, and the Param Vishisht Seva Medal. He was appointed honorary Aide De Campe to the President of India in January this year.
Pandit Jasraj : He is a famous Indian classical music legend. Sangeet Martand Pandit Jasraj was born 28 January 1930 is an Indian classical vocalist. belonged to the Mewati gharana (musical apprenticeship lineage). He received his primary education of music at home. He was trained by his elder brother Pandit Maniram and then later Gulam Kadar Khan of Mewat Gharana trained him. His musical career has spanned more than 80 years and led to numerous major awards. He was awarded Padma Vibhushan (2000), Padma Bhushan (1990), Padma Sri (1975), Lata Mangeshkar Award among many more. He has taught music in India, Canada and the US.
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) officially announced by the IAU with a citation on 23 September. It was said in a quote that classical music legend Pandit Jasraj is the pioneer of Indian classical singing. The minor planet 2006 VP32 orbiting sun between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter 2006 that was discovered on November 11, by A NASA-funded project Catalina Sky Survey will be named after the legendary singer Pundit Jasraj. He has become the first Indian to have a celestial body named after him. Earlier, other artists like Mozart, Tenor Luciano Pavarottia and Beethoven have received this honour
Minor Planet : It is a planet orbits the sun but it doesn’t look like a planet or comet. The Ceres, found in 1801, was the first minor planet. Minor Planets are also known as dwarf planets. More than 4 lakh minor planets have been discovered till date, however, 15,000 minor planets have been given official names.
Kalli Purie : She is a graduate in Politics, Philosophy & Economics from the Oxford University in England. She is currently serving as the Vice-Chairperson of the India Today Group. She began her work with the India Today Group as a marketing executive and reporter for the magazine, India Today, in 1996. She leads a wide range of media verticals including Aaj Tak, India Today Television, Aaj Tak HD, Tez, a digital newspaper, apps, and Dilli Aaj Tak. She is a well-received speaker at international (FIPP, GEN) and national media (AIM, E4M, FRAMES) industry events. In March 2017, She was named as the 5th most powerful woman at the sixth edition of Impact Magazine’s Awards. Just two weeks after receiving the Outstanding Media & Entertainment Award' at the annual 21st Century Icon Awards in London, She was honoured with “India’s Most Powerful Women in Media” award. She received the global honour at the prestigious Confluence Excellence Awards at the British Parliament on September 27, 2019.
Confluence Excellence Awards : Confluence Foundation whose chairperson and founder is Smita Srivastav is the main organizer for the event. This was the second edition of the awards.The award aims to recognize individuals for their innovative leadership and the success they have achieved through revolutionizing their field of work.
Kavitha Gopal: She created history by becoming the first girl student of the Indian Institute Technology-Madras to win the President of India Prize. This is the first time a girl student has won the award in 60 years. She received the prize and medals from Prime Minister Narendra Modi on the Institute’s 56th convocation.
With a CGPA of 9.95, she bagged the Bharat Ratna M. Visvesvaraya Memorial Prize and the B. Ravichandran Memorial Prize for the highest CGPA in B. Tech CSE. She shared the first two prizes with Pradyumna Venkatesh Chari of B. Tech (Electrical Engineering). She is graduated with a B.Tech degree in Computer Science and Engineering.
She is a student of the 2015-19 Computer Science batch. She studied at the Atomic Energy Central School, Anupuram and later at the Kendriya Vidyalaya, Kalpakkam. She is currently working as a software engineer at Google India, Bengaluru.
Surjit Bhalla : He is an Indian economist, author and columnist. He was appointed as a member of newly-formed Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister of India, Narendra Modi. He resigned as a member of PMEAC on December 1, 2018. The Indian government appointed economist Surjit S Bhalla as the executive director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) for a period of three years. The post which is technically called executive director, fell vacant after Subir Gokarn died in July this year. The Appointments Committee of the Cabinet has approved his appointment.
Sachin Tendulkar : He is an Indian former international cricketer and a former captain of the Indian national team. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest batsmen in the history of cricket. He is the highest run scorer of all time in International cricket.
The Cricket legend was awarded the most effective Swachhata ambassador award at the Safaigiri 2019 organized by the India Today group by the President Ram Nath Kovind on the occasion of 150th birth anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi. He was chosen because he utilized his fame and popularity to ensure India achieved its goal of Swachh Bharat. Prime Minister Modi had nominated him as one of India's swachhata ambassadors’ in 2014. Sachin Tendulkar launched Mission – 24 that aimed at improving the quality of Mumbai East ward as Mumbai was ranked the lowest in the Human Development Report. Sachin Tendulkar has been promoting cleanliness drives in India for almost 10 years. Tendulkar was honoured with Bharat Ratna in 2014, becoming the youngest recipient of the highest civilian award in the country.
Safaigiri Awards : It is an initiative of India Today group to celebrate the champions of Clean India campaign. The awards include cleanest village, cleanest religious place, cleanest railway station and cleanest city.
Indian Policy
MSMEs : It referes to Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) Nitin Gadkari while addressing women entrepreneurs in Chennai said that Centre was considering a proposal to introduce a rating system for small and medium enterprises (SME) to help them get loans easily.
The Central government is making all efforts to reduce finance costs and power price to the industry so as to tackle the prevailing sense of gloomy industrial scenario which is due to the business cycle, demand and supply issues and a global downtrend.
Mr. Gadkari said that the Central Government is in the process of introducing a national portal for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) to market their products easily and has fixed a target of generating five crores more jobs in the MSME sector in the next five year.
Trade apprentice: It refers to a person who undergoes apprenticeship training in any designated trade. It can be any occupation or trade, any subject field in technology or engineering or non – engineering and any vocational course as notified by Union Government. Any Class 8, 10, 12 and ITI (a certificate course) pass - outs are eligible to undergo apprenticeship in designated trades for trade apprentices. In some trades, B.Sc. pass is also a prescribed qualification.
Union Ministry for Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) has notified changes in Apprenticeship Rules (1992) as Apprenticeship (Amendment) Rules, 2019 with an aim to increase skilled manpower in the country, and raise minimum stipend payable to trade apprentices. It has issued a notification regarding minimum stipend payable to trade apprentices based on the qualification which will and range from Rs.5000 to Rs.9000 per month from now onwards.Those employers who have four or more workers are eligible to engage apprentices.
MSDE Ministry has also launched ‘Apprenticeship Pakhwada’, a 15-day cross-country event which is aimed at driving widespread awareness of the Apprenticeship. It is in collaboration with 22 organizations to provide apprenticeship training to more than 2.5 lakh youth in India. The government also seeks to create a new structure of Kaushal Vikas Mitra from the state level to the village level.qualification.
Welfare Schemes : The Government is implementing different welfare programmes or schemes at various levels for citizens benefit. Effective monitoring and measurement of the outcome and impact of such programmes or schemes is imperative at different levels through identified Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). Thus, as a part of welfare schemes, the Union Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MEITY) Ravi Shankar Prasad launched an Automated Real Time Performance Smart-board for effective monitoring and measurement of key programmes of government. The key programmes include Digital India, Aadhaar, Digital Payments among others. He also unveiled the Digital Charkha at the IT Ministry.
Smart-board : It is an automated real-time performance smart-board which will act as a single window access for Centre, State as well as for District specific projects implemented by the Ministry. It will promote transparency and enhance ease of working. The smart-board will also enhance analysis through data integration by using APIs (Application programming interface) or (web services) by consolidating multiple data sources into one centralised, easy-to-access platform.
Digital Charkha : It is is an amalgamation of the traditional design with a digital spin. The wheel of the Charkha is made up of interlinked digital grids in place of fine threads thus portraying that the core of Digital India is embedded in Gandhian philosophy of equality, unity, corruption free and empowerment of ordinary.
Indian polity
SC/ST Act : It refers to Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act of 1989 of the Parliament of India enacted to prevent atrocities against scheduled castes and scheduled tribes. The Act is popularly known as the SC/ST Act, POA, the Prevention of Atrocities Act, or simply the Atrocities Act.
The Supreme Court verdict was passed on March 20 last year setting in place guidelines to prevent misuse of SC/ST (Prevention of Atrocity) Act and by which the court had forbidden automatic arrest of an accused.
Supreme Court allowed the review petition filed by the Centre against Court's judgement of 'diluting' various stringent provisions of SC/ST (Prevention of Atrocities) Act. The apex court's three-judge bench restored the earlier position of the law and amended its own order about SC/ST Act. Now an FIR can be registered under this act without investigation. Experts said that the decision was taken not due to cast system but because of constitutional requirements. A bench of justices Arun Mishra, M R Shah and B R Gavai said the struggle of SC/ST people for equality is still not over and they still face untouchability, abuse and are socially outcast.
High Court : Under Article 141 of the constitution, all courts in India — including high courts — are bounded by the judgments and orders of the Supreme Court of India by precedence. Judges in a high court are appointed by the President of India in consultation with the Chief Justice of India and the governor of the state.
Qualifications : He/She should be a citizen of India. A person to be appointed as High Court Judge should have 10 years of experience of holding judicial office in India. He/She should have ten years of experience as an advocate of the high court(s).The appointment of a High Court judge doesn’t restrict qualified person with any age limit.
The Government has appointed seven Chief Justices to Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Punjab and Haryana, Gauhati, Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh and Sikkim High Courts.
Justice Ajay Lamba of Allahabad High Court has been appointed as Chief Justice of Guwahati High Court.
Justice Inderjit Mahanti of Bombay High Court has become Chief Justice of Rajasthan High Court.
Justice A Mani Kumar of Kerala High Court has been appointed as Chief Justice of Himachal Pradesh High Court.
Justice Ravi Shanker Jha of Madhya Pradesh High Court has been appointed as the Chief Justice of the Punjab and Haryana High Court.
Justice Bishwanath Somadar of Calcutta High Court.
Justice Vivek Agarwal of Telangana High Court have been sent to Allahabad High Court.
Arts
Aadi Mahotsav: It is a 10 day long festival which commenced on 1 December 2020. The virtual edition of Aadi Mahotsav- Madhya Pradesh was recently launched by the Union Minister for Tribal Affairs Arjun Munda. The festival is being hosted on the Tribes India website. The main focus is on the tribal craft and culture of Madhya Pradesh.
The next focus state of the programme would be Gujarat- from 11th December 2020, followed by West Bengal from the 21st December, 2020.
The Aadi Mahotsav – A Celebration of the Spirit of Tribal Culture, Crafts, Cuisine and Commerce – is a successful initiative that was commenced in 2017. This festival is a national tribal festival and a joint initiative of Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Government of India & Tribal Cooperative Marketing Development Federation of India (TRIFED).
The festival showcases traditional art and handicrafts and cultural heritage of the country so as to familiarise the people with the rich and diverse craft, culture of the tribal communities across the country, in one place.
The main objective of TRIFED is socio-economic development of tribal people in the country by way of marketing development of the tribal products
Guru Nanak Jayanti: It is also known as Gurpurab, Guru Nanak's Prakash Utsav and Guru Nanak Dev Ji Jayanti. This day is observed on the day of Kartik Poornima, which is the fifteenth lunar day in the month of Kartika according to the Hindu calendar. According to Gregorian calendar, this day falls in the month of November.
Guru Nanak Jayanti is celebrated all across the globe on the birth of the first of the ten Sikh gurus and the founder of Sikhism, Guru Nanak Dev Ji. One of the most celebrated Sikh gurus and the founder of Sikhism, Guru Nanak Dev is highly revered by the Sikh community. They celebrate this day with great zeal and enthusiasm. To honor the teachings of Guru Nanak, Sikh people put stalls at various places in their cities and treat other people with food.
This day is celebrated for three days and two days prior to Guru Nanak Jayanti, prayer and Akhand Paths are conducted at the Gurudwaras.
A procession known as Nagarkirtan is organized. The procession is led by five men, referred to as the Panj Pyare, holding the Sikh triangular flag, Nishan Sahib.
The main day of Gurpurab begins with the morning hymns, that is followed by the prayers and kathas that are performed in the praise of the guru. Later, langar is followed by a night prayer session that is conducted at Gurudwaras.
This year was the 551st birth anniversary of Guru Nanak and was celebrated on Monday, November 30.
Guru Nanak Ji: Sri Guru Nanak Dev Ji was the creator of Sikhism, and the first of the ten Sikh Gurus. Guru Nanak was born on 29 November 1469 in Nankana Sahib, in Punjab. This is now part of Pakistan. His father's name is "Mehta kalu" and mother's name is "Mata tripta". He died in Kartarpur on 22 September 1539. A Gurudwara was built on his birth place and the city is also known as Nankana Sahib and is located in the Punjab province of Pakistan.
According to the Sikh religion, one day Guru Nanak Ji was bathing in the river and god took him up to heaven. His family members were very worried as they had thought he died. After three days he returned with the message of god. He gave up his job to spread the message on how to be a good person.
He is considered a religious innovator. Guru Nanak travelled across South Asia and Middle East to spread his teachings. He advocated the existence of one God and taught his followers that every human being can reach out to God through meditation and other pious practices.
Guru Nanak Dev Ji brought down the arrogant walls of caste, creed and religion with love, compassion and humility. In his eyes, all were equal. Sarbat da bhala, (welfare of all) is one of the core principles of Sikhism that can lead us to a humane world.
His teachings were immortalized in the form of 974 hymns, which came to be known as ‘Guru Granth Sahib,’ the holy text of Sikhism. With more than 20 million followers, Sikhism is one of the important religions in India.
Economics
IOCL: It stands for Indian Oil Corporation Limited. IOCL was founded in 30 June 1959. It is an Indian public sector oil and gas company headquartered in New Delhi. The current Chairperson of IOCL is Shrikant Madhav Vaidya.
Recently, IOCL launched India’s first indigenously developed ‘100 Octane premium petrol. The new premium grade petrol – Octane 100 was manufactured in the Indian Oil Corporation Mathura Refinery located in Uttar Pradesh. The high octane premium grade petrol has been branded as‘XP100’.
This premium grade petrol was launched across ten cities by Dharmendra Pradhan, Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas. The cities are Delhi, Gurgaon, Noida, Agra, Chandigarh, Jaipur, Ludhiana, Mumbai, Pune and Ahmedabad.
Through this, India is becoming more self reliant. Earlier, India had leapfrogged from BS-IV (Euro-IV) fuel to BS-VI emission compliant fuel.
The availability of XP100 has put India in an elite group of countries that have such superior quality fuel. Till date, such quality of fuel is available only in six countries including USA, Germany, Greece, Israel, Indonesia and Malaysia.
Indian Oil also plans to roll-out XP100 premium grade petrol in 15 identified cities. It will be rolled out across the country in two phases.
SBI RuPay JCB Platinum Contactless Debit Card: The SBI RuPay JCB Platinum Contactless Debit Card was recenlty launched by NPCI (National payment Corporation of India), State Bank of India and Japan’s JCB International.
The card that has been launched on the RuPay network by SBI in association with JCB comes with a unique dual-interface feature. This feature enables customers to perform both contact and contactless transactions in the domestic market and seamless contact transactions overseas.
The customers can use the card to transact on ATMs (Automatic Teller Machines) and PoS (Point of Sale) terminals across the globe under the JCB network.
They can also the card to shop online from JCB-partnered international ecommerce merchants.
The card supports RuPay offline wallet-based transactions, enabling an additional payment mode within the card.
Consumers will be able to load the offline wallet and utilise it for transit in India (bus and metro), and retail (merchant) payments.
SBI RuPay JCB Platinum Contactless Debit Card holders can now use their cards at millions of locations in the world.
JCB International Co. Ltd: JVB formally called the Japan Credit Bureau is a major global payment brand and a leading credit card issuer and acquirer in Hapan. It is headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. The current Chairman & Cheif Esecutive Officer (CEO) is Ichero Hamakawa.
NPCI: It refers to the National Payment Corporation of India. NPCI is an umbrella organization for all retail payments in India. It was founded in 2008. It has been incorporated as a Not for Profit Company under the provisions of Section 25 of Companies Act 1956 (now Section 8 of Companies Act 2013). It is an initiative of Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Indian Banks Association (IBA) under the provisions of the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007 for creating a robust Payment & Settlement Infrastructure in India. It is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra. The current MD & CEO is Dilip Asbe.
KVIC: It refers to the Khadi and Village Industries Commission. KVIC is a statutory body formed in April 1957 (as per an RTI) by the Government of India (GoI), under the Act of Parliament, ‘Khadi and Village Industries Commission Act of 1956’. It is an apex organisation under the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises. The main objective of KVIC is to plan, promote, facilitate, organise and assist in the establishment and development of khadi and village industries in the rural areas in coordination with other agencies engaged in rural development wherever necessary.
Recently, KVIC, responding to the Prime Minister’s call for Aatmanirbhar Bharat engaged hundreds of migrant workers in Uttar Pradesh and Bihar with its flagship scheme like Honey Mission, Kumhar Sashaktikaran Yojana and Project DigniTEA among others.
The self-sustainability measures for Honey Mission initiated by KVIC in wake of the Covid-19 pandemic have begun yielding results. The distressed migrant workers who were engaged with KVIC’s Honey Mission in Uttar Pradesh in the month of August, have reaped their first honey harvest and are awaiting a bumper yield from December to March.
Honey Mission: Honey Mission launched by KVIC in 2017 in line with Prime Minister’s call for ‘Sweet Revolution’ in 2016. The mission aims at creating employment for farmers, Adivasis, women and unemployed youth by roping them with beekeeping and increasing India’s honey production. It also aims to promote beekeeping for increasing the crop productivity and pollination services avenue for beekeepers and farmers.
KVIC, under its Honey Mission, provides training and 10 bee boxes with live colonies to beneficiaries including farmers, beekeepers and unemployed youth. KVIC also runs beekeeping training programmes and courses.
Defence
DRDO: It is an acronym for the Defence Research and Development Organisation. DRDO is India's largest research organization. It was founded in 1958. It is headquartered in New Delhi, India. It is an agency under the Ministry of Defence, Government of India. It is charged with the military's research and development. It has a network of laboratories engaged in developing defence technologies covering various fields, like aeronautics, armaments, electronics, land combat engineering, life sciences, materials, missiles, and naval systems. The Minister currently responsible for DRDO is Rajnath Singh, Minister of Defence. The present Chairman of DRDO is Dr. G. Satheesh Reddy.
Recently, the DRDO launched a new laboratory named Defence Geo Informatics Research Establishment. The new lab was established by merging its two existing labs – the Manali-based Snow and Avalanche Studies Establishment (SASE) and the Delhi-based Defence Terrain Research Establishment (DTRL). This new lab will focus on researching terrain and avalanches along the borders with China. The main objective of this merger by DRDO is to be more result-oriented.
SASE:It is an abbreviation for Snow and Avalanche Studies Establishment. SASE is a Manali, Himachal Pradesh based Laboratory of DRDO. It was established in 1969. The primary function of SASE is its research in the field of snow and avalanches to provide avalanche control measures and forecasting support to Indian Armed Forces.
SASE has prepared avalanche atlas for more than 3000 on-road location in different parts of the country, especially in the terrains where the armed forces were deployed.
DTRL: It refers to the Defence Terrain Research Laboratory. DTRL is based in Delhi. It was set up in 1954. Its vision is to empower the Armed Forces with advanced Geo-spatial Intelligence. The primary function of the Laboratory is to provide real time data for terrain evaluation to Indian Army and to create Geo-spatial infrastructure to provide timely, relevant and accurate geo-spatial solutions for the Armed Forces.
DRDO Laboratories: There are different DRDO Laboratories. They are as follows:
- ANURAG: Advanced Numerical Research and Analysis Group located in Hyderabad Researches on Computational System
- ASL: Advanced Systems Laboratory located in Hyderabad Researches on Missiles and Strategic Systems
- ADRDE: Aerial Delivery Research and Development Establishment located in Agra Researches on Parachutes and Aerial Systems
- ADE: Aeronautical Development Establishment located In Bengaluru researches on Aeronautics
- ARDE: Armament Research and Development Establishment located in Pune Researches Armaments
- CABS: Centre for Airborne Systems located in Bengaluru Researches Airborne Systems
- CAIR: Centre for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics located in Bengaluru researches on Artificial Intelligence and Robotics
- CFEED: Centre for Fire, Explosives and Environment Safety located in Delhi researches on Explosives
- CHESS: Centre for High Energy Systems and Sciences located in Hyderabad researches High Energy Weapons
- CVRDE: Combat Vehicles Research and Development Establishment located in Chennai Researches Combat Vehicles
- DARE: Defence Avionics Research Establishment Located in Bengaluru Researches Avionics
- DEBEL: Difference Bioengineering and Electro Medical Laboratory located in Bengaluru Researches Bioengineering
- DEAL: Defence Electronics Application Laboratory located in Dehradun researches Electronics and Communication Systems
- DFRL: Defence Food Research Laboratory located in Mysore researches food
- DIBER: Defence Institute of Bioenergy Research Located in Haldwani researches Bioenergy
- DIHAR: Defence Institute of Higher Altitude Research located in Leh researches High Altitude Agro Animal Research
- DIPAS: Defence Institute of Physiology and Allied Sciences located in Delhi researches Physiology
- DIPR: Defence Institute of Psychological Research located In Delhi researches Psychology
- DL: Defence Laboratory Located in Jodhpur researches Camouflaging and Isotopes
- DLRL: Defence Electronics Research Laboratory located in Hyderabad researches Electronic Warfare
- DMSRDE: Defence Materials and Stores Research and Development Establishment located In Kanpur researches Textiles, Polymers and Composites
- DMRL: Defence Metallurgical Research Laboratory Located in Hyderabad researches Metallurgy
- DRDE: Defence Research and Development Establishment located In Gwalior researches Chemical and Biological Warfare
- DRDL: Defence Research and Development Laboratory located in Hyderabad researches Missile and Strategic Systems
- DRL:Defence Research Laboratory researches Health And Hygiene
- GTRE: Gas Turbine Research Establishment located In Bangalore
- HEMRL: High Energy Materials Research Laboratory located in Pune researches High Energy Materials
- INMAS: Institute of Nuclear Medicine and Allied Sciences located in Delhi
- JCB: Joint Cipher Bureau located in Delhi researches Cipher System
- LASTEC: Laser Science and Technology Centre located In Delhi researches Laser Technology
- LRDE: Microwave Tube Research and Development Centre located In Bengaluru researches Microwave Devices
- MTRDC: Naval Materials Research Laboratory located In Ambernath researches Naval Materials
- NPOL: Naval Physical and Oceanographic Laboratory located In Kochi researches Sonar Systems
- NSTL: Naval Science and Technological Laboratory located In Visakhapatnam researches Underwater Weapons
- PXE: Proof and Experimental Establishment located In Balasore researches Armament Testing
- RCI: Research Centre Imarat located in Hyderabad researches Missile and Strategic Systems
- R&DE: Research and Development Establishment located in Pune Researches Engineering Systems and Weapon Platforms
- SAG: Scientific Analysis Group located in Delhi researches Cryptology
- SASE: Snow and Avalanche Study Establishment located in Chandigarh researches Snow and Avalanche
- SSPL: Solid State Physics Laboratory located in Delhi researches Solid State and Semiconductor Materials
- TBRL: Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory Located in Chandigarh researches Palace Takes
- VRDE: Vehicles Research and Development Establishment located in Ahmednagar researches Wheeled Vehicles
China & Pakistan: China and Pakistan recently signed a new Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) related to Defence. The Memorandum of Understanding mainly focused on capacity building of the Pakistani army and is a continuation of a defence agreement signed in 2019. The agreement was signed behind closed doors and the details have been kept secret.
The MoU was signed when General Wei Genghe of the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) held talks with the chief of Pakistan Army, General Qamar Javed Bajwa at Pakistani army headquarters located at Rawalpindi.
During the meet the countries discussed matters of regional security and mutual interest. They further discussed the matters of mutual interest, regional security and enhanced bilateral defence collaboration. They also discussed about the China Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) in which the Pakistani army has a greater role.
Note: Pakistan has deepened ties with China in recent years as relations with the United States have faded.
CPEC: It refers to China Pakistan Economic Corridor. CPEC is one of the flagship projects of the Belt and Road Initiative of China. It is a 3000 km long Corridor and it consists of highways, Railways and pipelines. It also comprise of industrial and other infrastructure development projects which aims to link Gwadar of Pakistan with the Xinjiang province of China through was network of Railways and Highways.
Under the CPEC Framework, China is to setup 1,124 megawatt of Kohala hydro power project in the Pakistan occupied Kashmir. It is to be built on the Jhelum river.
India does not support the project because, the CPEC passes through the Pakistan-Occupied Kashmir region. India considers this against its sovereignty. The other reason is also that India shares trust deficit with China and Pakistan due to a history of conflicts with the countries.
Indian Navy Day: Indian Navy Day is celebrated by India every year on the 4th of December to commemorate Operation Trident – a key offensive during the 1971 India-Pakistan War, when the Indian Navy inflicted heavy damage on Pakistani vessels in Karachi harbour. The same day also marks the end of Navy Week, which, too, is celebrated annually.
The Navy Day was first observed on 4 December 1971. The day was designated in order to work towards securing marine borders and strengthen relationships with other countries through joint exercises, humanitarian missions, and relief operations.
The Navy organizes a Beating Retreat ceremony at Gateway of India in Mumbai on the eve of the Navy Day.
The Indian Naval Band performs across places between Gateway of India and Radio Club in Mumbai. The Indian Navy warships and aircraft are open to visitors, especially school children.
Operation Trident: Operation Trident was held on 4-5 December 1971. The India-Pakistan War of 1971 had begun on December 3, when the Pakistan Air Force launched pre-emptive strikes on airfields in Western India to which India responded by formally declaring war in the wee hours of December 4.
On that day under Operation Trident, the Indian Navy sank three vessels near the Pakistani port city of Karachi. INS Nipat, INS Nirghat and INS Veer played an important role in the attack. The stars of the mission were the then-recently acquired Soviet Osa missile boats, fitted with 4 SS-N-2 (P-15) Styx missiles. It was for the first time anti-ship missile was used in this operation.
On December 5, the Indian Navy’s Western C-in-C, Vice Admiral SN Kohli received the code word “Angaar”, which meant success in Operation Trident.
Recently, the Indian Navy day 2020 was celebrated in India. The theme of Navy Day 2020 is "Indian Navy Combat Ready, Credible & Cohesive".
Note: The Great Maratha Emperor, Chhatrapati Shivaji Bhosle, is considered as the Father of the Indian Navy.
Indian Navy: The Indian Navy is the naval branch of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Navy. The Chief of Naval Staff, a four-star admiral, commands the navy. It was founded in 5 September 1612. The current Chief of Navy Staff (CNS) is Karambir singh. Indian Navy day is celebrated on the 4th of December every year. The main objective of the Indian Navy is to protect the country’s maritime borders and help in the expansion of its forces.There are 3 commands under the Navy which are:
1. The Western Naval Command (Headquarters at Mumbai).
2. The Eastern Naval Command (Headquarters at Visakhapatnam)
3. The Southern Naval Command (Headquarters at Kochi)
The Indian Navy is the fifth largest in the world, employing 67,109 personnel.
PASSEX: The Indian Navy (IN) and the Russian Federation Navy (RuFN) recently undertook a Passage Exercise (PASSEX) in the Eastern Indian Ocean Region (IOR). The exercise was undertaken from 4-5 December 2020.
From the Indian side, IN was represented by indigenously constructed guided-missile frigate Shivalik and anti-submarine corvette Kadmatt along with integral helicopters. From the Russian side, RuFN was represented by guided-missile cruiser Varyag, the large anti-submarine ship Admiral Panteleyev and medium ocean tanker Pechenga.
The main aim of PASSEX exercise is to enhance the interoperability, improve understanding and imbibing best practices between both sides.
MARCOS: MARCOS is the short name of the Marine Commando and is officially called the Marine Commando (MCF). MARCOS is recently being deployed along with the Indian army in eastern Ladakh against the Chinese military. They are located near Pangong Tso Lake and will soon use boats for missions.
About MARCOS: MARCOS was established in February 1987. The Indian Navy's special forces are responsible for special operations. The force can operate in all types of environments; at sea, in the air and on land. It has gradually accumulated experience and enjoyed an international reputation professionally. It conducts specialized maritime operations in Jammu & Kashmir through the Jhelum River and Wular Lake regularly.
Lt Gen Rajeev Chaudhary: Lt Gen Rajeev Chaudhry recently assumed the charge as 27th Director General Border Roads (DGBR). He succeeds Lt Gen Harpal Singh who has been appointed as the new Engineer-in-Chief of the Indian Army.
Before taking over as Director General Border Roads, he was holding the appointment of ADG LW&E in QMG’s Branch at Integrated Headquarters of Ministry of Defence (Army). He was commissioned into the Corps of Engineers from Indian Military Academy (IMA), Dehradun in 1983. He was responsible for conceptualising and conducting the first-ever and only Engineer Brigade Exercise with US Engineer Brigade as part of EX YUDH ABHYAS. He was also nominated as Exercise Director of EX FORCE 18, multinational exercise involving 18 countries on Humanitarian Mine Action (HMA), in the year 2016.
BRO: It refers to the Border Roads Organization. In order to ensure coordination and expeditious execution of projects, the Government of India (GoI) set up the Border Roads Development Board (BRDB) with the Prime Minister as Chairman of the Board and Defence Minister as Deputy Chairman. The BRO was formed on 7 May 1960 to secure India's borders and develop infrastructure in remote areas of the north and north-east states of the country.
It develops and maintains road networks in India's border areas and friendly neighboring countries. It is responsible for the construction and maintenance of roads along the borders with China and Pakistan. Officers from the Border Roads Engineering Service (BRES) and personnel from the General Reserve Engineer Force (GREF) form the parent cadre of the Border Roads Organisation. BRO has been entirely brought under the Ministry of Defence. Earlier it received funds from the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
Environment
Alligators: Alligator are large semi-aquatic and predatory reptiles. They belong to the ‘Crocodilian’ species. Alligators are considered an important species for maintaining ecological diversity in wetlands, as their holes provide habitat for other animals during drought.
At present there are only two species of alligators - namely the American alligator and the Chinese alligator, native to United States, México and China.
Recently, a new study in Scientific Reports, found that similar to small reptiles like geckos, the alligators can also sacrifice and regrow their tails.
Young American alligators (Alligator mississippiensis) can regrow up to 18 percent of their total body length back, about 23 cm in length.
A team of scientists from Arizona State University and the Louisiana Department of Wildlife and Fisheries found that alligators that had regrown their tails had a central cartilage skeleton without any bone. The new tail growth showed features of both regeneration and wound repair.
Conservation of Alligators: The Chinese Alligator are under Critically Endangered category. They were last assessed in 2017. The American Alligators are under Least Concerned category. They were last assessed in 1996.
Mount Seemeru: Semeru, or Mount Semeru, is an active volcano in East Java, Indonesia. The volcano is located in the subduction zone, where the Indo-Australia plate subducts under the Eurasia plate. It is the highest mountain on the island of Java. This stratovolcano is also known as Mahameru, meaning 'The Great Mountain. Since 1818, around 55 eruptions have been recorded in Mt Semeru.
Recently, Mount Semeru has started picking up the activity again in Indonesia. Hot ash started to tumble at the three thousand metres down slopes of Mount Semeru on 1st December 2020. Indonesian authorities are closely monitoring activities of several volcanoes and are evacuating its people.
Stratovolcano: The stratovolcano also called a conical volcano is built by many layers of hardened lava. The lava of stratovolcano is highly viscous and has periodic effusive eruptions. It cools and hardens before spreading far. The lava from stratovolcano is not of significant threat to humans as they are highly viscous.
On the other hand, the Nyiragongo is the only dangerous stratovolcano in the world, as its magma are unusually low in silica which makes the lava quite fluid. This increases the flow rate of the lava.
Ring of Fire: The Ring of Fire, also referred to as the Circum-Pacific Belt, is a path along the Pacific Ocean characterized by active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes.
Its length is approximately 40,000 kilometers (24,900 miles). It traces boundaries between several tectonic plates—including the Pacific, Juan de Fuca, Cocos, Indian-Australian, Nazca, North American, and Philippine Plates. It lies in a horseshoe shape, and is associated with a nearly continuous series of oceanic trenches, volcanic arcs, and volcanic belts and plate movements. It has 452 volcanoes (more than 75% of the world's active and dormant volcanoes).
The abundance of volcanoes and earthquakes along the Ring of Fire is caused by the amount of movement of tectonic plates in the area.
Recently, Mount Ili Leotolok in eastern Indonesia within the Ring of Fire erupted, forcing thousands of people to evacuate. This mountain is among the three currently erupting volcanoes in the country. The other two includes Merapi on Java Island and Sinabung on Sumatra island.
Indonesia has more than 400 volcanos as it is the meeting point of three major continental plates. They are the Pacific plate, Indo-Australian plate and the Eurasian plate.
AIPA: It stands for the Implementation of the Paris Agreement. The Government of India (GoI) recently constituted a 17 member Apex Committee AIPA under the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC). The Apex Committee for AIPA was chaired by Environment Secretary Mr. Rameshwar Prasad Gupta.
It has been constituted to ensure coordinated response to climate change matters and to keep the country on track towards meeting its climate change obligations under the Paris Agreement, which includes Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs).
The NDCs will act as the national authority for regulating carbon markets in India under Article 6.2, Article 6.4 and Article 6.8 of the Paris Agreement.
The committee will also regularly communicate and report the progress of India’s status in achieving its NDC to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
The year 2021 seeks to mark the beginning of implementation of the Paris Agreement.
Paris Climate Agreement: It is a historic international accord which was signed in 2015. It brings almost 200 countries together in setting a common target to reduce global greenhouse emissions in an effort to fight climate change. The Paris Agreement comes under the broad umbrella of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
The pact seeks to keep global temperature rise to below 2 degrees celsius from pre-industrial levels, and to try and limit the temperature increase even further to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
For this, each country has pledged to implement targeted action plans that will limit their greenhouse gas emissions.
Under the agreement, rich and developed countries will provide financial and technological support to the developing world in their quest to fight and adapt to climate change.
Zebrafish: It is a tiny freshwater fish. It is barely 2-3 cm long. It can efficiently regenerate its damaged heart within a short time period. This fish is found in the tropical and subtropical regions. It is native to South Asia’s Indo-Gangetic plains, where they are mostly found in the paddy fields and even in stagnant water and streams. It is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name Danio. Zebrafish is also an important and widely used vertebrate model organism in scientific research, for example, in drug development, especially in preclinical development.
Recently, scientists at Pune-based Agharkar Research Institute have used the Zebrafish as a research model and identified genes that can promote heart regeneration. Scientists have sought to decode the heart regeneration processes using this animal model.
World Soil Day 2020: The day is celebrated every year on December 5 to raise awareness of the importance of soil quality for human well-being, food security and ecosystems.
This year, the official theme of World Soil Day, as suggested by the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) is ‘Keep soil alive, protect soil biodiversity’. The theme aims to raise awareness of the importance of sustaining healthy ecosystems and human well-being.
In 2002, the International Union of Soil Sciences recommended to celebrate World Soil Day annually on 5 December. Also, FAO supported the formal establishment of World Soil Day as a global awareness-raising platform under the leadership of the Kingdom of Thailand and within the framework of the Global Soil Partnership. The conference of FAO was unanimously endorsed World Soil Day in June 2013 and requested its official adoption at the 68th UN General Assembly. In December 2013, UN General Assembly at the 68th session declared 5 December as World Soil Day. The first World Soil Day was celebrated on 5 December, 2014.
Fifth December was chosen as World Soil Day because this date corresponds the birthday of the late H.M. King Bhumibol Adulyadej, King of Thailand who was one of the main proponents of this initiative.
Indian Policy
Sahakar Pragya: It is the name of the new initiative recently unveiled by the Union Minister Narendra Singh Tomar. Sahakar Pragya is an initiative of National Cooperative Development Corporation (NCDC). This initiative aims to help in capacity development of the cooperative sector in India, through the training programme.
Under the initiative, 45 new training modules have been developed for the farmers and would be imparted to primary cooperative societies in rural areas of the country by NCDC.
The training modules will impart knowledge and organisational skills and attempt to prepare the primary cooperative societies across the country to be able to play a big role in the government’s AtmaNirbhar Bharat initiative.
Narendra Singh Tomar: He is the Minister of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Rural Development, Panchayat Raj and Food Processing Industries.
Honey FPO Programme: It refers to the Honey Farmer Producer Organisation (FPO) Programme.
Recently, the Honey FPO Programme of National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India Limited (NAFED) was inaugurated by the the Union Minister of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, Narendra Singh Tomar virtually.
The inauguration programme was hosted online and attended by the new Honey FPOs, farmers and FPOs from various parts of the country.
The Honey FPO Programme for producing honey was launched in five states. NAFED will set up the FPOs at:
- Bharatpur (Rajasthan)
- East Champaran (Bihar)
- Morena (Madhya Pradesh)
- Sunderbans (West Bengal)
- Mathura (Uttar Pradesh)
The main objective of the Honey FPO Programme is to address the issues faced by the beekeeping industry. It will not only promote honey production in the country but will also help in achieving the goal of increasing farmer’s income.
The Honey FPO Programme has been launched under the Central Sector Scheme for Formation & Promotion of new 10,000 FPOs.
The Government has approved 2,200 FPOs for the current financial year 2020-21.
The task of creating these FPOs has been given to Nabard (600 FPOs), Small Farmers’ Agribusiness Consortium (500), National Cooperative Development Corporation (500) and NAFED which will support 50 commodity-specific FPOs and some State-level organizations.
Note: The First ever Honey FPO is the Chambal FED Shahad Utpadak Sahakari Samiti in Madhya Pradesh which was registered on 11 Nov 2020 under the Cooperatives Act, 1912.
NAFED: It refers to the National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India Ltd. NAFED is an apex organization of marketing cooperatives for agricultural produce in India. It was founded on the birthday of Mahatma Gandhi on 2 October 1958 to promote the trade of agricultural produce and forest resources across the nation. It is registered under Multi State Co-operative Societies Act. It is headquartered in New Delhi. The current Chairman of NAFED is Bijender Singh.
MoE: It refers to the Ministry of Education. MoE was formerly known as the Ministry of Human Resource Development (1985–2020). The ministry is responsible for the implementation and formulation of the National Policy on Education approved by Union cabinet of India and to ensure that it is implemented in letter and spirit. The Ministry is further divided into two departments. They are,
the Department of School Education and Literacy, which deals with primary, secondary and higher secondary education, adult education and literacy and the Department of Higher Education, which deals with a university education, technical education, scholarship, etc. The current Union Education Minister is Ramesh Pokhriyal 'Nishank.
Recently, the Union Education Minister Ramesh Pokhriyal 'Nishank has set up a Task Force for preparing a roadmap for implementation of proposal to impart technical education to students in their mother tongue.
The Task Force has been set up under the chairmanship of Secretary, Higher Education Amit Khare. The task force will submit a report in one month after taking into consideration the suggestions made by various stakeholders.
The decision to constitute a Task Force was taken at a high-level meeting chaired by Education Minister for the effective implementation of National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. According to Education Minister, the decision the decision in line with PM Modi’s vision of allowing students to pursue professional courses such as medicine, engineering, law, etc in their mother tongue.
The Minister said that no language will be imposed on any student but enabling provisions should be made so that bright students are not deprived of Technical Education due to lack of knowledge of English language.
Indian polity
Roshni Act: the Jammu and Kashmir State Land (Vesting of Ownership to the Occupants) Act, 2001, popularly known as the Roshni Act, was recently declared 'null and void' by the government of Jammu and Kashmir.
The Roshni Act of 2001, gave ownership rights to the unauthorised occupants of state land against payment of a premium.
Earlier, the Jammu and Kashmir State Land (Vesting of Ownership to the Occupants) Act, 2001, popularly known as the Roshni Act was passed by the then National Conference government to give ownership to people in possession of state land, with a cut-off of 1990, and against a payment as determined by the government.
Since the aim was to generate resources for hydroelectric power projects, it was called Roshni (Light) Act. The government said the revenue generated would be spent on commissioning hydroelectric power projects in the state, hence the name “Roshni”.
However, CAG (Comptroller and Auditor General) of India, in its 2014 report, termed the scheme a Rs-25,000-crore scam. In October 2018, then Governor Satya Pal Malik repealed the Roshni Act prospectively.
NCPCR: IT refers to the National Commissioner for Protection of Child Rights. The NCPCR recently established Maharashtra’s first “Child-friendly” police station as per its guidelines in Pune. The Child friendly police station has been established complying with the Juvenile justice act.
Pune police worked with Hope for Children Foundation to set up this. The foundation is to train the police on child friendly mechanism.
Child-friendly police station is an innovative concept which will work towards character building among children. It will not only create perception that police are not enemies but friends of people but also aim to prevent juvenile crimes and ensure children reforms.
The main objective of the Maharashtra Government is to create an environment that will enable children to report cases and crimes without fear and also to eliminate gratitude eyes against the police among the public.
JJ Act 2015: It refers to the Juvenile Justice Act 2015. JJ Act 2015 was passed on 7 May 2015 by the Lok Sabha. It was passed on 22 December 2015 by the Rajya Sabha. The Act is the major legal text on Child Protection in India.
Key Highlights of the JJ Act, 2015:
- The JJ Act guarantees the security, the protection, the education and the well-being of the children in need in India.
- The JJ Act recommends enquiries to determine if the situation of vulnerability of a child requires a placement in a children’s home.
- The JJJ Act makes it mandatory to set up Juvenile justice boards in every district.
- Under the JJ Act the Central Adoption Resource Authority (ACRA) was granted the status of statutory body.
- JJ Act makes it mandatory for the Child Care Institutions run by Non-Governmental organizations (NGOs) or state governments to register under the Juvenile Justice act.
The Juvenile Justice Board comprises of a Judicial Magistrate and two social workers. It is a judiciary body to which the children accused of a crime is brought. It is a separate court for the juveniles.
Note: The Act was recently amended in 2016 to provide an organized system for adoption of an orphan or an abandoned child. According to the Juvenile act, the minors in the age group between 15 and 18 years are to be treated as adults in the case of heinous crimes.
Juvenile: In India, a Juvenile is an individual below the age of 18 years. As per the Indian laws, a child below the age of 7 years cannot be convicted under any law for any crime.
International
World Computer Literacy Day: The World Computer Literacy Day is observed on 2nd December every year to create awareness and drive digital literacy in underserved communities worldwide.
The day is aimed at promoting technological skills, especially in children and women. The World Computer Literacy Day controls the advanced gap that exists in the world today.
The day was originally founded by the Indian computer company NIIT to mark its 20th anniversary in 2001. World Computer Literacy Day was first observed and held in the year 2001 on 2nd Dec.
International Day for the Abolition of Slavery: The day is observed on 2nd December since 1986 by the United Nations General Assembly every year.
The day focuses on eradicating contemporary forms of slavery, such as trafficking in persons, sexual exploitation, the worst forms of child labour, forced marriage, and the forced recruitment of children for use in armed conflict.
According to the International Labour Organization (ILO) more than 40 million people worldwide are victims of modern slavery. In addition, more than 150 million children are subject to child labour, accounting for almost one in ten children around the world.
The International Day for the Abolition of Slavery, 2 December, marks the date of the adoption, by the General Assembly, of the United Nations Convention for the Suppression of the Traffic in Persons and of the Exploitation of the Prostitution of Others (resolution 317(IV) of 2 December 1949).
ILO has adopted a new legally binding Protocol designed to strengthen global efforts to eliminate forced labour, which entered into force in November 2016.
World AIDS Day: The day is observed on the 1st of December every year to raise public awareness about Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome, AIDS. It is being observed since 1988. World AIDS Day was the first global health day to be celebrated.
The theme for 2020 is “Global solidarity, shared responsibility”.
Every year the last week of November is celebrated as AIDS awareness week. The first AIDS Awareness Week was celebrated in 1984 in San Francisco.
AIDS: It is the abbreviation for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. It is a chronic illness, which can also be potentially life-threatening. There is currently no cure for it. The disease is caused by the human immunodeficiency virus, HIV which affects the human immune system.
International institutions like the World Health Organisation (WHO), the Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS), national governments, health agencies and nonprofits across the world work tirelessly throughout the year, every year, to raise awareness about, conduct research on and find solutions for the disease.
NACO: It stands for National AIDS Control Organisation. NACO is a division of the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare that provides leadership to HIV/AIDS control programme in India through 35 HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control Societies. This organization was established in 1992. It is "the nodal organisation for formulation of policy and implementation of programs for prevention and control of HIV/AIDS in India. It conducts estimates of the disease once in every 2 years along with National Institute of Medical statistics and Indian Council of Medical Research.
Note: India is a signatory to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and has committed itself to achieving the target of ending the epidemic of AIDS by 2030. Since the inception of the National AIDS Control Program in 1992, India has done a commendable job in raising awareness and bringing down the number of HIV infections.
SCO Online International exhibition: The first ever SCO Online Exhibition on Shared Buddhist Heritage was launched recently by the Vice President of India & Chair of the SCO Council of Heads of Government in 2020 Venkaiah Naidu. He launched the exhibition during the 19th Meeting of the SCO Council of Heads of Government (SCO CHG), held in New Delhi, in video-conference format.
This SCO online International exhibition which is the first ever of its kind, is developed and curated by National Museum, New Delhi, in active collaboration with Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) member countries. The exhibition deploys state of the art technologies like 3D scanning, webGL platform, innovative curation, virtual space utilization, and narration methodology etc.
The visitors can explore the Indian Buddhist treasures from the Gandhara and Mathura Schools, Nalanda, Amaravati, Sarnath etc. in a 3D virtual format.
The Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) is connected with other countries through Buddhist philosophy and art of Central Asia.
IDPD: It refers to the International Day of Persons with Disabilities. IDPD is observed annually on 3 December to promote the full and equal participation of persons with disabilities and to take action for the inclusion of persons with disabilities in all aspects of society and development. It was originally called “International Day of Disabled Persons” until 2007.
This year, the International Day of Persons with Disabilities was commemorated throughout the week of 30 November to 4 December in conjunction with the 13th session of the Conference of States Parties to the Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities.
The theme this year is “Building Back Better: toward a disability-inclusive, accessible and sustainable post COVID-19 World”. WHO (World Health Organization) supported this theme by underlining the importance of fostering an inclusive culture and responding to the urgent needs of people with disability in all aspects of society, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.
The annual observance of the International Day of Disabled Persons was proclaimed in 1992 by United Nations General Assembly resolution 47/3. It aims to promote the rights and well-being of persons with disabilities in all spheres of society and development, and to increase awareness of the situation of persons with disabilities in every aspect of political, social, economic and cultural life.
USA: The United States of America (USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country consisting of 50 states, a federal district, five major self-governing territories, and various possessions. The 50 states covers a vast swath of North America, with Alaska in the northwest and Hawaii extending the nation’s presence into the Pacific Ocean. The currency used in USA is United States dollar - USD also abbreviated US$. The capital of US is Washington, D.C. The current President of US is Joe Biden.
Recently, US President-elect Joe Biden and Vice President-elect Kamala Harris announced an all-women team of the White House staff to serve in senior communication roles.
According to Biden’s office, this will be the first time the communications positions will be filled entirely by women. The move to appoint an all-women senior media team shows Biden’s continued commitment to building an administration that “looks like America”.
Four of the seven appointments are women of colour. Harris has called the team “barrier shattering”.
He has chosen former Barack Obama administration's State Department spokesperson Jen Psaki as his White House press secretary. He is also expected to nominate Indian-origin Neera Tanden as his budget chief.
Tanden is the president and CEO of the left-leaning think tank Centre for American Progress (CAP), and the CEO of the American Progress Action Fund.
National
National Organ Donation Day: National Organ Donation Day was celebrated on 27th November by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. This day is being observed since last 10 Years. This year marks the 11th National Organ Donation Day. It is organized by the National Organ & Tissue Transplant Organization (NOTTO) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Union Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India launched Organ Donation Day in the year 2010 in New Delhi.
The main aim of observing this day is to promote awareness and recognize the selfless contribution made by deceased donors to healthcare and mankind which re-instils our faith in humanity.
NOTTO: It refers to the National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization. NOTTO is a National level organization set up under Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India (GoI). It is headquartered in New Delhi. It has following two divisions:
- National Human Organ and Tissue Removal and Storage Network.
- National Biomaterial Centre.
Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994: Transplantation of Human Organs Act was passed in 1994 and subsequently amended in 2011 thus bringing in form Transplantation of Human Organs (Amendment) Act 2011.
National Human Organ and Tissue Removal and Storage Network will be established initially for Delhi and gradually expanded to include other States and Regions of the country. This division of the NOTTO will be the nodal networking agency for Delhi and it shall be the network for Procurement Allocation and Distribution of Organs and Tissues in Delhi.
NOTP: It refers National Organ Transplant Programme. NOTP provides financial grants for establishing Regional Organ & Tissue Transplant Organisations (ROTTOs), State Organ & Tissue Transplant Organizations (SOTTOs), developing new and upgrading existing retrieval and transplant centres.
Note: India ranked third in the world as per WHO Global Observatory on Donation and Transplantation (GODT) in terms of organ donation.
33rd PRAGATI Meet: The Prime Minister of India recently chaired the 33rd PRAGATI (ro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation) meeting to review multiple projects, grievances and programmes.
During the meeting:
- Grievances related to COVID-19 and to the PM Awas Yojana (Gramin) were taken up.
- Projects worth around Rs 1.41 lakh crore, related to ten states and union territories namely Odisha, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Jammu & Kashmir, Gujarat, Haryana,and Dadra and Nagar Haveli were reviewed.
- The projects that were reviewed were taken up by DPIIT (Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade), Ministry of Railways, Power Minister and Ministry of Road, Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
- The schemes including PM Awas Yojana and PM SVANidhi were also reviewed.
- PM Modi during the meeting asked the States to develop a State Export Strategy.
PRAGATI: It stands for Pro-Active Governance and Timely Implementation. PRAGATI was launched by the Government of India (GoI) on 25 March 2015. It is a multi-purpose and multi-modal platform that is aimed at addressing common man’s grievances. Its main objective is Project implementation, Project monitoring and Grievance redressal. It also monitors the projects and schemes of the central government. It was designed by the Prime Minister Office in coordination with National Informatics Centre (NIC).
The PRAGATI platform combines three latest technologies namely Digital data management, video conferencing and Geo-spatial technology. With the help of these three technologies it brings the Secretaries of GoI and the Chief Secretaries of the Sate on one stage. The Prime Minister is able to discuss the issues with the concerned Central and State officials and can also avail data with full information and latest visuals of the ground level situation. Thus, it binds the state and Centre together and thereby promotes Cooperative Federalism.
The key feature of PRAGATI is that it is a three-tier system that includes the Prime Minister Office, GoI secretaries and Chief Secretaries of the state.
Under PRAGATI, the Prime Minister holds monthly interactions with the secretaries and Chief Secretaries. The meeting takes place on the fourth Wednesday of every month called “PRAGATI Day”. On this day based on the database from public grievances, pending projects and ongoing programmes, the issues are flagged before the Prime Minister. The data bases are collected from Project monitoring groups and Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
In the previous 32 such meetings, a total of 275 projects worth Rs 12.5 lakh crore have been reviewed and 47 programmes/schemes and grievances across 17 sectors have been taken up.
India and Surinam: The 7th edition of India-Suriname Joint Commission Meeting (JCM) was held virtually by both the nations. The meeting was co-chaired by the Minister of State for External Affairs, V Muraleedharan, and the Minister of Foreign Affairs, International Business and International Cooperation of the Republic of Suriname, Ambassador Albert R. Ramdin.
During the meet, both the nations reviewed the bilateral ties, deepened political dialogue, and exchanged views on multilateral and regional cooperation.
Both the nations agreed to build cooperation in the sectors like Business and Investment and to establish industries in health, agriculture, mining, energy, defence and cultural & education. They also assured to undertake projects to improve South-South Cooperation.
Note: The diplomatic relations between India and Suriname were established in 1976 and the Indian embassy was opened in 1977 in Paramaribo while Suriname opened its embassy in New Delhi in 2000. The bilateral trade between both the nations stands at $228.49 million. Suriname had also supported India’s candidature for permanent seat in the United Nations Security Council (UNSC).
Suriname: Suriname officially known as the Republic of Suriname is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is one of the smallest countries in South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west and Brazil to the south. It is considered to be a culturally Caribbean country, and is a member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM). It is the only sovereign nation outside Europe where Dutch is the official and prevailing language of government, business, media, and education. The captal of Suriname is Paramaribo. The currency used here is Surinamese Dollar (SRD). The current President of Suriname is Chan Santokhi.
India & USA: India and the USA (United States of America) have recently signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) in the field of Intellectual Property Cooperation.
The MoU was signed by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, Ministry of Commerce and Industry and US Patent and Trademark Office, Department of Commerce of the US.
The Union Cabinet in its meeting on 19th February this year had given the approval for signing the MoU with USPTO in the field of IP Cooperation.
The main aim of the MoU is to increase IP co-operation between the two countries. It aims to facilitate exchange and dissemination of best practices, experiences and knowledge on IP among the public, and between and among the industry, universities, research and development organizations, and Small and Medium-sized Enterprises.
Both the two sides will develop Biennial Work Plan to implement the MoU which will include the detailed planning for carrying out of the co-operation activities including the scope of action.
National Pollution Control Day: The National Pollution Control Day is observed every year on December 2 to commemorate the life of people lost in the unfortunate incident of Bhopal Gas Tragedy that occurred in the year 1984 on the night of 2–3 December.
The year 2020 marks the 36th anniversary of the Bhopal Gas Tragedy. Through this day, awareness is created about the rising pollution of air, water, and soil, as well as shifts the attention of people with regards to the pollution control acts.
The main objectives of the day are as follows:
- To spread awareness of managing and controlling industrial disasters.
- To prevent the pollution produced by industrial processes or human negligence
- To make people and industries aware of the importance of pollution control acts
Indian government has launched various acts and rules for controlling and preventing pollution in India. They are as follows:
- Water (Prevention & Control of Pollution) Act of 1974
- Water (Prevention & Control of Pollution) Cess Act of 1977
- Air (Prevention & Control of Pollution) Act of 1981
- Environment (Protection) Rules of 1986
- Environment (Protection) Act of 1986
- Manufacture, Storage and Import of Hazardous Chemical Rules of1989
- Hazardous Waste (Management & Handling) Rules of 1989
- Manufacture, Storage, Import, Export & Storage of Hazardous Micro- Organisms Genetically Engineered Organisms or Cells Rules of 1989
- The National Environment Tribunal Act 1995
- Chemical Accidents (Emergency, Planning, Preparedness, and Response) Rules of 1996
- Bio-Medical Waste (Management & Handling) Rules of 1998
- Recycled Plastics Manufacture & Usage Rules of 1999
- Ozone Depleting Substances (Regulation) Rules of 2000
- Noise Pollution (Regulation & Control) Rules of 2000
- Municipal Solid Waste (Management & Handling) Rules of 2000
- Batteries (Management & Handling) Rules of 2001.
- Maharashtra Bio-Degradable Garbage (Control) Ordinance of 2006
- Environment Impact Assessment Notification of 2006
National Pollution Control Board (NPCB) is the main governing body, that regularly conducts checks on industries to know whether they are following environmental regulations or not.
People In News
AR Rahman: He is an Oscar and Grammy-winning Indian composer who has been roped in as ambassador of the BAFTA Breakthrough initiative in India. The full form of BAFTA is British Academy of Film and Television Arts.
The initiative marks BAFTA's first steps into India. The talent hunt initiative will enable the Academy to identify and nurture up to five talents working in film, games, or television in India. The exercise, known as BAFTA Breakthrough initiative, is part of the Academy's year-round effort to support new talent, coming up in the film, games and television industries in the UK, China, India and the US and gives them access to unique career development and mentoring opportunities.
Janet Yellen: She is the former Federal Reserve chairperson who has been named the treasury secretary by the US President elect the Joe Biden. She would be the first woman ever to hold the post.
Gitanjali Rao: She is a young Indian-American scientist and inventor who has been named first-‘Kid of the Year’ by TIME magazine.
The fifteen-year-old has been selected for her work using technology to combat issues ranging from contaminated drinking water to opioid addiction and cyberbullying. She created applications named ‘Kindly’ to help people, especially kids, fight opioid addiction and cyberbullying.
This is for the first time that the TIME magazine has launched the Kid of The Year” award. TIME magazine had partnered with Nickelodeon and searched social media and school districts across the country to shortlist the most influential child of 2020.
Anita Anand: She is a British Indian journalist and author who has won a prestigious history-literary prize in the UK. She won this award for her book 'The Patient Assassin: A True Tale of Massacre, Revenge and the Raj' that tells the story of a young man caught up in the 1919 Jallianwala Bagh massacre in Amritsar.
PEN Hessell-Tiltman Prize for History 2020, is awarded annually for a non-fiction book of specifically historical content.
About: Marjorie Hessell-Tiltman was a member of PEN during the 1960s and 1970s and on her death in 1999; she bequeathed 100,000 pounds to the PEN Literary Foundation to found a prize in her name. English PEN stands for Poets, Playwrights, Editors, Essayists, and Novelists. It is one of the world's oldest human rights organizations championing the freedom to write and read. It is the founding centre of PEN International, a worldwide writers' association with 145 centres in more than 100 countries.
Entries for the award are required to be works of high literary merit which can cover all historical periods and not primarily written for the academic market.
Varsha Joshi: She is an IAS officer of 1995 batch, AGMUT cadre who has been appointed by the Government of India (GoI) as the new Chairperson of National Dairy Development Board (NDDB). Her appointment will be effective from December 1, 2020.
She is presently served as Joint Secretary (CDD), Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, Government of India.
She will replace incumbent Dilip Rath, whose tenure as Chairman of NDDB ended on November 30, 2020.
Ranjitsinh Disale: He is a government teacher from Zilla Parishad Primary School, in Paritewadi village, Solapur district of Maharashtra. He is the first Indian to win this award, which carries prize money of $1 million (Rs 7.4 crore).
The 32-year-old has won the annual Global Teacher Prize 2020 in recognition of his efforts to promote girls’ education in his village and trigger a quick-response (QR) coded textbook revolution in India.
Disale made efforts and added QR codes to textbooks of primary classes to provide links to audio poems, video lectures, stories and assignments. He also worked towards education for girls and teaching people about the ill-effects of teenage marriage and even helped to achieve 100% attendance of girls.
He even created history by announcing to share half the prize money with the nine finalists from across the world for the award, where each one will receive about $55,000 each.
Global Teacher Prize: The Global Teacher Prize is an annual prize founded by the Varkey Foundation in 2014 to recognize an exceptional teacher who has made an outstanding contribution to the profession. The award is given in partnership with UNESCO.
Places In News
Uttarakhand: It is a state in northern India crossed by the Himalayas. It is known for the natural environment of the Himalayas, the Bhabar and the Terai and also for for its Hindu pilgrimage sites. Uttarakhand became the 27th state of the Republic of India on 9 November 2000. it was carved from the Himalayan districts of Uttar Pradesh. Its winter Capital is Dehradun and summer capital is Gairsain. The Chief Minister and the Governor of Uttarakhand are Trivendra Singh Rawat and Baby Rani Maurya respectively.
Recently, The Chief Minister of ttarakhand Trivendra Singh Rawat inaugurated the Suryadhar Lake at Doiwala, Dehradun.
The Suryadhar Lake is 28 meters wide and 10 meters deep with a capacity of 77,000 cubic meters and 550 meters long.
- The benefits of the lake are as follows:
- It will fulfill the drinking water and irrigational needs of 18-20 villages,
- It will recharge the water resources in the area and help build a healthy eco-system that will attract migratory birds.
The state government plans to organize a water sports festival at the lake either by Makar Sankranti or Basant Panchami next year to showcase the beauty of its surrounding environs.
Rajasthan: Rajasthan is a state in northern India. It comprises most of the wide and inhospitable Thar Desert (also known as the "Great Indian Desert") and shares a border with the Pakistani provinces of Punjab to the northwest and Sindh to the west, along the Sutlej-Indus river valley. It became a State after 1947 when the princely states and chiefships were integrated into India in stages, and the state took the name Rajasthan. It assumed its present form on November 1, 1956, when the States Reorganization Act came into force. The Capital of Rajasthan is Jaipur. The current Chief Minister and Governor of Rajasthan are Ashok Gehlot and Kalraj Mishra respectively.
Recently, the Union Minister of Railways, Piyush Goyal inaugurated the newly electrified Dhigawara-Bandikui section of North Western Railway (NWR) in the state of Rajasthan. The Minister also flagged off the first train on this newly electrified route.
The Dhigawara-Bandikui section is on Delhi-Ajmer route via Jaipur.
Aim: The Railways has set the target to electrify the entire percentage of railway lines across the country in a phased manner. Once these electrified trains start running, the trains that run on diesel will be stopped which, in turn, will not only eliminate pollution but also decrease the dependence on the fuel imported from outside. The electrified trains will run from the electricity produced in India, which is expected to save significant revenue.
Karnataka: It is a state in the south western region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as the State of Mysore, it was renamed Karnataka in 1973. It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, Goa to the northwest, Maharashtra to the north, Telangana to the northeast, Andhra Pradesh to the east, Tamil Nadu to the southeast, and Kerala to the south. It is the only southern state to have land borders with all of the other 4 southern Indian sister states. Its capital city is Bangalore. The current Chief Minister and Governor of Karnataka are B. S. Yediyurappa and Vajubhai Rudabhai Vala respectively.
Recently, the Karnataka government launched the Learning Management System (LMS) in digital mode. It will be implemented in government colleges within the state. It is to be implemented at a cost of Rupees 304 crores.
From this academic year i.e. 2020-21, the LMS will be implemented in 430 Government First Grade Colleges, 87 Polytechnics and 14 Government Engineering Colleges. The system is to be established in two ways such as establishing 2500 ICT enabled classes and learning management system based digital learning.
This digital platform will have multilingual e-content in the form of PPTs, videos, quizzes, assignment and e-study materials developed as per the University syllabus.
It is said to be the first of its kind initiative in the country aimed at encouraging digital learning and improving the Gross Enrolment Ration (GER) in higher education.
LMS for higher education institutions will facilitate earning of about 4.5 lakh students through around 24000 teachers.
GER: It refers to Gross Enrolment Ratio. GER is the number of students enrolled in an education system irrespective of their age. It is expressed in percentage of official school age population.
The details are provided by the AISHE (All India Survey on Higher Education)report prepared by the Ministry of Education (earlier Ministry of Human and Resource Development).
Nagaland: Nagaland is a mountainous state in northeast India, bordering Myanmar. It was formally inaugurated on December 1st, 1963, as the 16th State of the Indian Union. It is bounded by Assam in the West, Myanmar (Burma) on the east, Arunachal Pradesh and part of Assam on the North and Manipur in the South. Kohima is the capital of Nagaland. Unlike most states in India, Nagaland has been granted a great degree of state autonomy, as well as special powers and autonomy for Naga tribes to conduct their own affairs. Each tribe has a hierarchy of councils at the village, range, and tribal levels dealing with local disputes. The Chief Minister and the Governor of Nagaland are Neiphiu Rio and R.N. Ravi respectively.
Recently, Nagaland celebrated its 58th Statehood day. It became the 16th State of the Union of India on 1st December 1963.
History: After the independence of India in 1947, the area dominated by Naga ethnic groups remained a part of the province of Assam. Nationalist activities arose amongst a section of the Nagas. Phizo-led Naga National Council demanded a political union of their ancestral and native groups. In July 1960, following discussion between Prime Minister Nehru and the leaders of the Naga People Convention (NPC), a 16-point agreement was arrived at whereby the Government of India recognised the formation of Nagaland as a full-fledged state within the Union of India. Nagaland became the 16th state of India on 1 December 1963.
Meghalaya: It is a state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed by carving out two districts from the state of Assam: the United Khasi Hills and Jaintia Hills, and the Garo Hills on 21 January 1972. Its capital is Shillong. The current Governor and Chief Minister of Meghalaya are Satya Pal Malik and Conrad Sangama respectively.
Recently, the Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the Government of India have signed a USD 132.8 million loan agreement for Meghalaya Power Distribution Sector Improvement Project.
The project aims to strengthen and modernize the distribution network and improve the quality of power supplied to households, industries, and businesses in the northeastern state of Meghalaya.
This project seeks to support ‘24×7 Power for All’ initiative in Meghalaya. It will help the State reduce its high technical and commercial losses through network strengthening, metering and billing efficiency improvements.
Under this project:
- 23 substations will be constructed.
- 45 substations, including the addition of control room equipment and protection systems will be renovated and modernised.
- 2,214 km of distribution lines and associated facilities covering three out of the six circles in the State will be and installed and upgraded.
The installation of smart meters will benefit about 180,000 households.
West Bengal: West Bengal is a state in eastern India. It lies between the Himalayas and the Bay of Bengal. It borders Bangladesh in the east, and Nepal and Bhutan in the north. It also borders the Indian states of Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, Sikkim, and Assam. The state capital is Kolkata. It was established on 26 January 1950. The current Chief Minister and Governor of West Bengal are Mamta Banerjee and Jagdeep Dhankhar respectively.
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) and India have recently signed $50 million loan agreement to boost digital platforms for public finance reforms in West Bengal.
The agreement was signed on 2nd December 2020 to improve financial management procedures and operational efficiencies in West Bengal.
The project has been titled as the ‘West Bengal Public Finance Management Investment Programme’. The project will help to achieve more fiscal savings, promote informed decision making, and improve service delivery in the state.
ADB: It refers to the Asian Development Bank. ADB is a regional development bank established on 19 December 1966. It is headquartered in the Ortigas Center located in the city of Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines. It has 68 members including India and is committed to achieving a prosperous, inclusive, resilient and sustainable Asia & the Pacific, while sustaining its efforts to eradicate extreme poverty. The current President of ADB is Masatsugu Asakawa.
Science and Technology
ASKAP: It stands for Australian Square Kilometre Array Pathfinder. ASKAP is a new type of radio telescope developed by Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO).
ASKAP has mapped over three million galaxies in a record 300 hours during its first all-sky survey. The results provided by ASKAP are being used for the development of the SKA (Square Kilometer Array). SKA is an international project with the aim of building the largest telescope in the world.
About: ASKAP is a radio telescope that was designed to be a survey instrument capable of quickly observing the whole accessible sky. ASKAP surveys are designed to map the structure and evolution of the Universe, which it does by observing galaxies and the hydrogen gas that they contain.
The telescope is located at the Murchison Radio-astronomy Observatory (MRO) in Western Australia and is operated by the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization (CSIRO).
It uses novel technology developed by CSIRO, which is a kind of a “radio camera” to achieve high survey speeds and consists of 36 dish antennas, which are each 12m in diameter.
The present Rapid ASKAP Continuum Survey (RACS) taken by the ASKAP telescope is like a “Google map” of the Universe where most of the millions of star-like points are distant galaxies, about a million of which have not been seen before.
The key feature of the telescope is its wide field of view, which offered the ability to take panoramic pictures of the sky in great detail.
Mapping of Universe: Mapping of the Universe enables the astronomers to study the formation of stars and how galaxies and their supermassive black holes evolve and interact with each other.
HAL: It refers to the Hindustan Aeronautics Limited. HAL is an Indian state-owned aerospace and defence company and is governed under the management of the Indian Ministry of Defence. It is headquartered in Bangaluru, India. The founder of HAL is Walchand Hirachand. It was founded on 23 December 1940. The current Chairman and Managing Director is R Madhavan.
Recently, HAL delivered the biggest cryogenic propellant tank C32-LH2 to the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) in Bengaluru. The Tank has been designed by HAL.
The C32-LH2 tank is a developmental cryogenic propellant tank of aluminium alloy designed for improving the payload capability of GSLV MK-III launching vehicle of ISRO.
The tank can load 5755 kg propellant fuel in the 89 Cubic Metre Volume.
The welds have been done to meet 100% quality requirements on Dye-penetrant check, radiography and lead-proof.
HAL has also partnered with ISRO to supply satellite structures for the PSLV (Polar Satellite Lauch Vehicle), GSLV Mark II and III launch vehicles.
Cryogenic fuels: Cryogenic fuels are fuels that require storage at extremely low temperatures in order to maintain them in a liquid state. These fuels are used in machinery that operates in space because ordinary fuel cannot be used there due to the very low temperatures often encountered in space, and due to absence of an environment that supports combustion. Cryogenic fuels most often constitute liquefied gases such as liquid hydrogen.
‘Damaru’ Inspired Lattice: Researchers at IIT Kanpur have recently developed the "Damaru" Inspired Lattice, which is used in stealth submarines and high-speed trains. The research is sponsored by A SPARC project of Ministry of Education.
The researchers demonstrated how with the use of a micro-structured hour-glass shaped metastructure in the lattice unit, one can get a wider variation of propagation and stop bands.
In this application, IIT Kanpur researchers also showed the nature of stiffness of a vibrating medium could be altered drastically by controlling the lattice micro-structure from regular honeycomb to auxtetic honeycomb structure.
The hour-glasses are developed in the Smart Materials Laboratory of IIT Kanpur using additive manufacturing.
Inspiration of the lattice they developed has come from a two-headed drum called ‘Dambaru’ or ‘Damaru’ which is used in ancient Hinduism and Tibetan Buddhism. It is said that Lord Shiva created and regulated the universe by producing a special sound through this musical instrument.
The Lattice has a wide range of applications in the field of vibration isolation for high-speed trains, stealth submarines and helicopter rotors.
Sports
Women's Pro Golf Tour (WPGT): Recently, Sneha Singh, of Hyderabad won the second pro-title in a competitive field in the seventh leg of the Women's Pro Golf Tour (WPGT).
The 16 year old amateur won her second pro-title when she notched up a four-shot clear victory with rounds of 71, 72 and 74 for a total of one-over par.
She dominated from first day of the tournament in a competitive field which also included Vaani Kapoor and Diksha Dagar.
She won her first title on the Hero WPGT in 2019.
Golf: It is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible.
Bahrain Grand Prix 2020: Lewis Hamilton (Mercedes-Great Britain) recently won the 2020 Bahrain Grand Prix at Bahrain International Circuit, Bahrain.
The race was the fifteenth round of the 2020 Formula One World Championship. This is the 11th victory for Hamilton of the season, and 95th F1 win of his career.
Hamilton now holds the records for the most wins (95), in Formula One history. Red Bull Racing teammates Max Verstappen (Netherlands) and Alexander Albon (Thailand) were second and third respectively.
Senior Individual World Cup: The Senior Individual World Cup is to be held from 12 to 18th December Belgrade, Serbia. India will be represented by A contingent of 42 members (24 wrestlers, 9 coaches, 3 support staff and 3 referees). Ravi Kumar and Deepak Punia are among the 24 wrestlers who will be participating in the first international competition after the nationwide lockdown was imposed in March due to the coronavirus pandemic.
The wrestlers will participate in the tournament as follows:
Men’s freestyle: Ravi Kumar (57 kg), Rahul Aware (61 kg), Naveen (70 kg), Gourav Baliyan (79 kg), Deepak Punia (86 kg), Satyavart Kadian (97 kg), Sumit (125 kg)
Men’s Greco-Roman: Arjun Halakurki (55 kg), Gyanender (60 kg), Sachin Rana (63 kg), Ashu (67 kg), Aditya Kundu (72 kg), Sajan (77 kg), Sunil Kumar (87 kg), Hardeep (97 kg), Naveen (130 kg)
Women’s: Nirmala Devi (50 kg), Pinki (55 kg), Anshu (57 kg), Sarita (59 kg), Sonam (62 kg), Sakshi Malik (65 kg), Gursharan Preet Kaur (72 kg), Kiran (76 kg)
India has attained a total of four Olympic quotas in wrestling through Bajrang Punia (men’s freestyle 65 kg), Vinesh Phogat (women’s 53 kg), Ravi Kumar and Deepak Punia.
They will have 2 more opportunities to attain the remaining quotas at the Asian Qualification Tournament scheduled in March 2021 and the World Qualification Tournament scheduled from April 29 to May 2, 2021.
Kuldeep Handoo: He is a Srinagar born Wushu coach and the first Dronacharya Awardee from the Union Territory (UT) of Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), who has been appointed as the Ambassador of Fit India movement.
He has won 11 gold medals in National and 6 in International stage,. He is the Wushu coach of Team India. Under his guidance Athletes have won 2 gold medals at the world championship and one at the World Cup. He also serves as Inspector of police in Jammu and Kashmir.
Fit India movement: Fit India movement was launched in August 2019, to encourage Indians to include fitness activities and sports in their daily lives to pave the way for a healthy and fit lifestyle. The founder of FIT India is Suparno Satpathy
Arts
SAG Awards 2022: The 28th Annual Screen Actors Guild (SAG) Awards for 2022, were recently announced.
Key Highlights:
- The ceremony took place at the Barker Hangar in Santa Monica, California, commenced with speeches by Hamilton’s Daveed Diggs, Lin-Manuel Miranda, and Leslie Odom Jr.
- The event witnessed several significant, historic moments.
Winners of SAG Awards 2022 in Different Categories:
Film:
Outstanding Performance by a Cast in a Motion Picture:
Child of Deaf Adults (CODA) won the award for the best film and created history by becoming the first film with a predominantly deaf cast to take home the honours.
What’s more, the lead actor of the film, Troy Kotsur, too made history by becoming the first deaf actor to win an individual trophy.
The actor gave his acceptance speech using a sign-language interpreter.
Male and Female Actor in a Leading Role:
Will Smith won the award for Outstanding Performance by a Male Actor in a Leading Role for King Richard, while Jessica Chastain bagged the trophy for Outstanding Performance by a Female Actor in a Leading Role for The Eyes of Tammy Faye.
Outstanding Performance by a Stunt Ensemble in a Motion Picture:
No Time to Die
Outstanding Performance by a Male and Female Actor in a Supporting Role
Troy Kotsur – CODA as Frank Rossi and Ariana DeBose – West Side Story as Anita.
Lifetime Achievement Award.
Hollywood legend Helen Mirren was presented with the Lifetime Achievement Award.
Television:
Outstanding Performance by a Male and Female Actor in a Television Movie or Limited Series:
Michael Keaton – Dopesick (Hulu) as Dr. Samuel Finnix and Kate Winslet – Mare of Easttown (HBO) as Marianne "Mare" Sheehan
Outstanding Performance by a Stunt Ensemble in a Comedy or Drama Series:
The Korean series by Netflix Squid Game created a record by winning the title for Outstanding Action Performance as a Stunt Ensemble since it is the first non-English show to do so.
Outstanding Performance by a Male and Female Actor in a Drama Series
Squid Game (Netflix) also made history by winning in the Outstanding Performance by a Male and Female Actor in Drama series categories for Lee Jung-Jae and Jung Ho-Yeon, respectively.
Outstanding Performance by a Male and Female Actor in a Comedy Series:
Jason Sudeikis – Ted Lasso (Apple TV+) as Ted Lasso and Jean Smart – Hacks (HBO Max) as Deborah Vance.
Outstanding Performance by an Ensemble in a Drama Series:
Succession (HBO) – Nicholas Braun, Juliana Canfield, Brian Cox, Kieran Culkin, Dagmara DomiÅ„czyk, Peter Friedman, Jihae, Justine Lupe, Matthew Macfadyen, Dasha Nekrasova, Scott Nicholson, David Rasche, Alan Ruck, J. Smith-Cameron, Sarah Snook, Fisher Stevens, Jeremy Strong, and Zoë Winters
Outstanding Performance by an Ensemble in a Comedy Series:
Ted Lasso (Apple TV+) – Annette Badland, Kola Bokinni, Phil Dunster, Cristo Fernández, Brett Goldstein, Brendan Hunt, Toheeb Jimoh, Nick Mohammed, Sarah Niles, Jason Sudeikis, Jeremy Swift, Juno Temple, and Hannah Waddingham
About Screen Actors Guild (SAG) Awards:
- Screen Actors Guild Awards (also known as SAG Awards) are accolades given by the Screen Actors Guild-American Federation of Television and Radio Artists (SAG-AFTRA).
- The award was founded in 1952 to recognize outstanding performances in movie and prime-time television.
- SAG Awards have been one of the major awards events in the Hollywood film industry since 1995.
- Film:
Discovery of Old Stone Age culture: Scientists in China have recently found evidence of a 40,000 years old culture, located 100 miles away from Beijing.
Where was it discovered?
- The site of excavation is located in Nihewan Basin.
- It is a depression in the northern, mountainous region in China.
- The site is called Xiamabei.
- The researchers found evidence of the culture about 8 feet below ground.
What did the researchers find?
- The layer of silt they found was found to be 39,000 to 41,000 years old based on carbon dating and more techniques of analysis.
- The researchers have found hundreds of mammal bones, tools, lithics and more in the sediment.
- Remains seemed to be in their original spots after it was abandoned by the residents.
- The remains revealed a vivid picture of how people lived 40,000 years ago in Eastern Asia.
- This is the earliest-known ochre workshop in East Asia. As per researchers, Ochre was used as an additive to be used in processing hides. It was also used as an adhesive to affix handles to stone tools.
Earlier discovery in Xiaochangliang site:
Paleolithic remains in East Asia:
- Some of the earliest paleolithic remains were also found at the Xiaochangliang site in East Asia. This site is also located in the Nihewan Basin in Yangyuan County in China, which is famous for the stone tools discovered there.
- This site was first discovered in 1923, by US geologist George Barbour.
- The tool forms that were discovered include notches, burins, side & end scrapers, and disc cores.
Why is it difficult to date Asian sites?
- It is usually more difficult to date Asian sites than African sites because Asian sites lack volcanic materials, which can be dated isotropically.
Kerala Kaliyattam Festival: The Kaliyattam festival is an annual Theyyam festival held in the temples in Kerala’s Malabar region.
About Theyyam Festival:
- The folk culture of Theyyam is believed to be over 800 years old.
- Theyyam is the name of a grand dance festival that is held in different parts of Kerala, including Kasargod.
- Called “Dance of Gods”, the Theyyam celebrations mainly happen in the Northern Malabar regions of Kerala which consists of present-day Kannur Districts, Kasargod, Vadakara and Koyilandy Taluks of Kozhikode and Mananthavady Taluk of Wayanad across thousands of Temple in the area and beyond.
- A similar custom is followed in the Mangalore region of neighbouring Karnataka known as Bhuta Kola.
- The people of these districts where this festival is celebrated consider Theyyam as a channel to a god and they thus seek blessings.
- There are around 456 different varieties of Theyyam.
- Males perform Theyyam, with the exception of the Devakoothu Theyyam, which is the only Theyyam ritual done by women.
- It can only be seen at the Thekkumbad Kulom temple.
Performance of the Ritual:
- Theyyam consists of thousand-year-old rituals, traditions, and customs.
- The musical dance act is performed with elaborate Headdresses, make-up, masks and accompanied by musical instruments including Chenda – parade celebrations bringing their offerings to the Goddess – and barefoot ritual fire walking.
- Generally, the dance is performed in front of the village shrine.
- It is also practiced as ancestor worship in homes, with elaborate rituals and rites.
- For the performance, there is no stage, curtain, or another similar setup. The devotees would either be standing or sitting in front of the shrine on a sacred tree.
- The shrine’s performance of a particular deity, depending on its hierarchy and significance, lasts 12 to 24 hours with intervals.
- The chief dancer who worships the shrine’s central deity has to reside in the rituals.
- The dancer, accompanied by the drummers, recites the ritual song, which narrates the stories and tales of the shrine’s deity or the folk deity to be worshipped.
- Folk musical instruments are played in the background.
Festivals of Kerala:
- Many of the temples in Kerala hold festivals on specific days of the year.
- Some festivals include Poorams, the best known of these being the Thrissur Pooram.
- Other known festivals are Makaravilakku, Chinakkathoor Pooram, Attukal Pongala and Nenmara Vallangi Vela.
- Onam is a harvest festival celebrated by the people of Kerala and is reminiscent of the state's agrarian past.
Monumental Destruction: The massive Russian attack on Ukraine has put not only human lives and physical infrastructure, but also priceless works of art, cultural artifacts, and monuments at risk of destruction.
What is at risk of destruction?
- Ukraine is home to several historical sites and heritage structures, while its museums have significant specimens of Baroque and folk art.
- Thousands of museums in Ukraine have in its collections important works of Ukrainian and Russian art, classical and Byzantine artifacts and paintings by masters such as Francisco Goya, Giovanni Bellini, and Jacques-Louis David.
- Kyiv’s Museum of Freedom has a collection of 4,000 objects recording Ukraine’s pro-democracy movement.
- The Odessa Fine Arts Museum has a collection of more than 10,000 objects, including Ukrainian and Russian “orthodox icons”, dating back to the 16th-century artists such as Myhailo Vrubel, Ivan Aivazovskyi, Mykola Reryh, Valentyn Sierov, Kostiantyn Somov, Zinaida Serebriakova, and Vasyl Kandynskyi.
- The country is also home to seven world heritage sites including the St Sophia Cathedral, one of the most-recognized landmarks in Kyiv and Kyiv Monastery of the Caves or Kyiv Pechersk Lavra, an Eastern Orthodox Christian monastery.
About Heritage Sites in Ukraine:
1. Saint-Sophia Cathedral:
- The Saint-Sophia Cathedral is an Eastern Orthodox church that was constructed in the 11th century, soon after the Christianization of Kievan Rus, in present-day Istanbul.
- Mosaics and frescos from that period have been preserved in the interior. Monastic buildings around the cathedral were constructed in the 17th and 18th centuries in Ukrainian Baroque style.
- The Kyiv Pechersk Lavra is a monastic ensemble that was developing from the 11th to the 19th centuries.
- It comprises churches, monasteries, and caves where saints were buried.
- The church greatly influenced subsequent temples, and together with the nearby monastic complex known as Kyiv-Pechersk Lavra, or Kyiv Monastery of the Caves, it helped the area become a center of Orthodox faith and thought.
- The Church of the Saviour at Berestove, adjacent to the Lavra, was added to the site in 2005.
- Kyiv Monastery of the Caves was founded in 1051.
2. City of Lviv:
- The city of Lviv was founded in the late Middle Ages and still preserves its medieval topography.
- The city has been shaped by the interactions of the different communities that have lived there through centuries, including various Christian groups, Muslims, and Jews.
- The architecture of the city represents a fusion of styles from Eastern Europe with influences coming from Italy and Germany.
- Several buildings from the Renaissance and Baroque periods have been preserved.
3. Struve Geodetic Arc:
- The Struve Geodetic Arc is a cross-border scientific and cultural heritage object.
- It is a series of 258 triangles that create a chain of 256 main points, stretching over a distance of 2,820 kilometres (1,750 mi).
- Its southernmost point is in the Ukrainian town of Staro-Nekrasovka, on the Black Sea, while its northernmost point is in Hammerfest, Norway.
- The points were set up in a survey by the astronomer Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve.
- Built from 1816-55, the collaborative structure helped determine Earth's exact shape and size.
- Due to the arc, the correct shape and size of Earth were established and Newton’s theory that Earth is a three-dimensional oval was also proved.
- Originally, there were 265 station points.
- The World Heritage Site includes 34 points in 10 countries (North to South: Norway, Sweden, Finland, Russia, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Belarus, Moldova, Ukraine), four of which are in Ukraine (site marker in Felshtyn pictured).
4. Ancient and Primeval Beech Forests of the Carpathians:
- This site comprises undisturbed examples of temperate forests that show how European beech expanded postglacially from a few isolated refuges in the Alps, Carpathians, Dinarides, Mediterranean, and the Pyrenees.
- In 2007, the site was originally listed as the Primeval Beech Forests of the Carpathians, shared by Slovakia and Ukraine, extended in 2011 to include the Ancient Beech Forests of Germany, and further extended in 2017 and 2021 to include forests in a total of 18 countries.
- In Ukraine, 13 forest reserves are listed.
5. Chernivtsi - Residence of Bukovinian and Dalmatian metropolitans:
- The Residence of Bukovinian and Dalmatian Metropolitans was built for the Eastern Orthodox metropolitan bishop in the late 19th century when the region was under the rule of Austria-Hungary. Built by Czech architect Josef Hlavka from 1864-1882, the giant
- The ensemble is built in the historicist style and combines features of Byzantine, Gothic, and Baroque architecture.
- The complex served as the bishop's residence until World War II. In 1955, the property was transferred to Chernivtsi University.
6. Ancient city of Tauric Chersonese and its Chora:
- The ruins of Tauric Chersonese are located outside of Sevastopol, in southwest Crimea, which was illegally annexed by Russia in 2014.
- The city was founded by Dorian Greeks in the 5th century BCE on the coast of the Black Sea.
- The site includes public building complexes, residential neighborhoods and early Christian monuments as well as remnants of Stone and Bronze age structures.
- The area around the city was important due to its wine production, and the remains of ancient vineyards have been well preserved.
- In the following centuries, the city saw the interactions of Greek, Roman, and Byzantine communities in the Black Sea region.
7. Wooden Tserkvas of the Carpathian Region in Poland and Ukraine:
- This UNESCO World Heritage Site comprises 16 wooden churches (tserkvas) that are spread out over Poland and Ukraine in the mountainous Carpathian region.
- The churches were built between the 16th and 19th centuries by the communities of Eastern Orthodox and Greek Catholic faiths.
- The designs have been influenced by the Orthodox ecclesiastical traditions with local influences.
- They exemplify the timber-building tradition of Slavic countries.
- They feature wooden bell towers, iconostasis screens, and interior polychrome decorations, as well as churchyards, gatehouses, and graveyards.
- The Holy Trinity Church in Zhovkva is pictured.
Economics
E-bill Processing System: The Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on March 2, 2022, launched the E-bill Processing system under the Digital India eco-system and Ease of Doing Business (EoDB).
Key Highlights:
- The launch of this electronic bill (e-Bill) processing system took place in New Delhi on the occasion of 46th Civil Accounts Day at Dr. Ambedkar International Centre.
- The Finance Minister had announced the e-governance initiative in the Union Budget 2022-23 presented in Parliament on February 1, 2022.
Key points:
- The e- Bill system will be implemented across all Central Ministries and Departments.
- This will enhance transparency, efficiency, and a faceless- paperless payment system.
- The suppliers and contractors, through this system, will now be able to submit their claims online which will be trackable on a real-time basis.
- The e-Bill system has been developed by the Public Financial Management System (PFMS) Division in the office of the Controller General of Accounts in the Department of Expenditure, Ministry of Finance (MoF).
- The bills will be processed by First-In-First-Out (FIFO) method.
Objectives:
The objectives of the system are as follows:
- To provide convenience to all vendors and suppliers of the government to submit their bills and claims at any time, from anywhere.
- To eliminate the physical interface between suppliers and government officers.
- To enhance efficiency in the processing of bills and claims.
- To reduce discretion in the processing of bills through the "First-In-First-Out"(FIFO) method.
What is Electronic Billing?
- Electronic billing or eBilling is a method of sending and paying bills electronically, rather than through paper billing processes.
- eBilling makes it easy for customers to receive bills online, via email, or in machine-readable data formats.
- It enables customers and businesses to digitally send invoices and payments to each other, providing clear insight for each party.
- The eBilling process is quick, efficient, and streamlined for customers and businesses alike, which is why electronic billing is more suitable for modern accounts payable teams.
- It increases efficiency saves time and lowers error rates.
- The transition from paper-based to electronic bills improves an organization; fewer errors occur, reduce wastage and also help in protecting the environment.
Note: E-Bill Processing System is a major e-governance initiative that has been launched as part of ease of doing business and the Digital India eco-system.
About Digital India:
- The Government of India (GoI) launched the Digital India programme in 2015.
- This programme was launched to ensure that the government’s services are made available to the citizens electronically through increased Internet connectivity and improved online infrastructure, or by making the nation empowered digitally.
- The initiative has plans to connect the rural areas of India with high-speed internet networks.
- It consists of three core components which are -
- Digital deliverance of government services
- Development of stable and secure digital infrastructure
- Digital literacy
Civil Accounts Day 2022: The 46th Civil Accounts Day was recently celebrated on 2nd March 2022 at Dr. Ambedkar International Centre, Janpath, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman was the Chief Guest of the occasion.
- The Civil Accounts Day has been organized every year by the Indian Civil Accounts Service (ICAS), since its inception in 1976.
- ICAS is one of the Civil Services of India.
- It comes under the Department of Expenditure, Union Ministry of Finance.
CAD 2022 celebration:
- As a part of the celebration, FM Sivaraman launched a major e-governance initiative – the Electronic Bill (e-Bill) processing system as part of ease of doing business and Digital India eco-system.
- The e- Bill system will be implemented across all Central Ministries and Departments to enhance transparency, efficiency and a faceless- paperless payment system.
- This will be a further step to enhance transparency, efficiency and a faceless- paperless payment system.
- Suppliers and contractors will now be able to submit their claims online which will be trackable on a real-time basis.
About Indian Civil Accounts Service (ICAS):
- Indian Civil Accounts Service (ICAS) is one of the Civil Services of India ("Group A").
- ICAS is under the Department of Expenditure in the Union Ministry of Finance (MoF).
- Initially, the ICAS was carved out from the Indian Audit & Accounts Service (IA & AS), through the promulgation of an Ordinance amending the C & AG’s (Duties, Powers and Conditions of Service) Amendment Act, 1976.
- Later, the Departmentalization of Union Accounts (Transfer of Personnel) Act, 1976 was enacted and came into force on 01 March 1976, following which the ICAS celebrates March 1 every year as the “Civil Accounts Day”.
- Since 1977, personnel are selected from the Civil Services Examination conducted by Union Public Service Commission, like all other Central Civil Services.
- ICAS performs a key role in the delivery of financial management services for the Government of India (GoI),
- The organization provides payment services, supports the tax collection system, performs government-wide accounting, financial reporting functions, preparation of budget estimates and carries out Internal Audit in civil ministries of the Union Government.
- The Controller General of Accounts (CGA) in the Ministry of Finance (MoF) heads the organization and is responsible for administering this system.
- The current CGA is Deepak Das (ICAS).
Draft framework on Sustainable Financial Lending: The International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA), on March 2, 2022, invited public comments on the draft framework on sustainable and sustainability-linked lending by financial institutions in IFSCs.
Key Details:
The draft guidance framework seeks to encourage the IFSC banking units (IBU) and finance companies or finance units (FC/FUs) to internally develop a comprehensive board-approved policy on green or social or sustainable or sustainability-linked lending.
It intends to provide a broad framework for adoption of principles aligned with existing international standards including green or social loan principles developed by loan market association (LMA), Climate Bond Standards by Climate Bonds Initiative, bond principles developed by the International Capital Markets Association (ICMA) and any other similar recognized standards.
Recent activities of IFSCA:
- IFSCA and Indian Institute of Management Ahmedabad (IIMA) also recently signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) at the IIMA campus for cooperation and collaboration to strengthen active participation in conducting evidence-based policy research to aid policy formulation and also encourage research in emerging financial areas.
- IFSCA has also become an Associate Member of the International Organization of Securities Commissions (IOSCO), which is the international organization that brings together the world’s securities regulators.
- Budget 2022-23 had a proposal to allow the setting up of world-class financial institutions free from domestic regulations under IFSCA.
- It will give a boost to human resources development in IFSC.
About IFSCA:
- IFSCA is a statutory body established by the Ministry of Finance on April 27, 2020.
- It was established under the International Financial Services Centres Authority Act, 2019.
- It has been established as a unified regulator to develop and regulate financial products, financial services and financial institutions in the International Financial Services Centres (IFSCs) in India.
- It is headquartered in Gandhinagar (Gujarat).
Note: Prior to the establishment of IFSCA, the domestic financial regulators, namely, RBI, SEBI, PFRDA and IRDAI regulated the business in IFSC.
Functions of IFSCA:
Its key functions include:
- To regulate financial products like securities, deposits, or contracts of insurance, financial institutions and financial services.
- To regulate any other financial products, financial services, or financial institutions in an IFSC, notified by the central government.
- To recommend any other financial products, financial services, or financial institutions, to the central government, may be permitted in an IFSC.
IFSCA envisions GIFT- IFSC as a global hub for sustainable finance thereby acting as a gateway for channelizing foreign capital into India.
Currently, GIFT IFSC is the maiden international financial services centre in India.
Members of IFSCA:
- IFSCA comprises of 9 members, including:
- Chairperson of the authority
- A member each from the RBI, SEBI, IRDAI and PFRDA.
- Two members from the Ministry of Finance
- Two other members, were appointed on the recommendation of a Selection Committee.
- All the members are appointed by the central government.
- They serve for three years terms, subject to reappointment.
Sarjeraodada Naik Shirala Sahakari Bank: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently cancelled the license of Sarjeraodada Naik Shirala Sahakari Bank, Sangli, Maharashtra.
Key Details:
- The license was cancelled as the above-said bank did not have adequate capital and earning prospects.
- RBI in its release said "Consequent to the cancellation of its licence, Sarjeraodada Naik Shirala Sahakari Bank Ltd, Shirala, district Sangli, Maharashtra, is prohibited from conducting the business of ‘banking’, which includes acceptance of deposits and repayment of deposits as defined in Section 5(b) read with Section 56 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 with immediate effect"
- With the cancellation of the licence, Sarjeraodada Naik Shirala Sahakari Bank Ltd has ceased to carry on banking business with effect from the close of business hours on 2 March.
- The bank has failed to comply with the requirements of Sections 22(3) (a), 22 (3) (b), 22(3)(c), 22(3) (d) and 22(3)(e) read with Section 56 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949.
- The Commissioner for Cooperation and Registrar of Cooperative Societies, Maharashtra has also been requested to issue an order for winding up the bank and appoint a liquidator for the lender.
- On liquidation, every depositor would be entitled to receive deposit insurance claim amount of his/her deposits up to a monetary ceiling of Rs 5 lakh from the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) subject to the provisions of the DICGC Act, 1961.
About DICGC:
- Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) was founded on 15 July 1978.
- It is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra.
- The current Chairperson of DICGC is Michael Patra.
Defence
Armed Village Defence Groups: Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has recently given a nod to re-establish village defence committees (VDCs) in Jammu and Kashmir with a changed nomenclature.
Key Points:
- The VDCs will be called ‘village defence groups’ (VDGs) now.
- Residents from the villages of Jammu and Kashmir will be enrolled for local defence before the delimitation process of Union Territory starts.
- The VDGs can respond to threats in areas such as those with hilly terrain where the local police presence is thin.
- Each VDG will consist of 8 to 10 members of the same rank and pay, which the government will credit to their accounts every month.
- The VDGs will also operate in parts of the Kashmir valley.
- The nomads, who live in Dhoks or mud huts in the upper reaches, would also be allowed to form such defence groups.
- The current system of assigning one or two special police officers with VDGs will be discontinued.
Background:
- The concept of VDG has existed in Jammu and Kashmir for a while, but the members left after they were not paid for a long time.
- During peak terrorism in the 1990s, 4,125 VDCs existed in J&K.
- At that time VDGs helped people in remote areas and defended their areas from terror attacks.
- With the help of VDGs, the armed forces will be looking to eliminate all the terrorist activities that happen in that region.
Why were the village defence committees (VDCs) disbanded?
- The VDCs were constituted in 1995 in 10 districts of the Jammu region to fight militants in far-off places. Around 26,567 locals were recruited into them.
- Most of the VDCs were disbanded by the previous governments following allegations of misuse of weapons in several cases.
Modernization Plan-IV for Central Armed Police Forces: The Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has approved the scheme - Modernization Plan-IV for Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs) in continuation of the scheme “Modernization Plan-III for CAPFs.
Key Points:
- The Modernization Plan-IV will run from 1 February 2022 to 31 March 2026.
- The total financial outlay of Modernization Plan-IV for CAPFs is Rs.1,523 crore.
- Under this project the CAPFs will be equipped with modern state-of-the-art equipment and weapons as per the operational requirements, keeping in view their deployment pattern in different theatres.
- CAPFs will also be provided with upgraded IT solutions.
Implementation:
It is to be implemented by the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
Significance:
- Implementation of the scheme will equip CAPFs in improving the overall operational efficiency and preparedness.
- This in turn will positively impact the internal security scenario in the country.
- This scheme also aims to strengthen the government’s ability to address difficulties on the international border, Line of Actual Control (LAC) and Line of Control (LoC) as well as in various theatres such as areas afflicted by Left Wing Extremism, the Union Territories (UTs) of Ladakh and Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), and insurgency-hit North Eastern States.
About Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF):
- Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) refers to the uniform nomenclature of security forces in India under the authority of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- Their role is to defend the national interest mainly against internal threats.
- They are the Border Security Force (BSF), Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), Central Industrial Security Force (CISF), Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP) and National Security Guard (NSG) and Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB).
- The CAPF forces battle terrorists, insurgents and Naxalites and even play a role in the smooth conduct of elections.
- CAPF is tasked with doing the job of both the army and the police in guarding the borders as well as battling terrorists and insurgents.
DAP 2020: Ministry of Defence (MoD) has recently offered 4 projects to the Indian industry for design and development under the Make-I category of DAP 2020.
About Make-I category:
The Indian industry will be provided financial support for the prototype development of these projects.
The list of projects which were accorded ‘Approval In-Principle (AIP)’ by the Collegiate Committee of MoD is as follows:
- Indian Air Force: Communication Equipment with Indian Security Protocols (Routers, Switches, Encryptors, VoIP Phones and their software)
- Indian Air Force: Airborne Electro-Optical pod with Ground-Based System
- Indian Air Force: Airborne Stand-off Jammer
- Indian Army: Indian Light Tank
This is for the first time since the launch of DAP-2020 that the Indian Industry has been involved in the development of big-ticket platforms such as Light tanks and Communication Equipment with Indian security protocols.
Make-II procedure:
In addition, AIP, approval has also been granted to five projects under the Make-II procedure. They are as follows:
- Indian Air Force: Full Motion Simulator for Apache Helicopter
- Indian Air Force: Full Motion Simulator for Chinook Helicopter
- Indian Air Force: Wearable Robotic Equipment for Aircraft Maintenance
- Indian Army: Integrated Surveillance and Targeting System for Mechanised Forces
- Indian Army: Autonomous Combat Vehicle
Projects under the 'Make-II' category involve prototype development of equipment or their upgrades or their components, primarily for import substitution/innovative solutions.
However, no Government funding will be provided for prototype development purposes.
Significance:
The indigenous development of these projects in the country will help harness the design capabilities of the Indian defence industry and position India as a design leader in these technologies.
DAP 2020:
- Defence Procurement Procedure (DPP) was first initiated in 2002.
- It was to streamline the procurement of military hardware for the Armed Forces in a systematic and time-bound manner.
- In 2016, it was reformed putting an emphasis on indigenously designed, developed and manufactured weapon systems.
- It eventually moved towards self-reliance in the field of defence manufacturing.
- DPP-16 has been revised as Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP) 2020 to further promote self-reliance in the field of defence manufacturing.
- DAP 2020 has been aligned with the Government's vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat and empowering Indian domestic industry, especially to Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) through the Make in India initiative which is aimed towards turning India into a global manufacturing hub.
- It eases the procurement and acquisition of upgraded technology, products, and services for the Tri-Services and allied defence services.
- It also establishes public accountability, transparency, fair competition, and a level playing field in the defence sector.
Make Category:
Make category of capital acquisition is the cornerstone of the Make in India initiative:
Make-I refers to government-funded projects
Make-II covers industry-funded programmes.
Make-III covers military hardware that may not be designed and developed indigenously but can be manufactured in the country for import substitution.
- The Indian firms can manufacture these in collaboration with foreign partners.
Reservation in Categories for Indian Vendors:
The categories of Buy (Indian-IDDM), Make I, Make II, Production Agency in Design & Development will be exclusively reserved for Indian Vendors meeting the criteria of Ownership and Control by resident Indian Citizens with FDI not more than 49%.
National Security Day (NSD 2022): National Security Day or the Rashtriya Suraksha Diwas is celebrated on March 4th every year in India.
Key Facts:
- The year 2022 marks 51st NSD.
- NSD is celebrated in the honor of the Indian Security Forces who have given their lives in the service of preserving our country.
- On National Security Day, several events are planned to highlight how India's military has kept the country safe from both external and domestic threats.
- The country's security forces include policemen, para-military forces, guards, army officers, commandos, and other persons involved in security, who sacrifice their lives in maintaining the peace and security of the people of the country.
- Apart from this, National Security Week 2022 is being celebrated from March 4 to March 10, 2022.
History of the day:
- 4 March also marks the day when the National Security Council (NSC) of India was established, in 1966 by the Ministry of Labour under the Government of India.
- The first National Security Day (NSD) was held in 1972.
Objectives of National Security Day:
The objectives of National Security Day are as follows:
- To achieve the participation of the public in valuing the importance of safety.
- To promote the values and importance of safety in all sectors of life.
- To implement safe practices at the workplace by considering safety measures as a priority to prevent accidents and mishaps.
Some facts regarding India's security forces:
- According to the Global Fire Power annual ranking in 2022, India has the world's fourth-largest military, trailing only the United States, Russia, and China.
- India is second only to China in terms of active military manpower.
- India has a total of 1,450,000 active military personnel.
- With a workforce of 1,155,000 people, the country is rated third in the world in terms of reserve personnel.
- The country's defence budget has been boosted to Rs 5.25 lakh crore for the fiscal year 2022-23.
- In 1998, then-Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee established the National Security Council (NSC), which is the top council in charge of managing the country's political, strategic, economic, and energy security problems.
About National Security Council (NSC):
- The National Security Council (NSC) of India is an executive government agency tasked with advising the Prime Minister's Office on matters of national security and strategic interest.
- It was established by the former Prime Minister of India Atal Bihari Vajpayee on 19 November 1998.
- Ajit Doval is the current NSA and has the same rank as a Union Cabinet Minister.
Note: Brajesh Mishra was the first National Security Advisor.
Members:
Besides the NSA the Deputy National Security Advisors, the Ministers of Defence, External Affairs, Home, Finance of the Government of India (GoI), and the Vice Chairman of the NITI Aayog are members of the National Security Council.
Organizational Structure:
The NSC is the apex body of the three-tiered structure of the national security management system in India.
The three tiers are:
- The Strategic Policy Group (SPG),
- The National Security Advisory Board (NSAB)
- The National Security Council Secretariat.
Environment
Glycosmis Albicarpa: A team of scientists from the Botanical Survey of India (BSI) has discovered a new gin berry species 'Glycosmis albicarpa' has recently been discovered from the Kanyakumari Wildlife Sanctuary in Tamil Nadu by a team of scientists from the Botanical Survey of India (BSI),
Key Highlights:
- It was discovered as undergrowth in Tamil Nadu’s Tirunelveli semi-evergreen forests at the Panagudi forest section of the Kanyakumari Wildlife Sanctuary as a single population that covers around 2 sq. km. area.
- These recent findings have been published in the latest issue of Nordic Journal of Botany, Sweden.
About Glycosmis albicarpa:
- The species belongs to the Orange family Rutaceae.
- It is an evergreen small tree with short and broad leaves and large white fruits.
- The species, Glycosmis albicarpa, is endemic to the southern Western Ghats.
- Many of the related plants of these taxonomic groups are being utilised for their medicinal values and food.
- It is popular as an edible fruit because of its unique characteristic of ‘gin aroma’.
- The species is also a larval host plant for butterflies like other species of Glycosmis.
About Botanical Survey of India (BSI):
- Botanical Survey of India (BSI) is the apex taxonomic research organization of the country under the Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change, Government of India (GoI).
- It was established on 13th February 1890 by East India Company (EIC) under the direction of Sir George King.
- It is responsible for survey, research and conservation of plant wealth of India, flora and endangered species of India, including by collecting and maintaining germplasm and gene bank of endangered, patent and vulnerable plant species.
- It is headquartered in Kolkata, West Bengal.
Global Plastics Treaty: World leaders, ministers and other representatives from nearly 200 countries at a United Nations conference in Kenya have recently agreed to work together in the biggest-ever push to stem the flood of plastic pollution.
Key Points about the treaty:
- The resolution, entitled: “End Plastic Pollution: Towards an internationally legally binding instrument,” was adopted at the conclusion of a three-day fifth United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA 5.2) meeting.
- UNEA 5.2 was held from 28th February 2022 to 2nd March 2022 in Nairobi.
- The U.N. Environment Assembly voted to adopt a resolution that paves the way for a legally binding agreement on plastic pollution by 2024.
- The resolution, based on three initial draft resolutions from various countries, establishes an Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC), which will begin its work in 2022.
- According to the agreed mandate, the treaty makes it legally binding for the signatories to tackle the whole life cycle of plastic, from production to disposal and not just post-consumer waste.
- The text also recognizes the significant contributions of workers and waste pickers and in the informal economy, which are vulnerable to occupational health risks.
- However, the details of the final treaty are yet to be negotiated, but could include a ban on producing new plastic, and will take into account all aspects of plastic pollution — including particles in the ocean, soil and food chain.
- The resolution, which addresses the full lifecycle of plastic, including production, design and disposal, will be developed over the next two years.
- Inger Andersen, who is the Head of the U.N. Environment Programme, said that the plastics treaty would be the most significant environmental pact since the 2015 Paris Agreement.
- Earlier approaches focused on plastic as a “marine litter” issue.
Need for the treaty:
- By 2050 greenhouse gas emissions associated with plastic production, use and disposal would account for 15% of allowed emissions, under the goal of limiting global warming to 1.5°C (34.7°F).
- More than 800 marine and coastal species are affected by this pollution through ingestion, entanglement, and other dangers, while around 11 million tonnes of plastic waste flow each year into the ocean. This could triple by 2040.
- Toxic chemicals from plastic have been entering the human body through a variety of routes, causing infertility, cancers, metabolic dysfunction, and other disorders.
What is Plastic Pollution?
- Plastic pollution is the accumulation of plastic objects and particles (e.g. plastic bottles, bags and microbeads) in the Earth's environment that adversely affects humans, wildlife and their habitat.
- Plastics that act as pollutants are categorized by size into micro-, meso-, or macro debris.
Why is plastic so polluting?
- Plastic has become one of the most used substances.
- Plastics are inexpensive and durable making them very adaptable for different uses; as a result, humans produce a lot of plastic.
- It is also very easy to use as it can be used for almost anything either liquid or solid. Moreover, it comes in different forms which we can easily mold.
- The single-use plastics are cheap enough that it is used and thrown away without thinking about ways to reuse them.
- The chemical structure of most plastics renders them resistant to many natural processes of degradation and as a result, they are slow to degrade plastic that gets into ecosystems stays there for hundreds of years.
- Plastic pollution can afflict land, waterways and oceans.
- It can choke fish, entangle birds and leak toxins.
How big a problem is a plastic pollution?
- Plastic is one of the most useful materials on the planet.
- It's used in everything from food packaging to making up the fibers in the clothes.
- Its applications stretch to building materials and medical masks.
- But plastic is also responsible for destroying ecosystems and polluting waterways.
- In 1950 the world produced nearly 2 million tons of plastic.
- Annual production at present is more than 200 times greater.
- A landmark study in 2017 found that only 9% of the plastic that has been produced throughout history has been recycled and about 12 percent has been burned.
- The rest has been thrown away — either as litter or in landfills.
Causes:
- The trade-in plastic waste has been identified as "a main culprit" of marine litter.
- Countries importing waste plastics often lack the capacity to process all the material.
- As a result, the United Nations has imposed a ban on the waste plastic trade unless it meets certain criteria.
India’s initiatives:
- The Government of India (GoI) recently issued fresh guidelines for manufacturers, brand owners, importers of plastics making it mandatory to recycle plastic.
- GoI has drawn up a pathway to incorporate the large informal sector, which is involved in plastic recycling, in a more formal circular economy.
- The creation of this mandate recognizes the urgency of addressing the plastic crisis.
- Solving the plastic problem is crucial to protect human rights and achieve UN sustainable development goals (SDG).
- India has also banned single-use plastic, which will come into effect on July 1, 2022.
About the UN Environment Programme (UNEP):
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is the leading global voice on the environment.
- It was founded on 5 June 1972 by Canadian businessman and philanthropist Maurice Strong.
- It is responsible for coordinating the UN's environmental activities and assisting developing countries in implementing environmentally sound policies and practices.
- It is the global champion for the environment with programmes focusing on sustainable development, climate, biodiversity and more.
- It is headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya.
- The current Executive Director of UNEP is Inger Andersen and the current Regional Director and Representative for Asia and the Pacific, UNEP is Dechen Tsering.
Bomb Cyclone: Another violent bomb cyclone is grazing north just west of Ireland and UK with violent, hurricane winds and major waves.
- Thanks to still a very powerful southern lobe of the Polar Vortex aloft, the North Atlantic is yet to produce more dangerous storms this week.
- Earlier this year, a Bomb cyclone (Nor’easter) had hit the eastern US, which triggered transport chaos, outages.
What is a Bomb cyclone?
- Explosive cyclogenesis is referred to as a bomb cyclone or bombogenesis.
- It is also referred to as a weather bomb, meteorological bomb.
- It is a mid-latitude cyclone that intensifies rapidly.
- It has low pressure at its center, weather fronts and an array of associated weather, from blizzards to severe thunderstorms to heavy precipitation.
- Bomb cyclones put forecasters on high alert because they can produce significant harmful impacts.
How do bomb cyclones form?
- It becomes a bomb when its central pressure decreases very quickly—by at least 24 millibars in 24 hours quickly increasing in intensity.
Note: A millibar measures atmospheric pressure.
- This can happen when a cold air mass collides with a warm air mass, such as air over warm ocean waters.
- The formation of this rapidly strengthening weather system is a process called bombogenesis.
- The vast majority of such storms occur over the ocean.
- The lower the pressure, the stronger the storm.
- The storm can be tropical or non-tropical in nature.
- Most cyclones don’t intensify rapidly in this way.
Key features of Bomb Cyclones:
- Bomb cyclones have cold air and fronts.
- They form during winters.
- They occur over midlatitudes.
How does a Bomb Cyclone differ from a Hurricane?
- Bomb cyclones generally occur during colder months because cyclones occur due to cold and warm air meeting while hurricanes tend to form in tropical areas and are powered by warm seas.
- Bomb cyclones form over the northwestern Atlantic, northwestern Pacific and sometimes the Mediterranean Sea while Hurricanes form in tropical waters.
What is a polar vortex?
- A circumpolar vortex or simply polar vortex is a large area of low pressure and cold air surrounding both of the Earth’s poles.
- It always exists near the poles, but weakens in summer and strengthens in winter.
Features:
- The polar vortex spins in the stratosphere.
- The term polar vortex can be used to describe two distinct phenomena;
1. The stratospheric polar vortex
2. The tropospheric polar vortex
- The stratospheric and tropospheric polar vortices both rotate in the direction of the Earth's spin, but they are distinct phenomena that have different sizes, structures, seasonal cycles, and impacts on weather.
- When the vortex weakens, the stratosphere warms sharply in an event known as sudden stratospheric warming, in just a few days, miles above the Earth’s surface.
- The warming weakens the polar vortex, shifting its location somewhat south of the pole or, in some instances, ‘splitting’ the vortex up into ‘sister vortices’.
New Species of Orchid: Researchers have recently discovered an astounding new species of orchid in the cloud rainforest of Northern Ecuador.
The study is published in the open-access journal PhytoKeys.
Key Highlights:
- The new species of orchid has been scientifically named Maxillaria anacatalina-portillae.
- This plant is unique with its showy, intense yellow flowers.
- It was described by Polish orchidologists in association with an Ecuadorian company working in orchid research, cultivation and supply.
- The discovery was aided by the local commercial nursery, involved in cultivating these orchids.
Critically endangered species:
- Known from a restricted area in the province of Carchi, the orchid is presumed to be a critically endangered species because its rare populations already experience ill effects of climate change and human activity.
Genus Maxillaria:
- In the past few years, scientists have been working on classification and species delimitations within the Neotropical genus Maxillaria.
- It is one of the biggest genera in the orchid family.
- Scientists have investigated materials deposited in most of the world’s herbarium collections in America and Europe.
- They have conducted several field trips in South America to search for astonishing plants.
- The first specimens of Maxillaria anacatalina-portillae were collected in 2003 in Maldonado, Carchi Province of northern Ecuador.
About Orchidaceae:
- Orchidaceae are commonly called the orchid family.
- It is a diverse and widespread family of flowering plants.
- Its blooms are often colourful and fragrant.
- They are one among the two largest families of flowering plants. Orchidaceae have around 28,000 currently accepted species.
- They are distributed in 763 genera.
Sambhav and Svavlamban: Union Minister of State for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), Bhanu Pratap Singh Verma recently launched two special initiatives - Sambhav and Svavlamban initiatives.
About the initiatives:
- Sambhav and Svavlamban are the initiatives to tackle the issue of plastic waste in India.
- These initiatives were launched at the International Summit on Plastics Recycling and Waste Management.
- These initiatives aim to encourage young entrepreneurs, especially from the aspirational districts of India.
About International Summit on Plastics Recycling and Waste Management:
- It is a 2-day summit (4th – 5th March 2022), inaugurated by Union Minister of State for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), Bhanu Pratap Singh Verma.
- This summit is being organized in New Delhi by the MSME Ministry in association with the All India Plastics Manufacturers’ Association (AIPMA).
- Around 1350 MSMEs are expected to attend the summit, which is being conducted in hybrid mode.
Motto of the Summit:
- The motto of the summit is “Know your Waste and how Recycling is the right thing to do, which is to be done in a right way”.
Significance:
- This summit provides a platform for entrepreneurs, experts, businessmen, and other stakeholders to deliberate challenges and solutions in the MSME sector and plastics sectors.
- It will also create new livelihood and business opportunities in the plastics sector, at the same time helping India tackle the issue of plastic pollution and meet environmental goals.
- Thus, the ‘Sambhav’ and ‘Svavlamban’ initiatives and the summit will have multiple benefits i.e. formalizing the informal waste sector, job creation in the MSME sector, and reduction in plastic waste.
Indian Policy
Swadesh Darshan Awards: The Ministry of Tourism has constituted Swadesh Darshan Awards in different categories to acknowledge the efforts undertaken by the State Governments, Union Territory Administrations and various implementation agencies.
About:
- The awards will be awarded to recognize best practices in planning, design and operations, efficient project monitoring, ability to attract private investments in peripheral development and efforts undertaken to ensure optimal operations and maintenance, etc.
- The UT administrations and the State Governments have been asked to submit their entries via online mode.
- The Ministry of Tourism has decided to invite entries under the following categories:-
- Best Tourist Interpretation Centre
- Best MICE Facility
- Best Log Hut Facility
- Best Cafeteria
- Best Craft Haat/ Souvenir Shop facility
- Best Waterfront Development (Beach/ River/ Lake etc.)
- Best Sound and Light Show
About Swadesh Darshan Scheme:
- Swadesh Darshan is a Central Sector Scheme launched in 2014-15.
- This Scheme has been formulated by the Ministry of Tourism (MoT) for the integrated development of tourist circuits around specific themes.
- The Ministry of Tourism offers Central Financial Assistance (CFA) to State Governments/Union Territory Administrations for the development of circuit infrastructure under this scheme.
- Fifteen thematic circuits have been identified under this scheme which is Desert Circuit, Himalayan Circuit, Heritage Circuit, North East Circuit, Coastal Circuit, Buddhist Circuit, Eco Circuit, Krishna Circuit, Rural Circuit, Ramayana Circuit, Sufi Circuit, Spiritual Circuit, Tribal Circuit, Tirthankar Circuit, Wildlife Circuit.
- Under its flagship scheme of ‘Swadesh Darshan,’ the tourism ministry has sanctioned 76 projects in 31 States / Union Territories of India for more than Rs.5500 Crore.
- As part of this scheme, tourism-related infrastructure has been developed at more than 500 tourist destinations.
NaariShakti conversation, on STEM and Financial Literacy for Young Women: UNICEF YuWaah recently facilitated the #NaariShakti conversation, on ‘STEM and Financial Literacy for Young Women’.
About the event:
- The event was a part of the Ministry of Women and Child Development’s ‘Iconic Week’ celebrating International Women’s Day under the ‘Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav’.
- Smriti Irani, the Union Minister for Women & Child Development participated in the event.
- The event also witnessed the participation of adolescent girls from different parts of India.
- The participants shared their experiences, aspirations, and suggestions on gender equality in STEM.
- They discussed how to nurture young women to pursue careers in STEM-related fields and
- The benefits of women’s participation in STEM to India’s economic growth along with Government Programs promoting women’s participation in STEM were also discussed.
About STEM:
- The STEM acronym was introduced in 2001 by the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF).
- The idea to promote STEM education in India has been supported by the National Council for Science and Technology Communication along with the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India (GOI).
- It is a curriculum that promotes the idea of educating students in disciplines such as science, technology, engineering and mathematics.
- This aims at establishing a robust platform for innovation for the next generation.
- Under Article 51A of the Constitution of India, it is the duty of every citizen of India to develop the scientific temper, humanism and the spirit of inquiry and reform.
Note: India is one of the countries that produce the highest number of scientists and engineers, the growth of STEM has picked up significantly over the last few years.
Participation of Women in STEM:
- According to the All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE), 2018-19, around 43% of STEM graduates in India are women, which is the highest in the world.
- However, their share in STEM jobs in India is a mere 14%.
- This indicates a ‘leaky pipeline’ in STEM fields.
- The under-representation of women in STEM majors is common globally.
- In India even though the number of women enrolling in STEM programmes has been increasing year on year, the rising education levels aren't translating into employability or jobs.
Challenges to the participation of women in STEM:
- Stereotypical gender roles in society.
- Lack of physical safety during the commute to work.
- Sexual and other types of harassment in workplaces.
- Stressors related to marriage and childbirth.
- ‘Dual role’ syndrome (Professional decisions are affected by domestic responsibilities).
- Lack of suitable workplace or benefits like travel allowance, lodging, crèche, etc.
About YuWaah:
- YuWaah is a UNICEF-initiated multi-stakeholder global platform.
- It aims to prepare young people to transition from education and learning to productive work and active citizenship.
- It was launched in 2019.
- It was formed by UNICEF, together with public and private sector partners, UN Agencies, civil society organizations, foundations and young people as the Generation Unlimited (GenU) partnership in India.
India YuWaah, by 2030 aims to the following:
- Build pathways to aspirational socio-economic opportunities for 100 million young people.
- Facilitate 200 million young people to gain relevant skills for productive lives and the future of work.
- Partner with 300 million young people as change-makers and create spaces for developing their leadership.
About UNICEF:
- It is an acronym for United Nations Children's Fund.
- It was formerly known as United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund.
- UNICEF is a special program of the United Nations (UN) devoted to aiding national efforts to improve the health, nutrition, education, and general welfare of children.
- It was created in 1946 as the International Children’s Emergency Fund (ICEF) by the UN Relief Rehabilitation Administration to help children affected by World War II.
- It became a permanent part of the United Nations in 1953.
- It is headquartered in New York, United States.
- The current head of UNICEF is Henrietta H. Fore.
Note: UNICEF was awarded Nobel Prize for peace in 1965.
MoHUA Launches Swachh Survekshan 2022: The Minister of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) Shri Hardeep Singh Puri launched Swachh Survekshan 2022 (SS 2022), the world's largest urban cleanliness survey, for the seventh consecutive year on March 1, 2022.
Note: Swachh Survekshan is conducted by Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban (SBM-U).
Key Highlights:
- It coincides with the celebrations of the 75th year of India's independence; therefore SS 2022 will focus on the theme of Azaadi@75 spirit.
- SS 2022 is designed with the notion of ‘People First’ as its driving philosophy.
- It is meant to capture the initiatives of cities for the overall welfare and well-being of frontline sanitation workers.
- Priority to senior citizens and young adults' voices will be given during this survey.
About Swachh Survekshan 2022 (SS 2022):
- MoHUA kick-started this year's survey with nearly 3,000 assessors of Ipsos Research Pvt. Ltd. which is the assessment agency ready to assess cities' performance.
- In this year’s survey, the scope has been expanded to cover 100% wards for sampling, up from 40% in the previous years.
- SS 2022 will deploy a more significant number of assessors for the on-field assessment than last year to hold this exercise smoothly.
- In preparation for SS 2022, cities have been regularly filling in their data, updating their status in the Swachhatam Portal MIS, and running several citizen-centric campaigns.
- As part of this survey, senior citizens will be asked to provide feedback.
- To ensure diverse viewpoints, it will also reach out to young adults who will be the country’s and the Swachhata movement’s future leaders.
- SS 2022 aims to form A level playing field for smaller cities by introducing two population categories under 15,000 people and 15,000 to 25,000 people.
New Indicators added in SS 2022:
The following new indicators have been added to SS 2022.
- To commemorate 75 years of progressive India, the Urban Local Body (ULB) has joined hands with citizens to pick one Roundabout/ Chauraha in each city that could be decorated to reflect the spirit of India’s 75 years of independence.
- Another new indicator, the ‘Swachh Technology Challenge,’ launched by MoHUA in December 2021, has been included in Swachh Survekshan 2022.
- Under this challenge, individuals, organizations, and entrepreneurs across all Urban Local Bodies submitted ideas under four theme categories which are -
a)Zero dump (solid waste management), Social inclusion,
b)Transparency through digital enablement,
c)Plastic waste management.
- Two population categories have been introduced for smaller cities under 15k and between 15k - 25k.
- District rankings have also been introduced to further widen the Survekshan footprint.
About Swachc Survekshan:
- MoHUA introduced Swachh Survekshan in 2016.
- It was introduced as a competitive framework to encourage the cities of the nation to improve urban cleanliness while also promoting widespread citizen participation.
Note: The survey was initiated with 73 cities which in SS 2021, grew to 4,320 cities including 62 Cantonment Boards.
Quami Waqf Boards Taraqqiati Scheme: Union Ministry of Minority Affairs (MoMA) has revised the deadline for a long-delayed project to geotag all Waqf properties across India, from March 2022 to November 2023.
Key Facts:
- This project was started in 2017 under the ‘Quami Waqf Boards Taraqqiati Scheme’ (QWBTS).
- The Central Waqf Council, New Delhi is the Nodal Agency for the implementation of this Scheme.
- This scheme was envisaged based on recommendations of the Parliamentary Standing Committee in the past.
Aim of QWBTS:
Under the scheme, the government aims to map the immovable assets under Waqf boards, in order to ensure their proper utilization and monetization.
This move also aims to ensure that these properties are not lost to encroachments and other counter ownership claims.
Geotagging of Waqf Properties:
- As per estimates, there are more than six lakh Waqf properties.
- Out of this, 2 lakh properties have been geotagged in the last five years.
- To speed up the method, an autonomous body, 'Central Waqf Council' under the Minority Affairs Ministry, called bids by March 21 to impanel more agencies to hold out GIS or GPS surveys.
- A pre-bid meeting has been called for on March 2, 2022.
Hired Agencies:
- Central Waqf Council also rents 20 agencies to hurry up this work.
- In December 2021, it hired nine agencies that included IITs in Hyderabad, Jodhpur, and Kanpur, besides the Jamia Millia Islamia in Delhi.
Reasons for the delay:
- The delay was mainly because "realistic targets" supported actual experiences weren't set.
- It had been estimated earlier that by March 2020, 50 percent of the properties would be geotagged.
- But by February 2021, only 96,000 properties have been geotagged.
- Covid-19 pandemic was the prime reason for tardy progress.
About Central Wakf Council:
- Central Wakf Council is an Indian statutory body.
- It was established in 1964 under Wakf Act, 1954.
- It is of advisory nature on matters related to working of State Wakf Boards and proper administration of Wakfs in India.
- Wakf is a permanent dedication of movable or immovable properties for pious, religious, or charitable purposes, recognized by Muslim Law.
- The Chairman of Central Qaqf Council is Mukhtar Abbas Naqvi ( current Union Minister of Minority Affairs)
Indian polity
Article 80: The Chandigarh Municipal Corporation recently approved a proposal to amend Article 80 of the Constitution so that its councilors could send a representative to the Rajya Sabha.
About Article 80 of the Indian Constitution:
- Article 80 of the Constitution of India deals with the composition of the council of states also called the Upper House and Rajya Sabha (Upper House).
- According to Article 80, the Rajya Sabha shall consist of not more than 238 representatives of the States and of the Union territories, and 12 nominated members.
Key Points:
- So far, Chandigarh has no representation in the Rajya Sabha.
- In the case of Chandigarh, the Private Member Bill was introduced by Congress MP from Anandpur Sahib, Punjab, Manish Tewari, who is a resident of Chandigarh.
- The bill (Private Member Bill) sought the adding of a provision provided that the representative of the Union Territory of Chandigarh in the council of states shall be elected by an electoral college.
- The Electoral College should consist of elected members of the Municipal Corporation of Chandigarh constituted under the Punjab Municipal Corporation (Extension to Chandigarh) Act, 1994 in Article 80 of the Constitution.
- MP Tewari has also sought amendment of the Fourth Schedule of the Constitution with ‘Entry 32, Chandigarh.”
4th Schedule of the Constitution:
- The 4th Schedule of the Constitution contains provisions as to the allocation of seats in the Council of States.
- It contains the number of seats represented in the Council of states (Rajya Sabha) from each State and Union Territory.
Private Member Bill:
- The Private Member Bill is a bill introduced by a Member of Parliament (MP), who is not a minister.
- MPs sitting in the Opposition mostly bring Private Member Bills in the house.
Representation of Union Territories (UTs):
- The representatives of each Union Territory (UT) in the Rajya Sabha are indirectly elected by members of an electoral college specially constituted for the purpose.
- This election is also held in accordance with the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote.
- Out of the 9 Union Territories, only 3 (Delhi, Puducherry and Jammu & Kashmir) have representation in Rajya Sabha.
- The populations of the other 6 Union Territories are too small to have any representative in the Rajya Sabha.
Representation of States:
- The representatives of states in the Rajya Sabha are elected by the elected members of state legislative assemblies.
- The election is held in accordance with the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote.
- The seats are allotted to the states in the Rajya Sabha on the basis of population.
- Hence, the number of representatives varies from state to state.
- For example, Uttar Pradesh has 31 members while Tripura has 1 member only.
Sabka Vikas MahaQuiz: MyGov, on 1st March, 2022 has launched the “Sabka Vikas MahaQuiz” series.
Key Points about Sabka Vikas MahaQuiz series:
- Sabka Vikas MahaQuiz series was launched in order to build awareness amongst citizens about good governance.
- It aims to sensitize the participants about the various government schemes and initiatives.
- This is a year-long project and consists of 14 episodes, all hosted at Quiz.MyGov.in
- The quiz will be available in Hindi & English and all other major languages.
- Every week, the top 1000 winners will be announced.
- Every winner will receive Rs 2000/- each
- At the end of 52 weeks, there will be a bumper prize for those who took part in all the quizzes
- This is a timed quiz with 20 questions to be answered in 700 seconds
- The first quiz is on Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PM-GKAY).
About PM-GKAY:
PM-GKAY is a pro-poor package intended to reduce the challenges encountered by the poor as a result of disruptions due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
About MyGov:
- MyGov has been established as the Government of India's Citizen Engagement Platform.
- This platform collaborates with multiple Government bodies/ Ministries to engage with citizens for policy formulation and seeks the opinion of people on issues/ topics of public interest and welfare.
- It was established on 26th July 2014.
- Its main aim is to promote the active participation of Indian citizens in the governance and development of India.
- It also aims to create a common platform for Indian citizens in a bid to “crowdsource governance ideas from citizens”.
International
India-ITU Host Country Agreement (HCA): Union Minister of Communications Ashwini Vaishnaw and Houlin Zhao, Secretary-General of International Telecommunication Union (ITU), on 3rd March 2022, signed the Host Country Agreement (HCA) for the establishment of an Area Office & Innovation Centre of ITU in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- The HCA was signed in a virtual ceremony during the World Telecommunications Standardization Assembly-20 (WTSA-20) being held in Geneva, Switzerland.
- HCA provides the legal and financial framework for the establishment and operations of the Area Office and innovation center of ITU in New Delhi, India.
Area Office and the Innovation Centre:
- The Area Office and Innovation Centre of ITU at New Delhi is expected to serve South Asian countries namely Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Iran, Maldives, Nepal, Sri Lanka and India.
- It will give impetus to research and development in telecommunication technologies in the South Asian region.
- It will also provide opportunities to academics, start-ups, and Small & Medium Enterprises (SMEs) to showcase their innovation on a global stage.
- The Area Office and the Innovation Centre are expected to be operational by mid-2022.
About International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
- International Telecommunication Union (ITU) is the specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for information and communication technologies (ICTs).
- It was established in 1865 as the International Telegraph Union, making it the oldest UN agency.
- It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- ITU currently has a membership of 193 countries and over 900 private-sector entities and academic institutions.
World Telecommunications Standardization Assembly (WTSA):
- WTSA is a four-yearly global conference of ITU dedicated to standardisation of the Information and Communications Technologies (ICTs).
- It defines the general policy and adopts working methods and procedures for ITU-T.
- The functions of the WTSA are provided in Article 18 of the ITU Constitution and Article 13 of the ITU Convention.
- India has proposed to host the next WTSA to be held in 2024.
Quad Leaders Summit 2022: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi participated at a virtual summit of Quad leaders on 5 March 2022.
Highlights:
- The summit witnessed the participation of US President Joe Biden, Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison and Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida also.
- The QUAD leaders’ virtual summit was held in the backdrop of the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
- However, the agenda did not include the Ukraine crisis.
Note: India had chosen to abstain three times in a vote against Russia at the United Nations, while the other three QUAD members had voted in favour of Ukraine. Though, India has repeatedly urged Russia to cease its military operations in Ukraine.
Key Highlights of the summit:
- The progress on Quad initiatives since the September 2021 Quad Summit was reviewed by the leaders.
- The leaders agreed on accelerating cooperation to achieve concrete outcomes by the summit in Japan later this year.
- They discussed the developments in Ukraine, including its humanitarian implications.
- The leaders also discussed other topical issues, including the situation in Southeast Asia, the Indian Ocean region and the Pacific Islands.
- Japan is scheduled to host the next in-person summit of the Quad later this year.
- The leaders agreed to stay in touch and to work towards an ambitious agenda for the forthcoming Leaders’ Summit in Japan.
Note: This virtual meeting of Quad assumes significance amid the Russian invasion of Ukraine and western sanctions on Russia.
Statements of PM Modi:
- Prime Minister Modi underlined that the Quad must remain focused on its fundamental goal of promoting peace, stability and prosperity in the Indo-Pacific region.
- He called for concrete and practical forms of cooperation within the Quad, in areas like humanitarian and disaster relief, debt sustainability, supply chains, clean energy, connectivity, and capacity-building.
- He also emphasized the need to return to a path of dialogue and diplomacy.
- He reiterated the importance of adhering to the UN Charter, international law and respect for sovereignty and territorial integrity.
Background:
- Quad’s first in-person summit was held in Washington in September 2021.
About QUAD:
- The Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QSD), or QUAD, is a strategic security dialogue between the United States of America (USA), India, Australia and Japan that is maintained by talks between member countries.
- A shared vision of Quad members is “Free and Open Indo-Pacific,” and a “rules-based maritime order in the East and South China Seas.”
- The coalition also aims to offer, alternative debt financing for nations in the Indo-Pacific region.
- The dialogue was initiated in 2007 by Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, with the support of U.S. Vice President Dick Cheney, Australian Prime Minister John Howard, and Indian Prime Minister Manmohan Singh.
- During the 2017 ASEAN Summits in Manila, all four former members led by Japan's Prime Minister Abe, Australian Prime Minister Malcolm Turnbull, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi, and US President Donald Trump agreed to revive the quadrilateral alliance in order to counter China militarily and diplomatically in the "Indo-Pacific" region, particularly in the South China Sea.
Swiss Foreign Policy: As western leaders came together to condemn the Russian invasion of Ukraine, Switzerland broke its 200-year long neutrality policy to adopt all sanctions imposed on Moscow and its leaders.
- It also announced it would join the European Union (EU) in closing the Swiss airspace to Russian airplanes, curtailing entry to the Swiss with Russian connections and imposing financial sanctions on Russian President Vladimir Putin and other leaders.
About Swiss Neutrality:
- Swiss neutrality is one of the main principles of Switzerland, the tiny Alpine nation’s foreign policy which dictates that Switzerland is not to be involved in armed or political conflicts between other states.
- This policy is self-imposed and designed to ensure external security and promote peace.
- It has the oldest policy of military neutrality in the world
- It has had a neutrality policy was established by the Treaty of Paris in 1815.
- Its official website attests to this, noting that “permanent neutrality is a principle of Swiss foreign policy.”
- It pursues an active foreign policy and is frequently involved in peace-building processes around the world.
- Though it serves as the headquarters of several diplomatic missions and as the venue for historic treaties like the Geneva Convention, Switzerland is not a part of the European Union or NATO.
- It joined the United Nations only recently in 2002.
- During the Second World War, Switzerland, which shares borders with Germany, France and Italy, used a combination of military deterrence, strategic planning and economic neutrality to hold its own in 1940s Europe.
About Switzerland:
- Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a country situated in the confluence of Western, Central, and Southern Europe.
- It is a landlocked country bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east.
- It is geographically divided among the Swiss Plateau, the Alps, and the Jura.
- Its official language is German, Romansh, French, Italian.
- The Capital of Switzerland is Bern City.
- The currency used here is the Swiss franc.
- Simonetta Sommaruga is the current President of the Swiss Confederation.
World Civil Defence Day 2022: World Civil Defence Day is observed across the globe on 1st March annually.
Key Points:
- The day is observed to honour the significance of Civil Defence and the personnel who have sacrificed their lives for it.
- The main aim of World Civil Defence Day is to promote public awareness about civil defence, civil protection and emergency management in order to better prepare the civilian population to protect itself in the event of an emergency and to reduce the risk of disaster.
Theme of Civil Defence Day 2022:
- The theme of World Civil Defence Day 2022 is “Civil defence and management of displaced populations in face of disasters and crises; the role of volunteers and the fight against pandemics”.
Significance:
- The vital significance of civil protection and defence is that it is aimed at raising awareness of the preparedness for, and prevention and self-protection measures in the event of accidents or disasters.
- Be it the present Russia-Ukraine crisis or disasters such as tsunamis or earthquakes or pandemics.
History of the day:
- The day was integrated by the International Civil Defence Organisation (ICDO) in 1990.
- Civil Defence Day was officially inaugurated by the International Civil Defence Organisation (ICDO) in 2012.
- March 1st was chosen to commemorate the anniversary of the day on which the constitution of the ICDO came into force.
About ICDO:
- The International Civil Defence Organisation (ICDO) is an intergovernmental organization that contributes to the development and safety of citizens while safeguarding infrastructure and the surroundings.
- It consists of 59 countries that conduct training programs to improve civil defense human resource management in those countries.
- The Constitution of the ICDO was adopted on 17 October 1966.
- It came into force on 1st March 1972.
- It attributes the status of the intergovernmental organizations to the ICDO (United Nations, Treaty Series, volume 985, registration No. 14376).
History:
- It has its origins in the Association of Geneva Zones, which Surgeon-General George Saint-Paul founded in 1931.
- Saint-Paul was influenced by the horrors of the First World War and aimed to create safety zones where civilians could seek protection in times of wars or disasters.
Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power: A day after Russian forces allegedly attacked and captured Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant in southeastern Ukraine, a report claimed that the nuclear facility was back under Ukrainian control.
Russia had recently captured Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia nuclear power plant.
Key Points:
- The Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Station is located in the city of Energodar.
- It is the largest nuclear power plant in Europe and among the 10 largest in the world.
- It accounts for about one-quarter of Ukraine’s power generation.
- This comes after the Russian military forces began shelling at the nuclear power plant site, setting one of the buildings within the complex on fire, raising fears of a nuclear catastrophe.
- Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky warned that there are six power units at the nuclear power plant, one power unit exploded in Chernobyl!
- Enerhodar city’s mayor Dmytro Orlov also confirmed that the plant was on fire.
- However, Ukraine's State Emergency Service has reported that the fire had been put out at the Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Station.
Key Highlights of Russia-Ukraine War:
- Since the attack launched by the Russian President Vladimir Putin on the state on February 24, 2022, over 1.5 million people by the end of the weekend have fled Ukraine.
- The fighting has been on for over eleven days with Ukraine standing defiant and strong against the invading Russian forces.
- There have been huge casualties on both sides.
- Only one Ukrainian city, the southern port of Kherson, has fallen to Russian forces so far as Ukrainians refuse to give up.
- Russian forces launched hundreds of missiles and artillery attacks across the country, including powerful bombs dropped on residential areas of Chernihiv, a city north of the capital of Kyiv.
- Russia in their first move had captured the defunct Chernobyl nuclear power plant, which is located north of Ukrainian capital Kyiv.
- The world’s largest cargo aircraft, the Antonov An-225, also was “destroyed” by Russia in an attack on its base at Hostomel/Gostomel airport in Ukraine.
Note: Known formally as the “Cossack”, its North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) operating code, the world knew the “super-heavy transport plane” better by its Ukrainian name, “Mriya”, or “the Dream”.
- With Ukrainian civilians stranded in the cities under attack with no food and medical supplies, Russia and Ukrainian negotiators agreed to open up humanitarian corridors in their second round of talks to enable smooth evacuation of civilians and supply of essentials.
- The negotiators are expected to meet again next week.
- Ukrainian President Zelenskyy has in the meanwhile requested NATO’s support in establishing a no-fly zone over Ukraine and has also asked Russian President Vladimir Putin for face-to-face talks.
- NATO countries have ruled out policing a no-fly zone, which would bar all unauthorized aircraft from flying over Ukraine.
About Mriya:
- Known formally as the “Cossack”, its North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) operating code, the world knew the “super-heavy transport plane” better by its Ukrainian name, “Mriya”, or “the Dream”.
- It was a six-engine 84-meter-long behemoth, with its 32-wheel landing gear.
- It had its first flight on December 21, 1988, built mainly for the transportation of the Buran shuttle orbiter and components of the Energiya carrier rocket.
- It made its maiden landing in India, in May 2016, at Hyderabad’s Shamshabad airport en route to Perth to deliver a 117-tonne power generator (from Prague, the Czech Republic) to a mine in Australia.
- It played an important role too in the COVID-19 fight.
- It ferried nearly 100 tonnes of medicines, laboratory kits, medical masks and personal protective equipment in various missions across Europe, Canada, and Africa.
Budapest Memorandum on Security Assurances: President of Ukraine recently argued that Budapest Memorandum on Security Assurances provides no true guarantee of safety due to Russia’s coercive power.
The recent Russian invasion of Ukraine is being considered a violation of the Budapest Memorandum.
About the Memorandum:
- Budapest Memorandum on Security Assurances refers to three identical political agreements signed at the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) conference in Budapest, Hungary in 1994.
- The signatories of the memorandum agreed to provide security assurances to Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Ukraine in return for their accession to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT).
- It came after the Lisbon Protocol of 1992, which made Belarus, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan parties to the first Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty (START I).
- It was a treaty signed by the US and the Soviet Union in 1991 to reduce the number of nuclear weapons.
- As a result of the agreements and the memorandum, between 1993 and 1996, Belarus, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan gave up their nuclear weapons and became non-nuclear states.
- Ukraine at that time had the world’s third-largest nuclear arsenal.
Signatories:
The memorandum was originally signed by three nuclear powers:
- The Russian Federation
- The United Kingdom
- The United States
China and France gave somewhat weaker individual assurances in separate documents.
Provisions
According to the memorandum Russia, the US and the UK confirmed their recognition of Belarus, Kazakhstan and Ukraine becoming parties to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons and effectively abandoning their nuclear arsenal to Russia.
They agreed to the following:
- Respect Belarusian, Kazakh and Ukrainian independence and sovereignty in the existing borders.
- Refrain from the threat of the use of force against Belarus, Kazakhstan, or Ukraine.
- Refrain from using economic pressure on Belarus, Kazakhstan, or Ukraine to influence their politics.
- Seek immediate Security Council action to provide assistance to Belarus, Kazakhstan, or Ukraine if they "should become a victim of an act of aggression or an object of a threat of aggression in which nuclear weapons are used".
- Refrain from the use of nuclear arms against Belarus, Kazakhstan or Ukraine.
- Consult with one another if questions arise regarding those commitments.
Breaches:
2013 Belarus sanctions:
In 2013, Belarus complained that sanctions of the USA against it were in breach of Article 3 of the Memorandum.
Annexation of Crimea by Russia:
In 2014, Ukraine vigorously protested the annexation of Crimea by Russia as a violation of Article 1 of the Budapest Memorandum.
Kerch Strait incident:
In 2018, Ukraine again appealed to the signatories of the Budapest Memorandum to hold urgent consultations to ensure full compliance with the memorandum’s commitments and the immediate cessation of Russian aggression against Ukraine.
National
Janaushadhi Diwas Week: The Janaushadhi Diwas is being organized by the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers from 1st March to 7th March 2022.
Highlights:
- The 4th Jan Aushadhi Diwas will be celebrated on 7th March 2022.
- The Government of India (GoI) has set a target to increase the number of Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Kendras (PMBJKs) to 10,500 by the end of March 2025.
The theme of this week:
- The theme of the 4th Janaushadhi Diwas is “Jan Aushadhi-Jan Upyogi”.
Objective of the Janaushadhi Diwas Week:
- The main objective of the Janaushadhi Diwas Week is to create awareness about the benefits of Jan Aushadhi Pariyojana and the usages of generic medicines.
About PMBJP:
- The Pradhan Mantri Bhartiya Janaushadhi Pariyojana (PMBJP) was launched in 2008 by the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
- This initiative was launched with the objective of making high-quality medicines available to all at affordable prices, especially to the poor and underprivileged, through exclusive outlets such as Jan Aushadhi Medical store.
- It also looked to boost awareness regarding generic medicine usage within the country.
- The scheme makes quality drugs available at affordable prices through dedicated stores selling generic medicines.
- A public program was also started involving the govt., Private Sector, PSUs, Societies, NGOs, Co-operative Bodies, etc.
- Three IT-enabled PMBJP warehouses are functional at Chennai, Gurugram, and Guwahati, and a fourth one is set to begin operations at Surat.
- As of January 2022, the number of stores under this scheme has increased to 8675.
- PMBJP's product basket includes 240 surgical instruments and 1451 drugs.
- New nutraceuticals products and medicines such as malt-based food supplements, protein powder, protein bar, immunity bar, sanitizers, masks, oximeter, glucometer, etc. have also been launched.
- Thirty-nine distributors have been assigned to help the delivery of medicines to remote and rural locations across India.
Swacchagraha: Ministry of Culture in collaboration with Sulabh International organized “Swacchagraha: celebrating Swachhta and Swadhinta” on 5 March 2022.
It was organized under the aegis of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav to encourage mass awareness with the core thought of “Swachhta, Swadhinta and Sulabh”.
About Swacchagraha :
- The event was conducted in two sessions.
- In the first session Dr. Bindeshwar Pathak, founder of Sulabh Sanitation, Social Reform & Human Rights Movement addressed the audience.
- A special screening of the Amrit Mahotsav film was done on the occasion.
- The event also had a panel discussion on new ideas and measures for increasing Swacchtha, Swadhinta and Sulabh along with a song and film showcase.
- The evening session themed ‘Ek Shaam Sur, Taal aur Swachhta ke Naam’ was addressed by Chief Guest Shri Vijay Goel.
- The event featured a performance by Dhruva –The Sanskrit Band.
Note: This is the world’s only music band that is based on India’s oldest own tradition of Vedic–gaan and Stotra–gaan in the Sanskrit language.
What is Stotra?
- Stotra is a Sanskrit word that means "ode, eulogy or a hymn of praise."
- It is a literary genre of Indian religious texts designed to be melodically sung, in contrast to a shastra which is composed to be recited.
National ICT Award 2020 & 2021: The Union Minister Of State (MoS) for Education Smt Annpurna Devi has given National ICT Awards to 49 teachers from all over the country.
Speech by Smt Annpurna Devi:
- While presenting the awards, Annpurna Devi in her speech said that the NEP-2020 emphasizes the efficient use of technology in the field of teaching, which will remove the language barriers and increase access for DIVYANG students.
- She informed that the Information and Communication Technology [ICT] intervention under Samagra Shiksha also has inclusions to provide technological upgradations to schools and Teacher Education Institutes (TEIs).
- She also highlighted that DIKSHA, school MOOCs on SWAYAM, PMeVIDYA, ePathshala, ICT Curriculum for Teachers and Students and National Initiative for School Heads’ and Teachers’ Holistic Advancement integrated teacher training programme through online mode are among the flagship projects to bridge the digital divide.
- She appreciated the role of teachers in nation-building and a Guru (teacher) is given the most respectful person in Indian Society.
- The recent budget announcements by the Govt. of India have provided the impetus to each and every digital education initiative.
- Launching of 200 DTH TV channels, 750 Virtual labs in science and mathematics, transforming teachers as digital teachers are some of the new budget announcements of our Govt. for 2022-23.
Aim of ICT Awards:
- Recognition in the form of a National Award for ICT in Education for school teachers indirectly motivates instructors to utilize ICT extensively and significantly in their classrooms by combining content pedagogy and technology.
- It has now been foreseen to extend this Award to Teacher Educators (School Complexes, CRCs, BRCs, BIETs, DIETs, CTEs/IASEs, SCERTs/SIEs, SIETs, SIEMAT, etc. and for the States and UTs for their best educational practices.
- These ICT Awardees are also given the responsibility of serving as ICT Ambassadors, expanding the reach of ICT in Education through their ongoing efforts to mentor other teachers and also develop entrepreneurial skills among the students to develop a skilled workforce.
Arogya Vanam: The President of India Ram Nath Kovind, on March 1, 2022, inaugurated a newly developed Arogya Vanam at the President’s Estate in the presence of the Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi.
About Arogya Vanam :
- The Arogya Vanam has been developed in a 6.6-acre area
- It has been developed in the shape of a human sitting in the Yoga Mudra.
- It consists of around 215 herbs and plants like Neem, Tulsi, Bel, Arand, Arjun, Ashwagandha and Harsingar used for therapeutic purposes in Ayurveda.
- Some of the other features of this Vanam are water fountains, a Yoga platform, a water channel, a lotus pond and a viewpoint.
- The concept of Arogya Vanam has been conceived with the aim of publicizing the importance of Ayurvedic plants and their benefits on the human body.
- This Vanam will be now open for public viewing.
National Safety Day 2022: National Safety Day (NSD) is celebrated every year on the 4th of March.
Key Highlights:
- NSD is observed to commemorate the foundation of the National Safety Council (NSC) of India.
- The day aims to raise public awareness of all safety principles, including road safety, workplace safety, human health safety, and environmental safety.
- The year 2022 marks 51st NSD.
The theme of NSD 2022:
Every year, this day is celebrated with a different theme.
This year, the National Safety Council of India announced the theme to be ‘Nurture young minds – Develop safety culture’.
Significance of the day:
- National Safety Day is observed in order to ensure adequate workplace wellbeing.
- Learning a variety of safety measures comes in handy when one faces risky situations in our life.
- The development of a proactive attitude not only towards safety but also towards methods for identifying workplace dangers and reducing accidents and exposure to hazardous circumstances and substances, is critical to every employee’s job satisfaction.
History of the day
- In 1962, at the 22nd Labour Ministers' Conference recommendations were made to set up a National Safety Council (NSC) to promote accident prevention.
- The National Safety Council was set up on 4th March 1966 by the Ministry of Labour and Employment, Government of India (GoI).
- The idea behind this council was to create the SHE campaign.
- The SHE campaign stands for the safety, health, and environmental movement.
- In 1972, the Government decided to celebrate March 4th as national safety day, and it won’t be celebrated just for a day, but it will be more like an awareness week.
- The first National Safety Day was observed in 1972.
About National Safety Council (NSC):
- The NSC was established by The Ministry of Labour of the Government of India (GoI) in 1966.
- It is a non-profit tripartite body registered under the Societies Registration Act of 1860 and the Bombay Public Trust Act of 1950.
- It was to initiate, develop and maintain voluntary campaigns on Safety, Health and the Environment (SHE) at the national level.
- It is located in Navi Mumbai.
Activities of NSC:
Its activities include
- Organizing and carrying out specialized training programs and courses, conferences, seminars and workshops;
- Conducting consultancy studies, such as safety audits, safety levels, hazard evaluation and risk assessments;
- Designing and developing HSE promotional materials and publications;
- Promoting Organizations to celebrate and observe various campaigns, such as National Safety Day and Week, Fire Service Week, World Environment Day and Road Safety Week.
Members:
- Its Board of Governors consists of members from the government, employers’ organizations and trade union organizations.
- The chairperson of the NSC is appointed by the government and is usually a prominent industrialist.
Sanctions by the US on India: Amid Russia and US conflict over Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, the United States has announced that the country has been looking whether to apply or waive sanctions on India for its purchase of S-400 Triumf missile defence system from Russia, under the Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA).
Key Details:
- The latest move by the US against India has come as the country abstained from a UN vote to rebuke Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
- The voting results that were displayed on the screens at the United Nations General Assembly showed that 141 countries had voted in favour of condemning Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, while 5 nations were against it, with 35 countries, including India, abstaining.
- Under CAATSA, the US can also consider sanctions against India for continuing with defence deals with Russia amid the international crisis.
- According to CAATSA, any country working against US interests will be under sanctions.
- Helping Russian arms sales is not in the US interest.
- Russia has been in the dog house mainly because of annexing Crimea from Ukraine, for its role in Syria and interference in US elections.
- The CAATSA was basically aimed at Iran, Russia and North Korea, identified as states hostile to American interests.
- Therefore, any country purchasing the S-400 automatically comes under US sanctions.
- India went into the $5-billion deal with Russia in 2018.
- However, Biden Administration is yet to decide on applying sanctions on India under CAATSA.
Note: The US has already imposed sanctions on Turkey under the CAATSA for the purchase of a batch of S-400 missile defence systems from Russia.
What is CAATSA Act?
The 'Countering America's Adversaries Through Sanctions Act (CAATSA)' is a piece of US legislation that imposes sanctions on the American Adversaries- North Korea, the States of Iran, and Russia.
CAATSA Bill was passed back in 2017.
Provisions:
Countering Iran's Destabilizing Activities Act of 2017:
- CAATSA requires the President to impose sanctions against:
1)Iran's ballistic missile or weapons of mass destruction programs,
2)The sale or transfer to Iran of military equipment or the provision of related technical or financial assistance, and
3)Iran's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps and affiliated foreign persons.
- The President may impose sanctions against persons responsible for violations of internationally recognized human rights committed against individuals in Iran.
- The President may temporarily waive the imposition or continuation of sanctions under specified circumstances.
Countering Russian Influence in Europe and Eurasia Act of 2017:
- The President must submit for congressional review certain proposed actions to terminate or waive sanctions with respect to the Russian Federation.
- Specified executive order sanctions against Russia shall remain in effect.
- The President may waive specified cyber- and Ukraine-related sanctions.
- The bill provides sanctions for activities concerning:
(1) Cyber security,
(2) Crude oil projects,
(3) Financial institutions,
(4) Corruption,
(5) Human rights abuses,
(6) Evasion of sanctions,
(7) Transactions with Russian defense or intelligence sectors,
(8) Export pipelines,
(9) Privatization of state-owned assets by government officials
(10) Arms transfers to Syria.
The Department of State shall work with the government of Ukraine to increase Ukraine's energy security.
- The bill:
(1) Directs the Department of the Treasury to develop a national strategy for combating the financing of terrorism, and
(2) Includes the Secretary of the Treasury on the National Security Council.
- The act had imposed new sanctions on Russia for the interference in the 2016 US elections and its involvement in Ukraine and Syria, among others.
Korean interdiction and Modernization of Sanctions Act:
- The bill modifies and increases the President's authority to impose sanctions on persons in violation of certain United Nations Security Council resolutions regarding North Korea.
- U.S. financial institutions shall not establish or maintain correspondent accounts used by foreign financial institutions to provide indirect financial services to North Korea.
- A foreign government that provides to or receives from North Korea a defense article or service is prohibited from receiving certain types of U.S. foreign assistance.
- The bill provides sanctions against:
(1) North Korean cargo and shipping,
(2) Goods produced in whole or part by North Korean convict or forced labor,
(3) Foreign persons that employ North Korean forced laborers.
- The State Department shall submit a determination regarding whether North Korea meets the criteria for designation as a state sponsor of terrorism.
People In News
Shane Warne: Australian cricket legend Shane Warne passed away on 4th March 2022 from a suspected heart attack at the age of 52 years.
About Shane Warne:
- Shane Warne was a right-arm leg spinner cricketer from Australia.
- He is widely regarded as one of the finest bowlers in cricket history.
- He was named as one of Wisden's Five Cricketers of the Century in 2000 by a panel of experts.
- He was known as the King of Spin with a massive tally of 708 wickets in Test cricket, which is the most ever for an Australian and second in the world only after Muttiah Muralitharan, who broke his record on 3 December 2007.
- He had debuted in Test against India on January 2, 1992, and in ODI against New Zealand on March 24, 1993.
- His last test for the Australian side was against England on January 2, 2007, and his last ODI was on January 10, 2005.
- He was the only player to have scored more than 3,000 Test runs without a career century.
- He was a part of the Australian cricket team that won the World Cup in 1999 and won five Ashes series between 1993 and 2003.
- He was best remembered for one ball or that ball or Gatting Ball which is termed as the ball of the century, which he bowled to Mike Gatting of England at Old Trafford, Manchester.
- In 2005, he became the first bowler in the test format to reach 600 wickets.
- He was named as a bowler in Australia's "greatest ever ODI team".
- He was named in the all-time Test World XI by Wisden to mark 150 years of the Cricketers' Almanack.
- Shane Warne was inducted into the ICC Cricket Hall of Fame in 2013.
T20 Career:
- He was a significant part of the Indian Premier League (IPL).
- In 2008, he was appointed as the captain of Rajasthan Royals where he lead Rajasthan Royals to its fairy tale title win against Chennai Super Kings in the inaugural edition of the IPL.
- He continued to captain them for four more seasons, with 2011 being his final season with the team.
Sanjiv Kapoor: has been appointed as the new Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Jet Airways.
Key Highlights:
- His appointment will be effective from April 4, 2022.
- This is the second top-level announcement and it comes just few days after former Sri Lankan Airlines CEO Vipula Gunatileka was appointed as the chief financial officer of the airline.
- Former Indian Air Force (IAF) squadron leader and Nepal Airlines Corporation executive Captain PP Singh has also recently been appointed as the new accountable manager of Jet Airways, replacing Sudhir Gaur.
About Sanjiv Kapoor:
- He has over 20 years of experience in the airline industry.
- He started his airline career in finance and corporate planning with Northwest Airlines (now merged with Delta) in the US in 1997.
- Prior to being appointed as the new CEO of Jet Airways, he was the president of Oberoi Hotels.
- He has also worked as a chief operating officer at SpiceJet and chief strategy and commercial officer at Vistara.
About Jet Airways:
- Jet Airways was one of the largest airlines in India.
- It was founded by Naresh Goyal on 1 April 1992, in Mumbai.
- It ceased operations on April 17, 2019.
- The airline is, however, expected to restart its operations by early 2022.
- The Jalan Kalrock Consortium is the new promoter of Jet Airways.
- The consortium put forward a resolution, which was approved by the National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) on June 22, 2021.
Note: The NCLT in order has given the Ministry of Civil Aviation and the Directorate General of Civil Aviation 90 days for allotting airport slots to Jet Airways.
- This means that Jet Airways can take to the skies as early as this summer as a full-service domestic airline with a fleet of six aircraft.
Boltzmann Medal: Deepak Dhar from the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Pune, recently became the first Indian to be awarded the Boltzmann Medal by the Commission on Statistical Physics (C3) of the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics.
Key Highlights:
- C3 of the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP) presents this medal once in three years for contributions in the field of statistical physics.
- He shares the platform with American scientist John J. Hopfield who is known for his invention of an associative neural network, now named after him.
- The chosen two scientists will be presented with the medals at the StatPhys28 conference to be held in Tokyo, 7-11 August 2023.
- According to the website of the C3 Commission Prof. Dhar has been chosen for this award for his seminal contributions in the field of statistical physics, including exact solutions of self-organized criticality models, interfacial growth, universal long-time relaxation in disordered magnetic systems, exact solutions in percolation and cluster counting problems and definition of spectral dimension of fractals.
- Prof Dhar is currently the emeritus faculty at the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER), Pune.
About the award:
- This prestigious award was initiated in 1975.
- Nobel laureate (1982) K.G. Wilson was the first recipient.
- The award consists of the gilded Boltzmann medal with the inscription of Ludwig Boltzmann.
About Prof. Deepak Dhar:
- Prof Dhar was born in 1951.
- He completed his graduation in Science in 1970 from the University of Allahabad.
- He got his Masters’s in Physics from the Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur in 1972.
- In 1978, after completing his Ph.D. in The US he joined the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR) as a research fellow.
- He worked at TIFR over the years as a full-time professor and retired in 2016.
- Since then, he has joined IISER Pune as a visiting faculty.
General S F Rodrigues: Prime Minister, Shri Narendra Modi expressed deep grief over the passing away of former Indian Army Chief General S F Rodrigues.
- He passed away on March 4, 2022, at the age of 88.
About General S F Rodrigues:
- General Sunith Francis Rodrigues (1933 – 2022) was an Indian army officer who was Chief of the Army Staff of the Indian Army from 1990 to 1993.
- After his retirement, he served two terms on the National Security Advisory Board.
- He was also the Governor of Punjab from 2004 to 2010.
Military Service:
- He had joined the Joint Services Wing of the Indian Military Academy in 1949.
- He was commissioned on December 28, 1952, into the Regiment of Artillery.
- From 1975 to 1977, as a Brigadier, he commanded a mountain infantry brigade in a high-altitude sector.
- He was promoted to the Major General and then took over the command of a division in a high-altitude area.
- In 1986, after the promotion to the rank of Lieutenant General, he took command of a Corps in the Northern Sector.
- He was the Vice Chief of Army Staff from November 1987 to April 1989.
- He took over the Western Command from November 1, 1989, to June 30, 1990.
- He also served as the Chief of Army Staff from 1990 to 1993.
- The General Officer had participated in the Sino-Indian War of 1962, Indo-Pakistan War 1965, and Indo-Pak War 1971.
- SF Rodrigues retired on June 30, 1993, after nearly 41 years of service.
- He was also instrumental in the induction of women in the serving area of the Army in 1991, marking an important step towards empowering women to serve their country.
Awards:
He was awarded the Param Vishisht Seva Medal and Vishisht Seva Medal in recognition of his dedication and service.
Madhabi Puri Buch: Former banker Madhabi Puri Buch has been appointed as the new chairperson of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
Key Highlights:
- She has become the first-ever woman to head the capital markets regulator.
- 57-year-old Buch is also the first person from the private sector working at the regulator.
- She has been appointed for a three-year term.
- She will be replacing Ajay Tyagi whose tenure as SEBI chairman ended recently.
About SEBI:
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the regulatory body for the securities and commodity market in India under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Finance (MoF), Government of India (GoI).
- It was established on 12 April 1988 and given Statutory Powers on 30 January 1992 through the SEBI Act, 1992.
- The Preamble of the Securities and Exchange Board of India describes the basic functions of the Securities and Exchange Board of India.
- The main function of SEBI is to safeguard the rights and interests of the investor, reduce malpractices related to the stock exchange, establish a code of conduct and promote the healthy functioning of the stock exchange.
Note: Controller of Capital Issues was the regulatory authority before SEBI came into existence; it derived authority from the Capital Issues (Control) Act, 1947.
- It is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra.
Members:
- The SEBI is managed by its members, which consists of the following:
- The chairman is nominated by the Union Government of India.
- Two members, i.e., Officers from the Union Finance Ministry.
- One member from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
- The remaining five members are nominated by the Union Government of India, out of them at least three shall be whole-time members.
Places In News
Camel Protection and Development Policy: Faced with a declining number of camels in Rajasthan, the state government recently announced a ‘Camel Protection and Development Policy’ in its budget 2022-23.
Key Points:
- Chief Minister Ashok Gehlot proposed a budget of Rs 10 crore in the next financial year under the new policy for rearing, protection, and overall development of the state animal.
- The Rajasthan government had declared the camel as the state animal in 2014.
- The number of camels is continuously decreasing.
- According to the government figures, less than two lakh camels are left in Rajasthan and in the entire country.
- The number of camels has reduced by 1.5 lakh since 2012.
- There were about 2.5 lakh camels left when counted last in 2019.
- About 85% of the country’s camels are found in Rajasthan followed by Gujarat, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh.
Additional Info:
- World Camel Day is observed every year on 22 June to recognize the importance of camels to the livelihood of a large population.
About Rajasthan:
- Rajasthan is a state in northern India.
- It comprises most of the wide and inhospitable Thar Desert (also known as the "Great Indian Desert") and shares a border with the Pakistani provinces of Punjab to the northwest and Sindh to the west, along the Sutlej-Indus river valley.
- It became a State after 1947 when the princely states and chiefships were integrated into India in stages, and the state took the name Rajasthan.
- It assumed its present form on November 1, 1956, when the States Reorganization Act came into force.
- It is famous for its many historical forts, temples and palaces (Havelis), which predominantly drives tourism in the state.
- The Capital of Rajasthan is Jaipur.
- The current Chief Minister and Governor of Rajasthan are Ashok Gehlot and Kalraj Mishra respectively.
Pune Metro Rail Project: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi inaugurated the Pune Metro Rail Project.
Key Highlights:
- He also laid the foundation stone of various development projects.
- He was on his visit to Pune on 6th March 2022.
Projects inaugurated by PM Modi:
Statue of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj.
- PM Modi unveiled the grand statue of Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj at Pune Municipal Corporation.
- The seated statue made of gunmetal is 9.5 feet tall and weighs 1.85 tons.
Pune Metro Rail Project:
- He inaugurated a 12 km stretch of the total 32.2 km Pune Metro Rail Project.
- He also inaugurated and inspected the Exhibition at Garware Metro Station and will undertake a metro ride from there to Anandnagar Metro Station.
- He bought the first ticket of the Pune Metro before commencing his ride from Garware station to Anand Nagar.
- The following stretches were opened:
- Vanaz - Garware College (5 km elevated stretch with 5 stations)
- PCMC - Phugewadi stretch (7 km elevated stretch with 5 stations)
- Pune Metro is being built at a total project cost of Rs 11,400 crores.
- The government of India (GoI) had sanctioned the Pune Metro Rail Project in 2016 and the Foundation Stone was laid by Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi on 26th December 2016.
- The Metro will greatly improve urban mobility in the Pune Metropolitan area, which is among the fastest-growing urban areas in the country.
Mula-Mutha River Rejuvenation Project:
- He laid the foundation stone of Rejuvenation And Pollution Abatement of Mula-Mutha River projects under the ambitious National River Conservation Plan (NRCP) set up by the Centre.
- The Project will be implemented on the concept of “One City One Operator".
- The estimated cost of this project is over Rs 1470 crore, which includes the construction cost and operation and maintenance for 15 years period.
- The project, being funded by Japan International Cooperation Agency, JICA is likely to be completed in approximately 3 years.
- Rejuvenation of Mula-Mutha river will be done along a 9 Km stretch of the river.
- The projects involve works such as river edge protection, interceptor public amenities, sewage network, boating activity, etc.
- A total of 11 sewage treatment plants will be constructed under the project, with a combined capacity of around 400 MLD (million litres per day) with a 55 km long Sewage carrier pipeline.
- The capacity of each sewage treatment plant is 396 million MLD. PMC will also implement a River Front Development project on the lines of Sabarmati Riverfront development carried out in Ahmedabad.
Towards clean and green transport of Pune city:
- He dedicated a fleet of 150 Electric Buses, giving a boost to green urban mobility in Pune.
- An Electric Bus Depot, equipped with a charging station at Baner was also inaugurated.
R K Laxman Art Gallery:
- He also e- inaugurated the R K Laxman Art Gallery Museum located at Balewadi in Pune.
- The Gallery showcases cartoons drawn by the legendary cartoonist R K Laxman.
- The main attraction is a miniature model based on the village of Malgudi of the ‘Malgudi Days’ fame.
Symbiosis Arogya Dham:
- Prime Minister Modi participated in the Golden Jubilee celebration of Symbiosis Institutions.
- He inaugurated the integrated health complex ‘Symbiosis Arogya Dham’
- The 'Symbiosis Aarogya Dham', is spread over 70 acres of land at the Symbiosis International (Deemed University) Campus at Lavale, Pune.
- The Aarogya Dham consists of the Symbiosis Medical College for Women which is the first fully residential medical college for girls in the state of Maharashtra.
- The 900 bedded Symbiosis University Hospital & Research Centre (SUHRC) is attached to this medical college.
- Institutes and faculties of health sciences, biological sciences, sports sciences, nursing, yoga and emotional health etc are also housed in the integrated Arogya Dham.
Symbiosis has adopted 23 villages around the University Campus to provide quality healthcare through the 'Mobile Medical Van' and digital literacy through the Symbiosis Rural Digital Literacy Lab'.
About Symbiosis:
- Symbiosis Institution was established by Dr. S B Mujumdar.
- It began as a small international cultural centre with the objective of bringing foreign and Indian students together to promote international understanding and brotherhood.
- Today, it is a multi-location educational institution with campuses spread across Pune, Nashik, Nagpur, Bangalore, Hyderabad and Noida.
- Symbiosis has over 45,000 students from all states of India and 85 different countries.
Withdrawal of Consent to CBI: Meghalaya recently became the first NDA-ruled state and the ninth state of the country to withdraw consent to CBI to investigate cases in the state.
The decision means the CBI will now have to get consent from the state government for every case it registers in Meghalaya.
Key Highlights:
- The eight other states which had withdrawn consent to the CBI are Maharashtra, Punjab, Rajasthan, West Bengal, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Kerala, and Mizoram.
- The first state to withdraw consent was Mizoram which did so in 2015.
- This comes in the wake of several allegations of mass graft and corruption emerging in Meghalaya, especially in illegal coal extraction and transportation.
- The state governments ruled by the opposition parties had withdrawn the consent alleging that the CBI is not fair and impartial in its probe.
- The Congress has also accused the Chief Minister’s brother, James P K Sangma of being involved in corruption in the implementation of the state’s Soubhagya Scheme.
- The Soubhagya Scheme is aimed at providing electricity connections to all households including urban and rural across the country.
Note: The northeastern state is ruled by the Conrad Sangma-led National People’s Party which is a part of the BJP’s National Democratic Alliance.
About general consent:
- The Delhi Special Police Establishment (DSPE) Act, 1946, governs the CBI and it is mandatory to obtain the concerned state government’s consent before beginning to investigate a crime in a state.
- The CBI’s position is in this respect different from that of the National Investigation Agency (NIA), which is governed by The NIA Act, 2008, and has jurisdiction across the country.
- The consent can be either case-specific or general.
- States typically give general consent to assist the CBI in conducting a seamless investigation of cases of corruption involving central government personnel in their states.
- This is consent by default otherwise CBI would have to seek permission from the state government in every case, even for small tasks.
Case-specific and general: Given that the CBI has jurisdiction only over central government departments and employees.
- It can investigate a case involving state government employees or a violent crime in a given state only after that state government gives its consent.
What is the meaning of withdrawal of consent?
- It means that the CBI will not be able to file any new cases involving central government officials or private persons in the state without the permission of the state government.
- The CBI officers will lose all powers of a police officer as soon as they enter the state unless the state government has allowed them.
Under what provision can general consent be withdrawn?
- The state governments can withdraw the general consent accorded in the exercise of power conferred by Section 6 of the Delhi Special Police Establishment Act, 1946.
Can withdrawal mean that the CBI can no longer probe any case?
- No. The CBI would still have the power to investigate old cases registered when general consent existed.
- Also, cases registered anywhere else in the country, but involving people stationed in states which have withdrawn consent, would allow CBI’s jurisdiction to extend to these states.
Calcutta High Court verdict:
- Calcutta High Court’s judgment regarding the investigation conducted by CBI in a case of illegal coal mining and cattle smuggling in a state that has withdrawn consent.
- Calcutta HC had declared that the central agency cannot be stopped from investigating a central government employee in another state even if the central government employee is posted in a state that has withdrawn consent.
- The order has been challenged in the Supreme Court.
Vinay Mishra vs the CBI:
- In Vinay Mishra vs the CBI, Calcutta High Court ruled that corruption cases must be treated equally across the country, and a central government employee could not be “distinguished” just because his office was located in a state that had withdrawn general consent.
- The HC also said that withdrawal of consent would apply in cases where only employees of the state government were involved.
Options available for CBI:
- The CBI could use the Calcutta HC order to register a fresh case in any state.
- Alternatively, it could file a case in Delhi and continue to investigate people inside these states.
Issues faced by CBI Autonomy:
- After the 2018 amendments to the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988, the Centre has come to exercise power over the CBI not just administratively, but also legally.
- In 2018, the government pushed through Parliament amendments to Section 17A of the Act making it mandatory for the CBI to seek the Centre’s permission before registering a case of corruption against any government servant.
About Meghalaya:
- It is a state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed by carving out two districts from the state of Assam: the United Khasi Hills and Jaintia Hills, and the Garo Hills on 21 January 1972.
- It is one of the 7 sister states of North-East India.
- Its capital is Shillong.
- The current Governor and Chief Minister of Meghalaya are Satya Pal Malik and Conrad Sangama respectively.
Science and Technology
Kavach: The Union Minister of Railways Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw recently inspected the trial of the ‘Kavach’ working system between Gullaguda-Chitgidda Railway stations on Lingampalli-Vikarabad section in Secunderabad Division of South Central Railway.
Key Points:
- The Kavach (meaning armour in English) is an indigenously developed ATP system by Research Design and Standards Organization (RDSO) in collaboration with the Indian industry.
- This indigenous kavach system adheres to the spirit of Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- It is a state-of-the-art electronic system of Safety Integrity Level - 4 standards.
- It is meant to provide protection by preventing trains to pass the signal at Danger (Red) and avoid a collision.
- If the driver fails to control the train as per the speed restrictions then it automatically activates the train braking system.
- In addition, it prevents collision between two Locomotives equipped with a functional KAVACH system.
- It is also known as Train Collision Avoidance System (TCAS).
- ‘Kavach’ is one of the cheapest; Safety Integrity Level 4 (SIL-4) certified technologies with the probability of error are 1 in 10,000 years.
- It also opens avenues of export of this indigenous technology for Railways.
Note:
- It will be soon operational all over India in a gradual manner, as proposed in the Budget.
- As a part of Atmanirbhar Bharat, 2,000 km of the network will be brought under Kavach for safety and capacity augmentation in 2022-23.
- Around 34,000 Kms of the network will be brought under Kavach.
Background:
- It is being developed since 2012.
- In 2016 first field trials were conducted.
- Currently, it is operational in the Lingampalli & Vikarabad section of the South Central Railway (SCR) zone.
Features of Kavach:
- Prevention of Signal Passing at Danger (SPAD).
- Continuous update of Movement Authority with a display of signal aspects in Driver Machine Interface (DMI) / Loco Pilot operation cum Indication Panel (LPOCIP).
- Automatic Braking for Prevention of Over Speeding.
- Auto Whistling while approaching Level Crossing Gates.
- Prevention of collision between two Locomotives equipped with functional KAVACH.
- SoS Messages during emergency situations.
- Centralized live monitoring of Train movements through the Network Monitor System.
Cluster Bombs and Thermobaric Weapons: Human rights groups Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch accused Russia of using cluster bombs and vacuum bombs in the ongoing war.
Vacuum Bomb:
- A vacuum bomb sucks in oxygen from the surrounding area to generate a high-temperature explosion.
- It has the capability of vaporizing human bodies.
- Vacuum bombs are not prohibited by any international law or agreement, but their use against civilian populations in built-up areas, schools, or hospitals, could attract action under the Hague Conventions of 1899 and 1907.
Thermobaric weapon:
- Thermobaric weapons are also known as aerosol bombs, fuel-air explosives, or vaccum bombs.
- They use oxygen from the air for a large, high-temperature blast.
- A thermobaric weapon causes significantly greater devastation than a conventional bomb of comparable size.
- It can be fitted to hand-held launchers, can be fired as rockets from tank-mounted launchers, or dropped from aircraft.
Cluster munitions:
- According to the 2008 Convention on Cluster Munitions, a cluster munition means a “conventional munition that is designed to disperse or release explosive submunitions each weighing less than 20 kilograms, and includes those explosive submunitions”.
- Essentially, cluster munitions are non-precision weapons that are designed to injure or kill human beings indiscriminately over a large area, and to destroy vehicles and infrastructure such as runways, railway, or power transmission lines.
- They can be dropped from an aircraft or launched in a projectile that spins in flight, scattering many bomblets as it travels.
- Countries that have ratified the Convention on Cluster Munitions are prohibited from using cluster bombs.
Dangers of cluster munitions:
- These cluster munitions are non-precision weapons so they release many small bombs over a large area that can indiscriminately kill civilians.
- It is difficult to locate and remove such unexploded bombs.
- Many of these bombs don’t explode immediately but continue to lie on the ground.
- Hence, even long after the conflict is over they continue to pose threat to the life of civilians.
About Convention on Cluster Munitions (CCM):
- The Convention on Cluster Munitions (CCM) is an international treaty that prohibits all use, transfer, production and stockpiling of cluster bombs.
- It was adopted in Dublin, Ireland, in 2008.
- It entered into force on 1 August 2010, six months after it was ratified by 30 states.
- As of 10th February, 2022,123 states have joined the Convention, with 110 states that have ratified it, and 13 states have signed the Convention but not yet ratified it.
- Apart from prohibiting cluster bombs, the convention also establishes a framework to support the victim assistance, clearance of contaminated sites, risk reduction education, and stockpile destruction.
- It also specifically identifies “cluster munition remnants”, which include “failed or abandoned cluster munitions, unexploded submunitions, and unexploded bomblets.
Note: Ukraine and Russia are not signatories to this convention.
Obligations:
Countries that ratify the convention will be obliged “never under any circumstances to”:
- Use cluster munitions
- Develop, produce, otherwise acquire, stockpile, retain or transfer to anyone, directly or indirectly, cluster munitions
- Assist, encourage, or induce anyone to engage in any activity prohibited to a State Party under this Convention
Exceptions:
- However, the treaty allows certain types of weapons with submunitions that do not have the indiscriminate area effects or pose the same unexploded ordnance risks as cluster munitions.
- Permitted weapons must contain fewer than ten submunitions, and each must weigh more than 4 kilograms and must contain self-deactivation mechanisms.
- Weapons containing submunitions that all individually weigh at least 20 kg (44 lb) are also excluded.
- A limited number of prohibited weapons can be acquired for training and development of, detection, clearance, and destruction techniques and counter-measures.
Resilient Crops: Scientists at the Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI), in collaboration with several other research institutions, have identified about 15,000 selected germplasms of rice and wheat.
Key Details:
- These have been identified for developing varieties that are tolerant to floods, droughts, heatwaves, and diseases to mitigate the adverse impact of climate change on food production.
- This is being done to mitigate the adverse impact of rising in temperature because of climate change on food production.
- Agricultural scientists have sourced rice and wheat genetic resources from a gene bank located at the heart of Delhi as part of a Department of Biotechnology (DBT) project to develop improved crop varieties to combat climate change.
- This gene bank is managed by the National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR).
- The gene bank has around 4 lakh accessions (a unique identifier given to a protein sequence) in its collection.
- These accessions represent the wide natural genetic variation across the 15 agro-climatic regions in the country.
About the technology being used by scientists:
- After identification of genes, 'marker-assisted backcross breeding technology' is being used by the scientists for developing rice and wheat varieties, which could withstand extreme weather conditions such as drought, floods and heatwaves, as well as diseases such as bacterial blasts and blight.
- With the use of this technology, it takes three-five years to develop a new variety which previously used to take at least 10 years.
Varieties of Crops Developed:
- IARI has developed three different types of disease resistance basmati rice which are PB 1847, PB 1886, and PB 1885.
- These have been developed through projects funded by DBT and will be distributed to private sector seed companies for multiplication.
- An MoU with private seed companies will be entered into shortly.
- In the case of wheat, varieties to cope with new challenges with climate-changing scenarios are being developed by NBPGR in coordination with several other institutions.
How many such crop varieties have reached farmers?
- According to DBT, there is a development of 17 varieties of crop plants with enhanced nutritional content, resistance to pathogens and tolerance to abiotic stress.
- The varieties are divided into
- Rice: 8,
- Wheat: 4
- Maize: 2
- Of these, six varieties have already reached farmers’ fields after multiplication by private players.
International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture:
- India is a signatory to the International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture.
- It is a global agreement in harmony with the Convention on Biological Diversity.
- It aims at guaranteeing food security through the conservation, exchange and sustainable use of the world’s plant genetic resources for food and agriculture.
Sports
ISSF World Cup 2022: Indian shooter, Saurabh Chaudhary has clinched India’s first gold medal at the ongoing 2022 International Shooting Sport Federation (ISSF) World Cup in Cairo, Egypt.
Key Highlights:
- The 19-years Chaudhary defeated Michael Schwald of Germany 16-6 in the Gold Medal match of the Men’s 10m Air Pistol Event.
- The silver medal has been won by Germany’s Michael Schwald while Artem Chernousov of Russia claimed the bronze medal.
- In the women’s 10m air pistol section, India’s Esha Singh lost to Anna Korakaki of Greece to win the silver medal.
- Tokyo Olympics silver medalist Antoaneta Kostadinova claimed the bronze medal.
About ISSF:
- The International Shooting Sport Federation (ISSF) is the governing body of the Olympic shooting events in rifle, pistol and shotgun disciplines, and of several non-Olympic Shooting sport events.
- It was founded in 1907.
- It is headquartered in Munich, Germany.
Strandja Memorial Boxing Tournament: Indian boxers Nitu (48kg) and Nikhat Zareen (52kg) have won gold medals at the 73rd Strandja Memorial Boxing Tournament, held in Sofia, Bulgaria.
Key Highlights:
- Nitu prevailed 5-0 over Italy’s Erika Prisciandaro, a former youth world championship bronze-medallist.
- Zareen, on the other hand, outpunched Ukraine’s Tetiana Kob, a three-time European Championships medallist 4-1.
- Nandini also finished on the podium in the 81kg category and signed off with a bronze medal.
- The Indian contingent concluded their campaign with three medals at the tournament, which was part of India’s first exposure trip this year.
About:
- The Hyderabad-based Zareen, who is a multiple-time national medalist, had won a gold medal at the Strandja Memorial’s 2019 edition as well.
- Nitu is a two-time former youth world champion and is also a former gold medallist at the Asian youth championships.
World Taekwondo: World Taekwondo has stripped Russian Prez Vladimir Putin of black belt following his country's invasion of Ukraine.
Key Points:
- World Taekwondo strongly condemned the brutal attacks on innocent lives in Ukraine, which goes against its motto "Peace is More Precious than Triumph" and the World Taekwondo values of respect and tolerance.
- "In this regard, World Taekwondo has decided to withdraw the honorary 9th dan black belt conferred to Vladimir Putin in November 2013," stated an official statement.
- World Taekwondo also said that in solidarity with the International Olympic Committee, no Russian or Belarusian national flags or anthems will be displayed or played at World Taekwondo events.
- World Taekwondo and the European Taekwondo Union will not organize or recognize Taekwondo events in Russia and Belarus.
- The International Judo Federation too made a similar decision to remove Putin's title of honorary president and ambassador "in light of the ongoing war conflict in Ukraine."
Russian President Vladimir Putin had announced a military operation in Ukraine and warned other countries that any attempt to interfere with the Russian action would lead to "consequences they have never seen."
FIFA and UEFA: FIFA and UEFA have decided to indefinitely suspend all Russian teams, whether national representative teams or club teams, from participation in all competitions run by the two football bodies.
About FIFA:
- FIFA, Fédération Internationale de Football Association in French, is the highest global governing body of football (also known as soccer to distinguish it from American football), the world’s most popular game.
- It is also the international governing body for futsal (a kind of mini football played indoors on a hard court between two teams of five players each) and beach soccer (five-a-side played on a beach).
- It was founded on 21 May 1904.
- It is responsible for organizing and promoting football’s major international tournaments, most importantly the football World Cup, which began in 1930, and the Women’s World Cup which began in 1991.
- The membership of FIFA now comprises 211 national football associations around the world.
- FIFA is headquartered in Zurich, Switzerland.
- It supports these national associations financially and logistically through various programmes.
- The FIFA Congress is the supreme legislative body of FIFA, in which each of the 211 members of the organization has a vote.
About UEFA:
- Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) is the administrative body for football, beach soccer and futsal in Europe.
- It is among 6 continental confederations of world football’s governing body FIFA.
- It comprises 55 national association members apart from representing national football associations of Europe.
- It runs nation & club competitions such as UEFA European Championship, UEFA Nations League, UEFA Europa League, UEFA Europa Conference League, UEFA Champions League, and UEFA Super Cup.
- It also controls the prize money, regulations and media rights for these competitions.
Abey Kuruvilla: The former India pacer, Abey Kuruvilla is all set to take charge as the new General Manager of the Board of Control for Cricket in India (BCCI).
Key Facts:
- Kuruvilla's appointment was ratified during BCCI’s Apex Council meeting on March 2, 2022.
- The position of BCCI’s General Manager fell vacant after Dhiraj Malhotra had stepped down.
- Earlier in 2022, Abey Kuruvilla’s tenure as the national selection committee member got over and now he will be taking up the role of new General Manager of BCCI.
About Abey Kuruvilla:
- Abey Kuruvilla is a former Indian pace bowler of the mid-1990s
- The 53-year-old Kuruvilla in his brief international career played in 35 international matches, 25 one-day Internationals, and ten Tests, all in the same calendar year.
- He retired from all forms of cricket in 2000 and took up coaching.
- On September 27, 2012, he was appointed as the National Selector from the BCCI as the talent scout for Mumbai Indians.
- In December 2020, he was appointed as the national selector of the Indian Cricket Team.
About BCCI:
- It is an acronym of the Board of Control for Cricket in India.
- BCCI is the national governing body for cricket in India.
- The board was formed in December 1928 as a society, registered under the Tamil Nadu Societies Registration Act.
- It comes under the jurisdiction of the Youth Affairs and Sports Ministry, Government of India.
Note: It is an autonomous organization and does not come under the National Sports Federation of India.
- Its headquarters are in Wankhede Stadium, Mumbai.
- Grant Govan was its first president and Anthony De Mello its first secretary.
- It is the richest cricket board in the world.
- It is part of the big three of the International Cricket along with Cricket Australia and England and Wales Cricket Board.
- The current President of BCCI is Sourav Ganguly.
TATA IPL 2022: RuPay, a flagship product of the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI), has become the official partner for TATA IPL 2022.
Highlights:
- This was announced by BCCI's Indian Premier League Governing Council (IPL GC)
- This will be a multi-year partnership.
About RuPay:
- RuPay is a flagship product of the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI).
- It is the first-of-its-kind Global Card payment network from India.
- It provides a self-reliant card payments network with innovative features that have made it a successful interoperable card.
- It is widely accepted at POS devices, ATMs as well as on e-commerce websites and provides a self-reliant card payments network.
- RuPay cards are issued by more than 1,100 banks which include public, private, regional rural and co-operative banks.
Tata IPL 2022:
- The 15th edition of Tata IPL 2022 will start on 26th March 2022 and the final will be played on May 29, 2022.
- The tournament will be played in Mumbai and Pune in Maharashtra.
- A total of 70 league matches will be played across four international venues in Mumbai and Pune.
- The venue for the playoff matches will be decided later.
Arts
Rashtriya Sanskriti Mahotsav: The 11th edition of ‘Rashtriya Sanskriti Mahotsav was inaugurated by The Governor of West Bengal, Shri Jagdeep Dhankhar on February 14, 2021.
Key Highlights:
- The event was inaugurated at Cooch Behar Palace in West Bengal in the presence of Minister of State (I/C) for Culture and Tourism, Shri Prahlad Singh Patel.
- The festival was held in between 14th to 28th February, 2021
- The third and final leg of this 11th edition took place at Murshidabad, West Bengal.
- Various colourful performances were given by the local artists, including ‘Baul Gaan’, ‘Alkup Gaan’, ‘Leto gaan’, ‘Jhumuriya’ and Ranpa folk dances.
Note:
- Ten editions of the festival have successfully been organised ever since the festival was started in November, 2015.
- These 10 editions were organized in Delhi, Bengaluru, Varanasi, Tawang, Karnataka, Gujarat, Tehri and Madhya Pradesh.
Significance:
- The 11th edition is significant in the light of COVID Pandemic that has severely impacted the cultural sector.
- Through this event support and assistance will be provided to the artists by the ministry of culture.
About Rashtriya Sanskriti Mahotsav:
- It is a flagship festival of the Ministry of culture and tourism.
- The event is organized since 2015.
- It witnesses the active participation of Seven Zonal Culture Centres.
- These zonal centres play a key role in taking the vibrant culture of India to the masses rather than confining it to auditoria and galleries.
- This festival showcases the folk and tribal art, music, dance, cuisines and culture of one state in other states.
- Thus, it helps in reinforcing the goal of “Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat”.
- It also provided an effective platform for the artists and artisans to support their livelihood.
- It reconnects the people (especially the youth) with their indigenous culture, its multifaceted nature, magnificence, and historical importance in the context of ‘India as a Nation’ over the millennia.
About Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat:
- Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat is an initiative of the Ministry of Education.
- It was launched in 2015 on the occasion of the 140th birth anniversary of Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel.
- This initiative aims to promote engagement amongst the people of different States/UTs so as to enhance mutual understanding and bonding between people of diverse cultures, thereby securing stronger unity and integrity of India.
The broad objectives of the initiative are as follows:
- To celebrate the unity in diversity of our nation and to maintain and strengthen the fabric of traditionally existing emotional bonds between the people of our country;
- To promote the spirit of national integration through a deep and structured engagement between all states and union territories through a year-long planned engagement between states;
- To showcase the rich heritage and culture, customs and traditions of either state for enabling people to understand and appreciate the diversity that is India, thus fostering a sense of common identity;
- To establish long term engagements;
- To create an environment this promotes learning between states by sharing best practices and experiences.
Every State and UT in the country would be paired with another State/UT for a time period, during which they would carry out a structured engagement with one another in the spheres of language, literature, cuisine, festivals, cultural events, tourism etc
About Zonal Cultural Centres:
The centre aim to strengthen the ancient roots of Indian Culture and evolve and enrich composite National Culture.
There are seven Zonal Cultural Centres (ZCCs) in India.
They are as follows:
- Eastern Zonal Cultural Centre Kolkata,
- North Central Zone Cultural Centre Allahabad,
- North east Zone Cultural centre Dimapur,
- North Zone Cultural centre Patiala,
- South Central Zone Cultural Centre Nagpur,
- South Zone Cultural Centre Thanjavur,
- West Zone Cultural Centre Udaipur
These ZCCs organize various cultural activities and programmes all over the country on a regular basis.
Other schemes of ZCCs:
- Award to Young Talented Artists
- Guru Shishya Parampara
- Theatre Rejuvenation
- Shilpgram
- Octave
- National Cultural Exchange Programme (NCEP).
Ishan Manthan Festival: Union Minister for Culture, Tourism & DONER Shri G Kishan Reddy recently inaugurated the three-day North-East festival 'Ishan Manthan' at Indira Gandhi National Centre for the arts in New Delhi.
Key Points:
- The three-day Ishan Manthan program which celebrated the rich ethnicity and colors of North East India was held from 25 March to 27, 2022.
- The inaugural session also witnessed the publishing of two books titled 'Lok Beyond Folk,' a book on the Lok Culture edited by Shri J Nandalumar, and 'Jewels of North East India.'
Significance:
- The event gives a chance to understand the culture, art, music, folk dances, handicrafts, and traditional cuisines of Northeast India.
- Ishan Manthan is an endeavor to celebrate the plural expressions of northeast India. Hence, it can be understood as "North East Brainstorming."
Shambhaji Nagar: The Maharashtra cabinet, in a meeting chaired by Chief Minister Uddhav Thackeray on June 29, approved the renaming of Aurangabad city as Shambhaji Nagar, and Osmanabad city — which is named after the last ruler of Hyderabad, Mir Osman Ali Khan — as Dharashiv.
Key Points:
The decision to change the name was in accordance to the long-pending demand of Shiv Sena, which is a constituent of the three-party Maha Vikas Aghadi coalition government in the state.
The state cabinet has also given its nod to name the upcoming international airport in Navi Mumbai after D B Patil, which was a demand raised by the project-affected people (PAP).
Note: D B Patil is a late politician and social activist who is revered as a local hero by the residents of Uran, where the Navi Mumbai international airport is going to come up.
About Aurangabad:
- Aurangabad is a city in Maharashtra state, in India.
- The city is known as a major production center of cotton textile and artistic silk fabrics.
- The city is also a popular tourism hub, with tourist destinations like the Ajanta and Ellora caves lying on its outskirts, both of which have been designated as UNESCO World Heritage Sites since 1983.
- Other tourist attractions include the Aurangabad Caves, Daulatabad Fort, Grishneshwar Temple, Jama Mosque, Bibi Ka Maqbara, Himayat Bagh, Panchakki and Salim Ali Lake.
History of Aurangabad:
- Formerly, Aurangabad was home to many noted dynasties including Satavahanas, Chalukyas, Rastrakutas and Yadavas.
- Among the Hindu rulers, the Mauryans made significant contributions on the historical and religious background of the place.
- It was during their reign that numerous Buddhist cave temples were built inside and outside of the area during their rule.
- The world famous Ajanta and Ellora caves of the place are admired even today for their beautiful amalgam of Hindu, Jain and Buddhist architecture.
Muslim Rule:
- Aurangabad was founded in 1610 by Malik Ambar, the Siddi general of the Nizamshahi dynasty of Ahmadnagar.
- The city was named Khirki or Khadki at the time, and its name was changed to Fatehpur by Malik Ambar’s son Fateh Khan following Malik Ambar’s death in 1626.
- In 1653, the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb invaded the Deccan and set up his capital in the city, which he renamed Aurangabad. The city has borne the association of its name with Aurangzeb ever since.
- Chhattrapati Sambhaji Maharaj, the son and successor of Chhattrapati Shivaji Maharaj, was tortured and killed in brutal fashion on Aurangzeb’s orders in 1689.
- However after the death of Aurangzeb in 1707, Nizams of Hyderabad took over the control of the city.
- The legendary Nizams maintained and controlled the city until it was merged with Maharashtra in 1956.
Cardinals: Archbishop of Goa and Daman Filipe Neri Ferrão are among the 21 bishops chosen by Pope Francis to be made cardinals.
Key Points:
- Archbishop Filipe Neri António Sebastião di Rosário Ferrão is the Archbishop of Goa and Damão and -Archbishop Anthony Poola is the Archbishop of Hyderabad.
Note: Poola is the first Dalit from India to get the title.
- Apart from these two prelates, the others to receive the prestigious red hat will be one each from Mongolia, Ghana, Nigeria, Singapore, East Timor, Paraguay, and Brazil, in keeping with Francis' determination to have church leaders reflect the global face of the Catholic church.
- In all, 8 of the newly named Cardinals are from Europe, six from Asia, two from Africa, one from North America, and four from Central and Latin America.
- Pope Francis had announced that he will create 21 new Cardinals, including two from India at a Consistory on, 27 August, 2022 in the Vatican City.
- He also said that he will meet from August 29 and 30 with all the cardinals to reflect on the new Apostolic Constitution Praedicate evangelium.
Who is a cardinal?
- Cardinals rank second only to the Pope in the hierarchy of the Roman Catholic Church and serve as his closest advisors at home and around the world.
- The term “cardinal” comes from the Latin word “cardinalis,” from the word “cardo,” or “hinge.”
- They are considered “the hinges on which the Church revolves”.
- These cardinals represent the Church worldwide, and reflect a wide variety of cultures, contexts and pastoral ministries.
- Collectively, they constitute the College of Cardinals, and are appointed for life.
There are three ranks of cardinals –
- Cardinal bishop,
- Cardinal deacon, and
- Cardinal priest.
- Cardinals receive the symbolic red biretta and ring from the Pope when they are created at consistories.
- The ring signifies their marriage to the church.
- The prelates are also known for their distinctive red attire – the colour expressing the cardinals’ willingness to die for their faith,
- Only six cardinals hold the title of cardinal bishop.
- Cardinal priests are the most in number.
The College of Cardinals currently consists of 208 cardinals, of whom 117 are electors and 91 are non-electors.
As of 27 August, the number will grow to 229 Cardinals, of whom 131 will be electors.
All That Breathes: Delhi-based filmmaker Shaunak Sen’s “All That Breathes” won the 2022 L’Oeil d’Or (Golden Eye) for the best documentary at the 75th Cannes Film Festival, making it two in succession for India.
Key Highlights:
- The 90-minute long film was chosen the winner by the jury, comprising Polish filmmaker Agnieszka Holland, Ukrainian writer-director Iryna Tsilyk, French actor Pierre Deladonchamps, journalist Alex Vicente, and Moroccan writer-filmmaker Hicham Falah.
- Sen’s win is India’s second in Cannes in two years.
- In 2021, Payal Kapadia’s “A Night of Knowing Nothing”, which played in the parallel Semaine de la Critique (Cannes Critics’ Week) took home the L’Oeil d’Or.
- 'All That Breathes' is Sen's second project after his 2016 documentary 'Cities Of Sleep', about homeless people searching for a place to sleep in Delhi.
- In January, the documentary won the World Cinema Grand Jury Prize: Documentary at the 2022 Sundance Film Festival.
- The award includes a cash prize of 5,000 euros.
About “All That Breathes”:
“All That Breathes” is about two Delhi brothers Nadeem and Saud who, amid the city’s worsening air and deteriorating social fabric, devote their lives to saving migratory black kites that are at the mercy of mankind’s unthinking ways.
Other Winners:
- The best director prize went to Park Chan-wook for his work on Decision to Leave, which marks a clear departure for the Korean director in terms a tone and mood.
- The Grand Prix, the prize for the second-best film in Competition, witnessed a tie between 75-year-old French director Claire Denis’ Stars at Noon, set in mid-1980s Nicaragua, and young Belgian filmmaker Lukas Dhont’s sophomore venture Close, the story of a friendship between two teenage boys.
- Korean actor Song Kang-ho was adjudged the best actor in Japanese auteur Hirokazu Kore-eda’s Busan-set drama Broker, about a cobbled-together family reminiscent of the one in the director’s 2018 Palme d’Or.
About L'OEil d'Or award:
The L'OEil d'Or documentary award, also known as The Golden Eye award, was created in 2015 by French-speaking authors' society LaScam in collaboration with the Cannes Film Festival.
Economics
RAMP Programme: The Union Cabinet has approved the “Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance” (RAMP) programme that is also supported by the World Bank and will cost Rs 6,062.45 crore.
Key Details:
- The newly launched RAMP scheme would commence in the Financial Year 2022-23.
- The total financial outlay for the RAMP scheme is Rs.6,062.45 crore (USD 808 Million).
- A loan of Rs.3750 crore (USD 500 Million) for this programme will be provided by the World Bank and the remaining Rs.2312.45 crore (USD 308 Million) is being funded by the Central Government.
Background:
- The recommendations for the RAMP scheme were made by KV Kamath Committee, U K Sinha Committee, and Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (PMEAC).
- This was followed by Missions, extensive consultations with States and other stakeholders, technical and fiduciary assessments conducted by the World Bank.
Aim of this programme:
This scheme is aimed at the following:
- To support various COVID-19 related Recovery and Resilience Interventions of the Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises.
- To improve the access to credit and the market as well as strengthen the institutions and governance at the State and the Centre and State.
- To improve the partnerships of the Centre and the State as well as address the issues related to delayed payments.
- The MSME’s capacity will also be increased through this programme and will also scale up MSME coverages in the states and UTs.
- To bolster skill development, capacity building, technological up-gradation, quality enrichment, outreach, digitization, marketing promotion, etc.
- To help in the creation of jobs and bringing in greening initiatives in this sector.
Implementation and Monitoring of this scheme:
- For the implementaion of RAMP, Strategic Investment Plans (SIPs) will be created and all the states and UTs of the country will be invited to provide inputs.
- The SIPs will be used to develop an outreach plan for MSMEs mobilisation and identification.
- This programme will be monitored and evaluated by the National MSME Council, which will be led by the Minister for MSME and will include representatives from other Ministries as well as a secretariat.
Coverage of States and Districts:
- All the States and UTs of the country will be invited to prepare SIPs.
- The proposals that will be placed under the SIPs will be funded on the basis of their appraisals.
- The funds would be released based on the criteria of objective selection and the SIPs would be approved and appraised through a rigorous process set up by the MSME Ministry.
Local for Global: Prime Minister Narendra Modi made an appeal for 'local for global' in his 87th edition of the Mann ki Baat radio broadcast, following up on his 'voice for local' pitch.
Key Points:
- He lauded the exponential leap in Indian goods exports.
- Mr. Modi praised India for meeting its $400 billion export target, saying that while it may appear to be an issue of the economy at first glance, it was more about India's competence and potential.
- He stated that India's export figures stand at 400 billion dollars today which meant that the demand for items made in India is increasing all over the world.
- He pointed out that today new products from all corners of the country were reaching foreign shores, let they be leather goods from Hailakandi in Assam or handloom products from Osmanabad, or fruits and vegetables from Bijapur.
- He attributed the success of “Make in India” drive to farmers, artisans, weavers, engineers, small entrepreneurs and MSME sector, among others, and pitched for making the local ‘global’ and augment the prestige of Indian products further.
About Mann ki Baat:
- Mann Ki Baat meaning Inner Thoughts in English is an Indian radio programme hosted by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in which he addresses the people of the nation on All India Radio, DD National and DD News.
- The programme is India's "first visually enriched radio program".
- The first show was aired on 3 October 2014.
- The 83rd episode has been aired on 28th November 2021.
- The main purpose of the program is to "establish a dialogue with the citizens on issues of day-to-day governance".
PVR & INOX Leisure Merger: PVR & INOX Leisure recently announced merger of their two companies.
The announcement comes at a time when the film exhibition industry has been impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic and significant pressures on the theatrical business from the accelerated growth of digital OTT platforms.
Key Details:
- After the formalities of the merger, the company will be known as PVR Inox Limited.
- As per the agreement, Inox will have a 16.66% stake in the new firm and PVR will have a 10.62% stake.
- The Managing Director of PVR Inox Limited will be Ajay Bijli while Sanjeev Kumar will be executive director and Pavan Kumar Jain will be non-executive chairman of the consolidated board.
- The amalgamation is subject to approval by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), stock exchanges, and other regulatory approvals as required.
- PVR currently operates 871 screens across 181 properties in 73 cities, while Inox operates 675 screens across 160 properties in 72 cities.
- The combined entity aims to deliver an unparalleled consumer experience with a network of 1,546 screens across 341 properties in 109 cities.
- The merger will provide consolidation for the long-term sustainability of the business and also create value for stakeholders.
- It will also help in better administration, cost optimization, pooling of resources and creating better synergies.
About PVR Cinemas:
- PVR Cinemas was founded in June 1997.
- It is headquartered in Gurugram, Haryana.
- The founder & CEO of PVR Cinemas is Ajay Bijli.
L&T Infotech and Mindtree Merger: Larsen & Toubro (L&T) recently announced the merger of its two independently listed IT services companies - Larsen & Toubro Infotech (LTI) and Mindtree.
Key Points:
- This merger is in line with L&T's strategy of becoming more service-oriented.
- The combined entity will be known as “LTIMindtree”.
- LTIMindtree will be led by Mindtree CEO Debashis Chatterjee.
- Under the proposed merger, Mindtree and LTI would combine their strengths to form an efficient and scaled-up IT services provider worth more than USD 3.5 billion.
- Upon the merger coming into effect, Larsen & Toubro Infotech (LTI) shares will be issued to all Mindtree shareholders at a ratio of 73 LTI shares for every 100 Mindtree shares.
Benefits of the merger:
- Customers, investors, shareholders, and employees would benefit from this merger since the operations of Larsen & Toubro Infotech (LTI) and Mindtree are extremely complementary.
- This integration will help to build the combined strengths of both these organizations to unlock synergies through scale, cross-vertical expertise, and talent pool.
- The combined entity will also enable it to tap into broader market prospects, reduce costs, and lower risk.
- The merged business will overtake Tech Mahindra to become the fifth-largest IT services provider by market capitalization.
About Larsen & Tourbo:
- Larsen & Toubro Ltd, commonly known as L&T, is an Indian multinational conglomerate company, with business interests in engineering, construction, manufacturing, technology and financial services.
- The company is counted among world's top five construction companies.
- It was founded on 7 February 1938.
- It is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra.
- The current CEO L&T is Sanjay Jalona.
Centre of Excellence for Khadi (CoEK): The Centre of Excellence for Khadi (CoEK) was recently inaugurated by the Union Minister for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) Shri Narayan Rane.
Key Points:
- Khadi and Village Industries Commission have collaborated with National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) to set up Centre of Excellence for Khadi (CoEK).
- The National Institute of Fashion Technology (NIFT) in New Delhi serves as the hub of the Centre of Excellence for Khadi (CoEK), and its spokes are in Gandhinagar, Shillong, Kolkata, and Bengaluru.
Background:
- A memorandum of understanding (MoU) for setting up of CoEK, was signed between KVIC and NIFT in 2021.
- The project will be implemented over a period of 3 years.
Function of CoEK:
- The CoEK will work towards introducing the latest designs and adopting processes of international standards to create new fabrics and clothing as per the needs of the domestic and global buyers.
- The CoEK will also help in the branding and publicity, visual merchandising and packaging for new Khadi products.
- It will also contribute in increasing the global reach of Khadi by organizing Khadi Fashion shows and exhibitions in India and abroad.
Cotton Council of India (CCI): The Union Government recently announced the formation of the Cotton Council of India (CCI).
- The announcement came during a meeting with stakeholders from the cotton value chain, held under the Chairmanship of Union Minister of Textiles, Commerce & Industry and Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution Piyush Goyal.
Key Points:
- Shri Piyush Goyal announced that the CCI will be formed under the Chairmanship of renowned veteran cotton man Suresh Bhai Kotak.
- The Council will have representation from Textiles, Agriculture, Commerce, and Finance Ministries along with Cotton Corporation of India and Cotton Research Institute.
- The first meeting of the proposed council has been scheduled for 28th of May 2022.
- The council will discuss, deliberate, and prepare a robust action plan for bringing out a tangible improvement in this field.
About the meeting:
- In this meeting, a cross-section of views and suggestions were deliberated for softening cotton and yarn prices on an urgent basis to address unprecedented price rise witnessed in the current season.
- It was pointed out that cotton productivity is the biggest challenge in the country, resulting in less cotton production despite the largest area under cotton cultivation.
- Mr Goyal called upon spinning and trading community to ensure a hassle-free supply of cotton and yarn first to the domestic industry.
- The government is committed to protecting the interests of cotton farmers, spinners, and weavers, the Minister assured to actively consider the demand of the spinning sector for exemption from import duty on those import contracts in which bills of loading are issued up to September 30, 2022, to overcome the current cotton shortage and logistic issues.
About Cotton Industry in India:
- The textile industry plays a major role in the development of the Indian Economy.
- India is the largest producer of cotton globally.
- The Indian textiles industry contributes around 5% to country’s gross domestic product (GDP), 14% to industrial production and 11% to total export earnings.
- It is also the second-largest employer in the country after agriculture, providing employment to over 51 million people directly and 68 million people indirectly, including unskilled women.
- Cotton yarn and fabrics export account for about 23% of India’s total textiles and apparel export.
- India’s total production of cotton in the year 2021-22 was 34.1 million bales (bales of 170 kg each).
Cotton Production Distribution across India:
- India is the largest producer of cotton in the world where all the four known cultivated varieties of cotton are grown. More than 60% of cotton is grown in rainfed areas while less than 30% is grown in irrigated land areas.
- A major producer of cotton in India is Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana.
- India freely exports cotton to the rest of the world contributing 51% of the total exports.
- Cotton is exported to various countries including the USA, China, Vietnam, Indonesia, Taiwan, and Thailand.
- Bangladesh is also one of the major importers of cotton from India.
Defence
2nd squadron of P-8I aircraft-Condors: The Indian Navy commissioned its second P-8I aircraft squadron Indian Naval Air Squadron (INAS) 316 at INS Hansa, Goa.
Key Details:
- INAS 316 has been christened ‘Condors’ after one of the largest flying land birds with a massive wingspan.
- Condors are known for excellent sensory capabilities, powerful and sharp talons and large massive wings symbolizing the capabilities of the aircraft and envisaged roles of the squadron.
- INAS 316 will operate four P-8I aircraft procured as part of the optional clause in 2016 in a deal worth over $1 bn, the deliveries of which were completed recently by Boeing.
- The new air squadron will be commanded by Cdr Amit Mohapatra who is an accomplished Boeing P-18 pilot.
- The INAS 316 will operate the second batch of four additional P-8I aircraft, adding teeth to the armor of the Indian Navy, to 'deter, detect and destroy' any threat to the nation in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- The Defence Ministry has already approved a proposal for procurement of six more P-8Is but that is now under review as part of an overall review of all imports.
Significance:
- This ‘Game Changer’ aircraft is a potent platform for maritime surveillance and strike, electronic warfare missions, search and rescue, providing targeting data to weapon platforms, time-critical surveillance information to the Indian Army and the Air Force.
Missions undertaken by P8I aircraft:
- The P-8I aircrafts have been deployed for extensive search and rescue operations in the aftermath of Cyclone ‘Tauktae’.
- They have rendered Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) assistance post-cyclone ‘Hudhud’.
- They were also deployed for support to friendly foreign countries during the COVID-19 pandemic as part of the government’s ‘Vaccine Maitri’ initiative and participated with distinction in numerous multinational exercises, the Navy Chief asserted.
- The aircraft was also used for surveillance over the land. It has been in operation in Ladakh during the stand-off with China and also on the Indo-Pak border.
About Boeing P-81:
- The Boeing P-81 is the most sophisticated multi-role Long Range Maritime Reconnaissance Anti-Submarine Warfare (LRMR ASW) aircraft.
- It is powered by twin jet engines.
- It can be equipped with air-to-ship missiles and torpedoes.
- It is also the platform of choice for detecting and neutralizing enemy ships and submarines in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR).
- Since December 30, 2021, these aircraft have been operating from Hansa, and the squadron is integrated with full-spectrum surface and subsurface naval operations.
- The P-8I is an integral part of the Since its induction in 2013, Indian Navy's fleet and has surpassed 35,000 flight hours.
- The aircraft are a part of the 312A Naval Air Squadron based at Arakkonam in Tamil Nadu.
Note:
- The P-8 aircraft's first international customer was the Indian Navy.
- The aircraft is also operated by the US Navy, the Royal Australian Air Force, the United Kingdom's Royal Air Force, and the Royal Norwegian Air Force.
Other long-range surveillance aircraft squadrons with the Indian Navy:
- The Indian Navy also operates an IL-38 Squadron, INAS 315 called ‘The Winged Stallions’.
- This squadron is based in Goa.
- It was raised in 1977 with the IL-38 aircraft which received a mid-life upgrade in 2009.
Varuna: The 20th edition of the bilateral naval exercise that is named ‘Varuna’ was conducted by India and France in the Arabian Sea.
Key Highlights:
- Various units of the two navies which include submarines, ships, fighter aircraft, maritime patrol aircraft, and helicopters participated in this exercise.
- These exercises continue to allow both navies to learn from one another's best practices.
About VARUNA:
- The two Navies have been conducting bilateral naval exercises since 1993.
- The exercise was christened 'VARUNA' in 2001.
- It has become an important part of the bilateral strategic relationship between India and France.
- This exercise is conducted so that the participating units can polish and enhance their their maritime operating skills.
- The participating units also look to enhance their inter-operability so that they can undertake various maritime security operations.
- The units also demonstrate their commitment to the region's security, peace, and stability as an integrated force.
Objective:
- The scope of this exercise has grown over the years.
- These exercises provide the navies of India and France with various opportunities to the best possible practices from each other.
- This exercise plays the role of the significant driver for interactions at the operational level between the navies of both nations.
- Also, this exercise has highlighted the shared commitment of both countries to the safety, security, and freedom of the global maritime sector.
Fleet Card- Fuel on the Move: The Indian Air Force (IAF), along with Indian Oil Corporation Ltd. (IOCL), recently introduced a “Fleet Card- Fuel on the Move” for its varied fleet of vehicles.
Key Highlights:
- This innovative initiative taken by the IAF provides a paradigm shift to the logistics management of fuel.
- Fleet Card’, the energy security for IAF vehicles on move, was launched by Air Chief Marshal VR Chaudhari, Chief of Air Staff at Headquarters Western Air Command, Subroto Park in the presence of Air Marshal S Prabhakaran, Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief Western Air Command and Mr. SM Vaidya Chairman IOCL on 28 March 22.
- The headquarters was earmarked as lead agency in the implementation and execution of the “Fuel on Move” concept.
About Fleet Card:
- Availability of Fleet Card will permit the convoy to refuel at any IOCL fuel station thus increasing the pace of movement and reducing the lead time for readiness at operational locations across India.
- Personnel and other resources which are now involved in fuel management within the IAF can now be re-allocated towards other operational tasks.
- This in line with the Shekatkar Committee recommendations of improving the Teeth to Tail ratio with the armed forces.
CAPF Punarvaas: The Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) recently launched the ‘CAPF Punarvaas’ through the Welfare and Rehabilitation Board (WARB).
Key Points:
- CAPF Punarvaa has been launched to facilitate retired Central Armed Police Force (CAPF) and Assam Rifle personnel to secure employment with private security agencies.
- The portal will help retired personnel seeking re-employment to find an appropriate match by uploading their personal details on the WARB website along with their area of expertise and preferred employment location.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs also runs a portal under Private Security Agencies Regulation Act (PSARA) for the registration of Private Security Agencies (PSAs).
- Both websites have now been interlinked whereby the database of retired CAPFs personnel who have applied on ‘CAPF Punarvaas’ can be accessed by PSAs through PSARA website resulting in a single platform for both job seekers and job providers.
- This new initiative of MHA provides access to the data base under ‘CAPFs Punarvaas’ to PSAs digitally.
About CAPF:
- CAPF is an acronym for the Central Armed Police Forces.
- CAPF refers to uniform nomenclature of security forces in India under the authority of Ministry of Home Affairs.
- However, its operational control rests with the Ministry of Defence.
- Their role is to defend the national interest mainly against the internal threats.
They are the -
- Border Security Force (BSF),
- Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF),
- Central Industrial Security Force (CISF),
- Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP)
- National Security Guard (NSG) and
- Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB).
- Of the CAPFs, the AR, BSF, ITBP and SSB are Border Guarding Forces.
- The NSG is a commando trained force Organisation in India and is used for special operations.
- The CAPF forces battle terrorists, insurgents and naxalites and even play a role in the smooth conduct of elections.
- CAPF which are tasked with doing the job of both the army and the police in guarding the borders as well as battling terrorists and insurgents are 365 days swinging Machine.
These personnel also serve in various important organisations such as
- Research and Analysis Wing (RAW),
- Special Protection Group (SPG),
- National Investigation Agency (NIA),
- Intelligence Bureau (IB), Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI),
- National Disaster Response Force (NDRF),
- Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB)
- State Armed Police Force (Jharkhand Jaguars, Bihar Military Police etc.) on deputation
They have attachment/training in various levels/formations/courses along with the Indian Army.
- The CAPF’s are headed by DGP rank officers.
Welfare and Rehabilitation Board (WARB):
- The Welfare and Rehabilitation Board (WARB) was established by the Ministry of Home Affairs for welfare and rehabilitation of the Central Police Force personnel (CPF).
Shaurya Chakras: President of India, Ram Nath Kovind recently conferred 13 Shaurya Chakras which included six posthumous to the personnel of the Indian Armed forces for their conspicuous courage displayed during operations.
Key Highlights:
- The President also conferred 14 PVSM, four Uttam Yudh Seva Medals (UYSM) and 24 Ati Vishisht Seva Medals (AVSM) for distinguished service of an exceptional order.
- These awards of Gallantry and other Defence decorations conferred were approved by the President in January on the eve of the 73rd Republic Day celebrations this January.
- Army Chief General Manoj Pande was conferred with the Param Vishisht Seva Medal (PVSM) for his distinguished service of exceptional order at a defence investiture ceremony at Rashtrapati Bhawan.
- Gen Manoj Pande assumed the charge of the 29th Chief of the Army Staff on April 30.
- Before that, he was serving as the Vice Chief of Army Staff for three months and was the General Officer Commander in Chief, Eastern Command of the Army before that.
About Gallantary Awards:
- Gallantry Awards have been instituted by the Government of India (GoI) to honour the act of courage and self-sacrifice of the officers/personnel of the Armed Forces and in addition to other lawfully constituted forces and civilians.
- These gallantry awards are announced twice in a year that is first on the occasion of the Republic Day and on the occasion of the Independence Day.
The following are the gallantry awards:
War Time Gallantry Awards:
- Param Vir Chakra (PVC)
- Maha Vir Chakra (MVC)
- Vir Chakra
Peace Time Gallantry Awards:
- Ashok Chakra
- Kirti Chakra
- Shaurya Chakra
Shaurya Chakra: History
- Shaurya Chakra is an Indian military decoration awarded for gallantry, otherwise than in the face of the enemy.
- It may be awarded to civilians, also as military personnel, sometimes posthumously.
- On 4 January, 1952, it was established as the Ashoka Chakra, Class III by the Government of India, with effect from 15 August, 1947.
- On 27 January, 1967, the decoration was renamed as 'Shaurya Chakra' awarded for gallantry, otherwise than in the face of the enemy.
Environment
Mass Coral Bleaching: The management authority of the world’s largest coral reef system, Australia’s Great Barrier Reef, confirmed on March 25 that the reef is experiencing a mass coral bleaching event.
- This is the sixth time that the coral reef system is being hit by a widespread and damaging bleaching event and the fourth time in six years that such an event has occurred.
About The Great Barrier Reef:
- The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system.
- The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, Australia and can be seen from outer space.
- It is the world's biggest single structure made by living organisms.
- The structure is composed of and built by billions of tiny organisms, known as coral polyps.
- It supports a wide diversity of life.
- It hosts 400 different types of coral, gives shelter to 1,500 species of fish and 4,000 types of mollusc.
- It was selected as a World Heritage Site in 1981.
- It was also labeled as one of the seven natural wonders of the world by CNN.
- It was named as a state icon of Queensland by the Queensland National Trust.
About Coral reef:
- A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals.
- Reefs are formed by colonies of coral polyps that are held together by calcium carbonate.
- Most of the reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
- Coral belongs to the class Anthozoa in the animal phylum Cnidaria which includes sea anemones and jellyfish.
- Corals secrete hard carbonate exoskeletons that support and protect the coral.
- Corals share a symbiotic relationship with single-celled algae called zooxanthellae.
- The algae provide the coral with food and nutrients, which they make through photosynthesis, using the sun’s light.
- In turn, the corals give the algae a home and key nutrients.
- The zooxanthellae also give corals their bright colour
- Most reefs grow best in warm, shallow, clear, sunny and agitated water.
- Corals are also called as rainforests of the sea.
- Shallow coral reefs form some of Earth's most diverse ecosystems.
- Corals comprises of less than 0.1% of world’s ocean area.
- They are commonly found at shallow depths in tropical waters.
- In deep water and cold water, coral reefs exist on smaller scales.
Note: First ever coral reefs were appeared some 485 million years ago.
Types of Coral:
Corals are of two types i.e., hard coral and soft coral:
I.Hard corals, also called hermatypic or ‘reef building’ corals extract calcium carbonate (also found in limestone) from the seawater to build hard, white coral exoskeletons.
II.Soft coral polyps, however, borrow their appearance from plants; attach themselves to such skeletons and older skeletons built by their ancestors. Soft corals also add their own skeletons to the hard structure over the years and these growing multiplying structures gradually form coral reefs. They are the largest living structures on the planet.
About Coral Bleaching:
- Coral Bleaching occurs when corals experience stress in their environment due to changes in temperature, extremely low tides, pollution, or too much sunlight, dumping of dredging sludge and cyclic population.
- Under stressed conditions, the zooxanthellae or food-producing algae living inside coral polyps start producing reactive oxygen species, which are not beneficial to the corals.
- So, the corals expel the colour-giving zooxanthellae from their polyps, which expose their pale white exoskeleton, giving the corals a bleached appearance.
- Bleached corals continue to live but begin to starve after bleaching.
Why are Coral reefs under threat?
They are under threat from excess nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus), rising temperatures, oceanic acidification, overfishing (e.g., from blast fishing, cyanide fishing, spearfishing on scuba), sunscreen use, and harmful land-use practices, including runoff and seeps (e.g., from injection wells and cesspools).
International Day of Plant Health: The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) designated 12 May the International Day of Plant Health (IDPH) to raise global awareness on how protecting plant health can help end hunger, reduce poverty, protect biodiversity and the environment, and boost economic development.
Key Points:
- The Day is an important legacy of the International Year of Plant Health 2020, which took place between 2020 and 2021.
- The observance was unanimously adopted by the UN General Assembly in a resolution (A/RES/76/256) co-signed by Bolivia, Finland, Pakistan, the Philippines, Tanzania and Zambia in March 2022.
Significance:
- The resolution states that healthy plants are essential for all life on Earth, as well as ecosystem services, food security, and nutrition, and that plant health is critical for agriculture's long-term sustainability in order to feed a growing global population by 2050.
Objectives of IDPH:
- To raise awareness about the need of maintaining plant health in order to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 2 (Zero Hunger).
- To reduce the risk of plant pests spreading through international travel and trade.
- To protect plant health by strengthening early warning systems.
- To ensure long-term pesticide management and plant health.
- To encourage investment in plant health research and development.
Significance of Protection Plant Health:
- Life on earth depends on plants as well as plant health as plants contribute to 80% of food needs and 98% of oxygen.
- But, the plants are under threat as about 40% of food crops are lost due to plant pests and diseases every year.
- This is affecting both food security and agriculture, which is the primary source of income for rural populations.
- Climate change and destructive human activities are also altering the plant ecosystems contributing to the loss of biodiversity while creating new niches for pests to thrive.
- Pests and diseases are increasing as a result of increased international travel and trade, which has tripled in volume in the last decade.
Therefore, there is a need to take corrective action by all to protect plants both for people and the planet.
Amrit Sarovar: Union Minister for Minority Affairs Mukhtar Abbas Naqvi and Swatantra Dev Singh, Uttar Pradesh Jal Shakti Minister inaugurated India’s first Amrit Sarovar in Rampur, Uttar Pradesh on May 13, 2022.
Overview:
- Amrit Sarovar at Rampur’s Gram Panchayat Patwai has been constructed under the inspiration of Prime Minister Narendra Modi and the guidance of the Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh Yogi Adityanath.
- The participation and cooperation of the common people, villagers and District Administration also played an important role in the opening of India’s first Amrit Sarovar in Uttar Pradesh.
- In just a few weeks, a pond that had previously been clogged with garbage in Rampur was cleaned and revived.
Amrit Sarovar Initiative:
- PM Modi launched a new initiative named Mission Amrit Sarovar on 24th April 2022 with a view to conserve water for the future.
- As part of the Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav, 75 water bodies will be developed and regenerated as part of the Amrit Sarovar initiative.
- PM Modi had given a call for every district to have 75 ponds (Amrit Sarovar) during the 75th anniversary of India's independence, described as "Azadi Ka Amrit Kaal", to give a boost to water conservation and environment.
- He had emphasized water conservation in the country saying it is critical to the country’s prosperity and also namechecked Patwai in his 88th monthly radio address, ‘Mann ki Baat’.
Significance:
- The pond will not only help in protecting environment and conserving water but will also be an attraction for people of the nearby areas.
- Besides food court, fountains and lighting and other amusements, boating has also been made available there.
Ramgarh Vishdhari: Ramgarh Vishdhari Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan has recently been notified as Rajasthan’s 4th and the 52nd tiger reserve of India.
The other 3 tiger reserves in Rajasthan are -
- Ranthambore Tiger Reserve (RTR) in Sawai Madhopur
- Sariska Tiger Reserve (STR) in Alwar
- Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve (MHTR) in Kota.
Key Points:
- This was announced by the Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, Bhupender Yadav.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) had given in-principle approval to make Ramgarh Vishdhari Wildlife Sanctuary and adjoining areas as tiger reserves on July 5 last year.
- It will help to conserve biodiversity and bring ecotourism and development to the area.
Status of Tigers in India:
- According to the “Status of Tigers in India” report released in 2019, there are 2,967 tigers in 20 states across the country.
About Ramgarh Vishdhari Tiger Reserve:
- Ramgarh Vishadhri reserve is located mostly in the Bundi district and in part in Bhilwara and Kota districts.
- The Ramgarh Vishdhari Tiger Reserve will span across an area of 1,501.89 sq km.
- The Ramgarh Vishdhari Sanctuary includes the tiger habitat between Ranthambore Tiger Reserve in the northeast and Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve on the southern side.
- The reserve has been called 'critical' by wildlife experts and conservationists for the movement of Tigers between Ranthambore and Mukundra reserves.
- Apart from Tigers, the reserve is also home to other animals including leopard, Indian wolf, Nilgai, Striped hyena, Sloth bear, Golden jackal, Chinkara and fox.
Indian Policy
Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2022: The Lok Sabha recently passed a Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2022.
Key Points:
- The bill seeks to amend the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950 to include the Darlong community as a sub-tribe of the Kuki tribe on the list of Scheduled Tribes of Tripura.
- The Bill proposes “Darlong" community as a sub-tribe of "Kuki" in the list of Scheduled Tribes.
- Tribal Affairs Minister Arjun Munda, who introduced the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2022, in the Lok Sabha said that the Union government was working towards betterment of living conditions of the tribal communities.
About Darlongs:
- Darlongs is a small community of around 11,000 people living in the State of Tripura.
- Despite being a small community, Darlongs have made their mark in different fields including education, public service, music, art and culture.
- The prestigious Padma Shri was also awarded to a tribal musicologist and Rosem (a tribal instrument) maestro Thanga Darlong a few years ago for his contributions to culture.
- Darlongs, despite being Scheduled Tribes, were never given ST certificates.
- They were regarded a generic tribe under the Kuki community, and were handed their tribal certificates as members of ‘Kuki’ community.
- This identity crisis among them culminated in the demand for a separate statutory identity of their own in 1995.
- In 2016, a bill was introduced in Parliament to add Darlongs to the list of STs as a sub-tribe of the Kuki community.
Tribal Population in Tripura:
- Tripura houses 20 tribal communities including Tripuri,Uchai, Riang, Jamatia, Noatia, Chakma, Mog, Lushai, Kuki, Halam, Munda, Kaur, Orang, Santal, Bhil, Bhutia, Chaimal, Garo, Khasia, and Lepcha.
- The Halam community has several small tribal clans within it. Many of these are linguistically endangered groups like Karbongs, Bongcher, etc.
- They live in the Tripura Tribal Areas Autonomous District Council (TTAADC) formed on 18th January 1982.
- The tribal council encompasses about 70% of Tripura's total land area and is home to roughly 30% of the state's people.
- A large majority of them still depend on slash and burn cultivation and traditional livelihood for sustenance.
Status of Scheduled Tribes in India:
- As per Census-1931, Schedule tribes are termed as "backward tribes” living in the "Excluded" and "Partially Excluded" areas.
- The Government of India (GoI) Act of 1935 called for the first time for representatives of "backward tribes" in provincial assemblies.
- The criteria for recognition of Scheduled Tribes are not defined in the Constitution, hence the definition from the 1931 Census was utilized in the initial years after independence.
- However, Article 366(25) of the Constitution only provides process to define Scheduled Tribes: “Scheduled Tribes means such tribes or tribal communities or parts of or groups within such tribes or tribal communities as are deemed under Article 342 to be Scheduled Tribes for the purposes of this Constitution.”
- As per Article 342 (1), the President may after consultation with the Governor specify the tribal communities as Scheduled Tribes.
- As per Article 342 (2), Parliament may by law include in or exclude any tribal community from the list of Scheduled Tribes specified in a notification issued under clause (1).
- The Fifth Schedule lays out provision for Administration and Control of Scheduled Areas and Scheduled Tribes in states other than Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
- The Sixth Schedule of the Constitution deals with the administration of the tribal areas in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
What are the recent Steps taken by the Government of India for the betterment of the tribal population?
The steps taken by the Government of India for the betterment of the tribal population are as follows:
National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST):
- The National Commission for Scheduled Tribes (NCST) was established by inserting a new Article 338A in the Constitution through the Constitution (89th Amendment) Act, 2003.
Vanbandhu Kalyan Yojana (VKY):
- Vanbandhu Kalyan Yojana (VKY) was launched with an aim to create enabling environment for need based and outcome oriented holistic development of the tribal people.
Adi Adarsh Gram Yojana:
- Adi Adarsh Gram Yojana was implemented for integrated development in tribal villages spanning from health, education and drinking water.
STC funds:
- There have been gradual and a steady increase in Scheduled Tribe component (STC) funds since the last few years.
- A scheme of nearly Rs 7,000 crore to provide broadband and 4G connectivity in tribal hamlets under the STC funds was recently introduced by the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
Eklavya Model Schools:
- Eklavya Model Schools was set up to provide quality education to ST children in remote areas so that they may pursue higher and professional education and get employment in various sectors.
Scholarship Scheme:
- Around 30 lakh ST students are covered for financial help through DBT mode under the scholarship schemes.
Tribal Healthcare:
- The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) was recently allocated funds to conduct research in the field of tribal healthcare.
Livelihood opportunities:
Several schemes have been introduced to support marketing and development of activities for livelihood such as -
- The Van Dhan Scheme
- Institutional Support For Development And Marketing Of Tribal Products/Produce
- Marketing Of Minor Forest Produce (MFP) Through Minimum Support Price (MSP)
Changes in AFSPA: The Central Government recently announced its decision to reduce disturbed areas under Armed Forces Special Powers Act (AFSPA) in the states of Nagaland, Assam and Manipur after decades.
Key Highlights:
- This informed was given by Union Home Minister Amit Shah on March 31, 2022.
- The decision will result in considerable reduction in areas under AFSPA in Assam, Nagaland and Manipur from April 1,2022.
- However, AFSPA has not been completely removed.
AFSPA in India:
- The Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act was initially promulgated by the British to suppress the Quit India movement in 1942.
- The first Prime Minister of India Pt. Jawaharlal Nehru decided to retain the Act and brought in an ordinance and notified it as the Armed Forces (Special Powers) Act, 1958.
- The AFSPA Act was initially applicable to the Naga Hills, which was then part of Assam.
- Then it expanded to all seven states of the North-East - Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Tripura, Arunachal Pradesh and Mizoram and even Chandigarh, Punjab and Jammu and Kashmir (J&K).
- It was enacted with the aim of bringing the situation under control in all the conflict-hit areas of the country.
Special Powers to Armed Forces under AFSPA Act:
- The AFSPA act empowers security forces to use any means that is deemed necessary to maintain public order in the states where AFSPA is applicable.
- Section 4 of AFSPA Act 1958 accords special powers to the armed forces, authorising the security forces to arrest anyone without a warrant, open fire, enter and search any property without any warrant.
- Section 6 of AFSPA Act grants immunity to the security forces from prosecution or any other legal proceedings.
What are the Disturbed Areas?
- A disturbed area is an area that is declared by notification under Section 3 of the AFSPA.
- An area can be disturbed due to differences or disputes between members of different religious, racial, language or regional groups or castes or communities.
- As per Section 3, it can be invoked in places where “the use of armed forces in aid of the civil power is necessary”.
Who can declare/notify such areas?
- The Central Government or the Governor of the State or administrator of the Union Territory (UT) has the authority to declare the whole or part of the State or Union Territory as a disturbed area.
- A suitable notification would have to be made in the Official Gazette.
- Once declared ‘disturbed’, the region has to maintain status quo for a minimum of three months, according to The Disturbed Areas (Special Courts) Act, 1976.
Changes in AFSPA:
In Assam:
- The disturbed area notification has been in force in the whole of Assam since 1990.
- Now, AFSPA will be removed from 23 districts of Assa while in one district it will be applied partially with effect from April 1st.
In Manipur:
- The AFSPA has been in force in the whole of Manipur except the Imphal Municipality area since 2004.
- Now, the AFSPA jurisdiction will be removed from 15 police stations in 6 districts with effect from April 1st.
In Nagaland:
- AFSPA has been in force in the whole of Nagaland since 1995.
- Now, the jurisdiction of AFSPA will be removed in phased manner From 15 police stations in 7 districts of Nagaland.
In Arunachal Pradesh:
- In Arunachal Pradesh, AFSPA will be applicable in only 3 districts along with the jurisdiction of two police stations in another district.
The demand to repeal AFSPA:
The demand gained momentum in Nagaland after 6 coal mine laborers were killed in an ambush by security personnel while they were returning to their village of Oting.
- In Nagaland in 2021, security officers opened fire on six civilians travelling in a truck, mistaking them for militants from the National Socialist Council of Nagaland (NSCN).
- The citizens, after being anguished by the loss began to protest and widespread violence ensued.
- The Centre later formed a five-member committee to investigate the state of Nagaland's withdrawal of the AFSPA law.
- Home Minister Amit Shah also held key meetings with the respective Chief Ministers of the states.
Extension of PM-GKAY: The Union Cabinet, on March 26, 2022, extended the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PM-GKAY) by another six months till September 2022 (Phase VI).
Key Highlights:
- This decision was taken Keeping in view the continuous need to support the food-security of poor and and vulnerable sections of society.
- The Phase-V of PM-GKAY scheme was to end in March 2022.
About PM-GKAY:
- The PM-GKAY has been under implementation since April 2020, as the largest food security program in the world.
- This scheme is a part of Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Package (PMGKP) and was originally introduced in the first lockdown during the initial onset of the COVID pandemic providing free food grains to the affected population.
- Government on this day in March 2020 had announced the distribution of additional free-of-cost foodgrains to about 80 Crore National Food Security Act (NFSA) beneficiaries at the scale of 5 Kg per person per month under the scheme.
- Its nodal Ministry is the Ministry of Finance.
- Phase-I and Phase-II of this scheme was operational from April to June, 2020 and July to November, 2020 respectively. Phase-III of the scheme was operational from May to June, 2021.
- Phase-IV of the scheme is currently operational for July-November, 2021 months.
- Phase-V of this scheme was again extended from December 2021 to March 2022.
Note: Under the Phases I to V, the food ministry had allocated a total of about 759 lakh tonnes of foodgrains to the States/UTs, which is equivalent to about Rs 2.6 lakh crore in food subsidy.
PM-GKAY Salient Features:
- This policy would cover 80 crore people, i.e., nearly two-thirds of the Indian population.
- Under the Insurance Scheme, a cover of Rs 50 lakh will be provided for each health professional combating COVID-19.
- For the next three months, 80 crore underprivileged individuals would receive 5 kilogramme wheat or rice and 1 kg of selected legumes for free.
- 20 crore women Jan Dhan account holders to get Rs 500 per month for next three months.
- Increase in MNREGA wage to Rs 202 a day from Rs 182 to benefit 13.62 crore families.
- Government to front-load Rs 2,000 paid to farmers in first week of April under existing PM Kisan Yojana to benefit 8.7 crore farmers.
Expenditure:
- Government of India (GoI) will bear all expenditure of over Rs. 26,000 crore on account of food subsidy.
- Central assistance will be provided to states/UTs on account of intra-state transportation etc.
Abolishment of NOCC Charges by DoT: The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) has recently abolished the network operation and control center (NOCC) charges.
Key Points:
- The order shall be effective from April 1, 2022.
- DoT has removed The NOCC charges for the use of space segments for all services like VSAT, GMPCS (satellite phone service), NLD (national long distance) and other telecom licensees having unified licence or standalone license.
- The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) levied Rs 21 lakh per transponder every year for 36 MHz of spectrum on a pro-rata basis.
- Apart from this, the government also charged Rs 6,000 for every trial of antenna that is used for receiving and transmitting signals.
Why the NOCC charge is abolished?
- DoT has abolished the NOCC charge to provide a fillip to upcoming satellite broadband companies and also to ensure more competition and growth in the Indian satellite broadband market.
Benefit:
- As satellite communication companies no longer have to pay the NOCC for transponder bandwidth, Indians can expect lower broadband-from-space prices.
What is the NOCC charge?
- The Network operation and control center (NOCC) charge is a charge levied on the use of space segments by telecom service providers for satellite telephony, broadband, etc.
About NOCC:
- The NOCC levy regime was introduced in 2003.
- The NOCC was created under the DoT to control the transmissions from the ground segment (satellite earth stations) along with the master control facility under the Department of Space to manage the operation of satellites in orbit.
In India, which companies are aiming to provide satellite broadband services?
- Currently, Sunil Bharti Mittal’s OneWeb and Elon Musk’s Starlink are the providers planning to launch satellite broadband services in India using low-earth orbit satellites.
- Reliance Jio, in February had announced that it has formed a joint-venture with Luxembourgish satellite-based content connectivity solutions provider SES, and plans to deliver satellite broadband services across India.
National Youth Policy: The Central Government has recently prepared a new National Youth Policy (NYP).
Key Highlights:
- The NYP has been prepared after reviewing the existing National Youth Policy, 2014.
- The Department of Youth Affairs has sought suggestions, comments and views regarding the draft of the NYP from all stakeholders across the nation.
- The suggestions, as well as the comments regarding the new draft policy, must be sent within 45 days (by 13th of June 2022).
Key Points of NYP:
- The draft policy envisages a ten-year vision for youth development that the country seeks to achieve by 2030.
- It is aligned with the Sustainable Development Goals and serves to unlock the potential of the youth.
- It seeks to catalyze widespread action on youth development across the five following priority areas:-
1.Education
2.Employment & entrepreneurship
3.Youth leadership & development
4.Social justice
5.Health, fitness & sports
- The priority areas have been identified under the principle of social inclusion.
- This will help in achieving equitable progress by including the country’s most marginalized sections.
Who is responsible for drafting and implementing Draft National Sports Policy?
- Department of Youth Affairs, Ministry of Sports is responsible for drafting and implantation of the Draft National Sports Policy.
About National Youth Policy-2014:
- The National Youth Policy-2014 (NYP-2014) was introduced by the Union Cabinet replacing NYP-2003.
- The holistic vision of NYP-2014 for the youth of India is “to empower the youth of the country to achieve their full potential, and through them enable India to find its rightful place in the community of nations”.
- In order to achieve this Vision, all stakeholders must work towards meeting 5 key objectives.
- This requires specific action in one or more of 11 priority areas, identified as important for youth development.
The priority areas are -
1.Education,
2.Skill development and employment,
3.Entrepreneurship,
4.Health and healthy lifestyle,
5.Sports,
6.Promotion of social values,
7.Community engagement,
8.Participation in politics and governance,
9.Youth engagement,
10.Inclusion and
11.Social justice.
- It would result in the development of an educated and healthy young population, who are not only economically productive, but are also socially responsible citizens contributing to the task of nation-building.
- It will cover the entire country catering the needs of all youth in the age-group of 15-29 years, which constitutes 27.5 per cent of the population according to Census-2011, that is about 33 crore persons.
- It will replace NYP-2003, to take care of developments since 2003 and future policy imperatives.
Draft National Data Governance Framework Policy: The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) recently released the revised Draft National Data Governance Framework Policy (NDGFP) to mobilize non-personal data of citizens for use by both public and private entities to improve services.
Highlights:
- The Ministry has invited inputs on it before June 11th, 2022.
- NDGFP replaces Draft India Data Accessibility and Use Policy, 2022.
- In February 2022, ‘Draft India Data Accessibility and Use Policy, 2022’ was opened for public consultation but it was strongly criticized by many.
- It proposed allowing the licensing and sale of public data by the government to the private sector.
Key Points:
- This draft policy proposes the launch of a non-personal data based India datasets programme and addresses the methods and rules to ensure that non-personal and anonymised data from both government and private entities are safely accessible by the research and innovation ecosystem.
- The Framework will be of interest to artificial intelligence (AI) start-ups, AI research entities, and government departments.
- It would also speed up the transition of digital government and digitization of government with common standards, rules and guidelines for data storage and management across all departments.
- The draft proposes the setting up of an 'India Data Management Office (IDMO)', which shall be responsible for framing, managing and periodically reviewing and revising the policy.
About IDMO:
- The India Data Management Office (IDMO) will be set up under the Digital India Corporation (DIC) under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- According to the draft, the IDMO shall also be responsible for developing rules, standards, and guidelines under this policy.
- IDMO will also prescribe data anonymization standards for both government and private entities that deal with data.
- This is to ensure that informational privacy is well maintained.
- It is allowed to charge user fees for its maintenance/ service.
Scholarship for PM CARES Children: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently launched the Scholarship for PM CARES Children Scheme.
Key Highlights:
- He announced the benefits under the PM-CARES for Children Scheme 2022 while he was addressing the students around the country on 30 May 2022 via video conferencing.
- A passbook of PM CARES for Children, and health card under Ayushman Bharat – Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana was also handed over to the children during the programme.
- The event was held as a part of a massive public outreach campaign, which started from May 30 and will continue till June 14.
- The campaign has been started by the central government to mark the eighth anniversary of the Modi government.
About PM CARES for Children Scheme:
- PM Modi had launched the PM CARES for Children Scheme on 29 May, 2021.
- This initiative was launched with an aim to provide financial assistance to support such children who have lost both the Parents or legal Guardian or Adoptive Parents or Surviving Parent to COVID-19 pandemic during the period from 11 March 2020 to 28 February 2022.
The objective of the PM CARES scheme:
- The objective of the Scheme is to ensure comprehensive care and protection of Children in a sustained manner, and enable their well being through health insurance, empower them through education and equip them for self-sufficient existence with financial support on reaching 23 years of age.
- The portal is a single-window system which facilitates the approval process and all other assistance for children.
About Scholarship for PM CARES Children:
- Under the PM CARES for Children Scheme, in line with the Scholarship for PM CARES Children, the Department of Social Justice & Empowerment, Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment has decided to provide scholarship assistance to such Children who have lost both the Parents or legal Guardian or Adoptive Parents or Surviving Parent to COVID-19 pandemic to continue their education without any hindrance.
- Accordingly, a new Scheme was formulated for the purpose namely; SCHOLARSHIP FOR PM CARES CHILDREN as a Central Sector Scheme.
- A monthly allowance of Rs. 1,000 and an annual academic allowance of Rs. 8,000 would be provided under the Scheme Scholarship, which would cover the full cost of tuition, books, uniforms, shoes, and other educational supplies for each kid.
- The Scholarship will be disbursed through DBT to the Children from Class 1std until they pass out the 12 std Class.
Indian polity
Constitution (Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2022: The Rajya Sabha on 30 March 2022 approved The Constitution (Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes) Order (Amendment) Bill, 2022 to remove the Bhogta caste from the list of Scheduled Castes (SCs) and include additional communities in the list.
Overview:
- The Constitution (Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes) Orders (Amendment) Bill, 2022 was passed by a voice vote.
- The Bhogta caste will be included instead as a Scheduled Tribe in the State.
- The Bill also amends the schedule to the Scheduled Tribes order to include the Deshwari, Dautalbandi (Dwalbandi), Ganjhu, Patbandi, Maajhia, Raut, Khairi (Kheri), Tamaria (Tamadia) and Puran communities on the ST list.
- The main aim of the Bill is to help people get more benefits from the provisions of reservation in education and government jobs
Note: Based on requests from the states, the government keeps amending the lists originally notified in 1950.
The Scheduled Castes order specifies the castes, races and tribes deemed to be Scheduled Castes in various states and Union territories, while the Scheduled Tribes order specifies the same for tribes and tribal communities.
Delhi Municipal Corporation (Amendment) Bill, 2022: The Lok Sabha has passed the Delhi Municipal Corporation (Amendment) Bill, 2022 so that three municipal corporations of Delhi (MCD) can be merged into a single entity.
Key Highlights:
- This bill was passed by a voice vote.
- Various amendments that were moved by the Opposition members were rejected.
- This bill has been passed by a voice vote and various amendments that were moved by the Opposition members have been rejected.
- The Union Cabinet had approved the Bill for the unification of Delhi’s three Municipal corporations into one Municipal Corporation.
- A “Special officer” is to be appointed to discharge the elected wing of councilors’ functions till the new corporation’s first meeting is held.
- The Bill omits the provision for a Director of Local Bodies.
About the Bill:
- The Bill seeks to amend the Delhi Municipal Corporation Act, 1957 passed by Parliament.
- It envisages bringing about greater transparency, improved governance and more efficient delivery of civic service for the people of Delhi.
- The Act was amended in 2011 by Delhi Legislative Assembly to trifurcate the erstwhile Municipal Corporation of Delhi into:
1.South Delhi Municipal Corporation - SDMC
2.North Delhi Municipal Corporation - NDMC
3.East Delhi Municipal Corporation - EDMC
- The Bill seeks to unify the three corporations by replacing the three municipal corporations under the Act with one Corporation named the Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD).
- The Act as amended in 2011 empowered the Delhi government to decide various matters under the Act such as total number of seats of councilors, delimitation of wards etc. while this Bill instead empowers the central government to decide these matters.
- The Act provides that the number of seats in the three corporations taken together should not be more than 272 while the Bill states that the total number of seats in the new Corporation should not be more than 250.
- The Act provides for a Director of Local Bodies to assist the Delhi government and discharge certain functions while the Bill omits the provision for a Director of Local Bodies.
- The Bill provides that the central government may appoint a Special Officer to exercise powers of the Corporation until the first meeting of the Corporation is held after the commencement of the Bill.
Criminal Procedure (Identification) Bill, 2022: The Criminal Procedure (Identification) Bill, 2022 was recently introduced in the Lok Sabha.
Key Details:
- The Bill introduced would allow the police and prison authorities to collect, store and analyse physical and biological samples, including retina and iris scans.
- Resistance to or refusal to allow the taking of measurements under this Act shall be deemed to be an offence under section 186 of the Indian Penal Code.
- It also seeks to apply these provisions to persons held under any preventive detention law.
- The National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) will be the repository of physical and biological samples, signature and handwriting data that can be preserved for at least 75 years.
- The Bill seeks to repeal the Identification of Prisoners Act, 1920 whose scope was limited to recording finger impressions and footprint impressions of limited category of convicted and non-convicted persons and photographs on the order of a magistrate.
Significance of the Bill:
- The bill makes provisions for the use of modern techniques to capture and record appropriate body measurements.
- The existing law which is the Identification of Prisoners Act is dated back to 1920. It allows taking only fingerprint and footprint impressions of a limited category of convicted persons.
- The bill aims to increase the "ambit of persons" whose measurements can be taken as this will help the investigating agencies to gather sufficient legally admissible evidence and establish the crime of the accused person.
- The law establishes legal authority for taking proper body measurements of those who are required to submit such measurements, which would improve the efficiency and speed of criminal investigations while also improving the conviction rate.
Issues with the Bill:
- The opposition members have termed the Bill “unconstitutional”.
- Opposition members argued that the Bill was beyond the legislative competence of Parliament as it violated fundamental rights of citizens, including the right to privacy.
- They claimed that it violates Article 20 (3) of the Constitution as well as the Supreme Court judgment in the K.S. Puttaswamy case.
- Note: Article 20(3) says that 'No person accused of an offence shall be compelled to be a witness against himself'.
- The Bill, when implied use of force in collection of biological information, could also lead to narco analysis and brain mapping.
- It also violates human rights provisions as laid out in the United Nations charter.
Justices Sudhanshu Dhulia and JB Pardiwala: Justices Sudhanshu Dhulia and JB Pardiwala were recently sworn in as Supreme Court judges.
Key Highlights:
- The oath of office was administered to them by Chief Justice of India (CJI) NV Ramana in a swearing-in ceremony held in the auditorium of the Supreme Court’s additional building complex.
- After the appointment of the two new judges, the apex court will function at its full strength of 34.
- The Supreme Court Collegium, chaired by Chief Justice NV Ramana, had previously recommended that Justices Dhulia and Pardiwala be elevated to the position of top court judges to the Central Government.
Justice Pardiwala is in line to be appointed Chief Justice of India years from now.
- He would then have tenure of about two years and three months as the top judge of the country.
- He would be the sixth member of the Parsi community to become a Supreme Court judge.
Justice Dhulia is the second judge to be elevated from Uttarakhand High Court.
- He is from Madanpur, a remote village located in the Pauri Garhwal district of Uttarakhand.
Note: Of the 11 judges, Justice B.V. Nagarathna, is in line to be the first woman Chief Justice of India, albeit for 36 days, in 2027.
About Supreme Court of India:
- The Supreme Court of India (SCI) is the highest judicial forum and final court of appeal under the Constitution of India, the highest constitutional court, with the power of constitutional review.
- It consists of the Chief Justice of India and a maximum of 34 judges, it has extensive powers in the form of original, appellate and advisory jurisdictions.
- It is regarded as the most powerful public institution in India.
- It was established on 26 January 1950.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- The current CJI of the Supreme Court is Nuthalapati Venkata Ramana
Rajiv Kumar: Rajiv Kumar, an officer of the 1984 batch of the Indian Administrative Service of the Bihar/Jharkhand cadre has been appointed as the next Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) in the Election Commission of India (ECI).
Key Highlights:
- Kumar will take charge of the office from the 15th of May, 2022.
- He will be replacing Sushil Chandra who conducted the last five state assembly elections in 2022.
- Sushil Chandra will demit the Office of the Chief Election Commissioner on 14th of this month.
About Rajiv Kumar:
- Mr. Kumar has been a member of the three-person Election Commission of India since September 1, 2020.
- Prior to that, he served as the chairman of the Public Enterprises Selection Board.
- He retired from the civil service in February 2020 from the post of Union Finance Secretary.
Who has the power to appoint the Chief Election Commissioner (CEC and Election Commissioners (ECs)?
- The power to appoint the CEC and the ECs lies with the President of India under Article 324(2) of the Constitution.
- Article 324(2) states that “the President shall fix the number of ECs in a manner he sees fit, subject to the provisions of any law made by Parliament”.
- Thus, Article 324(2) left it open for the Parliament to legislate on the issue.
- However, in the absence of any Parliamentary law governing the appointment issue, the ECs are appointed by the government of the day, without pursuing any consultation process. There is no concept of collegium and no involvement of the opposition.
International
5th BIMSTEC Summit: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi on 30 March 2022 participated in the 5th BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) Summit.
Highlights:
- The 5th BIMSTEC Summit was hosted in virtual mode by Sri Lanka, the current chair of BIMSTEC.
- Prior to this, preparatory meetings at the Foreign Minister and Senior Official levels were held on the 28th and 29th of March.
- The summit concluded in Colombo.
Theme of the Summit:
The theme of the summit was “Towards a Resilient Region, Prosperous Economies, Healthy People.”
This theme captures the main current priorities of member states, and the efforts by BIMSTEC to develop cooperation activities that support member state’s programmes to deal with the economic and development consequences of the Covid-19 pandemic.
Key Points of the Summit:
- The adoption and signing of the BIMSTEC Charter, which formalizes the grouping into an organization made up of member states that are littoral to and dependent on the Bay of Bengal, was the main outcome of the Summit.
- Under this Charter, the members were expected to meet once in every two years.
- With the Charter, the BIMSTEC now has an international personality.
- It has an emblem, it has a flag.
- It has a formally listed purpose and principles that it is going to adhere to.
- It represents significant evolution of the grouping.
- The BIMSTEC leaders also witnessed the signing of three different BIMSTEC agreements, which demonstrate the group's success in ongoing collaboration efforts. The agreements that were signed are:
1.A BIMSTEC MoU on mutual cooperation for diplomatic training
2.A BIMSTEC convention on mutual legal assistance related to criminal matters
3.A MoA on the establishment of the BIMSTEC technology transfer facility.
- The summit saw the declaration of the Master Plan for Transport Connectivity that would provide a framework for regional and domestic connectivity.
- India will also provide USD 1 million to the BIMSTEC secretariat to assist it expand its operational budget.
- The BIMSTEC scholarship programme, which is sponsored by Nalanda International University, has also been expanded.
- The BIMSTEC connection agenda made progress as well, with the adoption of the 'Master Plan for Transport Connectivity.'
- This plan sets out a framework for all connectivity-related initiatives that will be implemented in the near future in this region.
- The PM Modi called for a Free Trade Agreement among the member countries.
- He mentioned the necessity for coastal shipping ecosystem and electricity grid interconnectivity, as two of the necessary components of the evolving shape of the BIMSTEC.
About BIMSTEC:
- BIMSTEC is acronym for “Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation”.
- It is a regional multilateral organization established on June 6, 1997 in Bangkok under the name BIST-EC (Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand Economic Cooperation).
- Myanmar was included to it in 1997 following which group was renamed as ‘BIMST-EC’ (Bangladesh, India, Myanmar, Sri Lanka and Thailand Economic Cooperation).
- After Nepal & Bhutan become full members in 2004, BIMSTEC was renamed to its current form.
Members of BIMSTEC:
- Seven members of BIMSTEC are littoral and adjacent areas of Bay of Bengal constituting a regional unity.
- 5 are South Asian countries namely Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal & Sri Lanka while 2 countries- Myanmar & Thailand- are from Southeast Asia.
Aim of BIMSTEC:
- BIMSTEC connects South and Southeast Asia besides ecologies of Great Himalayas and Bay of Bengal.
- It was established with the aims of creating an enabling environment for rapid economic development and accelerating social progress.
Mes Aynak Site: The Taliban regime in Afghanistan has stated that it will safeguard the ancient Buddha statues in Mes Aynak, which is also home to a copper mine that the Taliban is attempting to attract Chinese investment.
Key Points:
- The Taliban's current posture contrasts sharply with their previous leadership in Afghanistan, when they used artillery, explosives, and rockets to destroy centuries-old Buddha sculptures in Bamiyan.
- The leadership's apparent change of heart on the Mes Aynak monuments appears to be motivated by economic considerations, with the dictatorship in desperate need of the revenue that Chinese investment in copper mines may provide.
About Mes Aynak Site:
- Mes Aynak is a site that is located 40 km southeast of Kabul, Afghanistan.
- It is located in the Logar Province’s barren region.
- Mes Aynak contains Afghanistan's largest copper deposit.
- The remains of an ancient settlement with over 400 Buddha statues, stupas and a 40 ha (100 acres) monastery complex are also found in this region.
- Artifacts that date back to the Bronze Age, with some dating back over 3000 years have been recovered at this site.
- This site possesses a vast complex of Buddhist monasteries, homes, and market areas.
- Discovered in the 1960s by French geologists, the site was believed to have been an important stop along the Silk Road from the early centuries AD.
- The site's orientation on the Silk Road has yielded a mixture of elements from China and India.
- In 1973-74, the archaeological wealth of this site was discovered by Afghan and Russian geologists.
History of this site:
- Between the 5th and 7th century AD, Mes Aynak was at the peak of its prosperity.
- Alchon Hun monarchs Khingila and Mehama's coins were discovered here, confirming the Alchon presence in the area between 450 and 500 CE.
- The settlement's slow decline began in the 8th Century and it was abandoned 200 years later.
- During the 10th century, the city was ruled by Brahman Shahi, the king of Kabul, Jaypaldeva.
- However, it was later burned to ashes by a Gaznavaid invasion.
- Once the walls were destroyed, it was easy for the Gaznavi to travel across Hindi Kush and invade mainland India.
- The citizens of Mes Aynak generally followed Buddhism and Hinduism equally.
- The earliest Buddhist remains date from the Kushan era, although this gradually gave way to T'ang Chinese and Uyghur influences.
Etymology:
- The word Mes Aynak literally means "little source of copper"; mes is "copper", while aynak is a diminutive form of ayn which means "source".
About Afghanistan:
- Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country in Asia.
- It is bordered by Pakistan to the east and south; Iran to the west; Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Tajikistan to the north; and China to the northeast.
- Its Capital is Kabul.
- The currency used here is the Afghan afghani.
Emmett Till Anti-lynching Act: The President of the US Joe Biden recently signed a law that makes lynching a hate crime in the United States of America.
Key Details:
- This bill was earlier passed unanimously by the Senate of the US in March 2022.
- In the House of Representatives this bill was passed by a vote of 422-3.
- The Emmett Till Anti-Lynching Act is named after Emmett Till, a 14-year old African American whose brutal murder in Mississippi galvanized the US civil rights movement in the 1950s.
About the law:
- Under this law, a crime can be prosecuted as a lynching if a conspiracy to commit a hate crime results in death or significant physical injury.
- It also specifies a maximum punishment of 30 years in prison as well as fines that are to be levied.
Background:
- The first anti-lynching legislation was first considered by the US Congress over 120 years ago.
- Until March of 2022, they had failed to pass similar legislation around 200 times.
- The bill was first introduced in the year 1900 by George Henry White, then North Carolina Rep who was the only Black member of the Cogress at that time.
About the crime that started the movement in US:
- Emmett Till, 14, had traveled from his Chicago home to visit relatives in Mississippi in 1955 when it was alleged that he whistled at a white woman.
- He was kidnapped, beaten and shot in the head.
- A large metal fan was tied to his neck with barbed wire, and his body was thrown into a river.
- His murder and the dismissal of the charges by an all-white jury against the two white men who committed the crime started a movement in the country.
- After the two men confessed to the murder, public attention was drawn to the brutality endured by the country's African American communities, and a civil rights rallying cry was born.
India and Maldives: The External Affairs Minister of India Dr. S Jaishankar recently engaged in the review of the progress of various areas of bilateral cooperation between India and Maldives.
He was on a two-day official visit to the Maldives till March 27.
Key Points:
- During the visit, he inaugurated the National College of Policing and Law Enforcement (NCPLE) in Addu City in the southernmost atoll of the Indian Ocean archipelago that was established under Indian grant assistance.
- The establishment of the police academy had, till recently, been India’s largest grant-funded project prior to the Greater Male Connectivity Project for which India extended a $400 million line of credit in 2020.
- Furthermore, an MoU (Memorandum of Understanding) was signed between the Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel National Police Academy (SVPNPA), the prestigious training institute in Hyderabad, and the Maldives Police Service.
Significance:
- The Maldives is one of India's key maritime neighbours in the Indian Ocean Region and occupy a special place in Prime Minister Narendra Modi's vision of 'SAGAR' (Security and Growth for All in the Region) and Neighbourhood First.
- SAGAR or "Security and Growth for all in the Region" is aimed at cooperative measures for sustainable use of the oceans in the region.
- On the domestic level in the Maldives, the training academy would help strengthen law enforcement abilities to counter drug trafficking and growing Radicalisation, a major concern in the country.
- Defence security cooperation between India and the Maldives has been happening for some time now and a large number of their personnel travel overseas for training, including to India.
- The Colombo Security Conclave, a trilateral maritime security grouping of India, Sri Lanka and the Maldives, where intelligence sharing is also a part of this trilateral security cooperation.
About Maldives:
- The Maldives, officially the Republic of Maldives, is a small island nation in South Asia.
- It is situated in the Arabian Sea of the Indian Ocean.
- It lies southwest of Sri Lanka and India.
- The Capital of Maldives is Male.
- The Currency of the Maldives is the Maldivian Rufiyaa.
- The current President of the Maldives is Ibrahim Mohamed Solih.
Sri Lanka Economic Crisis: The Prime Minister of Sri Lanka Mahinda Rajapaksa has resigned on May 9, 2022 from his position amid the ongoing economic crisis in the country.
Key Details:
- The resignation was accepted, according to a gazette notification, and consequently, the Cabinet stands dissolved as per the Sri Lankan Constitution.
- 76 year old Rajapaksa sent his resignation to President Gotabaya Rajapaksa after violent scenes were witnessed in Colombo.
- Rajapaksa's resignation from the post has come days after President Gotbaya Rajapaksa in a special meeting requested the PM to step down as a solution to the ongoing political and economic crisis in Sri Lanka.
- With the resignation of the Sri Lankan PM, the Health Minister of Sri Lanka Prof Channa Jayasumana also handed over his letter of resignation to the President of the country.
- Now, the Sri Lankan President Gotbaya Rajapaksa is expected to invite all the political parties in the Parliament to form an all-party cabinet.
Sri Lanka Economic Crisis:
- Sri Lanka is currently experiencing unparalleled economic turbulence since gaining independence from the United Kingdom in 1948.
- Sri Lanka has been thrown into weeks of economic crisis as a result of a currency shortage, which has resulted in a dearth of vital goods such as food, fuel, and medications.
About Sri Lanka:
- Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an island country in South Asia.
- It is located in the Indian Ocean to the southwest of the Bay of Bengal and to the southeast of the Arabian Sea.
- The capitals of Srilanka are Colombo and Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte.
- Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte is the legislative capital while Colombo is the largest city and center of commerce.
- The currency used here is Sri Lankan rupee.
New Leader of Hong Kong - John Lee: John Lee Ka-chiu, a former security chief who oversaw the crackdown on Hong Kong's democracy movement has recently been elected with 99.2% of the vote from the election committee as the next leader of Hong Kong.
Key Highlights:
- This is widely interpreted as a move by the Chinese government to tighten its hold over the city.
- John Lee is replacing Carrie Lam who had served since 2017.
- From 1st July 2022, Lee will begin his five-year term as the city’s chief executive.
- The leaders of Hong Kong are selected by a closed-circle committee of around 1,500 members, who are nearly all pro-Beijing loyalists.
- However, this time there was only one contender for them to elect.
What role did Lee have in the violent crackdowns in 2019?
- As per BBC, Lee, a former police officer who became Hong Kong's security chief, Lee helped push for the city's controversial extradition bill that aimed to facilitate the extradition of Hong Kong residents to China to face trial
- As security chief, Lee was also responsible for the crackdown on the city's residents during the island's pro-democracy protests in 2019 and 2020.
- During the unrest, water cannons, tear gas, and even live ammunition were used to disperse those demonstrating against the bill.
Why did the United States put economic sanctions against John Lee?
- The US put economic sanctions against John Lee for being a key individual in charge of implementing a draconian national security law in Hong Kong that prosecutes those accused of colluding with foreign forces.
- Under the law, Hong Kong has convicted democracy protesters of terrorism, arrested teenagers, and banned pro-democracy candidates from standing for election.
About Hong Kong:
- Hong Kong, officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China (HKSAR) is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delta in South China.
- Hong Kong was transferred from Britain to China in 1997 under the agreement that rights such as freedom of assembly and freedom of speech would be guaranteed in the territory.
- Hong Kong is one of the most densely populated places in the world.
- It is also one of the three global financial centres and one of the most developed cities in the world.
Ranil Wickremesinghe: Ranil Wickremesinghe, Sri Lanka’s veteran political leader has been appointed as the next Prime Minister of Sri Lanka amid the ongoing protests in the country.
Key Points:
- President Gotabaya Rajapaksa appointed , 73-years old, Ranil Wickremesinghe after the resignation of former PM Mahinda Rajapaksa.
- He was administered the oath of office by the President, who in an address to the nation yesterday, declared that a Prime Minister and his cabinet will be put in place this week.
- Wickremesinghe, who has already served as the Prime Minister of Sri Lanka five times, appeared to be the only option as the crisis-hit island nation’s largest opposition party had refused to join a government headed by a member of Rajapaksa clan.
- He accepted the post after securing the support of Sri Lanka Podujana Peramuna (SLPP).
Sri Lanka Economic Crisis:
- Sri Lanka was already reeling from a crippling economic crisis due to widespread shortages of food and fuel, soaring prices of essential commodities and hours-long power cut.
- Groups of pro and anti-government activists clashed in Colombo, triggering curfew and a state of emergency across the island.
- Further, the country was thrown into upheaval on May 9 when former Prime Minister Mahinda Rajapaksa resigned amid the crisis, effectively ending the country's elected government.
- Anti-government protesters also want President Rajapaksa to step down and the Lankan parliament is expected to debate a no-confidence motion against the President on May 17, 2022.
Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity: India recently agreed to be a part of the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF) a US-led trade initiative comprising 12 countries.
Key Highlights:
- The IPEF meant to counter China’s aggressive expansion in the region was launched by United States President Joe Biden on May 23 in Tokyo, Japan.
- The IPEF seeks to strengthen economic partnership amongst participating countries with the objective of enhancing resilience, sustainability, inclusiveness, economic growth, fairness, and competitiveness in the Indo-Pacific region.
- India joined a dozen other nations to launch the IPEF.
- Apart from India, other countries backing the initiative are Australia, Brunei, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand and Vietnam, and the members jointly account for 40% of the global GDP.
- The economic framework broadly rests on four pillars. They are -
1.Fair and resilient trade (including digital, labour, environmental and other standards);
2.Supply chain resilience;
3.Infrastructure, decarbonisation and clean energy; and
4.Tax and anti-corruption.
- The framework of IPEF has been designed prioritising “flexibility and inclusion”.
- So participating countries can join IPEF without necessarily joining all the four pillars of the framework, which is also in India’s interest.
- A Joint Statement was issued on the occasion, which highlights the key elements envisaged within the IPEF.
Highlights of PM Modi's speech:
- PM Modi, in his comments during the launch ceremony, said that the announcement of IPEF is a declaration of a collective desire to make the Indo-Pacific region an engine of global economic growth.
- He also said that India has historically been at the centre of trade flows in the Indo-Pacific region, having the world’s oldest commercial port in Lohtal, Gujarat.
- He called for finding common and creative solutions to tackle economic challenges of the Indo-Pacific region.
- He expressed India’s commitment towards working with all Indo-Pacific countries for an IPEF which is both inclusive and flexible.
- He underlined that the foundation of resilient supply chains must be 3T’s – Trust, Transparency and Timeliness.
National
Merger of Film Media Units with NFDC: The Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (MIB) has transferred the mandate of production of documentaries and short films, organization of film festivals and preservation of films to the National Film Development Corporation (NFDC).
NFDC is a public sector undertaking that has been working under the Ministry.
Overview:
- As per the ministry, the bringing of all these activities under single management will reduce the overlap of activities and also ensure better utilization of public resources.
- The mandate of production of feature films is already being carried out by NFDC.
- It will give a strong impetus to the production of films of all genres including documentaries, feature films, animation films and children films, organizing various domestic festivals and preservation of the filmic content.
- The ownership of the assets available with these units will remain with the government.
- By orders issued on 31st March 2022, the mandate of production of documentaries that was earlier done by Films Division has been completely transferred to NFDC.
- The legacy and brand name of Films Division will be taken further and the Production Vertical for production of documentaries in the NFDC will be named as “Films Division”.
- Similarly, the organization of film festivals that was the mandate of DFF has been transferred to NFDC.
- This will integrate the activities of numerous national and international film festivals under one roof, resulting in higher synergy and a much more concentrated worldwide outreach.
- Some of the major upcoming Film Festivals to be organized by NFDC are the Mumbai International Film Festival, International Film Festival of India at Goa, and Children’s Film Festival.
Background:
In December 2020, the ministry, under former I&B minister Prakash Javadekar, had announced the government's decision to merge the four public bodies namely the National Film Archives of India (NFAI), Films Division (FD), Children’s Film Society of India (CFSI), and Directorate of Film Festivals (DFF) with NFDC by expanding the Memorandum of Articles of Association of NDFC, which will then carry out all the activities hitherto performed by them with the objective of ensuring synergy, convergence of activities & better utilization of resources.
About the Films Division (FD):
- Films Division (FD) was established in 1948.
- It produces, and distributes newsreels and documentary films on historical events and political figures.
- In Post-Independence, films made by the erstwhile colonial agencies of Information Films of India, Indian News Parade, and Army Film and Photographic Unit were handed over to Film Division (FD).
- It preserved audio and visual records of India’s history of decolonization and the process of nation-building.
- For example, it includes works of Satyajit Ray, MF Husain, Mani Kaul, Pramod Pati, and more recent films by contemporary filmmakers.
About the National Film Archive of India (NFAI):
- National Film Archive of India (NFAI) was established in 1964.
- It is the oldest of the four units.
- It has the mandate to trace, acquire, and preserve the heritage of fiction cinema in India.
- Built under the supervision of the renowned curator P K Nair, it preserves several thousand films, books, scripts, posters, and photographs dating back to the 1910s,
- It actively promotes film research and scholarship on Indian and South Asian cinema.
About the Children’s Film Society of India (CFSI):
- Children’s Film Society of India (CFSI) was established in 1955 with the specific objective of providing children and young people value-based entertainment through the medium of films.
About the Directorate of Film Festivals (DFF):
- Directorate of Film Festivals (DFF) was established in 1976 to promote Indian films and cultural exchange.
- It organizes the National Film Award, for example, Dada Saheb Phalke Award, and the International Film Festival of India (IFFI) etc.
All four of these institutions have historically provided original prints from their archives for screenings at film festivals, film societies, and educational institutions around the world.
The NFDC:
- The National Film Development Corporation (NFDC) is a public sector undertaking.
- It was established in 1975,
- Its aim is to promote filmmakers outside the mainstream film industries of India.
- It also contributed to the development of parallel cinema.
FASTER: Chief Justice of India NV Ramana recently launched the Fast and Secured Transmission of Electronic Records (FASTER) software.
The online introduction of the FASTER programme was attended by CJI Ramana, Justices AM Khanwilkar, DY Chandrachud, and Hemant Gupta, as well as Chief Justices and Judges of High Courts.
Key Points:
- The initiative ‘FASTER‘ was initiated when a bench led by CJI Ramana took suo motu notice of delays in convicts’ release even after they had been granted bail, citing reasons such as non-receipt or non-verification of legal orders.
- According to a Supreme Court press release, the FASTER system was developed on a war footing by the Registry in collaboration with the NIC.
- FASTER has been launched so that court orders can be transmitted securely and swiftly via electronic mode thus ensuring that judicial orders can be communicated quickly.
- Through the use of this software orders that were passed by the high courts (HC) and the Supreme Court (SC) will be transmitted safely without any third-party interference.
- 73 nodal officers have been selected at the HC level to ensure that this system reaches all of India’s districts.
- Jail authorities have also been selected through a network of judicial communication.
- By constructing a safe conduit, all Nodal Officers have been connected through a specific judicial communication network JCN.
- For this software a secure pathway email id has also been established.
Significance this software:
- Bail orders will be communicated via FASTER.
- For authentication purposes, it will include the institutional digital signatures as well as the digital signatures of the recognized nodal officers of the SC.
- In this manner, bail orders would be received by all interested parties without wasting much time, and they would be able to perform the appropriate actions quickly.
- Only email id holders would be able to communicate, assuring safety, secrecy, and security.
- A total of 1,887 email ids of the selected nodal officers have been connected.
Need for such software:
- In the past, inmates were not freed by the jail officials even after bail orders were passed because the hard copies of the certified bail orders arrived late.
- Thus, this software was implemented so that Article 21, Right to Life, could be implemented swiftly and the bail orders are executed on time.
Air Traffic Management Systems: In a major boost to Government’s “Make in India” Initiative, Airports Authority of India (AAI) has recently signed an agreement with the Defence Public Sector Undertaking Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL).
Key Points:
- The present agreement is in conformity with AAI’s R & D Policy to upgrade its ANS Infrastructure in systematic, efficient and cost-effective manner and in compliance with the ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ missions of the Government of India (GoI).
- The agreement has been signed for the joint indigenous development of systems for aircraft traffic management and surface movement at airports across the country were previously imported.
- This will reduce AAI’s foreign dependency for procurement of ANS infrastructure.
- Under this Agreement, they both will collaborate to develop the Civil air traffic Management System (ATMS) with Advanced-Surface Movement Guidance and system (ASMGCS).
- ASMGCS is a complex ground surveillance system that manages air traffic at airports and in Indian civil airspace to confirm safe flight operations.
- Air traffic control has two purposes:
1.To confirm safety by maintaining separation between many planes.
2.To manage airport operations efficiently.
- ASMGCS provides routing, guidance, and surveillance services to aircraft and vehicles on the ground in order to guarantee safe surface mobility in all weather situations at the airport
- The system accommodates air traffic in congested airports and airspaces, including military flights.
Significance:
- The goal of ATMS with ASMGCS is to provide the air traffic controller with the complete air traffic picture of the coverage area while interacting with Primary/Secondary Radar, Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B), Multi-lateration System (MLATs), and navigational equipment such as GPS, Instrument Landing System (ILS) and Doppler Very High Frequency Omni Range (DVOR).
- The system is used in congested airports and airspaces to serve large volume of air traffic, including military flights.
- The system comprises multiple, in-house developed technologies, such as Situation Display for Air traffic controller, Surveillance Data Processing (SDP), Flight Data Processing (FDP), Safety Net and Decision Support (SNET), Control & Monitoring Display (CMD), Advanced ASMGCS, etc.
- It helps in increasing capacity with improved safety by reducing controller workload, improving air traffic flow and minimizing flight delays.
- Enhanced system reliability and availability are provided through redundant and distributed architecture, safeguarding ATM operations.
Association of Asian Election Authorities (AAEA): India has been unanimously elected as the new Chair of the Association of Asian Election Authorities (AAEA) for 2022-2024.
Key Points:
- India was appointed as the new Chair AAEA at the meeting of the Executive Board and General Assembly in Manila, Philippines held on May 7th, 2022.
- Commission on Elections, Manila was the current chair of AAEA.
- India also served on the Executive Board of the AAEA as the Vice-Chair during 2011-13 and Chaired during 2014-16.
Election Commission of India:
- The Executive Board meeting at Manila was attended by The Election Commission of India 3-member delegation headed by Deputy Election Commissioner Shri Nitesh Vyas, along with CEO Manipur Shri Rajesh Agrawal and CEO Rajasthan Shri Praveen Gupta.
- The Indian delegation presented the work plan for 2022-23 presented the work plan for 2022-23 as also futuristic activities for 2023-24 to the Executive Board.
- They also presented on ‘Gender Issues in Elections’ which highlighted various interventions by India to break socio-political barriers in electoral and political processes for inclusive and participative elections.
About AAEA:
- Association of Asian Election Authorities (AAEA) was established in 1998.
- AAEA was established in pursuance of the resolution passed by participants of the Symposium on Asian Elections in the 21st Century held from January 26-29, 1997 in Manila, Philippines.
- It is a non-partisan forum that aims to provide a non-partisan forum in the Asian region for sharing experiences and best practices among election authorities to discuss and act upon ways to promote open and transparent elections to support good governance and democracy.
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) is the founding member of AAEA’s Election Management Body (EMB).
Members:
- The new member of the Executive Board now includes Russia, Uzbekistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives, Taiwan, and the Philippines.
- Currently, 20 Asian EMBs are members of AAEA.
PM MITRA Scheme: The Ministry of Textiles recently organized a National Conference on PM Mega Integrated Textile Regions and Apparel (PM MITRA) Parks Scheme.
Key Highlights:
- The conference provided a platform for presentations by officials of 13 state government, viz. – Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Punjab, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh
- The details of the 18 plans for the establishment of PM MITRA Parks in their respective states were outlined by each state representative.
- Each state government highlighted its advantages in the textiles industry, paying particular attention to scheme, policy, benefits, incentives and basic utilities provided for creating an industry-friendly ecosystem to populate the proposed PM-MITRA Parks.
Vision of PM MITRA scheme:
- The PM MITRA scheme is inspired by the 5F vision – Farm to Fibre to Factory to Fashion to Foreign.
- It aims to realize the dream of creating an Aatmanirbhar Bharat and cement India's position on the world textiles scene.
Features of PM MITRA Scheme:
- Under the project, PM Mitra Parks will be set up by a special purpose vehicle owned by the State Governments and the Centre in a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model.
- Each Park will have an incubation centre, common processing house and a common effluent treatment plant and other textile related facilities such as design centres and testing centres.
- The Master Developer will not only develop the Industrial Park but also maintain it during the concession period.
- Sites for PM MITRA Parks will be selected by a Challenge Method based on objective criteria.
- Proposals of States with ready access to contiguous and encumbrance-free land parcel of 1,000+ acres along with other textiles related facilities will be welcomed.
Funding:
- The Centre will provide capital support for common infrastructure development of Rs 500 crore for each greenfield Mitra park and Rs 200 crore for each brownfield.
Significance:
- It will offer an opportunity to create an integrated textiles value chain right from spinning, weaving, processing/dyeing, and printing to garment manufacturing at 1 location.
- It will reduce the logistics cost of the Industry and strengthen the value chain of the textile sector to make it globally competitive.
- It is intended to generate around 1 lakh direct and 2 lakh indirect jobs per park.
- The parks will not only attract cutting edge technology but will also boost local & foreign investment in the textiles sector.
- It will also help in achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 9: “Build resilient infrastructure, promote sustainable industrialization and foster innovation”.
Reconstitution of CABA: The Central Advisory Board on Archaeology (CABA), which was formed seven years ago to promote ties between the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and people working in the field of archaeological research, was re-established.
Key Points:
- The board has been reconstituted by ASI.
- The board has been formed to strengthen the bridge between archaeological research, Indian universities, and the Archaeological Survey of India.
- The reconstituted board includes the Culture Minister as chairperson and members including officials from the Culture Ministry and ASI, MPs, State government nominations, university representatives, scientists, and Indus Valley script experts.
- This board will also consist of 5 persons that will be nominated by the Indian Government along with the former Director-General of ASI.
Functions:
- The Board will meet once a year and will be advising the Central government regarding various archaeological matters.
- It will be looking to promote the application of antiquarian principles.
- It will also be promoting the training of future archaeologists and through various activities of the ASI, will be bridging ties between the state governments and the societies of India.
- It may also make suggestions on such matters for the consideration of the Government.
- It also set up a Standing Committee of the board to be chaired by the ASI D-G.
About ASI:
- The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is an Indian government agency attached to the Ministry of Culture that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural monuments in the country.
- ASI was founded in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham- the first Director-General of ASI. Alexander Cunningham is also known as the “Father of Indian Archaeology”.
- It administers more than 3650 ancient monuments, archaeological sites and remains of national importance.
- Its activities include carrying out surveys of antiquarian remains, exploration and excavation of archaeological sites, conservation and maintenance of protected monuments etc.
Gen Next Democracy Network: The 2nd batch of the 10 Ten day Gen Next Democracy Network programme of the Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) recently concluded.
The first batch was organized in India in November, 2021.
Key Highlights:
- 27 delegates from six countries-Ghana, Bangladesh, Peru, Nepal, Brunei and Norway visited India participated in the Gen Next Democracy Network programme.
- They all shared their experiences of visiting India in the closing ceremony.
About Gen Next Democracy Network:
- The Gen Next Democracy Network is a new inititative launched by the Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR).
- This programme will acquaint the young leaders of 75 democracies with India’s culture, heritage and the “Idea of India” by showcasing India’s contributions to addressing global issues through its democratic worldview.
- ICCR had organized the first batch of the Gen-Next Democracy Network Programme, constituting delegates from eight countries Bhutan, Jamaica, Poland, Malaysia, Sweden, Sri Lanka, Tanzania and Uzbekistan, in India in November, 2021.
- Under this progaramme, youth from democratic countries come to India to get acquainted with India’s heritage, culture and functioning of Indian democracy.
Aim:
- The programme aims at defining India’s democratic governance structure at various levels and provides an understanding of the success of India’s democratic journey across the world.
About Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR):
- Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) is an autonomous organisation of the Government of India (GoI).
- It was founded in 1950 by Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, the first Education Minister of independent India.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- It is involved in India’s global cultural relations, through cultural exchange with other countries and their people.
- It operates missions internationally, with established cultural centres in various countries.
- It also administers the Jawaharlal Nehru Award for International Understanding, established by the Government of India in 1965, whose last award was in 2009.
National Data and Analytics Platform: The country’s policy commission, the National Institution of Transforming India (NITI Aayog) recently launched the National Data and Analytics Platform (NDAP) for free public use.
Key Points:
- The platform aims to democratise access to public government data by making information accessible, interoperable, interactive, and available on a user-friendly platform.
- It houses basic datasets from a variety of government departments, organises them, and provides analytics and visualisation capabilities.
- This public debut comes after the platform’s beta release in August 2021, which gave a small number of users access for testing and feedback.
- To ensure that the datasets hosted on the platform are adapted to the needs of data users from government, academia, journalism, civil society, and the corporate sector, NDAP uses a use-case methodology.
- All datasets are standardised to the same schema, making it simple to combine them and do cross-sectoral analysis.
About NITI Aayog:
- The National Institution For Transforming India Aayog (NITI Aayog) is the premier policy 'Think Tank' of the Government of India (GoI).
- It was established on 1 January 2015 with an objective to foster cooperative federalism through structured support initiatives and mechanisms with the States on a continuous basis, recognizing that strong States make a strong nation.
- It provides directional and policy inputs.
- Apart from designing strategic and long-term policies and programmes for the government, NITI Aayog also provides relevant technical advice to the centre, states, and union territories.
- The Governing Council of NITI, with The Prime Minister as its Chairman, comprises Chief Ministers of all States and Lt. Governors of Union Territories (UTs).
- The current CEO of NITI Aayog is Parameswaran Iyer.
People In News
Vikas Kumar: Vikas Kumar has been appointed as the new Managing Director of the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC).
Key Points:
- He is succeeding Mangu Singh, whose tenure ended on March 31, 2022.
- Singh was the managing director of DMRC since January 1, 2012.
- Kumar is the third managing director of the DMRC after E Sreedharan and Mangu Singh.
- He will hold the post for a term of five years.
About Vikas Kumar:
- Vikas Kumar is a 1988-batch officer of the Indian Railway Traffic Service.
- He was holding the position of the Director (Operations) in the DMRC.
- He has over three decades of experience in rail-based urban transportation projects.
- He has worked with the Indian Railways in various capacities before joining the DMRC in September 2004.
- He has been associated with the urban transporter for more than 17 years in key management positions.
- In the DMRC, Kumar has headed the operations wing of the organization since 2007 in various leadership capacities, such as general manager (operations), executive director (operations) and director (operations).
- He has played a key role in ensuring the smooth commencement of metro services in Delhi-NCR.
About Delhi Metro Rail Corporation (DMRC):
- The Delhi Metro is a mass rapid transit (MRT) system serving Delhi and its satellite cities of Ghaziabad, Faridabad, Gurgaon, Noida, Bahadurgarh and Ballabhgarh, in the National Capital Region of India.
- It is by far the largest and busiest metro rail system in India, and the second oldest after the Kolkata Metro.
- Its construction started in 1998.
- The first elevated section (Shahdara to Tis Hazari) on the Red Line opened on 25 December 2002.
Ritu Khanduri: BJP MLA Ritu Khanduri has recently become tthe first woman Speaker of the state assembly.
Key Highlights:
- Daughter of former Uttarakhand chief minister Major General Bhuvan Chandra Khanduri was elected unopposed as the first woman speaker of the Uttarakhand Assembly.
- The announcement about her election was made by pro-tem speaker Banshidhar Bhagat.
- Her election to the post was a foregone conclusion as the main opposition Congress chose to stay out of contest.
- She won from Kotdwar by defeating former minister S S Negi by more than 3,000 votes.
- She had won her maiden assembly election from the Yamkeshwar constituency in 2017.
Shashi Sinha: IPG Mediabrands India CEO Shashi Sinha as the new chairman of the board of Broadcast Audience Research Council (BARC) India.
Key Highlights:
- He will take over from Punit Goenka, who served as chairman of the TV viewership measurement agency for the last three years.
- Sinha, who also represents the Advertising Agencies Association of India as its board member, has played a key role in the formation of BARC.
About the Broadcast Audience Research Council India:
- The Broadcast Audience Research Council (BARC) India is a joint industry body founded by organisations that represent Indian broadcasters, advertisers, and advertising and media agencies.
- It was founded in 2010.
- It is the world’s largest television measurement science industry body.
- It is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra.
Raj Subramaniam: Indian American corporate veteran Raj Subramaniam is set to succeed Frederick W Smith as the new CEO of the transportation company FedEx.
Key Points:
- Subramaniam, 54 is originally from Trivandrum, India.
- He went to IIT Bombay in 1987 to study chemical engineering and later earned a master’s degree in the same field from Syracuse University in 1989.
- He joined FedEx in 1991.
- He was elected to the FedEx Board of Directors in 2020.
About FedEx:
- FedEx Corporation, formerly Federal Express Corporation and later FDX Corporation, is an American multinational conglomerate holding company focused on transportation, e-commerce and services based in Memphis, Tennessee.
- The name "FedEx" is a syllabic abbreviation of the name of the company's original air division, Federal Express, which was used from 1973 until 2000.
Central Banking Awards 2022: Mario Marcel has won the Governor of the year award at the 9th edition of the Central Banking Awards 2022.
Key Highlights:
- Marcel is the Governor of the Central Bank of Chile (Banco Central de Chile is the name of the central bank of Chile).
- The Central Banking Awards 2022 recognize excellence in a community that had faced significant policy and operational challenges amid uneven economic recovery and inflationary pressures in the second year since the Covid-19 outbreak.
- The annual Central Banking Awards 2022 is made up of 17 central bank categories and 14 partner and service provider categories.
About Mario Marcel:
- Mario Marcel served as the governor of the Central Bank of Chile (BCCh) from 2016 to January 2022.
- He took over the leadership of an institution that had secured a reputation as one of the most independent and well-run central banks in Latin America.
- After resigning in January 2022 he became the finance minister under the new administration of Gabriel Boric, President of Chile.
- He has not only served as a consultant for international organizations and governments of different countries such as Columbia, Peru, Mexico and Vietnam but also served as a researcher for the Corporation for Latin American Sudies (Cieplan).
2022 International Man Booker Prize: Indian writer Geetanjali Shree along with American translator Daisy Rockwell has won the 2022 International Booker Prize for the book titled "Tomb of Sand" for Translated Fiction.
Key Highlights:
- The book written by Shree beat five other finalists including Argentina’s Claudia Piñeiro, Polish Nobel literature laureate Olga Tokarczuk, and Bora Chung, a South Korean author to be awarded this prize at a ceremony that was held in London.
- Shree and Rockwell will split the £50,000 prize money, giving the author and translator equal recognition.
About the book:
- This book was originally written in Hindi and is the first book in any Indian language to have won this high-profile award.
- The original name of the book is “Ret Samadhi.”
- Set in northern India, the novel follows the adventures of an 80-year-old woman who unexpectedly gains a new, and highly unconventional, lease of life.
- This book has also won the English PEN translation award.
About International Booker Prize:
- The International Booker Prize is awarded annually to a translated work of fiction that has been published in Ireland or the U.K.
- This award is run alongside the Booker Prize which is awarded for English-language fiction.
- The prize is one of the two literary awards that is handed out by the Booker Prize Foundation, a charity whose goal is to promote the value and art of literature for the benefit of the public as well as to acknowledge the often-unacknowledged work of the many literary translators.
- In 2005, International Booker Prize began with the name Man Booker International Prize and was given biennially till 2015.
- From 2016 onwards, the International Booker Prize opened for English translations of foreign language books.
- It equally recognized the work of both author and translator.
- The prize carries an award of 50,000 pounds that is divided equally between the translator and the author. Also, each shortlisted translator and author also receive 2,500 pounds.
- It’s distinct from the Booker Prize, which has been won by Indian writers like Arundhati Roy and Aravind Adiga in the past.
Places In News
Assam-Meghalaya Border Pact: The Chief Ministers of Assam and Meghalaya, on 29th March 2022 signed a border agreement.
- This MoU has been signed to resolve the case of the inter-state boundary dispute between Meghalaya and Assam with respect to 6 of the 12 areas of difference.
Key Details:
- The historic pact was signed in the presence of Shah and Chief Ministers of Assam and Meghalaya Himanta Biswa Sarma and Conrad Sangma respectively to resolve their five-decade-old border dispute in six of the 12 locations.
- The 6 areas of difference that have been taken into consideration in the first phase are Gizang, Tarabari, Boklapara, Hahim, Ratacherra, and Khanapara-Pillangkata.
- The 12 areas of difference are Gizang, Tarabari, Langpih (Lumpi), Hahim, Boklapara, Borduar, Khanapara-Pillangkata, Nongwah-Mawtamur (Garbhanga), Block-I & Block-II, Deshdoomreah, Khanduli and Psiar, and Ratacherra
- With this newly signed Memorandum of Understanding (MoU), Meghalaya will be gaining 18.33 square kilometers and Assam will be gaining 18.46 sq km out of the total of 36.79 sq km. in 6 out of 12 areas of differences that were resolved between the two states.
- As per the agreement, the MoU will be deemed a complete and final agreement.
- The locations described are based on a table-top exercise that was conducted using spatial technologies.
- It will be determined more precisely during the detailed survey for the demarcation and delineation of the boundary by the Survey of India, which will be done in the presence of representatives from both state governments.
Background:
- The boundary dispute has been going on between both states for a long period of time.
- The boundary dispute between Assam and Meghalaya has lingered for 50 years. However, the effort to resolve it gained pace in recent times.
- Meghalaya was carved out of Assam as a separate state in 1972 but the new state had challenged the Assam Reorganisation Act, 1971, leading to dispute in 12 locations in the border areas.
- In August 2021, the two states appointed three committees each to investigate the thorny boundary issue.
- The panels were formed after two rounds of talks between Sarma and Sangma, during which the two neighbours agreed to settle the matter in stages.
Note:
- Tripura, Meghalaya, Manipur, Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, Nagaland, and West Bengal share a 2743-kilometer border with Assam.
- Mizoram, Meghalaya, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh all have border conflicts with it.
Living Root Bridges of Meghalaya: Living Root Bridge also called the Jingkieng Jri has been included in the tentative list of World Heritage Sites of the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
Key Points:
- The Jingkieng Jri is found in over 70 villages in Meghalaya highlighting the socio-cultural, social and botanical links between people and nature.
- The living root bridges are grown by the villagers by training the ‘ficus elastica’ tree on both sides of water bodies over a period of about 10 to 15 years where the roots form the bridge.
- Often used as a path across a stream or a river, currently, there are about 100 known living root bridges spread across 72 villages in the state.
Note: One of the most famous living root bridge is in Nongriat, which is a double decker living root bridge and is spread across two levels.
- Villagers (particularly the Khasi and Jaintia tribal clans) have been building and maintaining these bridges for over 600 years.
Additional Info:
Other sites included in the list in 2022:
- Sri Veerabhadra Temple and Monolithic Bull (Nandi) at Lepakshi of Andhra Pradesh, The Geoglyphs of the Konkan region of Maharashtra have made it to the tentative list of UNESCO world heritage sites in 2022.
About UNESCO:
- The full form of UNESCO is United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization.
- UNESCO was founded on 6 November 1945.
- It is a specialized agency of the United Nations aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, the sciences, and culture.
- It is headquartered in Paris, France.
- The current head of UNESCO is Audrey Azoulay.
Odisha Day- Utkal Divas: Every year on April 1st, the state of Odisha celebrates Utkal Divas, also known as Utakala Dibasha or Odisha Day.
Key Points:
- This day is celebrated to remember Odisha’s formation after the struggle it faced to be recognized as an independent state of the country.
- The state was originally called Orissa but in 2011 the Orissa Bill and Constitution Bill (113rd amendment) was passed by the Lok Sabha and the state was renamed Odisha.
- On this day the shops and houses are decorated.
- Various competitions are organized across the state by local politicians such as fireworks competitions. Different types of cultural programs are also organized to commemorate this day.
History of this day:
- The present-day Odisha was a major part of the ancient Kalinga.
- The epic Kalinga War was witnessed by this region.
- This war was led by King Ashoka who in 260 BC had invaded and conquered this region.
- Later, the state was invaded and taken over by the Mughals.
- Then in the year 1803 the British took over power and divided this region into small units.
- The northern and western districts were merged with Bengal while the coastal region formed the basis of Bihar and Odisha (then known as Orissa).
- After struggling for decades under the leadership of Odisha’s eminent leaders, on 1st April 1936, the new province of Odisha came into existence.
- The state saw another facelift, now in terms of its name being changed from Orissa to Odisha.
- On 9 November 2010, the Parliament of India renamed Orissa as Odisha.
- Oriya language was also retitled as Odia.
About Odisha:
- Odisha also formerly Orissa, is an Indian state located on the eastern coast of India.
- It neighbors the states of West Bengal and Jharkhand to the north, Chhattisgarh to the west and Andhra Pradesh to the south.
- It is an eastern Indian state on the Bay of Bengal.
- It is known for its tribal cultures and its many ancient Hindu temples.
- The Jagannath Temple in Puri is a very sacred and religious temple of Hindus.
- More than 31% of the state has been covered with forests.
- The capital of Odisha is Bhubaneswar.
- The Governor and the Chief Minister of Odisha are Ganeshi Lal and Naveen Patnaik respectvely.
MyGov Platform: The Lieutenant Governor of Jammu and Kashmir Manoj Sinha recently launched MyGov platform for Jammu and Kashmir.
Key Highlights:
- MyGov Jammu and Kashmir was launched with the aim of achieving the goal of ‘Good Governance’ and taking forward the idea of citizen engagement.
- This platform is the 16th implementation of the MyGov platform in a state or UT.
- This is also the first UT in which the MyGov platform has been implemented.
About MyGov Platform:
- The MyGov platform was launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2014.
- The goal of this launch was to bring the government closer to the people of India by developing an interface that could be utilized for a healthy interchange of thoughts and ideas, so that they can be implemented for transforming India both economically and socially.
- Currently, this platform has over 2.29 Crore registered users.
- They are known as MyGov Saathis.
- They engage actively with MyGov and share all their suggestions and ideas related to various policy issues.
- They also participate in quizzes, pledges, and contests on this platform.
- MyGov has been promoting the positive use of social media and has been identifying unsung heroes and change-makers from across India who are contributing to the development of society.
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, MyGov has emerged to be a trusted information source for the citizens of the nation.
Implementation of MyGov platform:
- MyGov has been implemented in 15 States.
- They are Maharashtra, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Chhattisgarh, Tripura, Nagaland, Jharkhand, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Goa, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Now MyGov Jammu and Kashmir is the 16th implementation of the MyGov platform in a state or UT.
About Jammu and Kashmir:
- Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) is a region administered by India as a Union Territory.
- The current Lieutenant Governor of J&K is Former Union minister and BJP leader Manoj Sinha.
Utkarsh Samaroh: Prime Minister Narendra Modi on 12th May 2022 virtually addressed ‘Utkarsh Samaroh’ held at Bharuch in Gujarat.
Key Highlights:
- The event was organized to mark the celebration of 100 percent saturation of 4 key schemes of the state government in the district.
- These will help in providing timely financial assistance to those in need.
About Utkarsh Initiative:
The Utkarsh Initiative was carried out by the Bharuch district administration to ensure complete coverage of schemes providing assistance to widows, elderly and destitute citizens.
A total of 12,854 beneficiaries were identified under the four schemes that are -
- Indira Gandhi Vrudh Sahay Yojana
- Rashtriy Kutumb Sahay Yojana
- Niradhar Vrudh Aarthik Sahay Yojana
- Ganga Swaroopa Aarthik Sahay Yojana
During the drive from 1st January to 31st March 2022, taluka-wise Whatsapp helpline numbers were set up to collect information about those people who were not receiving benefits of the scheme.
Utkarsh Camps:
- The Utkarsh camps were organized in all villages and wards of municipality areas of the district, to collect the necessary documents for on the spot approval.
- Incentives were also given to Utkarsh assistants to further facilitate the drive.
About Indira Gandhi Vrudh Sahay Yojana:
- The Indira Gandhi Vrudh Sahay Yojana aims to assist all beneficiaries aged 60 and up who fall under the Below Poverty Line category.
About Niradhar Vrudh Aarthik Sahay Yojana:
- The Niradhar Vrudh Aarthik Sahay Yojana was set up to assist needy persons with disabilities, as well as destitute elderly people, in leading dignified lives by providing financial assistance.
About Rashtriy Kutumb Sahay Yojana:
- Under the Rashtriy Kutumb Sahay Yojana, the family members of a household living below the poverty line are eligible for financial compensation under this scheme when the main breadwinner dies.
About Gujarat Ganga Swaroopa Aarthik Sahay Yojana:
- This scheme was launched to help the women of the state who have lost their husbands.
- This scheme provides financial assistance to mothers so that they may care for their family.
Ladli Laxmi scheme-2.0: Madhya Pradesh Chief Minister, Shivraj Singh Chouhan recently launched the second phase of the Ladli Laxmi scheme (Ladli Laxmi scheme-2.0).
Key Highlights:
- The Ladli Laxmi scheme-2.0 was launched during a state-level function at Lal Parade Ground in Bhopal.
- The CM also dedicated the Ladli e-Samvad app to establish a continuous dialogue with Ladlis.
- In the app, all Ladli Laxmis will be linked to the education portal through Samagra ID which will enable continuous tracking of their educational status.
- Decision has also been taken to honour those gram panchayats as Ladli Friendly panchayat who will take care of the girl child for their economic empowerment, skill enhancement and protection of rights along with nutrition, health and education to boost their self-confidence.
What is Ladli Laxmi scheme-2.0?
Ladli Laxmi scheme – 2.0 is an innovative initiative to encourage girl children to pursue higher education and make them self-dependent.
About Ladli Laxmi scheme:
- The Ladli Laxmi scheme is being implemented by the government of Madhya Pradesh since 2007 to enhance the economic and educational status of the girls.
- It is a comprehensive scheme that offers financial assistance for a girl from birth until her marriage in installments.
To avail the benefits of the scheme the following criteria has to be me:-
- The family of the girl child should be a permanent resident of Madhya Pradesh.
- The family should come under below the poverty line (BPL), i.e., should not be an income taxpayer.
- A maximum of two daughters can be registered under this scheme.
Achievements under this scheme:
- Under Ladli Laxmi Yojana around 42,04,650 girls have been registered till April 2022 in MP.
- So far, more than 9 lakh girl students have been paid a scholarship amount of Rs 231 crore.
- The sex ratio at birth in the state has increased from 927 to 956 per thousand.
About Madhya Pradesh:
- Madhya Pradesh (MP) is the second largest Indian state by area.
- It borders the states of Uttar Pradesh to the northeast, Chhattisgarh to the southeast, Maharashtra to the south, Gujarat to the west, and Rajasthan to the northwest.
- Its capital is Bhopal.
- The current Chief Minister and Governor of Madhya Pradesh is Shivraj Singh Chouhan and Mangubhai C. Patel respectively.
Goa Statehood Day 2022: Goa celebrated its 35th Foundation Day on 30th May 2022.
Key Highlights:
- A grand ceremony was arranged today at Raj Bhavan in Dona Paula.
- Governor P.S. Sreedharan Pillai, Chief Minister Dr. Pramod Sawant, Union Minister Sripad Naik were among the dignitaries present on this occasion.
- Awards were given to persons from various walks of life for their outstanding achievement in respective fields including former Chief Ministers of Goa.
Significance of Statehood Day:
- Goa remained under Portuguese rule even after 14 years of India's independence.
- Goa was liberated from the Portuguese on 19th December 1961.
- Liberation Day is celebrated in Goa on 19th December.
- On May 30, 1987, Goa was given full statehood and Daman and Diu were made a separate union territory.
- Goa became India’s 25th state.
- Since then, 30th May is celebrated as the Statehood Day of Goa.
- After its establishment, Panaji was given the status of the capital of Goa and Konkani language as the official language.
History:
- Before 1961, Goa was a colony of Portugal.
- The Portuguese ruled Goa for about 450 years.
- After India achieved independence from the British in 1947, Goa, which was a Portuguese colony, remained a colony until 1961.
- In 1961, the Indian Army, as per the wishes of most of the Goan population liberated it from Portuguese rule by force.
- In 1961, India launched Operation Vijay and annexed Goa and Daman and Diu with the Indian mainland.
- The Portuguese government in Goa surrendered formally on 19th December 1961 ending more than 450 years of colonial rule in the state of Goa.
Note: Shri Dayanand Bhandarkar became the first elected Chief Minister of Goa.
About Goa:
- Goa is a state in western India with coastlines stretching along the Arabian Sea.
- It is surrounded by the Indian states of Maharashtra to the north and Karnataka to the east and south, with the Arabian Sea forming its western coast.
- Goa continued to remain a Union Territory until 1987 when it was accorded statehood.
- It became India’s 25th state even as Daman and Diu continue to be Union Territories.
- It is India's smallest state by area and the fourth-smallest by population.
- The capital of Goa is Panaji.
- The current Chief Minister and the Governor of Goa are Pramod Sawant and Bhagat Singh Koshyari respectively.
Science and Technology
Space Junk and NETRA Project: With space junk posing increasing threat to Indian assets in space, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) is building up its orbital debris tracking capability by deploying new radars and optical telescopes under the Network for Space Objects Tracking and Analysis (NETRA) project.
Overview:
- A space debris tracking radar with a range of 1,500 km and an optical telescope will be inducted as part of establishing an effective surveillance and tracking network under NETRA.
- The government has given the go-ahead for the deployment of the radar, which will be capable of detecting and tracking objects 10 cm and above in size.
- It will be indigenously designed and built.
- ISRO plans to have two such radars deployed 1,000 km apart for spatial diversity.
- Curently, ISRO has a Multi Object Tracking Radar at Sriharikota range, but it has a limited range.
- The SSA Control Center in Bengaluru coordinates ISRO's efforts in space situational awareness (SSA), which are administered by the Directorate of Space Situational Awareness and Management at ISRO headquarters.
What is Space Debris?
- The space debris or space junk is a term used to describe a group of unwanted objects in Earth's orbit, whether man-made or natural.
- Natural Debris is made up of natural bodies that orbit the sun, such as asteroids and meteors.
- Artificial space junk or debris consists of exhausted rocket stages, dead satellites, shards of space objects, and debris from the Anti-satellite (ASAT) System.
- These free floating space debris, hurtling through space at a speed of 27,000 kmph in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), pose a genuine hazard as collisions involving even centimetre-sized fragments can be lethal to satellites.
- These particles are a potential hazard for operational satellites and colliding with them can leave the satellites dysfunctional.
- This is referred to as Kessler Syndrome, named after National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) scientist Donald Kessler in 1978.
- According to Kessler Syndrome, if there is too much space trash in orbit, it could cause a chain reaction in which more and more objects hit and create additional space junk, eventually rendering Earth's orbit uninhabitable — a Domino Effect.
Project NETRA:
- NETRA project is an early warning system in space to detect debris and other hazards to Indian satellites.
- NETRA Project was initiated by ISRO in August 2020.
- Under NETRA, ISRO plans to put up the following:
- Many observational facilities:
- Connected radars,
- Telescopes;
- Data processing units and
- A control centre.
Note: Radars and optical telescopes are vital ground-based facilities for keeping an eye on space objects, including orbital junk.
- They can also spot, track and catalogue objects as small as 10 cm, up to a range of 3,400 km and equal to a space orbit of around 2,000 km.
- Once operational, it will give India its own capability in Space Situational Awareness (SSA) like the other space powers which is used to ‘predict’ threats from debris to Indian satellites.
- It also goes so far as to serve as an unstated warning against missile or space attack for the country.
- Under this project, SSA was first used for low-earth orbits or LEO which have remote-sensing spacecraft.
- NETRA’s ultimate goal is to capture the GEO, or geostationary orbit, scene at 36,000 km where communication satellites operate.
Why the need?
- With countries launching more and more satellites, each one a strategic or economic asset, preventing collisions may grow increasingly difficult in the future.
- In the year 2021, ISRO monitored 4,382 events in LEO and 3,148 events in the geostationary orbit where space objects closely approached Indian assets.
- For protecting its space assets, ISRO was forced to perform 19 Collision Avoidance Manoeuvres (CAM).
- Fragments from the Fengyun-1C satellite (part of the anti-satellite test (ASAT) by China in 2007) and the Cosmos 2251-Iridium satellite collision in 2009 accounted for the maximum number of these threats.
- The observations also covered 84 “close approaches of less than one km” between Starlink satellites and Indian assets.
PACER Scheme: The Polar Science and Cryosphere (PACER) scheme has been approved for continuation during 2021-2026.
About the PACER scheme:
- Polar Science and Cryosphere Research (PACER) scheme comprises of the Antarctic program, Indian Arctic program, Southern Ocean program and Cryosphere and Climate program.
- It is implemented through National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
Objective:
- The main objective of the scheme is to improve our understanding of Polar Science and the cryosphere system.
Components of PACER:
PACER encompasses the following six components.
1)Construction of polar research vessel
2)Construction of the third research base in Antarctica
3)Indian scientific endeavours in the Arctic
4)Polar expeditions-Antarctica
5)Replacement of Maitri station
6)Southern Ocean
PACER Scheme is one of the five major programs of MoES, other four are:
1)Atmosphere and Climate Research – Modelling, Observing Systems and Services (ACROSS).
2)Ocean Services, Technology, Observations, Resources, Modelling and Science (OSTORMS).
3)Seismology and Geosciences (SAGE).
4)Research, Education, Outreach and Training (REACHOUT).
Major achievements of the PACER scheme in the recent three years are:
- Executed 39th & 40th Indian Scientific Expedition to Antarctica.
- 41st Indian Scientific Expedition to Antarctica is ongoing.
- Clear-air atmospheric observatories containing automatic weather stations, a suite of sensors to measure aerosol and greenhouse gas concentrations has been established at Maitri and Bharati stations.
- Twenty-three research projects related to glaciology, marine science, polar biology, and atmospheric science were successfully carried out during 2019-20 Arctic Expedition.
- IndARC mooring system along with Hydrophone system was successfully retrieved and deployed in Kongsfjorden, Svalbard.
Studies in Western Himalayas:
- Glaciological field campaigns were carried out in six benchmark glaciers in Chandra basin of Lahaul-Spiti region of Western Himalaya.
- Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) and Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) survey were conducted.
- Snow, ice, meltwater, water and cryoconite samples were collected from various glaciers and lakes.
- Automatic Weather Station (AWS) systems were installed at Baralacha La, a high elevation site in the arid Spiti region to strengthen infrastructure across the Chandra basin.
Indian Antarctic Program:
- The Indian Antarctic Program is a multi-disciplinary, multi-institutional program under the control of the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research, Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- It was initiated in 1981with the first Indian expedition to Antarctica.
- The program gained global acceptance with India's signing of the Antarctic Treatyand subsequent construction of the Dakshin Gangotri Antarctic research base in 1983, superseded by the Maitri base from 1989.
- The newest base commissioned in 2012 is Bharati.
- Under the program, atmospheric, biological, earth, chemical, and medical sciences are studied by India.
- As of today, Maitri and Bharati are fully operational.
About NCPOR:
The National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), Goa—an autonomous institute under the Ministry of Earth Sciences—manages the entire Indian Antarctic program.
The Antarctic Treaty:
- The Antarctic Treaty was signed in Washington on 1 December 1959 by the twelve nations (Argentina, Australia, Belgium, Chile, France, Japan, New Zealand, Norway, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States and USSR).
- The Treaty, applies to the area south of 60° South latitude.
- The Treaty now has 52 signatories.
- India became a member of this treaty in 1983.
- It is headquartered in Buenos Aires, Argentina.
What is the cryosphere?
- The cryosphere is the frozen water part of the Earth system.
- The term “cryosphere” comes from the Greek word, “krios,” which means cold.
- Ice and snow on land are one part of the cryosphere.
- These are places on Earth that are so cold that water is frozen solid.
- These areas of snow or ice, which are subject to temperatures below 0°C 32°F for at least part of the year, compose the cryosphere.
- This includes the largest parts of the cryosphere, the continental ice sheets found in Greenland and Antarctica, as well as ice caps, glaciers, and areas of snow and permafrost.
- When continental ice flows out from land and to the sea surface, we get shelf ice.
- The other part of the cryosphere is ice that is found in water.
- This includes frozen parts of the ocean, such as waters surrounding Antarctica and the Arctic.
- It also includes frozen rivers and lakes, which mainly occur in polar areas.
Semicon India Conference 2022: The Semicon India Conference was recently held in Bangaluru Karnataka.
Key Highlights:
- It was inaugurated by Prime Minister Narander Modi.
- The flagship conclave with the theme ‘Catalysing India’s Semiconductor Ecosystem’ was held in Bengaluru from 29th April to 1st May 2022.
- The three day conference was organized by India Semiconductor Mission in partnership with industry associations with the focus being on catalysing India’s Semiconductor Ecosystem.
- The conference featured eminent specialists from industry associations, research organisations, and academia.
- They discussed policy, talent, and the government’s role and efforts in fostering a favourable growth environment for the country’s semiconductor ecosystem.
Objective:
- According to a Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) statement, the three-day conference was held to advance PM Modi’s objective of making India a global hub for Semiconductor Design, Manufacturing, and Technology Development.
- The conference aligns with the larger national narratives such as Make in India and Atmanirbhar Bharat and is pegged as the launchpad to India Semiconductor Mission (ISM).
Background:
- The Semicon India program was approved in March 2022 by the Union Cabinet for the development of the semiconductor and the display manufacturing ecosystem in India.
- With the fiscal outlay of 76000 crore, there are various schemes under this programme such as the scheme to set up Semiconductor fabs and display fabs, Design linked incentive schemes, schemes for setting up compound semiconductors.
Way forward:
- As India is known for its fast growing ecosystem it is projected to cross the consumption of semiconductors by $110 billion by 2030.
- India is considered an attractive destination for investment due to various factors some of them being the building of digital infrastructure to connect over 1.3 billion Indians.
HS200 Booster: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully carried out the static test of the human-rated solid rocket booster (HS200) solid rocket booster.
Key Highlights:
- The successful completion of this test marks a major milestone for the prestigious human space flight mission of ISRO, taking the space agency one more step closer to the keenly awaited Gaganyaan human spaceflight mission.
- The static test of HS200 for the Gaganyaan programme was completed at Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
About HS200:
- HS200 booster designed and developed at Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre, Thiruvananthapuram.
- The HS200 booster is the 'human-rated' version of the S200 rocket boosters used on the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk-III (GSLV Mk-III), also called the LVM3.
- The GSLV Mk-III rocket, which will be used for the Gaganyaan mission, will have two HS200 boosters that will supply the thrust for lift-off.
- The HS200 is a 20-metre-long booster with a diameter of 3.2 metres and is the world’s second largest operational booster using solid propellants.
- Since Gaganyaan is a manned mission, the GSLV Mk-III will have improvements to increase reliability and safety to meet the requirements of ‘human rating.’
- Out of the three propulsion stages of the GSLV Mk-III, the second stage known as L110-G uses liquid propellant while the third stage C25-G with cryogenic propellant are in the final phase of qualification, including tests with static firing.
About Gaganyaan Mission:
- Gaganyaan Mission is India's maiden space mission to send a three-member crew to space for a period of five to seven days by 2022.
- The space mission was first announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi in 2018 in his independence day address to the nation.
- However, this mission was delayed due to COVID-19 pandemic.
- Ahead of the manned mission, ISRO plans to send two unmanned missions to space as part of the Gaganyaan mission.
About ISRO:
- It is an abbreviation for the Indian Space Research Organization.
- ISRO is the space agency of the Government of India (GoI) and was formed in 15 august 1969.
- It superseded the erstwhile “Indian National Committe For Space Research” (INCOSPAR) which was established in 1962 by the efforts of Independent India's first prime minister‚ Jawaharlal Nehru‚ and his close aide and scientist Vikram Sarabhai.
- In 1972, the Government of India had set up a Space Commission and the Department of Space (DOS), bringing ISRO under the DOS.
- ISRO then embarked on its mission to provide the Nation space based services and to develop the technologies to achieve the same independently.
- Its vision is to “harness space technology for natural development while pursuing space science research & planetary exploration”. ISRO built India’s first Satellite Aryabhata.
- It is headquartered in Bangalore, India.
- The current Chairman of ISRO is eminent rocket scientist Dr S Somanath.
Use of Disposable in Cement Mixture: Researches recently demonstrated a solution to an environmental problem regarding single used masks.
- Single-use masks that were being used during the pandemic are now turning out to be an environmental problem.
- Disposable masks do not decay for decades and therefore they pose a risk to the ecosystem.
Key facts:
- They have found a way of to use these masks into a mixture of cement to create more durable and stronger concrete.
- The researchers, in a paper that was published in the journal named Materials Letters have demonstrated that the mixture made using mask materials was 47 percent stronger than the cement that is commonly used.
- This study was led by Zhipeng Li, a graduate student in WSU’s Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering.
- The study was funded by the US Department of Transportation’s National Center for Transportation Infrastructure Durability and Life Extension.
The global effect of Cement production:
- Cement production is a carbon-intensive process that is responsible for 8 percent of the world’s carbon emissions.
About the test:
- If concrete is reinforced by using microfibres, the amount of cement needed for a project can be reduced.
- Also, the concrete lasts longer thus saving money and cutting down on carbon emissions.
- There are fibres present in medical masks that can be useful for this industry.
- A process was developed by the researchers to fabricate tiny mask fibres that ranged from 5 mm to 30 mm in length. The fibres were then added to the cement concrete so as to strengthen it and prevent it from cracking.
- The cotton and metal loops from the masks were removed and then they were cut and incorporated into ordinary Portland cement.
- The mask microfibres were mixed into a solution of graphene oxide (GO) which provides an ultrathin layer that strongly adheres to the fibre surfaces to aid in the waste-mask mix (WMM) adhering to the cement mix.
- These were then incorporated into Portland cement, the most used type of cement in the world, which consists of just concrete, mortar and grout.
However, without the fibres, there will be microscopic cracks in the concrete that would later lead to wider cracks and the failure of the material.
Conclusions:
- Researchers are conducting more studies to test the idea about mask microfibres improving the durability of the concrete as well as protecting it from deicing chemicals and frost damage.
W Boson: Researchers from Collider Detector at Fermilab (CDF) Collaboration, in the U.S., recently announced, through a paper in Science, that they have made a precise measurement of the mass of the so-called W boson, one of nature's force-carrying particles.
Key Points:
- They stated that this precisely determined value did not match with the estimates from the standard model of particle physics.
- The recent experiment which measured the mass of the W boson as 80,433.5 +/- 9.4 Mev/c2 is more than what is expected from the standard model.
- The expected value using the standard model is 80,357 +/- 8 MeV/c2. This implies the incompleteness of the standard model description.
- This is a major claim, since the standard model has been extraordinarily successful in the past decades
- This mass discrepancy of the W boson needs to be checked and confirmed to the same accuracy by other research facilities.
What is W Boson?
- Discovered in 1983 at CERN, located on the Franco-Swiss border, the W boson is a fundamental particle.
- In contrast to the photon, which is massless, the W bosons are quite massive, so the weak force they mediate is very short ranged.
- Together with the Z boson, it is responsible for the weak force, one of four fundamental forces that govern the behaviour of matter in our universe.
- Particles of matter interact by exchanging these bosons, but only over short distances.
- The W boson, which is electrically charged, changes the very make up of particles.
- It switches protons into neutrons, and vice versa, through the weak force, triggering nuclear fusion and letting stars burn.
- This burning also creates heavier elements and, when a star dies, those elements are tossed into space as the building blocks for planets and even people.
- It is responsible for the nuclear processes that make the sun shine and particles decay.
What are the four fundamental forces at work in the universe?
There four fundamental forces at work in the universe are -
1.The strong force,
2.The weak force,
3.The electromagnetic force, and
4.The gravitational force.
- They work over different ranges and have different strengths.
- Gravity is the weakest but it has an infinite range.
Bharat Drone Mahotsav 2022: India's biggest Drone Festival - Bharat Drone Mahotsav 2022 was recently inaugurated at Pragati Maidan in New Delhi by the Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
Key Highlights of the Mahotsav:
- The inauguration ceremony was also attended by Union Ministers Shri Narendra Singh Tomar, Shri Giriraj Singh, Shri Jyotiraditya Scindia, Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw, Shri Mansukh Mandaviya, Shri Bhupendra Yadav, many Ministers of State and leaders and entrepreneurs of drone industry.
- PM modi interacted with Kisan drone pilots, witnessed open-air drone demonstrations and interacted with startups in the drone exhibition centre.
- He also gave away 150 drone pilot certificates.
- He highlighted the importance of drone technology in the fields of defence, disaster management, agriculture, tourism, film and entertainment.
- He pointed out that the use of this technology is bound to increase in the coming days.
- Appreciating the use of drones in PM-SVAMITVA scheme, he said, 65 lakh property cards have been generated with the help of drones.
- Drone industry in India is estimated to achieve 15 thousand crore rupees turnover by the year 2026.
- He also narrated the use of drones in his official decision making through examples of PRAGATI reviews and Kedarnath projects.
About Bharat Drone Mahotsav 2022:
- The Bharat Drone Mahotsav 2022 was a two day festival which took place from 27-28 May 2022.
- Several industry leaders, government officials, foreign diplomats, representatives from Public Sector Units (PSUs), private companies and drone start-ups are participated in the Mahotsav.
- They deliberated upon India’s Civil Aviation sector.
- More than 70 exhibitors showcased various drone use cases.
- Additionally, it saw the introduction of products, panel talks, flying demos, and the display of a Made in India Drone Taxi prototype, among other things.
Sports
KIUG 2021 Logo, Mascot and Anthem: The Khelo India University Games 2021 (KIUG 2021) logo, jersey, mascot and anthem were recently launched by Union Minister of Youth Affairs and Sports Anurag Singh Thakur and Governor of Karnataka, TC Gehlot at the Sree Kanteerava Stadium in Bengaluru.
Key details of KIUG 2021 event:
- Gehlot launched the logo and official mascot of the games – Veera while Thakur launched the official jersey of the games as well as the anthem, sung by Chandan Shetty and Nikhil Joshi.
- The logo of the event features the iconic Vidhana Soudha building, the Legislative House in Bengaluru with two elephants on either side.
- The mascot of KIUG 2021 is also an elephant, named Veera.
- The theme song has been composed by Kannada rapper Chandan Shetty.
- The official Khelo India mobile app was also launched on the occasion.
- Karnataka has also taken the decision to make it a Green Game that will not use single-use plastic and follow environment-friendly practices.
- As part of the Games being green, everything used in the Games outside the field of play will be made of reusable material.
- In addition, electric vehicles (EV) will be used for transportation.
- All waste will be segregated as wet and dry at the source in every venue.
- It will therefore be a zero-waste, zero-plastic Games.
About KUIG 2021:
- The 2nd edition of KIUG 2021 will be held in Karnataka between April 24 and May 3, 2022.
- KIUG 2021 was postponed due to the Covid crisis.
- The first edition was hosted by Odisha in 2020 at the Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology (KIIT).
- The upcoming Games will feature indigenous sports yogasana and mallakhamb along with 18 other sports.
- Around 4,500 athletes from across India are expected to participate in the event.
About Khelo India University Games (KIUG):
- The Khelo India University Games (KIUG) is a national level multi-sport event held in India.
- Athletes from universities across the country compete in different sports disciplines.
- The KUIG is a platform intended to identify and train capable athletes in the age group of 18 to 25 years for the Asian Games, CWG and the Olympics.
- It is organized by Sports Authority of India (SAI) and Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports along with Association of Indian Universities, Indian Olympic Association and National Sports Federation.
- It is the largest university level sports competition in India.
The inaugural edition held in Odisha started on 22 February and concluded on 1 March 2020.
Madrid Open: Teenager Carlos Alcaraz has become the first tennis player to consecutive victories over tennis legends at the Madrid Open final on May 7th.
Key Highlights:
- The 19-year-old Spaniard clinched a stirring 6-7(5), 7-5, 7-6(5) win over Novak Djokovic at the ATP Masters 1000 event.
- He beat Rafael Nadal in the quarterfinals to pave way for the biggest win of his career against world no. 1 Djokovic in the semifinals.
- He went on to win the men's singles event after beating Alexander Zverev in the finals.
- Alcaraz’s outstanding 2022 season has seen the teenager win a maiden Masters 1000 title in Miami and break the Top 10 of the ATP Rankings for the first time.
Sporting Events of National Importance: The Information and Broadcasting Ministry has notified several sporting events as that of national importance under the Sports Broadcasting Signals (Mandatory Sharing with Prasar Bharati) Act.
Key Details:
- The notification, which supersedes the earlier one issued in March 2021, has declared all Olympics Games, Commonwealth Games and Asian Games as events of national importance.
The following list is not exhaustive:
Under the cricket category:
- All official One-Day, Twenty-20 and Test matches played by the Indian team and all International Cricket Council (ICC) Test matches featuring India; semi-finals and finals of ICC One-Day international World Cup; semi-finals and finals of ICC Twenty-20 World Cup have been recognised.
Under the tennis category
- It includes all matches featuring India in Davis Cup, and in Grand Slam tournaments, finals of men’s singles, women’s singles and all matches featuring Indian player from the quarter-finals onwards.
Under the hockey category
- The notification states that under the hockey category, World Cup - all matches featuring India and semi-finals and finals; Champions Trophy - all matches featuring India and finals; Indira Gandhi Gold Cup for women semi-finals and finals; Hockey India sub-junior national championship and Hockey India Academy National Championship; Hockey Men’s Junior Men World Cup (only when India is the host country); Sultan Azlan Shah Cup - all matches featuring India, semi-finals and finals; and International Hockey Federation - Hockey Pro League matches have been recognised.
Under football category
- The football category includes World Cup - opening match, quarter finals, semi-finals and finals; Asia Cup - all matches featuring India and semi-finals and finals; Santosh Trophy - semi-finals and finals; Asian Women’s Football Cup (only when India is the host country); under-17 Federation Internationale de Football Association Women’s World Cup (only when India is the host country); and World Cup (under-17) - opening match, quarter finals, semi-finals and finals.
Under badminton category
- The badminton events are all England Open Badminton Championship - all matches featuring Indian players, semi-finals and finals; and Badminton World Federation World Cup Championship - all matches featuring Indian players, semi-finals and finals.
Under Kabaddi World Cup
- While Kabaddi World Cup - all matches featuring India, semi-finals and finals - has also been recognised.
Other Sporting events of National Importance:
- Khelo India Games, Khelo India School Games, Khelo India Youth Games, Khelo India University Games, Khelo India Games for differently-abled persons, Khelo India Games for Indigenous Sports and Khelo India Winter Games have also been listed as events of national importance.
- The other events include International Shooting Sport Federation World Cup, Commonwealth Shooting Championship and Commonwealth Archery Championship (only when India is the host country), and international events organized by the National Sports Federations have been recognized by the Central government.
Monaco F1 Grand Prix 2022: Red Bull’s Sergio Perez registered his first Formula One win of the season in the rain-marred Monaco Grand Prix on 29th May 2022.
Key Highlights:
- He won the Formula 1 (F1) Grand Prix (GP) De Monaco 2022 with 25 points, held at Circuit de Monaco, Monaco, Europe.
- With this victory, Sergio Pérez becomes the first Mexican to win the Monaco Grand Prix, and the first North American to win it since Gilles Villeneuve in 1981.
- The Second position was occupied by the Ferrari racing driver Carlos Sainz Jr. (Spanish) with 18 points.
- The third position was taken by the Belgian-Dutch racing driver Max Emilian Verstappen who drove for Red Bull Racing. The Monacan race driver Charles Leclerc who drove for Ferrari finished the race fourth.
The event took place from May 27 to May 29 2022.
UEFA Champions League: Real Madrid became European champion for a record-extending 14th time after beating Liverpool 1-0 in a Champions League final.
Champions League final started 37 minutes late because of disturbing crowd issues outside the Stade de France near Paris.
Key Highlights:
- Brazil winger Vinícius Júnior applied a close-range finish in the 59th minute from Federico Valverde’s drive across the face of goal, securing a win that gave Madrid coach Carlo Ancelotti a record fourth European Cup title.
- Madrid cemented its status as the king of European soccer, given the Spanish giant owns double the number of European Cups as the No. 2 on the list, AC Milan.
- Liverpool stayed on six.
Arts
Johar Greetings: The 15th President of India, Droupadi Murmu, assumed office with a ‘Johar’ greeting to the country.
About Johar:
- ‘Johar’essentially means salutation and welcome.
- It is used within the tribal communities of Jharkhand, and in parts of Chhattisgarh and Odisha.
- According to several tribal leaders from Jharkhand, the word ‘Johar’ also means ‘paying respect’.
- Tribal communities are nature worshippers and follow Sarna religion code, although it is not an official religion.
- There are 32 tribal communities in Jharkhand who speak different dialects.
- Almost all, including tribal Christians, use the word ‘Johar’ along with some other words for salutation.
- Johar, is predominantly used by Santhali, Munda and Ho communities that share some similarities.
- People belonging to the Oraon community use the word ‘Jai Dharam’, apart from Johar, as a salutation.
Har Ghar Tiranga: The Government has declared that spending on ‘Har Ghar Tiranga’ campaign is a Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) activity under Companies Act.
Key Points:
- The Minstry of Corporate Afffairs (MCA) has stated that that companies can spend their CSR funds for activities related to the Har Ghar Tiranga campaign.
- MCA has clarified that `Har Ghar Tiranga’ campaign under the aegis of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav, is aimed to invoke the feeling of patriotism in the hearts of the people and to promote awareness about the Indian National Flag.
- The Government is organising the “Har Ghar Tiranga Campaign” as a part of Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- The campaign is intended to encourage people to hoist national flag at their home to celebrate the 75th years of India’s independence.
- Under the Companies Act, 2013, certain class of profitable companies are required to shell out at least 2% of their three-year annual average net profit towards CSR activities.
- Accordingly, MCA has issued General Circular No. 08/2022 dated 26th July 2022.
- The circular states that spending of CSR funds for the activities related to this campaign, such as mass scale production and supply of the National Flag, outreach and amplification efforts and other related activities, are eligible CSR activities under item no. (ii) of Schedule VII of the Companies Act, 2013 pertaining to promotion of education relating to culture.
- It has been stated that the companies may undertake the aforesaid activities, subject to fulfillment of the Companies (CSR Policy) Rules, 2014 and related circulars/clarifications issued by the Ministry thereof, from time to time.
Objective of Har Ghar Tiranga Initiative:
- The main objective of this initiative is to invoke the feeling of patriotism in heats of people.
- The campaign also seeks to raise awareness on the Indian National Flag.
Economics
Critical Information Infrastructure: The Union Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) has declared IT resources of ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank and UPI managing entity National Payment Corporation of India (NPCI) as ‘critical information infrastructure’ (CII).
Key Points:
- They have been declared as CII under Section 70 of the IT Act, 2000.
- The Computer resources of their associated dependencies will also be regarded as the protected systems.
- IT resources under CII include Core Banking Solution, Real Time Gross Settlement and National Electronic Fund Transfer (NEFT) comprising Structured Financial Messaging Server.
- The notification to this effect was issued on June 16, 2022.
Why the protection of CIIs is necessary?
- IT resources are the backbone of numerous crucial processes in a nation's infrastructure and given their interconnectedness, disruptions can have a cascading effect across sectors.
- Power grid outages caused by information technology issues can have a devastating effect on other industries, including banking and healthcare.
- The decision to put IT resources under CII has been taken due to cypber attacks which raised the need for a protected system by all the banks and financial institutions.
For instance -
Recent attacks on various infrastructure and businesses like
- 2017 WannaCry and NotPetya ransomware attacks,
- The 2015 attack on Ukrainian power grids and
- 2010 Stuxnet attack on Iranian nuclear reactor.
- Cyber Wars: States are deploying cybersecurity attacks in order to have geo-political gains.
What is critical information infrastructure?
- The "Critical Information Infrastructure" (CII) is a "computer resource" as defined by the Information Technology Act of 2000.
- The incapacitation or loss of such a resource has a crippling effect on national security, public health, the economy, or public safety."
- According to the official notification, any harm to them could have an impact on national security, and anyone unauthorised accessing these resources could face a 10-year prison sentence.
Who has the power to declare entity as Critical Information Infrastructure?
- The Union government, under Section 70 of the IT Act, 2000 has the power to declare any data, IT network, and database or communications infrastructure as Critical Information Infrastructure in order to protect that digital asset.
- The government, under the Act, has the power to declare any data, database, IT network or communications infrastructure as CII to protect that digital asset.
Protection of CIIs in India:
- The National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC), established in 2014 is the nodal agency taking all measures for protecting CIIs in India.
NCIIPC is mandated to guard CIIs from:-
- Unauthorized access,
- Use,
- Modification,
- Incapacitation,
- Disclosure,
- Disruption, or
- Distraction”.
- It monitors and forecasts national-level threats to CII for policy guidance, situational awareness and expertise sharing for early alerts or warning.
- In case of threat to CII, the NCIIPC may call for information and provide directions to critical sectors or persons having a critical impact on CII.
- As per NCIIPC, the basic responsibility for protecting the CII system shall lie with the agency running that CII.
About NCIIPC:
- The National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC) is an organization of the Government of India (GoI).
- NCIIPC was created under the Section 70A of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (amended 2008), through a gazette notification in 2014.
- It is designated as the National Nodal Agency in terms of Critical Information Infrastructure Protection.
- It was founded on 16 January 2014
- It is a unit of the National Technical Research Organisation (NTRO) and therefore comes under the Prime Minister’s Office (PMO).
NCIIPC has broadly identified the following as ‘Critical Sectors’:
- Government.
- Strategic & Public Enterprises
- Power & Energy.
- Banking, Financial Services & Insurance.
- Telecom.
- Transport.
Vision:
Its vision is "To facilitate safe, secure and resilient Information Infrastructure for Critical Sectors of the Nation."
11th Agricultural Census 2021-22: Union Minister Narendra Singh Tomar on July 28, 2022 launched the 11th Agriculture Census 2021-22.
Key Points about Agricultural Census 2021-22:
- The fieldwork for the census will start in August 2022.
- It was launched to gather data on several parameters, including operational holdings.
- For first time the data will be collected via smartphones and tablets for the first time.
- The agriculture Census is conducted every 5 years.
- The census is being undertaken now after a delay due to COVID-19 pandemic.
- The main focus of the census is to increase the income of the farmers and empower them by organizing small farmers.
Operational Guidelines for Census:
On the occasion, Shri Tomar also released the Handbook on Operational Guidelines for Census for the use of States/UTs and launched the Data Collection Portal/App.
The new initiatives highlighted in the presentation include
- The use of digital land records like land title records and survey reports,
- Collection of data through app/software using smartphone/tablet,
- Complete enumeration of all villages in states with non-land records during Phase-I as done in states having land records, and
- Real-time monitoring of progress and processing.
Agriculture Census in India:
- Agricultural Census is the main source of information on a variety of agricultural parameters at a relatively minute level, such as the number and area of ​​operational holdings, their size, class-wise distribution, land use, tenancy and cropping pattern, etc.
- The Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare (DA&FW) conducts Agriculture Census in India every 5 years in collaboration with States and Union Territories (UTs) following standard concepts, definitions and methodology.
- The agriculture Census Scheme is being undertaken by Agriculture Ministry from 1970-71.
- Since then ten Agriculture Censuses have been conducted.
- The last edition of the Agriculture census was conducted in 2015-16.
- It is being conducted in India, on the basis of guidelines of decennial World Census of Agriculture (WCA) that has been formulated by Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations.
Note:
- The Agriculture Census Scheme was converted to Central Sector Scheme, from a Centrally-Sponsored Scheme, in 2007-08.
- Therefore, the central government provides 100% financial assistance to States or UTs for payment of salaries, honoraria, office expenses, and printing of schedules, etc.
International Bullion Exchange IIBX: Prime Minister Narendra Modi on the 29th of July 2022 launched ‘India International Bullion Exchange (IIBX)’, at the Gujarat International Finance Tec-City (GIFT City) near Gandhinagar, Gujarat.
Key Points:
- IIBX is India’s first international bullion exchange.
- The bullion exchange is expected to facilitate efficient price discovery with the assurance of responsible sourcing and quality, apart from giving impetus to the financialization of gold in India, given that gold is tightly regulated in the country.
- At present, there are nominated banks and agencies which have been approved by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to conduct trade or import gold and sell it to dealers.
- The IIBX with its technology-driven solutions seeks to facilitate the transition of Indian bullion market towards a more organized structure by granting qualified jewelers’ direct access to import gold directly through the exchange mechanism.
- The exchange, which was announced in Budget 2020, will sell physical gold and silver.
- The exchange will be open for jewelers with a net worth of Rs 25 crore and above to participate.
Other inaugurations in GIFT-City:
- PM Modi also laid the foundation stone for a Rs 200 crore headquarters building of the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA).
- He presided over the exchange of memorandums of understanding (MoUs) by IFSCA with foreign regulatory authorities and the Department of Space.
- He launched the NSE IFSC-SGX Connect platform which is a framework between NSE’s subsidiary in GIFT IFSC and Singapore Exchange.
- Through this platform, clients, investors and trading members of SGX who used to trade in NSE listed Indian securities through SGX would now trade in these securities through NSE IFSC.
Defence
Key Amendments to Agnipath Scheme: Amid outrage and violent protests, the central government has rolled out several amendments and support measures in the recently unveiled Agnipath recruitment scheme into the armed forces.
This has been done to calm down the protestors because protestors in several parts of the country are of the view that, this scheme will limit the opportunities for permanent jobs in defence forces, that provide fixed salaries, pensions along with other benefits.
About Agnipath scheme:
- Under the scheme, youths will be enrolled for four years into service.
- After completion of the tenure, 25% of Agniveers will be retained or re-enlisted into regular cadre.
- 75% will be demobilized with a generous exit package of Rs 11.71 lakh,.
- They will be given priority in government services like CAPFs, state police forces.
What are the amendments?
The lists of amendments made in the Agnipath scheme are as follows:
- Defence Minister Rajnath Singh has approved reservation of 10 per cent of the job vacancies in Ministry of Defence for Agniveers who meet the requisite eligibility criteria.
- It would be in addition to existing reservation for ex-servicemen.
- The 10 percent reservation will be implemented in the Indian Coast Guard and defence posts, and all the 16 Defence Public Sector Undertakings (HAL, BEL, BEML, BDL, GRSE, GSL, HSL, MDL, Midhani, AVNL, AWEIL, MIL,YIL, GIL, IOL, TCL).
- The Centre has decided to increase the upper age limit in the eligibility criteria of Agnipath scheme from 21 years to 23 years for the recruitment cycle of 2022.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has announced a 10 per cent reservation in vacancies and upper age limit for recruitment in Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs) and Assam Rifles for Agniveers after completing four years.
- Thus, the upper age limit for CAPFs now stands at 26 years.
- For the first batch of Agniveers, the age relaxation will be of five years taking it to 28 years.
- The Directorate General of Shipping under Ministry of Ports Shipping and Waterways (MoPSW) along with Indian Navy has announced a system for the smooth induction of the Agniveers into the Merchant Navy.
- The National institute of Open Schooling (NIOS) under Department of school education has announced that it will start a special programme, to enable 10th pass Agniveers to further their education and obtain 12th class pass certificate through customized courses.
- A three-year skill-based bachelor’s degree programme for Agniveers will be launched by the Ministry of Education (MoE) in order to recognise the skill of the Agniveers and to equip them for various job roles in civilian sector.
- Skill India and the ministry of skill development and entrepreneurship will work collaboratively with the Armed Forces to train students in additional skills to make them better suited for civilian jobs.
Cantonments Act, 2006: The Government of India (GoI) has proposed amendments in the Cantonments Act, 2006.
Key Points:
- The amendment proposes incorporating provisions for imparting, inter-alia, greater democratisation to Cantonment Boards including direct election of Vice-President.
- This information was given by Defence Minister Rajnath Singh in a written reply in the Lok Sabha.
- He said the draft bill is under finalization.
- The elections to Cantonment Boards are proposed to be held thereafter.
- Defence Minister stated that a framework for cutting out civil areas of certain Cantonments and to merge them with neighbouring State municipalities is under consultation with concerned States.
- He said that this will provide uniformity in local governance and greater ease of living for citizens in the process.
- He also said that several suggestions were received from public representatives and general public on the administrative structure of the Cantonment Boards.
- The suggestions mainly pertain to direct election of Vice-President, financial powers to Vice-President, empowerment of Civil Area Committee, power to vary the constitution of Boards, and power to suspend decisions of the Board.
Indigenous Aircraft Carrier (IAC) ‘Vikrant: On July 28, 2022, the Indian Navy created maritime history by taking delivery of the prestigious Indigenous Aircraft Carrier (IAC) ‘Vikrant from her builder Cochin Shipyard Limited (CSL), Kochi.
Key Highlights:
- With the delivery of Vikrant, India has joined a select group of nations having the niche capability to indigenously design and build an Aircraft Carrier.
- The Indigenous Aircraft Carrier would soon be commissioned into the Indian Navy as Indian Naval Ship (INS) Vikrant which would bolster India's position in the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) and its quest for a blue water Navy.
About Vikrant:
- Vikrant has been designed by Indian Navy's inhouse Directorate of Naval Design (DND) and built by CSL, a Public Sector Shipyard under Ministry of Shipping (MoS).
- The carrier is christened after her illustrious predecessor, India's first Aircraft Carrier which played a vital role in the 1971 war.
- The 262 m long carrier is substantially longer and more modern than her predecessor, with a full displacement of around 45,000 tonnes.
- The ship is powered by four Gas Turbines totaling 88 MW power and has a maximum speed of 28 Knots.
- It has been built at an overall cost of close to Rs. 20,000 Crs.
- The project has been progressed in three Phases of contract between MoD and CSL, concluded in May 2007, Dec 2014 and Oct 2019 respectively.
- The ship's keel was laid in Feb 2009.
- It was launched in Aug 2013.
- With an overall indigenous content of 76%, IAC is a perfect example of the nation's quest for "Aatma Nirbhar Bharat” and provides thrust to Government's 'Make in India' initiative.
Environment
5 New Ramsar Sites: India has designated five new wetlands of International importance as Ramsar Sites.
The Ramsar sites have been increased from 49 to 54 Ramsar sites.
The five newly designated wetlands are:
- Karikili Bird Sanctuary, Tamil Nadu
- Pallikaranai Marsh Reserve Forest, Tamil Nadu
- Pichavaram Mangrove, Tamil Nadu
- Pala wetland, Mizoram
- Sakhya Sagar, Madhya Pradesh.
About:
Karikili Bird Sanctuary:
- Karikili Bird Sanctuary is a 61.21-hectare protected area located in the Kancheepuram District of Tamil Nadu.
- The sanctuary is about 75 km from Chennai, south of Chengalpattu.
Pallikaranai Marsh Reserve Forest:
- Pallikaranai wetland is a freshwater marsh located in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
- It is the only surviving wetland ecosystem of the city and among the few and last remaining natural wetlands of South India.
Pichavaram Mangrove:
- Pichavaram mangrove is located in a village near Chidambaram in Cuddalore District of Tamil Nadu.
- The mangrove is one of the largest mangrove forests in India, covering 1100 hectares.
Pala wetland:
- The Pala wetland is the largest natural wetland in Mizoram.
- The renowned landmark is surrounded by green woodlands and home to rich diversity of animal species including a range of animals and birds.
Sakhya Sagar:
- Sakhya Sagar Lake is an integral part of the beautiful ecology of the Madhav National Park in Shivpuri, Madhya Pradesh.
Ramsar Wetlands in India:
- India’s Ramsar wetlands are spread over 11,000 sq.km — around 10% of the total wetland area in the country — across 18 States.
- No other South Asian country has as many sites, though this has much to do with India’s geographical breadth and tropical diversity.
- The main goal of the Ramsar wetlands in India is to develop and maintain an international network of wetlands that are important for the conservation of global biological diversity and sustaining human life.
What is Ramsar Site?
- A Ramsar Site is a wetland site designated to be of international importance under the Ramsar Convention.
About Ramsar Convention:
- The Ramsar convention is an intergovernmental environmental treaty that was established by UNESCO on February 2, 1971.
- The convention got its name from Ramsar city in Iran on the Caspian Sea, where the treaty was signed.
- The Ramsar convention came into force in 1975.
- It provides for international cooperation and national action regarding conservation of wetlands and sustainable use of their resources.
- The Ramsar convention identifies wetlands of international importance across the globe, especially those that are home to diverse biodiversity.
American bullfrog and the Brown tree snake: According to a study published in Scientific Reports, two invasive species, the American bullfrog and the brown tree snake, cost the world an estimated $16 billion between 1986 and 2020, by causing problems ranging from crop damage to power outages.
Key points:
- Scientists have discovered two invasive species that are responsible for economic damage caused by invading pests than any other.
- The American bullfrog and brown tree snake have collectively caused $16.3bn (£13.4bn) in global damage since 1986.
- In addition to ecological harm, the invasive pair have ruined farm crops and triggered costly power outages.
- The brown tree snake, or boiga irregularis, has multiplied uncontrollably on Pacific islands including Guam and the Marianna Islands, where the species was introduced by U.S. troops in World War II.
- The snake's massive population now causes mass power cuts because they slither over electrical wires and cause expensive damage.
- In Europe exploding numbers of American bullfrogs have required ambitious and costly management programmes.
- Officials have been obliged to erect pricey frog-proof fencing around known mating locations in order to stop the spread of the brown-and-green frog known as lithobates catesbeianus, which can grow up to 30cm (12 inches) in length and half a kilo (17.6oz) in weight.
- The amphibian is said to eat nearly anything, including other bullfrogs.
- Another species, the common coqui frog, was blamed for causing economic damage in a different way: their extremely loud mating song is believed to have triggered a decline in property values in the areas where they have infested.
This signals the need for investment controlling global transport of invasive species in order to prevent having to pay for mitigation after the invasions happen.
Indian Policy
New Norms for Mission Vatsalya: Ministry of Women and Child Development (WCD) is implementing a centrally sponsored scheme through State/UT Governments namely Mission Vatsalya.
Key Points:
- Under it, a monthly grant of Rs. 4000/- per child is provided for family based non-institutional care including Sponsorship (kinship) or Foster Care or After Care.
- The Mission Vatsalya in partnership with States and Districts provides support to a 24x7 helpline service for children as defined under the JJ Act, 2015.
- It is aimed at setting up Cradle Baby Reception Centres in at least one Specialized Adoption Agency (SAA), preferably government run orgaization, in each District, to save the abandoned children and look after them with due care and affection till he/she is given in adoption.
- It is implemented in partnership with States/UTs as per prescribed norms in the guidelines.
- Under Mission Vatsalya Scheme, States/UTs need to focus on special need children in Child Care Institutions (CCIs), who are not able to go to school due to physical/mental disabilities.
- Special provisions are required to be made in the CCIs to provide services including Special Educators/therapist and Nurse required for such children in CCIs for occupational therapy, speech therapy, verbal therapy and other remedial classes as per the children’s need.
- The capacity building of the Special Unit staff in sign language, Braille etc. are undertaken with help of resource institutions by States/UTs for such Homes.
About Mission Vatsalya:
- Mission Vatsalya is a centrally sponsored scheme for child protection services in the country since 2009-10 for the welfare and rehabilitation of children.
- It is essentially a renamed version of the pre-existing scheme called Child Protection Services.
Implementation of Mission Vatsalya:
- It is being implemented by the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- All the States/UTs have signed the Memorandum of Undertaking (MoU) with the Ministry for implementation of the Scheme.
- Mission Vatsalya will be implemented as a centrally sponsored scheme as per prescribed cost sharing ratio between the Centre and State/UT Governments.
Objectives:
The objective of Mission Vatsalya are as follows:
- To secure a healthy and happy childhood for each and every child in India,
- To ensure opportunities to enable them to discover their full potential and assist them in flourishing in all respects, in a sustained manner,
- To foster a sensitive, supportive and synchronized ecosystem for development of children,
- To assist States/UTs in delivering the mandate of the Juvenile Justice Act 2015 and achieve the SDG goals
Components under Mission Vatsalya include:
- Improve functioning of statutory bodies;
- Strengthen service delivery structures;
- Upscale institutional care/services;
- Encourage non-institutional community-based care;
- emergency outreach services;
- Training and capacity building.
Funding Mechanism:
- It will be implemented as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme in partnership with state governments and UT administrations, with a fund-sharing pattern in a 60:40 ratio.
- However, for the eight states in the Northeast — as well as Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and the UT of Jammu and Kashmir — the Centre and state/UT’s share will be 90:10
Background:
Prior to 2009, the WCD Ministry implemented the following three schemes for children in need of protection.
- The juvenile justice programme for children in need of care and protection as well as children in conflict with the law,
- The integrated programme for street children,
- The scheme for assistance to children's homes.
In 2010, these three schemes were merged into a single plan known as the Integrated Child Protection Scheme.
In 2017, it was renamed "Child Protection Services Scheme," and again in 2021-22 as Mission Vatsalya.
National Anti-Doping Bill, 2021: The National Anti-Doping Bill, 2022 was passed in the Lok Sabha on 27th July 2022.
Key Points:
- The Bill was introduced in December 2021 by Union Sports Minister Anurag Thakur.
- It was passed considering that, legislative powers would put brake on doping.
Important provisions of the bill:
- Bill would help in establishing National Board of Anti-Doping in sports, comprising of competent and independent personnel.
- It seeks to achieve time-bound justice for athletes.
- It will improve cooperation among agencies to fight against doping.
- It also seeks to give effect to the UNESCO International Convention against doping in sports and compliance of such other obligations and commitments.
- It will help in setting up robust, independent mechanism for anti-doping adjudication.
- It will provide legal sanctity to functioning of NADA and National Dope Testing Laboratory (NDTL).
- The legislation prohibits athletes, athlete support personnel, and other persons from engaging in doping in sports.
- Under the new legislation, violation of anti-doping rules may result in disqualification of results including forfeiture of medals, points, and prizes, ineligibility to participate in a competition or event for a prescribed period, and financial sanctions.
- It would lead to setting up of more dope testing laboratories in India, besides providing support in academic research and manufacture of things related to anti-doping.
- It would lead to setting up of more dope testing laboratories in India, besides providing support in academic research and manufacture of things related to anti-doping.
Thus, the National Anti-Doping Bill 2022 provide a statutory framework in the form of legislation, to stop doping in sports in India.
Presently, the National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA) has been performing anti-doping measures in accordance with the norms of World Anti-Doping Agency.
National Anti-Doping Agency (NADA):
- NADA is the national organisation, that promotes, coordinates, and monitor the doping control program in all forms of sports in country.
- It was established by Central Government, under the societies Registration Act.
- It deals with adoption and implementation of anti-doping rules and policies, in line with the World Anti-Doping Agency.
Indian polity
Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA): The Supreme Court has upheld the core amendments made to the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA).
Key Points:
• This act gives the government and the Enforcement Directorate (ED) virtually unbridled powers of summons, arrest, and raids, and makes bail nearly impossible while shifting the burden of proof of innocence on to the accused rather than the prosecution.
• The apex court called the PMLA a law against the “scourge of money laundering” and not a hatchet wielded against rival politicians and dissenters.
• The verdict came on an extensive challenge raised against the amendments introduced to the 2002 Act by way of Finance Acts.
• The court noted “Money laundering is an offence against the sovereignty and integrity of the country, It is no less a heinous offence than the offence of terrorism”.
• The three-judge Bench said the method of introduction of the amendments through Money Bills would be separately examined by a larger Bench of the apex court.
• Over 240 petitions were filed against the amendments which the challengers claimed to violate personal liberty, procedures of law and the constitutional mandate.
About PMLA, 2002:
• Prevention of Money Laundering Act, 2002 is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted by the NDA government to prevent money-laundering and to provide for confiscation of property derived from money-laundering.
• The Act and Rules notified there under impose obligation on banking companies, financial institutions and intermediaries to verify identity of clients, maintain records and furnish information in prescribed form to Financial Intelligence Unit - India (FIU-IND).
• The act was amended in the year 2005, 2009 and 2012.
Objectives:
The PMLA seeks to combat money laundering in India and has three main objectives:
• To prevent and control money laundering.
• To confiscate and seize the property obtained from the laundered money; and
• To deal with any other issue connected with money laundering in India.
Who controls PMLA?
Under Section 19 of PMLA, the Director, Deputy Director, Assistant Director or any other officer authorized in this behalf by the Central Government by general or special order, has the power to arrest a person.
Flag Code of India, 2002: The Centre recently amended the Flag Code of India, 2002, allowing for the tricolour to be flown by the public both day and night.
Key Points:
- This is in line with the “Har Ghar Tiranga” campaign launched by the government from August 13 to 15 as part of the ‘Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav’ to commemorate 75 years of a progressive independent India.
Note: The display, hoisting and use of the Indian national flag is governed by the Flag Code of India, 2002 and the Prevention of Insults to National Honour Act, 1971.
Amendments made in Flag Code of India, 2002:
- First amendment permits tricolour to be flown day and night.
- Earlier, the tricolour was allowed to be flown from sunrise to sunset, irrespective of weather conditions.
The Flag Code of India, 2002 has been amended through an order on July, 20, 2022 and clause
(xi) of paragraph 2.2 of Part-II of the Flag Code of India, 2002 shall now be read as under: –
(xi) “where the Flag is displayed in open or displayed on the house of a member of public, it may be flown day and night”.
- Now, a member of the public, a private organisation or an educational institution is allowed to hoist the flag on all days and occasions, ceremonial or otherwise, consistent with dignity and honour of the national flag.
- Similarly, the Flag Code of India was earlier amended on December 30, 2021, allowing the use of polyester, apart from cotton, wool, silk and khadi for making hand-spun, hand-woven and machine-made flags.
The amendment in December 2021 said, “The National Flag shall be made of handspun and hand woven or machine made, cotton/ polyester/ wool/ silk khadi bunting.”
Shape and Size of the National Flag:
- The national flag of India must be in rectangular shape.
- It can be made in any size. But it shall follow a length to width ratio of 3:2.
Flag Code of India (FCI):
- The Flag Code of India 2002 was formulated by the Government of India.
- The Flag Code of India was operationalized on January 26, 2002.
- The use, display and hoisting of the National Flag in the country is guided by this code.
- It brings together all laws, conventions, practices, and instructions for the display of the National Flag.
The Flag Code of 2002 is divided into three parts:
- Part I of the Code contains a general description of the National Flag.
- Part II of the Code is devoted to the display of the National Flag by members of public, private organisations, educational institutions, etc.
- Part III of the Code relates to display of the National Flag by Central and State governments and their organisations and agencies.
Assembly sittings in 2021: Kerala has been ranked at top slot, in terms of holding State Assembly Session in 2021 with its House sitting for 61 days, the highest for any State.
Key Points:
In 2020, the state had slipped to the eighth slot in holding the sittings of the State Assembly during the first wave of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The report on the functioning of State Assemblies for 2021 is published by the PRS Legislative Research (PRS), a New Delhi-based think tank.
Important findings of the report:
- Kerala, in fact, between 2016 and 2019, remained at the top with an average of 53 days.
- Despite enjoying the record of having the highest number of sittings in 2021, Kerala (where the Left Democratic Front is in power since May 2016) had promulgated 144 ordinances, also the highest in the country.
- Kerala is followed by Odisha, with 43 sitting days.
- Karnataka is ranked at 3rd place, with 40 sitting days.
- Tamil Nadu has been ranked at 4th with 34 sitting days.
- Of the 28 State Assemblies and one Union Territory’s legislature, 17 met for less than 20 days.
- Andhra Pradesh, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura and Delhi met for less than 10 days.
- The figures for Uttar Pradesh, Manipur and Punjab were 17, 16 and 11, respectively.
- Between 2016 and 2021, the PRS points out, 23 State Assemblies met for an average of 25 days.
- As for the ordinance route, which should be, according to the Supreme Court, used under exceptional circumstances, 21 out of 28 States promulgated ordinances in 2021
Rules for minimum sittings:
- The National Commission to Review the Working of the Constitution (2000-02), headed by former Chief Justice of India M.N. Venkatachaliah, had prescribed the standards for working of legislatures.
- The standards provide that, House of State of Union Territories legislatures like Puducherry, with lower than 70 members shall meet for at least 50 days in a year.
- On the other hand, Houses like in Tamil Nadu shall meet for at least 90 days.
- States like Manipur, Punjab, Odisha, and Uttar Pradesh provides for minimum number of sitting days under Rules of Procedure.
- It prescribes 40 days sittings in Punjab while 90 days in Uttar Pradesh.
kangaroo Court: according to Chief Justice of India N V Ramana, A "growing number of media trials" is proving to be a barrier to delivering justice and “kangaroo courts” run by the media are causing harm to the health of the democracy.
About Kangaroo Court:
- A kangaroo court is a court that ignores recognized standards of law or justice, carries little or no official standing in the territory within which it resides, and is typically convened ad hoc.
- Oxford Dictionary defines kangaroo court as “an unofficial court held by a group of people in order to try someone regarded, especially without good evidence, as guilty of a crime or misdemeanour”.
- In a less literal sense, it is used to refer to proceedings or activities where a judgement is made in a manner that is unfair, biased, and lacks legitimacy.
- The origin of the phrase is not clearly known, but it is believed that the phrase “kangaroo court” originated in 19th-century America to describe any illegitimate court proceedings, as were often held by mutineers or prisoners.
- Why the word ‘kangaroo’ is used is also not clear, but there are several theories.
- The Collins Dictionary argues that it could be to evoke a sense that “justice progresses by leaps and bounds” in case of kangaroo court verdicts.
All India District Legal Services Authorities Meet: Prime Minister Narendra Modi addressed the inaugural session of the first All India District Legal Services Authorities Meet in New Delhi on July 30, 2022.
Key Points about the meet:
- The first-ever national level meet of District Legal Services Authorities (DLSAs) is being organized from 30-31 July 2022 at Vigyan Bhawan by National Legal Services Authority (NALSA).
- Chief Justice of India Justice N V Ramana, Supreme Court Judges Justice UU Lalit, Justice D Y Chandrachud, Union Minister, Shri Kiren Rijiju, Shri S. P. Singh Baghel, Other Supreme Court Judges, Chief Justices of High Courts, Executive Chairpersons of the State Legal Services Authorities (SLSAs) and Chairpersons of the District Legal Services Authorities (DLSAs) were present on the occasion.
- The Prime Minister also released a commemorative postal stamp on the ‘Right to free legal aid’.
- The meeting deliberated on the creation of an integrated procedure to bring homogeneity and synchronization across DLSAs.
About DLSAs:
- District Legal Services Authorities (DLSAs) is formed under Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987.
- There is a total of 676 District Legal Services Authorities (DLSAs) in the country.
- Section 9(1) of the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987 states that the DLSA is a body that shall be constituted by the State Government in consultation with the Chief Justice of the High Court.
- They are headed by the District Judge who acts as Chairman of the authority.
- Through DLSAs and State Legal Services Authorities (SLSAs), various legal aid and awareness programs are implemented by National Legal Services Authority.
- The DLSAs also contribute towards reducing the burden on courts by regulating the Lok Adalats conducted by NALSA.
About NALSA:
- The National Legal Services Authority (NALSA) was established on November 9, 1995, in accordance with the authority of Legal Services Authorities Act 1987.
- It was founded with the goal of organizing Lok Adalats to speedily resolve issues and offering free legal assistance to qualified candidates.
- Chief Justice of India acts as the patron-in-chief of NALSA.
- On the other hand, second senior-most Judge of Supreme Court of India acts as the Executive-Chairman.
- Similar mechanism is followed at the state level, headed by Chief Justice of High Courts and district level, headed by Chief Judges of District courts.
- Its main objective is to reduce burden of judiciary through speedy disposal of cases.
International
Khuvsgul Lake National Park: UNESCO recently added the Khuvsgul Lake National Park of Mongolia to the World Network of Biosphere Reserves along with 10 more new biosphere reserves in 8 countries, including three countries for the first time: Chad, Georgia and Zambia.
Two existing biosphere reserves in Spain have also been extended.
Key Points:
- The decision was made during the 34th session of the International Co-ordinating Council of the Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme, which is composed of 34 representatives of UNESCO Member States.
- The meeting took place from 13 to 17 June at UNESCO’s Headquarters in Paris, France.
About Man and Biosphere Programme:
- The Man and Biosphere Programme is an intergovernmental scientific program.
- It was set up in early 1970s by UNESCO.
- New biosphere reserves are designated every year by the MAB International Coordinating Council.
About Khuvsgul Lake:
- Khuvsgul Lake is located in the northern Mongolian province of Khuvsgul near the Russian border.
- Located at about 200 km west of Lake Baikal it freezes over completely in winter.
- The lake is 1,645 meters above sea level.
- It is 136 km long and 262 meters deep.
- It holds nearly 70 per cent of Mongolia’s fresh water, or 0.4 per cent of the world’s total.
Note: According to the Mongolian Ministry, a total of nine sites from Mongolia have so far been registered in the network.
UNESCO newly designated biosphere reserves:
- UNESCO has approved the designation of 11 new biosphere reserves in 9 countries, including three countries for the first time: Chad, Georgia and Zambia.
- Two existing biosphere reserves in Spain have also been extended.
The 11 newly designated biosphere reserves are:
- Sunshine Coast Biosphere Reserve (Australia)
- Doumba-Rey Biosphere Reserve (Cameroon)
- Sena Oura Biosphere Reserve (Chad)
- Dedoplistskaro Biosphere Reserve (Georgia)
- Three Alazani Rivers Biosphere Reserve (Georgia)
- Burabay Biosphere Reserve (Kazakhstan)
- Markakol Biosphere Reserve (Kazakhstan)
- Khuvsgul Lake Biosphere Reserve (Mongolia)
- Harrat Uwayrid Biosphere Reserve (Saudi Arabia)
- Kafue Flats Biosphere Reserve (Zambia)
- Chimanimani Biosphere reserve (Zimbabwe)
Two extensions:
- El Hierro Biosphere Reserve (Spain)
- Sierra del Rincón Biosphere Reserve (Spain)
With the new designations, the World Network of Biosphere Reserves totals 738 sites in 134 countries.
About World Network of Biosphere Reserves:
- UNESCO's World Network of Biosphere Reserves comprises biosphere reserves, which are internationally declared protected regions.
- The reserves are intended to show how nature and people may coexist in harmony.
- They are created under Man and the Biosphere Programme.
- It comprises of a dynamic and interactive web network.
- It strives to encourage harmonious integration of people and nature to attain sustainable development by means of participatory dialogue, poverty reduction, human well-being improvements, knowledge sharing, and respect for cultural values.
International Day for Countering Hate Speech 2022: The International Day for Countering Hate Speech is observed in June 18.
Key Points:
- This day is observed to highlight the need for combating hate speech and promoting tolerance and dialogue between different communities.
- According to the UN, hate speech is any kind of speech or writing that attacks or discriminates against a person or a group based on religion, ethnicity, nationality, descent, gender, race, color, or any other identity factor.
- This year marks the first time the day will be observed.
Theme:
The first International Day of Countering Hate Speech was observed under the theme “Role of education to address the root causes of hate speech and advance inclusion, non-discrimination, and peace”.
History:
- In July 2021, the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) adopted a resolution “promoting inter-religious and intercultural dialogue and tolerance in countering hate speech”.
- The global body also drew attention to concerns over the proliferation of hate speech all around the globe.
- The resolution recognizes the need to counter discrimination, xenophobia and hate speech.
- UNGA further called on all relevant actors, including States, to increase their efforts to address this phenomenon, in line with international human rights law.
- It declared June 18 as the International Day for Countering Hate Speech.
Significance:
- This day is significant for countering hate speech as hate speech goes against the core principles of the UN Charter such as equality, peace, and respect for human dignity.
- It has the ability to undermine social cohesiveness and tolerance, as well as to produce violence and conflict, as well as physical, emotional, and psychological suffering to those impacted.
- The catastrophic impact of the phenomenon has been further been compounded by social media and other forms of communication.
- Hate speech, if allowed uncontrolled, can result in widespread human rights violations, escalate conflicts, and destabilize peace and development efforts.
- The escalation from hate speech to violence has had a major role in the most horrific crimes of the modern world, from the anti-Semitism driving the Holocaust, to the 1994 genocide in Rwanda.
Background:
- This initiative which was started in 2019, builds upon UN Strategy and Plan of Action on Hate Speech.
- It emphasizes the "need to combat hate in a comprehensive manner while maintaining complete respect for freedom of expression and opinion."
- It also provides a framework for global body to complement states in resolving this issue.
Fair Repair Act: The U.S. state of New York recently passed the Fair Repair Act.
Key Points:
- According US’s Fair Repair Act, manufacturers must provide repair manuals, equipment, and supplies to independent repair shops and not just their own stores or partners.
- This provides consumers with the right to repair and refurbish their purchased goods.
- Independent repair businesses will finally be able to compete with manufacturers if they have access to the necessary tools and service instructions.
- The rationale behind the “right to repair” is that the individual who purchases a product must own it completely.
- This means that buyers must have the ability to fix and change the product however they see fit in addition to being able to utilize it.
What are the concerns of the manufacturers?
- While right to repair is a victory for consumer rights, privacy, security and quality concerns along with blatant intellectual property (IP) rights violations of the manufacturers cannot be sidelined.
- Manufacturers claim that allowing user and outsider repairs could have a negative impact on the product's quality and functionality.
- They are so terrified that they include terms in the warranty that expire when the device is fixed by a third party.
Right To Repair in India:
- Monopoly in the repair industry violates the 2019 Consumer Protection Act's "freedom to chose" for customers.
- Consumer disputes jurisprudence in the country has also partially acknowledged the right to repair.
For instance - In India, currently, there’s no legislation or any provision dealing with ‘Right to Repair’ but in Shamsher Kataria v Honda Siel Cars India Ltd (2017)the Competition Commission of India ruled that restricting the access of independent automobile repair units to spare parts by way of an end-user license agreement was anti-competitive.
Provisions in Other Countries:
Many nations have taken steps, implemented regulations, and even attempted to enact laws that recognises the "right to repair" to reduce electronic waste. Some jurisdictions offer limited scope for exercising the right to repair.
- The UK also introduced the path-breaking “right to repair” which came into force on July 1, 2021 that made mandatory for manufacturers to make spares available to both consumers and third-party repair technicians.
- The remaining European nations will abide by EU laws and rules.
- The manufacturers have two years to make the necessary changes and follow the new laws.
- The legislation is considered as a positive step in minimizing e-waste by encouraging gadget repair instead of dumping in the scrap.
- The Massachusetts Motor Vehicle Owners’ Right to Repair Act, 2012 requires automobile manufacturers to provide spare parts and diagnostics to buyers and even independent third-party mechanics.
- France requires manufacturers to display a repairability index on their products which consists of five parameters.
- This helps consumers understand whether the products are repairable, difficult to repair or not repairable at all.
- The duration of imposing product liability may differ depending on the product and its longevity.
Commonwealth Diplomatic Academy programme: India and UK recently announced the establishment of a joint Commonwealth Diplomatic Academy programme.
Key Points:
- The meeting was held by both the Foreign Ministers of India S Jaishankar and of the UK Liz at Kigali, Rwanda, where the heads of the Commonwealth countries met this week to discuss human rights, the Ukraine crisis and the post-pandemic recovery.
- A joint statement by Truss and External Affairs Minister, S Jaishankar on the establishment of an India-UK Commonwealth Diplomatic Academy programme was released on the occasion.
- As per the joint statement the India-U.K. Commonwealth Diplomatic Academy programme will be hosted in New Delhi.
- The programme aims to cater to young diplomats from all Commonwealth Member States with expertise and training on global challenges.
- They underlined the U.K. and India's dedication to bringing the Commonwealth family a truly connected, inventive, and revolutionary future that supports the needs and expectations of all Member States.
BM-SEAL-11 Project: The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) recently approved additional investment of USD 1,600 million (about Rs. 12,000 crore) by Bharat Petro Resources Ltd. (BPRL) for development of BM-SEAL-11 Concession Project in Brazil.
- BPRL is a wholly owned subsidiary of Bharat Petroleum Corporation Limited (BPCL)
Key Points:
- The production from BM-SEAL-11 project is expected to start from 2026-27.
- BPRL has 40% Participating Interest (PI) in this Concession along with Petrobras, National oil company of Brazil, as the Operator with 60% Participating Interest.
Significance:
This will help in:
- Accessing to equity oil to strengthen India’s energy security.
- Diversifying India’s crude oil supply and Indian oil companies have expressed interest in sourcing more crude oil from Brazil.
- Strengthening India’s foothold in Brazil, which will further open business avenues in neighbouring Latin American countries.
- Further strengthening the bilateral ties between the countries.
About Brazil:
- Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in both South America and Latin America.
- Brazil is the world's fifth-largest and sixth-most populous country, composed of 26 states and the Federal District.
- It is the largest country to have Portuguese as an official language and the only one in the Americas.
- Brazil is bounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the east and it covers roughly half of South America's landmass and borders all other countries in the continent, except Ecuador and Chile.
- Its Amazon basin includes a vast tropical forest, home to diverse wildlife, a variety of ecological systems, and extensive natural resources spanning numerous protected habitats.
- This unique environmental heritage makes Brazil one of the seventeen megadiverse countries.
- The capital of Brazil is Brasilia.
- The currency used here is Brazilian real.
National
Vanijya Bhawan & NIRYAT: Prime Minister Narendra Modi, on June 23 2022 inaugurated the new premises of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Vanijya Bhawan in New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- PM Modi also launched a new portal- National Import-Export Record for Yearly Analysis of Trade (NIRYAT).
- The New Vanijya Bhawan and NIRYAT Portal will represent the aspirations of an 'Aatmanirbhar Bharat'.
- It seeks to bring positive changes in the field of trade and commerce, especially for MSMEs.
- PM Modi during the unveiling of Vanijya Bhawan and NIRYAT Portal said that despite the global disruptions, India exported a total of $670 billion- Rs. 50 lakh crores.
- Exports are vital to a country’s progress.
- He further said that programmes like "Vocal for Local" have also enhanced India's exports.
About Vanijya Bhawan:
- Vanijya Bhawan is the new premises of the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- It is constructed near the India Gate.
- It is designed as a smart building that incorporates the principles of sustainable architecture with a special focus on energy saving.
- It will serve as an integrated and modern office complex that will be used by the two Departments under the Ministry that is, the Department of Commerce and the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
About NIRYAT Portal:
- NIRYAT Portal is a one-stop platform for the stakeholders to get all the necessary information related to India’s foreign trade.
- The Portal will help promote healthy competition between the states in the area of export.
NIPUN: An innovative project for skill training of construction workers called ‘NIPUN’ (National Initiative for Promoting Upskilling of Nirman) workers was recently launched by Shri Hardeep Singh Puri, Minister of Housing & Urban Affairs and Petroleum & Natural Gas, Government of India.
Key Highlights:
- The project NIPUN is an initiative of the MoHUA under its flagship scheme of the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Urban Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NULM).
- DAY-NULM is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, being implemented since 2014-15, with the aim to reduce poverty and vulnerability of urban poor households in the country by enabling them to access self-employment and skilled wage employment opportunities, resulting in an appreciable improvement in their livelihoods on a sustainable basis.
Implementation of NIPUN:
- The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC), the nodal agency under the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship (MSDE), Government of India (GoI), will be the Implementation Partner for the project NIPUN.
The NIPUN project implementation is divided into three following parts:-
- Training through Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL) at construction sites,
- Training through Fresh skilling by Plumbing and Infrastructure SSC, and
- International Placement through industries, builders, and contractors.
Aim of NIPUN:
- Its main aim is to train over 1 lakh construction workers, through fresh skilling and upskilling programmes in partnership with the NSDC under DAY-NULM.
- This project will also provide work opportunities in foreign countries.
Significance of NIPUN Project:
- By enhancing their capacities and diversifying their skill sets, this initiative will enable Nirman employees to become much more proficient and skilled while forcing them to adopt future trends in the construction business.
- It will also enable the construction workers to seek better job opportunities, increase their wages and even pursue overseas placements - an indication of a new eco-system.
- By offering upskilling and employment possibilities to urban people, especially the youth, the National Urban Livelihoods Mission has significantly reduced the vulnerability of urban poor households.
Har Ghar Tiranga Initiative: The Centre is organizing the Har Ghar Tiranga initiative on the occasion of India’s 75th year of Independence.
Key Highlights:
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi took to Twitter to ask Indians to hoist or display the National Flag at their homes from August 13 to August 15 as part of the Har Ghar Tiranga initiative of the government.
- In a series of tweets, which marked the anniversary of the adoption of the National Flag in 1947, Mr. Modi said -
- 22nd July has a special relevance in our history.
- It was on this day in 1947 that our National Flag was adopted.
- Also, this movement will deepen our connect with the national flag.
National Flag Day:
- The National Flag Day is celebrated in India every year on July 22, 2022.
- It was on this day that the Constituent Assembly adopted the Tricolor in its present form in 1947.
National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj (NIRDPR): The Union Cabinet, chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, recently approved the signing of MoU between National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj (NIRDPR) and University of Reading (UoR), United Kingdom (UK).
Key Points:
- The MoU was signed in March 2022.
- It calls for collaboration in the field of agriculture and rural development in developing countries.
- It seeks to help NIRDPR faculty in acquiring and expanding their knowledge, and develop an international professional network in agriculture, nutrition and rural development.
About NIRD&PR:
- The National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj (NIRDPR) is an autonomous organisation under the Union Ministry of Rural Development.
- It is a premier national centre of excellence in rural development and Panchayati Raj.
- It is recognized internationally as one of the UN-ESCAP Centres of Excellence.
- The Institute is located in Hyderabad, Telangana.
- In addition to the main campus at Hyderabad, this Institute has North-Eastern Regional Centre at Guwahati, Assam.
Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS): Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi launched the Ministry of Power’s flagship Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme.
- RDSS scheme was launched during a programme marking the culmination of ‘Ujjwal Bharat Ujjwal Bhavishya – Power @2047’ on 30 July at 12.30 pm via video conferencing.
Key Points of Revamped Distribution Sector Scheme (RDSS):
- The scheme is aimed at improving the operational efficiencies and financial sustainability of the power distribution companies (discoms).
- The scheme, with an outlay of Rs.3,03,758 crore over a period of five years from FY 2021-22 to FY 2025-26, aims to provide financial assistance to DISCOMs for modernization and strengthening of distribution infrastructure, aiming at improvement of the reliability and quality of supply to end consumers.
- It also aims to reduce the AT&C (aggregate technical and commercial) losses to pan-India levels of 12-15% and ACS-ARR (average cost of supply-average revenue realised) gap to zero by 2024-25. REC and PFC have been nominated as nodal agencies for the scheme.
- RDSS mandates compulsory installation of smart meters across the country.
- The Centre has set an ambitious target of installing 250 million smart meters by 2025.
- With this new scheme coming into force, all other previous schemes such as Integrated Power Development Scheme, Deendayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana and Ujjwal Discom Assurance Yojana (UDAY) would stand subsumed.
Family Courts’ Amendment Bill, 2022: The Lok Sabha passed the Family Courts’ Amendment Bill, 2022 by voice vote.
Key Points:
- It seeks to amend the Family Courts Act, 1984.
- The Act allows state governments to establish Family Courts.
- The Bill validates the existence of the three family courts in Himachal Pradesh and Two in Nagaland with retrospective effect.
- It also seeks validation of the decisions taken by the two states and the family courts.
- The family courts located at Shimla, Dharmashala, and Mandi in Himachal Pradesh will come into force, with a retrospective effect of February 15th 2019.
- The Family Courts located at Dimapur and Kohima in Nagaland will come into force with retrospect effect from November 12th 2008 on enactment of the Bill.
- The enactment was necessitated as it came to light in connection with a case that the central Government notifications were not existing with respect to these five family courts.
People In News
Ruchira Kamboj: The Ministry of External Affairs (MEA) recently announced that Ruchira Kamboj has been appointed as the next Permanent Representative of India to the United Nations at New York.
Key Highlights:
- Ruchira Kamboj is currently the Indian Envoy to Bhutan.
- She will succeed TS Tirumurti and is expected to take up as India’s Permanent Representative to UN shortly.
About Ruchira Kamboj:
- She was the All India Women’s topper of the 1987 Civil Services batch and the topper of the 1987 Indian Foreign Service (IFS) batch.
- She had joined the Indian Foreign Service in the same year.
- She began her diplomatic journey in Paris, France, where she was posted as the Third Secretary in the Indian Embassy to France from 1989-91.
- She has been the Permanent Representative of India to UNESCO in Paris, Indian High Commissioner in South Africa.
- From 2011-2014 she was the Chief of Protocol in New Delhi.
- She is the first and only woman diplomat so far in the Indian Government to have held this position.
- She was earlier posted as the Counsellor at India’s Permanent Mission to the United Nations in New York from 2002-2005, where she had dealt with wide range of political issues.
- She has also served in Mauritius, Cape Town in South Africa as India’s Consul General, and at the Commonwealth Secretariat in London.
Role of India’s Permanent Representative to UN:
- The Permanent Representative of India to the United Nations (UN) is the head of a country's diplomatic mission to the United Nations.
- The role of India’s Permanent Representative to UN is to represent the country in the global body on various issues.
Pranay Kumar Verma: Pranay Kumar Verma has been appointed as new High Commissioner of India to Bangladesh
Key Points:
- He is an experienced diplomat and IFS official from the 1994 batch.
- He is currently the ambassador of India to Vietnam.
- His appointment was announced by the Ministry of External Affairs (MEA).
- He is expected to take up the assignment shortly in place of the current High Commissioner Vikram Doraiswami who is tipped to take over as the High Commissioner of India to UK.
About Pranay Kumar Verma:
- Ambassador Pranay Kumar Verma has held diplomatic positions in Kathmandu, Hong Kong, San Francisco, Beijing, and Washington DC.
- He worked joint Secretary of the East Asia Division at the Ministry of External Affairs
- He also handled India’s nuclear diplomacy as the Joint Secretary for External Relations at the Department of Atomic Energy.
Other Appointments:
- Sandeep Arya, an IFS officer from the 1994 batch, has also been named as India’s new ambassador to the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
- Sandeep Arya is currently posted as an Additional Secretary in the MEA.
US-India Strategic Partnership Forum (USISPF): Former Indian Army chief Gen Naravane, has been honoured by the US-India Strategic Partnership Forum (USISPF) for his contribution to fostering ties between India and the US.
Key Highlights:
- In addition to Naravane, the public service award has also been given to former US Defense Secretary General Jim Mattis.
- The USISPF gave prizes for public service and global leadership to those who have been instrumental in strengthening ties between the US and India.
Key Points:
- General Mattis, during his time as the Defense Secretar worked to make India a US strategic ally.
- According to the USISPF, Gen. Naravane, during his time as Chief of Staff of the Indian Army, helped to modernize the Indian army, along with improving defence partnerships and growing interoperability between the US and India.
About Gen. Narvane:
- Gen. Naravane retired on April 30 and has since moved into his newly assigned residence in Delhi Cantonment.
- In his illustrious four-decade military career, Naravane had the distinction of holding important command and staff positions in both peace and combat, in the North-East and in Jammu & Kashmir.
- He was also a part of the Indian Peace Keeping Force in Sri Lanka.
- Former Indian Army Chief led a Strike Corps in the Western Theatre, created an Infantry Brigade, was Inspector General of the Assam Rifles (North), and commanded a Rashtriya Rifles Battalion.
- His staff assignments included stints as a Brigade Major of an Infantry Brigade, Defence Attache at Yangon, Myanmar, an instructional appointment in the Army War College as Directing Staff in the Higher Command Wing as well as two stints at the Integrated Headquarters of MoD (Army), New Delhi.
About the U.S.-India Strategic Partnership Forum (USISPF):
- The US-India Strategic Partnership Forum (USISPF) is committed to creating the most powerful partnership between the United States and India.
- As the only independent not-for-profit institution dedicated to strengthening the U.S.-India partnership in Washington, D.C. and in New Delhi, USISPF is the trusted partner for businesses, non-profit organizations, the diaspora, and the governments of India and the United States.
Sir Winston Churchill Leadership Award: Sir Winston Churchill Leadership Award was recently presented to the Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy.
Key Highlights:
- British Prime Minister Boris Johnson awarded Zelensky with the prestigious award drawing comparisons between the two leaders in times of crises.
- Zelenskyy accepted the award by video link during a ceremony at Johnson’s London office.
- The event was attended by members of the Churchill family, Ukrainian Ambassador Vadym Prystaiko and Ukrainians who have received training from British soldiers.
- The Ukrainian leader received a standing ovation in the British Parliament in March when he invoked one of Churchill’s most famous speeches and vowed to fight Russian troops in the air, sea and on the streets.
About the Churchill leadership award:
- The Churchill leadership award was first presented in 2006.
- Past recipients include Prince Charles, former British Prime Ministers Margaret Thatcher and John Major, and former US Secretary of State Madeleine Albright.
About Zelensky:
- Volodymyr Oleksandrovych Zelenskyy (born 25 January 1978), is a Ukrainian politician and former comedian actor.
- He has served as the sixth and current president of Ukraine since 2019.
- Prior to his acting career, he obtained a degree in law from the Kyiv National Economic University.
- Zelenskyy announced his candidacy in the 2019 Ukrainian presidential election on the evening of 31 December 2018, alongside the New Year's Eve address of then-president Petro Poroshenko on the TV channel 1+1.
- He won the election with 73.23 percent of the vote in the second round, defeating Poroshenko.
- He has positioned himself as an anti-establishment and anti-corruption figure.
Global Energy Prize 2022: Indian-origin Kaushik Rajashekara who is the professor of Engineering at the University of Houston, USA, recently won the Global Energy Prize for 2022.
The prize honors “outstanding scientific research and scientific-technical developments in the field of energy which promote greater efficiency and environmental security for energy sources on Earth in the interests of all mankind.”
Key Highlights:
- Kaushik is among only three people in the world who were selected for the prestigious award in 2022, by the Global Energy Association.
- He was given the award in the New Ways of Energy Applications category for his contributions to transportation electrification and energy efficiency technologies while reducing power generation emissions.
The other two 2022 laureate are:
- Mercouri Kanatzidis – professor of chemistry and materials science at Northwestern University and senior researcher at the Argonne National Laboratory. He is one of the most highly cited chemists, with more than 1,450 published scientific papers.
- Viktor Orlov – chief specialist of the Centre for Innovative Technologies (Rosatom in Russia) and pioneer in thermonuclear physics.
- The laureates were selected by the international committee of scientists from 11 countries: the United States, Italy, China, Hungary, India, Japan, Singapore, South Africa, Switzerland, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and South Korea.
- The awarding ceremony will be held during Russian Energy Week in Moscow on October 12-14.
About Rajashekara:
- Originally from India, Rajashekara, grew up in a small village in South India.
- He received his B.Eng., M. Eng, and PhD degrees from the Indian Institute of Science in Bangalore from 1971-1984.
- From 1977 to 1984, he worked as an assistant professor/senior scientific officer at the Indian Institute of Science.
- Later he earned an MBA from Indiana Wesleyan University, the USA in 1992.
- He was elected a member of the U.S. National Academy of Engineering in 2012, the Indian National Academy of Engineering in 2013 and the China National Academy of Engineering in 2021 for his contribution to development of the power conversion systems in transportation.
- He has published more than 250 articles in international journals and conference proceedings, co-authored one book with IEEE Press, and has written six monographs and individual chapters for eight books.
- He is a laureate of the IEEE Medal for Environmental and Safety Technologies (2021), the Richard Kaufman Award (2013) and several other prestigious awards.
Places In News
Floating Solar Power Plant: Prime Minister Narendra Modi virtualy dedicated the 92-MW floating solar power plant set up at National Thermal Power Corporation’s (NTPC) Kayamkulam unit to the nation recently.
Key Points:
- PM Modi launched the solar project while participating in the grand finale of ‘Ujjwal Bharat Ujjwal Bhavishya - Power @2047’, a programme organised to showcase the achievements in the power sector in the last eight years as part of the ‘Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav’.
- Prime Minister said that India had resolved to generate 175 GW of renewable energy by the time the nation completed 75 years of Independence.
- He highlighted that so far, about 170 GW capacity has been installed from non-fossil sources in India.
India is among the top four-five countries in terms of installed solar capacity.
About Kayamkulam plant:
- The Kayamkulam plant is the second-largest floating solar power project of the NTPC after the 100-MW plant at Ramagundam in Telangana.
- The floating solar system was built on a 450-acre lake area adjacent to the NTPC’s Rajiv Gandhi Combined Cycle Power Project (RGCCPP).
- The project is implemented at a cost of Rs 465 crore
- It consists of around three lakh Made in India solar PV panels floating on water.
- A total of 2.16 lakh solar panels has been mounted on floaters.
- The electricity thus generated will be transmitted to the KSEB pool.
- For this, the KSEB signed an agreement with the NTPC for purchasing power from the solar station at Rs 3.16 per kWh.
Significance:
- The power generated from the plant seeks to light up around 26,000 households every day.
- It could help reduce carbon emissions by 1.73 lakh tonnes every year.
Gujarat Semiconductor Policy 2022-27: The Government of Gujarat recently unveiled a dedicated ‘Gujarat Semiconductor Policy 2022-27’.
Key Points:
The policy aims created at least 2,00,000 new employment opportunities during a period of five years.
Gujarat is the first state in India to release a dedicated semiconductor policy.
The Government has also proposed to develop a special ‘Semicon City’ as a part of Dholera Special Investment region (SIR)where land, power and water will be provided at subsidised rates.
This dedicated policy for semiconductors is expected to co-exist with an Electronic Policy 2016-’21 of the state government that is expected to be revised soon.
Key Points about the poicy:
Under the Gujarat Semiconductor Policy 2022-27,
- Gujarat Government will provide heavy subsidies on power, water and land tariffs for entrepreneurs who are interested in investing in semiconductors or display fabrication manufacturing in Gujarat.
- The main goal of the policy is making the state first in developing Electronics System Design & Manufacturing (ESDM) ecosystem.
- It will provide for effective and timely execution of eligible projects, in a bid to set up a robust semiconductor and display fabrication ecosystem.
- It focuses on providing guidance to a significant portion of investments under the India Semiconductor Mission policies towards Gujarat.
- It also aims to develop a ‘Semicon City’.
- Under it, an additional capital assistance will be provided at 40% of the capex assistance provided by the central government, for projects approved under India Semiconductor Mission.
- The semiconductor policy will help one project each, semiconductor and display fabrication.
- In case of multiple applications, the State-appointed high-powered committee will make recommendations on the basis of credentials of projects.
- As per reports, projects approved under Design-linked Incentive scheme of Union government will not be eligible to avail benefits under new policy.
- Eligible projects will be given 75% subsidy to procure first 200 acres of land in Special Investment region.
- On the other hand, additional land required for the project or for other projects approved under India Semiconductor Mission for upstream or downstream projects will be given 50% subsidy on land cost.
- The subsidy on land shall be provided only to projects set up at Dholera SIR.
India Semiconductor Mission (ISM):
- Ministry of Electronics and IT (MeitY) launched ‘India Semiconductor Mission’ in 2021, with total financial outlay of Rs 76,000 crore.
- It is a part of the broader program for the nation's sustainable semiconductor and display ecosystem growth.
- The mission is aimed at providing financial support to companies that invest in semiconductors, design ecosystem and display manufacturing.
- ISM, which would serve as the nodal organisation for effective, cogent, and seamless execution of the plans, is envisaged to be directed by international leaders in the Semiconductor and Display industries.
What are Semiconductors:
- Semiconductors are materials which have a conductivity between conductors (generally metals) and nonconductors or insulators (such as most ceramics).
- Semiconductors can be pure elements, such as silicon or germanium, or compounds such as gallium arsenide or cadmium selenide.
Semiconductors are divided into two categories:
- Intrinsic Semiconductor.
- Extrinsic Semiconductor.
Semiconductors are an essential component of electronic devices, enabling advances in communications, computing, healthcare, military systems, transportation, clean energy, and countless other applications.
History of Semiconductors:
- In 1874, Karl Braun discovered and documented the first semiconductor diode effect.
- Braun observed that current flows freely in only one direction at the contact between a metal point and a galena crystal.
- In 1901, the very first semiconductor device, called "cat whiskers," was patented.
About Gujarat:
- Gujarat is a state on the western coast of India most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula.
- The state is bordered by Rajasthan to the northeast, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu to the south, Maharashtra to the southeast, Madhya Pradesh to the east, and the Arabian Sea and the Pakistani province of Sindh to the west.
- Its capital city is Gandhinagar.
- The Governor and Chief Minister of Gujarat are Acharya Devvrat and Bhupendrabhai Patel respectively.
Mukhyamantri Mahtari Nyay Rath Yatra: The Chief Minister of Chhattisgarh Bhupesh Baghel recently launched an initiative named 'Mukhyamantri Mahtari Nyay Rath Yatra’.
Key Highlights:
- On the occasion of the Hareli Tihaar festival, CM Baghel administered the oath of protection, justice and empowerment of women as he flagged off the ‘"Mukhyamantri Mahtari Nyay Rath Yatra".
- The Rath Yatra was flagged off with the slogan of "Baat He Abhimaan Ke, Mahila Man Ke Samman Ke".
- This initiative has been taken by the Chhattisgarh State Commission for Women with the aim of making women of the state aware of their constitutional rights and laws.
Key Points about Mukhyamantri Mahtari Nyay Rath Yatra:
- Mukhyamantri Mahtari Nyay Rath Yatra will go from village to village in all the districts to create mass awareness about the legal provisions and constitutional rights of women through short films, messages, and brochures.
- For Mahtari Nyay Rath, the state government has made specific adjustments to the DMF policy.
- The district will operate Nyay Rath with the DMF money it has received.
- In the first phase, the Rath will cover nine districts of the state namely Durg, Raipur, Rajnandgaon, Balodabazar-Bhatapara, Mahasamund, Janjgir-Champa, Gariaband, Dhamtari and Kanker.
- The remaining districts will be covered in the next phase.
- Two attorneys will ride in each chariot, listening to women’s complaints and offering information and counsel.
- Through these carts, women will be able to apply to the Women’s Commission for the resolution of their complaints.
- Nationally recognised instructional short films in Hindi and Chhattisgarhi will be shown on a sizable LED screen.
About Chhattisgarh:
- Chhattisgarh is a heavily forested state in central India known for its temples and waterfalls. It is one of the fastest-developing states in India.
- The state was formed on 1st November 2000 by partitioning ten Chhattisgarhi and six Gondi-speaking southeastern districts of Madhya Pradesh.
- The capital city of Chattisgarh is Raipur.
- The current Chief Minister and Governor of Chhattisgarh are Bhupesh Baghel and Anusuiya Uikey respectively.
Science and Technology
Anti-Gravity Body Suit: Experts at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS-Delhi) have developed an anti-gravity body suit that will allow astronauts to perform yoga in space.
This was announced by the doctors of AIIMS doctors on the eve of International Yoga Day on 21 June.
About the Anti-Gravity Body Suit:
- This is India’s first bodysuit for astronauts.
- The space journey of astronauts adversely affects the functioning of muscle and bones.
- The anti-gravity gear will help astronauts to strengthen antigravity musculature and will also prevent atrophy (a health condition in which the size of body part decreases) in microgravity environment,
- It will help astronauts strengthen muscles and prevent loss of bone density minerals.
- It will increase their weight by more than 70% in space to prevent them from floating.
The claim has been validated by the National Institute of Technology, Jalandhar, and the proof of concept will be presented to ISRO.
How will it work?
It is known that when the astronauts reach space, their body weight becomes zero.
- When an astronaut wears this body gear, his body weight can be increased in a controlled manner and he will become comfortable and further stick to the surface of the defined ground in space by velcro-magnetic force.
Significance:
- Space physiology is one of the emerging focus areas for India in space sciences and technology development.
- This would be the first-such body suit for astronauts in the world.
- The anti-gravity body suit has been developed at a time when ISRO is preparing to fly Gaganyaan, its first manned space travel mission.
IOC launches Surya Nutan: The Indian Oil Corporation (IOC) recently unveiled its patented indigenous solar cook top called Surya Nutan.
Key Points:
- Surya Nutan is an indigenous indoor solar cooking system that has been developed by IndianOil R&D Centre, Faridabad.
- It is a Stationary, rechargeable, and always kitchen-connected indoor solar cooking.
- While charging, the system provides an online cooking mode.
- Pilot projects are currently being conducted in 60 locations, including Leh (Ladakh), to ascertain several operational and commercial aspects related to its implementation.
The solar cook top is in line with the steps taken by Ministry in ongoing global energy crisis, including:
- Pursuing green hydrogen mission in refineries.
- Increasing procurement price of Compressed Bio-Gas from Rs 45 per kg to Rs 54 per kg, under SATAT scheme.
- Increasing ethanol blending to 20%, and
- Increasing area under Exploration and Production from 7-8% to 15% of geographical area.
Cost of Surya Nutan:
- The solar cooktop initially cost Rs 12,000 for the base model and Rs 23,000 for the top model.
- With economies of scale, this expense is probably going to be far lower.
How does it work?
- It works on a Hybrid Mode which means that it can work on both solar & auxiliary energy source simultaneously.
- The insulation design of Surya Nutan minimises conductive and radiative heat losses.
- This makes the Surya Nutan a reliable cooking solution for all weather conditions.
- It can be used in all weather and seasons including when the Sun is not available for long durations or for continuous days, such as monsoons and extreme winters.
About SATAT Scheme:
Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) is an initiative of Government of India (GoI).
This initiative is aimed at setting up of Compressed Bio-Gas production plants and making it available in the market for use in automotive fuels by inviting Expression of Interest from potential entrepreneurs.
The Scheme was launched in October 2018 by the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas in collaboration Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) Oil Marketing Companies (OMC) like Indian Oil Corporation Ltd., Bharat Petroleum Corporation Ltd. and Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Ltd.
SATAT has following four objectives:
- Utilization of more than 62 million metric tonnes of waste generated every year in India,
- Cutting down of import dependence,
- Creation of job creation India.
- Reduction of vehicular emissions and pollution from burning of agricultural or organic waste.
The scheme will help to maintain India’s commitment towards reducing carbon emissions, fulfilling agreements such as the Paris Agreement.
Benefits of the SATAT Scheme:
Through the use of Compressed Biogas (CBG), the SATAT has the following benefits -
- Responsible waste management, reduction in carbon emissions and pollution
- Additional revenue source for farmers
- Boost to entrepreneurship, rural economy and employment
- Support to national commitments in achieving climate change goals
- Reduction in import of natural gas and crude oil
- A safety net against crude oil/natural gas fluctuations.
Sports
Canadian Grand Prix 2022: Red Bull wunderkind Max Verstappen claimed his fifth win at the 2022 Canadian Grand Prix and also claimed his sixth victory of the Formula 1 season.
Key Highlights:
- Verstappen narrowly claimed his sixth victory of the Formula 1 season after withstanding pressure from Ferrari’s Carlos Sainz in the closing stages of the Canadian Grand Prix.
- Mercedes’ Lewis Hamilton got his second podium this campaign in third.
- Verstappen’s teammate Sergio Perez was, for the second time, forced to retire from the race due to engine problems.
International Olympic Day 2022: International Olympic Day is observed annually on June 23 across the globe to celebrate sport, health and being and together.
Key Points:
- The main reason for celebrating this day is also to commemorate the beginning of the modern Olympic Games.
- The day marks the foundation of the International Olympic Committee (IOC).
Theme:
- The theme for 2022 International Olympic Day is “Together For A Peaceful World.”
- The theme represents the ability of sports to unite the people from all over the world and minimize the differences.
Significance:
- The vision behind this day is to inspire individuals to take part in various Olympic sports regardless of their age, sex, race, gender, or other characteristics.
- It focuses and highlights the three values of Olympics – Excellence, Respect, and Friendship – and guides people to imbibe these values in their everyday lives.
History:
- The idea of celebrating a World Olympic Day was introduced in 1947, by Doctor Gruss, who was a Czech IOC member.
- The proposal of celebrating an Olympic Day was adopted in 1948 at the 42nd International Olympic Committee (IOC) Session in St Moritz.
- The day was decided as June 23 to commemorate the founding of the International Olympic Committee at Sorbonne, Paris in 1894 where Pierre de Coubertin revived the Olympic Games.
- The inaugural Olympic day was observed on 23 June 1948 in several countries such as Greece, Canada, Austria, Portugal, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, Uruguay, Venezuela, and Belgium.
About IOC:
- International Olympic Committee (IOC) is a non-governmental sports organization.
- It was established on 23 June 1894.
- It was founded by Pierre de Coubertin and Demetrios Vikelas.
- It is headquartered in Lausanne, Switzerland.
- It is responsible to organize the modern Summer and Winter Olympic Games.
- The current President of IOC is Thomas Bach.
Motto of IOC:
- The Olympic motto is made up of three Latin words: CITIUS – ALTIUS – FORTIUS (Faster, Higher, Stronger) adopted in 1894.
44th Chess Olympiad: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently inaugurated the 44th Chess Olympiad at Chennai in Tamil Nadu.
Key Highlights:
International, National and State level Chess masters participated in the inaugural event.
The Olympiad torch which crossed the 75 iconic cities of the Country was brought to the Stadium by five-time world chess champion Vishwanathan Anand.
It was handed over to Prime Minister Modi and Chief Minister MK Stalin and was later given to the chess prodigy Grandmaster Rameshbabu Pragnananda.
About the Chess competition:
- This is the first Chess Olympiad to take place in India.
- The world’s largest team chess competition, with players from 187 countries, is being held in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India from 28 July to 10 August 2022.
- It is being held at a hotel in Mamallapuram, south of Chennai.
- The event was initially supposed to take place in Khanty-Mansiysk, along with the Chess World Cup 2019, but was moved to Moscow and scheduled for the period from 5 to 17 August 2020.
- However, it was postponed as a result of the growing concerns around the COVID-19 pandemic and finally relocated to Chennai following Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
- The Chief Arbiter of the event is France's International Arbiter Laurent Freyd.
Indian polity
ECI : It is the Election Commission of India (ECI). Chief Election Commissioner (CEC) Sunil Arora announced the elections dates for the Assembly elections in Maharashtra and Haryana. The elections in both the states will be held on 21st October 2019 and counting will be held on the 24th of October 2019. The term of the Maharashtra assembly and Haryana assembly ends on November 9th and November 2nd respectively. Model Code of Conduct (MCC) will now come into force, following which the current state governments will not be able to roll out last minute schemes.
Karnataka Bypolls 2019 : The bypolls to 15 Karnataka seats, which the Election Commission will be held on December 5, according to a new notification issued. The counting will take place on December 9. As per the new schedule, the nomination process will restart on November 11 as per the new schedule and November 21 will be the last date of withdrawing from the polls.
Dantewada Assembly by-poll : Congress' Devti Karma won the bypoll for the seat, reserved for Scheduled Tribes, by a margin of 11,192 votes, a poll official said. Devti Karma is the wife of senior Congress leader Mahendra Karma who was killed in the Jhiram Valley Maoist attack in 2013. Opposition BJP's Ojaswi Mandavi stood second with 38,836 votes and Communist Party of India (CPI) candidate Bhimsen Mandavi stood third 7,664 votes.Voting was held on September 23.
Indian Policy
UNMID, NIDAN : UNMID refers to the Unique Methods of Management and treatment of Inherited Disorders whereas NIDAN refers National Inherited Diseases Administration.
The Union Minister for Science & Technology, Earth Sciences and Health & Family Welfare, Dr. Harsh Vardhan todaylaunched UMMID initiative and inaugurated NIDAN (National Inherited Diseases Administration) Kendras, which is being supported by Department of Biotechnology (DBT),M/o Science and Technology to tackle themenace of genetic diseases in newborns.
The main aim of UNMID initiaive is the expensive treatment of genetic diseases in newborns cheaper so that it is within the reach of all the people.
The NIDAN kendras have been established under the UMMID initiative. These centres will provide counselling, prenatal testing / diagnosis and management in government hospitals of the country. Another objective is to produce skilled technicians in Human genetics to screen pregnant women and newborn babies for inherited genetic diseases. Five NIDAN kendras have been launched and established.
KCST : It refers to Kalam Centre for Science and Technology. The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Ministry of Defence and Central University of Jammu (CUJ) signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) for the establishment of Kalam Centre for Science and Technology (KCST) at the university. The MoU was signed in a ceremony was held in the presence of Defence Minister Rajnath Singh in New Delhi.
The main objective of the MoU is to undertake and facilitate multidisciplinary directed basic and applied research and technology development in the identified research verticals,specifically the computational system security and sensors. KCST will also be equipped with state-of-the-art facilities and equipment leading to increase in research scholars in these areas.
Krishi Kisan Mobile app and CHC Farm Machinery : Union Minister for Agriculture and Farmers Welfare Narendra Singh Tomar on Tuesday launching two mobile apps – CHC Farm Machinery and Krishi Kisan App for Geo-Tagging - for farmers to have easy access to high value and technical agricultural equipment at their doorstep. The apps were launched with an aim to help farmers take benefit of field demonstration of new farm technologies, seed hubs as well as weather advisories. The Minister encouraged the farmers to utilize these services for betterment of their cultivation methods and thereby ensuring higher agricultural productivity.
Krishi Kisan App : Krishi Kisan App will provide farmers information of best demonstration of high-yielding crops and seeds at nearby area. Officials in the Ministry Informed that Farmer with high quality of crops can demonstrate his best practices of cultivation to other farmers so that production of these farmers could increase to a significant level. Besides providing demonstration of high-yielding variety (HYV) of crops and seeds the App will also help in geo-fencing and geo-tagging of crop.It isfree of cost and can be downloaded easily. The Farmers have to login and get details of nearest crop demonstration fields. The government is distributing seed mini-kits to farmers for multiplication and since as they are geo-tagged, the government can track whether mini-kits are being used or not. This app will also be useful in provinding the farmers information about the weather forecast. Bhopal (Madhya Pradesh), Varanasi (Uttar Pradesh), Rajkot (Gujarat), and Nanded (Maharasthra) will be provided farm level weather advisory on a pilot basis by the government.
CHC App : The Custom Hiring Service Centers or CHC App will allow farmers to avail the custom hiring services of CHCs located in the radius of 50 Kilometers. This App will help small level farmers to get agriculture Machinery on rental basis to enhance their production. The App will connect the farmers with Custom Hiring Service Centers in their area.
People In News
Sonu Nigam : He is an Indian playback singer, composer, live performer, host, and actor. He sings predominantly in Hindi and Kannada language films. He has also sung in English, Bengali, Manipuri, Gujarati, Tamil, Telugu, Marathi, Tulu, Assamese, Odia, Nepali, Maithili, Malayalam and various Indian languages. He has been honoured with the Magnificent Performing Arts Award at the annual 21st Century Icon Awards in London. He was among a host of winners across a range of categories at a gala awards ceremony last week, devised as a celebration of dynamic entrepreneurs and successful individuals chosen from hundreds of nominations from around the world.
Madhukar Kamath : He is the chairman emeritus of DDB Mudra group and mentor of Interbrand India, has been elected chairman of the Audit Bureau of Circulations (ABC) for 2019-20. Kamath has also been the president of Advertising Agencies Association of India IAAAI) and chairman of the Advertising Standards Council of India (ASCI).He has more than 4 decades of experience in advertising and marketing services. He was unanimously elected for the top post at the 71st annual general meeting of the ABC. He has served as chairman of brand consultancy Interbrand and has led several industry bodies.
ABC: It refers to Audit Bureau of Circulations (ABC) of India. It is a voluntary organisation initiated in 1948 that operates in different parts of the world. It is a non-profit circulation-auditing organisation. It certifies and audits the circulations of major publications, including newspapers and magazines in India.
Amitabh Bachchan : He is an Indian film actor, film producer, television host, occasional playback singer and former politician. He first gained popularity in the early 1970s for films such as Zanjeer, Deewaar and Sholay, and was dubbed India's "angry young man" for his on-screen roles in Bollywood. He was initially named Inquilaab Srivastava later changed to Amitabh. His father was Harivansh Rai Bachchan who was an Indian poet of the Nayi Kavita literary movement of early 20th century Hindi literature and mother Teji Bachchan, who was a social activist. He has starred in a multitude of films. Amitabh Bachchan's career spans over five decades in the Hindi film industry. Amitabh Bachchan has been selected for the highest Indian film honour- Dadasaheb Phalke award for the year 2019. The actor was awarded with the Padma Shri in 1984. In 2001, he received the Padma Bhushan, 2001 and the Padma Vibhushan in 2015. He was also bestowed with France's highest civilian honour, the Knight of the Legion of Honour, by the French Government in 2007 for his "exceptional career in the world of cinema and beyond". He also won the prestigious National Award for his performances in 'Agneepath', 'Black', 'Paa' and 'Piku'.
Dadasaheb Phalke Award: The Dadasaheb Phalke Award is India's highest award in cinema introduced by the Government of India to commemorate Dadasaheb Phalke's contribution to Indian cinema. Dadasaheb Phalke who is often regarded as "the father of Indian cinema", was an Indian filmmaker who directed India's first full-length feature film, Raja Harishchandra (1913). It is presented anually at the National Film Awards ceremony by the Directorate of Film Festivals, an organisation set up by the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting. It was first presented in1969. The award is awarded for "outstanding contribution to the growth and development of Indian cinema" and is selected by a committee consisting of eminent personalities from the Indian film industry.As of 2017, the award comprises a Swarna Kamal (Golden Lotus) medallion, a shawl, and a cash prize of ?1,000,000.
Greta Thunberg : She is a Swedish environmental activist focused on the risks posed by global warming. Greta Thunberg wins The Right Livelihood Award which is also known as the Alternative Nobel. She is being recognized 'for inspiring and amplifying political demands for urgent climate action reflecting scientific facts.' The teen activist, whose impassioned speech at the U.N. Climate Action Summit made international headlines this week.
The Right Livelihood Award is an international award to "honour and support those offering practical and exemplary answers to the most urgent challenges facrd by the world. The prize was established in 1980 by German-Swedish philanthropist Jakob von Uexkull, and is presented annually in early December.
Ponung Doming : She is the first woman army officer from Arunachal Pradesh to become Lieutenant Colonel In Indian Army. She is a resident of Pasighat in East Siang district of Arunachal Pradesh. She was commissioned into the Indian Army in 2008. She then got a degree in civil engineering.She served the UN Peace keeping force in Congo in 2014.She is currently posted in Pune, Maharashtra.
The Indian army for the first time in 2019 issued notification inviting female applicants for the position of Soldier General Duty, personnel below officer rank. Initially, women in armed forces were recruited only in the officer’s rank till 2018. In India, females are not allowed to serve in combat units like armoured corps, infantry and Mechanised infantry. With the introduction of Indian Military Nursing Service by the British Raj, the role of woman in the Indian Army began and it was only in 1992 that the Indian Army started recruiting women in non-medical roles also. Later in 2007, the UN first all female peace keeping force was deployed to Liberia by India. This was first of its kind not only in India but throughout the world.
Places In News
Jammu and Kashmir : J&K becomes first state to issue highest number of golden cards under Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY). Within 90 days after the scheme was launched over 11 lakhs of golden cards have been issued.Under the scheme, 155 Hospitals including 126 public and 29 private hospitals have been empanelled to provide free and cashless treatment to the entitled beneficiaries while as per Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) 6.30 lakh poor and vulnerable families of J&K are entitled to it.
Ayushman Bharat Yojana : It is also known as Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) or National Health Protection Scheme. It is a centrally sponsored scheme launched in 2018, under the Ayushman Bharat Mission of MoHFW in India.The main of the scheme is making interventions in primary, secondary and tertiary care systems, covering both preventive and promotive health, to address healthcare. It is a combination of two major health initiatives namely, Health and Wellness centres and National Health Protection Scheme (NHPS). Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and the Deputy CEO of Ayushman Bharat Yojana is Indu Bhushan and Dr. Dinesh Arora respectively.
Kerala : Vice President inaugurates 150th Birth Anniversary celebrations of Vaidyaratnam P.S. Warrier at Kottal in Kerala.Vaidyaratnam P S Warrier : He was an Ayurvedic physician who founded Kottakal Arya Vaidyasala in 1902 for manufacture and sale of Ayurvedic medicines in India. The present Ayurveda college, earlier known as Ayurvedic patsala in 1917. It has now 5 hospitals, 3 medicine factories, R&D centres, 200 acres of herbal gardens. The headquarters of Arya Vaidya Sala The Arya Vaidya Sala institutions are at Kottakkal, Malappuram district.It also operates 5 hospitals and a charitable centre. The Ayurvedic pills discovered by the center has revolutionized Ayurvedic medicines. It also assists in the Ministry of Ayush. It also works on researches with Council of Scientific and Industrial Research of Government of India (CSIR) . Government of India has issued postage stamps in his honour. In 1933, he was conferred with the title “Vaidyaratna” in recognition of his services to humanity by the then Governor General of India.
Odisha : Department of Women & Child Development and Mission Shakti, Government of Odisha, in collaboration with United Nations International Children’s Emergency Fund (UNICEF) unveiled a mascot named ‘Tikki Mausi’ with an aim to combat malnutrition among children and women and their development. Women and Child Development Minister Tukuni Sahu and UNICEF's state Chief Monika O Nielsen unveiled the mascot and also launched the state level communication strategy to make the public aware about child and woman's nutrition and their development. The mascot Tikki Mausi has been named so in reference to second mother of a child. It is projected to spread awareness for better health care of children and their development. The mascot will also take care of providing the right information about state government projects for women and children to every household for better future of children in the state and thereby spread awareness for better health care of children and their development.
Uttarakhand : A 14-day joint military exercise Between India and Kazakhstan named KAZIND 2019 to counter-terrorism operations is scheduled to be held in the mountainous terrain from 3rd to 15th of Octoer 2019. It will be held in Pithoragarh in Uttarakhand. The exercise will comprise of nearly 100 soldiers from both Indian and Kazakhstan Army who would be sharing their experience gained during conduct of various counter insurgency and counter terrorism operations in the past.
KAZIND 2019 : It is the fourth edition of the annual event. The joint military exercise is conducted alternatively in Kazakhstan and India every year. The objective of this exercise is to conduct company level joint training and enhancing the level of defence cooperation further fostering bilateral relations between the two nations. It will help counter terrorism operations in mountainous terrain. During the exercise, aspects of emerging trends of global terrorism and hybrid warfare have also been included.
Ladakh : Ladakhi Shondol dance created history by entering into the Guinness Book of World Records as the largest Ladakhi dance. It was performed by 408 women dressed up in traditional dresses and beautiful headgears and performed the dance. It was performed on the occasion of the annual Naropa Festival 2019. Swapnil Dangarikar, the official adjudicate of The Guinness Book of World Records, presented the certificate to the Drukpa Thuksey Rinpoche who is chairman of the Naropa Festival Organising Committee.
Shondol dance: It is also known as the the royal dance of Ladakh. It was performed by the artists dressed up in traditional dresses and beautiful headgears and for the king of Ladakh.
Naropa Festival 2019: It is celebrated every 12th year of the Tibetan calendar. It is also known as the Kumbh Mela of the Himalayas. It aims to celebrate the life of Buddhist philosopher and scholar Naropa. As many as 408 women attired in traditional dresses and beautiful head gears performed the dance. It was held near the Hemis Monastery. The Hemis Monastery is 11th-century world-famous monastery in Ladakh.concluding day of the ongoing Buddhist carnival Naropa festival near the Hemis Monastery. The festival had begun on September 16 and concluded on Friday.
The festival also aims to end the use of plastics and also sensitize the leaders of the religious community on plastic waste management and recycling process.
Sports
Kyle Abbott : He is a right-arm fast-medium bowler. He represented South Africa in Test, One Day International and Twenty20 International cricket between 2013 and 2017, before retiring to take up a contract with Hampshire in English county cricket. He created history with a total of 17 wickets in 120th Specsavers County Championship in Hampshire. He recorded the best match figures in first-class cricket this century.The County Championship, currently known as the Specsavers County Championship for sponsorship reasons, is the domestic first-class cricket competition in England and Wales and is organised by the England and Wales Cricket Board. It became an official title in 1890.
The Best FIFA Football Awards 2019: It is an Association football award presented annually by the sport's governing body, FIFA. The first awarding ceremony was held on 9 January 2017 in Zurich, Switzerland. The award is aimed at reviving the FIFA World Player of the Year.Football legend Argentinian Lionel Messi bagged his sixth FIFA's Best Men's Player Award for his outstanding performance throughout the year. He defeated his biggest rival Cristiano Ronaldo. On the other side, in women’s category, USA World Cup winner Megan Rapinoe received her first FIFA best player award for 2019 at the Best FIFA Football Awards 2019 ceremony held at the Teatro alla Scala in Milan, Italy.
The other FIFA Best Player 2019 Awards were awarded to :-
FIFA Best Men’s Coach 2019 to Jurgen Klopp
FIFA Best Women’s Coach 2019 to Jill Ellis
FIFA Puskas Award to Daniel Zsori
FIFA Best Men's Goalkeeper 2019 to Marc-Andre ter Stegen
FIFA Best Women's Goalkeeper 2019 to Sari van Veenendaal
FIFA Best Fan Award 2019 to Silvia Grecco
FIFA Best fair play award to Leeds United and Marcelo Bielsa
World Boxing Championships : It is The AIBA World Boxing Championships and the AIBA Women's World Boxing Championships are biennial amateur boxing competitions organised by the International Boxing Association (AIBA), which is the sport governing body. Alongside the Olympic boxing programme, it is the highest level of competition for the sport.Amit Panghal a young boxer Amit Kumar Panghal from Rohtak created history by becoming the first Indian male boxer to reach final World Boxing Championships 2019. He defeating Kazakhstan's Saken Bibossinov by split decision (3-2) in the 52kg semi-final on Friday in Ekaterinburg, Russia. He is the reigning Asian Games gold medallist. Manish Kaushik finished with a bronze after losing the 63kg semi-final
World Wrestling Championships : It is an Amateur Wrestling World Championships organized by the United World Wrestling. The Men's Greco-Roman Wrestling tournament began in 1904, and the Men's Freestyle Wrestling tournament began in 1951. The Women's Freestyle championships were first staged in 1987.Indian wrestler Deepak Punia secures quota for 2020 Tokyo Olympics. He became the fourth athlete from the country to secure quota for the 2020 Tokyo Olympics after booking his place in the semi-finals of the on-going World Wrestling Championship at Nur Sultan, Kazhakstan. He won silver in men’s 86 kg freestyle and Rahul Aware bagged a bronze medal in men’s 61kg category while other wrestlers to qualify for the 2020 Olympics in their respective weight categories are Bajrang Punia, Ravi Kumar and Vinesh Phogat. India finished with its best-ever medal haul at World Championships by winning 5 medals in Nur-Sultan. The 5 medal includes- 1 silver and 4 bronze medals.
IAAF Veteran Pin Award : It is The International Association of Athletics Federations Veteran Pin Award. The award is given to those players who have made matchless contributions to athletics. IAAF president Sebastian Coe presented IAAF Veteran Pin Award to former India’s track and field and Olympian legend P.T. Usha for her outstanding service to the sport. She received the award at the 52nd IAAF conference in Doha.
P.T. Usha or Pilavullakandi Thekkeparambil Usha is a retired Indian track and field athlete. She has been associated with Indian athletics since 1979. She is often called the "queen of Indian track and field". She won five gold medals in 100 metres(m), 200m, 400m, 400 m hurdles and the 4x400 m relay besides a bronze in the Asian Games which were held at Jakarta in 1985 .
Adille Sumariwalla : He is an Indian Parsi athlete and entrepreneur, popular for representing India at the 1980 Moscow Olympics. He is also an entrepreneur and owns many media businesses in India, after tenures at some media companies including the American Media Company. has been re-elected as member of Council of International Association of Athletics Federations (IAAF) for a second four-year term during the 52nd Congress of the sport’s world governing body. He received 121 votes to get elected as one of the 13 individual members of the IAAF Council.
IAAF : It is the International Association of Athletics Federations and is the international governing body for sport of athletics. It was established on 17 July 1912 in Stockholm, Sweden. It is headquartered in Monaco. it consists of 215 member federations.
St Petersburg Open: It is a professional men's tennis tournament played on indoor hard courts. It is part of the ATP World Tour 250 series of the Association of Tennis Professionals World Tour. India's Divij Sharan and partner Igor Zelenay of Slovakia won Men’s Doubles Title at ATP Tour Tennis Tournament held in St. Petersburg in Russia. In the final, the duo defeated Italian pair of Matteo Berrettini and Simone Bolelli. The 49th-ranked Divij has won five Tour titles ,16 Challenger and 19 Futures doubles titles.
World Athletics Championships: The IAAF World Athletics Championships, is a biennial athletics event organized by the International Association of Athletics Federations (IAAF). It is held between 27 September and 6 October 2019 in Doha, Qatar.
Kenya's Ruth Chepngetich won the world championship midnight marathon on Friday, in a gruelling test of survival that saw nearly a third of the 70 starters fail to reach the finish line.
Economics
EAC-PM : It refers to Economic Advisory Council to PM. It is an independent body constituted to advise the government (especially prime minister) on economic and related issues. It has reconstituted Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM) under existing Chairman Bibek Debroy. The reconstitution is for a period of two years, with effect from 26 September 2019. Ratan P Watal will continue as Member Secretary of the EAC-PM. The EAC-PM will have 2 part-time members as against 3 in outgoing panel. Ashima Goel will continue to be one of part-time members and Sajjid Chinoy (Chief India economist at J.P. Morgan) has been added as the new member. Two existing part-time members, Rathin Roy and Shamika Ravi have been dropped in reconstituted EAC-PM.
Preventive Vigilance portal: Punjab National Bank (PNB) launched a Preventive Vigilance (PV) portal during a function held at PNB Corporate Office, chaired by Central Vigilance Commissioner Sharad Kumar. The portal aims to facilitate its staff members to check procedural lapses as well as promote good practices.Besides PV portal e-pledge mission was inaugurated. About Preventive Vigilance portal To promote vigilance awareness in the banking system, PNB introduced the first of its kind technology based solutions through Preventive Vigilance portal. PV portal will facilitate all staff members to contribute towards arresting procedural lapses and unhealthy practices. It will also usher in a coherent climate conducive to banking for modern age. It's the first of its kind portal which includes other activities, such as the inauguration of the e-pledge mission, social outreach through technological platforms. The bank promoted the portal under the central theme Integrity-A way of Life.
CBDT : It refers to The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), that frames policy for the Income-tax department. It will set up National e-Assessment centre (NeAC) in New Delhi as part of the government’s ambitious plan to launch faceless and nameless assessment for income tax payers from October 2019.
NeAC : It will be an independent office that will look after the work of e-assessment scheme which headed by a Principal Chief Commissioner of Income-tax (PCCIT) as its chief. It is the recently notified scheme for faceless and nameless assessment for income taxpayers. It will have 16 officials. CBDT has appointed K M Prasad, a 1984-batch Indian Revenue Service (IRS) officer as chief or PCCIT of NeAC while Ashish Abrol, a 1993-batch IRS officer has been appointed as the Commissioner or second-in-command of new unit. NeAC will also serve notices to assess specifying the issues for selection of their case for assessment and once a response is received from them within a period of 15 days, the centre will allocate case to an assessing officer using an automated system.
e-assessment scheme : It is a scheme set up to facilitate faceless assessment of income-tax returns via completely electronic communication between tax officials and taxpayers. The scheme will be rolled out from ‘Vijayadashami’ on 8 October 2019.
Multipurpose ID Card : It refers to one single use card for all utilities like Aadhaar, passport, bank account, driving licence & voter card. On 23 September 2019 Union Home Minister Amit Shah proposed the idea of a single multipurpose identity card for citizens. He also said the Census 2021 data will be collected through mobile app. moving away from traditional pen and paper, to promote Digital India. He said that National Population Register was being prepared for the first time in the 2021 census. He laid the foundation stone of a new building of the Registrar General of India and Census Commissioner in New Delhi. He stated that there should also be a system that when a person dies, the information is updated automatically in the population data. The massive nationwide exercise will be carried out in 16 languages at a cost of Rs 12,000 crore.
Digital Census 2021 : It is the 16th in the series which was first conducted in the 1860s. It will have about 60 questions, right from the amenities available in a household, source of drinking water and power, to the religion, occupation, and the languages spoken by the family. The exercise will be carried out during the house-listing phase of Census 2021, during April to September 2020, in all the states and union territories, except Assam, where a National Register of Citizens was recently released. Then the Census data will be collected through a mobile app which will be used for the census exercise. He said the 2021 census will help in future planning of the country, especially for development initiatives and welfare schemes, and it will be a ‘Jan Bhagidari’ (people’s participation) exercise.
NPR : It is the National Population Register (NPR). It is a register of the ‘usual’ residents of the country. A usual resident is defined as a person who has resided in a local area for the past six months or more, or a person who intends to reside in that area for the next 6 months or more. The database under the NPR is maintained by the Registrar General of India and Census Commissioner of India, Ministry of Home Affairs. The NPR is prepared at the local (Village or sub-Town), sub-District, District, State and National level, under provisions of the Citizenship Act 1955 and the Citizenship (Registration of Citizens and Issue of National Identity Cards) Rules, 2003. It is mandatory for every usual resident of India to register in the NPR.
Science and Technology
Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prizes 2019 : It is the highest multidisciplinary science awards in India which is presented for outstanding Indian work in science and technology. It is presented annually by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) for notable and outstanding research, applied/fundamental, in environmental science, biology, mathematics, Physics, chemistry, engineering, and medicine. This prestigious science award is named after the founder Director of CSIR, Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar. It was 1st awarded in 1958.
President of India Ram Nath Kovind presented awards for outstanding contributions in science and technology. The awards were presented on the occasion of Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) Foundation Day.
Prize Recipients of the prestigious awards are :-
Biological Sciences winners: Dr. Kayarat Sai Krishnan (Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Pune); Dr. Soumen Basak (National Institute of Immunology, New Delhi)
Chemical Sciences: · Dr. Raghavan B Sunoj (IIT, Bombay); Dr. Tapas Kumar Maji (Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Bengaluru).
Earth, Atmosphere, Ocean and Planetary Sciences: Dr. Subimal Ghosh (IIT, Bombay)
Engineering Sciences: Manik Varma (Microsoft Research India, Bengaluru) Mathematical Sciences: Dr. Dishant Mayur Bhai Pancholi (Institute of Mathematical Sciences, Chennai), Dr. Nina Gupta (Indian Statistical Institute, Kolkata)
Medical Sciences: Dr. Dheeraj Kumar (International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, New Delhi), Dr. Mohammad Javed Ali (LV Prasad Eye Institute, Hyderabad)
Physical Sciences: Dr. Aninda Sinha (IISc, Bengaluru), Dr. Shankar Ghosh (TIFR, Mumbai)
Hazzaa Al Mansoori : He is a 35 year old former pilot in the The United Arab Emirates (UAE) armed forces. He will be the first Emirati astronaut and first Arab on orbiting laboratory of ISS. Before him Prince Sultan Bin Salman Abdulaziz Al Saud from Saudi Arabia and Muhammed Faris from Syria - have been to space. Both of their missions took place in the 1980s.
On 25 September 2019 he launched aboard the Soyuz MS-15 spacecraft to the International Space Station accompanied by Oleg Skripochka of Russia and NASA astronaut Jessica Meir onboard. He will stay for eight days at International Space Station (ISS) doing scientific experiments with other international astronauts.
The Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Center provided Al Mansoori with a 10kg bag, which includes important elements of Emirati heritage, culture and history, which will be placed in museums upon his return.
As part of UAE’s space plans, the Arab nation has announced its aim to also become the first Arab country to send an unmanned probe to orbit Mars by 2021. The country has named its Mars mission as “Hope”. In the long-term, UAE also plans to build a “Science City” to replicate life on Mars. It also aims to create the first human settlement on red planet by 2117.
Environment
U.N : It referes to The United Nations. It is an intergovernmental organization tasked with maintaining international peace and security, developing friendly relations among nations, achieving international co-operation, and being a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations. António Guterres is the present UN Secretary-General.
UN Climate Action Summit : The purpose of the Summit is to bring leaders from around the world together urgently to address climate change and achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement. The first summit had taken place in California in 2018. According to the U.N. reports Average global temperature between 2015-2019, 2019 set to be hottest on record.
The UN Climate Change Summit, 2019 was held in New York. It launched an initiative to guide heavy industries towards low-carbon economy. Along with other World leaders Prime Minister Modi too attended the summit where he urged world leaders to take actions to protect the environment and to ban single-use plastic.
AURANGABAD: A new species of snakes has been discovered in the Western Ghats in Maharashtra and named after Tejas Thackeray, the younger son of Shiv Sena chief Uddhav Thackeray, for his contribution to the find. The species falls in the category commonly called as cat snakes and belong to the genus Boiga. The first Boiga to be described from the western ghats in 125 years. It is Known to feed exclusively on tree frogs & their eggs. It is found on trees over hanging rain fed streams in it's misty montane rainforest habitat. The new species was found in the Koyna region of Satara district in western Maharashtra.
Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS) of Gujarat : The country's first 'Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS)’ has been launched by the Gujarat chief minister Vijay Rupani in Surat to encourage and incentivize the industrial units to cut air pollution. Gujarat Pollution Control Board (GPCB) chose Surat as the pilot city for the project because it is a densely-populated industrial centre and its textile and dyeing industries emit heavy pollution.As industries in Surat have already installed Continuous Emission Monitoring Systems so that makes it possible to estimate the mass of PM being released.
ETS is a regulatory tool that is aimed at reducing the pollution load in an area and at the same time minimising the cost of compliance for the industry. GPCB spent two years developing pollution monitoring devices (called Continuous Emissions Monitoring Systems, or CEMS.
The ETS will function by defining the total total mass of pollution that can be released into air over a certain fixed period by all industrial units or factories collectively, under the cap and trade market.
Gandhi Solar Park : Prime Minister Narendra Modi along with UN chief Antonio Guterres and other world leaders inaugurated the Gandhi Solar Park and Gandhi Peace Garden at the UN headquarters in New York. This gesture highlighted India's attempt to not only talk about climate change but also take action.
The 50 kilowatt Gandhi Solar Park is a $1 million-solar park that will produce 50 kilowatts of electricity from the roof of the conference building at the UN headquarters.The energy generated in park is equivalent to energy that would have been created through use of 30,000 kilograms of coal. It also has a carbon sequestration of 1000 seedlings which will grow into trees over a period of 10 years.India gifted 193 solar panels for the project—one panel each for every UN member state.
Gandhi Peace garden : It was inaugurated at the State University of New York at Old Westbury in Long Island. About 153 trees were planted in the garden to honour Mahatma Gandhi on his 150th anniversary. The peace garden is a crowd project which will give people a chance to adopt trees in memory of their loved ones.
The leaders also launched a United Nations (UN) postage stamp of Mahatma Gandhi that marks his 150th anniversary. On the very same day, Narendra Modi was also conferred with the Global Goalkeeper Award for the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (Clean India Mission) launched by his government. He received the award from Microsoft founder Bill Gates.
World Rhino Day : This day is celebrated on September 22 every year to celebrate the world’s five rhinoceros species, and to reflect on the challenges facing them. Non-Governmental Organisation (NGO), zoos, and public celeberate rhinos in their own unique ways.
The World Rhino Day was launched by World Wildlife Fund (WWF)-South Africa on September 22 in the year 2010. The day is internationally observed across both African and Asian rhino bearing countries.
World’s Five Rhinoceros Species living in Africa and Asia– Javan Rhinos (Rhinoceros sondaicus), Critically Endangered (IUCN), Sumatran rhinos (Dicerorhinus sumatrensis), Critically Endangered (IUCN) Black rhinos (Diceros bicornis), Critically Endangered (IUCN) White rhinos (Ceratotherium simum), Near Threatened (IUCN) Greater One-Horned Rhinos (Rhinoceros unicornis), Vulnerable (IUCN).
International Coastal Clean-up Day : It is celebrated every year on the third Saturday of September. This year it was celebrated on 21st of September. It was started in 1986. It was begun by Linda Maraniss and Kathy O Hara. They worked on ocean conservancy. Around 2,800 volunteers participated in the first clean up session. The International Coastal Cleanup Day is celebrated so as to encourages people to clean beaches, remove the garbage plaguing it. It has now has 6 million volunteers participating from 90 countries globally. The theme of this year is marine animal, The Pelican.
In India, on this day programmes were conducted in several coastal cities like, Mumbai and Chennai. Thousands of volunteers joined the cleaning of the shores and beaches programmes t Chennai Besant Nagar beach and Mumbai Versova Beach. Huge quantity of non – biodegradable waste and handed over to municipal authorities for proper disposal.
International
World Tourism Day : This day is celebrated on the 27th of September every year. Since 1980, The United Nations World Tourism Organization has celebrated World Tourism Day as international observances. 27th September was chosen as the World Tourism Day because on that day in 1970, the Statutes of the UN World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) were adopted. The adoption of these Statutes is considered a milestone in global tourism. The day aims at creating awareness on social, political, cultural and economic values among international community.
This year, the theme of World Tourism Day is "Tourism and jobs: a better future for all" and is being hosted by India. India was chosen because India can offer a tourist different tourism choices, diverse cuisines, faiths, arts, music forms, adventures places,language and history. Indian leaders have urged the youth to explore India and its diverse cultural heritage. Chief Ministers of various states have also invited various people to visit their states.
The main objectives of the theme are to maximise the potential of tourism through fresh policies so that it can create more jobs for both youth and women. According to UNWTO, Tourism generates 10% of world jobs. As per the International Labor Organization unemployment around the world is a great cause of concern. More than 190 million people are unemployed so it is very essential to create jobs. The main focus of UNEWTO is creating equitable employment to achieve social inclusion, peace and security.
UNGA 2019 : It refers to United Nations General Assembly. It is the parliament of the world. It is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations, the only one in which all member nations have equal representation, and the main deliberative, policy-making, and representative organ of the UN. It not only takes decision on important matters such as peace and security but also discusses various global issues and budgetary matters. It decides on matters such as the admission of new members.Every year in September, all the Members meet in this unique forum at Headquarters in New York for the General Assembly session.
The 74th session of the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) was currently on at the UN headquarters in New York. The meeting was held amid the global concerns like the US-Iran tensions and rising extremism,recent attacks on major Saudi Arabian oil facilities, rift between India and Pakistan, climate change after massive fire in the world's largest Amazon rainforest.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi in his address at the 74th session of the UN General Assembly (UNGA) on Friday in New York urged all the world's nations to unite in the fight against terrorism, saying that it was the greatest threat to humanity and the biggest global challenge. He highlighted the reform agenda of his government, and also about actions taken to tackle climate change, as well as health and cleanliness initiatives.PM Modi was the fourth speaker to deliver a speech at UNGA.
China's Amphibious Assault Ship : The new ship is the first in China's Type 075 class of amphibious assault ships. It is also defined as a type of landing helicopter dock. It has been independently developed by China. The ship will have a strong capability to carry out attacks on the enemy territory from the sea after undergoing equipment debugging, mooring and navigational trials.
Its first amphibious assault ship with strong capacity in amphibious operations and performing a variety of tasks has been launched by the Chinese Navy in Shanghai. This amphibious assault ship will enable Chinese army to carry out attacks on the enemy territory from the sea.
Kristalina Georgieva : She is a 66 year old economist from Bulgaria. She is a former World Bank CEO. she also served as the Vice-President of the European Commission under Jean-Claude Juncker from 2014 to 2016. She even served in a number of positions and eventually becoming the vice president and corporate secretary in March 2008 in the World Bank Group from 1993 to 2010. She served as a member of the trustee board and associate professor in the Economics Department of the University of National and World Economy in Bulgaria previously. According to an unwritten rule, a European has led the IMF since its creation in 1945 after the Second World War and the leader of the World Bank has been designated by the United States. Kristalina Georgieva is the first person from an emerging economy to lead the IMF.
Kristalina Georgieva was selected as the new chief and Managing Director of International Monetary Fund on September 25, 2019 by the 24-member Executive Board of the IMF. She has become the second-ever woman to lead the IMF. IMF comprises 189 member states. She is to take up her position as managing director on October. She will replace Christine Lagarde, who is set to take over the European Central Bank (ECB).
National
Gully Boy : It is a hindi bollywood film directed by Zoya Akhter. This film is about the street rappers in Mumbai.The story revolves around the underground rap movement in India. It is inspired by the lives and work of rappers Naezy and Divine. The film features Ranveer Singh and Alia Bhatt in the lead roles and Kalki Koechlin, Siddhant Chaturvedi, Vijay Raaz and Vijay Varma in pivotal roles. The film Gully Boy showcases Murad's (Ranveer Singh) journey from the slums of Dharavi to the centrestage of rap.
The movie Gully Boy has been selected as India's official entry to the 92nd Oscar Awards in the 'Best International Feature Film' category. The film also received the Promotion of Asian Cinema (NETPAC) Award held at South Korea including the NETPAC Award for Best Asian Film at the Bucheon International Fantastic Film Festival. Bollywood is the Indian Hindi-language film industry based in Mumbai.
Oscar Award - It is the Academy Awards, also officially and popularly known as the Oscars. It is given annually by the Academy of Motion Picture Arts and Sciences (AMPAS) for an international recognition of excellence in cinematic achievements as assessed by the Academy's voting membership. The winners for various categories in cinema are awarded a copy of a golden statuette, officially called the "Academy Award of Merit" or the Oscar. It is the most prestigious award ceremony of Hollywood.
NATGRID :It means National Intelligence Grid. It is an integrated intelligence grid connecting databases of core security agencies of the Government of India (GoI)to collect comprehensive patterns of intelligence that can be readily accessed by intelligence agencies. It was first proposed in the aftermath of the terrorist attacks on Mumbai in 2008. The project is worth Rs.3400 crores. The government of India in July 2016 appointed Ashok Patnaik as the Chief Executive Officer of the National Intelligence Grid. The work on the NATGRID has been speeded up after Union Home Minister Amit Shah reviewed the progress recently. The NATGRID is likely to be operational by January 2020. The data recovery centre of the NATGRID has been constructed in Bengaluru, Karnataka and its headquarters is nearing completion in Delhi. It will have data related to all immigration entry and exit, banking and financial transactions, credit card purchases, telecom, individual taxpayers, air and train travels besides others to generate intelligence inputs. The work on the National Intelligence Grid (NATGRID) is set up to track any terror suspect and prevent terrorist attacks with real-time data.In the first phase 10 users agency which are, Intelligence Bureau (IB), Research & Analysis Wing (R&AW), Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI), Enforcement Directorate (ED), Directorate of Revenue Intelligence (DRI), Financial Intelligence Unit (FIU), Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), Central Board of Excise and Customs (CBEC), Directorate General of Central Excise and Intelligence (DGCEI) and Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) will be able to access the NATGRID data on real-time basis. Along with it 21 service providers too will be connected with the NATGRID while in the later stages 950 organisations and in subsequent years another 1,000 organisations will be connected with it. Initially, no state agencies will be given direct access to the NATGRID data.
ICGS Varaha: It is a Coast Guard offshore patrol vessel. The ICGS Varaha is the fourth in the series of seven 98-m Offshore Patrol Vessels (OPV) of the Indian Coast Guard (ICG). It has been designed and built indigenously by Larsen & Toubro (L&T) at its Katupalli ship building yard in North Chennai. It is fit with the latest technology, navigation and communication equipment.
Defense Minister Rajnath Singh formally commissioned the Coast Guard offshore patrol vessel 'Varaha' at the Chennai Port Trust.The ship would be based at New Mangalore under the administrative and operational control of Commander Coast Guard region (west) from where it will operate covering up to Kanyakumari.It will have on board 14 officers and 89 men.The ship will add to the strength of ICG in responding to threats of smuggling, drug trafficking, collision, grounding and oil spills, maritime terrorism and challenges of maritime enforcement.
International Day of Sign Languages : It is celebrated annually across the world on 23 September every year along with International Week of the Deaf. The choice of 23 September is the same date that the World Federation of the Deaf was established in 1951. The UN General Assembly decided to commemorate the day as the International Day of Sign Languages in order to raise awareness of the importance of sign language in the full realisation of the human rights of people who are deaf. The first International Day of Sign Languages was observed across the world on September 23, 2018 with the theme “With Sign Language, Everyone is Included!”
International Day of Sign Languages” was celebrated by Indian Sign Language Research and Training Centre (ISLRTC) under Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (Divyangjan), Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment with Shri Krishan Pal Gurjar, Minister of State for Social Justice and Empowerment was the Chief Guest on the occasion.
Arts
Ugadi: It is a major festival celebrated to mark the beginning of the Hindu Lunar calendar which comes in the Chaitra month (March or April) as per the Gregorian calendar (Hindu Lunar calendar). It is also called Yugadi which is a combination of two words Yug meaning age and Adi meaning Beginning. According to the Hindu mythology, it was on this day that Lord Brahma created the universe. He then went on to create days, weeks, months, and years. So, Ugadi is believed to be the first day of the creation of the universe. This auspicious festival is celebrated in Telangana and Andhra Pradesh. The Telegu People on this occasion, savor Ugadi chutney which is made by Neem flower, Jaggery, Salt, Sugar cane, Tamarind, and Mango. Prayers are offered in temples to welcome the New Year while people clean their homes and decorate them with Rangolis—a traditional way to decorate floors by creating various patterns with colored rice or flower petals. Recently, Telegu New year day was celebrated across India. It was celebrated on the 25th of March 2020.
Gudi Parva: This day is celebrated as Gudi Parva in Maharashtra and Goa. It is a spring-time festival that marks the traditional New Year for Marathi and Konkani Hindus. It is celebrated in and near Maharashtra and Goa on the first day of the Chaitra month to mark the beginning of the New Year according to the lunisolar Hindu calendar. The festival is observed with colorful floor decorations called rangoli, a special Gudhi flag (garlanded with flowers, mango and neem leaves, topped with upturned silver or copper vessel), street processions, dancing and festive foods. Gudhi Padva signifies the arrival of spring and to the reaping of Rabi crops.
Cheti Chand: The Sindhi community celebrates this day as Cheti Chand as the new year and observed as the emergence day of Lord Jhulelaal. Prayers are offered to Lord Jhulelaal and the festival is celebrated by making delicacies like Tehri (sweet rice) and Saai Bhaaja (Palak made in dal).
Economics
Invest India: It is India’s national Investment Promotion & Facilitation Agency. The agency functions under DPIIT, Ministry of Commerce and Industry, GoI. It was founded in 2009. It works with several states/UTs of India to build capacity and bring the best global practices in investment targeting, promotion and facilitation areas. The current Managing Director and CEO of Invest India is Deepak Bagla.
Recently, Invest India launched "The Invest India Business Immunity Platform" (BIP). It has been launched under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry. The platform is hosted on the Invest India website. It has been launched to assist businesses and investors in getting real-time updates on India’s active response to COVID-19. The BIP is the active platform for business issue redressal, operating 24/7, with a team of dedicated sector experts and responding to queries at the earliest.
Invest India has teamed up with Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) for responding and resolving queries for MSMEs. The platform, through the partnership, will to provide all the information they require while staying in the comfort of their homes due to the lockdown in the country.
Karur Vysya Bank: Karur Vysya Bank (KVB) is a Scheduled Commercial Bank in India. The KVB bank operates in the treasury, corporate/ wholesale banking and retail banking segments. It has completed 100 years of operation and is one of the leading banks in India. It was founded in 1916. It is headquartered in Karur in Tamil Nadu. It was set up by M. A. Venkatarama Chettiar and Athi Krishna Chettiar. The current Chairman and MD & CEO are Mr. N. S. Srinath and Mr. P. R. Seshadri respectively.
Recently, the KVB launched India's 1st prepaid card 'Enkasu' to reduce cash transactions. It is a prepaid card. The Enkasu prepaid card works on Near Field Communication Technology and this prepaid card will be very useful to Merchants & Customers. The users can easily recharge their card through KVB DLite app, NEFT, UPI or through any KVB branches.
Defence
Indian Army: The Indian Army is the largest branch of the Indian Armed Forces and is responsible for land-based military operations. Its primary mission is the National Security and Defense of India from external aggression and threats, and maintaining peace and security within its borders. It was founded on 1 April 1895. It is headquartered in New Delhi, India. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and it is commanded by the Chief of Army Staff, who is a four-star general. The current Commander-in-Chief is President Ram Nath Kovind. The 28th Chief of Army Staff is General Manoj Mukund Naravane. The motto of Indian Army: “Service Before Self”.
Recently, in an attempt to combat the spread of the deadly Coronavirus or COVID-19, Army Chief General Manoj Mukund Naravane, launched ‘Operation Namastey’. The operation was launched by Army Chief General Manoj Mukund Naravane on 27th March.
The Indian Army has set up eight quarantine facilities across the country. Under the operation, the army will help the Government of India (GoI) fight against the deadly Covid-19 pandemic.
MoD: It refers to the Ministry of Defence (MoD). MoD is charged with coordinating and supervising all agencies and functions of the government relating directly to national security and the Indian armed forces. The President of India is the ceremonial commander-in-chief of the armed forces of the country. It is headquartered in New Delhi. It was formed on 15 August 1947. The first defence minister of independent India was Baldev Singh, who served in Prime Minister Jawaharlal Nehru's cabinet during 1947–52. The current Defence Minister is Rajnath Singh.
Recently, MoD announced that it has acquired land from the State Governments of Tamil Nadu and Uttar Pradesh. It was announced in the Parliament on the 23rd of March 2020. The lands were acquired by the Government of India (GoI) to increase Defence Exports to five billion USD in the next five years.
Regarding this, the GoI has taken several initiative such as The “Strategic Partnership” Model where the manufacturers can enter into partnerships with Indian Entities and set up manufacturing units through technology transfers, the FDI Policy was also revised for the defence sector which allows 100% investment through Government route and Defence Investor Cell was created so that the cell would address the issues related to investments and its related regulatory measures.
Environment
Sikkim: Sikkim is a state in northeast India. It borders Tibet in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Nepal in the west, and West Bengal in the south. Being a part of the Himalayas, the area has a dramatic landscape that includes India’s highest mountain, 8,586m Kanchenjunga. Sikkim is also home to glaciers, alpine meadows and thousands of varieties of wildflowers. Sikkim is the least populous and second smallest among the Indian states. Its Capital is Gangtok. The Chief Minister and the Governor of Sikkim are Prem Singh Tamang and Ganga Prasad respectively.
Recently, the Scientists from the Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology (WIHG) conducted a study and found that glaciers in Sikkim are melting at a higher magnitude than the other Himalayan regions. The study was published in the international scientific journal, Science of the Total Environment.
The study has assessed around 23 glaciers and their spread since 1991 to 2015. The larger glaciers are thinning in size and smaller glaciers are retreating. During these years, major shift in behavior was noted since 2000. Since then, the Western and Central Himalayan glaciers have slowed down melting whereas the rate of the Sikkim Glaciers has increased. It is noted that the increase in summer temperature is the main cause for glacier changes.
This study, for the first time, studied multiple glacier parameters, namely length, area, debris cover, snowline altitude (SLA), glacial lakes, velocity, and downwasting, and explored interlinkage among them to present a clear picture about status and behavior of glaciers in the Sikkim.
WIHG: It refers to Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology. It is an autonomous research institute at Dehradun under the Department of Science and Technology, Ministry of Science & Technology, Government of India. It was founded in 1968 in Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India. The institute provides advisory and consultancy services to various organizations. It also gives advises on geotechnical feasibility of hydel projects, their foundation and site selection.
World Water Day: World Water Day is celebrated every year on the 22nd of March every year since 1993. At the conference, the UN passed a resolution to observe World Water Day in 1992. The day is celebrated by United Nations as well along with various other organizations all over the world. It is celebrated globally to raise awareness of the importance of freshwater. The aim of celebrating this day is to inspire people around the world to learn more about water-related issues and to take action to make a difference.
Recently, on 22 March 2020, World Water day was celebrated. The theme for the 2020 World Water Day is 'Water and Climate Change'. In 2020, in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, there was an additional focus on hand washing and hygiene.
World Meteorological day: It is celebrated annually on 23rd March globally. It is celebrated on 23 March as on this day the World Meteorological Organization was established in 1950.This organization announces a slogan for World Meteorology Day every year, and this day is celebrated in all member countries.
The theme slogan for 2020 is 'Water and Climate Change'. The main objective of this day is to highlight the contribution of Meteorological and Hydrological Services for the safety and wellbeing of the global community. This day is also remembered for the contribution that National Meteorological and Hydrological Services make to the safety and well-being of society.
Indian Policy
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is an Indian government ministry charged with health policy in India. It is also responsible for all government programs relating to family planning in India. The Minister of Health and Family Welfare holds cabinet rank as a member of the Council of Ministers. It was founded in 1976. Its headquarters is in New Delhi. The current Minister of Health and Family welfare is Harsh Vardhan.
Recently, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare declared the Hydroxycholoroquine as a Schedule H1 drug. Under the H1 schedule the export of Hydroxycholoroquine has been banned. The drug listed under Schedule H1 has to be labeled as “Rx” in red colour. The label should also carry precautionary warnings. The supply if H1 drugs have to be registered in a separate register and the name and address of the prescriber and the patient has to be registered in it.
WHO declared the Hydroxychloroquine drug as an essential drug to treat COVID-19 patients so that is why this drug has been banned.
NBT: It refers to the National Book Trust. NBT is an Indian publishing house. It is an autonomous body under the Ministry of Education of the Government of India. NBT now functions under aegis of Ministry of Human Resource Development, Govt. of India India's first Prime Minister Pt. Jawarhrlal Nehru. It was established in 1957. It is headquartered in New Delhi.The trust activities include publishing, promotion of Indian books, children literature, etc. The current President of NBT is Govind prasad sharma.
Recently, NBT launched Stay Home India with Books initiative. Under the initiative more than 100 books can be downloaded from the NBT website. It is providing people its select and best selling titles for FREE Download. The books uploaded by NBT are mostly children books and they are in different languages like English, Hindi, Tamil, Telegu, Bengali, Nepali etc. Apart from the childrens books various genres such as fiction, biography, popular science and many more are too uploaded. This initiative was taken by GoI to help people spend time during this lockdown due to coroanavirus.
SWAYAM: It stands for Study Webs of Active Learning for Young Aspiring Minds. It is a national online education platform. It was launched 2004. The main objective of the online platform is to provide best quality education to maximum numbers of students around India. SWAYAM was developed by Ministry of HRD with the help of NPTEL, IIT Madras and Google.
Recently, the Ministry of HRD (Human Resources Department) claimed the traffic on the national online education platform SWAYAM and other digital initiatives has tripled since the lockdown due to coronavirus.
An increased traffic is also being witnessed by the education portals of NCERT like Diksha, e-pathasala, NROER and NIOS and the other ICT initiatives like Robotics education (e-Yantra), Open Source Software for Education (FOSSEE), Virtual experiments (Virtual Labs) and Learning programming (Spoken tutorial).
SWAYAM: It stands for Study Webs of Active Learning for Young Aspiring Minds. It is a national online education platform. It was launched 2004. The main objective of the online platform is to provide best quality education to maximum numbers of students around India. SWAYAM was developed by Ministry of HRD with the help of NPTEL, IIT Madras and Google.
Recently, the Ministry of HRD (Human Resources Department) claimed the traffic on the national online education platform SWAYAM and other digital initiatives has tripled since the lockdown due to coronavirus.
An increased traffic is also being witnessed by the education portals of NCERT like Diksha, e-pathasala, NROER and NIOS and the other ICT initiatives like Robotics education (e-Yantra), Open Source Software for Education (FOSSEE), Virtual experiments (Virtual Labs) and Learning programming (Spoken tutorial).
Indian polity
Lok Sabha: The Lok Sabha, or House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by adult universal suffrage. Under the constitution of 1950, its members are directly elected for a term of 5 years by territorial constituencies in the states. The maximum strength of the House allotted by the Constitution of India is 550. Currently, the house has 543 seats which are made up by the election of up to 543 elected members and at a maximum. Two additional members were appointed by the president to represent the Anglo-Indian community earlier but was abolished in January 2020 by the 104th Constitutional Amendment Act, 2019.
Recently, amid the nationwide lockdown over coronavirus pandemic, Lok Sabha passed Finance Bill, 2020 without any discussion. The Bill with several amendments was introduced by the Finance Minister Nirmala Sitaraman.
International
25th March: Every year 25th of March is celebrated as the International Day of Remembrance of the Victims of Slavery and the Transatlantic Slave Trade across the globe. The main objective of celebrating this day is to honor and remember those who suffered and died at the hands of the brutal slavery system. This day was celebrated for the first time in 2008. The theme was 'Breaking the Silence, Lest We Forget'.
On 25th March 2020 the theme for International Day of Remembrance of the Victims of Slavery and the Transatlantic Slave Trade is 'Confronting Slavery’s Legacy of Racism Together'.
Saudi Arabia: Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, is a country in Western Asia constituting the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula. it is bordered by Jordan and Iraq to the north, Kuwait to the northeast, Qatar, Bahrain, and the United Arab Emirates to the east, Oman to the southeast and Yemen to the south; it is separated from Egypt and Israel by the Gulf of Aqaba. Its Capital city is Riyadh. The currency used here is Saudi riyal.
Recently, the Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas Dharmendra Pradhan announced that Saudi Arabia has assured India on uninterrupted LPG supply amidst growing threat of COVID-19. The Union Minister made this announcement after his discussions with Saudi Minister of Energy, Prince Abdulaziz bin Salman, on global oil market developments.
India is the second largest importer of LPG in the world. It fulfils half of its requirements from the Middle East countries such as Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Oman and Qatar.
United States (US): The United States of America (USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country consisting of 50 states, a federal district, five major self-governing territories, and various possessions. The 50 states covers a vast swath of North America, with Alaska in the northwest and Hawaii extending the nation’s presence into the Pacific Ocean. The capital of US is Washington, D.C. The current President of US is Donald Trump.
Recently, the President of US Donald Trump invoked the Defence Production Act. The act has been invoked in order to direct General Motors, a Multinational Corporation to manufacture ventilators needed to fight COVID-19.
Defence Productin Act: The Defense Production Act (Pub. L. 81–774) is a United States federal law. It was enacted on September 8, 1950 in response to the start of the Korean War. It was part of a broad civil defense and war mobilization effort in the context of the Cold War. It was enacted by the 81st United States Congress.
The Act contains three major sections.
1. The act authorizes the president of the United States to make or even force a business to accept and prioritize contracts that are essential for defence of the country. It also allows the president to designate materials to be prohibited from hoarding or price gouging.
2. It authorizes the President to frame regulations, order to allocate services, materials and facilities that will promote defence of the country.
3. It authorizes the President to control the civilian economy so that scarce and critical materials necessary to the national defense effort are available for defense needs.
National
CDSCO: It refers to Central Drugs Standard Control Organization. CDSCO is the national regulatory body for Indian pharmaceuticals and medical devices. ait works under Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India. It is headquartered in New Delhi, India. The function of CDSCO is to bring out transparency, accountability and uniformity in its services in order to ensure safety, efficacy and quality of the medical product manufactured, imported and distributed in the country. Under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, CDSCO is responsible for approval of Drugs, Conduct of Clinical Trials, laying down the standards for Drugs, control over the quality of imported Drugs in the country and coordination of the activities of State Drug Control Organizations by providing expert advice with a view of bring about the uniformity in the enforcement of the Drugs and Cosmetics Act.
Recently, CDSCO approved the first Made in India “Mylab PathoDetect COVID-19 Qualitative PCR kit”. CDSCO has given the commercial approval to the COVID-19 diagnostic test kit made by Mylab Discovery Solutions Pvt Ltd which is also known as the Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) test. The kit has been developed as per WHO/CDC guidelines. This was achieved with an emphasis on ‘Make in India’ along with support from local and central government.
At present, the GoI was importing kits from Germany’s Altona Diagnostics to facilitate testing to diagnose Coronavirus patients across India. But the supply of these german kits was facing troble due to grounded airlines.
The lady behind this achievement is Mylab's research and development chief, Minal Dakhave Bhosale. The coronavirus testing kit called Patho Detect was developed in just six weeks. She submitted the kit to the National Institute of Virology (NIV) for evaluation on March 18th, just a day before delivering her daughter.
India & Germany: The Union Cabinet chaired by PM Modi approved MoU signed between India and Germany. The MoU was signed on 25 March 2020 between Ministry of Railways and DB Engineering and Consulting GMBH of Germany. The agreement was signed in February 2020 for technological cooperation in the Railway Sector.
As per the provisions under the MoU, it will facilitate freight operations including automotive transport, cross-border transport and logistics. It will not only help in infrastructure building but also enhance the development of a modern, competitive railway organization, IT solutions for railway operations, marketing and sales and administrative purposes.
In order to modernize the Railway sector, the Ministry of Railways has signed several agreements, memorandum of cooperation, technical cooperation, with foreign governments.
CDRI: It refers to the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure. CDRI is an India-led global climate initiative. The initiative was announced by the Indian Prime Minister Narender Modi in September 2019 at the UN Climate Action Summit 2019 held in New York City, USA. It was formed through consultations with more than 35 countries. The highest policy-making body of the CDRI is its Governing Council which is co-chaired by India and a representative of another national government nominated by rotation every two years. The main objective of CDRI is to enable a measurable reduction in infrastructure losses from disasters. It aims to develop the resilience of infrastructure systems to climate and disaster risks by linking governments, UN agencies, banks, private sector groups, and academia.
Recently, The United Kingdom (UK) has been confirmed as the first co-chair of the Governing Council of Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI).
Shaheed Diwas: Shaheed Diwas is celebrated in India every year on 23 March. This day celebrated to pay tribute to Indian revolutionary Bhagat Singh, Sukhdev Thapar, and Shivaram Rajguru. On this day in 1931, they were hanged by the British in Lahore (Pakistan).
Recently, India celebrated Shaheed Divas on the 23rd of March 2020. People across the nation remembers the sacrifice made young inspirational souls like Bhagat Singh on this day. Schools and colleges hold events on poetry, speech or drama to pay tribute to the revolutionaries, who were not deterred even in the face of death.
People In News
Zoya Akhtar: She is an Indian film director and screenwriter. She completed her diploma in filmmaking from NYU. She has assisted directors such as Mira Nair, Tony Gerber and Dev Benegal. She turned a writer/director with her directorial debut with Luck By Chance in 2009.
Recently, Zoya Akhter was honored with IIFTC Tourism Impact Award 2020 at the 8th India International Film Tourism Conclave at a glittering award ceremony held recently in Mumbai. She was awarded for her outstanding contribution to world tourism through her cinema. The award was presented by Naheed Nenshi - Mayor of Calgary, Alberta, Canada.
She has promoted tourism through her films like Zindagi Na Milegi Dobara which was filmed in Spain, and ‘DilDhadakne Do’ which was a comedy drama shot in Turkey.
IIFTC: It refers to International Film Tourism Conclave. IIFTC is Asia’s largest film tourism event. The award was founded in 2013. IIFTC’s single minded objective is to bring the global film locations to the Indian film industry.
CBDT: It refers to Central Board of Direct Taxes. CBDT is the apex policy-making body of the Direct Tax department. It functions under the Department of Revenue of the Ministry of Finance. The current Chairperson of CBDT is Pramod Chandra Mody.
Recently, the Appointment Committee of the Cabinet approved the appointment of two Indian Revenue Service (IRS) officers Satish Kumar Gupta and Krishan Mohan Prasad as members of the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) Board.
Satish Kumar Gupta: He is a 1984 batch IRS officer. He currently serves as the Principal Chief Commissioner (PCCIT) of I-T (Income Tax) in Mumbai, Maharashtra. He has also served as Director-General of Investigation of Bhopal and Jaipur.
Krishan Mohan Prasad: He is a 1984 batch IRS officer. He currently serves as the head of Faceless e-Assessment scheme as first Principal Chief Commissioner of Income-tax, National e-assessment centre in Delhi.
Places In News
Tamil Nadu: It is located in the extreme south of the subcontinent. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the east and south and by the states of Kerala to the west, Karnataka (formerly Mysore) to the northwest, and Andhra Pradesh to the north. It also shares a maritime border with Sri Lanka. It was formerly the Madras Presidency of British India but was renamed Madras (State) after independence in 1947. Madras (State) was again renamed Tamil Nadu in 1968. Its Capital is Chennai. The Governor and Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu are Banwarilal Purohit and Edappadi K. Palaniswami respectively.
Recently, Mayiladuthurai has become the 38th district of Tamil Nadu after bifurcating the Nagappattinam district. This announcement was made by the Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu Shri Edappadi K. Palaniswami. The new Tamil Nadu 38th District will be headquartered at Mayiladuthurai, in the heart of the Delta region.
Madhya Pradesh: Madhya Pradesh (MP) is the second largest Indian state by area. It borders the states of Uttar Pradesh to the northeast, Chhattisgarh to the southeast, Maharashtra to the south, Gujarat to the west, and Rajasthan to the northwest. Its capital is Bhopal. The Chief Minister and Governor of Madhya Pradesh are Kamal Nath and Lal Ji Tandon respectively.
Recently, BJP leader Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan has become the new Chief Minister Madhya Pradesh. He is the 17th Chief Minister of the State. It is the 4th time that he is elected as the Chief Minister of MP. He was administered the oath of office and Secrecy at Rajbhavan by the Governor of Madhya Pradesh Shri Lalji Tandon. He holds the record as the state's longest-serving Chief Minister.
Uttarakhand: Uttarakhand, a state in northern India crossed by the Himalayas. It is known for the natural environment of the Himalayas, the Bhabar and the Terai and also for for its Hindu pilgrimage sites. It is often referred to as the "Devabhumi" (literally "Land of the Gods"). Uttarakhand became the 27th state of the Republic of India On 9 November 2000. it was carved from the Himalayan districts of Uttar Pradesh. Its winter Capital is Dehradun and summer capital is Gairsain. The Chief Minister and the Governor of Uttarakhand are Trivendra Singh Rawat and Baby Rani Maurya respectively.
Recently, the Government of Uttarakhand abolished reservation in promotion in the state government jobs. This major decision was taken by the Trivendra Rawat-government on completion of three years of its tenure. Following the state government's order, the employees from the General-OBC categories ended their strike. The state government also issued orders regarding the departmental promotion committee (DPC).
The government employees from the General-OBC category in the state had been staging a protest, demanding the implementation of the Supreme Court's decision on the issue.
Odisha: Odisha also formerly Orissa, is an Indian state located on the eastern coast of India. It neighbors the states of West Bengal and Jharkhand to the north, Chhattisgarh to the west and Andhra Pradesh to the south. It is an eastern Indian state on the Bay of Bengal. It is known for its tribal cultures and its many ancient Hindu temples. The capital of Odisha is Bhubaneswar. The Governor and the Chief Minister of Odisha are Ganeshi Lal and Naveen Patnaik respectvely.
Recently, the Chief Minister of Odisha Naveen Patnaik launched "Mo Jeeban" programme in Odisha. The programme was launched for the containment of COVID-19 pandemic. Through Mo Jeeban programme, the chief minister of Odisha urged people to take an oath in name of their children and parents to cooperate and support by not stepping outside and take precautionary measures like washing hands for at least 20 seconds etc.
Science and Technology
ARI: It refers to Agharkar Research Institute. ARI is an autonomous institute of Government of India (GoI). It functions under the department of Science & Technology, GoI.
Recently, Scientists from Agharkar Research Institute (ARI) have developed biofortified high quality wheat MACS 4028. It has high protein content. It not only has a better nutritional quality having zinc 40.3 ppm, and iron content of 40.3ppm and 46.1ppm but also it has a good milling quality and overall acceptability. This semi-dwarf variety which matures in 102 days has shown the superior and stable yielding ability of 19.3 quintals per hectare. It is resistant to stem rust, leaf rust, foliar aphids, root aphids, and brown wheat mite. The development of MACS 4028 was published in the Indian Journal of Genetics and Plant Breeding.
The MACS 4028 variety is also included by the Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) programme for United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) to reduce malnutrition in a sustainable way. This new variety of wheat can boost the Vision 2022 “Kuposhan Mukt Bharat”, the National Nutrition Strategy. Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has also tagged this variety under the Biofortified category during the year 2019.
Kuposhan Mukt Bharat: It is an initiative of the GoI to tackle the hidden hunger in the rural areas of India.
USSF: It refers to United States Space Force. The USSF is the space warfare service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services. It was founded on 20 December 2019. It is headquartered at The Pentagon, Arlington, Virginia, United States. It was established by the Trump administration to identify and develop new space defence technologies. The Space Force is established also to prove US dominance in the Space among other force that is quietly establishing their powers in Space. The current and the first Chief of Space Operations is Gen John W. Raymond
Recently, The USSF launched an Advanced Extremely High-Frequency satellite (AEHF-6) for its military communications. With the launch of the satellite, US have begun its first National Security Mission.
The launching of The Lock Heed Martin AEHF-6 (Advanced Extremely High Frequency) satellite took place from the Atlas V551 rocket from Cape Canaveral, Florida. The satellite is to provide global protected communications. This will enhance tactical operating warfare skills of the US on ground, aerial and maritime platform.
Sports
Mountaineering: Mountaineering is the sport of climbing a mountain. Mountaineering may involve using technical equipment and combining a series of related skills like scrambling, climbing, glacier travel, ice climbing or mixed climbing. Some of the famous mountain climbers are Tenzing Norgay, Edmond Hillary, George Mallory, Reinhold Messner etc,
Recently, Indian mountaineer Satyarup Siddhanta has become the first youngest Indian to climb the Seven Volcanic Summits. This West Bengal-based IT professional, who currently works in Bengaluru achieved the unique feat at the age of 35 years and 262 days breaking the previous world record of Australia's Daniel Bull who did it at the age of 36 years and 157 days. He has been nominated for the coveted Limca Book of World Records for his extra-ordinary achievement to be the first Indian to climb the highest volcanoes of each of the 7 continents.
His Seven volcanic summits are: Ojos del Salado (6,893 m) - Chile - South America
Mt Kilimanjaro (5,895 m) - Tanzania - Africa Mount Elbrus (5,642 m) - Russia - Europe
Mount Pico de Orizaba (5,636 m) - Mexico - North America
Mt Damavand (5,610 m) - Iran - Asia
Mt Giluwe (4,368 m) - Papua New Guinea - Australia
Mt Sidley (4,285 m) - Antarctica.
Other than this feat he is also the first Indian to climb Mt. Sidley, highest volcano of Antarctica, the first Indian to climb Mt. Giluwe, highest volcano of Papua New Guinea,
the first Indian to climb Mt. Wilhelm, highest mountain of Papua New Guinea, the third Indian to climb Mt. Ojos Del Salado, the highest volcano of Chile, the first person to play the Indian National Anthem on flute in Antarctica.
The list of Records made by Satyarup Siddhanta are Guinness Book of World Records, Limca Book of Records, Asia Book of Records, India Book of Records, Champion Book of Records and British Book of Records.
FIFA: It is an acronym for Federation Internationale de Football Association or International Federation of Association Football. FIFA is a non-profit organization and the highest governing body of Football. It was founded on 21 May 1904. It is headquartered in Zurich, Switzerland. The current President of FIFA is Gianni Infantino.
Recently, FIFA named Indian Football team Captain Sunil Chhetri among 28 others for FIFA’s COVID-19 Campaign. The campaign is called “Pass the message to kick out Corona Virus”.
The FIFA and World Health Organization (WHO) have joined hands to launch an awareness campaign to combat Corona Virus. The campaign promotes 5 key steps for people to follow to protect their health in line with WHO guidance, focused on hand washing, coughing etiquette, not touching your face, physical distance and staying home if feeling unwell.
Some of the best known players like Argentine superstar Lionel Messi and World Cup winners like Philip Lahm, Iker Casillas and Carles Puyol are also inclided in the campaign.
Sunil Chhetri: He is an Indian professional footballer who plays as a striker or winger and captains both the Indian Super League side Bengaluru and the Indian national team. He has been awarded the Padma Shri and Arjuna Award for Football.
Tokyo Olympics: The 2020 Summer Olympics, officially the Games of the XXXII Olympiad and commonly known as Tokyo 2020, is a forthcoming international multi-sport event to be held in Tokyo, Japan. Tokyo had hosted the Summer Olympics in 1964.
Recently, the International Olympic Committee and Tokyo Olympic organizers agreed to postpone the games. It was originally scheduled to take place between 24 July and 9 August 2020, the Games have been rescheduled for 23 July to 8 August 2021. Japan’s Prime Minister Shinzo Abe and the head of the International Olympic Committee agreed to postpone the Tokyo 2020 Games in response to the 2019–20 coronavirus pandemic.
It is for the first time in history that the start of an Olympics will be delayed to another year.
Arts
 Mandu Festival: The famous three day Mandu Festival was organized at the historic town of Mandu in Dhar district of Madhya Pradesh. The festival began on February 13, 2021, and culminated on February 15, 2021.
Mandu Festival: The famous three day Mandu Festival was organized at the historic town of Mandu in Dhar district of Madhya Pradesh. The festival began on February 13, 2021, and culminated on February 15, 2021.
Highlights:
- The festival was organized by the state government of Madhya Pradesh. The festival showcased each and every aspect of the ancient Mandu city, ranging from food, music, history & heritage, art & craft etc.
- During the festival, the state culture and tourism minister Usha Thakur inaugurated the newly constructed Dino Adventure Park and Fossils Museum in Mandu.
- The Dinosaur Park is the first modern fossil park in India which has 24 eggs and other fossils of dinosaurs on display.
About Mandu
- Mandu or Mandavgad is an ancient city in the present-day Mandav area of the Dhar district. It is a world-famous picturesque tourist destination located in Dhar district in the Malwa region of western Madhya Pradesh.
- It is surrounded by stone walls dotted with darwazas (gateways). It's also known for its Afghan architectural heritage. Landmark buildings include Hoshang Shah’s Tomb, a domed marble mausoleum, and the vast Jami Masjid mosque, with courtyards framed by colonnades. The imposing, centuries-old Jahaz Mahal palace stands between 2 lakes.
About MP:
- The Chief Minister and the Governor of Madhya Pradesh (MP) are Shivraj Singh Chouhan and Anandiben Patel. The Capital of MP is Bhopal.
 Rashtriya Sanskriti Mahotsav: The Governor of West Bengal, Shri Jagdeep Dhankhar recently inaugurated the 11th edition of ‘Rashtriya Sanskriti Mahotsav’ at Cooch Behar Palace in West Bengal.
Rashtriya Sanskriti Mahotsav: The Governor of West Bengal, Shri Jagdeep Dhankhar recently inaugurated the 11th edition of ‘Rashtriya Sanskriti Mahotsav’ at Cooch Behar Palace in West Bengal.
Highlights:
- The event was inaugurated on February 14, 2021, in the presence of Minister of State (I/C) for Culture and Tourism, Shri Prahlad Singh Patel.
- Ten editions of the festival have successfully been organized ever since the festival was started in November, 2015.
- These 10 editions were organized in Delhi, Bengaluru, Varanasi, Tawang, Karnataka, Gujarat, Tehri and Madhya Pradesh.
 Basant Panchami: Basant Panchami or Vasant Panchami marks the beginning of the spring season - Basant means spring and Panchami means "the fifth day" (or Panchmi of Shukla Paksha in Magh Maas).
Basant Panchami: Basant Panchami or Vasant Panchami marks the beginning of the spring season - Basant means spring and Panchami means "the fifth day" (or Panchmi of Shukla Paksha in Magh Maas).
The day is also celebrated as Saraswati Puja and the Hindu goddess of wisdom and knowledge, Saraswati, is worshipped on this day.
Saraswati Puja on Vasant Panchami is more popular in Bengal, Odisha and North Indian states like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, and Madhya Pradesh.
Highlights of the Puja:
- On this day, the Hindus visit temples and pray to Goddess Saraswati.
- Several schools begin their session on Saraswati Puja day.
- Men, women and children dress up in the vibrant yellow colour as mustard fields in northern parts of India blooms during this season.
- Yellow flowers are offered to Goddess Saraswati and the festive yellow dishes like sweet saffron rice, kesari sheera, boondi ke ladoo, rajbhog and khichdi are prepared in homes.
 'Shauryanjali' Programme: The Union Home Minister Amit shah recently attended the 'Shauryanjali' programme.
'Shauryanjali' Programme: The Union Home Minister Amit shah recently attended the 'Shauryanjali' programme.
Highlights
- The programme was organized to commemorate the 125th birth anniversary of Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose.
- He paid homage to the great freedom fighters of Bengal who laid down their lives in the struggle for freedom of the country.
- At the event, He also flagged off a cycle rally.
- Three teams, namely Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose, Rasbehari Bose and Khudiram Bose, are participating in the rally which will create awareness in different parts of West Bengal about the great sacrifices made by the revolutionaries of Bengal in the freedom movement.
Rash Behari Bose: Rash Behari Bose (1886 – 1945) was an Indian revolutionary leader against the British Raj. He was born in West Bengal. Following the attempt to assassinate Lord Hardinge on 23 December 1912 in Delhi, Rash Behari was forced to go into hiding. He was one of the key organisers of the Ghadar Mutiny, and later the Indian National Army.
Khudiram Bose: Khudiram Bose (3 December 1889 – 11 August 1908) was an Indian revolutionary who opposed British rule of India. For his role in the Muzaffarpur Conspiracy Case, along with Prafulla Chaki, he was sentenced to death and subsequently executed, making him one of the youngest martyrs of the Indian Independence Movement.
 Chhatrapati Shivaji Jayanti: Shiv Jayanti or Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Jayanti is celebrated in India on 19 February every year. The day marks the birth anniversary of the great Maratha king Shivaji. This year marks the 391st birth anniversary of the Maratha ruler.
Chhatrapati Shivaji Jayanti: Shiv Jayanti or Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Jayanti is celebrated in India on 19 February every year. The day marks the birth anniversary of the great Maratha king Shivaji. This year marks the 391st birth anniversary of the Maratha ruler.
About Shivaji:
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj is considered as one of the most valiant and distinguished rulers in the history of India.
- He is the founder, and torch-bearer of the illustrious Maratha Empire was born on 19th February 1630 at the Shivneri Fort near Pune.
- The 1659 episode of Shivaji’s life in which he defeated Afzal Khan in the famous battle of Pratapgarh holds testimony of Shivaji’s leadership acumen and mental fortitude at the age of 29.
- It is his meticulous planning, strong spy-network, and unique guerilla warfare tactics that make him one of the greatest rulers in India’s history.
- His exploits against the Mughals, especially against Aurangzeb are notable feats that reflect his greatness, his conquest against the Mughal viceroy under Aurangzeb and against Mirza Raja Jai Singh; Aurangzeb’s general being the most prominent ones.
- Shivaji’s escape from Agra with his son was another enthralling episode from Shivaji’s life.
- The king was known for his wit and was one of the first Indian rulers who is said to have introduced the concept of “naval force” to defend the Konkan side of Maharashtra.
- He also employed many Muslim soldiers in his battalion and was secular to his core.
Why Shivaji Jayanti is celebrated in India?
- The Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj Jayanti or Shiv Jayanti was first celebrated in India in 1870, when Mahatma Jyotirao Phule discovered the tomb of Shivaji Maharaj on Raigad, around 100 km from Pune.
- Freedom fighter Bal Gangadhar Tilak followed the tradition later and popularized the image of Shivaji Maharaj by highlighting his contributions and brought people together by means of it during the Independence movement.
- The day is associated with the pride of the people of Maharashtra.
- The eve is also celebrated in Goa and Karnataka.
Economics
 Carbon-Neutral Oil: Billionaire Mukesh Ambani’s Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) has recently sourced the world’s first consignment of ‘carbon-neutral oil’ from the US.
Carbon-Neutral Oil: Billionaire Mukesh Ambani’s Reliance Industries Ltd (RIL) has recently sourced the world’s first consignment of ‘carbon-neutral oil’ from the US.
- The move comes as the company looks to become a net zero-carbon company by 2035.
- Carbon-neutral oil was delivered to Reliance by Oxy Low Carbon Ventures (OLCV), a division of US oil Major Occidental. RIL got 2 million barrels of consignment Permian basin.
- The Very Large Crude Carrier (VLCC) Sea Pearl containing the carbon-neutral oil from Permian basin, unloaded the cargo at Jamnagar on January 28, 2021.
- Reliance operates the world’s largest single location oil refining complex at Jamnagar in Gujarat with capacity of 68.2 million tonnes a year.
- The transaction is a first step in the creation of a new market for climate-differentiated crude oil.
Background:
- Mukesh Ambani had in July 2020 unveiled plans to turn Reliance into a net carbon zero company by 2035. This will be done by embracing new technologies to convert its carbon dioxide emissions into useful products and chemicals.
- Occidental is the first US-based international energy company to announce an ambition to achieve net-zero GHG emissions associated with the use of its products by 2050. The company has been using carbon-dioxide in its enhanced oil recovery operations in the Permian Basin for over 40 years.
About RIL: Reliance Industries Limited (RIL) is an Indian multinational conglomerate company. The company is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. Reliance owns businesses across India engaged in energy, petrochemicals, textiles, natural resources, retail, and telecommunications. RIL was founded by Dhirubhai Ambani on 8 May 1973.
 Mobile Components Unit in Tamil Nadu: Tata Electronics a subsidiary of Tata group signs MoU (Memorandum of Understanding) with Tamil Nadu to set up a facility to manufacture mobile components.
Mobile Components Unit in Tamil Nadu: Tata Electronics a subsidiary of Tata group signs MoU (Memorandum of Understanding) with Tamil Nadu to set up a facility to manufacture mobile components.
- The facility will be established in Krishnagiri to manufacture the mechanical enclosures of mobile phones.
- This project of Tata Electronics will cost around Rupees 4684 crores.
- The project seeks to help in creating jobs for 18,250 people in the state.
A MoU has also been signed by Tamil Nadu with the Grasim Industries Ltd in order to establish a paint manufacturing unit at Cheyyar with an investment of Rupees 750 crore.
Tamil Nadu, in total, has signed 28 MoUs for the projects for which the budget outlay is Rupees 28,000 crore.
About Tata Group:
- The Tata Group is an Indian multinational conglomerate. It is a private Company.
- It was founded in 1868 by Jamsetji Tata. It is headquartered in Mumbai.
- The company is one of the biggest and oldest industrial groups of India. Each of the Tata Company is operating independently under its own board of directors and shareholders.
The companies affiliated under the Tata include
- Tata Communications
- Tata Chemicals
- Tata Consumer Products
- Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)
- Tata Motors
- Tata Cliq
- Tata Elxsi
- Taj Air
- Tata Power
- Jamshedpur FC
- Tata Steel
- Indian Hotels Company Ltd
- CromÄ
- Tata Starbucks
- Vistara
- Tanishq
- Voltas
- Tata Projects Ltd
- Tata Capital
- Titan
- Trent
About Grasim Industries Ltd:
- Grasim Industries Limited is an Indian manufacturing company based in Mumbai, Maharashtra. It was established in 1947 as a textile manufacturer in India.
- Grasim Industries was ranked 154th in a list of the world's best regarded firms compiled by Forbes. It is a subsidiary of Aditya Birla Group.
- The work of the company is diversified into Viscose Staple Fibre, sponge iron, cement, chemicals and Diversified Financial Services.The industry is the world’s largest producer of viscose rayon fibre that accounts for 24 per cent of the market share.
 Drones for Agriculture: The Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare (MoAFW) was recently allowed to use drones.
Drones for Agriculture: The Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare (MoAFW) was recently allowed to use drones.
Highlights:
- The Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA) and Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA) granted conditional exemption for Remotely Piloted Aircraft System (RPAS) usage to the MoAFW.
- The permission allows drone deployment by the MoAFW for remote sensing data collection in agricultural areas of 100 districts of the country under Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY).
- It will be used in production estimates at the gram Panchayat level.
- The exemption shall be valid from the one year from the date of issue of the permission or until the operationalisation of the Digital Sky Platform.
- However, this exemption shall be valid only if all conditions and limitations are strictly adhered to.
- In case of violation of any condition, this exemption shall become null & void and action may be initiated.
 Takeover of DHFL Ltd by Piramal Group: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently approved the acquisition of Diwan Housing Finance Corporation Ltd (DHFL) by Piramal Capital And Housing Finance.
Takeover of DHFL Ltd by Piramal Group: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently approved the acquisition of Diwan Housing Finance Corporation Ltd (DHFL) by Piramal Capital And Housing Finance.
The decision was taken by central bank after a month a Committee of Creditors (CoC) of DHFL voted in favor of Piramal’s bid. Following this, the resolution plan of the company has been approved by the RBI.
Now, the Piramal Group will require to take permission of National Company Law Tribunal to take over the DHFL.
Issue:
- DHFL was sent to bankruptcy court in December 2019 after the company defaulted to its lenders on debt worth Rs 90,000 crore.
- The Enforcement Directorate (ED) conducted a raid in the company and found links of money laundering activity with respect to the loans given to closely linked firms.
- Following this, in accordance with the RBI Act of 1934, RBI removed the board of directors DHFL alleging inadequate governance in the company.
- Piramal’s plan is to recover Rs 37,250 crore over the next five years for DHFL’s lenders.
About Dewan Housing Finance Corporation Ltd. (DHFL): DHFL is a deposit-taking housing finance company. It is headquartered in Mumbai. It was established in order to enable the access to the economical housing finance for the lower- and middle-income groups in the semi-urban and rural India. The company is the second housing finance company of India.
About Piramal Group: Piramal Group is a global business conglomerate with interests in Pharma, Financial Services, Information Management, Glass Packaging and Real Estate.
With offices in 30 countries and brand presence in over 100 markets, the Piramal Group has a global team of over 10,000 people from 21 diverse nationalities. It was founded in 1984. The current Chairman of Piramal Group is Ajay Piramal.
Defence
 Delhi Police: Minister of Defence Sh. Rajnath Singh recently honoured Delhi Police with the Best Marching Contingent Trophy during Republic Day 2021. Delhi police were honoured on 15th February, in the midst of glittery ceremony at South Block.
Delhi Police: Minister of Defence Sh. Rajnath Singh recently honoured Delhi Police with the Best Marching Contingent Trophy during Republic Day 2021. Delhi police were honoured on 15th February, in the midst of glittery ceremony at South Block.
Defence Minister highly appreciated the Delhi Police for showing exceptional professionalism in the recent highly stressful time.
About Delhi Police:
- The Delhi Police is the law enforcement agency for the National Capital Territory of Delhi.
- Delhi Police comes under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India.
- It was founded in 1867.
- In 2015, sanctioned strength of Delhi Police was 84,536 making it one of the largest metropolitan police forces in the world.
- The elected officer responsible for Delhi police is Amit Shah, Minister of Home Affairs (India).
 E-Chhawani: Raksha Mantri Rajnath Singh recently launched E-Chhawani portal and mobile app in New Delhi to facilitate ‘ease of living’ and ‘ease of doing’ for the residents of the Cantonment Boards across the country.
E-Chhawani: Raksha Mantri Rajnath Singh recently launched E-Chhawani portal and mobile app in New Delhi to facilitate ‘ease of living’ and ‘ease of doing’ for the residents of the Cantonment Boards across the country.
Key points about the portal:
- The portal can be accessed at https://echhawani.gov.in/
- The portal has been created to provide online civic services to over 20 lakh residents of 62 Cantonment Boards across the country.
- Through the portal, the residents of cantonment areas will be able to avail basic services like renewal of leases, application for birth & death certificates, water & sewerage connections, trade licences with just a click of a button.
- The portal has been jointly developed by eGov Foundation, Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL), Directorate General Defence Estates (DGDE) and National Informatics Centre (NIC).
What is a Cantonment board?
- A cantonment board is a civic administration body in India. The board functions under control of the Ministry of Defence. It takes care of mandatory duties such as the provision of public health, water supply, sanitation, primary education, and street lighting etc.
.jpg) Arjun Main Battle Tank (MK-1A): Prime Minister Modi recently handed over the indigenously developed Arjun Main Battle Tank (MK-1A) to the Indian Army at a ceremony in Chennai.
Arjun Main Battle Tank (MK-1A): Prime Minister Modi recently handed over the indigenously developed Arjun Main Battle Tank (MK-1A) to the Indian Army at a ceremony in Chennai.
The army will get 118 units of the Main Battle Tank. It has been indigenously designed, developed and manufactured by CVRDE and DRDO along with 15 academic institutions, eight labs and several MSMEs.
About Arjun Main Battle Tank MK-1A:
- The project- Arjun Main Battle Tank was started by DRDO in 1972.
- It was initiated along with the Combat Vehicles Research and Development Establishment as its lead laboratory
- The mass production of the Arjun Battle Tank began in the year 1996 at Indian Ordnance Factory in Avadi facility.
- The Indian Army received the first batch of 16 tanks in 2004 and they were inducted as a squadron of the 43 Armoured Regiment.
- In 2009, the first Arjun regiment of the Indian Army had 45 tanks.
Special Features of Arjun Main Battle Tank MK-1A:
- The major speciality of Arjun tanks is - Fin Stabilised Armour Piercing Discarding Sabot' (FSAPDS) ammunition and 120-mm calibre rifled gun.
- It also has a computer-controlled integrated fire control system with stabilised sighting that works in all lighting conditions.
- The secondary weapons include a co-axial 7.62-mm machine gun for anti-personnel and a 12.7-mm machine gun for anti-aircraft and ground targets.
- The tank also known as the Hunter Killer makes it the most potent tank in India.
Objective of Arjun Main Battle Tank MK-1A
The objective of the Arjun tanks was to create a state of the art tank with superior fire power, high mobility and create an excellence in protection.
What is different in MK-1A?
- The Mk-1A version has 14 major upgrades than the previous version.
- It is also supposed to have missile firing capability as per the design, but this feature will be added later as final testing of the capability is still on.
- The latest version is 54.3 per cent indigenous content against the 41 per cent in the earlier model.
Note: India is now one of the countries in the league of 10 nations worldwide to design and develop their own MBT.
The other nations that are in this league are UK, Germany, USA, France, Israel, South Korea, Russia, China and Japan. The Arjun MBT has outperformed the Russian T-90s in 2010 in the exercise which took place during a desert trial conducted by the Army.
 Helina and Dhruvastra Missile Systems: In a major boost for the Indian armed forces, joint User Trials for the helicopter-launched version of the Nag anti-tank guided missile, ‘Helina’, and its Air Force variant ‘Dhruvastra’ have been carried out from Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) at the Pokhran deserts in Rajasthan.
Helina and Dhruvastra Missile Systems: In a major boost for the Indian armed forces, joint User Trials for the helicopter-launched version of the Nag anti-tank guided missile, ‘Helina’, and its Air Force variant ‘Dhruvastra’ have been carried out from Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) at the Pokhran deserts in Rajasthan.
Helina (Army Version) and Dhruvastra (Air Force Version) Missile Systems have been designed and developed by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
Five missions were carried out. Four missions for evaluating missile capabilities in minimum and maximum range of 7 kms and the final mission was carried out with warhead missile against a derelict tank.
About Helina and Dhruvastra:
- Developed indigenously by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Helina and Dhruvastra are a third-generation, Lock on Before Launch (LOBL) fire and forget class anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) system mounted on the ALH.
- Helina is the helicopter-launched version of the Nag missile system.
- The system has all- weather day and night operational capabilities and can defeat battle tanks with conventional armour as well as explosive reactive armour (ERA).
- It is one of the most-advanced anti-tank weapons in the world.
- The Helina missile can engage targets both in direct hit mode as well as top attack mode.
- While the Helina weapon systems has been developed for the Indian Army, its Indian Air Force (IAF) variant Dhruvastra has also been developed by the DRDO and now both variants are ready for induction into services.
 INS Pralaya: The Indian Naval Ship (INS) Pralaya recently participated in the NAVDEX 21 (Naval Defence Exhibition) and IDEX 21 (International Defence Exhibition) which were scheduled from 20 to 25 February 2021.
INS Pralaya: The Indian Naval Ship (INS) Pralaya recently participated in the NAVDEX 21 (Naval Defence Exhibition) and IDEX 21 (International Defence Exhibition) which were scheduled from 20 to 25 February 2021.
INS Mysore (an indigenously built guided missile destroyer deployed in the Persian Gulf) also participated in the exhibition.
IDEX and NAVDEX, and the International Defence Conference are organised by the Abu Dhabi National Exhibitions Company (ADNEC), in cooperation with the Ministry of Defense and the General Command of the UAE Armed Forces.
The exhibitions take place bienially. The event showcase the latest technologies and innovation in the global defence sector, support the growth of UAE’s defence industry, and forge new relationships between major international companies.
About INS Pralaya:
- INS Pralaya is the second ship of the indigenously built Prabal Class Missile Vessels.
- The ship was built indigenously at Goa Shipyard Limited.
- It was commissioned in the Indian Navy on 18 December 2002.
- The 56 m long ship, displacing about 560 T is capable of speeds in excess of 35 knots and is fitted with an impressive array of weapons and sensors. These include a 76.2 mm medium range gun, 30 mm close range guns, chaff launchers and long range surface to surface missiles.
 Iran-Russia Maritime Security Belt 2021: India has recently joined the “Iran-Russia Maritime Security Belt 2021″. It is a two-day naval exercise.
Iran-Russia Maritime Security Belt 2021: India has recently joined the “Iran-Russia Maritime Security Belt 2021″. It is a two-day naval exercise.
- The exercise is being held in the northern part of the Indian Ocean.
- The drill was participated by the forces and vessels from navy divisions of both the Iranian army and Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC).
- Several vessels from the Russian navy also participated in the drill. Indian Navy has also joined the exercise with selected vessels.
- The drill will also be participated by the Chinese Navy.
- It will cover an area of 17,000 square kilometres.
- The naval exercise will carry the range of activities which also includes the shooting at sea targets, air targets, liberation of the hijacked ships, anti-piracy operations and search & rescue operations.
About IRGC:
- Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), also called Pasdaran, is a branch of the Iranian Armed Forces. It was founded by the order of Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini in April 1979 after the Iranian Revolution.
- It was formed to defend the country's Islamic system, and to provide a counterweight to the regular armed forces.
- The participation of the IRGC in the Iran-Iraq War (1980–88) led to the expansion of both its role and its might, making it Iran’s dominant military force, with its own army, navy, and air force and, later, its own intelligence wing.
- The Naval forces are the primary forces having operational control of the Persian Gulf.
- The naval force also controls the paramilitary Basij militia.
- Sepah News is the media arm of the IRGC.
Environment
 Tree Cities of the World: Hyderabad recently won a green contest among cities in India, and emerged one of the ‘Tree Cities of the World’.
Tree Cities of the World: Hyderabad recently won a green contest among cities in India, and emerged one of the ‘Tree Cities of the World’.
The title has been bestowed by the Arbor Day Foundation and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
Hyderabad was selected for its commitment to growing and maintaining urban forestry under the State government’s Haritha Haram programme and its Urban Forest Parks plan.
With this recognition, the city joins 120 others from 23 countries, including the United States the United Kingdoms, Australia and Canada.
The city was evaluated on five metrics. They are:
- Establish Responsibility
- Set the Rules
- Know What You Have
- Allocate the Resources
- Celebrate the Achievements
 Asia Environmental Enforcement Award-2020: The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) recently awarded the Asia Environmental Enforcement Award-2020 to the Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB).
Asia Environmental Enforcement Award-2020: The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) recently awarded the Asia Environmental Enforcement Award-2020 to the Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB).
WCCB has received this award twice in three years.
WCCB has been awarded this year under the Innovation category. Earlier, the Bureau had received the award in 2018 under the same category.
Wildlife Crime Control Bureau (WCCB):
- WCCB is a statutory body constituted under the WildLife (Protection) Act, 1972.The Bureau functions under the Ministry of Environment and Forests. Its task is to combat organized wildlife crime in the country.
- The Bureau has it’s headquarter in New Delhi and five regional offices at Delhi, Kolkata, Mumbai, Chennai and Jabalpur.
- WCCB has developed an online Wildlife Crime Database Management System to get real time data to analyse trends in wildlife crimes across India. This system has been successfully used for carrying out operations such as Operation Save Kurma, Thunderbird, Wildnet, Lesknow, Birbil, Thunderstorm, Lesknow-II etc resulting in huge seizures of Tiger, Leopard Skin, bones, Rhino Horn, Elephant Ivory etc.
About UNEP:
- It is an abbreviation for United Nations Environment Programme.
- UNEP was founded on 5 June 1972 by a Canadian businessman and philanthropist Maurice Strong.
- It is responsible for coordinating the UN's environmental activities and assisting developing countries in implementing environmentally sound policies and practices.
- It is the global champion for the environment with programmes focusing on sustainable development, climate, biodiversity and more.
- It is headquartered in Nairobi, Kenya.
- The current Executive Director of UNEP is Inger Andersen and the current Regional Director and Representative for Asia and the Pacific, UNEP is Dechen Tsering.
 Usha Rao-Monari: India’s Usha Rao-Monari who is a leading investment professional, has recently been appointed as Under-Secretary-General and Associate Administrator of the UNDP by UN chief Antonio Guterres. She has now joined a growing list of women from the country appointed to helm key agencies of the global organisation.
Usha Rao-Monari: India’s Usha Rao-Monari who is a leading investment professional, has recently been appointed as Under-Secretary-General and Associate Administrator of the UNDP by UN chief Antonio Guterres. She has now joined a growing list of women from the country appointed to helm key agencies of the global organisation.
Rao-Monari previously served as Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of Global Water Development Partners, a Blackstone portfolio company. She held several senior positions, including Director of the Sustainable Business Advisory Group at the International Finance Corporation, part of the World Bank Group.
She currently serves on the Boards of several organisations in the field of sustainable development and has held various Board and advisory positions in the areas of water, natural capital, biodiversity and environment.
Indian Policy
 Pilot Pey Jal Survekshan: The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) recently launched a Pilot Pey Jal Survekshan under Jal Jeevan Mission- Urban, JJM-U.
Pilot Pey Jal Survekshan: The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA) recently launched a Pilot Pey Jal Survekshan under Jal Jeevan Mission- Urban, JJM-U.
- As the part of the survey, Pilot Pey Jal Survekshan 2021 will be conducted in cities to ascertain equitable distribution of water and reuse of wastewater through a challenge process.
- It will also help in mapping the water bodies with respect to quantity and quality of water through a challenge process.
- The Pilot survey, as its first step, will be launched in 10 cities, which are Agra , Badlapur, Bhubaneswar, Churu, Kochi, Madurai, Patiala, Rohtak, Surat and Tumkur.
- Based on responses received in all 500 cities, the survekshan will be extended to AMRUT (Atal Mission for Rejunevation and Urban Transformation) cities.
Jal Jeevan Mission- Urban (JJM-U):
- JJM-U was announced during the Union Budget for FY 2021-22 under the Ministry Housing and Urban Affairs.
- The mission seeks to provide universal coverage of water supply to all households with functional taps which also includes sewerage and septage management in 500 AMRUT cities to make them water-secure and rejuvenation of water bodies to augment sustainable freshwater supply and create green spaces and sponge cities to reduce floods and enhance amenity value through an Urban Aquifer Management plan.
- JJM-U is designed to provide universal coverage of water supply to all households through functional taps in all 4,378 statutory towns.
- The mission has been launched in accordance with Sustainable Development Goal- 6.
- The total outlay proposed for JJM (U) is 2 lakh 87 thousand crore rupees which includes 10 thousand crore rupees for continuing financial support to AMRUT Mission.
- The mission also complements the Jal Jeevan Mission (Rural) that was launched to ensure the supply of 55 litres of water per person per day to every household in rural areas.
- It aims to provide Functional Household Tap Connections (FHTC) in the rural areas by 2024.
AMRUT Mission:
- The Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) was launched by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), Government of India (GoI).
- The mission was launched on 24 June 2015 by Prime Minister Narendra Modi with the aim of providing basic civic amenities like water supply, sewerage, urban transport, parks as to improve the quality of life for all especially the poor and the disadvantaged.
 National Hydrogen Energy Mission (NHEM): Recently, the Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in her budget speech formally announced the National Hydrogen Energy Mission (NHEM) which aims for generation of hydrogen from green power resources fulfilling the announcement made by Prime Minister in November 2020. The government plans to produce green hydrogen by using the country vast renewable resources.
National Hydrogen Energy Mission (NHEM): Recently, the Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in her budget speech formally announced the National Hydrogen Energy Mission (NHEM) which aims for generation of hydrogen from green power resources fulfilling the announcement made by Prime Minister in November 2020. The government plans to produce green hydrogen by using the country vast renewable resources.
The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has disclosed that the draft regulations for NHEM will be finalised by the end of this month and will thereafter proceed for approval of the Union Cabinet
The reason for NHEM by the Government is because of the following advantages:
- It is a clean-burning molecule, which can decarbonize a range of sectors including iron and steel, chemicals, and transportation.
- Renewable energy that cannot be stored or used by the grid can be channelled to produce hydrogen.
- The proposal in the Budget will be followed up with a mission draft in the couple of months — a roadmap for using hydrogen as an energy source.
Philosophy behind NHEM:
- The electricity grid of India is predominantly coal-based and will continue to be so.
- In several countries that have gone in for an EV push, much of the electricity is generated from renewables — in Norway for example, it is 99 per cent from hydroelectric power.
- Experts believe hydrogen vehicles can be especially effective in long-haul trucking and other hard-to-electrify sectors such as shipping and long-haul air travel.
- Using heavy batteries in these applications would be counterproductive, especially for countries such as India, where the electricity grid is predominantly coal-fired.
Hydrogen as an element:
- It is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all baryonic mass.
- However, this most common element in nature is not found freely. It exists only combined with other elements and has to be extracted from naturally occurring compounds like water (which is a combination of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom).
- Hydrogen is a colourless, odourless, tasteless, flammable gaseous substance that is the simplest member of the family of chemical elements.
- It is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1.
- With a standard atomic weight of 1.008, hydrogen is the lightest element in the periodic table.
- Non-remnant stars are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state.
- Hydrogen gas was first artificially produced in the early 16th century by the reaction of acids on metals.
- This fuel can be produced from various sources like natural gas, nuclear power, biomass, and renewable power like solar and wind.
There are three types of hydrogen – grey, blue and green.
- The fuel produced from fossil fuels is called grey hydrogen. This constitutes the bulk of the hydrogen produced today.
- Those produced from fossil fuels with carbon capture and storage options are called blue hydrogen.
- Those produced from renewable power sources are called green hydrogen.
- The most common methods for producing hydrogen are natural gas reforming and electrolysis.
- Being a zero-carbon fuel, hydrogen is considered to be one of the key sources of clean energy for the future.
Efforts in India on transportation so far:
In October 2020, Delhi became the first Indian city to operate buses running on hydrogen spiked compressed natural gas (H-CNG) in a six-month pilot project.
The buses will run on a new technology patented by Indian Oil Corp for producing H-CNG — 18 per cent hydrogen in CNG — directly from natural gas, without resorting to conventional blending.
Advantages of H-CNG:
- The use of H-CNG is the elimination of carbon monoxide emissions.
- H-CNG as a fuel reduces carbon dioxide and hydrocarbon emissions.
- Hydrogen up to one-fifth by volume can be blended with CNG as fuel for buses.
- H-CNG makes the fuel less expensive than CNG.
Disadvantages of H-CNG:
- Safety is seen as a concern. Hydrogen is pressurized and stored in a cryogenic tank, from there it is fed to a lower-pressure cell and put through an electrochemical reaction to generate electricity.
- Determining the most optimized H2/ NG (Natural Gas) ratio.
- It requires new infrastructures for preparing H-CNG.
- Many steps need to be taken for commercializing it at a large scale.
- A big barrier to the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles has been a lack of fuelling station infrastructure. There are less than 500 operational hydrogen stations in the world today, mostly in Europe, followed by Japan and South Korea.
- Current cost of H2 is more than the cost of Natural Gas. So, HCNG’s cost is more than CNG.
 All India Surveys: A Software Applications and instruction manuals with questionnaires for five All India Surveys on Labour was recently launched by the Labour and Employment Minister Santosh Kumar Gangwar.
All India Surveys: A Software Applications and instruction manuals with questionnaires for five All India Surveys on Labour was recently launched by the Labour and Employment Minister Santosh Kumar Gangwar.
Highlights:
The five All India Surveys are being conducted by Labour Bureau in Chandigarh.
These five surveys being undertaken by Labour Bureau are:
- All India survey on employment generated in Transport Sector.
- All India Survey on Migrant workers
- All India survey on Domestic Workers
- All India survey on employment generated by Professionals
- All-India Quarterly Establishment based Employment Survey (to assess the employment situation in establishments with more than 10 workers and also less than 10 workers)
About Labour Bureau:
Labour Bureau is an attached office of Ministry of Labour & Employment. The bureay has been at the forefront in fulfilling the data needs of various stakeholders in the field of labour and employment since 1920.
 PLI Scheme for Telecom and Networking Products: The Union Cabinet has recently approved the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Telecom and Networking Products.
PLI Scheme for Telecom and Networking Products: The Union Cabinet has recently approved the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for Telecom and Networking Products.
Highlights:
- PLI scheme on telecom sector will be effective from April 1, 2021.
- The Scheme aims to promote manufacture of Telecom and Networking Products in India.
- The scheme proposes a financial incentive to boost domestic manufacturing and attract investments in the target segments of telecom and networking products.
- The main component of the scheme is to offset the imports of telecom equipment worth more than Rs 50,000 crore.
- The scheme will also encourage exports of telecom and networking products 'Made in India'.
Main features of PLI Scheme are:
- The outlay of the scheme is Rs. 12,195 Crores over 5 years.
- Support under the Scheme will be provided to companies/entities engaged in manufacturing of specified telecom and networking products in India like Gigabit Passive Optical Networks (GPON), base routers, Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM), Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS/ IPMPLS) and 5G/4G radios.
- The eligibility for the scheme will be subject to achievement of a minimum threshold of cumulative incremental investment over a period of 4 years and incremental sales of manufactured goods net of taxes (as distinct from traded goods) over the Base Year 2019-2020.
- The minimum investment threshold for MSME has been kept at Rs.10 crore with incentives from 7% - 4 % and for others it has been kept for Rs.100 crore with incentives from 6% - 4 % over 5 year above Base Year.
- The applicants with higher investments than specified threshold under MSME and Non MSME categories will be selected through transparent process.
About PLI scheme:
- This scheme was launched in the March 2020 in a bid to boost the domestic manufacturing.
- It seeks to cut down on import bills.
- The scheme was launched with the aim of giving the companies incentives on incremental sales of the domestically manufactured products.
- This scheme does not stop any foreign companies to set shop in India, but at the same time it also encourages the local companies to set up or expand the existing manufacturing units.
 Dictionary.png) Indian Sign Language (ISL) Dictionary: Union Minister for Social Justice and Empowerment Thaawarchand Gehlot virtually released the 3rd edition of the Indian Sign Language (ISL) Dictionary on 17th February 2021.
Indian Sign Language (ISL) Dictionary: Union Minister for Social Justice and Empowerment Thaawarchand Gehlot virtually released the 3rd edition of the Indian Sign Language (ISL) Dictionary on 17th February 2021.
The 3rd edition of the ISL dictionary contains a total of 10,000 terms including 6,000 of the first and second edition of the dictionary.
Details of ISL Dictionary are as follows:
- The Dictionary has been developed by the Indian Sign Language Research and Training Centre (ISLRTC), an autonomous Institute under the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (Divyangjan), Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment.
- The 3rd edition of the ISL Dictionary contains total 10,000 terms of everyday use, academic terms, legal & administrative terms, medical terms, technical terms and agricultural terms.
- The Dictionary also contains regional signs used in different parts of the country.
- The 1st edition of the ISL Dictionary was launched on 23rd March 2018 with 3000 terms.
- The 2nd edition was launched on 27th February 2019 with 6000 terms including earlier 3000 terms.
Importance:
- The launch of the ISL dictionary is an important step towards fulfilling needs of hearing and speech impaired in accordance with the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPWD) Act, 2016.
- It also complies with the initiative by the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) called “Accessible Digital Textbooks for All”.
The ISL will be essential in enhancing the vocabulary and the capabilities to understand concepts of the impaired
Provisions by the Government for hearing impaired are as follows:
- The Rights of Persons with Disabilities (RPWD) Act, 2016 was passed to Include provisions for hearing impaired.
- The government started the accessibility of news and educational videos by incorporating sign language or written text subtitles and transcripts.
- New Education Policy, 2020 also contain provisions of universalization of education for all including the disabled with 100% Gross Enrolment ratio from preschool to secondary level by 2030.
- National Program for Prevention and Control of Deafness (NPPCD) was launched in 2006 to tackle high incidence of deafness.
International
.jpg) Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA): The Union Cabinet, recently chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, has approved the signing of the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA) between India and Mauritius.
Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA): The Union Cabinet, recently chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, has approved the signing of the Comprehensive Economic Cooperation and Partnership Agreement (CECPA) between India and Mauritius.
Key highlights of India-Mauritius CECPA are as follows:
- The India-Mauritius CECPA is the first trade Agreement to be signed by India with an African country.
- The main purpose is to liberalize norms to boost two-way commerce between the two countries.
- The CECPA between India and Mauritius will cover 310 export items for India, while 615 products for Mauritius
- The Agreement is a limited agreement, which will cover Trade in Goods, Rules of Origin, Trade in Services, Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT), Sanitary and Phytosanitary (SPS) measures, Dispute Settlement, Movement of Natural Persons, Telecom, Financial services, Customs Procedures and Cooperation in other Areas.
- CECPA provides for an institutional mechanism to encourage and improve trade between the two countries.
- Both sides have also agreed to negotiate an Automatic Trigger Safeguard Mechanism (ATSM) for a limited number of highly sensitive products within two years of the Signing of the Agreement.
 World Solar Bank: The International Solar Alliance (ISA) have planned to launch the World Solar Bank (WSB) at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in Glasgow that is scheduled for November 2021.
World Solar Bank: The International Solar Alliance (ISA) have planned to launch the World Solar Bank (WSB) at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in Glasgow that is scheduled for November 2021.
Key points of WSB are as follows:
- The development of the WSB will support India’s attempt to secure its leadership in the climate arena.
- The development of the bank is significant because the green finance will be one of the priority themes at the climate meet called COP-26.
- COP-26 will be organized in the backdrop of US re-joining the Paris climate accord.
- The headquarters of the World Solar Bank is expected to be set up in India. It will be first multilateral development bank (MDB) that will be set up in India.
- The WSB have planned to disburse around $50 billion to the member countries of ISA over next 10 years.
- The WSB will be launched because many member countries of the ISA face the challenge of raising finances on their own.
About International Solar Alliance (ISA):
- The ISA is an alliance of 121 countries initiated by India, most of them being sunshine countries, which lie either completely or partly between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- The alliance was founded on 30 November 2015 climate change conference in Paris.
- It is the first treaty-based international government organization which is headquartered in Gurugram, India. It is the nodal agency to implement the global electricity grid plan of India called “One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG)”.
- The current leader of ISA is Upendra Tripathy.
About OSOWOG:
- The One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) was launched with the objective of transferring the solar power generated in one region to feed the electricity demands of another region.
- Under the OSOWOG vision, India aims to replicate its global solar leadership through phased development of a single globally connected solar electricity grid.
- This would have multiple benefits such as Low cost, Zero pollution
 Sama Lukonde: The Congo President Felix Tshisekedi on February 15 appointed Jean-Michel Sama Lukonde Kyenge, director-general of Gécamines (General Quarries and Mines) as the new DRC Prime Minister.
Sama Lukonde: The Congo President Felix Tshisekedi on February 15 appointed Jean-Michel Sama Lukonde Kyenge, director-general of Gécamines (General Quarries and Mines) as the new DRC Prime Minister.
The 43-year-old Tshisekedi is a former sports minister and an ex-party member of the former governor of Katanga Moïse Katumbi, who recently postured his political lean in support of the President.
Congo: The Democratic Republic of the Congo, also known as Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DROC, or simply either Congo or the Congo, and historically Zaire, is a country in Central Africa. Congo achieved independence from Belgium on 30 June 1960 under the name Republic of the Congo. Congolese nationalist Patrice Lumumba was elected the first Prime Minister, while Joseph Kasa-Vubu became the first President. The Capital of Congo is Kinshasa. The currency used here is Congolese franc.
 Anti-extremism bill: The lower house of the French Parliament recently voted in favour of a law to battle “Islamist separatism” that is billed by the government as a riposte to religious groups attempting to undermine the secular state. This major decision was taken after the recent beheading in France.
Anti-extremism bill: The lower house of the French Parliament recently voted in favour of a law to battle “Islamist separatism” that is billed by the government as a riposte to religious groups attempting to undermine the secular state. This major decision was taken after the recent beheading in France.
The centrist party of President Emmanuel Macron hugely supported the law with 347 National Assembly lawmakers voting in favour, 151 against and 65 abstaining.
The text will now be submitted to the upper house Senate, where Macron’s party does not hold a majority.
France: France officially the French Republic is a country consisting of metropolitan France in Western Europe and several overseas regions and territories. It is historically and culturally among the most important nations in the Western world. France has also played a highly significant role in international affairs, with former colonies in every corner of the globe. The capital of France is Paris. The currency of France is Euro, CFP franc. The current President of France is Emmanuel Macron. The current Prime Minister is Jean Castex.
 International Mother Language Day: International Mother Tongue Day: The International Mother Tongue Day (IMLD) is observed on 21st February every year globally.
International Mother Language Day: International Mother Tongue Day: The International Mother Tongue Day (IMLD) is observed on 21st February every year globally.
The objective of this day is to promote linguistic and cultural goodwill among the diverse population. It aims to foster unity among various nations as it promotes the preservation and protection of all languages used by people all over the world.
The theme of the 2021 IMLD is “Fostering multilingualism for inclusion in education and society,”.
This year’s observance is a call on policymakers, teachers and educators, parents and families to scale up their commitment to multilingual education, and inclusion in education to advance education recovery in the context of COVID-19.
History of IMLD:
- The idea of celebrating International Mother Tongue Day is an initiative of Bangladesh.
- It was approved at the UNESCO General Conference in 1999 and has been observed all over the world since 2000.
- On 16 May 2007 the United Nations General Assembly in its resolution A/RES/61/266 called upon the Member States "to promote the preservation and protection of all languages used by peoples of the world".
- The date pays tribute to the students in Bangladesh who gave their life on this day in 1952 for the recognition of their language 'Bangla' as one of the two national languages.
- The police gunned down four students of Dhaka University Abul Barkat, Abdul Jabbar, Sofiur Rahman, Abdus Salam, when they marched towards the East Bengal Legislative Assembly breaking the curfew.
- In Bangladesh, this day is celebrated as Shaheed Day commemorating the sacrifice of the martyrs for the language of Bengali.
- On February 29, 1956, Bengali was recognized as the second official language of Pakistan under article 214(1) of the constitution which states "The state language of Pakistan shall be Urdu and Bengali."
What do you mean by mother language or the mother tongue?
- The mother language or the mother tongue is the first language (also native language) or languages that a person has learned from birth.
- Children who are brought up speaking two languages have more than one native language and are called bilingual.
- A child’s mother language is part of his personal, social, and cultural identity.
Significance of Mother Tongue:
- Linguistic diversity is increasingly imperiled as more and more languages disappear. One language disappears on average every two weeks, taking with it a whole cultural and intellectual heritage.
- Real values of any culture can only be conserved if there is an honor for mother tongue and heritage.
- All the scripts and religious books are composed in local languages which show us the right path to living life.
Quote: ¨If you talk to a man in a language he understands, that goes to his head. If you talk to him in his language that goes to his heart. – Nelson Mandela
Indian polity
 Justice Puligoru Venkata Sanjay Kumar: Justice Puligoru Venkata Sanjay Kumar has recently been sworn-in as the Chief Justice of Manipur High Court.
Justice Puligoru Venkata Sanjay Kumar: Justice Puligoru Venkata Sanjay Kumar has recently been sworn-in as the Chief Justice of Manipur High Court.
Justice PV Sanjay Kumar was appointed as Chief Justice of the High Court of Manipur by the President of India on 12th February, 2021 at Raj Bhavan, Imphal.
Prior to this, he served as a Judge in the Punjab and Haryana High Court.
 Dr. Kiran Bedi: Dr. Kiran Bedi has recently been removed from the post of Puducherry Lieutenant Governor amid a political turmoil in the Union territory following the resignation of Congress MLAs from the V Narayanasamy government.
Dr. Kiran Bedi: Dr. Kiran Bedi has recently been removed from the post of Puducherry Lieutenant Governor amid a political turmoil in the Union territory following the resignation of Congress MLAs from the V Narayanasamy government.
- The additional charge of Telangana Governor has been given to Dr. Tamilisai Soundararajan who is the Lieutenant Governor of Puducherry.
- Ms. Bedi was the fourth woman incumbent of the post of Lt Governor.
- She assumed office of Lt Governor on May 29, 2016 and had been at loggerheads with Chief Minister V. Narayanasamy on various issues.
Article 153 of the Indian constitution:
Article 153 of the Indian constitution states that here shall be Governor for each State. Nothing in this article shall prevent the appointment of the same person as Governor for two or more States.
 Kotia Cluster: Andhra Pradesh recently held panchayat elections in three villages in the Kotia cluster, which is at the centre of a dispute between Andhra Pradesh and Odisha.
Kotia Cluster: Andhra Pradesh recently held panchayat elections in three villages in the Kotia cluster, which is at the centre of a dispute between Andhra Pradesh and Odisha.
This is the first time Andhra has held panchayat polls in any of these villages.
Key highlights of these disputed villages are as follows:
- These villages in the Kotia Cluster, with a population of nearly 5,000, are located on a remote hilltop on the inter-state border.
- These are inhabited by Kondh tribals.
- The region was once a Maoist hotbed and still reports sporadic incidents of violence.
- The region is also rich in mineral resources like gold, platinum, manganese, bauxite, graphite and limestone.
Background of the Andhra-Odisha Boundary Dispute:
- Prior to April 1, 1936, villages under Kotia panchayat were part of Jeypore Estate.
- In the Constitution of Orissa Order, 1936, the Government of India (GoI) demarcated Odisha from the erstwhile Madras Presidency.
- The Presidency included the present-day Andhra Pradesh.
- In 1942, the Madras government contested the boundary and ordered re-demarcation of the two states.
- In a joint survey of Bihar, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha, seven villages of Kotia gram panchayat were recorded as revenue villages and revenue was collected by the Odisha government. But, the exercise left out the 21 villages now under dispute.
- The villages were not surveyed by the Andhra Pradesh government either when the state of Andhra Pradesh was created in 1955.
- In the early 1980s, Odisha filed a case in the Supreme Court demanding right and possession of jurisdiction over the 21 villages.
- In 2006 however, the court ruled that since disputes belonging to the state boundaries are not within the jurisdiction of the Supreme Court, the matter can only be resolved by Parliament and passed a permanent injunction on the disputed area.
Current Status:
- In Andhra, Vizianagaram District collector said the three villages are separate gram panchayats and fall under Salur Mandal, hence elections were held.
- However, the villages participate in Assembly and Lok Sabha elections for both states. They are registered as voters for -
- Salur Assembly and Araku Lok Sabha seats of Andhra
- Pottangi Assembly and Koraput Lok Sabha seats of Odisha.
- The villagers enjoy benefits from both states under various schemes.
- A day after Andhra notified the panchayat elections here; Odisha Chief Minister Naveen Patnaik inaugurated projects worth Rs 18 crore.
 Juvenile Law: The Union Cabinet has recently approved the proposal of the Ministry of Women and Child Development to amend the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015. The proposal seeks to introduce measures for strengthening Child Protection set-up to ensure best interest of children.
Juvenile Law: The Union Cabinet has recently approved the proposal of the Ministry of Women and Child Development to amend the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015. The proposal seeks to introduce measures for strengthening Child Protection set-up to ensure best interest of children.
The key highlights under the proposed act are as follows:
- The amendments include authorizing District Magistrate including Additional District Magistrate to issue adoption orders under Section 61 of the JJ Act, in order to ensure speedy disposal of cases and enhance accountability.
- Under the act, the District Magistrates have been further empowered to ensure its smooth implementation, as well as garner synergized efforts in favour of children in distress conditions.
- Some of the other aspects of the proposal are - defining eligibility parameters for appointment of CWC members, and categorizing previously undefined offences as ‘serious offence’.
- Several difficulties faced in implementation of various provisions of the Act have also been addressed.
Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015:
- The Indian Parliament passed The Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2015 on December 22, 2015 amid intense controversy, debate and protest over many of its provisions by the Child Rights fraternity. It came into force on January 15, 2016.
- The act replaced the Indian juvenile delinquency law -Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act, 2000.
- The act allows juveniles between the age of 16-18 years, who are involved in Heinous Offences, to be tried as adults.
- The Act also seeks to create a universally accessible adoption law for India, superseding the Guardians and Wards Act (1890) (applicable to Muslims) and the Hindu Adoptions and Maintenance Act (1956), which is applicable to Hindus, Jains, Buddhists and Sikhs). It does not replace them though.
 Governing Council of NITI Aayog: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently chaired the sixth meeting of the Governing Council of NITI Aayog.
Governing Council of NITI Aayog: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently chaired the sixth meeting of the Governing Council of NITI Aayog.
About:
- The meeting which was held on 20th February 2021 included the following objectives:
- Making India a Manufacturing Powerhouse
- Reimagining Agriculture
- Improving Physical Infrastructure
- Accelerating Human Resources Development
- Improving Service Delivery at Grassroots Level
- Health and Nutrition.
- The Governing Council presented a platform to discuss inter-sectoral, inter-departmental and federal issues.
- It comprises the Prime Minister, Chief Ministers of States and Union Territories (UTs), with Legislatures and Lt Governors of other UTs.
- The sixth meeting was attended by Ladakh for the first time, in addition to the participation of Jammu and Kashmir as a UT. This time, other UTs headed by administrators were also invited to join.
- The meeting was attended by the ex-officio members of the Governing Council, Union Ministers, Vice Chairman, Members and CEO of NITI Aayog, and other senior officials of Government of India.
NITI Aayog: It refers to the National Istitution For Transforming India Aayog. NITI Aayog is the premier policy 'Think Tank' of the Government of India (GoI). It was established on 1 January 2015 with an objective to foster cooperative federalism through structured support initiatives and mechanisms with the States on a continuous basis, recognizing that strong States make a strong nation.
The Governing Council of NITI, with The Prime Minister as its Chairman, comprises Chief Ministers of all States and Lt. Governors of Union Territories (UTs). The current CEO of NITI Aayog is Amitabh Kant.
National
 TECHNOGRAHIS: An Enrolment Module for TECHNOGRAHIS, has been launched by Shri Durga Shanker Mishra, Secretary, The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
TECHNOGRAHIS: An Enrolment Module for TECHNOGRAHIS, has been launched by Shri Durga Shanker Mishra, Secretary, The Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA).
- TECHNOGRAHIS are students from IITs, NITs, engineering, planning and architecture colleges, faculty members, academicians, and stakeholders.
- MoHUA is promoting six Light House Projects (LHPs) as Live Laboratories for transfer of technology to the field.
- The LHPs are model housing projects. About 1,000 houses at each location are being built with allied infrastructure facilities.
- The interested candidates can register themselves to visit these live laboratories at six LHP sites for learning, consultation, generation of ideas and solutions, experimentation, innovation, and technical awareness.
- Till the completion of the LHPs within a period of twelve months, the ‘Technograhis’ will get regular updates from the sites for information dissemination.
- This can enable the ‘Technograhis’ in adapting and adopting the technologies as per their requirements in the construction sector for a ‘Make in India’ approach”.
- Additional info: An E-Newsletter and Six State-Wise Booklets on LHPs were also launched at the event.
About Light House Project (LHP):
- The LHP is being constructed under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U) as part of the Global Housing Technology Challenge-India (GHTC-India).
- Approximately 1,000 houses in each location are building with related infrastructure facilities.
- This initiative seeks to be an important driving force for India's technological transformation.
- This technological revolution is cost-effective, environment- friendly, strong in disaster resistance, and can speed up construction.
 “Go Electric” Campaign: Union Minister for Road Transport & Highways Nitin Gadkari recently launched the “Go Electric” Campaign.
“Go Electric” Campaign: Union Minister for Road Transport & Highways Nitin Gadkari recently launched the “Go Electric” Campaign.
The campaign has been launched to spread awareness on the benefits of e-mobility and EV Charging Infrastructure as well as electric cooking in India.
Highlights of the campaign are as follows:
- Go Electric Campaign is an important initiative which seeks to help in reducing the import dependence of India in the coming years and would be an important step towards a cleaner and greener future.
- The campaign is aimed at creating awareness at PAN-India level and is expected to boost the confidence of Electric Vehicle manufacturers.
- The Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE) will extend technical support to the State Designated Agencies (SDAs) to implement the ‘Go Electric’ campaign at National and State level.
- As a Central Nodal Agency, BEE will provide content and details to State Designated Agencies and other partners to ensure uniformity of information.
What is the importance of Electric fuel?
- Electric fuel is a major alternative for fossil fuels which have an import bill of Rs. 8 lakh Crore.
- Electric fuel when compared to conventional fuels the electric fuel has low cost, reduced emissions and it is also indigenous.
 NTLF 2021: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently addressed the 29th NTLF 2021 (NASSCOM Technology and Leadership Forum 2021).
NTLF 2021: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently addressed the 29th NTLF 2021 (NASSCOM Technology and Leadership Forum 2021).
Highlights:
- February 2021 marks the 29th year of NASSCOM Technology & Leadership Forum - a platform which has been the voice of the 190-billion-dollar industry eco-system.
- The forum was organized by NASSCOM (National Association of Software and Service Companies) virtually on the theme "Shaping the future towards a better normal".
- It is a platform that brings together key leaders from the world of technology and innovation.
- The event is hosting almost 1600 participants from more than 30 countries.
- More than 30 products will be showcased during the three-days of talks.
- NTLF 2021 aims to achieve three key objectives. They are:
- To celebrate technology which has served as a backbone to boost businesses during the crisis,
- To draw a roadmap for the way ahead towards building a better future
- To bring out the importance of trust and responsible tech in this hyper virtual world.
NASSCOM:
The full form of NASSCOM is National Association of Software and Service Companies.
- NASSCOM is a non-profit industry association established in 1988.
- It is the premier trade body and chamber of commerce in the Indian technology industry.
- It is composed of more than 2,800 member companies, including India and multinational organizations with branches in India.
- It is committed to accelerating the pace of industry transformation, making it the preferred driving force for global digital transformation.
- Its mission is to help India's technology products and service industries to be trustworthy and innovative on a global scale.
 Use of Steel on National Highway: The Ministry of Road Transport & Highways recently issued an order to allow all steel (whether produced by melting ore, billets, pellets or scrap) to be used for the construction of National Highways. However, the steel must meet the required standards for a specific grade of steel.
Use of Steel on National Highway: The Ministry of Road Transport & Highways recently issued an order to allow all steel (whether produced by melting ore, billets, pellets or scrap) to be used for the construction of National Highways. However, the steel must meet the required standards for a specific grade of steel.
- The recommended steel will be tested in NABL accredited laboratories before being approved as a third-party check before approval.
- The step has been taken to ensure cost reduction in the building highways through use of new technology, reducing restrictions on suppliers and making the procurement system transparent.
- With this step, the supplier base for steel used in the construction of national highways would increase. This in turn will lead to more competition and better price discovery by the markets.
People In News
 Marc Llistosella: He has recently been appointed as the new Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and Managing Director (MD) of Tata Motors.
Marc Llistosella: He has recently been appointed as the new Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and Managing Director (MD) of Tata Motors.
He will be taking over from the current incumbent Guenter Butschek, who has preferred to relocate to Germany, his native place.
Llistosella was most recently the president and CEO of Fuso Truck and Bus Corporation and head of Daimler Trucks in Asia.
He was earlier the MD and CEO of Daimler India Commercial Vehicles Pvt Ltd.
 Dr Ajay Mathur: The International Solar Alliance (ISA) recently announced Dr. Ajay Mathur as its new Director General (DG) following his election at the first special assembly of ISA members.
Dr Ajay Mathur: The International Solar Alliance (ISA) recently announced Dr. Ajay Mathur as its new Director General (DG) following his election at the first special assembly of ISA members.
Dr. Mathur replaces Mr. Upendra Tripathy, who has served as Director General since the ISA was founded in 2015.
ISA accelerate the demand for and use of safe, sustainable, and affordable solar energy for all. It aims to mobilize over $1 trillion USD of investment into solar projects by 2030 through focused advocacy, policy and regulatory support, capacity building, and by overcoming perceived investment barriers.
ISA: It is an abbreviation for International Solar Alliance.
- The ISA is an alliance of 121 countries initiated by India, most of them being sunshine countries, which lie either completely or partly between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- The alliance was founded on 30 November 2015 climate change conference in Paris.
- It is the first treaty-based international government organization which is headquartered in Gurugram, India.
- It is the nodal agency to implement the global electricity grid plan of India called “One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG)”.
 Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala: She is the first female and first African who has recently been chosen as the head the World Trade Organization (WTO).
Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala: She is the first female and first African who has recently been chosen as the head the World Trade Organization (WTO).
WTO has handed her the task of restoring trust in a rules-based global trading system.
Highlights:
The WTO’s 164 members unanimously selected the 66-year old Nigerian economist to serve a four-year term as director general.
The appointment came after United State's new President Joe Biden endorsed her candidacy, which had been blocked by former President Donald Trump.
About: Okonjo-Iweala, formerly Nigeria’s finance minister, had a 25-year career at the World Bank (WB), where she rose to the number-two position of managing director. She holds both US and Nigerian citizenship.
World Trade Organization (WTO)
- The World Trade Organization is an international body that deals with the rules of trade between nations.
- It was established on 1st January 1995 in accordance with the Marrakesh Agreement.
- It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. The WTO has over 160 members representing 98% of world trade.
Marrakesh Agreement:
- The Marrakesh Agreement was signed after the Marrakesh Declaration in April 1994. The agreement was signed in Marrakesh, Morocco.
- The agreement was signed by 123 nations in April 1994.
- The Marrakesh Agreement had replaced the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT).
- The agreement is supplemented by agreements on issues like sanitary and phytosanitary measures, trade in services, intellectual property rights etc.
 YS Jagan Mohan Reddy: He is the Chief Minister (CM) of Andhra Pradesh (AP). He has recently been conferred with the SKOCH Chief Minister of the Year Award.
YS Jagan Mohan Reddy: He is the Chief Minister (CM) of Andhra Pradesh (AP). He has recently been conferred with the SKOCH Chief Minister of the Year Award.
SKOCH Group Chairman Sameer Kochhar called on the CM Reddy at his camp office at Tadepalli on Tuesday and presented the award to him.
He has been selected for the SKOCH Chief Minister of the Year Award based on a year-long study of results of projects being implemented by governments in various States of the country.
Andhra Pradesh: Andhra Pradesh is situated in the south-eastern part of India. It came into existence in its present form in 1956 as a result of the demand of the Andhras for a separate state. Its Capitals are Visakhapatnam (executive capital), Kurnool (judicial capital, Amaravati (legislative capital.) The current Governor and the Chief Minister of Andra Pradesh is Biswabhusan Harichandan and Y. S. Jaganmohan Reddy respectively.
 Ajai Malhotra: He has recently become the first Indian to be elected as Chairperson of the Advistory Committee of the Human Rights Council (HRC).
Ajai Malhotra: He has recently become the first Indian to be elected as Chairperson of the Advistory Committee of the Human Rights Council (HRC).
Malhotra has also served as the Ambassador of India to the Russian Federation till his retirement in 2013. After retirement, he served from 2015 to 2019 as Independent Director of India’s public sector Oil and Gas Company, Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC), as also of ONGC Videsh (2017–2019).
He has been on the Indian team negotiating issues such as biological diversity, climate change, desertification, education, energy, forestry, health, human rights, human settlements, intellectual property, international law, labour, ozone depletion, sustainable development and trade.
About Human Rights Council:
- HRC is the Human Rights Council is an inter-governmental body within the United Nations system. It is located at the UN Office at Geneva. It was founded on 15 March 2006 by the UN General Assembly Resolution 60/251.
- Its main task is to investigate allegations of breaches of human rights in UN member states. It also addresses important thematic human rights issues such as freedom of expression, women's rights, LGBT rights, and the rights of racial and ethnic minorities.
Places In News
 Bridges in Assam: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently laid the foundation stone of India's longest bridge which will connect Dhubri in Assam to Phulbari in Meghalaya. He also launched the Mahabahu-Brahmaputra programme and participated in the bhumi pujan for the two-lane Majuli Bridge which will connect Majuli to Jorhat in Assam, through video conferencing.
Bridges in Assam: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently laid the foundation stone of India's longest bridge which will connect Dhubri in Assam to Phulbari in Meghalaya. He also launched the Mahabahu-Brahmaputra programme and participated in the bhumi pujan for the two-lane Majuli Bridge which will connect Majuli to Jorhat in Assam, through video conferencing.
To mark the launch of Mahabahu-Brahmaputra, he inaugurated the Ro-Pax vessel operations between Neamati-Majuli Island, North Guwahati-South Guwahati and Dhubri-Hatsingimari. He also laid the foundation stone of Inland Water Transport (IWT) Terminal at Jogighopa and various tourist jetties on river Brahmaputra and launched digital solutions for Ease-of-Doing-Business.
The program is aimed at providing seamless connectivity to the Eastern parts of India and includes various development activities for the people living around River Brahmaputra and River Barak.
About Dhubri Phulbari Bridge:
- PM Modi laid the foundation stone for the four lane bridge over the Brahmaputra between Dhubri (on North Bank) and Phulbari (on South Bank).
- The proposed Bridge will be located on NH-127B, originating from Srirampur on NH-27 (East-West Corridor), and terminating at Nongstoin on NH-106 in the State of Meghalaya.
- It will connect Dhubri in Assam to Phulbari, Tura, Rongram and Rongjeng in Meghalaya.
- It will reduce the distance of 205 Km to be travelled by Road to 19 Km, which is the total length of the bridge.
- The bridge will be built at a total cost of approximately 4,997 crore.
About Majuli Bridge
- Prime Minister performed the Bhumi Pujan for the two-lane Bridge on the Brahmaputra between Majuli (North Bank) and Jorhat (South Bank).
- The bridge will be located on NH-715K and will connect Neematighat (on Jorhat side) and Kamalabari (on Majuli side).
About Assam: Assam is a state in northeastern India known for its wildlife, archeological sites and tea plantations. It is situated south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam is known for Assam tea and Assam silk. The state was the first site for oil drilling in Asia. Its capital is Dispur. The current Governor and the Chief Minister of Assam are Professor Jagdish Mukhi and Sarbananda Sonowal respectively.
 Key Projects in Assam: Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in his third visit to the poll-bound state of Assam recently launched several oil and gas projects, inaugurated an engineering college and laid the foundation stone of another.
Key Projects in Assam: Prime Minister Narendra Modi, in his third visit to the poll-bound state of Assam recently launched several oil and gas projects, inaugurated an engineering college and laid the foundation stone of another.
PM Modi dedicated to the nation the following:
- INDMAX Unit at Indian Oil’s Bongaigaon Refinery
- Oil India Limited's Secondary Tank Farm at Madhuban, Dibrugarh
- A Gas Compressor Station at Hebeda Village, Makum, Tinsukia.
He inaugurated the Dhemaji Engineering College. The college has been built on 276 “bighas” of land, at a cost of about ₹45 crore. It is the seventh government engineering college in the state and will offer BTech courses in civil, mechanical and computer science engineering..
He also laid the foundation stone for Sualkuchi Engineering College in Assam.
 Mega Projects in Tamil Nadu: The Prime Minister Narendra Modi during his recent visit to Tamil nadu inaugurated and laid the foundation stones for several key projects at Chennai.
Mega Projects in Tamil Nadu: The Prime Minister Narendra Modi during his recent visit to Tamil nadu inaugurated and laid the foundation stones for several key projects at Chennai.
The mega projects are as follows:
He inaugurated the Chennai Metro Rail Phase-I extension, fourth Railway line between Chennai Beach and Attipattu, Railway Electrification of single line section in Villupuram - Cuddalore - Mayiladuthurai - Thanjavur and Mayiladuthurai-Thiruvarur.
He also laid the foundation stone for two projects. They are:-
- The extension, renovation and modernization of the Grand Anicut Canal System crucial for irrigation in the delta districts to be taken up at ₹2,640 crore.
- Discovery Campus to come up at IIT Madras for ₹1000 crore in the first phase. The Campus is to be built at Thaiyur near Chennai at an estimated cost of 1000 crore rupees in the first phase, over an area of 2-lakh square metre.
The Central Government has accepted the long-standing demand of DevendrakulaVelalar community to be known officially as DevendrakulaVelalar. They will now be known by their heritage name and not the six to seven names listed in the Schedule to the Constitution.
Modi is the only Indian Prime Minister to visit Jaffna. To boost connectivity, the railway network to Jaffna and to Mannar is being re-built. Flights have been established from Chennai to Jaffna. India has built the Jaffna Cultural Centre which will open soon.
During the visit, PM Modi also handed over the Arjun Main Battle Tank (MK-1A) to the Army in Chennai.
The MK-1A tank is indigenously designed, developed and manufactured by CVRDE, DRDO in collaboration with 15 academic institutions, eight labs and certain MSMEs.
About Tamil Nadu: It is located in the extreme south of the subcontinent. It was formerly the Madras Presidency of British India but was renamed Madras (State) after independence in 1947. Madras (State) was again renamed Tamil Nadu in 1968. Its Capital is Chennai. The Governor and Chief Minister of Tamil Nadu are Banwarilal Purohit and Edappadi K. Palaniswami respectively.
 Oil & Gas Projects In Tamil Nadu: Prime Minister Narendra Modi dedicated to the nation and laid the foundation of key projects of the oil & gas sector in Tamil Nadu
Oil & Gas Projects In Tamil Nadu: Prime Minister Narendra Modi dedicated to the nation and laid the foundation of key projects of the oil & gas sector in Tamil Nadu
Thoothukudi Natural Gas Pipeline:
- He dedicated to the nation the Ramanathapuram – Thoothukudi natural gas pipeline. The Ramanathapuram – Thoothukudi section (143 km) of the Ennore- Thiruvallur- Bengaluru- Puducherry- Nagapattinam- Madurai- Tuticorin Natural Gas Pipeline has been laid at the cost of about Rs. 700 crores.
- It will not only help utilize gas from ONGC Gas fields but also deliver natural gas as feedstock to industries and other commercial customers.
Gasoline Desulphurisation Unit at Chennai Petroleum Corporation Limited, Manali:
- He dedicated the Gasoline Desulphurisation Unit at Chennai Petroleum Corporation Limited, Manali. The unit has been constructed at the cost of around Rs 500 crore.
- It will produce low sulphur (less than 8 ppm) environment-friendly gasoline, help reduce emission and contribute towards a cleaner environment.
Cauvery Basin Refinery at Nagapattinam:
- He laid the foundation stone of Cauvery Basin Refinery at Nagapattinam.
- It will have a capacity of 9 million metric tonnes per annum. It will be set up through a Joint Venture of IOCL and CPCL at an estimated project cost of Rs. 31,500 crore.
- It will produce Motor Spirit and Diesel meeting BS-VI specifications, and Polypropylene as a value-added product.
 Mega Projects in Kerala: Prime Minister on his recent visit to Kerala inaugurated and laid the foundation stones for several key projects.
Mega Projects in Kerala: Prime Minister on his recent visit to Kerala inaugurated and laid the foundation stones for several key projects.
The projects are as follows:
- Propylene Derivative Petrochemical Project (PDPP) of BPCL:
PM Modi dedicated to the nation the Propylene Derivative Petrochemical Project (PDPP) of BPCL. It will produce Acrylic Acid, Acrylates and Oxo-Alcohol which are at present predominantly imported, and is expected to result in saving of about Rs 3700 to 4000 crore per annum in foreign exchange which in turn will strengthen India’s journey towards being Aatmanirbhar. It has been constructed at a capital cost of about Rs 6000 crore.
- Inauguration of the International Cruise Terminal ‘Sagarika’:
He inaugurated the International Cruise Terminal ‘Sagarika’ at Cochin Port which is situated at the Ernakulam Wharf on Willingdon Island. It is India’s first full-fledged international cruise terminal. It has state-of-the-art facilities and has been constructed at a cost of Rs 25.72 crore.
- Inauguration of the Marine Engineering Training Institute:
He inaugurated the Marine Engineering Training Institute of Cochin Shipyard Ltd. Vigyan Sagar, the new knowledge campus of Cochin Shipyard would particularly help those wanting to study marine engineering.
- Foundation stone for Reconstruction of South Coal Berth:
He laid the foundation stone of Reconstruction of South Coal Berth at Cochin Port. The South Coal Berth seeks to bring down logistics costs and improve cargo capacities.
- Inauguration of the Ro-Ro Vessels:
He reopened the Ro-Ro Vessels at Willingdon Islands in Cochin. According to the government, the International Waterway Authority of India will deploy two new Roll-on/Roll-off (Ro-Ro) vessels between Bolgatty and Willingdon Island on National Waterway-3. These will have the capacity to carry six 20-feet trucks, three 20-feet trailer trucks, three 40-feet trailer trucks and 30 passengers each.
With Ro-Ro Vessels, a distance of almost thirty kilometres on road will become 3.5 kilometres through waterways leading to less congestion and more convenience, commerce and capacity-building.
- 50 MW Kasaragod Solar Power Project:
He dedicated to the nation the 50 MW Kasaragod Solar Power Project in kerala.It has been developed under the National Solar Energy Mission. It has been set up over 250 acres of land spread across Paivalike, Meenja and Chippar villages of Kasaragod district. It has been built with Central Government’s investment of around Rs. 280 crores. More than 20 lakh solar power pumps are being given to farmers under PM-Kusum Yojana.
- Foundation stone for Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC):
He laid the foundation stone of the Integrated Command and Control Centre (ICCC) at Thiruvananthapuram, kerala. The project is to be built at a cost of Rs 94 crores. It is being set up to host Smart Solutions for Thiruvananthapuram Municipal Corporation. It will act as a common point of action during emergency situations to facilitate coordinated action.
The control rooms or War Room at the ICCC will only act as a single point of coordinated action and decision making among various agencies like police, civil supplies, revenue, health and fire fighting.
- Inauguration of 75 MLD Water Treatment Plant:
He inaugurated the 75 MLD (million litres per day) Water Treatment Plant at Aruvikkara in Kerala. The water treatment plant will boost supply of drinking water to people of Thiruvananthapuram and help avoid disruption of drinking water supply to the city in the event of maintenance work in the existing treatment plants in Aruvikkara. It is being built under the AMRUT Mission.
About AMRUT Mission:
Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) was launched in 2015 with the aim of providing basic civic amenities like water supply, sewerage, urban transport, parks as to improve the quality of life for all especially the poor and the disadvantaged.
About Kerala: It is a state on the southwestern Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganization Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile states of Travancore-Cochin and Madras. Its capital is Thiruvananthapuram. The current Governor and Chief Minister of Kerala are Arif Mohammad Khan and Pinarayi Vijayan respectively.
 Maa Scheme: West Bengal (WB) Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee recently launched “Maa” canteens for providing subsidized cooked meals for the poor and the destitute at a nominal cost of ₹5.
Maa Scheme: West Bengal (WB) Chief Minister Mamata Banerjee recently launched “Maa” canteens for providing subsidized cooked meals for the poor and the destitute at a nominal cost of ₹5.
- This new initiative is for the common people.
- The govt. will give a subsidy of ₹15 and people have to pay ₹5. The kitchen will be run by Self-Help Groups (SHGs).
- The Budget tabled by the Chief Minister earlier this month allocated ₹ 100 crores for this project.
Even though free rations are given there is still a huge demand for cooked food. Therefore, these community kitchens have been started by the WB Government.
 Railway Projects in West Bengal: The Union Minister of Railways Piyush Goyal recently dedicated series of projects for the development of rail infrastructure in poll-bound West Bengal. He inaugurated various infrastructure development and passenger amenity-related works in the North Bengal area through video conferencing.
Railway Projects in West Bengal: The Union Minister of Railways Piyush Goyal recently dedicated series of projects for the development of rail infrastructure in poll-bound West Bengal. He inaugurated various infrastructure development and passenger amenity-related works in the North Bengal area through video conferencing.
These projects aim to not only enhance passenger experience but also help in faster movement of goods.
He inaugurated 2nd Foot Over Bridge at Santragachi, Freight Terminal at Sankrail (Phase-I) & Vivekananda Meditation Centre at Howrah and dedicated to the Nation an Executive Lounge at Sealdah station, 2 Escalators at Sealdah station and 2 lifts at Sealdah station.
- Santragachi Station:
Santragachi station is one of the busiest stations over Howrah-Kharagpur section. It is being developed with all modern amenities.
- Sankrail Freight Terminal:
Sankrail Freight Terminal (Phase-I) has been developed with modern facilities for freight rake handling. This Freight Terminal will serve around 40 sq.km. industrial belt spreading over Kolkata and Howrah in West Bengal.
- Vivekananda Meditation Centre:
The Vivekananda Meditation Centre is constructed at a cost of Rs 65 lakh of which Rs 30 lakh has been arranged from the Members of Parliament Local Area Development Scheme (MPLADS) fund of MP Pradip Bhattacharya.
The total built-up area of this centre is 3,528 sqft and the meditation hall area is 2,100 sqft.
It has the capacity to hold 70 persons.
- Integrated Security System at Barddhaman Station:
In order to augment security of passengers & railway property, an Integrated Security System has been commissioned at Barddhaman station.
- Executive Lounge at Sealdah
The Executive Lounge at Sealdah Station is another novel initiative of Railways to provide more comfort for passengers.
The executive lounge covers an area of 2,000 sq ft and is provided with a separate capsule lift for easy access.
A fully air-conditioned premium waiting lounge has been set up at Kolkata station.
He also launched the Foot Over Bridge at Jhamatpur Baharan and Nimo stations, Extension of platform shed at Balagarh and Guptipara Stations and Escalator at Tarkeswar and Nabadwip Dham stations.
Note: The Ministry has taken it upon itself to contribute big time to the mission of Sonar Bangla.
Science and Technology
 Geo-spatial sector in India: The Ministry of Science and Technology Monday recently released new guidelines for the Geo-spatial sector in India.
Geo-spatial sector in India: The Ministry of Science and Technology Monday recently released new guidelines for the Geo-spatial sector in India.
Highlights:
- The guidelines deregulate existing protocol and liberalises the sector to a more competitive field.
- The move is aimed at liberalizing geospatial services.
About Geospatial Data:
- Geospatial data is a data about objects on the surface of the earth, both natural and manmade.
- The location may be static in the short-term, like the location of a road, an earthquake event, malnutrition among children, or dynamic like a moving vehicle or pedestrian, the spread of an infectious disease.
- Geo-spatial data combines location information, attribute information (the characteristics of the object, event, or phenomena concerned), and often also temporal information or the time at which the location and attributes exist.
- Geo-spatial data usually involves information of public interest such as roads, localities, rail lines, water bodies, and public amenities.
- The past decade has seen an increase in the use of geo-spatial data in daily life with various apps such as food delivery apps like Zomato or Swiggy, e-commerce like Amazon or even weather apps.
The present policy on geo-spatial data is as follows:
- There are strict restrictions on the collection, storage, use, sale, dissemination of geo-spatial data and mapping under the current regime.
- The policy had not been renewed in decades and has been driven by internal as well as external security concerns.
- The sector so far is dominated by the Indian government as well as government-run agencies such as the Survey of India and private companies need to navigate a system of permissions from different departments of the government (depending on the kind of data to be created) as well as the defence and Home Ministries, to be able to collect, create or disseminate geo-spatial data.
- Initially conceptualized as a matter solely concerned with security, geo-spatial data collection was the prerogative of the defence forces and the government.
- GIS mapping was also rudimentary, with the government investing heavily in it after the Kargil war highlighted the dependence on foreign data and the need for indigenous sources of data.
Expected impact of new guidelines:
- By liberalizing the system, the government will ensure more players in the field, competitiveness of Indian companies in the global market, and more accurate data available to both the government to formulate plans and administer, but also for individual Indians.
- Startups and businesses can now also use this data in setting up their concerns, especially in the sector of e-commerce or geo-spatial based apps – which in turn will increase employment in these sectors.
- Indian companies will be able to develop indigenous apps, for example an Indian version of google maps.
 SANDES: The National Informatics Centre (NIC), under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, has launched an instant messaging platform called Sandes (Sandes in hindi means message).
SANDES: The National Informatics Centre (NIC), under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, has launched an instant messaging platform called Sandes (Sandes in hindi means message).
Key Highlights:
- This instant messaging platform is similar to WhatsApp.
- Like WhatsApp, the new government instant messaging systems (GIMS) platform can be used for all kinds of communications by anyone using a mobile number or email id.
- GIMS, like other instant messaging apps in the market, uses a valid mobile number or email id to register the user for the first time. It also offers features such as group making, broadcast message, message forwarding and emojis.
- Although there is no option to transfer the chat history between two platforms, the chats on GIMS can be backed up to a users’ email.
- The instant messaging app, called Sandes, has an interface similar to many other apps currently available in the market.
- The need to build a home-grown messaging platform was felt by the government to ensure secure communication between people as they worked from home, following the nationwide lockdown imposed to contain the spread of Covid-19.
- The app can be used by central and state government officials for intra-organisational and inter-organisational communication.
- The Sandes app is also a part of the government strategy to encourage the use of India-made software so as to build an ecosystem of indigenously developed software and products.
- Sandes was initially launched for Android users and mainly for government officers. Later, the service was also extended to iOS users and it is now available for the common public as well.
Background:
- In 2020, the ministry of home affairs had issued the advisory for the government employees to not use the platforms like Zoom for official communications because of security concerns.
- Before that, the Computer Emergency Response Team (Cert-In) had also issued an advisory against Zoom with respect to the safety and privacy concerns.
About National Informatics Centre (NIC):
- National Informatics Centre (NIC) under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) is the technology partner of the Government of India (GoI).
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- It was established in 1976 with an objective to provide technology-driven solutions to Central and State Governments in various aspects of development.
- NIC has been instrumental in adopting and providing Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and eGovernance support to Central Government.
- The current Director-General (DG) is Neeta Verma.
 Perseverance on Mars: The American space agency NASA successfully landed its fifth rover 'Perseverance' on Mars 18 February 2021 Successfully.
Perseverance on Mars: The American space agency NASA successfully landed its fifth rover 'Perseverance' on Mars 18 February 2021 Successfully.
- It landed in a deep crater near the planet's equator called Jezero.
- It touched down the surface of Mars after successfully overcoming a risky landing phase known as the seven minutes of terror.
- Then it began sending images of the local area back to Earth.
- The rover is only the fifth ever to set its wheels down on Mars. This feat was first accomplished in 1997 and all so far has been American.
Background:
- Perseverance’s mission officially began on July 30, 2020, when NASA launched the $3 billion Mars 2020 mission from Florida’s Cape Canaveral.
Perseverance’s mission
- The Perseverance rover is expected to continue exploration for at least one Martian year, which is 687 Earth days.
- Its goal is to explore the Jezero crater, which scientists have speculated was once an 820ft lake that existed around 3.5 billion years ago.
- The six-wheeled vehicle will now spend at least the next two years drilling into the local rocks, looking for evidence of past life.
About Preserverance: It is about the size of an SUV. It weighs a ton. It is equipped with a seven feet long robotic arm, has 19 cameras, two microphones and a suite of cutting-edge instruments to assist in its scientific goals. It has a laser spectrometer on board that will be able to examine rocks using different wavelengths of energy.
Note: The shadow of NASA’s Perseverance rover was seen on the surface of Mars as it landed on the planet. With this, NASA is set to become the first space agency to fly a drone in the atmosphere of another planet.
 Snakepedia: A team of scientists, doctors and photographers in Kerala have launched a mobile application named “Snakepedia”.
Snakepedia: A team of scientists, doctors and photographers in Kerala have launched a mobile application named “Snakepedia”.
Highlights of Snakepedia:
- This mobile app will present all relevant information on snakes, to help the public as well as doctors in treating snake bites.
- The app aims to help the public identify snakes and avail proper treatment on time for snakebites. It will also help in busting myths about snakes, and protect snakes as well as snakebite victims.
- The android mobile application documents information on snakes with the help of pictures, infographics and podcasts and analyses its first aid, treatment, myths and superstitions.
Sports
 Rashtrapati Bhavan Krida Sthal: The President of India, Ram Nath Kovind, recently, inaugurated the Rashtrapati Bhavan Krida Sthal (renovated Football Ground and Basketball Court) in the President’s Estate.
Rashtrapati Bhavan Krida Sthal: The President of India, Ram Nath Kovind, recently, inaugurated the Rashtrapati Bhavan Krida Sthal (renovated Football Ground and Basketball Court) in the President’s Estate.
On the occasion, an ‘Exhibition Football Match’ was played between the children of My Angels Academy, Vikaspuri, New Delhi – a Trust working for the cause of underprivileged children.
The main aim of developing these state-of-art sports facilities are to cater to the needs of the employees of Rashtrapati Bhavan and their families.
An inter-departmental football tournament with five teams namely – President’s Secretariat Heroes, Household Youngs, PBG Warriors, Army Guard Daredevils and Delhi Police Stalwarts also started to encourage the employees and their family members to take part in the sports activities.
 Kings XI Punjab: The IPL Franchise, Kings XI Punjab has formally been renamed as Punjab Kings ahead of the Indian Premier League auction.
Kings XI Punjab: The IPL Franchise, Kings XI Punjab has formally been renamed as Punjab Kings ahead of the Indian Premier League auction.
The new brand name and logo of the team was officially released by the management.
The Punjab-based IPL franchise ‘Punjab Kings‘ is co-owned by Bollywood actress Preity Zinta, along with businessman Ness Wadia, Mohit Burman and Karn Paul.
The side is currently led by batsman KL Rahul, with former Indian captain Anil Kumble as its head coach.
 National Table Tennis Title: Manika Batra recently won the 82nd Senior National Table Tennis Championship.
National Table Tennis Title: Manika Batra recently won the 82nd Senior National Table Tennis Championship.
- She beat Reeth Rishya by 8-11, 10-12, 11-1, 11-9, 11-5, 11-6 at the Tau Devi Lal Sports Complex in Panchkula.
- It was Manika’s second Nationals title. She won her maiden national title in 2015 in Hyderabad.
- Batra will now compete at two WTT Contender events which will start on February 28.
- This will be followed by the World Olympic qualifiers and Asian Olympic qualifiers in Doha which is scheduled for March 14 and 18 respectively.
About Manika Batra: She is an Indian table tennis player. She is the top-ranked female table tennis player as of November 2020. She is ranked 63rd in world. The player specializes in playing the long-pimples on her backhand. It is not often played by top players.
Her Achievements:
- In 2020, she also received the Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna award.
- In 2018 she was the only Indian who received “The Breakthrough Star Award” by ITTF.
- In 2015, she won three medals at Commonwealth Table Tennis Championships.
- In 2011, she won silver medal in the under-21 category of the Chile Open.
- She represented India in 2014 Commonwealth Games at Glasgow. She finished to the quarterfinalist. She also took part in 2014 Asian Games.
Table Tennis Federation of India (TTFI):
The Table Tennis Federation of India (TTFI) is the governing body for table tennis in India. The TTFI was established in 1926, and was a founding member of the International Table Tennis Federation. TTFI's membership includes 32 state units and 37 institutions.
As of 2019, India’s Men’s TT Team are ranked 10th in the world while Women’s team are ranked 22nd.
Table Tennis (TT) is a popular indoor recreation sport in the country. It mostly played in the states of West Bengal, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu and Gujarat.
 Seiko Hashimoto: Former Olympian Seiko Hashimoto was recently named as president of the Tokyo Olympic organizing committee. She was named as the President of the committee after a meeting of its executive board.
Seiko Hashimoto: Former Olympian Seiko Hashimoto was recently named as president of the Tokyo Olympic organizing committee. She was named as the President of the committee after a meeting of its executive board.
She replaces 83-year-old Yoshiro Mori, a former Japanese prime minister who was forced to resign recently after making sexist comments about women.
Tokyo Olympic organizing committee after a meeting of its executive board, which is 80% male, a committee with a 50-50 gender split, was formed to find a successor to Mori.
 Ankita Raina: India’s Ankita Raina claimed her maiden WTA title by lifting the Phillip Island Trophy along with Russian partner Kamilla Rakhimova.
Ankita Raina: India’s Ankita Raina claimed her maiden WTA title by lifting the Phillip Island Trophy along with Russian partner Kamilla Rakhimova.
This feat will catapult her into the top-100 in the doubles for the first time in her career.
Ankita and Kamilla erased a one-set deficit to beat the Russian combination of Anna Blinkova and Anastasia Potapova 2-6 6-4 10-7 in the summit clash here.
Ankita will become only the second player to crack the doubles top-100 since Sania Mirza, who is a six-time Grand Slam champion.
Arts
 World Sanskrit Day:
World Sanskrit Day:
World Sanskrit Day, also known as Vishva-samskrita-dinam is an annual event focused around the ancient Indian language of Sanskrit.
Key Points:
-
The event incorporates lectures about the language and is aimed to promote its revival and maintenance.
-
The basic objective of celebrating Sanskrit Day and Sanskrit Week is to spread the word of Sanskrit language.
-
It is celebrated on Shraavana poornima, i.e., the full moon day of the Shraavana month in the Hindu calendar.
-
The Sanskrit organization Samskrita Bharati is involved in promoting the day.
-
In the year 2021, this day is celebrated on August 22.
-
This year, India is observing the Sanskrit Week from August 19 to August 25, 2021, to promote, popularize and cherish the importance of ancient language.
History:
The Government of India (GoI) decided to celebrate World Sanskrit Day in 1969, on the occasion of Raksha Bandhan that falls on the full moon day of the Hindu month of Shravana.
Why was Shraavana poornima chosen as Sanskrit day?
-
Shravani Purnima i.e. Raksha Bandhan is considered to be the festival of remembrance and worship of sages and worship for their dedication.
-
In Vedic literature it was called Shravani.
-
On this day, before the study of Vedas in Gurukulas, Yajñopavita which is a sacred thread is worn.
-
This ceremony is called Upanayana or Upakarma Sanskar.
-
The old Yajñopavita is also changed on this day.
-
Priests also tie raksha-sutras to the hosts.
-
Rishis are the original source of Sanskrit literature, hence Shravani Purnima is celebrated as Rishi Parv and World Sanskrit Day.
-
This day was chosen because the academic year in ancient India started on this day.
-
On this day the students start the study of Vedas in the gurukulas.
-
From the full moon of the month of Paush to the full moon of the month of Shraavana, the studies are stopped to learn other Vedantic scriptures.
-
This tradition is still unbroken in modern Vedic schools.
Note:
-
The New Education Policy (NEP) has laid an ambitious path for “mainstreaming” Sanskrit.
-
NEP also stated that Sanskrit universities will be turned into multi-disciplinary institutions of higher learning.
-
The Sanskrit language was declared as the second official language of Uttarakhand.
Purpose of Sanskrit Day Celebration:
Sanskrit language, which has the status of Dev language, is now losing its existence.
In India too, the number of people who read, write, and understand it is very less. Sanskrit day (Sanskrit Diwas / National Sanskrit Day) is celebrated to remind society of the importance and necessity of Sanskrit. So that as time progresses people do not forget that Sanskrit is also a language.
Origin of Sanskrit language:
-
Sanskrit is known as the “mother of all languages" is now one of the least spoken.
-
Numerous languages arose from this language.
-
The Sanskrit language has the largest vocabulary of about 102 Arab 78 crores 50 lakh words.
-
The term Sanskrit is derived from the conjoining of the prefix 'Sam' meaning 'Samyak' which indicates 'entirely' and 'krit' indicates 'done'.
-
In terms of communication, reading and hearing Sanskrit term indicates perfectly or entirely done.
-
It is believed to be an Indo-Aryan language, which is said to have originated around 3500 years ago.
-
However, in the scriptures, the Sanskrit language is thought to have originated in the second millennium BCE, when the Rig Veda was composed.
-
This Indo-Aryan language has been designated as a classical language recognized for its scientific composition and is in high demand all over the world.
-
This language is also termed as Dev Vani means Gods language.
-
It is believed that Sanskrit language have been generated by the God Brahma who passed it to the rishis or sages that were living in celestial abodes and further they communicated it to their earthly disciples from where it spread on the earth.
-
In the written form the origin of the Sanskrit language is traced back to the 2nd millennium BCE when the Rig Veda a collection of hymns is assumed to have been written.
-
Sanskrit in literary terms is classified into two different periods,
-
The Vedic period
-
The Classical period.
-
In the Vedas sacred texts, Vedic Sanskrit is found mainly in the Rig Veda, the Puranas and the Upanishads.
-
The Vedas were composed in the period 1000 to 500 BCE.
Additional Info:
-
The language impressed some Europeans.
-
Sir William Jones, an English scholar, arrived in India in 1783 as a judge of the British Supreme Court in Calcutta.
-
He was the Asian Society’s founder.
-
He translated the Sanskrit author Kalidasa’s Abhijnana Shakuntala and Ritu Samhara as well as Jayadeva’s Gita Govinda into English.
-
Manusmriti was also translated into English by Jones.
-
Another scholar Sir Charles Wilkins in 1785 translated the Bhagavad Gita in to English.
-
The German philologist Max Muller also translated Hitopdesh which is a collection of Indian fables into German.
Some interesting facts about Sanskrit language:
-
Sanskrit language has an organized grammatical structure.
-
Even the vowels and consonants are arranged in a scientific pattern.
-
It is said that a person can express himself or herself in Sanskrit in one word only.
-
In English language too there are words whose origin can be traced back to Sanskrit like bangle from bangri, sugar from sakara, cash from karsha etc.
-
In Karnataka, everyone in the village is Mattur in Shimoga district speaks in Sanskrit language.
-
Sanskrit language is declared as an official language of Uttarakhand.
-
Sudharma is the only daily newspaper in the world in Sanskrit language.It has been published since 1970 from Mysore, Karnataka and is available online.
-
In classical music that is in the Carnatic and Hindustani, Sanskrit is used.
-
Sanskrit language has the largest vocabulary of about 102 arab 78 crore 50 lakh words.
-
The most computer friendly language is Sanskrit.
-
According to NASA scientist Rick Briggs, Sanskrit is the only unambiguous language in existence.
-
There is a University in America dedicated to Sanskrit.
-
Also, NASA has a department for research on Sanskrit manuscripts.
 Onam:
Onam:
Onam is an annual harvest festival celebrated in the Indian state of Kerala.
-
This year, the harvest festival began on August 12 and concluded on August 23, 2021.
Key Points about Onam:
-
Onam is also called Thiruonam and it is celebrated at the beginning of the month Chingam of Malayalam calendar.
-
It is the most revered and celebrated festival and is celebrated every year by the Malayali community across the world.
-
The 10-day long festival marks the beginning of harvest season as well as the appearance of the Vaman avatar of Lord Vishnu along with the homecoming of King Mahabali.
-
The festival begins from Atham (Hasta) nakshatram, and ends on Thiruvonam (Shravana) nakshatram.
-
The 10 days of the festival are named on the names of astrological stars as per the Malayalam calendar.
-
The ten days of celebration includes cultural activities like Atthachamayam, Pulikali, boat race, Kummati kali and tug of war.
The following are the 10 days of Onam and its significance:
-
The celebration of Onam begins with Atham. People in Kerala decorates their home with yellow flowers known as Pokkalam.
-
The 2nd day of the festival is known as Chithira. On this day, people clean their entire houses and add another layer of flowers to the Pokkalam.
-
The 3rd day of Onam is observed by meeting family members and exchanging gifts, known as Onakodi and jewellery.
-
The 4th day is considered the most auspicious one that marks the preparation of Onam Sadhya.
-
On the 5th day, the annual boat race known as the Vallamkali boat race is conducted from the town Aranmula on the banks of the Pamba river in Pathanamthitta. People of the Malayali community participate in this.
-
Thriketta is the 6th day of this harvest festival. From this day, the schools remain closed and kids start preparing for the devotional prayers.
-
With just two days left for the festival, the 7th day marks the beginning of the preparation for Onam Sandhya in which several dance performances are held.
-
The 8th day holds significance in festivities as the idols of Vamana and King Mahabali are prepared by using clay and placed in the centre of the Pokkalam.
-
On the 9th day of Uthradom, the festivities begin on a large scale. People start preparation for traditional meals by using fruits and vegetables.
-
The 10th day of the festival is the most important day of the carnival of Onam. It is believed that on Thiruvonam, the spirit of legendary King Mahabali visits the state of Kerala and hence, the festivities begin from early morning. The grand feast of Onam called Onam sadhya is also prepared on this day.
Legend:
-
The story behind Onam festival is interesting. According to legends, the asura king, Mahabali, who ruled Kerala, became very powerful.
-
He was a noble and just king and he was expanding his kingdom.
-
He conquered the earth and the netherworld, which made the gods in heaven restless.
-
They were threatened by the growing power of Mahabali.
-
To seek help, the gods went to Vishnu, who agreed to help them.
-
Vishnu, disguised as a dwarf Brahmin,Vamana, went to meet Mahabali, who was in the middle of a yagna (fire sacrifice).
-
Mahabali had declared that if anyone sought anything from him during the yagna, he would grant their wish.
-
Hence, the dwarf Brahmin asked Mahabali to give him land equivalent to his three paces. As soon as Mahabali agreed to give him the land, Vamana grew in stature.
-
With the first step he covered the sky and with the second step, he covered the earth. As one more step was remaining, Mahabali asked him to place the third step on him head.
-
With the final step, Vamana sent the Mahabali to netherworld but he granted Mahabli’s one wish to visit the earth and meet his people once a year.
-
Onam is celebrated on the day Mahabali returns to earth to meet his subject.
 Saroops:
Saroops:
Recently, Union Minister Hardeep Singh Puri carried on one of the saroops of the holy Guru Granth Sahib on his head which was flown in from Afghanistan.
About Saroop:
-
Saroop is a physical copy of Sri Guru Granth Sahib, also called Bir in Punjabi.
-
Every Bir has 1,430 pages, which are referred to as Ang.
-
The verses on every page remain the same.
-
The Sikhs consider the saroop of Guru Granth Sahib a living guru and treat it with utmost respect.
-
They believe that all the 10 Gurus were the same spirit in different bodies, and the Guru Granth Sahib is their eternal physical and spiritual form.
-
It was the fifth Sikh master, Guru Arjan Dev, who compiled the first Bir of the Guru Granth Sahib in 1604, and installed it at the Golden Temple in Amritsar.
-
Later, the tenth Sikh master, Guru Gobind Singh, added verses penned by the ninth master, his father Guru Tegh Bahadur, and compiled the Bir for the second and last time.
-
It was in 1708 that Guru Gobind Singh declared the Guru Granth Sahib the living Guru of the Sikhs.
-
Guru Granth Sahib is a compendium of hymns written by six Sikh gurus,15 saints, including Bhagat Kabir, Bhagat Ravidas, Sheikh Farid and Bhagat Namdev, 11 Bhatts (balladeers) and four Sikhs. The verses are composed in 31 ragas.
About the significance of the act of carrying the Saroop on one’s head:
-
The installation and transportation of Guru Granth Sahib is governed by a strict code of conduct called rehat maryada.
-
Under ideal circumstances, five baptised Sikhs are required to transfer the Guru Granth Sahib from one place to another.
-
As a mark of respect, the Bir of the Guru Granth Sahib is carried on the head, and the person walks barefoot.
-
Whenever a devout sees the Bir of Guru Granth Sahib passing by, s/he removes her shoes and bows.
-
A ceremonial whisk is waved high over the Guru Granth Sahib either on the move or while reading from it.
-
Gurdwaras have a separate resting place for the Saroop, called ‘Sukh Asan Sthan’ or ‘Sachkhand’ where the Guru rests at night. This takes place at the end of the day when the holy book is ceremoniously shut and rested.
-
In the morning, the saroop is again installed in a ceremony called ‘prakash’.
Note: Many tourists specially come to watch the prakash and sukha asan ceremony of the Guru Granth Sahib at the Golden Temple.
 Hari singh Nalwa:
Hari singh Nalwa:
Recently the old cliché that states the Afghanistan is a “graveyard of empires” has been restored.
-
The reason for this is that during recent times the 2 superpowers of the world including erstwhile USSR and the USA decided to pull out their troops from Afghanistan as over the years, Afghanistan has been notoriously difficult to govern.
-
But Hari Singh Nalwa, a legendary Sikh commander, had once tamed the turbulent forces in Afghanistan and earned the reputation of being the “most feared Sikh warrior”.
About Hari Singh Nalwa:
-
Hari Singh Nalwa (1791–1837) was Commander-in-chief of the Sikh Khalsa Fauj, the army of the Sikh Empire.
-
He was born in Gujranwala, in the Majha region of Punjab to Dharam Kaur and Gurdial Singh Uppal, in a Sikh Uppal Khatri family. After his father died in 1798, he was raised by his mother.
-
He was one of the main and most trustworthy commanders of Maharaja Ranjit Singh’s force.
-
He remained Governor of Kashmir, Hazara and Peshawar.
-
He is known for his role in the conquests of Kasur, Sialkot, Attock, Multan, Kashmir, Peshawar and Jamrud.
-
He defeated various Afghans and established control over various regions along the boundary of Afghanistan and prevented Afghans from entering Punjab through Khyber pass.
Note: Khyber Pass was the main route to enter India by the foreign invaders from 1000 AD till early 19th century.
-
During a hunt in 1804, a tiger attacked him and also killed his horse.
-
His fellow hunters attempted to protect him but he refused their offers and allegedly killed the tiger by himself bare handedly by tearing the tiger apart from its mouth, thus earning the cognomen Baghmar (Tiger-killer) and because of this Nalwa was attached to his name.
-
In 1818, Sikh army under Nalwa won the Battle of Peshawar and Nalwa was asked to be stationed there.
-
Nalwa took control over Jamrud in 1837, a fort at the entryway to Afghanistan through Khyber Pass.
Note: For his bravery and ferocity, the government of India released a stamp on the name of Nalwa in 2013.
Fun Fact:
-
Legend has it that Afghan mothers used to quieten their newborns by taking Nalwa's name and for young Afghans, his name was a terror spoken in hush hush.
-
And probably that's why even American generals used to tell Nalwa's story to motivate their troops when US-Afghan war was in its thick.
Economics
 FRP for Sugarcane:
FRP for Sugarcane:
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA), on August 25, 2021, approved the highest ever fair & remunerative price (FRP) for sugarcane farmers.
Key Points:
-
The cost of production of sugarcane for the sugar season 2021-22 is Rs. 155 per quintal.
-
FRP of sugarcane for sugar season 2021-22 (October - September) has been increased at Rs. 290/- per quintal for a basic recovery rate of 10%.
-
This FRP of Rs. 290 per quintal at a recovery rate of 10% is higher by 87.1% over production cost, thereby giving the farmers a return of much more than 50% over their cost.
-
If recovery is less than 9.5%, then farmers will be given a FRP of Rs 275 per quintile.
-
The FRP has been determined on the basis of recommendations of Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) and after consultation with State Governments and other stake-holders.
Benefits:
-
This approval is the highest ever FRP.
-
It is going to benefit 5 crore sugarcane farmers and their dependents.
-
It will also benefit 5 lakh workers who are employed in sugar mills and related ancillary activities.
What is Fair and remunerative price (FRP)?
-
FRP is the minimum price at which sugarcane is purchased by sugar mills from farmers.
-
This price is fixed by Union government based on the recommendations of Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP).
-
It is determined under Sugarcane (Control) Order, 1966.
-
FRP is determined by considering various factors like cost of production, domestic & international prices, demand-supply situation, inter-crop price parity etc.
-
This FRP is uniformly applicable all over the country.
Note: However, some states namely Haryana, Punjab, UP, Uttarakhand, and TN announce a State Advised Price, which is usually higher than the FRP.
 Forum for Decarbonizing Transport:
Forum for Decarbonizing Transport:
NITI Aayog and World Resources Institute (WRI), India, on 23rd August 2021, jointly launched the ‘Forum for Decarbonizing Transport’ in India.
Key Points:
-
This forum has been launched virtually as a part of the NDC-Transport Initiative for Asia (NDC-TIA) project.
-
The project aims at bringing down the peak level of GHG emissions (transport sector) in Asia (in line with a well below 2-degree pathway), resulting in problems like congestion and air pollution.
Why is it needed?
-
It is needed for the following reasons:
-
India has a massive and diverse transport sector which is also the third most CO2 emitting sector.
-
Transports emits more than 20 percent of the energy related CO2 which has increased the global warming.
-
This is because transport relies on the oil for more than 90 percent of its energy so it is particularly hard to decarbonize.
-
Data from (IEA, 2020; Ministry of Environment Forest and Climate Change, 2018) suggests that within the transport sector, road transport contributes to more than 90% of the total CO2 emissions.
Steps taken by the Government:
-
The Government of India (GoI), through various policy measures and initiatives, is continuously working towards the decarbonization of road transport.
-
GoI's major focus has been on the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in the country.
-
NITI Aayog has been at the helm of the promotion of EVs and sustainable mobility through the National Mission on Transformative Mobility and Battery Storage.
About NDC-TIA:
The NDC Transport Initiative for Asia (TIA 2020-2023) is a joint programme of seven organisations that will engage China, India, and Vietnam in promoting a comprehensive approach to decarbonizing transport in their respective countries over the period 2020-2024.
-
The seven organizations are as follows:
-
World Resources Institute (WRI)
-
International Transport Forum (ITF)
-
Agora Verkehrswende (AGORA)
-
Partnership on Sustainable, Low Carbon Transport (SLoCaT) Foundation
-
Renewable Energy Policy Network for the 21st Century e.V. (REN21)
-
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH
-
International Council on Clean Transportation (ICCT).
-
This project is a part of the International Climate Initiative (IKI).
-
The Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety (BMU) support the initiative on the basis of a decision adopted by the German Bundestag.
Features of the Forum:
-
This programme focuses on developing a coherent strategy of effective policies and the formation of a multi-stakeholder platform for decarbonizing transport in India.
-
The forum will be a one-stop platform for initiating dialogues between the stakeholders and partners that will help in achieving specific results in reducing emissions from the transport sector.
-
It will unite the CEOs, researchers, academics, multilateral agencies, financial institutions as well as the Central and state government on a common platform.
-
This, in turn, will help in the development of innovative business models resulting in targeted results and the holistic growth of the electric mobility space in India.
-
NITI Aayog is the implementing partner for the India component of the project.
About NITI Aayog:
-
NITI Aayog refers to the National Institution For Transforming India Aayog.
-
It is the premier policy 'Think Tank' of the Government of India (GoI).
-
It was established on 1 January 2015 with an objective to foster cooperative federalism through structured support initiatives and mechanisms with the States on a continuous basis, recognizing that strong States make a strong nation.
-
The Governing Council of NITI, with The Prime Minister as its Chairman, comprises Chief Ministers of all States and Lt. Governors of Union Territories (UTs).
-
The current CEO of NITI Aayog is Amitabh Kant.
About WRI India:
WRI India (World Resources Institute, India) is an independent charity, legally registered in India driving transformative solutions through five inter-related programs:
-
Sustainable Cities
-
Climate
-
Energy
-
Sustainable Landscapes and Restoration
-
Climate Resilience
It works with local and national governments, businesses, and civil society to address India’s development challenges
About WRI:
-
The World Resources Institute (WRI) is a global research non-profit organization.
-
It was established in 1982 with funding from the MacArthur Foundation under the leadership of James Gustave Speth.
-
WRI's activities are focused on seven areas: food, forests, water, energy, cities, climate and ocean.
 SAMRIDH Scheme:
SAMRIDH Scheme:
Minister of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) Ashwini Vaishnaw launched Startup Accelerators of MeitY for pRoduct Innovation, Development and growth (SAMRIDH) programme.
Aim:
-
SAMRIDH programme aims to help growing startups.
-
This initiative will not only provide funding to startups, but will also help in bringing skill sets together which will help them become successful.
-
The programme aims to further the Indian startup growth which has seen the emergence of 63 unicorns (Startups with over $1 billion valuation), making India the third largest unicorn hub globally with a total valuation of $168 billion.
Key Points:
-
The SAMRIDH programme is being implemented by MeitY Start-up Hub (MSH).
-
This initiative is in line of the vision of Prime Minister Narendra Modi to utilise the energy of youngsters to create an inclusive atmosphere of development.
-
Under this MeitY will create a conducive platform for Indian software product startups to enhance their products and secure investments for scaling their business.
-
The Government will support startups and entrepreneurs in the most challenging phase which is the initial risk phase, Vaishnaw had said earlier.
-
The programme will focus on accelerating 300 start-ups by providing customer connect, investor connect, and international expansion opportunities in the next three years.
-
Also, an investment of up to Rs 40 lakh to startups, based on their current valuation and growth stage will be provided through selected accelerators.
-
It will also facilitate equal matching investment by the accelerator or investor.
About MeitY:
-
MeitY refers to the Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology. MeitY was previously known as "The Department of Information Technology". It was renamed to The Department of Electronics and Information Technology in 2012.
-
It is an executive agency of the Union Government of the Republic of India.
-
It was carved out of the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology on 19 July 2016 as a standalone ministerial agency responsible for IT policy, strategy and development of the electronics industry.
-
The current Union Minister of Electronics & Information Technology is Ashwini Vaishnaw (Cabinet Minister) and Rajeev Chandrasekhar, Minister of State.
 EASE 4.0:
EASE 4.0:
The fourth edition of Public Sector Bank (PSB) Reforms Agenda called ‘EASE 4.0’ for the financial year 2021-22 was recently unveiled by the Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman.
Note: EASE stands for Enhanced Access & Service Excellence.
Key Highlights:
-
The Ease 4.0 launch event was organized by the Indian Banks Association (IBA).
-
She unveiled the annual report for the PSB Reforms Agenda EASE 3.0 for 2020-21.
-
She also participated in the awards ceremony to felicitate best performing banks on EASE 3.0 Banking Reforms Index.
Best performing banks on EASE 3.0:
-
State Bank of India, Bank of Baroda and Union Bank of India has won the awards for best performing banks for PSB Reforms EASE 3.0 based on the EASE index.
-
Indian Bank won the award for the best improvement from the baseline performance.
-
SBI, BoB, Union Bank of India, Punjab National Bank and Canara Bank won the top awards in different themes of the PSB Reforms Agenda EASE 3.0.
What is EASE 4.0?
-
EASE 4.0 is a common reform agenda for Public Sector Banks (PSBs) aimed at institutionalising clean and smart banking.
What is the aim of EASE 4.0?
-
EASE 4.0 aims to further the agenda of customer-centric digital transformation and deeply embed digital and data into PSBs’ ways of working.
-
It sets the agenda and roadmap to transform all PSBs into digital-attacker banks working hand-in-hand with key constituents of the financial services ecosystem to offer industry-best customer experience.
Theme for EASE 4.0:
-
The major theme for EASE 4.0 is “Technology-enabled, simplified, and collaborative banking.”
Key Initiatives under EASE 4.0:
EASE 4.0 reforms look after four key initiatives to be adopted by public sector banks:
-
Smart Lending for Aspiring India
-
New Age 24×7 banking with resilient technology
-
Collaborative banking for synergistic outcomes
-
Tech-enabled Ease of Banking
-
Institutionalizing Prudent Banking
-
Governance and Outcome Centric HR
EASE Agenda Background:
-
EASE Agenda is a common reform agenda for Public Sector Banks (PSBs), which is aimed at institutionalizing clean and smart banking.
-
The first edition of EASE 1.0 was launched in January 2018 and EASE 2.0 followed this to build on the foundation laid in EASE 1.0.
-
EASE 2.0 was launched to further progress on reforms. The reform actions of EASE 2.0 were aimed at making the reforms journey irreversible, strengthening processes and systems and driving outcomes.
-
EASE 3.0 was launched in February 2020 with the aim of enhancing the ease of banking in all customer experiences, using technology; alternate data, as well as analytics. It was instrumental in enabling digital lending to customers.
-
The Public Sector Banks showed significant improvement in the Action Points of the EASE Reforms Agenda since its introduction.
Defence
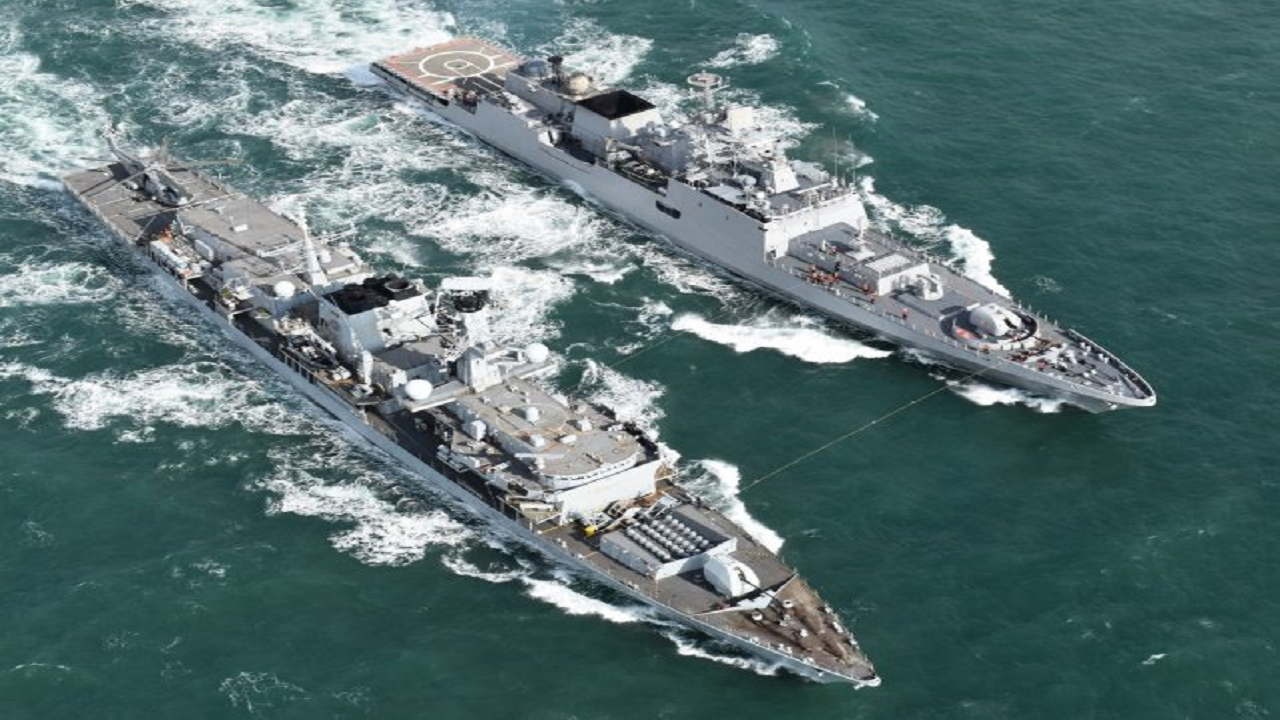 Exercise Konkan 2021:
Exercise Konkan 2021:
Exercise Konkan 2021 was held between INS Tabar and HMS Westminster on 16 August 2021 in the English Channel.
Key Points:
-
The Indo-UK Naval exercise included the participation of integral helicopters of the two ships and the Falcon Electronic Warfare aircraft.
-
A wide range of exercises like co-ordinate anti-submarine procedures, combined maritime picture compilation, firing drills, replenishment at sea and combat formation maneuvering were conducted during the exercise.
-
These along with the diverse professional engagements held earlier in harbour, have enabled Exercise Konkan 2021 consolidate interoperability which in turn have helped cement the strong bonds of friendship between the two navies.
About Konkan exercise:
-
The bilateral naval exercise Konkan is being held every year since 2004.
-
The Indian Navy and Britain’s Royal Navy hold this bilateral naval exercise to enhance the interoperability, synergy and cooperation between both navies. It is based on the long-term strategic relationship between them.
About INS Tabar:
-
INS Tabar is the third Talwar-class frigate in Indian Navy.
-
It was commissioned on April 19, 2004 in Kaliningrad, Russia.
-
The current Commanding Officer (CO) of INS Tabar is Captain Mahesh Mangipudi.
-
It reached the home-port of Mumbai on July 31, 2004.
-
INS Tabar is assigned to Western Naval Command of Indian Navy, which is headquartered in Mumbai.
-
This warship can handle air or surface or subsurface missions and defend herself.
About HMS Westminster:
-
It is a Type 23 frigate of the Royal Navy of England.
-
It was launched on February 4, 1992.
-
It has been named after Dukedom of Westminster.
 Malabar Naval Exercise:
Malabar Naval Exercise:
The navies of the Quad countries—India, the US, Australia and Japan are all set to conduct the Malabar Naval Exercise from August 26, 2021.
Key Details:
-
On August 21, 2021, Indian stealth frigate INS Shivalik and anti-submarine warfare corvette INS Kadmatt arrived in Guam to take part in the exercise that will feature an array of complex drills.
-
The annual exercise will be four-day affair.
-
The next edition of the high-voltage Malabar naval exercise will be conducted from 26th August to 29th August 2021 amid mounting global concerns over China’s growing military muscle-flexing in the Indo-Pacific region.
-
This exercise will be conducted off the coast of Guam which is an island territory of the U.S. in the Western Pacific.
-
It is located 2,500 km east of the Philippines.
-
It will be conducted with the aim of enhancing inter-operability, gaining from best practices and developing a common understanding of procedures required for maritime security operations.
-
The Malabar-21 will witness high-tempo exercises among destroyers, frigates, corvettes, submarines, helicopters and long-range maritime patrol aircraft of the participating navies.
-
Complex surface, sub-surface and air operations including live weapon firing drills, anti-surface, anti-air and anti-submarine warfare drills, and joint manoeuvres and tactical exercises will also be conducted during the exercise
About Malabar Exercise:
-
Malabar exercise is an annual naval exercise between the navies of India, Australia, Japan, and the USA.
-
It is held alternately in the Indian Ocean and Pacific Ocean.
Background:
-
The Malabar exercise started in 1992 as a bilateral drill between the Indian Navy and the U.S. Navy in the Indian Ocean.
-
Japan became a permanent member of the exercise in 2015.
-
This annual exercise was conducted off the coast of Guam in 2018 and off the coast of Japan in 2019.
-
Last year, the exercise was hosted in two phases in the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea.
-
Following India's invitation, Australia participated in the Malabar exercise last year that effectively made it a drill by all four member nations of the Quad.
Aim of the exercise:
-
The Malabar exercise which is conducted annually aims to support free, open and inclusive Indo-Pacific region.
-
Its aim is also to remains committed to a rule based international order.
-
It also seeks to achieve interoperability with an emphasis on humanitarian assistance, anti-submarine warfare, gunnery training, surface war manoeuvres, counter-terror operations, and aerial surveillance.
 Women in Army:
Women in Army:
A Selection Board of the Indian Army, for the first time has approved the promotion of five women officers to the rank of colonel (time scale) rank, post completion of 26 years of reckonable service.
Note: Army officers are given the rank of time scale colonels after they complete 26 years in service.
Key Details:
-
The five women officers selected for Colonel Time Scale rank are Lt Col Sangeeta Sardana from the Corps of Signals, Lt Col Sonia Anand and Lt Col Navneet Duggal from the Corps of EME and Lt Col Reenu Khanna and Lt Col Ritcha Sagar from the Corps of Engineers.
-
Previously, only women officers serving in the Army Education Corps (AEC), Judge Advocate General (JAG), and the Army Medical Corps (AMC) were applicable for promotion to the Colonel Time Scale rank.
Background:
-
In a landmark verdict in February 2020, the Supreme Court had directed that women officers in the Army be granted a permanent commission, rejecting the Centre’s stand of their physiological limitations as being based on “stereotypes” and “gender discrimination against women”.
-
In yet another feat, on August 18, 2021, the Apex Court passed an interim order to allow women to take the admission exam to National Defence Academy (NDA) where only men could appear. The exam is scheduled for September 5, 2021.
-
The bench added that admissions, etc be subjected to its final order.
Significance:
-
The widening of promotion avenues to more branches of the Indian Army is a sign of increasing career opportunities for women officers.
-
Along with permanent commission to women officers as well as allowing women to appear for NDA exam are steps of the Indian Army towards a gender-neutral Army.
 China's Missile Silos:
China's Missile Silos:
A new report by the Federation of American Scientists (FAS) shows that China is building more than 100 new missile silos in the desert near its Yumen city.
Key Details:
-
Satellite images have revealed that China is building at least three missile silo fields in Yumen in Gansu province, near Hami in Xinjiang province, and at Hanggin Banner, Ordos City, in Inner Mongolia.
-
It seems that China is constructing around 120 missile silos at Yumen, around 110 silos in Hami, and 29 in the Hanggin Banner field.
-
Earlier this year, 16 missile silos were detected in the People’s Liberation Army Rocket Force’s (PLARF) Jilantai training area, also in Inner Mongolia.
-
China, for several decades before these discoveries in 2021, operated only 20 missile silos for its DF-5 liquid-fuel intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM).
-
On completion of the ongoing work, China could have 250-270 new missile silos, more than 10 times the number it had maintained for several decades.
-
This comes in the backdrop of a June 30 report from the Middlebury Institute of International Studies which showed the first new Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) silo field at Yumen in Gansu province could have 120 under-construction silos.
How were the fields discovered?
-
The Yumen field was discovered by commercial satellite images obtained by researchers at the James Martin Center for Nonproliferation Studies, California.
-
The Hami field was identified by nuclear experts at the Federation of American Scientists (FAS) using Planet Labs satellite images.
-
The Hanggin Banner field was discovered by researchers at the China Aerospace Studies Institute, Washington DC.
Why is China building missile silos?
There could be three possible explanations. They are as follows:
-
Firstly, some Chinese political scientists believe this could be China’s attempt to move towards a launch-on-warning (LOW) nuclear posture.
Note: LOW refers to a launch at an adversary on detection of an incoming missile before the adversary’s missile hits its target.
-
Secondly, it enables China to achieve its goal of increasing its nuclear warhead stockpile.
-
Thirdly, China could maybe use these silos as decoys.
Significance for India:
The matter assumes a great significance for India because India and China are locked in a military standoff at the Line of Actual Control in eastern Ladakh since 2020.
Even after a disengagement of troops from both sides at the contentious Pangong Tso area in March 2021, there has been no further breakthrough in military and diplomatic talks between the two countries.
Although both China and India have pledged nuclear ‘no first use’ doctrines, India’s modest ballistic missile defence capabilities and China’s nuclear ambiguity are matters of concern for India.
What is a Missile Silo?
-
A missile launch facility, also known as an underground missile silo, launch facility (LF), or nuclear silo, is a vertical cylindrical structure constructed underground, for the storage and launching of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs).
-
The structures typically have the missile some distance below ground, protected by a large "blast door" on top. They are usually connected, physically and/or electronically, to a missile launch control center.
 KAZIND-21:
KAZIND-21:
The 5th edition of Indo- Kazakhstan Joint Training Exercise, “KAZIND-21” will be held from August 30 to September 11, 2021, at Training Node, Aisha Bibi, Kazakhstan.
Key Details:
-
KAZIND-21 is being held as part of military diplomacy and to strengthen the growing strategic relation with Kazakhstan.
-
The exercise is a joint training between both the Armies, which will boost the bilateral relations between India and Kazakhstan.
-
It is also a platform for the Armed Forces of India & Kazakhstan to train for Counter Insurgency and Counter-Terrorism operations in the mountainous, rural scenarios under UN mandate.
-
The Indian Army contingent represented by a battalion of The Bihar Regiment consists of a total of 90 personnel led by a Contingent Commander. The Kazakhstan Army will be represented by a company group.
 MANTHAN 2021:
MANTHAN 2021:
On 26th August 2021, Bureau of Police Research and Development (BPR&D) and All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) have jointly launched the MANTHAN 2021 hackathon.
About MANTHAN 2021 Hackathon :
-
MANTHAN 2021 Hackathon is a unique national initiative to identify innovative concepts and technology solutions for addressing the security challenges of the 21st century faced by our intelligence agencies.
-
This hackathon will have two phases.
-
In the first phase, participants would submit their concepts against the problem statements which they wish to solve on the portal.
-
These submitted ideas will be evaluated by group of experts in the field and only the innovative ideas will be selected for the Grand Finale or 2nd round scheduled from 28 November 2021.
-
During this 36 hours online hackathon, scheduled from 28th November to 1st December 2021, selected youths from education institutions across the country and registered start-ups will participate to offer strong, safe and effective technology solutions using their technical expertise and innovative skills.
-
Participants are expected to develop digital solutions under 6 themes for 20 different challenge statements such as using new technologies like Artificial Intelligence, Deep Learning, Augmented reality, Machine Learning, etc. for ever-changing protection associated challenges, which include photo/video analysis, Fake Content Identification alongside with the information of creator, predictive Cyber Crime records analytics, etc.
-
The winning teams will receive a prize of Rs 40 lakhs.
 ARMY-2021:
ARMY-2021:
The International Military and Technical Forum ‘ARMY 2021’ was organised in Moscow, Russia from August 22 to 28, 2021, at Patriot Expo, Kubinka Air Base and Alabino military training grounds.
Key Points:
-
The ARMY 2021 is the 7th edition of the annual International Military-Technical Forum.
-
Delegations from at least 70 nations participated in this high-profile event.
-
The forum showcased over 730 pieces of Russian weapons and equipment, as well as 28,000 exhibits from industrial enterprises for a free inspection.
About the India Pavilion:
-
The India Pavilion at the Army-2020 International Military and Technical Forum was inaugurated by Secretary (Defence Production) Raj Kumar and Indian Ambassador DB Venkatesh Verma outside Moscow, the Indian Embassy in Russia.
-
The Indian pavilion was represented by Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO), Goa Shipyard Limited, Bharat Dynamics Ltd. (BDL), BEML and Ordnance Factory Board (OFB).
-
The DRDO showcased its 11 products, having the capability of being exported.
-
These include:
-
Beyond Visual Range Air to Air Missile (BVRAAM) ‘ASTRA’,
-
Anti Tank Guided Missile (ATGM)-NAG and HELINA, Surface to Air Missile (SAM) ‘Akash’, Light Combat Aircraft (LCA)-Tejas,
-
Airborne Early Warning and Control System (AEW&C),
-
Identification of Friend and Foe (IFF), Advanced Towed Artillery Gun System (ATAGS), Joint Venture Protective Carbine (JVPC),
-
Arjun Main Battle Tank (MK1A),
-
Rohini Radar and Air Defence Fire Control Radar (ADFCR)-Atulya Radar.
About the forum:
-
The International Military and Technical Forum ‘ARMY’ is being organized by the Ministry of Defence of the Russian Federation since 2015.
-
This Forum is the world’s leading exhibition of armament and military equipment and the authoritative platform for discussing innovative ideas and developments for the armed forces by various foreign exhibitors, delegations and visitors.
Environment
 SUJALAM Campaign 2021:
SUJALAM Campaign 2021:
The Ministry of Jal Shakti recently began ‘SUJALAM’, a ‘100 days campaign.
Highlights:
-
The launch of SUJALAM campaign started on 25 August 2021 as part of the Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav celebrations and will continue to run for 100 days.
-
The Jal Shakti began SUJALAM campaign to create more Open Defecation Free (ODF) plus villages by undertaking waste water management at the village level.
About the Campaign:
-
The campaign will not only build desired infrastructure like soak pit for management of greywater in villages but will also aid in sustainable management of water bodies.
-
As the disposal of waste water and clogging of water bodies in the villages or on the outskirts of the villages remain one of the major problems so the campaign would help in management of the wastewater which in turn would help to revive the water bodies.
-
Furthermore, the campaign would boost the momentum of SBMG (Swachch Bharat Mission Grameen) phase II activities through community participation and will increase awareness about ODF-plus activities. Hence ensuring long-term maintenance and sustainability of built infrastructure
Aim:
-
The main aim of the SUJALAM’ Campaign is to achieve ODF Plus Status for villages across India in an accelerated manner in a short time.
Focus:
-
The focus area of this campaign is to ensure that all newly emerging Households in the village have access to toilets.
Significance:
-
The Campaign would help in management of the wastewater and in turn would help to revive the water bodies through creation of 1 million Soak-pits and also other Grey water management activities.
What are the key activities that will be organized under SUJALAM campaign?
-
The key activities that will be organized in the villages under SUJALAM campaign include:
-
Organizing Community consultations, Khuli Baithaks and Gram Sabha meetings to analyze the current situation
-
Pass resolution to maintain ODF sustainability and achieve needed number of soak pits to manage the grey water
-
Develop a 100 days’ plan to undertake sustainability and soak pit construction related activities
-
Construct requisite number of soak pits
-
Retrofit toilets where needed through IEC and community mobilization and
-
Ensure all newly emerging Households in the village have access to toilets.
About Jal Shakti Ministry:
-
Ministry of Jal Shakti is a ministry under Government of India.
-
It was founded in May 2019 under the second Modi ministry.
-
This was formed by merging of two ministries which are Ministry of Water Resources, River Development & Ganga Rejuvenation and Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation.
-
The ministry was formed with an aim not only to clean the river Ganges but also encompass any international or national disputes between inter-state water bodies and the rivers which are shared by India along with other neighboring countries.
-
Gajendra Singh Shekhawat is the Minister of Jal Shakti.
 World Water Week 2021:
World Water Week 2021:
World Water Week is celebrated by Stockholm International Water Institute (SIWI) every year in order to highlight the global water issues and related concerns of international development since 1991.
About World Water Week:
-
It is a week-long global water conference held each year in late August or early September.
-
The weeklong event is attended by some 4,000 participants from 135 countries.
-
During the week, awards such as the Stockholm Water Prize, the Stockholm Junior Water Prize, and the Stockholm Industry Water Award are given out at their respective award ceremonies.
-
The event consists of a broad array of parallel activities convened by leading international organizations on a broad array of water-related topics, ranging from food security and health to agriculture, technology, biodiversity, and the climate crisis.
Key Points:
World Water Week 2021 is being observed between August 23rd, 2021 and August 27th, 2021.
Theme of 2021:
The theme for World Water Week 2021 is ‘Building Resilience Faster’.
History:
The World Water Week was started in Stockholm, Sweden as the Stockholm Water Symposium in 1991.
In 2001, the Stockholm Water Symposium was officially named as the World Water Week.
Water+ city:
-
Recently, Surat city was awarded a ‘Water+ certification’ under the Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM).
-
It was the first city from Gujarat to get recognition.
-
It was awarded by the ministry of housing and urban Affairs (MoHUA) in the field of adopting best practices in waste water management.
Important Info:
-
SMC was the only civic body from India that was invited at the panel discussion on the topic “Zero Liquid Discharge Cities”.
-
SMC was invited to discuss at SWWW because, Surat’s achievement in treating sewage water and reusing it has been recognized by world’s top institute in water governance.
-
Surat treats about 1,400 MLD sewage water out of which 320 MLD (33%) is reused.
Note: According to City municipal commissioner, Banchhanidhi Pani, by 2030, the city would be able to reuse 100% of sewage water after treatment.
About SIWI:
-
Stockholm International Water Institute (SIWI) is a Stockholm-based policy institute.
-
It generates knowledge and guides decision-making towards water wise decisions.
-
It was founded in 1991.
 Acetabularia jalakanyakae:
Acetabularia jalakanyakae:
A team of marine biologists from the Central University of Punjab (CUP) recently discovered a new species of marine green algae from Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Key Points:
-
It has been named Acetabularia jalakanyakae.
Note: Jalakanyaka in Sanskrit literally means mermaid and a goddess of oceans.
-
The scientists say they were influenced by the fictional character Little Mermaid in the the fairy tale “The Little Mermaid” by Danish writer Hans Christian Anderson.
-
It will be published in the Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences, published by CSIR.
About Acetabularia jalakanyakae:
-
The newly discovered algae are small and resemble an umbrella or a mushroom in bright green colour with a size of 20 to 40 mm.
-
They have grooves on its cap measuring 15 to 20 mm in diameter.
-
The main feature of the newly discovered species is that the plant is made up of a single gigantic cell with one nucleus.
-
An important characteristic of Acetabularia genus is that they are regenerative (able to regrow a part again even if it is cut off) in nature.
-
This discovery is significant because the last new algae species found in Andaman and Nicobar Islands was in 1984.
Background:
-
In May 2019, Professor Felix Bast had discovered this new species and after various studies and analysis with other species it was confirmed as a new species.
 Hawaii’s Kilauea Volcano:
Hawaii’s Kilauea Volcano:
Scientists at the Hawaiian Volcano Observatory recently noticed a surge of earthquakes and the ground swelling at the southern part of the crater at Kilauea’s summit.
Key Details:
-
There are indications magma is shifting about a half-mile to a mile (1 to 2 kilometers) below the surface.
-
This has caused the scientists to warn that the mountain could once again disgorge lava.
-
However, there is no indication an eruption is imminent because the volcano, which is among the world’s most active, has behaved similarly in the past without any magma breaking the surface.
Where is this activity occurring?
-
The activity is occurring at the summit of Kilauea volcano, an uninhabited area within Hawaii Volcanoes National Park on the Big Island.
-
This is about 200 miles southeast of Honolulu, which is on a different island called Oahu.
About Kilauea:
-
Kilauea also known as Mount Kilauea is an active shield volcano in the Hawaiian Islands.
-
It is located on the southeastern part of the island of Hawaii, Hawaii state, U.S.
-
The volcano is between 210,000 and 280,000 years old and emerged above sea level about 100,000 years ago.
-
The volcano’s 4,090-foot (1,250-metre) summit has collapsed to form a caldera, a broad shallow depression nearly 3 miles (5 km) long and 2 miles (3.2 km) wide with an area of more than 4 square miles (10 square km).
-
Kilauea’s slopes merge with those of the nearby volcano Mauna Loa on the west and north.
-
Kilauea has erupted 34 times since 1952. From 1983 to 2018, it erupted almost continuously, in some cases sending streams of lava that covered farms and homes.
-
Its most recent eruption began on December 20, 2020 and ended on May 23, 2021 creating a lake with enough lava to fill 10 Hoover dams.
Additional Info:
-
The most famous Hawaiian volcanoes are the shield type volcanic landforms.
-
The shield type volcanic landforms are mostly made up of basalt, a type of lave that is very fluid when erupted.
-
These volcanoes are not steep.
What is a volcano?
-
A volcano is an opening in the earth’s crust through which lava, volcanic ash, and gases escape.
-
Beneath a volcano, liquid magma containing dissolved gases rises through cracks in the Earth's crust.
-
As the magma rises, pressure decreases, allowing the gases to form bubbles.
-
When volcanoes erupt they can spew hot, dangerous gases, ash, lava and rock that can cause disastrous loss of life and property, especially in heavily populated areas.
Where are the volcanoes found on earth?
-
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater.
-
For example, a mid-oceanic ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates.
-
Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande Rift in North America.
About Volcano Eruption:
-
A volcano can be active, dormant or extinct.
-
Volcanic eruptions happen when lava and gas are discharged from a volcanic vent.
-
An eruption takes place when molten rock called magma rises to the surface.
-
Magma is formed when the earth's mantle melts.
-
Although there are several factors triggering a volcanic eruption, three predominate: the buoyancy of the magma, the pressure from the exsolved gases in the magma and the injection of a new batch of magma into an already filled magma chamber.
-
Melting may happen where tectonic plates are pulling apart or where one plate is pushed down under another.
-
Magma is lighter than rock so rises towards the Earth's surface.
-
As the magma rises, bubbles of gas form inside it.
-
Runny magma erupts through openings or vents in the earth's crust before flowing onto its surface as lava.
-
Another way an eruption happens is when water underneath the surface interacts with hot magma and creates steam.This can build up enough pressure to cause an explosion.
The material that is expelled in a volcanic eruption can be classified into three types:
-
Volcanic gases, a mixture made mostly of steam, carbon dioxide, and a sulfur compound (either sulfur dioxide, SO2, or hydrogen sulfide, H2S, depending on the temperature).
-
Lava, the name of magma when it emerges and flows over the surface.
-
Tephra, particles of solid material of all shapes and sizes ejected and thrown through the air.
Indian Policy
 Karmayogi:
Karmayogi:
Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) Science & Technology; Minister of State (Independent Charge) Earth Sciences; MoS PMO, Personnel, Public Grievances, Pensions, Atomic Energy and Space, Dr Jitendra Singh recently inaugurated the “Karmayogi” Digital Learning Facility.
-
On the occasion, Dr. Jitendra Singh also released a special edition of the bi-annual ISTM Journal of Training, Research and Governance on Mission Karmayogi.
About “Karmayogi” Digital Learning Facility:
-
This facility has been launched for Civil Servants at the Institute of Secretariat Training & Management (ISTM), a premier Central Training Institution under the Department of Personnel & Training (DoPT).
-
It will help further in extending the citizen centric reforms initiated by the Government under ‘Mission Karmayogi’.
-
It is meant to upgrade the skills of central government officers and personnel.
-
This path-breaking initiative has been taken to shift the working and functioning of the Civil Servants from ‘Rule to Role’, so that they are equipped to perform the tasks assigned to them.
-
Mission Karmayogi aims to create a dedicated work force not only of the Civil Services but more than that; it would serve the cause of the citizen at large.
Background:
-
The National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (‘NPCSCB’) – “Mission Karmayogi” was approved by the Government on 2nd September, 2020.
-
It was approved with the main objective of enhancing governance through Civil Services Capacity Building.
-
NPCSCB was launched with the following institutional framework:-
-
Prime Minister's Public Human Resources (HR) Council,
-
Capacity Building Commission.
-
Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) for owning and operating the digital assets and the technological platform for online training.
-
Coordination Unit headed by the Cabinet Secretary.
Features:
-
NPCSCB has been carefully designed to lay the foundations for capacity building for Civil Servants so that they remain entrenched in Indian Culture and sensibilities and remain connected, with their roots, while they learn from the best institutions and practices across the world.
-
The training of Civil Servants at various Academies is being restructured to include optimum use of the digital learning platform of Integrated Government Online Training (iGOT).
 e-Shram portal:
e-Shram portal:
Labour and Employment Minister Bhupendra Yadav recently lauched a portal named e-Shram portal for the labours working in the unorganized sector of the country.
Highlights:
-
e-Shram portal is a national database of unorganized sector workers.
-
It was handed it over to the States/UTs in the presence of the Minister of State for Labor and Employment and Petroleum and Natural Gas, Rameshwar Teli.
Key Details:
-
The main aim of the government is to register 38 crore unorganised workers, such as construction labourers, migrant workforce, street vendors and domestic workers, among others.
-
The service will help in creating a National Database of Unorganized Workers (NDUW) in the country.
-
The Government of India (GoI) will prepare a national database through this service.
-
The GoI will have an aadhaar-based database of the unorganized workers across various sectors in the country.
-
Under this initiative e-shram cards will be issued to the workers.
-
This card will have a 12-digit UAN.
-
It will be valid everywhere in the country.
-
It will also help in including them in social security schemes.
-
The Labour Ministry, state governments, trade unions and CSCs will coordinate the registration of workers on the portal.
-
A national toll free number — 14434 — will also be launched to assist and address the queries of workers seeking registration on the portal.
E Shram Card Registration 2021:
-
To do E Shram Card Registration 2021, the workers have to visit the website eshram.gov.in.
-
They have to register themselves, for which Aadhaar number and mobile number linked with Aadhaar will be required.
-
On this, information like name, profession, address, education, skill will have to be entered.
-
Then the workers will be provided with an e-SHRAM card which will have a 12 digit unique number.
-
The objective behind the move is the integration of Centre’s social security schemes.
-
The details of workers will also be shared by the state government and departments. Following the launch of the portal, the workers from the unorganised sector can begin their registration on the same day.
Note: Earlier on August 24, 2021, the Minister for Labour and Employment Bhupender Yadav had unveiled the logo for the E-Shram portal.
 Drone Rules 2021:
Drone Rules 2021:
Ministry of Civil Aviation recently repealed the Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UAS) Rules, 2021 and replaced the same with the liberalized Drone Rules, 2021.
Key Points:
-
The step has been taken based on the feedback received by the Government.
-
The earlier UAS Rules 2021 was perceived by academia, Startups, end-users and other stakeholders as being restrictive in nature as they involved considerable paperwork, required permissions for every drone flight and very few “free to fly” green zones were available.
-
The new rules are aimed at making it significantly easier for people and companies to own and operate drones.
-
They also streamline a labyrinthine certification process for manufacturers, importers and users.
Some Key features of Drone Rules 2021:
-
According to the new rules, some of the key features of Drone Rules 2021 are as follows:
-
Special drone corridors will be developed for cargo deliveries.
-
Several approvals have also been abolished. They include unique authorization number, unique prototype identification number, certificate of manufacturing and airworthiness, certificate of conformance, certificate of maintenance, import clearance, acceptance of existing drones, operator permit, authorization of R&D organization, student remote pilot licence, remote pilot instructor authorization, drone port authorization etc.
-
No pilot licence will be required for micro drones (for non-commercial use), nano drones and for R&D organisations.
-
Number of forms reduced from 25 to 5.
-
Types of fee reduced from 72 to 4.
-
Quantum of fee reduced to nominal levels and delinked with size of drone. For instance, the fee for a remote pilot license fee has been reduced from INR 3000 (for large drones) to INR 100 for all categories of drones; and is valid for 10 years.
-
Digital sky platform shall be developed as a user-friendly single-window system.
-
The human interface will be minimal and most permissions will be self-generated.
-
No permission required for operating drones in green zones.
-
Yellow zone reduced from 45 km to 12 km from the airport perimeter.
-
No remote pilot licence required for micro drones (for non-commercial use) and nano drones.
-
Features of safety and security such as no permission – no takeoff, geo-fencing, real-time tracking beacon, etc. to be notified in future. For compliance, industry will be provided with a six-month lead time.
-
The maximum penalty for violations is reduced to INR 1 lakh.
-
Drone promotion council to be set up by Government with participation from academia, startups and other stakeholders to facilitate a growth-oriented regulatory regime.
About Ministry of Civil Aviation of India:
-
The Ministry of Civil Aviation of Government of India (GoI) is the nodal Ministry responsible for the formulation of national policies and programmes for development and regulation of Civil Aviation and for devising and implementing schemes for the orderly growth and expansion of civil air transport.
-
Its functions also extend to overseeing airport facilities, air traffic services and carriage of passengers and goods by air.
-
The Ministry also administers implementation of the Aircraft Act, 1934, Aircraft Rules, 1937.
-
This Ministry is administratively responsible for the Commission of Railways Safety.
-
The current Union Minister of Civil Aviation is Jyotiraditya M. Scindia.
 Recent Initiatives of NEP-2020:
Recent Initiatives of NEP-2020:
The Government of India (GoI) on 24 August 2021 launched various initiatives of National Education Policy (NEP) 2020.
Highlights:
-
These initiatives were launched jointly by Union Education Minister Dharmendra Pradhan and Social Justice and Empowerment Minister Dr Virender Kumar in New Delhi.
-
These initiatives seek to make education more inclusive and prepare students for 21st century.
Key Points about the initiatives launched:
-
The Ministers also launched Booklet on the 1-year-NEP-2020 Acheivement Document.
-
They also launched the National Initiative for Proficiency in Reading with Understanding and Numeracy Bharat FLN tools.
-
Along with, ‘Priya’- Accessibility booklet, resources on DIKSHA (Digital Infrastructure fro Knowledge Sharing) platform, virtual school on National Institute of Open Schooling (NIOS), Alternate Academic Calendar 2021-22 of NCERT, NIPUN Bharat Mission were also launched to mark the occasion.
-
The Government urged both the Departments of School Education & Literacy and Department of Higher Education to take up the task of creating accessible educational infrastructure and content on a mission mode, consistently progressing towards Inclusive Education which is a vital component of the new NEP.
About Booklet on one-year NEP-2020 Achievement Document:
-
A booklet on one-year achievements of the National Education Policy Implementation was unveiled.
-
The booklet has been prepared by the department of school education and literacy, ministry of education in order to commemorate one year of the implementation of NEP 2020.
About Priya -The Accessibility Warrior:
-
"Priya -The Accessibility Warrior" will sensitize the students on accessibility related issues for Divyangs.
-
Special emphasis has been laid to make the booklet simple, interesting and interactive to create awareness on accessibility in children right from their formative years.
-
It is the outcome of collaborative efforts of Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (Divyangjan), Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment and Department of School Education and Literacy.
-
It provides glimpses into the world of a girl named Priya who met an accident and could not walk, due to plastered leg.
-
The story depicts how Priya managed to participate in all activities at school, and in the process learnt the importance of the accessibility.
-
She, therefore takes the pledge of being an accessibility warrior.
-
The comic book is also available with Indian Sign Language (ISL) explanatory videos.
About Virtual School of NIOS:
-
Virtual School of NIOS is first-of-its-kind initiative in the country which will provide advanced digital learning platforms through Virtual Live Classrooms and Virtual Labs.
-
This school is a new model of learning and is an example how leveraging technology and innovation can facilitate greater inclusion in education.
About Alternate Academic Calendar 2021-22 of NCERT:
-
Alternate Academic Calendar of NCERT has been developed to facilitate teachers and parents to assess the progress in the learning of children.
-
It contains week-wise plan of interesting and challenging activities, with reference to learning outcomes, themes and chapters taken from syllabus or textbook.
About NIPUN Bharat Mission:
-
NIPUN Bharat Mission aims to ensure that every Indian chid attains foundational literacy and numeracy by the end of Grade 3, by; 2026-27.
-
The main objective of this initiative is to cover the learning needs of children under the age group of 3-9 years.
-
This mission has been launched under the aegis of the centrally sponsored scheme of 'Samagra Siksha'.
-
It will be implemented by the Department of School Education and Literacy.
-
NIPUN Bharat FLN tools and resources has been made available under a separate vertical for FLN resources developed under DIKSHA to assist and mentor States/UTs and teachers for implementing NIPUN Bharat guidelines.
-
This vertical has infographics and videos on learning outcomes and assessment tools for teachers to facilitate them.
Aim:
-
The Government is working towards digitalization of education and strengthening the sector so the initiatives are aimed at promoting inclusive education and bringing transformative changes in the lives of disabled.
-
The National Education Policy also seeks to help boosting the country’s development.
About MoE:
-
MoE refers to the Ministry of Education.
-
It was formerly known as the Ministry of Human Resource Development (1985–2020).
-
The ministry is responsible for the implementation and formulation of the National Policy on Education approved by Union cabinet of India and to ensure that it is implemented in letter and spirit.
-
The Ministry is further divided into two departments.
-
They are, the Department of School Education and Literacy, which deals with primary, secondary and higher secondary education, adult education and literacy and the Department of Higher Education, which deals with a university education, technical education, scholarship, etc.
-
The current Union Minister of MoE is Dharmendra Pradhan.
Indian polity
 Governor of Manipur:
Governor of Manipur:
Senior BJP leader from Tamil Nadu La. Ganesan was on 22nd August 2021, appointed as the new governor of Manipur.
Highlights:
-
The post of the Governor had fallen vacant after the retirement of Najma Heptulla earlier this month.
-
A communique from the Rashtrapati Bhavan said Ganesan will be the new "Governor of Manipur with effect from the date he assumes charge of his office".
-
Heptulla had demitted office on August 10 and on the same day the charge was given to Sikkim Governor Ganga Prasad.
 Procedure of Arresting a Cabinet Minister in India:
Procedure of Arresting a Cabinet Minister in India:
Recently, 3 FIRs were registered against Union Minister and Rajya Sabha member Narayan Rane in connection with a speech at Raigad where he spoke against Chief Minister Uddhav Thackeray.
Highlights:
The Maharashtra Police team was sent to arrest him.
Meanwhile, Narayan Rane was granted bail by a magistrate court in Mahad.
What is the procedure to arrest a Cabinet Minister in India?
The procedure to arrest a Cabinet Minister as per the constitution of India is as follows:
-
If Parliament is not in session, a cabinet minister can be arrested by a law enforcement agency in case of a criminal case registered against him.
-
However, as per Section 22 A of the Rules of Procedures and Conduct of Business of the Rajya Sabha, the Police, Judge or Magistrate would have to intimate the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha about the reason for the arrest, the place of detention or imprisonment in an appropriate form.
What is the Role of the Chaiman of Rajya Sabha in this regard?
-
The Chairman is expected to inform the Council if it is sitting about the arrest. If the council is not sitting, he/she is expected to publish it in the bulletin for the information of the members.
What about the privileges of the Rajya Sabha members vis-a-vis arrests?
-
In civil cases, they have freedom from arrest during the continuance of the House and 40 days before its commencement and 40 days after its conclusion, as per section 135 of the Code of Civil Procedure.
-
The privilege of freedom from arrest does not extend to criminal offences or cases of detention under preventive detention.
Can a person be arrested from the precincts of the House?
-
No arrest, whether of a member or of a stranger, can be made within the precincts of the House without the prior permission of the Chairman/Speaker and that too in accordance with the procedure laid down by the Home Ministry in this regard.
-
Similarly no legal process, civil or criminal, can be served within the precincts of the House without obtaining the prior permission of the Chairman/Speaker whether the House is in Session or not.
 MP Implements NEP 2020:
MP Implements NEP 2020:
Madhya Pradesh (MP) Government on August 26, 2021 implemented the National Education Policy-2020 (NEP-2020) in the state.
Key Points:
-
With this MP has become the second state to implement NEP-2020 after Karnataka.
-
The MP Government will implement NEP 2020 within four years in all the regions of the state, which includes 16 government universities and 40 private universities.
-
The aim of education is to impart knowledge, skills, and values of citizenship.
-
The students, before this were required to study subjects prescribed in a course. But now they will have the option to choose their subjects according to their interests.
-
The government will also be introducing agricultural science as a subject in Vikram University and Rani Durgavati University.
-
The new policy also focuses on National Service Scheme (NSS, National Cadet Corps (NCC) and skill-based subjects.
Key Points about National Education Policy, 2020:
-
The NEP 2020 was approved by the Union Cabinet on July 29, 2020.
-
It envisions major reforms in the school and higher education systems.
-
This policy was launched not only with an aim to introduce several changes in Indian education system, from school to college level but also with the aim of making “India a global knowledge superpower”.
-
NEP proposes for universalization of education from preschool to secondary level and seeks to achieve 100% Gross Enrolment Ratio (GER) in school education by the year 2030.
-
It will bring 2 crores out of school children back into the mainstream by the means of open schooling system. 10+2 system has been replaced by a new 5+3+3+4 curricular structure under the new policy.
-
Emphasis has been laid on Foundational Literacy & Numeracy and provides for no rigid separation between academic streams, vocational streams and extracurricular streams in schools.
-
As per the policy, Vocational Education will start from Class 6 with Internships.
-
It also provides for teaching up to at least Grade 5 in mother tongue or regional language. No language will be imposed on student.
-
On its first anniversary last month, Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched SAFAL (STRUCTURED Assessment For Analyzing Learning), a competency-based assessment for grades 3, 5, and 8 introduced by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE).
International
 BRICS 2021 NSA Meeting:
BRICS 2021 NSA Meeting:
India's National Security Advisor (NSA) Ajit Doval hosted the 11th Meeting of the BRICS High Representatives Responsible for National Security through video conferencing.
Note: BRICS members comprise Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
About the BRICS 2021 NSA Meeting:
The 13th BRICS Summit is a series of events that are being held under India's Chairship in 2021.
This is the third time India is hosting the BRICS Summit after 2012 and 2016.
The theme for this edition is 'BRICS @ 15: Intra-BRICS Cooperation for Continuity, Consolidation and Consensus'.
The meeting of NSAs of the member countries is being amid the held the Taliban's hostile takeover of Afghanistan and discussion on the future of Afghanistan is expected to be the agenda.
The meeting of the NSAs aims to strengthen security cooperation among the member countries.
Key Points of the meeting:
-
The meeting was attended by the Secretary of the Security Council of Russia Gen Patrushev, Chinese Politburo Member Yang Jeichi, South African Deputy Minister of State Security Ncediso Goodenough Kodwa and Gen Augusto Heleno Ribeiro Pereira, Minister of State and Head of the Institutional Security Cabinet of the Presidency of Brazil.
-
At the meet, India launched a veiled attack on Islamabad, saying that terrorist groups like Lashkar-e-Taiba and Jaish-e-Mohamed are enjoying state support and are threatening peace.
-
The BROCS NSA meeting adopted and recommended the BRICS counter-terrorism action plan for consideration by the BRICS Summit.
-
The Action Plan aims to further strengthen existing mechanisms of cooperation in areas such as financing and combating terrorism, misuse of the internet by terrorists, curbing the travel of terrorists, border controls, protection of soft targets, information sharing, capacity building, and regional and international cooperation.
-
The Afghanistan scenario and developments in Iran, West Asia and the Gulf region was discussed by NSA Ajit Doval and other top security officials of the BRICS.
-
The health safety and healthcare issues amid COVID-19 outbreak was discussed by the Top security officials of the BRICS.
-
India took a dig at Pakistan over cross-border terrorism at BRICS meet.
Additional info:
-
India hods th chairship of BRICS for 2021 which coincides with the 15th anniversary of the BRICS grouping.
-
The BRICS Summit is scheduled to be hosted by India in September 2021.
Background:
-
Under India's chairship in the earlier summit, the BRICS members' space agencies heads signed an agreement for cooperation in remote sensing satellite data sharing.
-
The agreement enables building a virtual constellation of specified remote sensing satellites of BRICS space agencies and their respective ground stations that will receive the data.
-
This will contribute to strengthening multilateral cooperation among BRICS space agencies in meeting the challenges faced by mankind, such as global climate change, major disasters and environmental protection.
-
In July, the BRICS meeting of the Contact Group on Economic and Trade Issues was held.
-
During the three-day meeting, the BRICS members agreed on various proposals circulated by India, for strengthening and increasing the intra-BRICS cooperation and trade.
 International Day for the Remembrance of the Slave Trade and its Abolition:
International Day for the Remembrance of the Slave Trade and its Abolition:
International Day for the Remembrance of the Slave Trade and its Abolition is observed on August 23, every year.
This day is observed in the memory of millions of people who were the victims of the trans-Atlantic slave trade.
How this day is celebrated?
-
UNESCO Member States celebrate this day by organizing events and inviting participation from young people, artists, educators and intellectuals.
-
The year 2001 saw the participation of the Mulhouse Textile Museum in France in the form of a workshop for fabrics called "Indiennes de Traite" (a type of calico) which served as currency for the exchange of slaves in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries.
History:
The day was designated by UNESCO to memorialize the transatlantic slave trade.
It is a day to honour the memory of the men and women who, in Saint-Domingue in 1791, revolted and paved the way for the end of slavery and dehumanization.
Significance of the day:
-
It was on the night of 22 and 23 August 1791, in Santo Domingo (today Haiti and the Dominican Republic) that saw the beginning of the uprising that would play a crucial role in the abolition of the transatlantic slave trade.
-
It is against this background that the International Day for the Remembrance of the Slave Trade and its Abolition is commemorated on 23 August each year.
-
The Day was first celebrated in a number of countries, particularly in Haiti on 23 August 1998 and at Goree in Senegal on 23 August 1999.
The Slave Route Project:
-
This International Day is intended to inscribe the tragedy of the slave trade in the memory of all peoples.
-
In accordance with the goals of the intercultural project "The Slave Route", it should offer an opportunity for collective consideration of the historic causes, the methods and the consequences of this tragedy, and for an analysis of the interactions to which it has given rise between Africa, Europe, the Americas and the Caribbean.
-
The Director-General of UNESCO invites the Ministers of Culture of all Member States to organize events every year on that date, involving the entire population of their country and in particular young people, educators, artists and intellectuals.
About UNESCO:
-
The full form of UNESCO is United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization.
-
UNESCO was founded on 6 November 1945.
-
It is a specialized agency of the United Nations aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, the sciences, and culture.
-
It is headquartered in Paris, France.
-
The current head of UNESCO is Audrey Azoulay.
 India and Maldives:
India and Maldives:
India and Maldives have recently signed a pact on one of the major connectivity initiatives called “Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP)”.
Key Points:
-
GMCP is the largest infrastructure project in in the Maldives.
-
It is also the biggest new development project by India in its neighbourhood in recent years.
-
The project will be funded by an Indian grant of $100 m and a Line of Credit of $400 m.
-
The USD 400 million LoC will be provided by the Export-Import Bank of India (Exim Bank).
About the Project:
-
GMCP is the flagship project of President Solih’s presidency and will be an enduring symbol of India-Maldives partnership.
-
The project will be developed by Indian construction and engineering firm, AFCONS, based in Mumbai, Maharashtra.
-
The GMCP comprise of 6.74 km long bridge and causeway link that will connect the national capital Male with three neighbouring islands namely: Villingili, Thilafushi and Gulhifahu.
-
It will be started to connect people, business, and industry.
About Maldives:
-
The Maldives, officially the Republic of Maldives, is a small island nation in South Asia.
-
It is situated in the Arabian Sea of the Indian Ocean.
-
It lies southwest of Sri Lanka and India.
-
The Capital of Maldives is Male.
-
The Currency of the Maldives is Maldivian Rufiyaa.
-
The current President of the Maldives is Ibrahim Mohamed Solih.
 International Day Commemorating the Victims of Acts of Violence Based on Religion or Belief 2021:
International Day Commemorating the Victims of Acts of Violence Based on Religion or Belief 2021:
The International Day Commemorating the Victims of Acts of Violence Based on Religion or Belief day is observed on the 22nd of August every year.
Key Points:
-
The day is observed to strongly condemn continuing violence and acts of terrorism targeting individuals, including persons belonging to religious minorities, on the basis of or in the name of religion or belief.
-
The day was adopted at the 73rd UN General Assembly on 28 May 2019 as proposed by Poland.
-
The main purpose of this day is to create awareness among people to attain justice for the survivors of past abuses.
-
It is the duty of every government in the world that must take the right decision to ‘never again’ tolerate genocide or other atrocities.
Universal Declaration of Human Rights:
-
Freedom of religion or belief, freedom of opinion and expression, the right to peaceful assembly and the right to freedom of association are enshrined in articles 18, 19 and 20 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
 Women's Equality Day:
Women's Equality Day:
The day is observed on 26th august every year.
Key Points:
-
It is observed primarily in the US on August 26, to commemorate American women getting the constitutional right to vote.
-
The 19th Amendment to the US Constitution was adopted in 1920.
-
The law prohibits denying citizens, of the United States, the right to vote on the basis of gender.
-
Women's Equality Day is now often observed across the world to encourage and spread awareness about women's empowerment.
-
Some of the other Western states in 1910 began to give women the right to vote.
-
Also, several Eastern and Southern states refused to give women the right to vote.
History of Women's Equality Day:
-
Women carried out a protest regarding the right to opportunity and social status.
-
It began in 1848 with a peaceful protest in New York.
-
But in 1971, United States Congress Representative Bella Abzug introduced a bill with a nationwide ‘ strike for equality ' with a day completely dedicated to women’s rights known as Women’s Equality Day.
-
The strike was based on the following three goals:
-
Free abortion on demand
-
Equal opportunity for working
-
Free childcare.
-
Finally, in 1973, the 37th President of the United States, Richard Nixon, along with the United States Congress declared August 26 as Women's Equality Day.
-
So, on 26 August, 1920, women's right to vote became a part of the US constitution.
Significance:
-
The day plays a significant role in celebrating the achievements of women in various sectors.
-
There has always been a difference in pay disparity, abortion rights, equality opportunities, gender-based violence, and discrimination compared with males.
-
This day not only marks the commemoration of the of the 19th Amendment of the US Constitution but it also acknowledges the important achievements made by women in various fields that were once designated only for men.
Ismail Sabri Yaakob:Ismail Sabri Yaakob has been appointed as the new Prime Minister of Malaysia.
Highlights:
-
Before his appointment as the PM, he was the Deputy Prime Minister of Malaysia.
-
He will succeed Muhyiddin Yassin, who resigned from the post after losing majority support in the lower house of parliament.
-
The appointment of Yaakob was done by Malaysia’s King Sultan Abdullah Sultan Ahmad Shah.
About Malasia:
-
It is a Southeast Asian country occupying parts of the Malay Peninsula and the island of Borneo.
-
The capital of Malaysia is Kuala Lumpur.
-
The currency used here is Malaysian ringgit.
-
The current King of Malasia is Sultan Abdullah Sultan Ahmad Shah.
 G20 Ministerial Conference on Women’s Empowerment:
G20 Ministerial Conference on Women’s Empowerment:
The Union Minister of Women & Child Development, Smriti Irani, on August 26, 2021, addressed the First ever G20 Ministerial Conference on Women’s Empowerment.
Highlights:
-
The conference was held at Santa Margherita Ligure, Italy in a hybrid format.
Note: Hybrid format means people participated in physical form and via video conference also.
-
It was chaired by the Italian Minister for Equal Opportunities and Family Elena Bonetti.
About the G20 Conference on Women Empowerment:
-
G20 Conference acknowledged the common objectives and shared responsibilities to advance the goals of equality and development of women and girls in all spheres including STEM, Financial and Digital Literacy, Environment and Sustainability.
-
The main focus of this conference is:
-
Policies to enhance women's talents and skills.
-
Access to better quallity jobs for women.
-
Increasing women's representation in leadership.
-
Definition and protection of women's rights.
-
Tackling gender-based violence.
-
The results of the discussions will be collected by the Italian Presidency and will be brought to the attention of the G20 leaders ahead of the 2021 Rome summit which will be held on 30-31st October 2021.
-
Smt. Irani while addressing the meet on behalf of India reaffirmed India’s commitment towards addressing gender and women-centric issues through mutual cooperation.
-
She also highlighted several initiatives undertaken by Prime Minister Narendra Modi led government in India towards bringing gender equality, strengthening women’s safety & security and ensuring better healthcare.
About G20:
-
The G20 means the Group of Twenty.
-
It is an international forum for the governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union (EU).
-
The membership of the G20 consists of 19 individual countries plus the European Union.
-
The members of the G20 group are Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Republic of Korea, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States and the European Union (EU).
-
The EU is represented by the European Commission and by the European Central Bank. It was established on 26 September 1999 with an aim to discuss policy pertaining to the promotion of international financial stability.
-
The objective of G20 is to unite world leaders around shared economic, political and health challenges.
-
The current Chairman of G20 is Mario Draghi (2021).
Note: In 1999, in the wake of the 1997 economic crisis, the G7 Finance Ministers announced the creation of the “Group of 20”, aimed at including other countries in their discussions related to global economics and finance.
The first official meeting of the G20 was held in Berlin in December that same year.
National
 National Monetization Pipeline:
National Monetization Pipeline:
Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Nirmala Sitharaman has unveiled the asset monetization pipeline of Central ministries and public sector entities: ‘National Monetization Pipeline (NMP)’.
-
National Monetization Pipeline has been designed to attract more investors to the country and encourage alternative financing.
What is Monetization?
-
Monetization is defined as the process of earning revenue from an asset business by converting the assets into cash or a form that is easily convertible into cash.
-
Real estate investment trusts (REITs) and infrastructure investment trusts (InvITs) are some of structures that will be used to monetize assets in roads and power sectors.
What Is Asset Monetization?
-
Asset Monetization means a limited period license/ lease of an asset, owned by the government or public authority, to a private sector entity for upfront or periodic consideration.
What is National Monetization Pipeline (NMP)?
-
The National Monetization Pipeline (NMP) lists out assets and asset classes, under various infrastructure ministries, which will be monetized over a period of time. Which means assets will be monetized.
-
The pipeline has been developed by NITI Aayog (National Institution of Transforming India), in consultation with infrastructure line ministries, based on the mandate for ‘Asset Monetization’ under Union Budget 2021-22.
-
NMP estimates aggregate monetization potential of Rs 6.0 lakh crores through core assets of the Central Government, over a four-year period, from FY 2022 to FY 2025.
What Are The Assets Identified For Monetization?
-
The NMP does not include monetization through disinvestment and of non-core assets.
-
Currently, it includes only the assets of central government ministries and CPSEs in infrastructure sectors.
-
The sectors included are roads, ports, airports, railways, warehousing, gas & product pipeline, power generation and transmission, mining, telecom, stadium, hospitality and housing.
-
The top 5 sectors capture about 83% of the aggregate pipeline value.
-
These top 5 sectors include-
-
Roads (27%)
-
Railways (25%)
-
Power (15%)
-
Oil & gas pipelines (8%)
-
Telecom (6%)
Assets in the NMP list:
Assets on the NMP list include-
-
26700 km of roads, railway stations, train operations & tracks
-
28608 CKT km of power transmission lines
-
6 GW of hydroelectric & solar power assets
-
86 lakh km fibre assets & 14,917 towers in the telecom sector
-
8154 km of natural gas pipelines and
-
3930 km of petroleum product pipelines.
Framework:
-
The pipeline has been prepared based on inputs and consultations from respective line ministries and departments, along with the assessment of total asset base available therein. Monetization through disinvestment and monetization of non-core assets have not been included in the NMP.
-
Further, at present, only assets of central government line ministries and CPSEs in infrastructure sectors have been included. Process of coordination and collation of asset pipeline from states is currently ongoing and the same is envisaged to be included in due course.
-
The framework for monetization of core asset monetization has three key imperatives.
-
Monetization of Rights Not ownership, Assets handed back at the end of transaction life
-
Brownfield de-risked assets, stable revenue streams
-
Structured partnerships under defined contractual frameworks with strict KPIs and performance standards.
Objective:
-
The strategic objective of the programme is to unlock the value of investments in Brownfield public sector assets by tapping institutional and long-term patient capital, which can thereafter be leveraged for further public investments,
-
The NMP comprises a four-year pipeline of the Central Government's Brownfield infrastructure assets.
Significance of the monetization:
-
Monetization seeks to help in creating further value for infrastructure creation India and exploring innovative ways of private participation without transferring the government ownership.
-
The National Monetization Pipeline book will be released in the presence of Vice Chairman of NITI Aayog, Dr Rajiv Kumar, CEO, Shri Amitabh Kant, and Secretaries of relevant line ministries whose assets constitute the monetization pipeline.
Key challenges of the scheme:
Major key challenges in the NMP roadmap include:
-
Lack of identifiable revenue streams across various assets,
-
Level of capacity utilization across gas and petroleum pipeline networks,
-
Dispute resolution mechanism,
-
Regulated tariffs in power sector assets, and
-
Low interest among investors for national highways below four lanes.
Background:
-
The Union Budget 2021-22 identified and laid a lot of emphasis on Asset Monetization as a means to raise innovative and alternative financing for infrastructure, and included a number of key announcements.
-
The Finance Minister had made a lot of significant announcements regarding asset monetization and stressed on the fact that the government is looking at innovative ways to raise finances.
 Endemic Stage of COVID:
Endemic Stage of COVID:
The Chief Scientist of the World Health Organization (WHO) Dr. Soumya Swaminathan recently said that COVID-19 in India may be entering the stage of endemicity where there is a low or moderate level of transmission going on.
Note: The endemic stage is when a population learns to live with a virus. It's very different from the epidemic stage when the virus overwhelms a population.
Key Details:
-
While talking about the clearance to India’s homegrown COVID-19 vaccine ‘COVAXIN’, she said that she is confident that the technical team of WHO will be satisfied to give clearance to be its authorized vaccines.
-
In an interview to journalist Karan Thapar for news website The Wire, she explained that given the size of India and the heterogeneity of the population and immunity status in various parts of the country, it is very feasible that the situation in India may continue like this with ups and downs in various parts of the country.
-
She added that India may be entering the stage of endemicity where moderate or low level of transmission will continue to happen however, no exponential growth or peaks will be there.
-
Dr. Swaminathan was hopeful that by the end of 2022, India maybe in that position where 70% of vaccine coverage will have been achieved and then the nations can get back to normal.
COVID-19 among children:
-
On the issue of prevalence of COVID-19 among children, Dr. Swaminathan said that parents need not panic.
-
She explained that, according to Sero Survey, it is possible that children can get infected and transmit.
-
But they will be having mild illness most of the time.
-
Very small percentage will get sick & inflammatory complications and few will die.
-
But the number will be much less than the adult population.
-
However, she further added that it is good to be prepared.
-
Preparing hospitals for pediatric admissions, pediatric intensive care is going to serve India’s health system in many ways for other illnesses children that children have.
Can drugs be used for COVID-19 treatment?
-
On use of drugs like Remdesivir, HCQ or Ivermectin for treatment, she stated that, as of now there is no evidence of role of Ivermectin or HCQ in reducing mortality or morbidity in people infected with the COVID-19 virus.
-
These drugs also have no role in preventing the infection.
 National Food and Nutrition Campaign:
National Food and Nutrition Campaign:
The Union Minister of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, Narendra Singh Tomar recently launched the National Food and Nutrition Campaign for the farmers.
Key Details:
-
This campaign is organized by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR).
-
ICAR has been working successfully on which crops should be cultivated and which seeds should be invented for rainfed and other areas.
-
Efforts are also being made to make agriculture and farmers connected with new technology.
-
The present government has been working continuously since the year 2014 based on a comprehensive approach.
-
The Government has also resolved to solve the problem of malnutrition problem and has also launched several schemes and programs in this direction.
-
Union Minister of State for Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Shri Kailash Choudhary said that the year 2023 will be celebrated as the International Year of Millets under the leadership of India, which is a matter of pride for India.
-
It is the responsibility of farmers associated with Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) to motivate other farmers for improved farming and ensure participation of all farmers in various schemes including Farmers Producer Organizations (FPO), Agri Infra Fund, and increasing the area of organic farming under traditional farming.
About MoA&FW:
-
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare (MoA&FW) is a branch of the Government of India (GoI).
-
It is the apex body for formulation and administration of the rules and regulations and laws related to agriculture in India.
-
The three broad areas of scope for the Ministry are agriculture, food processing and co-operation.
-
It was formed in 1947 and is headquartered in New Delhi.
-
Currently the agriculture ministry is headed by Minister of Agriculture Narendra Singh Tomar and the Minister of State in the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare is Shri Kailash Choudhary.
 BH-series:
BH-series:
The Ministry of Road Transport & Highways vide notification dated 26 Aug 2021, has introduced a new registration mark for new vehicles i.e. “Bharat series (BH-series)”.
Key Points:
-
It has been introduced in order to facilitate seamless transfer of vehicles.
-
The vehicles bearing the BH-series mark will not require the assignment of a new registration mark when the owner of the vehicle shifts from one State to another.
About BH-series:
-
The new BH series notification will be available for select vehicle owners who are subject to frequent transfers and relocations.
-
It will be available on a voluntary basis to Defense personnel, employees of Central Government/ State Government/ Central/ State Public Sector Undertakings and private sector companies/organizations, which have their offices in four or more States/Union territories.
-
Motor vehicle tax will be levied for two years or in multiple of two. After completing fourteenth year, this tax will be levied annually and it will be half the amount that was charged earlier for that vehicle.
-
The following are the format of Bharat series (BH-series) Registration Mark :
Registration Mark Format: –
-
YY BH #### XX
-
YY – Year of first registration
-
BH- Code for Bharat Series
-
####- 0000 to 9999 (randomized)
-
XX- Alphabets (AA to ZZ)
Why were the new BH Series launched?
The new BH-series were launched considering the following difficulty.
-
The Government as well as private sector employees undergo station relocation.
-
Such movements create a sense of unease in the minds of such employees with regard to the transfer of registration from the parent state to another state.
-
The reason for this is that, under section 47 of the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988, a person is allowed to keep the vehicle for not more than 12 months in any state other than the state where the vehicle is registered.
-
Instead a new registration with the new state- registering authority has to be made within the stipulated time of 12 months.
People In News
 Kalyan Singh:
Kalyan Singh:
Former Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh Kalyan Singh passed away on August 22, 2021 after a prolonged illness at the age of 89.
Key Points:
-
He was one of the most prominent BJP leaders who helped shape rise of the Ram Temple movement.
-
He was the UP chief minister when the Babri mosque was demolished by a mob in Ayodhya on December 6, 1992.
-
He had resigned from the post after the demolition.
More about Kalyan Singh :
-
Kalyan Singh (1932 – 2021) , a Hindutva icon and a Bharatiya Janata Party veteran had served as the Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh twice from June 1991 – December 1992 and then from September 1997 – November 1999.
-
Born on January 5, 1932, Kalyan Singh first became an MLA in 1967.
-
He had been a member of the Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh while he was still in school.
-
He had also served as the Member of Parliament for Lok Sabha from 2009 to 2014 from Etah constituency in Uttar Pradesh.
-
He then served as the Governor of Himachal Pradesh from January 2015 till August 2015.
-
He was later appointed as the 21st Governor of Rajasthan from September 2014 till September 2019.
-
He then again served for the second term as Chief Minister in 1997 but was removed in 1999.
-
He won nine more elections from the constituency as a representative of Bharatiya Jana Sangh, BJP, Janata Party and the Rashtriya Kranti Party.
 Gail Omvedt:
Gail Omvedt:
She was a researcher, author and one of the intellectual voices of the Bahujan movement who passed away at the age of 81.
About Gail Omvedt:
-
Gail Omvedt (2 August 1941 – 25 August 2021) was an American-born Indian sociologist and human rights activist.
-
She was a prolific writer and published numerous books on the anti-caste movement, Dalit politics, and women's struggles in India.
-
She not only contributed as a researcher in social movements, saints’ literature, traditions but also was involved in Dalit and anti-caste movements, environmental, farmers' and women's movements, especially with rural women.
-
She also participated in various people’s movements, including the one for the rights of people displaced by the Koyna Dam.
-
Omvedt authored over 25 books, including In Colonial Society – Non-Brahmin Movement in Western India, Buddhism in India, Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar, Seeking Begampura, Mahatma Phule, Dalit and the Democratic Revolution, Understanding Caste, We Will Smash the Prison and New Social Movement in India.
-
She was the head of Phule-Ambedkar chair in the Department of Sociology of the University of Pune; Professor at the Institute of Asian Studies, Copenhegan; and the Nehru Memorial Museum and Library in New Delhi.
-
She was a consultant for FAO, UNDP and NOVIB.
-
She was a senior fellow at the Nehru Memorial Museum and Library and research director of the Krantivir Trust.
-
Omvedt co-founded Shramik Mukti Dal with her husband and activist Bharat Patankar.
 Chairperson of Stop TB Partnership Board:
Chairperson of Stop TB Partnership Board:
The Health and Family Welfare Minister of India Shri Mansukh Mandaviya , on 26th August 2021, took over charge as the Chairperson of Stop TB Partnership Board.
Key Details:
-
The Minister will hold the responsibility with immediate effect until 2024.
-
Mansukh Mandaviya replaces Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare, Dr Harsh Vardhan as the chairman.
-
As the Chairman of Stop TB Partnership Board Mr. Malvia will lead the efforts of the Stop TB Partnership Secretariat, partners, and TB community in order to reach towards reaching United Nations TB targets by 2022, a milestone moment in the effort to end TB by 2030.
Important Info:
-
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has set an aim to eliminate tuberculosis (TB) in India by 2025.
About Stop TB Partnership:
-
Stop TB Partnership has been administered by the United Nations Office for Project services (UNOPS) since 2015.
-
Earlier it was hosted by the World Health Organization (WHO).
-
It was formed in 2001.
-
It was established in a bid to eradicate tuberculosis (TB) as a public health problem.
-
The secretariat is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
-
Dr Lucica Ditiu is the current Executive Director of the Stop TB Partnership.
 Sandeep Bakhshi:
Sandeep Bakhshi:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) recently approved the re-appointment of Sandeep Bakhshi as the MD & CEO of ICICI Bank.
Key Points:
-
It will be with effect from October 15, 2021, till October 3, 2023.
-
The appointment of Mr Bakhshi for a period effective from October 15, 2018, up to October 3, 2023 had already been approved in the shareholders at the Annual General Meeting held on August 9, 2019.
-
Bakshi, who was hand-picked by his mentors- KV Kamath and N Vaghul, took over the charge in October 2018, after his predecessor Chanda Kochhar’s exit following the ICICI Bank-Videocon loan controversy.
About ICICI:
-
ICICI Bank is a leading private sector bank in India.
-
ICICI Bank was established by the Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI), an Indian financial institution, as a wholly owned subsidiary in 1994 in Vadodara.
-
However, the parent company was formed in 1955 at the initiative of the World Bank, the Government of India and representatives of Indian industry.
-
The bank was founded as the Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India Bank, before it changed its name to ICICI Bank.
-
The parent company was later merged with the bank.
-
It is headquartered in Mumbai, Maharashtra.
-
The tagline of ICICI Bank is Hum Hai Na, Khayal Apka.
 Ahmad Massoud:
Ahmad Massoud:
Ahmad Massoud has been leading the National Resistance Front of Afghanistan.
-
He is the man building an anti-Taliban resistance.
About:
-
Ahmad Massoud is the son of Ahmad Shah Massoud, who was one of the main leaders of Afghanistan’s anti-Soviet resistance in the 1980s.
-
Ahmad Shah Massoud was assassinated on September 9, 2001, at the behest of the Taliban and al-Qaeda.
-
Ahmad Massoud has been leading the National Resistance Front of Afghanistan and is gathering mujahideen fighters in the Panjshir Valley who are prepared to once again take on the Taliban.
Note: The Panjshir Valley is Afghanistan’s last remaining holdout where anti-Taliban forces seem to be working on forming a guerrilla movement to take on the fundamentalist group.
Places In News
 Smog Tower:
Smog Tower:
Delhi Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal, on 23rd August 2021, India''s first smog tower in Delhi's Connaught Place.
Highlights:
-
Delhi, ahead of its notorious smog season, got a ‘smog tower’, a technological aid that will purify 1,000 cubic metres of air per second within a radius of around 1 km.
-
The tower is located behind the Shivaji Stadium Metro station in Connaught Place.
-
According to a senior official of the Delhi Pollution Control Committee (DPCC), the total project cost, including two years of operational cost, is around Rs 20 crore.
Note: The DPCC is the nodal agency for the tower, while NBCC is the project management consultancy and the executing agency was Tata Projects Limited.
-
The tower has been set up as a pilot project and initial trends will be available within a month.
-
If the pilot project is successful, more smog towers will be installed.
-
A two-year pilot study will be carried out by IIT Delhi and IIT Bombay, technical advisors for the project.
-
Central government will also build a 25-metre-tall smog tower at Anand Vihar which is likely to become operational by August 31.
Key Features of smog tower:
-
The structure is 24 m high, about as much as an 8-storey building — an 18-metre concrete tower, topped by a 6-metre-high canopy.
-
A total of 40 fans have been installed at its base, 10 on each side. Air will be sucked in from the top, filtered and released through the fans at the bottom
-
Each fan can discharge 25 cubic metres per second of air, adding up to 1,000 cubic metres per second for the tower as a whole.
-
The tower comprises 5,000 filters. These are electrostatic air filters that can filter out microparticles, including those that constitute smoke, household dust and pollen
-
The filters and fans have been imported from the United States.
-
A Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) system has been installed in the tower to collect data and monitor its functioning.
Background:
This project was approved by Delhi cabinet in October 2020 after the Supreme Court of India directed the central government in January 2020 to construct a smog tower in order to reduce pollution at Anand Vihar and Delhi government to install it at Connaught Place in three months.
What is smog tower?
-
Smog towers are structures that are designed as large-scale air purifiers in order reduce air pollution particles.
-
The prototype for such structure was built in 2017 by Dutch artist Daan Roosegaarde, in Beijing (China).
Smog Towers around the world:
-
Smog towers have been experimented with in recent years in cities in the Netherlands, China, South Korea and Poland.
-
The first such tower was erected in 2015, in Rotterdam, Netherlands.
-
A 100-metre tower was built in Xi’an, Shaanxi in 2018 in a bid to tackle pollution.
How does it work?
-
Smog towers are fitted with multiple layers of air filters and fans at the base to suck the air.
-
The 20-metre (65 feet) high tower will trap particulate matter of all sizes suspended in the air.
-
Large-scale air filters shall draw in the air through fans installed at the top before passing it through the filters and releasing it near the ground.
-
After the polluted air enters the smog tower, it is purified by the multiple layers before being re-circulated into the atmosphere.
About Delhi:
-
It is an urban district located in the city of Delhi.
-
New Delhi officially the National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT), is a city and a union territory of India.
-
It serves as the capital of India is the seat of the State Government of Delhi and the Government of India, as well as the city or local governments as per the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act.
-
Union Territories are governed by the Union Government.
-
The current Chief Minister and Governor of Delhi are Arvind Kejriwal and Shri Anil Baijal respectively.
 Mission Vatsalya:
Mission Vatsalya:
Maharashtra government launched a special mission called “Mission Vatsalya”.
Key Points:
-
This mission has been launched in in order to help women who lost their husbands to COVID-19.
-
Under Mission Vatsalya several services and some 18 benefits will be provided to those women under one roof.
-
This initiative has been designed for widows, with a special focus on widows coming from rural areas, poor backgrounds and deprived sections.
-
Under this mission, schemes like Sanjay Gandhi Niradhar Yojana and Gharkul Yojana will benefit those for women.
-
This mission is being implemented by women and child development (WCD) Department.
-
Officers from WCD department, child development project officers, Anganwadi workers and local unit officers are visiting homes these women to provide them services.
Number of beneficiaries:
-
In the last 18 months, about 15,095 women have lost their husbands due to a coronavirus infection.
-
District Task Force has listed 14,661 such women in order to provide them benefits of the scheme.
-
As of now, WCD department has reached out to 10,500 women.
About Sanjay Gandhi Niradhar Yojana:
-
Government of Maharashtra implemented this scheme with the aim of providing financial assistance to destitute persons, disabled, blind, divorced women, women freed from prostitution, orphan children, persons suffering from major illnesses, Transgender, etc.
-
Under this scheme, each beneficiary gets Rs 600 per month while the family with more than one beneficiary gets Rs 900 per month.
-
This benefit will be given to beneficiary till their children turns 25 years old or when they get employed.
About Maharashtra:
-
Maharashtra is a state in the western peninsular region of India occupying a substantial portion of the Deccan Plateau.
-
It was formed on 1 May 1960. It was formed by merging the western and south-western parts of the Bombay State, Berar and Vidarbha, and the north-western parts of the Hyderabad State and splitting Saurashtra (in present-day Gujarat) by the States Reorganization Act.
-
Its capital is Mumbai.
-
The Chief Minister and the Governor of Maharashtra are Uddhav Thackeray and Bhagat Singh Koshyari respectively.
 India’s Highest Herbal Park:
India’s Highest Herbal Park:
India’s highest altitude herbal park has recently been inaugurated at Mana village in the Chamoli district of Uttarakhand.
Highlights:
-
The herbal park is situated at a height of 11,000 feet was and is close to the Indo-China border.
Note: Mana is the last Indian village in Chamoli bordering China and is adjacent to Badrinath temple.
-
The herbal park has around 40 species found in high altitude alpine areas in the Himalayan region.
-
The main aim of the herbal park is to conserve various medicinally and culturally important alpine species, and facilitate a study on the propagation of these species, as well as their ecology.
About the Park:
-
The garden, inaugurated by Mana sarpanch Pitambar Maulfa, has been developed in 3 years under the central government’s Compensatory Afforestation Fund Management and Planning Authority (CAMPA) scheme.
-
The research wing of the forest department of the Uttarakhand government has developed the park.
-
Around 40 species of herbal plants found in high alpine areas in the Himalayan region are conserved in this park.
-
Many of these are included in the “red list” of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), and declared “endangered and threatened” by the State Biodiversity board as well.
-
The first section contains species associated with Lord Badrinath such as Badri Tulsi, Badri Ber, Badri Tree, and the sacred tree of Bhojpatra.
-
The second contains Ashtavarga species, a group of 8 herbs found in Himalyan region: Riddhi, Vriddhi, Jeevak, Rishbhak, Kakoli, Ksheer Kakoli, Maida and Maha Maida.
-
These are important ingredients of Chyawanprash.
-
Out of these, four herbs belong to lily family and the rest to orchid family. Kakoli, Ksheer Kakoli and Rishbhak are rare.
-
The third section consists of Saussurea species and includes Brahmakamal, which also happens to be the State flower of Uttarakhand.
-
The fourth section has other miscellaneous species which includes Ateesh, Meethavish, Vankakdi and Choru, all of which are very important medicinal herbs.
About Uttarakhand:
-
It is a state in northern India crossed by the Himalayas.
-
It is known for the natural environment of the Himalayas, the Bhabar and the Terai and also for its Hindu pilgrimage sites.
-
It is often referred to as the "Devabhumi" (literally "Land of the Gods").
-
Uttarakhand became the 27th state of the Republic of India On 9 November 2000.
-
It was carved from the Himalayan districts of Uttar Pradesh.
-
Its winter Capital is Dehradun and summer capital is Gairsain.
-
The Chief Minister and the Governor of Uttarakhand are Pushkar Singh Dhami and Baby Rani Maurya respectively.
Science and Technology
 Fossil-Free Steel:
Fossil-Free Steel:
The first fossil free steel in the world had been manufactured in Sweden.
Key Points:
-
The first delivery of 'green steel' was done in Sweden by Hybrit to truck-manufacturer Volvo AB as a trial run.
-
SSAB, which accounts for 10% of Sweden's and 7% of Finland's carbon dioxide emissions, said the trial delivery was an "important step towards a completely fossil-free value chain".
-
The full-scale production of the material will begin from 2026 as Volvo plans to start production of prototype vehicles using green steel by the end of this year.
Note: The steel industry is one of the major contributors to greenhouse emissions, accounting for up to 8% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
About Fossil Free Steel:
-
The steel was made using Hydrogen Breakthrough Iron making Technology, which uses 100% fossil-free hydrogen instead of coal and coke.
-
The development for the Hybrit project, which was set up in 2016 is owned by SSAB, energy firm Vattenfall and LKAB, a mining and minerals group.
-
Both Vattenfall and LKAB are owned by the Swedish state.
-
The idea underpinning Hybrit is to use “100% fossil-free hydrogen” rather than coal and coke in steel production.
-
HYBRIT started test operations at its pilot plant for fossil-free steel in Lulea, northern Sweden, a year ago.
-
The company aims to replace coking coal, traditionally needed for ore-based steel making, with fossil-free electricity and hydrogen.
-
Hydrogen is a key part of the EU's plan to reach net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050.
 NeoBolt:
NeoBolt:
Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras has developed India’s first indigenous motorised wheelchair vehicle called NeoBolt.
Key Details:
-
The researchers collaborated extensively with organizations and hospitals working for people with locomotor disabilities and built the products after factoring in their experiences and making constant design adjustments.
-
It has been developed to empower wheelchair users with a convenient, safe and low-cost mode of outdoor mobility as compared to cars, auto rickshaws and modified scooters.
-
According to IIT Madras, the wheelchair will be available to users at an approximate price of ₹55,000.
About NeoBolt:
-
NeoBolt can be used not only on roads but even on uneven terrains.
-
It has a maximum speed of 25 kmph.
-
It is powered by a Lithium-Ion Battery.
-
It can travel up to 25 km per charge.
-
It is a motor-powered attachment that converts the wheelchair into a safe, road-worthy vehicle that can navigate any kind of terrain that we may normally encounter — drive through unpaved streets or climb a steep gradient. And do this comfortably as it has suspensions to absorb the shocks.
Who developed the wheelchair?
-
NeoBolt was developed by a team led by Prof. Sujatha Srinivasan, Department of Mechanical Engineering, IIT Madras.
Note: Prof. Sujatha Srinivasan also led the team that developed India’s first indigenously-designed Standing Wheelchair called ‘Arise,’ which enables a wheelchair user to shift from sitting to standing position.
-
It has been commercialized through a startup called 'NeoMotion'.
-
The Startup has been co-founded by Prof. Sujatha Srinivasan and an IIT Madras Alumnus Swostik Sourav Dash, who is the CEO of NeoMotion.
Significance:
-
It is estimated that around three lakh wheelchairs are sold annually in India, of which 2.5 lakh are imported.
-
Nearly 95% of all wheelchairs sold in India are ‘one-size-fits-all,’ which restricts mobility, damages health, and lowers self-confidence.
-
Products with features comparable to NeoBolt are also available in the global market but are at least three to five times more expensive.
-
NeoFly and NeoBolt developed by the IIT Madras Team are intended at addressing these issues.
 Yuktdhara:
Yuktdhara:
The Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) for the Ministry of Science and Technology, Jitendra Singh recently launched a new Geospatial Planning Portal under Bhuvan named “Yuktdhara” under Bhuvan.
Yuktdhara has been launched to enable the planning of new MGNREGA (Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act) assets using Remote Sensing and GIS-based information.
Key points about Yuktdhara:
-
The Yuktdhara portal has been jointly developed by ISRO and the Ministry of Rural Development.
-
The portal will serve as a repository of assets (Geotags) created under various national rural development programmes such as MGNREGA, Integrated Watershed Management Programme, Per Drop More Crop and Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana etc., along with field photographs.
-
It would ensure the quality of the plan, enable a long term monitoring of the assets created over the years for relevance, and facilitate identification of new works for resource allocation.
Additional Info:
-
Shri Jitendra Singh also holds the portfolio of the Ministry of Earth Sciences and Union Minister of State for Prime Minister’s Office; Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions; Department of Atomic Energy and Department of Space.
About Ministry of Rural Development:
-
Ministry of Rural Development: The Ministry of Rural Development is a branch of the Government of India (GoI).
-
It was founded in June 2011.
-
It is entrusted with the task of accelerating the socio-economic development of rural India.
-
Its focus is on health, education, drinking water, housing and roads.
-
The ministry has two departments which are
-
Department of Rural Development and
-
Department of Land Resources.
Note: On July 7, 2021, during the first cabinet reshuffle of the second Modi Ministry, Narendra Singh was replaced by Giriraj singh as the Union Minister of Rural Development.
 Havana Syndrome:
Havana Syndrome:
Recently, US Vice-President Kamala Harris's flight to Vietnam was delayed by several hours due to an "anomalous health incident" with similarities to so-called Havana syndrome.
About Havana Syndrome:
-
The mysterious syndrome first affected people at the US and Canadian embassies in Havana in 2016 and 2017.
-
This mysterious illness came to be called the “Havana Syndrome”.
-
Some officials called it anomalous health incidents while some called attacks.
-
In 2018, U.S. diplomats in China reported problems similar to those reported in Cuba, as did undercover CIA agents working in other countries with partner agencies to counter Russian covert operations.
-
Most recent cases were reported in Asia in 2018 and in central Europe in 2021.
Causes:
-
The cause of Havana syndrome has sparked several theories — from a 'microwave attack' to weapons that focused on ultrasound, poison, and even a reaction to crickets.
-
However, in December 2020, a report by the National Academies of Sciences (NAS) found “directed energy beams” as a “plausible” cause of the Havana Syndrome.
Symptoms:
-
The patients said they heard strange sounds and experienced odd physical sensations in their hotel rooms or homes.
-
They said they had symptoms of nausea, severe headaches, fatigue, dizziness, sleep problems and hearing loss.
What action has been taken by the US Government?
-
In 2017, Donald Trump accused Cuba of perpetrating unspecified attacks causing these symptoms.
-
However, Havana denied this accusation.
-
The U.S. reduced staff at their embassy to a minimum in response.
-
Now, State Department and the Central Intelligence Agency have established an internal task force to investigate the matter. Helping American Victims Afflicted by Neurological Attacks (HAVANA) Act was also passed unanimously in Congress.
-
It will authorize additional medical and financial support to the intelligence officers and diplomats affected by the bill. Bill has also been introduced in the House.
 Flag-bearer in Tokyo Paralympics:
Flag-bearer in Tokyo Paralympics:
Javelin thrower Tek Chand lead India's charge during Opening Ceremony of the Tokyo Paralympics.
Key Details:
-
He replaced Mariyappan Thangavelu, 2016 Rio Paralympic Games gold medalist as he was quarantined following close contact with a COVID-19 positive person on their flight to Tokyo.
-
Tek Chand carried the tri-colour as India made its way during the Opening Ceremony of Tokyo 2020 Paralympics on 24th August 2021 at the Japan National Stadium.
Tokyo Paralympics 2021:
-
The Tokyo 2020 Paralympic Games will take place between August 24, 2021 and September 5th, 2021.
-
It will feature 539 medal events across 22 sports.
-
A total of 54 para-athletes from India across nine sports disciplines will be featuring in the Paralympic Games.
-
This is India's biggest ever contingent to the Games.
 Chess:Barcelona Open:
Chess:Barcelona Open:
Indian Grandmaster S.P. Sethuraman has won the Barcelona Open chess tournament title while compatriot Karthikeyan Murali finished third.
Key Details:
-
Sethuraman (Elo 2644) collected 7.5 points from nine rounds to emerge winner on the basis of a better tie-break score after Daniil Yuffa of Russia also finished level with the Indian player.
-
In the ninth and final round played, Sethuraman beat Hakobyan in a Catalan Closed variation game.
-
Sethuraman, who was the top seed, remained unbeaten through the nine rounds, winning six matches and drawing three.
-
Sethuraman gained 8.5 Elo points thanks to the triumph while Murali (Elo 2606) increased his by 6.4 points. Sethuraman and Murali had played out a draw in the fifth round.
-
Murali won six games, drew two and went down to Hakobyan in the sixth round.
-
Chithambaram took the fifth spot while Arjun Kalyan (6.5 points) ended ninth, followed by Visakh in 10th place after a handful of players finished with 6.5 points.
-
Indian International Master N R Vignesh and Vaishali scored six points to finish 15th and 16th respectively.
 National Sports Day 2021:
National Sports Day 2021:
National Sports Day is observed in India on the 29th of August every year to commemorate the birth anniversary of Indian Hockey Legend Major Dhyan Chand Singh.
Highlights:
-
Year 2021 is his 116th birth anniversary.
-
Sports Minister Anurag Thakur launched the 'Fit India' app on the occasion of National Sports Day 2021.
Background:
-
In 2019, on National Sports Day, Prime Minister Narendra Modi had launched the Fit India Movement.
-
On August 6, 20221, PM Modi announced that the Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna Award, the country’s highest sporting honour, is being renamed as Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna Award in the memory of the legendary Olympian, on popular demand.
Key Points:
-
The first National Sports Day was celebrated on 29th August 2012.
-
The day is celebrated to create awareness among the general public on the importance of sports and to attract attention towards sports in India.
-
The main objective of this day is also to spread awareness about the importance of physical activities and sports in life.
-
The celebration of this day is organized at the Rashtrapati Bhavan where the sports related awards like Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna, Arjuna Award and Dronacharya Award are distributed.
-
The National Sports Day is also called Rashtriya Khel Divas in some part of India.
-
In 1979, the Indian Postal Department paid tribute to Major Dhyan Chand after his death and renamed the National Stadium of Delhi as Major Dhyan Chand Stadium, Delhi.
Major Dhyan Chand:
-
Major Dhyan Chand also known as the wizard of a hockey player as during his period was born on 29th August 1905, in Allahabad.
-
Dhyan Chand, who passed away on December 3, 1979, at the age of 74, was a member of the Indian Men’s Hockey teams.
-
He had an extraordinary talent for scoring goals, due to which India won hockey gold medals in the Olympic Games of 1928, 1932, and 1936.
-
His era is called the "golden period" of Indian hockey.
-
He was so passionate about hockey, which he used to practice for the game at night in the moonlight that his fellow players started addressing him with the nickname "Chand".
-
After India's first match at the Berlin Olympics of 1936, crowds of people started to gather at the hockey ground to watch Dhyan Chand's magical hockey.
-
He was popularly known as “The Wizard” for his magical touch, superb control, creativity and extraordinary goal-scoring feats.
-
Hockey magician Dhyan Chand's autobiography is titled "Goal", published in 1952.
-
He announced his retirement from hockey in the year 1948.
-
He had scored more than 400 goals in his entire international career.
-
He was awarded the Padma Bhushan, the third-highest civilian honor, in the year 1956 by the Government of India (GoI).
 Princepal Singh:
Princepal Singh:
Princepal Singh recently became the first Indian to be part of an NBA title-winning team when his side Sacramento Kings clinched the 2021 NBA Summer League crown.
About:
-
The 6-foot-9 forward made history by being the first Indian to be part of a championship roster at any level of the NBA.
-
The Kings dominated the championship game against the Boston Celtics, clinching the title with a 100-67 win.
-
Princepal has set a high bar for future NBA Academy India graduates with his championship win.
-
Earlier in the year, Singh had become the first-ever NBA Academy Global alumni to sign a G League contract and the first-ever NBA Academy India alumni to sign a professional contract when he agreed to a deal with the Ignite.
-
The 20-year-old's appearance in the championship game comes exactly a week after he made his brief yet landmark debut at the Summer League, where he checked in for the final 1:22 minutes of a Kings' victory over the Washington Wizards.
 WAU20 Championships:
WAU20 Championships:
Shaili Singh recently claimed the women’s Long Jump silver medal in the World Athletics U20 (WAU20) Championships.
Key Highlights:
-
She jumped a distance of 6.59m in her third attempt, which was her best show at the event.
-
It was only 1cm short of the gold medal jump by Sweden’s Maja Askag but her silver medal ensured that Indian athletics continues to showcase the progress it has been making.
-
Ukraine’s Mariia Horielova settled for bronze with a jump of 6.50m.
-
She was India’s third medal in the World Athletics U20 Championships, coming after the bronze won by the Mixed Team in the 4x400m Relay and the silver by Amit Khatri in the men’s 10,000m Race Walk.
-
Shaili Singh currently holds the Indian junior record of 6.48m. Her recent jump of 6.59m will not be included in the record books due to wind assistance.
-
India finished 21st on the medal table, aware that a gold would have lifted it to the top 15.
 Tokyo Paralympics 2020:
Tokyo Paralympics 2020:
India's paralympic table tennis player Bhavina Patel created history on August 28, 2021 by becoming the first Indian to advance into table tennis finals in the Paralympics and secure a silver medal.
Highlights:
-
Bhavina Patel stormed into the finals after beating China's Zhang Miao 3-2 in her Class 4 match.
-
She will face China's Ying Zhou in the Gold medal event on August 29, 2021 at 7:15 am.
-
She had entered the knock-off round after winning one and losing one match in the group round.
-
Another Indian paddler, Sonalben Manubhai Patel bowed out of the Tokyo Paralympic campaign after losing both of her group matches.
-
In Tokyo Paralympics table tennis event, there will be no bronze-medal play-off and both the losing semifinalists will be awarded a bronze medal.
Arts
Pandit Jasraj Cultural Foundation: Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi recently paid rich tribute to Pandit Jasraj on the occasion of the Jayanti of the doyen of Indian Classical Music.
About:
- On this occasion, PM Modi launched the Pandit Jasraj Cultural Foundation.
- PM Modi while speaking at the launch of the Pandit Jasraj Cultural Foundation via video conferencing talked of the personification of immortal energy of music by Pandit Jasraj.
- He lauded Durga Jasraj and Pandit Shaarang Dev for keeping alive the glorious legacy of the maestro.
- He said that the World is entitled to benefit from Indian music like they have from Yoga and that like Yoga, Indian music too has the capacity to stir the depth of the human mind and the world is entitled to be benefited from it.
About Pandit Jasraj:
- Pandit Jasraj (28 January 1930 – 17 August 2020) was an Indian classical vocalist.
- He belonged to the Mewati Gharana.
- His career in music spanned over 80 years resulting in national and international fame.
- He has taught music in and outside India such as Canada and the US. He died on August 17, 2020, at his home in New Jersey, USA, due to cardiac arrest.
- He received several accolades including the prestigious Padma Shri, Padma Bhushan, and Padma Vibhushan.
- In 2006, Asteroid 300128 was discovered by astronomers with the Mount Lemmon Survey and was named in his honour- Panditjasraj.
- The legendary classical vocalist passed away at the age of 90 on August 17, 2020.
Dhaka International Film Festival: India's film Koozhangal from India won the best film award in the Asian Film Competition section at the 20th Dhaka International Film Festival.
Key Highlights:
- The film Koozhangal has been directed by P S Vinothraj.
- The awards were given away by the Information and Broadcasting Minister of Bangladesh Hasan Mahmud as Chief Guest during the concluding session organized at the National Museum auditorium in Dhaka.
The list of the award for different categories is:
- The best actor award was given to Jayasurya for Ranjith Sankar-directed film Sunny.
- The Best Script Writer Award went to Indranil Roychowdhury and Sugata Sinha for Indranil Roychowdhury-directed India-Bangladesh film Mayar Jonjal.
- The special audience award was given to Aimee Baruah Directed the film Semkhor.
- Sujit Bidari directed the film Aina Jhyal Ko Putali from Nepal got the best director award.
- In the Women film maker’s section, the best feature film award was given to Maryam Bahrololumi directed the film Shahrbanoo (Lady from the City) from Iran.
- Two Bangladeshi films, Nurul Alam Atique directed Lal Moroger Jhuti and N Rashed Chowdhury directed Chandrabati Kotha got the Audience Award.
Goat Head Yogini: Culture Minister G Kishan Reddy announced that a 10th century stone idol of Goat Head Yogini which was discovered in England is being returned to India.
Key Facts:
- The sculpture, which is part of a Yogini set from Lokhari Temple in the Banda district of Bundelkhand, will now be dispatched to the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) in New Delhi.
- The idol had been illegally removed from a temple in Lokhari, Banda, Uttar Pradesh.
- Earlier, the High Commission of India in London announced the recovery and repatriation of the 10th century stone idol that had been illegally removed.
- The sculpture was that of a goat-headed Yogini that originally belonged to a group of stone deities in sandstone and was installed in Lokhari temple.
- The goat-headed Yogini went missing from Lokhari in the 1980s and had briefly surfaced in the art market in London in 1988.
Background:
- In October 2021, the High Commission of India had received information about the finding of a goat-headed Yogini Sculpture that had matched the description of the Lokhari set, in the garden of a private residence near London.
About Yoginis:
- Yoginis are a group of powerful female divinities associated with the Tantric mode of worship.
- They are worshipped as a group, often 64, and are believed to possess infinite powers.
Unsung Women Freedom Fighters: As a part of Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav, the Union Minister of State for Culture, Meenakshi Lekhi recently released a pictorial comic book titled ‘India’s Women Unsung Heroes’.
Key Points:
- It has been released as a tribute to the forgotten women freedom fighters of the country who led the charge and lit the flame of rebellion throughout the country.
- It contains stories of queens who battled imperialism and dedicated their lives to Motherland India.
- The book has been prepared by the Ministry of Culture in partnership with Amar Chitra Katha.
- Amar Chitra Katha is an Indian publisher of Indian comics and graphic novels.
- The book celebrates the lives of 75 unsung women freedom fighters of India, including Rani Abbakka, Matangini Hazra, Gulab Kaur, Velu Nachiyar, Padmaja Naidu, Jhalkari Bai, Durgabhai Deshmukh, among others.
Some of the key leaders covered include:
Rani Abbakka Chowta:
- Rani Abbakka Chowta thwarted Portuguese attacks for several decades.
- She was the first Tuluva Queen of Ullal who fought the Portuguese in the latter half of the 16th century.
- She belonged to the Chowta dynasty and ruled over parts of coastal Karnataka (Tulu Nadu), India.
- Their capital was Puttige.
Matangini Hazra:
- Matangiri Hazra was a freedom fighter from Bengal who laid down her life in the struggle.
- She participated in the Indian independence movement until she was shot dead by the British Indian police in front of the Tamluk Police Station (of erstwhile Midnapore District) on 29 September 1942.
- She was affectionately known as Gandhi buri, Bengali for old lady Gandhi.
- In 1930, she took part in the Civil Disobedience movement and was arrested for breaking the Salt Act.
Gulab Kaur:
- She fought against British rule after abandoning her own dreams of a life abroad.
- In Manila, Gulab Kaur joined Ghadar Party, an organization founded by Indian immigrants with the aim to liberate the Indian Subcontinent from British Rule.
Velu Nachiyar:
- Velu Nachiyar was the first Indian queen to wage war against the East India Company.
- She was a queen of Sivaganga estate from 1780–1790.
- She is known by Tamils as Veeramangai (“brave woman”).
- She fought the East India Company with the support of Haider Alis Army, feudal lords, marudhu brothers, Dalit commanders and thandavarayan pillai.
Padmaja Naidu:
- Padmaja Naidu was the daughter of Sarojini Naidu and a freedom fighter.
- She was also a politician who was the 5th Governor of West Bengal from 3 November 1956 to 1 June 1967.
- At the age of 21, she co-founded the Indian National Congress in the Nizam ruled the princely state of Hyderabad.
- She was jailed for taking part in the “Quit India” movement in 1942.
- After Independence, she was elected to the Indian Parliament in 1950.
Jhalkari Bai:
- Jhalkari Bai was a soldier and adviser to the Rani of Jhansi who played an important role in the Indian Rebellion of 1857.
- At the height of the Siege of Jhansi, she disguised herself as the queen and fought on her behalf, on the front, allowing the queen to escape safely out of the fort.
Chakali Ilamma:
- Chakali Ilamma's act of defiance against the local zamindar inspired many during the rebellion in Telangana region.
Economics
Coal Directory of India 2020-21: Coal Controller’s Organization (CCO), a subordinate office under the Ministry of Coal recently released its flagship publication “Coal Directory of India 2020-21”.
The Statistical Publication was released by the Secretary, Ministry of Coal, Dr. Anil Kumar Jain at the Office of the Coal Controller, Delhi.
About Coal Directory of India 2020-21:
- The ‘Coal Directory of India 2020-21’ contains information regarding the performance of the Coal and Lignite sectors during the financial year 2020-21.
- It incorporates the grade-wise data of production and dispatch and reserves of coal.
- In addition, the publication provides information on pit head closing stock, import-export and prices of coal for the last few years.
- It also provides a valuable and comprehensive ready reference of data to all the stakeholders, policymakers, researchers, industry and institutions.
- The Directory is accessible from the official websites of the Coal Controller’s Organization and Ministry of Coal.
About Coal Controller Organisation (CCO):
- Coal Controller Organisation (CCO) was founded in 1916.
- CCO is a subordinate office under the Ministry of Coal.
- It is one of the oldest offices in the Indian Coal sector.
- CCO is responsible to ensure fair production and commercial transactions.
- It collects and maintains coal production data of all public as well as private sector coal mines in India.
- It collects information on a monthly basis.
Key Responsibilities of CCO:
- To inspect collieries so as to ensure the correctness of the class, grade, or size of coal.
- To issue directives for the purpose of declaration and maintenance of grades of coal of a seam mined in a colliery.
- To act as the appellate authority in case of dispute between consumers and owner arising out of the declaration of grade and size of coal.
- To regulate the disposal of stock of coal or the expected output of coal in the colliery.
- Quality surveillance with respect to maintenance of grade, loading of coal in wagons/ trucks according to laid down procedures regarding grades and sizes.
- To grant opening or re-opening permission of coal mine, seam.
- To assess and collect excise duty levied on all raw coal raised and dispatched.
- To submit monthly coal data to different ministries of Central and State Government, national and international organizations.
Air India Officially Handed Over to Tata Group: After a long journey of 69 years, Air India was officially handed over to Tata Group recently.
Key Highlights:
- The Union government, on 27th January 2022, transferred its shares in Air India, along with control and management, to Tata Sons subsidiary, Talace.
- This move has ended a disinvestment process that started five years ago.
- The transaction covers three entities namely, Air India, Air India Express and Air India SATS (AI SATS).
- Under the deal, the Tata group will also be handed over Air India Express and a 50 percent stake in ground handling arm AI SATS.
- Air India has been a public sector undertaking since 1953.
- Tata will get Air India’s fleet of 141 planes.
- It will also get ownership of iconic Brands such as Indian Airlines, Air India, and the Maharajah.
- Maharaja is the official mascot of Air India which operates globally apart from domestic operations.
- According to the available data in 2020, “Air India operates around 101 destinations including 57 domestic operations including 33 countries on four continents around the world.”
Airlines owned by Tata:
Tata Group owns three airlines.
- In Vistara, tata has 51% stake.
- In AirAsia India, it has 84% stake.
- These three airlines together account for 24% of the market share in the aviation sector.
History of disinvestment of Air India:
- The Union Cabinet had given in-principle nod for disinvestment of Air India, in June 2017.
- In 2018, the government invited bids for a 76% stake in the airline which failed to attract any buyers.
- Atal Bihari Vajpayee Government, in 2000-2001, also attempted to sell 40% stake in Air India but failed.
- In January 2020, the government again launched a fresh effort to offer to sell its 100% stake in Air India.
About Air India:
- Air India was founded in 1932.
- The inaugural flight was piloted by JRD Tata, between Karachi and Bombay.
- It was then known as Tata Airlines.
- The government acquired a 49% stake in the carrier in 1948
- The airline was nationalized in 1953.
Deccahorn: Swiggy has recently become the fourth Indian company to earn the tag Deccahorn.
Swiggy is a Bengaluru-based Company.
It is a Food delivery platform.
Key Points:
- The other three companies that hold the tag already are Paytm, a FinTech, Oyo (a hotel aggregator) and Byjus (an Edtech).
- Facebook was the first Deccahorn to earn the tag in 2007.
- It became a Deccahorn after Microsoft invested 240 million USD in Facebook.
- Alibaba of China was the second Deccahorn. It achieved the status in 2009.
What are Deccahorns?
- Deccahorns are private firms whose value exceeded over ten billion USD.
- Most of the Deccahorns are start-up companies.
- There are now roughly 51 deccahorns on the globe.
- Many businesses earned the title by 2021 as compared to 2020.
- Their numbers have increased with the increase in rise of consumer techniques.
Which companies cannot be described as Deccahorns?
- Deccahorn cannot be used to describe a company that has been acquired by another company.
For example - Flipkart is worth more than ten billion dollars. But Flipkart, on the other hand, was purchased by Walmart. As a result, Flipkart cannot be referred to as Deccahorn.
- Furthermore, a government corporation also cannot be called Deccahorn.
Popular Deccahorn sectors:
- On-Demand
- Artificial Intelligence
- FinTech, transportation
- E-commerce
- Marketplace
- Big data
- Blockchain
- Hardware
- Consumer electronics
- Social
- Gaming
- internet software
- Hardware
- Computer hardware
- Biotechnology
About Unicorn, Deccahorn, And Hectocorn:
Unicorn:
A company with a market capitalization of more than 1 billion USD.
Deccahorn:
A Company whose worth is more than 10 billion USD.
Hectocorn:
A Company whose worth is more than 100 billion USD.
- Bytedance was the first hectocorn to be formed.
- Tik Tok's parent company is Bytedance.
- In May 2020, it was worth 100 billion dollars.
- SpaceX was designated as the second hectocorn.
- These are privately owned businesses. They are not traded on the stock exchange.
Defence
Gallantry Awards: The President of India Ramnath Kovind has approved awards of 384 gallantry and other defence decorations on the eve of the 73rd Republic Day celebrations, which includes 12 Shaurya Chakras.
Key Points:
The 384 awards approved by the President on the eve of 73rd Republic Day include -
- 29 Param Vishisht Seva Medals,
- 4 Uttam Yudh Seva Medals,
- 53 Ati Vishisht Seva Medals,
- 13 Yudh Seva Medals,
- 3 Bar to Vishisht Seva Medals,
- 122 Vishisht Seva Medals,
- 3 Bar to Sena Medals (Gallantry),
- 81 Sena Medals (Gallantry),
- 2 Vayu Sena Medals (Gallantry),
- 40 Sena Medals (Devotion to Duty),
- 8 Nao Sena Medals (Devotion to Duty), and
- 14 Vayu Sena Medals (Devotion to Duty).
- This year's list of defence decorations also includes gallantry medals for soldiers and police forces involved in counterterrorist operations in Jammu and Kashmir and the northeast.
- The central and state police forces have been accorded 189 medals for gallantry. The highest numbers of medals have been awarded to the Jammu and Kashmir Police, involved in counter-terror operations.
- This is followed by 30 to the CRPF, 10 to the Chhattisgarh Police, 9 to the Odisha Police, 7 to the Maharashtra Police, 3 each to the ITBP and the SSB and 2 to the BSF, among others.
- In addition, the President has awarded one President’s Tatrakshak Medal (PTM), three Tatrakshak Medals (TM) and one TM for meritorious service to Coast Guard personnel.
Shauriya Chakra Awrdees:
- Indian Army’s six soldiers have been conferred with the Shaurya Chakra Medals for their conspicuous acts of gallantry.
- Five of them have been awarded posthumously with the country’s third-highest peacetime bravery award for operations in Jammu and Kashmir and along the Line of Control (LoC).
- The five personnel conferred Shaurya Chakra posthumously are Naib Subedar M. Sreejith and Sepoy Maruprolu Jaswanth Kumar Reddy from the 17 Madras Regiment; Havildar Anil Kumar Tomar from the Rajput Regiment; Havildar Kashiray Bammanalli from the Corps of Engineers and with the 44 Rashtriya Rifles (RR); and Havildar Pinku Kumar from the Jat Regiment and with the 34 RR.
- The sixth Shaurya Chakra awardee is Rifleman Rakesh Sharma, 5 Assam Rifles.
- Rifleman Sharma was part of an ambush that took place after receiving information on the movement of insurgents for extortion and killing of civilians in a village in Assam in May 2021.
About Gallantry Awards:
- The President honours the country's military personnel with the gallantry awards for their show of gallantry and valour.
- These gallantry awards are announced twice in a year - first on the occasion of Republic Day and then on the occasion of Independence Day.
- The order of precedence of these awards is the Param Vir Chakra, the Ashoka Chakra, the Mahavir Chakra, the Kirti Chakra, the Vir Chakra and the Shaurya Chakra.
Investiture Ceremony:
- Gallantry awards along with some other Defence Distinguished Service awards are conferred to the awardees/Next-of-Kins (NoKs) by the President at the Defence Investiture Ceremony held every year at the Rashtrapati Bhawan.
- However, the Param Vir Chakra and the Ashoka Chakra are conferred by the President to the awardees/NoKs on the occasion of the Republic Day Parade at the Rajpath.
History:
- Post-independence, the first three gallantry awards namely Param Vir Chakra, Maha Vir Chakra and Vir Chakra were instituted by the Government of India on 26th January 1950 which were deemed to have effect from the 15th August 1947.
- Thereafter, other three gallantry awards i.e. Ashoka Chakra Class-I, Ashoka Chakra Class-II and Ashoka Chakra Class-III were instituted by the Government of India on 4th January 1952, which were deemed to have effect from the 15th August 1947. These awards were renamed Ashoka Chakra, Kirti Chakra and Shaurya Chakra respectively in January 1967.
Pilot Shivangi Singh: Flight Lieutenant Shivangi Singh is India’s first woman fighter pilot on the Rafale combat aircraft.
Key Points:
- Singh, who hails from Varanasi, was a part of the Indian Air Force (IAF) Tableau at the 73rd Republic Day celebrations.
- She was flying MiG-21 Bison before being inducted into the Golden Arrows squadron of the IAF.
- She joined the Indian Air Force in 2017. She is the only second woman pilot to participate in the Indian Air Force Tableau.
- Fighter Jet pilot Bhawna Kanth was the first woman pilot to participate in the IAF tableau.
Note: The IAF was the first force to have allowed women officers in combat and has the highest percentage of female officers.
IAF Tableau:
- The tableau of the IAF at the Republic Day parade displayed the theme ‘Indian Air Force Transforming for the Future.
- The tableau showcased the scaled-down models of MiG-21, Gnat, Light Combat Helicopter (LCH), Aslesha radar, and Rafale aircraft.
About:
The MiG-21s strike worked as the final trigger to capitulate the adversary and bring about a decisive victory in the 1971 war.
- Gnat, also known as ‘Sabre Slayer was the first indigenous aircraft, armed with 30 mm Aden guns and rockets.
- Gnat was considered to be the best aircraft to take on an enemy aircraft in a dog fight.
- The indigenously developed Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) is capable of high altitude operations and is armed with Dhruvastra anti-tank guided missile.
- Aslesha MK-1 is a three-dimensional Low-Level Light Weight and multi-beam ground-based 3D Surveillance Radar.
- It is deployed in diverse terrains and has the capability to detect and track heterogeneous air targets, including helicopters, fighters, and UAVs at low and medium altitudes.
- GSAT 7A is a Geostationary satellite.
- It enhances IAF’s Network Centric Warfare capabilities by interlinking all ground-based Radars, airbases, Airborne Early Warning, and Control Radars for detecting aircraft and vessels.
- Rafale with its advanced technology, equipped with a wide range of weapons is a game-changer to attain air supremacy.
Anti-armour weapon AT4: Swedish defence company ‘Saab’ has been selected by the Indian Army and the Indian Air Force (IAF) for the supply of single-shot anti-armour weapon AT4.
Key Details:
- Saab was selected through a competitive programme.
- The Indian armed forces are a new customer for AT4.
- AT4 will be used by the Indian Army and the IAF.
- The order includes the AT4CS AST, which can be fired from confined spaces such as from inside buildings, bunkers and other urban environments.
Note: Carl-Gustaf system of Saab is being already used by the Indian Armed Forces.
About the AT4:
- AT4 will be operated by a single soldier. The single-shot system has proven efficacy against structures, landing craft, helicopters, armoured vehicles and personnel.
- It is 84 mm calibre warhead offers enhanced power and performance.
- The AT4 systems are combat-proven across the world.
- They are lightweight, single-shot, fully disposable and truly characterized by their ease of use and handling.
- The weapon can be fired with a range of projectiles, such as high-explosive anti-tank rounds, anti-structure tandem-warheads, and high explosive rounds.
- It can penetrate more than 17.5 inches (44 centimetres) of armour.
About Saab:
- Saab is a Swedish defence company.
- It was founded in 1937.
- It is headquartered in Stockholm, Sweden.
- The current President and CEO is Micael Johansson.
Environment
Spot-billed pelicans: A nematode infestation has led to mass mortality of spot-billed pelicans (Pelicanus philippensis) at Telineelapuram Important Bird Area (IBA) in Andhra Pradesh (AP).
Key Details:
- Over 150 spot-billed pelicans have succumbed to the infestation since December, based on Forest officers, with 21 birds dying up to now 72 hours alone.
- Solely grown-up birds have succumbed to the infestation until date.
- Preliminary inquiry suggests that nematode infestation is the cause for the death of the spot-billed pelicans.
- Note: The nematode parasite is suspected to be transferred through fish and snails in particular, when the birds prey in the aqua ponds.
- The spot-billed pelican is capable of hunting huge fish from the water bodies and swamps and thus, it is vulnerable to infestation.
- Till now, in South India, the Telineelapuram IBA is the prime winter sojourn for the spot-billed pelican for breeding. The identical IBA can be a breeding habitat for the painted stork (Mycteria leucocephala).
- However, as per the studies carried out by experts in Karnataka State, the nematode infestation would not spread from one species to another species.
- Thousands of spot-billed pelicans and a few hundred painted storks migrate from the Siberian region to breed in the Telineelapuram IBA and a majority of them prefer to stay here instead of going back home.
About spot-billed pelican:
- The spot-billed pelican (Pelecanus philippensis) is also called grey pelican.
- It is a member of the pelican family.
- It breeds in southern Asia from southern Iran across India east to Indonesia.
- It is a bird of large inland and coastal waters, especially large lakes.
Features:
- The spot-billed pelican is a relatively small pelican but still a large bird.
- It is 125–152 cm (49–60 in) long and has a weight of 4.1–6 kg (9.0–13.2 lb).
- It is mainly white, with a grey crest, hindneck and a brownish tail.
- The feathers on the hind neck are curly and form a greyish nape crest.
Habitat:
- It is not migratory but is known to make local movements and are more widely distributed in the non-breeding season.
- The species is found to breed only in peninsular India, Sri Lanka and Cambodia.
- The main habitat is in shallow lowland freshwaters.
Conservation status:
Near Threatened under IUCN Red List.
Red Sanders: The Red Sanders (or Red Sandalwood) has recently fallen back into the ‘endangered’ category.
Key Highlights:
- The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) recently reclassified Red Sanders as 'endangered' on its Red List.
Note: A fictional account of red sandal smuggling is provided by the recently released and trending Telugu movie plot.
- In 2018, it was designated as a 'near threatened' species.
- When a species was removed from the endangered list for the first time since 1997, it was a cause for celebration.
- For the past three generations, the Red Sanders species has seen its population drop by 50-80%.
- As a result, it was once again placed in the endangered category.
- About Red Sanders:
- Pterocarpus santalinus is the scientific name for the Red Sanders species.
- It is an Indian endemic tree species, with a restricted geographical range in the Eastern Ghats.
- The species is only found in a small area of woodland in Andhra Pradesh.
Significance of Red Sanders:
- Red Sanders are prized for their deep color and medicinal benefits.
- They are in considerable demand in Asia, particularly in China and Japan, for usage in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
- Furniture, woodcraft, and musical instruments are all made using it.
Status of legal protection in India:
The Union Environment Ministry had decided to keep Red Sanders (red sandalwood) OUT of the Schedule VI of Wild Life Protection Act, 1972, arguing that this would discourage the cultivation of the rare plant species.
Note: Schedule VI regulates and restricts the cultivation, possession, and sale of a rare plant species.
CITES Status:
- The Red Sanders is listed in CITES Appendix II. As a result, foreign trade is prohibited.
- The tree's harvest is likewise regulated throughout states, yet there is still unlawful commerce.
IUCN Red List:
- IUCN is in charge of maintaining the Red List.
- It is a list of flora and fauna species that are classified according to their conservation status.
The following are the current conditions:
Least concern: It is for the species, which are abundant in numbers.
Extinct: It is for those species, which have completely disappeared from the planet.
Critically endangered: This category is for threatened species.
Endangered: Threatened species are added to this list
Vulnerable: The category is reserved for threatened species.
Songs of Frog Species: Recently researchers, in a new study, documented the songs of frog species.
Key Highlights:
- This study was conducted by researchers from the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bengaluru, and the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER), Pune.
- It has been published in the journal Animal Behaviour.
Key points:
- The new study found that frogs have different types of calls to suit different occasions.
- It was known that birds sing different songs depending on the context, yet this kind of behaviour has not been documented among the so-called simpler animals, the anurans (frogs and toads).
- The group studied two species of frog – Humayun’s Night Frog (Nyctibatrachus humayuni) and Amboli Bush Frog (Pseudophilautus amboli).
- As per the study, the N. humayuni produces calls with two notes (ascending and descending) while P. amboli produces calls with six-note types.
- Both species of anurans are endemic to the Western Ghats.
- This is the first study to examine “sequences” of vocalizations in frogs.
Indian Policy
Non-Renewal of FCRA Registration: The Supreme Court recently declined to entertain a plea seeking interim relief to allow the continuation of Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA) licenses of nearly 6,000 NGOs, which were only valid till September end 2021.
Key Points:
- The Apex Court asked them to go back to the government for redressal of their grievances on the non-renewal of their FCRA registration.
- The plea filed by US-based NGO 'Global Peace Initiative' had come up for hearing before a bench comprising Justices A M Khanwilkar and C T Ravikumar.
- The Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2020 was introduced in Lok Sabha on September 20, 2020, which amended FCRA Act, 2010.
- The Act regulates the acceptance and utilization of foreign contributions by individuals, associations, and companies.
- The plea claimed the FCRA Amendment Act, 2020 significantly hampered their activities and operations.
About Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act (FCRA), 2010:
- The Foreign Contribution (Regulation) Act, 2010 is an act of the Parliament of India, by the 42nd Act of 2010.
- The FCRA Act is implemented by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The act, in its consolidating form, was originally passed in 1976 and majorly modified in 2010.
- FCRA, 2010 has been enacted by the Parliament to consolidate the law to regulate the acceptance and utilization of foreign contribution (especially monetary donation) or foreign hospitality by certain individuals or associations, or companies.
- The act regulates the foreign funding of voluntary organizations in India.
- Under the Act, donating organizations need to register themselves every 5 years.
- A person with a definite educational, cultural, economic, religious, or social programme can accept foreign contributions after registration or permission from the Central Government.
- However, election candidates, members of any legislature (MP and MLAs), Political parties, publishers of a registered Newspaper, judges, government servants, or employees of any corporation owned by the government cannot accept the foreign contributions.
- This Act prohibits the acceptance and utilization of foreign contribution or foreign hospitality for any activities detrimental to national interest and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- The Act has been used by the Government of India to freeze bank accounts of certain NGOs who it found were affecting India's national interest for wrong purposes.
Draft UGCF 2022: The Delhi University recently released a draft Undergraduate Curriculum Framework 2022 (UGCF-2022) formulated in accordance with the National Education Policy and sought feedback from stakeholders.
Key Highlights:
- The new UG curriculum will come into force from next year when the university shifts to a four-year undergraduate programme (FYUP).
- As per the statement issued by the university, the Draft UGCF has been uploaded on the website of the university and a link for submitting feedback through a Google form will remain active till January 31, 2022.
- The UGCF is an attempt to include two of the most talked-about features of the NEP – multi-disciplinarity and multiple exit points (leaving the course at the end of each year with a different degree).
Key points about UGCF-2022:
- The UGCF provides the curriculum framework that will be adopted in the 2022-23 academic session when DU shifts to an FYUP.
- However, it does not include the syllabi for courses, which is prepared independently.
- The new draft has a total of 176 credits on offer.
- The number of credits is determined by the study load.
- To clear a semester, students need a certain number of credits which are determined by the importance of the course and the teaching-learning hours that are put into it.
- As per the new framework, to get a four-year UG degree with a major in a specific discipline, students need to get a minimum of 50% of credits (88) in that discipline.
- As of now, DU follows the Choice Based Credit System, according to which there are a total of 148 credits for a three-year Honours programme, and 132 credits for a Programme course – which is a course in which a combination of subjects is taught, as opposed to the focus being on one main subject in Honours courses.
- For instance, a BA Programme in Economics & History.
Objective:
The objective of the UGCF is to “align with the NEP” so as -
- To promote each student’s holistic development in both academic and non-academic spheres.
- To provide flexibility to students so that learners have the ability to choose their learning trajectories and programmes.
- To eliminate harmful hierarchies among disciplines/fields of study and silos between different areas of learning, among others.
About University of Delhi:
- The University of Delhi, informally known as Delhi University, is a collegiate public central university located in New Delhi, India.
- It was founded in 1922 by an Act of the Central Legislative Assembly and is recognized as an Institute of Eminence by the University Grants Commission (UGC).
- It consists of three colleges, two faculties, and 750 students at its founding, the University of Delhi has since become India's largest institution of higher learning and among the largest in the world.
- The university has 16 faculties and 86 departments distributed across its North and South campuses.
- It has 77 constituent colleges and five other institutes.
- The Vice President of India serves as the university chancellor.
- Its motto is निषà¥à¤ ा धृति: सतà¥à¤¯à¤®à¥ (Nishtha Dhriti Satyam (Sanskrit)) meaning Dedication, Steadfastness and Truth.
Mobile App “MyCGHS”: Union Minister for Health and Family Welfare Dr. Mansukh Mandaviyadigitally launched the revamped CGHS (Central Government Health Scheme) website (www.cghs.gov.in) and mobile app, “MyCGHS” on January 24, 2022.
Key Highlights:
- The new CGHS website and its extension as a Mobile Application called “MyCGHS” is a significant move.
- The Website has been developed in accordance with GIGW (Guidelines for Indian Government Websites).
- The website has been made 3U compliant, i.e., Usable, User-Centric and Universally Accessible.
- The updated features include various beneficiary-friendly features.
About The Updated Features:
- It has been designed for ease of service delivery for the beneficiaries within the safe confines of his home, especially during the covid pandemic.
- The new features will benefit more than 40 lakh beneficiaries (both in-service and retired personnel) with real-time information from the convenience of their homes.
- As mandated by the GIGW, the site has been made Bilingual (Hindi and English) with the provision to make it multi-lingual in the future.
- There is a direct link to the eSanjeevani Teleconsultation facility through the CGHS website.
Aim:
The move aimed for ease of service delivery for the beneficiaries within the safe confines of his home especially during the COVID pandemic.
About eSanjeevani:
- eSanjeevani also called the National Teleconsultation Service is the first-ever online OPD (outpatient) consultation service offered by the government of India to citizens.
- The scheme was started in November 2019.
- It is run by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- It is a doctor to doctor telemedicine system which is being implemented under the Ayushman Bharat Health and Wellness Centre (AB-HWCs) Programme.
- According to the government, this is the first time the government of a country is offering a service of this kind to its citizens.
- It aims to provide healthcare services to patients in their homes.
- It tackles the issues of uneven distribution of healthcare personnel and infrastructure by bridging the divide that exists between urban and rural, rich and poor, in terms of access to healthcare services.
Note: The first state to launch this service was Andhra Pradesh.
About Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS):
- The Central Government Health Scheme (CGHS) is the nodal healthcare provider to Central Government employees, pensioners and certain other categories of beneficiaries and their dependents enrolled under the scheme.
- It caters to the healthcare needs of eligible beneficiaries covering all four pillars of the democratic setup in India namely Legislature, Judiciary, Executive and Press.
- It is unique of its kind due to the large volume of its beneficiary base and pan India presence providing healthcare through allopathic as well as indigenous systems of medicine.
- In order to cater to India’s increasing digital penetration, it has laid emphasis on the delivery of services through various online channels.
Indian polity
New Districts of Andhra Pradesh: The Andhra Pradesh government, led by Chief Minister YS Jagan Mohan Reddy, has recently formed 13 new districts.
Key Highlights:
- The new districts have been formed based on Parliamentary constituencies.
- Now, there are a total of 26 districts in the Andhra Pradesh.
- The new districts are likely to be formed on Ugadi, March 2.
- A notification was issued specifying the revenue boundaries and district centres of the total 26 districts.
- According to a notification issued by the government, the reorganization of the districts is being done under Section 3 of the Andhra Pradesh Districts (Formation) Act, 1974.
- In a significant political move, the state government has decided to name the Vijayawada district after the founding president of Telugu Desam Party (TDP) and the former Chief Minister NT Rama Rao (NTR).
About the new districts:
- The new districts include Manyam, Alluri Seetarama Raju, NTR, Anakapalli, Konaseema, Eluru, Bapatla, Palnadu, Nandyala, Sri Satyasai, Kakinada, Annamaiah, Sri Balaji and Parvathipuram.
- The Araku Lok Sabha constituency in Visakhapatnam was divided into two districts.
- According to the notification, the new districts and their district headquarters (in brackets) are Srikakulam (Srikakulam), Vizianagaram (Vizianagaram), Manyam (Parvathipuram), Alluri Sitharama Raju (Paderu), Visakhapatnam (Visakhapatnam), Anakapalli (Anakapalli), Kakinada (Kakinada), Konaseema (Amalapuram), East Godavari (Rajamahendravaram), West Godavari (Bheemavaram), Eluru (Eluru), Krishna (Machilipatnam), NTR (Vijayawada), Guntur (Guntur), Bapatla (Bapatla), Palnadu (Narsaraopeta), Prakasam (Ongole), SPS Nellore (Nellore), Kurnool (Kurnool), Nandyal (Nandyal), Ananthapuram (Ananthapuram), Sri Satyasai (Puttaparthy), YSR Kadapa (Kadapa), Annamayya (Rayachoty), Chittoor (Chittoor) and Sri Balaji (Tirupati).
What is the procedure for the creation of new districts in India?
- The power to create new districts or alter or abolish existing districts rests with the State governments.
- This can either be done through an executive order or by passing a law in the State Assembly.
- Many States prefer the executive route by simply issuing a notification in the official gazette.
Role of Center in the creation of Districts:
- The Central Governments have no role in creating new districts.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs is included only when the state government wishes to change the name of a district or a railway station.
Why are new districts created?
The idea behind creating new districts is generally to provide effective governance. However, it is sometimes driven by local demands.
What are the advantages of the creation of new districts in India?
The advantages of creating new districts are as follows:
- Better administration and governance as there will be more officers for less population.
- The grievances of the people shall be redressed easily.
- Scheme implementations and fund transfers become easy.
- Increase in employment as new districts require new officials from top-down.
Current scenario of Indian districts:
- According to the 2011 census, there were 593 districts in India.
- Between 2001 and 2011, 46 districts were created.
- Though the 2021 Census is yet to happen, but according to Know India, a website run by the Government of India (GoI), it says currently there are 718 districts in the country.
- The number increased due to the bifurcation of Andhra Pradesh into A.P. and Telangana in 2014.
- Telangana at present has 33 districts and A.P. has 13 districts.
Digital Sansad App: The Lok Sabha secretariat recently unveiled a new official mobile application of the Parliament called "Digital Sansad."
Key Highlights:
Digital Sansad App was launched by the Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla.
The App has been launched to make the Parliament proceedings accessible not just to the members but also to the public at large.
About the Digital Sansad App:
- The app will enable citizens to watch the Parliamentary proceedings in the Parliament and check what their members of the Parliament are doing and the debates that they are participating in.
- Through Digital Sansad App, citizens will be able to watch the initiatives taken by the temple of democracy at the click of a button on the phone.
- The App will also make it convenient for citizens to access general information about Members of Parliament, their participation in sessions, budget speeches since 1947 and proceedings from 12th Lok Sabha to 17th Lok Sabha.
- The App will also contain the live telecast of Sansad proceedings.
- Apart from a virtual tour of the Parliament, it will allow citizens to access live proceedings of the House, including the Union Budget 2022 live.
How will this app prove useful for the Members of Parliament (MPs)?
- The MPs will be able to use the App to access services such as House bulletins, the status of their notifications, and so on.
- The MPs are not permitted to use Laptops inside the House of Commons. Therefore, this App will prove very useful for getting parliamentary data during any debate in the House.
- MPs will be able to use this App to log in for attendance, give questions during Question Hour, and submit notices for debates or adjournment motions in the future.
- Digital Sansad App is an empowering realization of Parliament’s holistic efforts to keep progressing towards the goal.
What makes Digital Sansad App more significant in Digital India?
- The new age of Digital India flourishes even in the remotest corners of India, the Parliament of the world’s largest democracy too has been expanding its footprints. Parliament’s Digital Sansad App is a step in this direction.
- As India is a sovereign democratic Republic, it is the duty of the Indian Parliament to uphold the highest standards of transparency. Digital Sansad App is a realization to keep progressing towards that goal.
Background:
Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla, during the last winter session of Parliament, had informed that the application was being worked upon and would be live soon.
12th National Voters' Day 2022: Election Commission of India (ECI) celebrated the 12th National Voters' Day (NVD) on 25th January 2022.
Key Highlights of NVD 2022:
- Hon’ble Vice President of India, Shri Shri M. Venkaiah Naidu had consented to be the Chief Guest for the national function but due to his inability to attend the function in person, his message was virtually-delivered during the function.
- Union Minister for Law and Justice, Shri Kiren Rijiju graced the function as the Guest of Honour.
- On the occasion, National Awards for the Best Electoral Practises for the year 2021-22 was conferred to officers for their outstanding performance in the conduct of elections in different spheres such as IT initiatives, Security Management, Election Management, Accessible Elections and contribution in the field of voter awareness and outreach.
- In addition, awards were also conferred on Govt. Departments and Media Houses for their outstanding contribution in the field of voter awareness and outreach.
- The ECI launched a publication ‘Leap of Faith: Journey of Indian Elections’.
- The book narrates India's electoral history and the growth of representative and electoral principles in India as it evolved from the nineteenth to twenty-first century.
- The book focuses on the Election Commission of India’s persistent efforts to make the elections genuinely reflective of people’s verdict.
- Another Publication ‘Pledging to Vote – A decadal Journey of The National Voter’s Day in India’ was also released.
- The book presents the journey of National Voter’s Day celebrations by ECI from Diamond Jubilee celebration onwards.
- During the function, five newly enrolled voters from Delhi were also felicitated and handed over their Elector Photo Identity Card (EPIC).
The theme of NVD 2022:
The theme for this year’s NVD is ‘Making Elections Inclusive, Accessible and Participative’,.
- The theme envisages focusing on ECI’s commitment to facilitate the active participation of voters during the elections and to make the complete process hassle-free and a memorable experience for all categories of voters.
About NVD:
- NVD is celebrated on 25 January.
- The main objective behind the celebration is to encourage, facilitate, and maximize enrolment, especially for new voters.
- Dedicated to the voters of the country, on this day, voters are being made aware of promoting informed participation in the electoral process.
- New voters or first-time electorate are handed over their Elector Photo Identity Card (EPIC) in the National Voters' Day function.
History of NVD:
- The Voters' Day celebration was initiated in 2011 by the then President of India, Pratibha Devi Patil, on the 61st foundation day of the Election Commission of India.
- The Election Commission of India, or ECI, was established on January 25, 1950.
- The ECI is a Constitutional body that is bound by its responsibility to conduct free and fair elections in India at all levels of the legislature.
Importance of Voting:
- Voting is a basic process that helps to form a country's government.
- In India, people vote once in every five years to elect representatives to the national, state and local legislative bodies.
- Voting rights of the people are very important as one has the direct power to put the right people into positions of governance.
Eligibility of the Voters:
- The eligibility age of the voter was 21 years but in 1988 it was lowered to 18 years.
- The Sixty-First Amendment Bill of 1998 lowered the voter's eligibility age in India.
International
Nordic "Clinker Boats": United Nations (UN) culture agency, UNESCO, in December 2021 added Nordic “clinker boats” to its list of traditions that represent the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
Key Highlights:
- Denmark, Iceland, Finland, Sweden and Norway jointly sought the UNESCO designation.
- The UNESCO nomination was signed by around 200 communities and cultural bearers in the field of construction and traditional clinker boat craftsmanship, including Sami communities.
- For thousands of years, these wooden sailboats allowed the peoples of Northern Europe to spread influence, trade, and sometimes war across seas and continents.
- The term “clinker” is believed to refer to the way its wooden boards were fastened together.
- Supporters of the successful nomination hope it will safeguard and preserve the boat-building techniques that drove the Viking era for future generations as the number of active clinker craftsmen fades and fishermen and others opt for vessels with cheaper glass fiber hulls.
- There are only about 20 practicing clinker boat craftsmen in Denmark, perhaps 200 across all of northern Europe.
Characteristics of Wooden Clinker Boats:
- Wooden clinker boats are characterized by the use of overlapping longitudinal wooden hull planks that are sewn or riveted together.
- Builders strengthen the boats internally by additional wooden components, mainly tall oak trees, which constitute the ribs of the vessel.
- They stuff the gaps in between with tar or tallow mixed with wool, animal hair, and moss.
Viking Ship Museum in Roskilde:
- The Viking Ship Museum is located in Roskilde, west of Copenhagen.
- The museum not only exhibits the remains of wooden vessels built 1,000 years ago but also works to rebuild and reconstruct other Viking boats.
- The process of construction involves the use of experimental archaeological methods to gain a deeper and more practical understanding of the Viking Age.
About World Heritage Site:
- World Heritage Site is an area or landmark, which is legally protected by an international convention administered by United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
- These Sites are designated by UNESCO for having historical, cultural, scientific, or other forms of significance.
- The sites are judged for comprising “cultural and natural heritage worldwide, considered to be important to humanity”.
World Heritage Sites in India and World:
- At present, there are 40 World Heritage Sites located in India.
- Out of these, 32 are cultural, 7 are natural, and 1 is mixed (meeting both cultural and natural criteria), as determined by the organization's selection criteria.
- India has the sixth-largest number of sites in the world.
- As of July 2021, there are 1,154 World Heritage Sites, across 167 countries.
- Out of them, 897 are cultural, 218 natural, and 39 are mixed properties.
- Italy, with 58 selected areas, is the country with the greatest number of sites on the UNESCO List.
America COMPETES Act of 2022: The United States House of Representatives, On January 25, unveiled the ambitious America Creating Opportunities for Manufacturing, Pre-Eminence in Technology, and Economic Strength Act of 2022 ( in short America COMPETES Act of 2022).
COMPETE Act of 2022 proposes to open up new vistas for talented individuals from across the world with a new start-up visa.
Key Features of the Act:
- The act is an important step forward in advancing the legislation that would establish new innovation initiatives and set funding targets that, if met, would add billions of dollars to the current annual budgets of selected research agencies.
- It would also help to outcompete China and the rest of the world for decades to come.
- The Bill provides 52 million USD to encourage semiconductor production in the US and 45 million USD to provide grants and loans and improve manufacturing and supply chain resilience.
- In addition, the fund has also been allocated to address climate change, social and economic inequality and immigration
- Furthermore, the Bill also authorizes 600 million USD a year to construct manufacturing facilities to make the US less reliant on solar components made in Xinjiang, China.
- The act creates a new green card for entrepreneurs and also offers an exemption for STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering and Mathematics) experts.
- The act creates a new “W” classification. They are the non–immigrant entrepreneurs.
Objectives of the Act:
- The main objective of this act is that it seeks to represent the sort of transformational investments in the American industrial base and research and development that helped power the US to lead the global economy in the 20th century.
- It also helped to expand opportunities for middle-class families.
Importance of the act for the Indians:
- It would mean more opportunities for Indian talent and for skilled workers in the US.
- The Indians use H1-B work permits predominantly.
- They have a major share in H1-B. The act further widens the opportunities for Indian professionals.
Background:
- Every year, the US administration provides a specific number of VISAs every year to fill in the job vacancies.
- This is done to allow the low – cost highly skilled IT professionals to fill in the vacancies.
- Through these VISAs, the companies on foreign soil send their employees to the US.
- The companies gain knowledge as assets and US gains cheap workers.
Visas offered by the US Government:
- H1-B visa: They are issued for people in Specialty operations.
- The people should have higher educational qualification to obtain this visa.
- This visa is popular among Indians.
- H2-B Visa: They are for seasonal workers in hospitality industries.
- L-1 Visa: The VISA allows American companies to transfer workers to American soil for a period of seven years.
- H-4 Visa: It is used by the dependents of H-1B Visa holders.
- J-1 Visa: It is used by students entering American soil for study purposes
India-Central Asia Summit: Prime Minister Narendra Modi hosted the 1st India-Central Asia Summit in virtual format on 27 January 2022.
Key Highlights:
- This first India-Central Asia was attended by Presidents of the Republic of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Republic of Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Republic of Uzbekistan.
- The summit coincided with the 30th anniversary of the establishment of diplomatic relations between India and Central Asian countries.
Key Points of the summit:
- During the Summit, in a historic decision, the Leaders agreed to institutionalize the Summit mechanism by deciding to hold it every 2 years.
- They also agreed on regular meetings of Foreign Ministers, Trade Ministers, Culture Ministers and Secretaries of the Security Council to prepare the groundwork for the Summit meetings.
- An India-Central Asia Secretariat in New Delhi would be set up to support the new mechanism.
- The Leaders discussed far-reaching proposals to further cooperation in the following areas:-
- Trade and connectivity
- Development cooperation
- Defence and security and
- On cultural and people to people contacts
- These included a Round-Table on Energy and Connectivity; Joint Working Groups at senior official level on Afghanistan and use of Chabahar Port; showcasing of Buddhist exhibitions in Central Asian countries and commissioning of an India-Central Asia dictionary of common words, joint counter-terrorism exercises, visit of 100 member youth delegation annually from Central Asian countries to India and special courses for Central Asian diplomats.
- PM Modi also discussed the evolving situation in Afghanistan with the Central Asian leaders.
- The leaders reiterated their strong support for a peaceful, secure and stable Afghanistan with a truly representative and inclusive government.
- They also agreed to set up Joint Working Groups (JWG) at the senior official level in Afghanistan.
- Prime Minister conveyed India’s continued commitment to providing humanitarian assistance to the Afghan people.
Objective of the summit:
- The main objective of the summit is to make it clear that the cooperation between India and Central Asia is essential for regional security and prosperity.
- The objective is not only to give an effective structure to the cooperation but also to create an ambitious roadmap for this cooperation.
India - Central Asia Cooperation:
- The cooperation between Uzbekistan and the Central as well as the State Government of India is increasing.
- India and Krygyzstan are partners in the field of high-altitude research and education.
- Kazakhstan is a vital partner for India's energy security.
- India and Tajikistan cooperate in the field of security.
- Turkmenistan is an important part of the Indian vision in the field of regional connectivity.
International Holocaust Remembrance Day: International Day of Commemoration in memory of the victims of the Holocaust (International Holocaust Remembrance Day) is observed on 27 January every year.
The day is also observed to mark the anniversary of the liberation of the Auschwitz concentration camp in 1945.
Theme for 2022:
- The theme for 2022 is guiding the United Nations Holocaust remembrance and education is “Memory, Dignity and Justice”.
- The theme focuses on safeguarding historical records, remembering victims, and challenging distortion of history, which is often expressed in contemporary antisemitism.
- It also encourages action to challenge hatred, champion compassion and strengthen solidarity.
Objective:
- The objective of Remembrance Day is to commemorate the anniversary of the tragedy of the Holocaust that occurred during the Second World War.
- The Day also aims to promote Holocaust education, an especially timely mission with antisemitic incidents and Holocaust denialism on the rise in the U.S. and other parts of the world.
History of the day:
Nearly two decades ago, the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) in 2005 designated January 27th an annual day of commemoration for its member states, in honor of the 6 million Jewish victims of the Holocaust and millions of other victims of Nazism. (In addition to marking the anniversary of Auschwitz-Birkenau, many countries hold national commemoration ceremonies on other dates connected to the Holocaust).
- Genocide occurred during World War II in which Nazi Germany, aided by its collaborators, systematically murdered some six million European Jews, around two-thirds of the Jewish population of Europe, between 1941 and 1945.
Xiomara Castro: Xiomara Castro has become the first female president of Honduras on January 27, 2022 with United States Vice President Kamala Harris in attendanc.
Key Highlights:
- She is a former first lady of Honduras, as she is the wife of former President Manuel Zelaya who was deposed in a coup in 2009.
- Castro won on her third try for the presidency.
- The inauguration ceremony was witnessed by thousands of people amid a sea of waving flags in the national stadium in the country's capital, Tegucigalpa.
- Castro’s inauguration has brought an end to the 8-year rule of Juan Orlando Hernandez, a one-time US ally, who is currently facing charges of corruption in US courts.
About Honduras:
- Honduras, officially Republic of Honduras, is a country in Central America.
- The republic of Honduras is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the southwest by El Salvador, to the southeast by Nicaragua, to the south by the Pacific Ocean at the Gulf of Fonseca, and to the north by the Gulf of Honduras, a large inlet of the Caribbean Sea.
- Its capital and largest city is Tegucigalpa.
- The currency used here is Honduran lempira.
Note: The literal meaning of the term "Honduras" is "depths" in Spanish.
World's-Largest Canal Lock: The world’s largest canal lock has been inaugurated at Ijmuiden, a small port city, in the Port of Amsterdam, The Netherlands by Dutch King Willen-Alexander.
Key Points:
- Ijmuiden is a port city connecting the North Sea Canal with the port of Amsterdam.
- The sea lock at Ijmuiden is 500 meters (1,640 ft) long and 70 meters broad.
- The construction of the major infrastructure project began in 2016 and and was supposed to be completed by 2019.
- It also exceeded the initial budget by €300 million due to construction setbacks.
- The Ijmuiden lock was designed to allow large, modern cargo ships to reach the port of Amsterdam.
- The ships will no longer have to wait for a favourable water level to enter the canal as the structure is deep enough.
- With almost nine meters above the sea leave, the structure is also a defence against the threat of flooding.
About Netherlands:
- The Netherlands is a country located in Western Europe with overseas territories in the Caribbean.
- Note: the Netherlands means low-lying country.
- It is a republic with a constitutional monarchy.
- The country is sometimes called Holland, but the name only applies to two provinces, North and South Holland, which border the North Sea in Amsterdam and The Hague.
- The four largest cities in the Netherlands are Amsterdam, Rotterdam, The Hague and Utrecht.
- Its capital city is Amsterdam.
- The currency used here is Euro.
Protests against Lithium Mining: The Serbia government has revoked the licenses for lithium mining to Rio Tinto following protests for nearly two months.
Rio Tinto is an Anglo-Australian multinational mining organization.
Key Highlights:
- Serbian Prime Minister Ana Brnabic has put an end to Rio Tinto in the country.
- All the licences linked to the lithium project had been declared invalid and it was an end for the project.
Why were the Serbians Protesting?
- Serbians have been protesting against Rio Tinto’s plans to mine lithium in the Jadar valley near Lozinca town in the country.
- Rio Tinto had discovered lithium deposits in the country in 2006 and had bought land in the Lozinca area in Serbia
- The mine would have produced enough lithium to operate one million electric vehicles along with boric acid and sodium sulfate.
- When fully functional, the mine would have created “58,000 tonnes of refined battery-grade lithium carbonate” every year, which would have made it Europe’s most lithium-producing mine.
What’s the concern?
- While Rio Tinto has been said to be fulfilling all Serbia’s and European Union’s environmental standards, protestors have been pointing out that the country has already been ridden with industrial pollution and lithium mining in the $2.4-billion project would irrevocably pollute the drinking water.
- Serbian capital Belgrade is surrounded by lignite mines and coal power plants powered by these mines, which only make the pollution worse.
Note:
- Serbia has ranked as Europe’s fifth and the world’s 32nd most polluted country in a list of 98 countries.
- According to a 2019 report by Global Alliance on Health and Pollution, Serbia is one of the top ten countries with the most deaths due to pollution — 175 deaths per 100,000.
About Lithium:
- Lithium is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3.
- It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal and a rare metal.
- Under standard conditions, it is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element.
- Like all alkali metals, it is highly reactive and flammable and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil.
Key Characteristics and Properties:
- It has the highest specific heat capacity of any solid element.
- Lithium’s single balance electron allows it to be a good conductor of electricity.
- It is flammable and can even explode when exposed to air and water.
Uses:
- Lithium is a key element for new technologies and finds its use in glass, ceramics, telecommunication and aerospace industries.
- The well-known uses of Lithium are in Lithium-ion batteries, lubricating grease, high energy additives to rocket propellants, optical modulators for mobile phones.
- It is also used as a convertor to tritium used as a raw material for thermonuclear reactions i.e. fusion.
- For related reasons, lithium has important uses in nuclear physics.
- The transmutation of lithium atoms to helium in 1932 was the first fully man-made nuclear reaction, and lithium deuteride serves as a fusion fuel in staged thermonuclear weapons.
About Serbia:
- Serbia, officially the Republic of Serbia is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe.
- It is located at the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkans, bordering Hungary to the north, Romania to the northeast, Bulgaria to the southeast, North Macedonia to the south, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west, and Montenegro to the southwest, and claiming a border with Albania through the disputed territory of Kosovo.
- It is a unitary parliamentary constitutional republic.
- The capital city of Serbia is Belgrade.
- The currency used here is Serbian dinar.
National
Parakram Diwas: Prime Minister Narendra Modi, on January 23, 2022, paid floral tributes to Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose on his 125th birth anniversary in the central hall of the Parliament.
Key Highlights:
- PM Modi wished all the countrymen a very Happy Parakram Diwas.
Note: In 2021, the Government had declared 23rd January as Parakram Diwas to commemorate the 125th birth anniversary of Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose.
- In a first, India began its Republic Day celebrations from January 23 instead of January 24, to include Netaji's birth anniversary.
- The Government had declared that from 2022, the Republic Day celebrations will start on Netaji's birth anniversary on January 23rd and conclude on January 30th, the death anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi.
- A full dress rehearsal was held at Rajpat with the parade taking the same route that it will take on January 26th.
Ahead of Republic Day:
Statue of Netaji:
- PM Modi had announced earlier on January 21st that a grand statue of Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose will be installed at India Gate as a symbol of the country's "indebtedness" to him.
- Till the statue is installed, a hologram statue of his would be present at the same place.
- The dimension of Netaji’s statue is expected to be 28 feet in height and 6 feet in breadth.
- It will be made of granite.
- The hologram statue was unveiled by PM Modi on the occasion of Netaji's 125th birth anniversary.
What is a hologram?
- It is a three-dimensional image formed by the interference of light beams from a laser or other coherent light source.
- The hologram technology projects an image.
- The image is projected in such a way that, it looks so realistic.
- Also, the image appears 3D.
Merger of AJJ with NWMF: The eternal flame called the Amar Jawan Jyoti (AJJ) at the India Gate will be extinguished after 50 years and will be merged with the flame at the adjoining National War Memorial (NWM) in the run-up for Republic Day.
- Amar Jawan Jyoti was built after Indo – Pakistani War, 1971.
- It was built to honour the soldiers who lost their lives in the war.
- NWM was created in 2019.
Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar:
- The Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar has been set up by the central government to honour the invaluable contribution rendered by individuals and organizations in India in the field of disaster management.
- The award is announced every year on the occasion of the birth anniversary of the iconic freedom fighter.
- The award carries a cash prize worth Rs 51 lakh and a certificate in the case of an organization and Rs 5lakh and a certificate in the case of an individual.
- The Subhash Chandra Bose Aapda Prabandhan Puraskar 2022 was conferred upon Gujarat Institute of Disaster Management (GIDM) and Sikkim State Disaster Management Authority’s Vice Chairman Vinod Sharma.
About Netaji Subash Chandra Bose:
- Subhas Chandra Bose (23 January 1897 – 18 August 1945) was an Indian nationalist who defied British colonial rule.
- He played a major role in India's freedom struggle.
- He had set up the Azad Hind Fauj to help liberate India from the clutches of the British.
- He became a hero among Indians, but his wartime alliances with Nazi Germany and Fascist Japan gave intimations of authoritarianism and anti-Semitism.
- The honorific Netaji which means "Respected Leader" was first applied to Bose in Germany in early 1942 by the Indian soldiers of the Indische Legion and by the German and Indian officials in the Special Bureau for India in Berlin.
- It is now used throughout India.
- Netaji started a newspaper called “Swaraj”.
- He had written a book called “The Indian Struggle”. The book covers the Indian Independence movement between 1920 and 1942.
- The term “Jai Hind” was coined by Netaji Subhash Chandra Bose.
- With the slogan “Give me blood and I will give you freedom”, he awakened the country towards fighting against the British.
Key Points:
- He was born into a wealthy Bengali family in Orissa.
- The early recipient of an Anglocentric education, he was sent to take the Indian Civil Service examination in England after college.
- He succeeded with distinction in the vital first exam but he left the studies midway citing nationalism as a higher calling.
- He returned to India in 1921 and joined the Indian nationalist movement led by Mahatma Gandhi and the Indian National Congress.
- He became Congress president in 1938.
- After re-election in 1939, there were differences between him and Gandhi and Bose eventually resigned as President and was ousted from the party later.
- He arrived in Nazi Germany in 1941 seeking German aid to free India.
- Bose was able to acquire funds Netaji built a force known as the Azad Hind Fauj (Indian National Army) giving the slogan of “Dilli Chalo”.
- The Azad Hind Fauj recruited Indian prisoners of war and expatriates in Europe.
- The Azad Hind Fauz planned a land invasion of India.
- Adolf Hitler, who had met Bose once in late May 1942 offered to arrange a submarine for Bose.
- Bose boarded the German submarine in February 1943 and then he was transferred to a Japanese submarine from which he disembarked in Japanese-held Sumatra in May 1943.
- With the support of the Japanese, he revamped the Indian National Army (INA).
- A Provisional Government of Free India was declared on the Japanese-occupied Andaman and Nicobar Islands and nominally presided by Bose.
- However, Although Bose was unusually driven and charismatic, the Japanese considered him to be militarily unskilled, and his soldierly effort was short-lived.
- In late 1944 and early 1945, the Indian Army reversed the Japanese attack on India. Almost half the Japanese forces and the participating INA contingent were killed.
- The remaining INA was driven down the Malay Peninsula and surrendered with the recapture of Singapore.
- Bose is known to have escaped to Manchuria to seek refuge in the Soviet Union.
- As per reports, he died when his overloaded plane crashed in Taiwan on August 18, 1945.
- However, some Indians did not believe that the crash had occurred.
National Girl Child Day: National Girl Child Day is celebrated every year on 24th January.
Key Points:
- Gender discrimination is a major problem that girls or women face throughout their life.
- The objective behind celebrating the National Girl Child Day is to provide all support and opportunities to the girls of the country.
- It also aims towards promoting awareness about the rights of the girl child and to increase awareness on the importance of girls’ education, and their health and nutrition.
History:
- National Girl Child Day was first initiated in 2008 by the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- The main focus is on changing society’s attitude towards girls, decreasing female feticide, and creating awareness about the decreasing sex ratio.
Steps taken by the Government to improve the condition of girl child:
The government has taken several steps over the years to improve the conditions of girls and has started several campaigns and programmes.
These are -
- Save the Girl Child,
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao,
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana,
- CBSE Udaan Scheme,
- Reservation for women in colleges and universities, and
- National Scheme of Incentive to Girls for Secondary Education.
National Girl Child 2022:
- Ministry of Culture will organize Rangoli Utsav ‘Umang’ as part of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- In the event, it is proposed that the participating teams will make Rangoli decorations for about one kilometer of length on the roads and squares that have been named after the female freedom fighters or the female role models of the country.
- The rangoli decorations are being done at more than 50 locations across the country.
- The Ministry said that it would be a great opportunity to celebrate the Girl Child Day and Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav through this event.
About Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav:
- Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav’ is an initiative of the Government of India to celebrate and commemorate 75 years of progressive India and the glorious history of its people, culture, and achievements.
Portal of NIPER: Union Minister for Chemicals and Fertilizers Dr Mansukh Mandaviya recently launched the research portal of the National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research, (NIPER), in New Delhi.
Minister of State for Chemicals and Fertilizers Bhagwanth Khuba and Niti Aayog member, Health, Dr V. K Paul were also present on the occasion.
Aim:
NIPER Research Portal has been created with the aim to disseminate the information about all the NIPERs and their research activities, patents filed and Publication information in one place so that industry and other stakeholders know about them.
Purpose:
- The purpose of this portal is to authenticate the availability of the research work that is ongoing.
- It will help other researchers and especially the industry to get in touch with the relevant organization so that they can work together and make the research more purposeful and meaningful.
- For long, research institutes have been working in silos or isolation.
- The research portal will try to bring together research institutions spread across different departments within government and also these institutions with industries.
About NIPER:
- National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPERs) are a group of national-level institutes of pharmaceutical sciences in India.
- NIPERs were established in 1998.
- The Government of India (GoI) has declared the NIPERs as Institutes of National Importance.
- They operate as autonomous bodies under the aegis of the Department of Pharmaceuticals, Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers.
- They are located in 7 cities in India: Ahmedabad, Guwahati, Hyderabad, Hajipur, Kolkata, S.A.S. Nagar and Raebareli.
Swachhata Start-Up Challenge: The Ministry of Housing & Urban Affairs (MoHUA) in partnership with the Department of Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) and Agence Française de Développement (AFD) launched the Swachhata Start-Up Challenge on 27th January 2022.
Key Points:
The official notice about this Start-Up was released in the Press Information Bureau PIB, Government of India page.
The Swachhata Start-Up Challenge has been launched for the following reasons:-
- To provide an impetus to innovative start-ups to come forward and drive catalytic transformation in the sanitation and waste management sector.
- In line with Hon’ble Prime Minister’s vision for ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ and ‘Make in India’ the Challenge seeks to promote an enabling environment for enterprise development under Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban 2.0 (SBM-U 2.0).
- To capitalize on the start-up movement by providing opportunities for entrepreneurship to young innovators to create socially impactful and market-ready business solutions.
Eligibility:
The Challenge is open to start-ups registered in India and French actors collaborating with an Indian start-up (as a joint venture).
Thematic Areas:
The challenge is open across four thematic areas viz.
I.Social inclusion,
II.Zero dump (solid waste management),
III.Plastic waste management and
IV.Transparency through digital enablement.
Awards and Prizes:
- Top 10 startups will receive ₹25 lakhs along with one year of dedicated incubation support from French Tech which is the French government’s initiative to promote start-ups.
- The eligible startups will get additional incentives which include up to ₹ 50 Lakhs follow-on investment from Villgro, the implementation partner of the Challenge and up to 100,000 USD worth of credits and technology support from technology partner Amazon Web Services, to each winner.
73rd Republic Day: India is celebrated the 73rd Republic Day on 26 January 2022.
Key Highlights:
- The celebrations this year are special as India is in the 75th year of Independence – being celebrated as ‘Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav’.
- India did not have a Chief Guest this year due to the global situation arising out of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- According to the Ministry of Defence (MoD), for the first time, an Indian Air Force (IAF) showcased a grand flypast by 75 aircraft or helicopters.
- Again, for the first time around 480 dancers performed during the cultural programme at the parade.
- They were selected through a nationwide Vande Bharatam dance competition.
- A total of 24 tableaux were a part of the Republic Day parade.
- The musical representation of India showcased its unity and diversity and portrayed how traditional meets modern, folk meets contemporary, popular meets unexplored in a melting pot of styles and rhythms.
- Earlier, the government had dropped Abide With Me, a hymn that has been used in the Beating the Retreat ceremony since 1950 from the ceremony.
- It has been replaced by Kavi Pradeep’s Aye Mere Watan Ke Logon, which was written in the wake of the Sino-Indian War.
Beating Retreat:
- Beating the Retreat marks the last ceremony of the nation's Republic Day celebrations, which started on 23 January with PM Modi unveiling the hologram statue of Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose at India Gate.
- A drone show by 1,000 indigenously developed drones has been planned for the Beating the Retreat ceremony, along with projection mapping will be shown for the first time.
Republic Day:
- Every year, Republic Day is celebrated in India on 26 January to commemorate the date on which the Constitution of India came into effect and the country became a republic.
- This day defines the importance of having a proper constitution that all the citizens must abide by.
- It is celebrated with festivities and patriotic fervor all around the country.
- About the Indian constitution:
- The Constitution of India or the Bharatiya Samvidhana is the supreme law of India.
- The document lays down the framework demarcating fundamental political code, structure, procedures, powers, and duties of government institutions and sets out fundamental rights, directive principles, and the duties of citizens.
- The Constitution of India was adopted by the Constituent Assembly on 26th November 1949 but came into force on 26th January 1950.
Background:
- India became independent on the 15th of august, 1947.
- The laws, before the enactment of the constitution, were running on the basis of the Government of India (GoI) Act 1935.
- GoI appointed a Drafting Committee on 28th of August 1947 to draft it and Dr, B. R. Ambedkar as the Chairman of the Drafting Committee.
- After almost 3 years, the 308 members of the Assembly, after many consultations and a few modifications finally signed a constitution on the 24th of January 1950.
- It came into effect on the 26th of January 1950.
- Since then, 26th January is celebrated as Republic Day in India.
- And the Constitutional head of India, the President hoists the national flag on this day.
People In News
Param Vishisht Seva Medal (PVSM): Subedar Neeraj Chopra, who created history last year by winning India’s first athletics gold medal in Olympics, was awarded Param Vishisht Seva Medal and fourth highest civilian honour Padma Shri.
Key Points:
- In Tokyo Olympics 2020, Chopra won the gold medal throwing javelin to 87.58 metres.
- The 24-year-old was only the second Indian after shooter Abhinav Bindra to win an individual gold medal at the Olympics. Bindra’s gold came in 2008 in Beijing.
- Along with Chopra, 18 other serving and retired personnel of the Indian Army have been awarded Param Vishisht Seva Medal.
Achievements of Chopra:
- Neeraj Chopra was conferred with the Arjuna Award in 2018.
- Vishisht Seva Medal (VSM) in 2020 for his excellence in sports.
- Chopra was enrolled into the 4 Rajputana Rifles as a Naib Subedar on May 15, 2016.
Note: Naib Subedar is a rank in the Indian army. The Naib Subedars are Junior Commissioned officers. Their ranks are lower than lieutenants and higher than havidars.
- He was a part of the Mission Olympics Wing that operated at the Army Sports Institute located in Pune.
- The Mission Olympics Wing is an initiative of the Indian Army to identify young athletes and give them a secure career so that they can concentrate on sporting activities.
About Param Vishisht Seva Medal (PVSM):
- Param Vishisht Seva Medal (PVSM) is a military award of India.
- It was constituted in 1960.
- It is awarded in recognition to peace-time service of the most exceptional order and may be awarded posthumously.
- All ranks of the Indian Armed Forces including Territorial Army, Auxiliary and Reserve Forces, Nursing officers and other members of the Nursing services and other lawfully constituted Armed Forces are eligible for the award.
- The PVSM is usually accorded to three-star officers for distinguished service to the nation.
- It is equivalent to Sarvottam Yudh Seva Medal.
History:
- The PVSM was originally instituted as the "Vishisht Seva Medal, Class I" on 26 January 1960.
- Five other medals were instituted on the same day: the Sainya Seva Medal, Sena Medal, Nao Sena Medal and the Vayu Sena Medal.
- It was renamed on January 27, 1961, and the badge signed.
Structure of the Medal:
- The medal is round in shape.
- It is 35 mm in diameter.
- It is made of gold gilt.
- A five pointed star is embossed over the medal.
- On the other side, the medal has Indian state emblem.
Additional Info:
Other Military Awards in India:
Peacetime: Param Vishisht Seva medal, Ati Vishishi Seva Medal and Vishisht Seva Medal
Wartime: Yudh Seva Medal, Uttam Yudh Seva Medal, Sarvottam Yudh Seva Medal
Wartime or Peacetime service awards: Vayu Sena Medal (Air Force), Sena Medal (Army) and Nau Sena Medal (Navy)
Dr. V. Anantha Nageswaran: The Government of India (GoI), on 28 January 2022 appointed Venkatraman Anantha Nageswaran as its Chief Economic Advisor (CEA).
Key Highlights:
He has replaced former CEA KV Subramanian.
Prior to this appointment, Dr. Nageswaran has worked as a writer, author, teacher and consultant.
About Dr. V. Anantha Nageswaran:
- Dr Venkatraman Anantha Nageswaran is a distinguished economist and is also involved primarily in the field of academia.
- He was the Dean of the IFMR Graduate School of Business and a distinguished Visiting Professor of Economics at Krea University.
- He holds a Post-Graduate Diploma in Management from the Indian Institute of Management, Ahmedabad and a doctoral degree from the University of Massachusetts in Amherst.
- He has also been a part-time member of the Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister of India from 2019 to 2021.
- He has written various books such as ‘The Economics of Derivatives’ and ‘The Rise of Finance: Causes, Consequences and Cures’.
PM Economic Advisory Council:
- It is an independent body.
- Currently Dr Bibek Debroy is the Chairman of the council.
- The council advises the PM on national and international economic issues.
Padma Awards 2022: The Government of India (GoI), on the eve of 73rd Republic Day announced the Padma Awards 2022.
Key Highlights:
- The Padma Awards are one of the highest civilian awards of India which are given in various disciplines -- literature and education, arts, science and engineering, trade and industry, civil services, public affairs, sports, and medicine.
- The awards are announced on Republic Day every year and are conferred by the President at a ceremonial function around March or April.
- In 2022, the Padma awards are being presented to a diversified list of recipients.
- The President has approved conferment of 128 Padma Awards including 2 duo cases (in a duo case, the Award is counted as one).
- The list comprises 4 Padma Vibhushan, 17 Padma Bhushan and 107 Padma Shri Awards.
- Of them, 34 are women, 13 awards are posthumous, and 10 awards are for persons from the category of Foreigners/NRI/PIO/OCI.
- Most of them accepted the awards gracefully, while the former West Bengal CM Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee refused to accept it.
List of Padma Awards 2022:
Padma Vibhushan (4):
- Padma Vibhushan is to be presented to
- General Bipin Rawat (Posthumous)
- Shri Kalyan Singh (Posthumous)
- Shri Radheyshyam Khemka (Posthumous)
- Ms. Prabha Atre
Padma Bhushan (17):
- Shri Ghulam Nabi Azad
- Shri Victor Banerjee
- Ms. Gurmeet Bawa (Posthumous)
- Shri Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee
- Shri Natarajan Chandrasekaran
- Shri Krishna Ella and Smt. Suchitra
- Ella* (Duo)
- Ms. Madhur Jaffery
- Shri Devendra Jhajharia
- Shri Rashid Khan
- Shri Rajiv Mehrishi
- Shri Satya Narayana Nadella
- Shri Sundararajan Pichai
- Shri Cyrus Poonawalla
- Shri Sanjaya Rajaram (Posthumous)
- Ms. Pratibha Ray
- Swami Sachidanand
- Shri Vashishth Tripathi
Padma Shri (107):
- Shri Prahlad Rai Agarwala
- Prof. Najma Akhtar
- Shri Sumit Antil
- Shri T Senka Ao
- Ms. Kamalini Asthana and Ms.
- Nalini Asthana* (Duo)
- Shri Subbanna Ayyappan
- Shri J K Bajaj
- Shri Sirpi Balasubramaniam
- Srimad Baba Balia
- Ms. Sanghamitra Bandyopadhyay
- Ms. Madhuri Barthwal
- Shri Akhone Asgar Ali Basharat
- Dr. Himmatrao Bawaskar
- Shri Harmohinder Singh Bedi
- Shri Pramod Bhagat
- Shri S Ballesh Bhajantri
- Shri Khandu Wangchuk Bhutia
- Shri Maria Christopher Byrski
- Acharya Chandanaji
- Ms. Sulochana Chavan
- Shri Neeraj Chopra
- Ms. Shakuntala Choudhary
- Shri Sankaranarayana Menon Chundayil
- Shri S Damodaran
- Shri Faisal Ali Dar
- Shri Jagjit Singh Dardi
- Dr. Prokar Dasgupta
- Shri Aditya Prasad Dash
- Dr. Lata Desa
- Shri Malji bhai Desai
- Ms. Basanti Devi
- Ms. Lourembam Bino Devi
- Ms. Muktamani Devi
- Ms. Shyamamani Devi
- Shri Khalil Dhantejvi (Posthumous)
- Shri Savaji Bhai Dholakia
- Shri Arjun Singh Dhurve
- Dr. Vijaykumar Vinayak Dongre
- Shri Chandraprakash Dwivedi
- Shri Dhaneswar Engti
- Shri Om Prakash Gandhi
- Shri Narasimha Rao Garikapati
- Shri Girdhari Ram Ghonju (Posthumous)
- Shri Shaibal Gupta (Posthumous)
- Shri Narasingha Prasad Guru
- Shri Gosaveedu Shaik Hassan (Posthumous)
- Shri Ryuko Hira
- Ms. Sosamma Iype
- Shri Avadh Kishore Jadia
- Ms. Sowcar Janaki
- Ms. Tara Jauhar
- Ms. Vandana Kataria
- Shri H R Keshavamurthy
- Shri Rutger Kortenhorst
- Shri P Narayana Kurup
- Ms. Avani Lekhara
- Shri Moti Lal Madan
- Shri Shivnath Mishra
- Dr. Narendra Prasad Misra (Posthumous)
- Shri Darshanam Mogilaiah
- Shri Guruprasad Mohapatra (Posthumous)
- Shri Thavil Kongampattu A V Murugaiyan
- Ms. R Muthukannammal
- Shri Abdul Khader Nadakattin
- Shri Amai Mahalinga Naik
- Shri Tsering Namgyal
- Shri A K C Natarajan
- Shri V L Nghaka
- Shri Sonu Nigam
- Shri Ram Sahay Panday
- Shri Chirapat Prapandavidya
- Ms. K V Rabiya
- Shri Anil Kumar Rajvanshi
- Shri Sheesh Ram
- Shri Ramachandraiah
- Dr. Sunkara Venkata Adinarayana Rao
- Ms. Gamit Ramilaben Raysingbhai
- Ms. Padmaja Reddy
- Guru Tulku Rinpoche
- Shri Brahmanand Sankhwalkar
- Shri Vidyanand Sarek
- Shri Kali Pada Saren
- Dr. Veeraswamy Seshiah
- Ms. Prabhaben Shah
- Shri Dilip Shahani
- Shri Ram Dayal Sharma
- Shri Vishwamurti Shastri
- Ms. Tatiana Lvovna Shaumyan
- Shri Siddhalingaiah (Posthumous)
- Shri Kaajee Singh
- Shri Konsam Ibomcha Singh
- Shri Prem Singh
- Shri Seth Pal Singh
- Ms. Vidya Vindu Singh
- Baba Iqbal Singh Ji
- Dr. Bhimsen Singhal
- Shri Sivananda
- Shri Ajay Kumar Sonkar
- Ms. Ajita Srivastava
- Sadguru Brahmeshanand Acharya Swami
- Dr. Balaji Tambe (Posthumous)
- Shri Raghuvendra Tanwar
- Dr. Kamlakar Tripathi
- Ms. Lalita Vakil
- Ms. Durga Bai Vyam
- Shri Jyantkumar Maganlal Vyas
- Ms. Badaplin War
About Padma Awards:
- The Padma Awards are among the highest civilian awards of India and are conferred in three categories-- Padma Vibhushan, Padma Bhushan, and Padma Shri.
- The Padma Awards are announced each year on the occasion of India's Republic Day. They are conferred every year by the President of India at ceremonial functions held at Rashtrapati Bhawan between March and April.
- The Padma Awards are being awarded to the citizens since 1954.
- The awards are being presented under the categories such as medicine, literature, industry, public affairs, social service education, and sports.
- Padma Vibhushan is awarded for exceptional and distinguished service.
- Padma Bhushan for distinguished service of a high order.
- Padma Shri for distinguished service in any field.
Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar 2022: 29 Children have been conferred the Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar (PMRBP) for the year 2022.
Key Highlights:
These winners include 15 Boys and 14 Girls, belonging to 21 States and UTs.
They have been selected from all regions of the country for their exceptional achievements in the following categories:-
1)Innovation
2)Social Service
3)Scholastic
4)Sports
5)Art & Culture
6)Bravery
- In order to felicitate and motivate the exceptional works of children, a function was held virtually Due to COVID-19 situation in the country.
- They were facilitated on the occasion of National Girl Child Day today and also as part of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav.
- The Awardees of PMRBP 2021 and 2022 along with their parents and concerned District Magistrate of their respective district joined the event from their district Head Quarters.
- During the function, Hon’ble Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi gave digital certificates to the 61 winners of PMRBP 2021 and 2022 using a Block Chain-driven technology developed by IIT Kanpur under the National Blockchain Project.
- The digital certificates are stored on digital wallets installed on the mobile devices of the recipients.
- The digital certificates issued using blockchain-driven technology are unforgeable, globally verifiable, selectively disclosable and sensitive to user content.
- BlockChain Technology is being used for the first time for giving certificates to awardees.
- During the programme, the cash prize of Rs.1,00,000/- was given to the awardees of PMRBP 2022 which was transferred online to the respective accounts of winners.
List of the winners of PMRBP 2022 is given below:
For Art& Culture:
1)Gauri Maheshwari from Rajasthan
2)Remona Evette Pereira from Karnataka
3)Deviprasad from Kerala
4)Syed Fateen Ahmed from Karnataka
5)Daulas Lambamayum from Manipur
6)Dhritishman Chakraborty from Assam
For Bravery:
1)Gurugu Himapriya from Andhra Pradesh
2)Shivangi Kale from Maharashtra
3)Dhiraj Kumar from Bihar
For Innovation:
1)Shivam Rawat from Uttarakhand
2)Vishalini N C from Tamil Nadu
3)Jui Abhijit Keskar from Maharashtra
4)Puhabi Chakraborti from Tripura
5)Aswatha Biju from Tamil Nadu
6)Banita Dash from Odisha
7)Tanish Sethi from Haryana
For Scholastic:
1)Avi Sharma from Madhya Pradesh
For Social Service:
1)Meedhansh Kumar Gupta from Punjab
2)Abhinav Kumar Choudhary from Uttar Pradesh
3)Pal Sakshi from Bihar
4)Aakarsh Kaushal from Haryana
For Sports:
1)Arushi Kotwal from Jammu & Kashmir
2)Shriya Lohia from Himachal Pradesh
3)Telukunta Virat Chandra from Telangana
4)Chaudhary Singh Choudhary from Uttar Pradesh
5)Jiya Rai from Uttar Pradesh
6)Swayam Patil from Maharashtra
7)Tarushi Gaur from Chandigarh
8)Anvi Vijay Zanzarukia from Gujarat
About PMRBP award:
- The Prime Minister’s National Award for Children, commonly known as the Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Puraskar (PMRRBP), is a civilian award in India.
- It was first awarded in 1996.
- The award had two categories:
1. Bal Kalyan Puraskar
- The Bal Kalyan Puraskar, previously the National Child Welfare Awards, was instituted by the Ministry of Women and Child Development in 1979.
- It was awarded to individuals or organizations that have made outstanding contributions in child development, child protection, or child welfare.
2. Bal Shakti Puraskar
- The Bal Shakti Puraskar, previously the National Child Award, was instituted by the NGO Indian Council for Child Welfare in 1996.
- It was awarded to Indian citizens under the age of 18 for outstanding achievement in innovation, scholastic achievements, social service, arts and culture, bravery, or sports.
- In 2018, the two awards were renamed and combined into the Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar, which is administered by the Ministry of Women and Child Development.
- It is conferred by the President of India in the week preceding Republic Day, 26 January, in the Durbar Hall of Rashtrapati Bhavan in New Delhi.
- The PMRBP award is given by the Government of India (GoI) to children with exceptional abilities and outstanding accomplishments in 6 categories.
- The award carries a cash prize of Rs.1,00,000/-.
Ratan Tata conferred the Assam Baibhav Award: The government of Assam has conferred its highest civilian award ‘Assam Baibhav’ to Industrialist Ratan Tata.
Key Highlights:
The former chairman of Tata Sons received the Asom Baibhav award from Assam governor Jagdish Mukhi.
This prestigious award was conferred to Ratan Tata for his contribution to setting up cancer treatment facilities in the state.
Other Awards winners:
Assam Saurav Award:
Assam Saurav award was conferred on Professor Dipak Chand Jain, Lovlina Borgohain, Professor Kamalendu Deb Krori, Dr Lakshmanan S, and Neel Pawan Baruah.
Assam Gaurav Award:
Assam Gaurav award was conferred on Manoj Kumar Basumatary, Munindra Nath Ngatey, Dharanidhar Boro, Hemoprabha Chutia, Dr Basanta Hazarika, Kaushik Baruah, Khorsing Terang, Akash Jyoti Gogoi, Namita Kalita, Dr Asif Iqbal, Kalpana Boro, Boby Hazarika, and Bormita Momin.
About Ratan Tata:
- Ratan Naval Tata (born 28 December 1937) is an Indian industrialist, philanthropist, and former chairman of Tata Sons.
- He was also chairman of Tata Group, from 1990 to 2012.
- He was then again, the interim chairman, from October 2016 through February 2017.
- He continues to head its charitable trusts.
- He is a scion of the Tata family, and son of Naval Tata who was later adopted by Ratanji Tata, son of Jamsetji Tata, the founder of Tata Group.
Awards:
- He has been awarded the Padma Bhushan (2000), Padma Vibhushan (2008), CNN-IBN Indian of the Year in Business.
Places In News
Tiwa and Gorkha Extremists: Almost 250 members of two extremist organizations in Assam laid down their arms before Chief Minister Himanta Biswa Sarma at a formal programme in Guwahati.
Key Points:
- The organizations are the Tiwa Liberation Army (TLA) and the United Gorkha People’s Organisation (UGPO).
- Out of them, 169 were UGPO cadres and 77 were TLA cadres.
- Both were ethnicity-based extremist organizations.
- The TLA was formed in 2014 to cater to the aspirations of the Tiwa community. This group was active in Morigaon, Nagaon and West Karbi Anglong districts of central Assam.
- The UGPO was formed in 2007.
- It was most active in the Bodoland Territorial Region and Biswanath district.
- With this only two active insurgent groups now remain in the state, namely the United Liberation Front of Asom-Independent (ULFA-I) and Kamtapur Liberation Organisation (KLO).
Note: Bodo Peace Accord was signed with the Centre two years ago.
About Tiwa:
- Tiwa (Lalung) is an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the states of Assam and Meghalaya in north-eastern India but
- are also found in some areas of Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur and Nagaland.
- They are recognized as a Scheduled tribe within the State of Assam.
- They were known as Lalungs in the Assamese Buranjis and in Colonial literature and in the Constitution of India, though members of the group prefer to call themselves Tiwa.
- Tiwa means "the people who were lifted from below".
About Assam:
- Assam is a state in northeastern India known for its wildlife, archeological sites and tea plantations. It is situated south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys.
- Assam is known for Assam tea and Assam silk.
- The state was the first site for oil drilling in Asia.
- Its capital is Dispur.
- The current Governor and the Chief Minister of Assam are Professor Jagdish Mukhi and Himanta Biswas Sarma respectively.
Sangolli Rayanna: Karnataka State Government is set to build a military school in the name of Sangoli Rayanna at a cost of Rs 180 crores.
Key Points:
- This was announced by the Chief Minister of Karnataka Basavaraj Bommaion on the Remembrance Day of the braveheart Sangolli Rayanna who fought the Britishers bravely.
- The school will be administrated by the defence ministry.
Other developments to honour Sangolli Rayana:
- Work on developing Sangolli Rayana's tomb at the spot where he attained martyrdom is also going to be taken up.
- Further, the development of a rock garden on 10 acres of land at his birthplace Sangolli has also been approved.
- These memorials are being built to provide a glimpse into the life of Rayanna for the youth.
- In 2015, the main railway station was renamed as Sangoli Rayanna railway station.
About Sangolli Rayanna:
- Sangolli Rayanna (15 August 1796 – 26 January 1831) was an Indian military Shetsanadi (solider) and warrior from the Kittur princely state of Karnataka.
- He fought against the Doctrine of Lapse alongside Rani Chennamma till his death.
- The Britishers killed the king and prince of Kittur kingdom.
- As there was no legal heir to the throne, they wanted to take control over Kittur kingdom under the Doctrine of Lapse.
1824 rebellion:
- He played a major role in the 1824 rebellion.
- Most of the land in Kittur kingdom was confiscated and the leftover land was heavily taxed.
- He created a guerrilla army.
- He and his army moved from place to place, burnt government offices, plundered treasuries.
- He trained and built an army from the common people.
- The Britishers caught him in 1830.
- He was hanged to death in a Banyan tree in Belagavi district in 1831.
- His last words to the British were “You might hang me but remember, a Rayanna from every home of this country will be born until we get independence.”
- Rayanna was buried near Nandagad.
In the memory of Krantiveera Sangolli Rayanna:
- Rayanna was helped by Gajaveera, a Siddi warrior in his revolt against the British in 1829-30.
- Gajaveera planted a Banyan tree in his grave.
- To this date, the tree stands majestic. A temple has been built for Rayanna under the tree.
- Also, Ashoka Stambha was installed near the tree.
- The temple has a statue of Rayanna with two wooden weights.
- The weights were used by Rayanna himself for bodybuilding.
About Karnataka:
- It is a state in the southwestern region of India.
- It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act.
- Originally known as the State of Mysore, it was renamed Karnataka in 1973.
- It is bordered by the Arabian Sea to the west, Goa to the northwest, Maharashtra to the north, Telangana to the northeast, Andhra Pradesh to the east, Tamil Nadu to the southeast, and Kerala to the south.
- It is the only southern state to have land borders with all of the other 4 southern Indian sister states.
- Its capital city is Bangalore.
- The current Chief Minister and Governor of Karnataka are Basavaraj Bommai and Thawar Chand Gehlot respectively.
First Graphene Innovation Center of India: India's first graphene innovation center is going to be established in Kerala.
Key Points:
- This centre is going to be established by the Digital University Kerala (DUK), along with the Centre for Materials for Electronics Technology (C-MET) in Thrissur for Rs 86.41 crore.
- This will be the first graphene Research and Development (R&D) incubation centre in the country.
- Tata Steel Limited is set to be the industrial partner of the centre.
- This project was approved by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, Government of India (GoI).
- The project is going to be implemented with the support of the Kerala government.
- It is expected to accelerate the state’s growth in the knowledge industry sector.
What is Graphene?
- Graphene is an allotrope of carbon consisting of a single layer of atoms arranged in a two-dimensional honeycomb lattice nanostructure.
- The name is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, reflecting the fact that the graphite allotrope of carbon contains numerous double bonds.
- Graphene is known for its extraordinary electrical and electronic properties, and as per the latest research, it could replace indium and thereby bring down the cost of OLED (organic light-emitting diode) screens in smartphones.
- Graphene has good chemical stability, high electrical conductivity and a large surface area while being transparent and lightweight.
About Kerala:
- It is a state on the southwestern Malabar Coast of India.
- It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile states of Travancore-Cochin and Madras.
- It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Lakshadweep Sea to the west. Its capital is Thiruvananthapuram.
- The current Governor and Chief Minister of Kerala are Arif Mohammad Khan and Pinarayi Vijayan respectively.
Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve (STR): Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve (Erode district, Tamil Nadu) has recently been awarded the prestigious TX2 award after its tiger numbers doubled to 80 since 2010.
About STR:
- Sathyamangalam wildlife sanctuary was declared a tiger reserve in 2013.
- The reserve spreads across 1,411.60 sq km.
- It is an important link between the Nilgiris and Eastern Ghats landscape.
- The Nilgiri biosphere landscape that this reserve is part of is currently the home to the largest tiger population in the world.
- It is connected to other well-established tiger habitats like Bandipur Tiger Reserve, Mudumalai Tiger Reserve, and BR Hills Tiger Reserve.
- Apart from the STR, the Bardia National Park in Nepal has won this year’s TX2 award for doubling the population of wild tigers.
About the TX2 award:
- The award acknowledges the efforts by the State governments and the local communities which have played one of the most important roles to turn a relatively new tiger reserve into one of the source populations of tigers in India.
- The awards are presented by the Conservation Assured Tiger Standards (CA|TS), Fauna and Flora International (FFI), Global Tiger Forum (GTF), IUCN’s Integrated Tiger Habitat Conservation Programme (ITHCP), Panthera, UNDP, The Lion’s Share, Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) and WWF.
Science and Technology
Detection of Oral Cancer: Scientists from IIT Kharagpur have developed a portable, user-friendly, and non-invasive device for detecting oral cancer in resource-constrained clinical settings.
Key Highlights:
The researchers from the Guru Nanak Institute of Dental Sciences in West Bengal supervised the clinical trials, and have established the efficacy of the new method in differentiating cancerous and precancerous stages of suspected oral abnormalities, as verified by high-standard biopsy reports.
The research has been published recently in the prestigious Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), USA.
About the new technology:
- This is a low-cost, handheld imaging device.
- The device screens the cancerous stage by measuring the blood flow rate in the tissues.
- The blood perfusion imager, which combines a miniature far-infrared camera and a humidity sensor, are electronically controlled and interfaced with a combined physics-based and data-driven software engine.
- The device has sensors and controllers. The biological data collected by these elements are fed into a computer-simulated software engine.
- The engine classifies pre-cancer and cancer cases.
Need for the technology:
- Cancer of the oral cavity remains one of the major causes of morbidity and mortality in socially-challenged and underserved communities.
- Around a fifth of the women population suffers from cancer.
- Also, oral cancer is high in India which is mainly because of tobacco.
- In the last decade, the incidence of oral cancer has increased among young adults and women.
- There is an 80% chance on average of a five-year survival rate if diagnosed early.
- The survival rate drops to 65% or less in more advanced stages of the disease.
Efforts by the Indian Government:
- The Government of India (GoI) has set up National Cancer Control Programme.
- The programme has launched regional cancer centres.
About NPCDCS:
- NPCDCS is the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular disease and Stroke.
- NPCDCS was launched in 2010.
- The main objective of this programme is strengthening infrastructure, human resource development, health promotion, early diagnosis, management and referral.
Ultra-Long Period Magneta: Scientists have detected what appears to be an incredibly dense star behaving unlike anything else ever seen.
Key Points:
- They suspect it might be a type of exotic astrophysical object whose existence has until now been only hypothesized.
- The object was spotted using the Murchison Widefield Array telescope in outback Western Australia.
- It unleashed huge bursts of energy roughly three times per hour when viewed from Earth during two months in 2018.
- It may be the first known example of what is called an”ultra-long period magnetar.”
- This is a variety of neutron stars - the compact collapsed core of a massive star that exploded as a supernova - that is highly magnetized and rotates relatively slowly, as opposed to fast-spinning neutron star objects called pulsars that appear from Earth to be blinking on and off within milliseconds or seconds.
- It is located relatively close to Earth in cosmic terms, roughly 4,200 light-years away, where a light-year is the distance light travels in a year, 9.5 trillion km.
- Neutron stars including pulsars are among the universe's densest objects.
- They are roughly 12 km in diameter - akin to the size of a city - but with more mass than our Sun.
- The researchers said that a neutron star with an extreme magnetic field, a magnetar, could potentially power the radio pulsations.
Vikas Engine: The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully test-fired the Vikas engine that would power India’s first human-carry rocket (Gaganyaan human space mission).
Key Highlights:
- This qualification test of the Vikas Engine for the Gaganyaan human space mission was conducted by ISRO at Mahendragiri, Tamil Nadu.
- The test was carried out to verify the robustness of the engine by operating beyond its nominal operating conditions (fuel-oxidizer ratio and chamber pressure).
- The performance of the engine met the test objectives and the engine parameters were closely matching with the predictions during the entire duration of the test.
Objective of Gaganyaan Programme:
The objective of the Gaganyaan programme is to demonstrate the capability to send humans to low earth orbit onboard an Indian launch vehicle and bring them back to earth.
Note: Gaganyaan is India's first manned mission to space.
About ISRO:
- ISRO is an abbreviation for the Indian Space Research Organization.
- ISRO is the space agency of the Government of India (GoI) and was formed on 15 August 1969.
- It superseded the erstwhile “Indian National Committee For Space Research” (INCOSPAR) which was established in 1962 by the efforts of Independent India's first prime minister‚ Jawaharlal Nehru‚ and his close aide and scientist Vikram Sarabhai.
- In 1972, the Government of India had set up a Space Commission and the Department of Space (DOS), bringing ISRO under the DOS. ISRO then embarked on its mission to provide the Nation space-based services and to develop the technologies to achieve the same independently.
- Its vision is to “harness space technology for natural development while pursuing space science research & planetary exploration”.
- ISRO built India’s first satellite Aryabhata.
- It is headquartered in Bangalore, India. The current Chairman of ISRO is Eminent rocket scientist Dr S Somanath.
Data Privacy Day 2022: Data Privacy Day is celebrated on January 28, every year across the world.
Key Points:
The purpose of Data Privacy Day is to raise awareness and promote privacy and data protection best practices.
It is currently observed in the United States, Canada, Israel, Nigeria and 47 European countries.
Theme of 2022:
- The theme for 2022 is ‘Privacy Matters’.
- It instills a sense of accountability that Privacy is integral to every individual’s life.
Key Facts:
- Observance of the day is “an international effort of creating awareness on the importance of respecting privacy, enabling trust and safeguarding data”.
- Data privacy has been one of the hot topics of discussion in a digitally connected world.
- The issue has become an important topic of discussion in the digitally connected world, especially at the time of the coronavirus disease (Covid-19) pandemic when more and more people are forced to spend time in the online world.
- Now, people are more concerned about protecting their data, with the proliferation of instant messaging mobile applications like WhatsApp and Telegram.
- Failure in safeguarding one’s privacy could result in exploitation as well as criminal offences against internet users.
Objective:
- The main objective of the day is to sensitize individuals and disseminate privacy practices and principles.
- It encourages everyone to own their privacy responsibilities to create a culture of privacy.
History:
- The Council in Europe first initiated Data Privacy Day in 2007.
- Their mission grew to a global platform. In 2009, the United States House of Representatives recognized National Data Privacy Day.
- The United States Senate later recognized Data Privacy Day in 2010 and 2011.
- Since then, various groups and organizations continue supporting the observance annually.
Why is it necessary to ensure data privacy?
It is necessary to ensure data privacy for the following reasons:-
- Personal data has been collected, manipulated, and shared or sold for decades, then manipulated further for profit by banking institutions, product manufacturers, political parties, nonprofit organizations, ad agencies, polling groups, airlines, grocery stores, credit agencies, and many others.
- Personal data is collected through a variety of media.
- Digital technologies have made the collection of personal data easier, both legally and illegally.
What is being done to ensure data privacy?
- To ensure data privacy, some companies have rolled out many security features on mobile applications, such as “end-to-end encryption”. For instance, WhatsApp and Telegram are providing this feature.
- This feature ensures that the exchange of information is not visible to anyone and it remains restricted to two people involved in a particular conversation.
Note: In India, at present, sensitive data is regulated by the Information Technology Act 2000.
Difference between Data Privacy and Data security:
- Data privacy is not the same thing as data security, although the two are closely connected and interdependent.
- Data security is like putting steel bars on windows to make it difficult for others to burglarize your home; whereas data privacy is more like pulling down the window shades so no one can look inside to see any of your activities.
Sports
ICC Women Cricketer of the year 2021: Indian opener Smriti Manadhana of India has won the Rachael Heyhoe Flint Award for the ICC Women Cricketer of the year 2021.
Key Highlights:
- The left-handed opener beat competition from Tammy Beaumont of England, Lizelle Lee of South Africa and Gaby Lewis of Ireland to clinch the honour.
- Mandhana is the only Indian to win the award twice in her career, having earlier been awarded the trophy in 2018.
- The only other Indian to receive the award was Jhulan Goswami in 2007.
- Australian all-rounder Ellyse Perry of Australia was the first woman player to win the award and remains the only player to win the award three times.
ICC Women’s ODI Cricketer of the year:
- Lizelle Lee of South Africa whose average is 90.28 was named as the ICC Women’s ODI Cricketer of the year, 2021.
- In March 2021, Lee played a crucial role in South Africa’s win against India.
- During the test series, Lee hit 288 runs that led the team to win against India. Lee was named as the Player of the series.
About Smriti Mandhana:
- Smriti plays for the Indian cricket team.
- She entered the national team in 2017 and on that very same year she played for the world cup.
- Star batter Mandhana, 25, has scored 855 runs in 22 internationals at an average of 38.86 with one century and five half-centuries in 2021.
- In 2019, Smriti became the captain of the team.
- She won the CEAT International Woman Cricketer award in 219.
- She was the third fastest cricketer to score 2000 runs in WODI.
- She had a huge role in India's two wins against South Africa at home; scoring an unbeaten 80 in India's chase of 158 in the second ODI and later helped India level the series with her 48 not out in the win in the final T20I match.
About the award:
- The ICC Women Cricketer of the year is presented as a part of the ICC Awards ceremony.
- The award was introduced in 2006.
- It adjudges the best international cricketer based on their twelve-month period performances.
- In 2017, the award was renamed as Rachael Heyhoe Flint.
- Rachael Heyhoe Flint is a woman cricketer who was the captain of the British cricket team between 1966 and 1978.
- Between 2006 and 2011, the award was presented in a single category called “Women’s Player of the Year”.
- In 2017, separate categories were introduced for One Day and T20 cricket.
ICC Awards 2021 winners: International Cricket Council recently announced the 17th edition of ICC Awards 2021 winners.
Key Highlights:
- The cricketers from across the world were honored for their magnificent performances in the previous year between January 01, 2021, and December 31, 2021.
- ICC awards 2021 include Emerging Cricketer of the Year, T20I Cricketer of the Year and Associate Cricketer of the Year for both men’s and women’s cricket among others.
Winners are listed below:
- Rachael Heyhoe Flint Trophy for ICC Women’s Cricketer of the Year: Smriti Mandhana (India)
- Sir Garfield Sobers Trophy for ICC Men’s Cricketer of the Year: Shaheen Afridi (Pakistan)
- ICC Umpire of the Year: Marais Erasmus
- ICC Men’s T20I Cricketer of the Year: Mohammad Rizwan (Pakistan)
- ICC Women’s T20I Cricketer of the Year: Tammy Beaumont (England)
- ICC Emerging Men’s Cricketer of the Year: Janneman Malan (South Africa)
- ICC Emerging Women’s Cricketer of the Year: Fatima Sana (Pakistan)
- ICC Men’s Associate Cricketer of the Year: Zeeshan Maqsood (Oman)
- ICC Women’s Associate Cricketer of the Year: Andrea-Mae Zepeda (Austria)
- ICC Men’s ODI Cricketer of the Year: Babar Azam (Pakistan)
- ICC Women’s ODI Cricketer of the Year: Lizelle Lee (South Africa)
- ICC Men’s Test Cricketer of the Year: Joe Root (England)
World Rapid Chess Champion 2021: Uzbekistan's Nodirbek Abdusattorov recently won the World Rapid Chess Championship 2021.
Key Highlights:
- Abdusattorov defeated Ian Nepomniachtchi (Russia) in a tiebreaker to win the World Rapid Chess Championship 2021.
- This win by Abdusattorov has dethroned Magnus Carlsen who is the current World Number 1.
- Magnus Carlsen won the FIDE Championship in 2020.
- Nodirbek took home the title and a $60,000 prize after losing only one match to Ukrainian Anton Korobov and tying in five others.
- The Uzbeki Grand Master (GM), received the Mard Uglon (“Brave Son”) Presidential medal.
Arts
GI Tag for Narasingapettai Nagaswaram: The geographical indication tag has recently been awarded to the Narasingapettai Nagaswaram, under the category of musical instruments of class 15.
Key Highlights:
- Narasinghapettai nagaswaram is a classical wind music instrument of Tamil Nadu.
- The musical instrument is traditionally made by artisans based in a village near Kumbakonam who make them through specialized processing skills, a technique inherited from their forefathers.
- It is manufactured by them through a process that requires specialized skills.
- The application for receiving the GI tag was filed by Tamil Nadu’s Nodal Officer for GI Registration of Products on behalf of Thanjavur Musical Instruments Workers Co-operative Cottage Industrial Society Limited.
About the Narasingapettai Nagaswaram:
- Nagaswaram is a wind instrument made of wood and metal.
- The instrument has also been accorded a high status as a ‘Mangala Vadyam’ and is played in religious ceremonies, auspicious occasions, and classical concerts.
- The nagaswaram that is being used by artists nowadays is named Pari nagaswaram and that is longer than the Thimiri.
- This musical instrument has a body that is cylindrical in shape and takes the shape of a bell at the bottom.
- This form of the nagaswaram provides volume and tone.
- The instrument’s length is two and a half feet.
About the manufacturing process of Narasinghapettai nagaswaram:
The double-reeded instrument is made up of wood and has two parts. They are -
1.A conical tube and
2.A metal bell.
- The major portion of the ‘Narasinghapettai nagaswaram’ is made from the Aacha or Hardwickia binata tree.
- Most of the time, to make nagaswaram, the artisans use drilling machines, carpentry tools, and sometimes, woods from the parts of old houses are also used.
- The horn-like portion of Nagaswaram is known as ‘Olavi’ and the loudspeaker-like portion is called ‘anasu’.
- Jeevali is played at one end of the horn.
- It is through this ‘jeevali’ that air is blown.
Note: It is believed that Lord Shiva gifted the instrument to the demon, Nagasuran. Furthermore, it has the shape of a snake, and nagas (meaning snakes) used this instrument, hence it came to be known as nagaswaram.
The advantages of obtaining a GI tag:
Getting the GI tag can be beneficial in many ways. The product and the manufacturer, both get benefits in addition to economic and cultural benefits.
Financial Assistance:
- The GI tag will help the artisans receive financial assistance from the Indian government.
- Further, it can also boost the trade of nagaswaram makers.
Benefits to country:
- Furthermore, as a country, it is not just a matter of pride but the GI tag is also an indicator of quality.
- When a product gets the tag, it means that the place it originates or belongs too, has the best quality products.
- This increases the significance and the popularity of the product.
- It enhances export opportunities.
- It also promotes government projects such as Vocal for Local, Buy Tribal, domestic and rural tourism, and other initiatives.
Protects the culture:
- Indian artisans possess unique skills and knowledge of traditional practices and methods, passed down from generation to generation, which needs to be protected and promoted.
- With GI tags, the products get due acknowledgment, promotion, and protection.
Dol Utsav: The 'Dol Utsav' or 'Dol Jatra,' which is the festival of colours was celebrated in West Bengal, marking the spring season's onset.
This year, the festival will be celebrated on 18 March 2022 as per the Hindu calendar.
About Dol Jatra:
- Dol Jatra is celebrated to revel in the everlasting bond of love between Lord Krishna and Radha.
- It is believed that on this special day, Lord Krishna expressed his love for his beloved Radha.
- According to the Hindu calendar, Dol Purnima or Dol Jatra falls on the full moon day in the month of Phalgun.
- It also marks the final festival of the year in the Bengali calendar.
- It is predominantly celebrated in West Bengal, Odisha and Assam.
- In the Eastern region of India, the festival of spring is well known as Dol Jatra, Dol Utsav, Dol Purnima and Basanta Utsav.
- The majestic festival is well known for throwing 'gulaal' or 'aabir' on others and singing and dancing in cultural programs.
- The festival has an added significance for people living in Bengal, as the day marks the birth anniversary of Chaitanya Mahaprabhu(1485–1533).
- Chaitanya Mahaprabhu was a great 16th century Vaishnava saint and poet, who was also regarded as an incarnation of Krishna by some.
- Besides being a great spiritual leader, he was also the founder of Gaudiya Vaishnavism.
- One of the best and most famous celebrations of Dol Purnima is well known within the temples of ISKON and particularly the one in Mayapur, the headquarters.
Note: Dol Jatra differs from Holi as it is the last festival of the Bengali Year. Coloured powder is a key part of this festival, and is known as 'phag' in Bengal.
Economics
Gulf Business & Investment Summit: Delegates from 33 companies from the United Arab Emirates (UAE), Saudi Arabia and Hongkong recently arrived in Srinagar to instill confidence and familiarize with “growing conducive situation in J&K for investments.
- It will also see that the MoUs amounting to Rs. 3,000 crores, signed earlier this year, are utilized properly.
Key Points about the Meet:
- The Gulf Business & Investment Summit was organized at the Sher-e-Kashmir International Convention Centre (SKICC) in Srinagar on 22March 2022.
- The Investment Summit was attended by CEOs of top UAE and Hong Kong Companies; Women Entrepreneurs, Start-up representatives and Exporters.
- For the first time in Jammu Kashmir's history, Saudi Arabia-based investor has shown interest in business opportunities in Jammu & Kashmir.
- Women entrepreneurs, who are being provided assistance in the form of capacity building, access to credit, and market linkages under the “Hausla- inspiring her growth” programme also pitched their models for further investment. These included- SEED solutions, Ecokash, and Masha.
- Managing Director, Jammu and Kashmir Trade Promotion Organization (JKTPO), Ms. Ankita Kar gave a detailed presentation on Investment opportunities in Jammu and Kashmir highlighting the investment plans, policy support, focus sectors and ease of doing business.
- Meanwhile, Pashmkaar, Sarveshwar Group, Sky Robo Drones Pvt Ltd, BST Organics Pvt Ltd, ESPA Learn Pvt Ltd, Fastbeetle, Reem Automotives, Orchardly, JKTDC, Peaks Group of Companies, other entrepreneurs and startups showcased their products.
- They pitched their ideas to the investors for investment and answered their queries during the interactive session.
- Lt Governor Manoj Sinha also addressed a press conference on the sidelines of the ongoing Gulf Business & Investment Summit which is aimed at providing a platform for the foreign business delegates to explore a host of investment opportunities in the UT of Jammu & Kashmir.
Background:
- The J&K government had signed the MoUs in January with the UAE–based companies, including industrial giants like Emaar, Lulu, MATU Investments, Al Maya Group, GL Employment Brokerage LLC, Century Financial, IT giant Noon e–commerce etc.
- Around 16,000 kanals (1,999.9 acres) land bank has already been opened for investments in Kashmir.
- This conference is in accordance with the government's efforts to build favourable infrastructure for the promotion of a business-friendly environment and regional exports.
Note: In February, the UAE and India signed a free trade agreement that cuts duties on almost 90 percent of goods traded between them, including metals, minerals, petrochemicals, and petroleum.
Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH): The Governor, Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Shri Shaktikanta Das inaugurated the Reserve Bank Innovation Hub (RBIH) today (March 24, 2022) in Bengaluru.
Key Points:
- The RBI has set up the RBIH as a Section 8 company under Companies Act, 2013.
- The hub has been set up with an initial capital contribution of Rs 100 crore to encourage and nurture financial innovation.
- The new unit has an independent board with Shri Senapathy (Kris) Gopalakrishnan as Chairman and other eminent persons from industry and academia as members.
- RBIH aims to create an ecosystem that focuses on promoting access to financial services and products for the low-income population in the country.
- This is in line with the objective behind establishment of RBIH i.e., to bring world class innovation to financial sector in India, coupled with the underlying theme of financial inclusion.
- The Hub would bring convergence among various stakeholders (BFSI Sector, Start-up ecosystem, Regulators & Academia) in the financial innovation space.
About RBI:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is India's central bank, which controls the issue and supply of the Indian rupee.
- It carries out India's monetary policy and exercises supervision and control over banks and non-banking finance companies in India.
- RBI was set up in 1935 under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- It was nationalized in 1949.
- It is headquartered in Mumbai.
- Note: It was first headquartered in Kolkata, West Bengal
- RBI plays an important part in the Development Strategy of the Government of India.
- The current Governor of RBI is Shaktikanta Das.
About RBI's Central Board of Directors:
- The RBI is governed by the Central Board of Directors.
- The directors are appointed by the Government of India under the Reserve Bank of India Act.
- The Central Board consists of Governor, four Deputy Governors, two finance ministry representatives and four directors to represent local boards.
- These local boards are headquartered in Kolkata, Mumbai, Chennai and New Delhi.
- The concept of RBI was based on the strategies formulated by Dr Ambedkar in his book “The Problem of the Rupee”.
Export of Regional and GI Agri Products: The Ministry of Commerce and Industry is working to identify new GI-tagged Agri products so that they can be exported to new destinations.
Key Points:
- Great emphasis has also been placed by the government on connecting farmer producer companies, farmer producing organizations and exporters to create an export hub in Lal Bahadur Shastri International Airport, Varanasi.
- The country’s agriculture sector has played an important role in exports, especially during the pandemic thus cementing India’s place as an emerging major global food and agriculture product supplier.
About GI tag:
- A geographical Indication (GI) tag is a unique identifier that is given to a product, which defines the region of origin of that product.
- This tag also signifies the product’s origin as that region’s intellectual property.
- GI tag is a unique identity that one country cannot claim to be its own.
About GI products are exported from India:
- Darjeeling Tea and Basmati rice are the two most popular products that are exported from India.
- The government is trying to identify other such products which if marketed properly can reach more buyers across the world.
Trial Shipments of GI Products:
Keeping in mind the Vocal for Local and Atmanirbhar Bharat initiatives the government, through the Agricultural and Processed Food Export Development Authority (APEDA), has been trialling shipments into new markets across the world for certain products like
- Naga Mircha,
- Kala Namak rice,
- Bangalore Rose onion,
- Assam Kaji Nemu,
- GI varieties of Mangoes,
- Nagpur oranges,
- Bhalia wheat,
- GI-tagged Shahi Litchi,
- Bardhaman Sitabhog and Mihidana,
- Madurai Malli,
- Jalgaon Banana,
- Dahanu Gholvad Sapota,
- Marayoor jaggery,
- Vazhakulam pineapple, etc.
A lot of new GI products have been exported from the country to various locations across the world in 2021 such as -
- Joynagar Moa from West Bengal to Bahrain.
- GI tagged products like mangoes; litchis have also been exported to other countries like Italy, South Korea, the UK, the USA, and the UAE etc.
- GI tagged products from the northeast like Mizo Chilli, Meghalaya Khasi Mandarin, etc are also being promoted.
Promotion of GI Products of India:
- APEDA is constantly working towards promoting GI products across the world so that they can be exported to a global market.
- To promote the unique GI Products from the North Eastern Region such as Manipur Black Rice (Chak-Hao), Manipur Kachai Lemon, Mizo Chilli, Arunachal Orange, Meghalaya Khasi Mandarin, Assam Kaji Nemu, Karbi Anglong Ginger, Joha Rice, and Tripura Queen Pineapple, Centre through APEDA has been organizing buyer-seller meets.
- It has been conducting awareness and capacity-building workshops with the participation of representatives of the NER States, FPOs/FPCs, Exporters, Associations, and Government Departments such as Indian Railways, AAICLAS, NAFED, DGFT, IIFPT etc.
Defence
Cold Response 2022: The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) has organized the massive military drill ‘Cold Response 2022’ in Norway.
Key Highlights:
- It began on March 14, 2022, and will continue till April 1, 2022.
- Around 30,000 troops from 27 nations are taking part in the 2022 edition of the exercise, with about 220 aircraft and more than 50 vessels.
- This is the largest ‘Cold Response’ being exercise conducted in Norway since the 1980s.
- The exercise is held in Norway every two years, for NATO Allies and partners.
About the exercise:
- The Cold Response is a long-planned and defensive exercise where Norway and its allies exercise in defending Norway against external threats.
Note: This exercise was planned and informed about long before the war in Ukraine.
- The Norwegian-led exercise provides an opportunity to train together in cold weather conditions over challenging terrain.
- It demonstrates NATO’s ability to respond decisively to any threat, from any direction.
- This exercise has been held off Norway’s coast since 2006.
- The main aim of this exercise is to improve the collaboration and military capability of the alliance.
- It is held in a combat environment that portrays the harsh Arctic setting with cold weather and rough terrain.
About Norway:
- Norway officially the Kingdom of Norway is a Nordic country in Northern Europe whose mainland territory comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula.
- The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of Norway.
- Norway is bordered by Finland and Russia to the north-east, and the Skagerrak Strait to the south, with Denmark on the other side.
- The capital of Norway is Oslo.
- The currency used here is the Norwegian krone.
About NATO:
- NATO is an acronym for North Atlantic Treaty Organization.
- It is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 North American and European countries.
- NATO was founded on 4 April 1949, Washington, D.C., United States.
- The organization implements the North Atlantic Treaty that was signed on 4 April 1949.
- It is headquartered in Brussels, Belgium.
Assam Rifles Raising Day 2022: The 187th Raising Day of the Assam Rifles was observed on 24th March 2022.
- Assam Rifles Raising Day is observed every year on March 24 in India to celebrate and honour the Assam rifles who served the country in several conflicts including both the World Wars.
About Assam Rifles:
- The Assam Rifles is the oldest paramilitary force of India.
- The unit can trace its lineage back to a paramilitary police force that was formed under the British in 1835 called Cachar Levy to mainly protect British Tea estates and their settlements against tribal raids.
- Since then the Assam Rifles have undergone a number of name changes— the Assam Frontier Police (1883), the Assam Military Police (1891) and Eastern Bengal and Assam Military Police (1913), before finally becoming the Assam Rifles in 1917.
- It is headquartered in Shillong, India. Since 2000, they are guarding the Indo-Myanmar Barrier under “one border one force” policy of the Government of India. Its governing body is the Ministry of Home Affairs and the Ministry of Defence of India.
- It is the only paramilitary force with a dual control structure. which means that while the control of the force is with the Indian Army, the salaries and infrastructure of the force are provided by the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- Its Motto is 'Sentinels of the North East'.
- The current Director-General of the Assam Rifles (DGAR) is Lt Gen Pradeep Chandran Nair, AVSM, YSM.
Contributions of Assam Rifles:
- Assam Rifles have served in a number of conflicts including World War 1, where they served in the Middle East and Europe while World War II, where they served mainly in Burma.
- They have also served after the Chinese annexation of Tibet where they were tasked with manning the Tibetan border of the Assam Himalayan Region.
- The force has also been instrumental in maintaining the law and order in Arunachal Pradesh.
- It made a substantial contribution to the opening of the Assam region to administration and commerce, earning the moniker "right arm of the civil and left arm of the military" over time.
- Two battalions of the Assam Rifles are stationed in Jammu and Kashmir, as well as one National Disaster Relief Force battalion, which is playing its active role in case of natural disasters.
- Although India has long contributed to UN peacekeeping, the establishment of the Assam Rifles Riflewomen Team adds a social and human dimension to India's commitment to the community of nations.
- The other services performed by Assam Rifles also include the provision of aid to the civilians at the time of emergency, education in remote areas, medical assistance, and provision of communications, among others.
Suraksha Kavach 2: The Indian Army with Maharashtra Police recently conducted “Suraksha Kavach 2” Exercise.
Key Points:
- The joint exercise “Suraksha Kavach 2” was organized by the Indian Army's “Agnibaaz Division” with Maharashtra Police at Lullanagar, Pune.
- The exercise involved the participation of the Counter-Terrorism Task Force (CTTF) of the Indian Army, Anti-Terrorism Squad of Maharashtra Police along with Quick Reaction Teams (QRTs), Dog Squads, and Bomb Disposal Teams of both agencies.
Aim:
- The main aim of this exercise is to counter any terrorist actions in Pune.
- The exercise also aimed to harmonize the drills and procedures undertaken by Army and Police to counter-terrorism.
- This exercise looked to improve the interoperability between both organizations.
Environment
Rhino Bond: The World Bank has issued the Wildlife Conservation Bond (WCB) also known as “Rhino Bond” to support of South Africa’s efforts to conserve endangered species of Black Rhino.
Overview:
- It is the world's first wildlife conservation bond.
- It is a five-year $150 million Sustainable Development Bond.
- It includes a potential performance payment from the Global Environment Facility (GEF).
- The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development, IBRD of the World Bank announced that the returns paid by the five-year bond will be determined by the rate of population growth of animals in two reserves of South Africa namely the Addo Elephant National Park (AENP) and the Great Fish River Nature Reserve (GFRNR).
- If this program is successful it could be expanded for the protection of black rhinos in Kenya along with other wildlife species like lions, tigers, gorillas and orangutans.
Note: Similar bonds have earlier been issued to finance various outcomes from education of girls in rural India to the marine projects in Seychelles.
About Black Rhinos:
- There are five rhino species globally, with most of the animals in South Africa and almost all them white rhino.
- Black rhinoceroses are two-horned members of the endangered rhinoceros family that can only be found in Africa.
- According to documentation from the World Bank, their numbers have dropped to about 2,600 from 65,000 in 1970, and may once have been as high as 850,000.
- These black rhinos can weigh as much as 1.4 tons and are much smaller than the white rhino.
- Rhinos are under threat from poaching, mostly because of demand in Vietnam and China for the powder from their horns, which is believed to cure cancer and improve virility.
Identification of New Carangid Species: The Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI) has identified a new carangid (Vatta) species from the Indian coast of Kerala.
Overview:
- Following extensive taxonomic and genetic analysis, CMFRI confirmed it as a new species.
- When compared to closely related species, the fish has a distinct deep ovate body, concave dorsal head profile, and stoutness, as well as fewer gill rakers on the first gill arch.
- It belongs to the ‘queen fish’ group and is named scomberoides pelagicus.’
- The fish is locally known as pola vatta.
- There are more than sixty species of carangids in the Indian ocean.
- Out of the 60 species, 4 belong to the ‘Queen Fish’ group and the newly identified fish is number five.
Significance:
- Identifying Scomberoides pelagicus would help better Indian marine biodiversity status.
- The identification would greatly assist policy makers, marine scientists and other stakeholders to work on management and conservation efforts.
- Three queen fishes are extinct due to a lot of reasons like climate change, overfishing, etc. across the globe.
- The fish, which is found along the country's coasts, including Kerala, is highly regarded and in high demand in domestic markets.
About Queen Fish:
- The queenfish (Seriphus politus) is a type of fish in the Sciaenidae family, which also includes drums and croakers.
- This is the only species in the monotypic genus Seriphus.
- When compared to closely related species, the fish has a distinct deep ovate body, concave dorsal head profile, and stoutness, as well as fewer gill rakers on the first-gill arch.
- It is native to the eastern Pacific Ocean.
- It is also known commonly as the queen croaker.
- This is the only species in the monotypic genus Seriphus.
- This species is up to 30 centimeters long and has an elongated, compressed body.
- It feeds on marine invertebrates and small fish.
- It is blue-grey to tan in colour with a shiny silver belly and a dark horizontal line running the length of the body.
- The pectoral fin is dark and the other fins are yellowish.
- The mouth contains one or two rows of pointed teeth.
- It occurs in coastal waters, such as bays and sloughs, moving to deeper waters at night.
About CMFRI:
- The Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI) was established by the Government of India in 1947 under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- It was later joined the ICAR family in 1967.
- It is headquartered in Kochi, Kerala.
- The current Director of CMFRI is Dr. A. Gopalakrishnan.
Acheivements of CMFRI:
- During the course of over 65 years, the Institute has emerged as a leading tropical marine fisheries research institute in the world.
- One of the major achievements of CMFRI is the development and refinement of a unique method for estimation of fishery catch and effort from the over 8000 km coastline called the “Stratified Multistage Random Sampling Method”.
- With this methodology, the Institute maintains the National Marine Fisheries Data Centre (NMFDC) with more than 9 million catch and effort data records from all maritime states of India of above1000 fished species.
National Dolphin Day: Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEF&CC) Shri Bhupendra Yadav announced that the 5th of October will be celebrated as National Dolphin Day every year to be celebrated every year as a historic step in creating awareness for the conservation of Dolphins.
Overview:
- The decision to designate October 5 as National Dolphin Day was taken at the 67th meeting of the Standing Committee of the National Board for Wildlife (NBWL) on March 25, 2022.
- The first-ever National Dolphin Day will be observed on 5th October 2022.
- The aim of the government is to generate awareness and encourage community participation in the conservation of dolphins including the Gangetic Plain.
- The focus will also be given to improving the Ganga and its tributaries’ water quality and flow so that Gangetic dolphins can survive.
Importance of Dolphins:
- Healthy aquatic ecosystems help in maintaining the overall health of the Planet.
- Dolphins act as a perfect indicator of a healthy aquatic ecosystem, thus the conservation of dolphins is of utmost importance.
- Their conservation will help the species' existence as well as the people who rely on the aquatic system for their livelihood.
About Gangetic Dolphins:
- The Gangetic dolphin acts as an indicator species.
- The Uttar Pradesh forest department along with WWF- India, in 2012 and 2015 recorded 1,272 dolphins in the Ganga, Chambal, Yamuna, Betwa, Ken, Sharda, Son, Gahagra, Geruwa, Rapti, and Gandak.
- The majority of Gangetic dolphins, a species of freshwater dolphin, are spotted in deep river reaches in Rajasthan, Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh, Assam, Madhya Pradesh, and West Bengal in India.
- According to official data, there are about 3,700 Gangetic dolphins in the Indian River system.
- Gangetic Dolphins have been categorized as endangered species under the International Union for the Conservation of Nature Red List.
- The Gangetic Dolphins are threatened due to water diversion, pollution, habitat fragmentation, etc.
- In 2010, the Ganges river dolphin has designated a national aquatic species.
- Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced ‘Project Dolphin’ in August 2020 to conserve both freshwater and marine dolphins.
More about the 67th Standing Committee Meeting:
- The Standing Committee also discussed several important policy issues and the proposals for wildlife clearances forwarded by the State Governments and the Union Territory administrations prior to declaring the day of national importance.
- The Environment Ministry has been taking up several activities for the protection and conservation of dolphins and their habitats.
- The Standing Committee also considered 46 proposals for wildlife clearance and recommended several projects such as providing electricity in remote villages in Himachal Pradesh and Ladakh and drinking water supply to villagers in Karnataka.
- Projects of strategic importance such as road and border outpost in Ladakh were also recommended during the meeting.
- The Standing Committee recommended 4 proposals for the construction of earthen dams in Haryana to improve irrigation facilities.
- It recommended a road project under Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) in Uttarakhand in order to provide connectivity to remote villages with appropriate animal passage structures.
Note: The MoEF&CC has already undertaken the pan-India enumeration project for dolphins, the report for which is expected by June-July 2022.
Indian Policy
Appropriation Bill 2022: The Lok Sabha on 24th March 2022 passed the Demands for Grants and Appropriation Bill, 2022.
Overview:
- The Bill was passed by a voice vote, giving the government authorization to withdraw money from the Consolidated Fund of India for its working as well as the implementation of programmes and schemes for the fiscal beginning April 1.
- This completes two-thirds of the budgetary exercise by the Lok Sabha..
- The bill, introduced by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, was passed after cut motions, moved by various opposition members, were rejected.
- The Finance Bill, which essentially comprises the government's tax ideas, will now be debated in the Lok Sabha.
- With the passage of the Finance Bill, the budget process will be completed.
Note:
- Appropriation and finance bills are both categorized as money bills, which do not require Rajya Sabha's express approval.
- The bills are only discussed and returned in the upper house.
- The Finance Bill becomes the Finance Act after it is passed, and the final Budget is authorized.
Earlier, the Lok Sabha passed the Demand for Grants for the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways.
Sujalam 2.0 Campaign: The Sujalam 2.0 campaign was launched by Gajendra Singh Shekhawat, the Union Minister of Jal Shakti on 23rd March 2022.
Key Highlights:
- This campaign was launched at an event held virtually by the Ministry of Jal Shakti’s Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation (DDWS).
- It has been launched for greywater management.
- A joint advisory was signed by nine ministers to look into how greywater management can be planned based on the convergence model along with those who are associated directly with the implementation of this programme.
- The nine Ministers are as follows:
1.M/o Rural Development,
2.M/o Jal Shakti,
3.M/o Youth Affairs and Sports,
4.M/o Women & Child Development,
5.M/o Health and Family Welfare,
6. M/o Tribal Affairs,
7.M/o Environment, Forest and Climate Change,
8.M/o Education,
9.M/o Panchayati Raj
- Funds for greywater management will be provided from the Swachh Bharat Mission-Gramin Phase II or through grants under the 15th Finance Commission as well as the MGNREGS or through the convergence between all of them.
Theme of Sujlam 2.0:
The theme for this campaign is ‘Groundwater: making the invisible visible.
Objective of Sujlam 2.0:
- The main objective of the Sujlam 2.0 campaign is to manages greywater through the participation of the people.
Under this campaign, there are plans to mobilize communities such as schools, panchayats, and anganwadis to help in greywater management.
What is Greywater?
- Greywater refers to the domestic wastewater that is generated in households, office buildings, etc., and is without faecal contamination.
- Sources of greywater include showers, sinks, washing machines, baths, etc.
- Since greywater contains fewer pathogens compared to domestic wastewater, it is safer to treat, handle, and reuse for the purpose of landscape, toilet flushing, crop irrigation, etc.
How can Greywater be managed?
- It can be best managed in areas where greywater is produced.
- If greywater is allowed to gather and stagnate then it turns into a major management and infrastructure challenges.
Indian polity
Uttarakhand CM Oath Ceremony: Pushkar Singh Dhami was sworn in as the 11th Chief Minister of Uttarakhand in a grand ceremony on March 23, 2022.
Overview:
- The 46-year-old is the youngest Chief Minister of the state.
- This will be his second consecutive term.
- Governor Lieutenant General Gurmit Singh administered him the oath of office and secrecy at the Parade Ground in Dehradun.
- Eight Cabinet Ministers were also sworn in along with the Chief Minister.
- The 8 Cabinet Ministers include Premchand Aggarwal, Satpal Maharaj, Ganesh Joshi, Subodh Uniyal, Dhan Singh Rawat, Rekha Arya, Chandan Ram Das and Saurabh Bahuguna.
- The oath-taking ceremony of Uttarakhand CM was attended by all the Chief Ministers of BJP-ruled states including Goa CM-designate Pramod Sawant, UP CM-designate Yogi Adityanath, Rajasthan BJP leader Vasundhara Raje, Union Minister Nitin Gadkari, Defence Minister Rajnath Singh and other BJP leaders.
Uttarakhand Election Results 2022:
- The Uttarakhand Assembly Polls 2022 were held in a single phase on February 14th.
- In the elections, the BJP won 47 seats in the 70-member state assembly
- The Congress won 19 seats, while BSP won 2 seats and two independents also won one seat each.
- However, the two key candidates - incumbent Uttarakhand Chief Minister Pushkar Singh Dhami and former Uttarakhand CM Harish Rawat were defeated in their respective constituencies.
About Pushkar Singh Dhami:
- Pushkar Singh Dhami was born in 1975 Kanalichhina village in Pithoragarh district.
- He is the son of an ex-serviceman and holds a law degree.
- He initially worked as a Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh (RSS) volunteer.
- He was also previously a member of the Akhil Bharatiya Vidyarthi Parishad (ABVP), the student organization affiliated to RSS.
- Dhami also served as the president of BJP Yuva Morcha in Uttarakhand twice between 2002 and 2008.
- He is believed to be a protégé of Bhagat Singh Koshyari, the former Chief Minister of Uttarakhand.
Delhi MCD Merger: The Union Cabinet has approved a bill for the unification of Delhi’s three Municipal corporations into one Municipal Corporation.
- The Delhi Municipal Corporation (Amendment) Bill, 2022 is likely to be tabled in the ongoing budget session of Parliament.
Key Details:
- The national capital has five local bodies namely the
- North Delhi municipal corporation (NDNC)
- East Delhi municipal corporation (EDMC)
- South Delhi municipal corporation (SDMC)
- Delhi Cantonment Board
- New Delhi Municipal Council
- The North, South, and East Delhi corporations cover the majority of Delhi's territory.
- Before 2012, these three corporations were known as the Municipal Corporation of Delhi (MCD).
- The erstwhile Delhi Municipal Corporation was trifurcated into three Municipal Corporations in the year 2012 as per the Delhi Municipal Corporation amendment Act, 1911 (Delhi Act, 12 of 2011).
- South Delhi Municipal Corporation - SDMC
- North Delhi Municipal Corporation - NDMC
- East Delhi Municipal Corporation - EDMC
- North and South Municipal Corporations currently comprise 104 Wards each while East Delhi Municipal Corporation has 64 Wards.
- MCD was the second-largest civic body in the world after the Tokyo Metropolitan Area when it was trifurcated by the then Congress establishment.
- It was headed by a commissioner, assisted by six additional commissioners, 22 directors and department heads, to oversee key functions such as sanitation, horticulture, education, and engineering, among others.
- After the unification of the three corporations, Delhi will have one Mayor in place of existing three Mayors.
Phangnon Konyak: Over 59 years since the Statehood, creating history, BJP's S Phangnon Konyak has become the second woman ever from Nagaland to be elected to either House of the Parliament or the State Assembly.
Overview:
- Konyak, 44 years old is the incumbent Mahila Morcha President Nagaland unit, hailing from Mon district.
- She is the second lady parliamentarian from Nagaland, the first being Rano M Shaiza who was elected to the Lok Sabha from the state in 1977.
- Nagaland has not had a single woman MLA since it got statehood in 1963.
- She was elected unopposed to the Upper House earlier this week.
- Phangnon was declared ‘duly elected uncontested’ by Returning Officer, Khruohituonuo Rio, Additional Secretary, Nagaland Legislative Assembly(NLA), after the last hour for withdrawal of candidature on March 24, it said.
- She was later handed over the certificate of election by the Returning Officer.
Yogi Adityanath: Yogi Adityanath took oath as Chief Minister of Uttar Pradesh (UP) for his second term in office.
Overview:
- He was administered the oath of office and secrecy by Governor Anandiben Patel at Lucknow’s Atal Bihari Vajpayee Ekana Stadium in the presence of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, Union Ministers Amit Shah, Rajnath Singh and other central ministers.
- Brajesh Pathak and Keshav Prasad Maurya also took oath as the Deputy Chief Ministers in the new government.
- The Yogi Adityanath-led BJP government created history with its comeback as no other CM has been able to repeat a government in the state in 37 years.
- The BJP-led NDA secured 274 seats out of 403, becoming the first party in over three decades to form a government for a second consecutive time in the state.
- The Congress had returned to power with a majority in the state 37 years ago.
- After this, CM Yogi Adityanath has not just made history by completing five successful years of governance but by also returning to power with a thumping majority.
- He has become the first such BJP leader to become the CM for the second consecutive term.
Background:
- In the 2017 Assembly elections, Adityanath was chosen as the Chief Minister by BJP after winning the poll.
- After becoming the CM of the state, he kept 36 ministries under his direct control, including Home, Economics and Statistics, Home Guard, Sainik Welfare, Personnel and appointment, as well as Civil Defence.
- Before being sworn as UP chief minister in 2017, he was Gorakhpur MP for five consecutive terms from 1998 to 2017.
About Yogi Adityanath:
- Yogi Adityanath was born on June 5, 1972, in a village in Uttarakhand.
- He was named Ajay Singh Bisht by his parents.
- He left home to join the movement for the construction of Ram Temple and became a disciple of Mahant Avaidyanath of Gorakhnath Temple in Gorakhpur.
- He commenced his political journey in 1998 becoming the youngest MP from Gorakhpur.
International
Finlandization: The French President recently suggested that Finlandization might be a realistic outcome for Ukraine if and when the Russia-Ukraine war ends.
What is Finlandization?
- Finlandization refers to the policy of strict neutrality between Moscow (Russia) and the West that Finland followed during the decades of the Cold War.
- The principle of neutrality was rooted in the Agreement of Friendship, Cooperation, and Mutual Assistance (or YYA Treaty) that Finland signed with the USSR in April 1948.
- Article 1 of the treaty reads: “In the eventuality of Finland, or the Soviet Union through Finnish territory, becoming the object of an armed attack by Germany or any state allied with the latter (meaning, essentially, the United States), Finland will, true to its obligations as an independent state, fight to repel the attack.
- Finland will in such cases use all its available forces for defending its territorial integrity by land, sea, and air, and will do so within the frontiers of Finland in accordance with obligations defined in the present agreement and, if necessary, with the assistance of or jointly with, the Soviet Union.
- In such cases, the Soviet Union will give Finland the help that it requires, subject to mutual agreement between the contracting parties.
Ukraine and Finlandization:
- Ukraine, formerly a part of the Soviet Union, has increasingly tilted toward the West, economically and politically, while resisting Russian influence.
- In 2008, NATO said it planned eventually for Ukraine to join the alliance, a popular idea within the country, though it has never actually applied for membership and NATO officials say it would not happen any time soon.
- “Finlandization” would allow Moscow a heavy hand in Ukrainian affairs.
- It goes against what Ukraine has been striving for, that is joining NATO and the E.U.
What did Finland do when the Russian War ended?
- The 1948 treaty formed the basis of Finland-Russia relations until 1992, when Finland signed a new agreement with post-Soviet Russia.
- It lays at the heart of Finland’s foreign policy doctrine especially 1946 to 1982 and is known in international relations studies as the “Paasikivi-Kekkonen line”.
- From the perspective of Finland — whose capital Helsinki is situated just across the Gulf of Finland from St Petersburg (Leningrad) — the treaty protected it from being attacked or incorporated into the USSR like the Baltic and eastern European states.
- It allowed the country to pursue the path of democracy and capitalism while staying out of the conflict between the great powers.
- Finland did not participate in the Marshall Plan. It took neutral positions on matters on which the Soviet Union and the West disagreed. It stayed aloof from North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) and European military powers, and used this positioning to ward off pressure from Moscow to become part of the Soviet bloc or the Warsaw Pact.
- Marshall Plan was a U.S.-sponsored program designed to rehabilitate the economies of 17 western and southern European countries in order to create stable conditions in which democratic institutions could survive in the aftermath of World War II.
Way Forward for Ukraine:
- Ukraine should be able to select its economic and political alliances freely, including with Europe.
- Ukraine should not become a member of NATO. It should be allowed to form a government that reflects the expressed wishes of its citizens.
- It should pursue a posture comparable to that of Finland.
- That country declares its staunch independence and works cooperatively with the West in most areas, but avoids institutional enmity toward Russia.
International Day of Remembrance of the Victims of Slavery 2022: The International Day of Remembrance of the Victims of Slavery and Transatlantic Slave Trade is observed on March 25th every year to honor and remember those who suffered and died at the hands of the brutal slavery system.
Key Points:
- This day aims to raise awareness about the horrors of slavery and racism that happened and continues to happen all around the world.
- Between the 16th and the 19th century, almost 20 million people were forcibly shipped off from Africa to North and South America and Europe.
Theme:
The theme of International Day of Remembrance of the Victims of Slavery 2022 is “Stories of Courage: Resistance to Slavery and Unity against Racism”.
- The theme aims to showcase the tales of people who were forcibly taken from their families and homelands, as well as those who battled back against tyrants and won their freedom despite all obstacles.
- Despite the abolishment of the slavery system, the stories continue today as people continue to fight racism, which is the most persistent legacy of the transatlantic slave trade.
- The Black Lives Matter movement is an example of large-scale anti-racism and anti-prejudice movement that originated in the United States and gradually extended around the world.
- It is a decentralized political and social movement that aims to bring attention to the racism, injustice, and inequality that black people face.
Objective:
- The main objective of this day is to end racial discrimination, marginalization, and exclusion of these people, as well as enable political, economic, and structural transformations to eliminate power imbalances that continue to deny equality of opportunity and justice to all.
- The day's commemoration is a call to all people to unite against racism and work together to establish societies based on dignity, equality, and solidarity.
Significance:
- The International Day of Remembrance of the Victims of Slavery and Transatlantic Slave Trade commemorates the massive crimes against humanity, unprecedented human trafficking, degrading economic transactions and atrocious human rights violations that were brought upon the enslaved Africans during the transatlantic trade.
- The International Day of Slavery Victims' Remembrance provides an opportunity to learn about what happened and reflect on such stories.
- It is a day to pay tribute to the millions of Africans who were forcibly removed from their homelands, and stand in solidarity against racism, which is a byproduct of the slave trade system and continues to confront people of African descent around the world.
History:
- The International Day of Remembrance of the Victims of Slavery and Transatlantic Slave Trade was established by the UN General Assembly (UNGA) through a resolution on December 17, 2007, to commemorate the struggles and challenges faced by the victims of the slave trade.
UN Rememberance Programme:
In 2007, a Remember Slavery Programme was established by UNGA to honour the memory of the victims of slavery and the transatlantic slave trade.
- Under the programme, a range of educational activities are organized throughout the year.
- A memorial has also been created at the UN headquarters in New York to permanently honor the victims of slave trade.
What is Transatlantic Slave Trade?
- The Transatlantic Slave Commerce was a three-way trade between America, West Africa, and Europe that featured vast human trafficking and the enslavement of men, women, and children. It has been dubbed the worst human rights violation in history.
- Between the 16th and 19th centuries, almost 15-20 million individuals were sold as slaves.
- Approximately 2.4 million people perished on the lengthy and difficult journeys, while millions more died after arriving in these countries due to a variety of factors including excessive mistreatment, famine and human rights violations.
- The slaves were considered cargo rather than human beings by the ship-owners, and they were shipped in the cheapest way possible.
- After that, the slaves were sold to labour in plantations, mines, rice fields and even as home servants.
Abolition of Slavery:
- Britain was the first country to pass legislation banning the slave trade in 1807.
- Britain then pressured Spain, France, Portugal and the Netherlands to also ban slavery by 1815.
- The United States made the slave trade punishable by death in 1820.
- The US officially abolished slavery in 1865.
Solomon Islands & China Deal: The Solomon Islands recently confirmed that it has signed a policing deal with China.
Key Highlights:
- The memorandum of understanding (MOU) was signed by Anthony Veke, Minister for police in the Solomon Islands with Wang Xiaohong, executive vice minister of China's Ministry of Public Security in a virtual meeting on March 18, 2022.
- An official of the Pacific island nation’s government said that it will send a proposal for a broader security agreement covering the military to its Cabinet for consideration.
- If approved, it would be the first time a strategic adversary has been within striking distance of Australia since World War II.
- A draft copy of a security MOU circulated on social media states that it would cover Chinese police, armed police and the military assisting the Solomon Islands on social order, disaster response and protecting the safety of Chinese personnel and major projects in the Solomon Islands.
- The draft also provides for Chinese naval ships to carry out logistical replenishments in the Solomon Islands, fuelling anxiety in Canberra it would be a step toward a Chinese military base in the region.
- The Solomon Islands switched diplomatic ties from Taiwan to Beijing in 2019, which partly fuelled discontent that led to riots in the capital, Honiara, in November.
Concern over China's move into the Pacific:
- The arrangements are likely to concern the U.S., which said in February it would open an Embassy in the Solomon Islands.
- The security treaty, if concluded, would be a major inroad for China in a region that U.S. allies Australia and New Zealand have for decades seen as their “back yard.
- Australia has a bilateral security agreement with the Solomon Islands covering the deployment of police and armed forces, signed in 2018.
- Australia has historically provided security support to the Solomon Islands and led a policing mission to restore order in the wake of riots, at the request of Prime Minister Manasseh Sogavare.
About Solomon Islands:
- The Solomon Islands are a sovereign country.
- It consists of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and northwest of Vanuatu.
- Its capital is Honiara which is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal.
- The currency used here is the Solomon Islands dollar.
Serdar Berdymukhamedov: Serdar Berdimuhamedow has been sworn in as the President of Turkmenistan.
Key Highlights:
- Berdymukhamedov, secured 72.97 percent of the votes election to lead the gas-rich country.
- He succeeds his father and former president Gurbanguly Berdimuhamedov.
- Gurbanguly Berdimuhamedov had become president in 2006 and has served till 2022.
Note: The presidential elections in Turkmenistan are held every seven years.
About Turkmenistan:
- Turkmenistan also known as Turkmenia, is a sovereign country in Central Asia.
- It is bordered by the Caspian Sea and largely covered by the Karakum Desert.
- Its Capital is Ashgabat.
- Its official language is Turkmen.
- The currency used here is Turkmenistan manat.
Joint Declaration on Privacy and the Protection of Personal Data: The European Union (EU) along with nine countries which also include India has called for fostering international cooperation to promote high data protection and privacy standards based on certain core elements increasingly shared across the Indo-Pacific region, Europe and beyond.
About the Declaration:
- In a ‘Joint Declaration on Privacy and the Protection of Personal Data: Strengthening trust in the digital environment’ the countries have called for rapid technological developments, in the area of digital and information technologies as new challenges are coming up for the protection and privacy of personal data.
- To foster free data flow, as also acknowledged by the G20 Rome Leaders’ Declaration, is the key to harnessing the opportunities which are presented by the digital economy.
- It must also be ensured by the countries’ respective legal frameworks, that an individual’s right to privacy as well as the protection of personal data is treated as a fundamental freedom and adhered to.
Which are the countries that have called for data protection?
- The countries along with the European Union are India, Australia, Comoros, Japan, Mauritius, New Zealand, the Republic of Korea, Singapore, and Sri Lanka have called for data protection.
Why did this declaration come to the forefront?
- The joint declaration has been issued because there is a lack of trust in how data is handled and this has had a negative impact on the economies and societies of the respective countries.
- As a result of this, reluctance on the part of communities and individuals to adopt new technology, sharing personal data with business exchanges and overseas partners has become a major challenge.
- So to face this challenge this declaration has been issued so that high data protection and privacy standards can be promoted and will help in the development of the said nations.
National
Shahid Diwas 2022: Shaheed Diwas, also known as Martyrs' Day is being observed all around India on 23 March 2022.
Key Facts:
- The day is observed every year on 23 March to mark the day when the British hanged Bhagat Singh, Rajguru and Sukhdev, India's three young revolutionaries, in the year 1931.
- These revolutionaries dedicated their lives to India's freedom and their ideas were immensely popular popular among the masses.
- Newly elected Punjab Chief Minister Bhagwant Mann, on 22 March 2022, officially declared 23 March as a holiday in the state, commemorating the death anniversary of Shaheed-e-Azam Sardar Bhagat Singh.
- A resolution has also been passed in the Punjab Assembly to install statues of Shaheed Bhagat Singh and BR Ambedkar.
History:
- On March 23, three heroes of our nation were hanged to death, namely Bhagat Singh, Shivaram Rajguru, and Sukhdev Thapar by the British.
- Bhagat Singh was born on September 28, 1907, in Lyallpur, Punjab.
- He, together with his companions Rajguru, Sukhdev, Azad, and Gopal, fought for the assassination of Lala Lajpat Rai.
- He became an inspiration for youngsters due to his daring adventures.
- He and his companions, on April 8th, 1929, threw bombs over the Central Legislative Assembly by reading the slogan "Inquillab Zindabad".
- And for this, a murder case was charged against them.
- On March 23rd, 1931, in the Lahore Jail, they were hanged.
- Their bodies were cremated on the banks of the Sutlej River.
Additional Info:
To honour the martyrs of the nation, several other days at the national level were also declared as Sarvodaya or Shaheed Diwas.
- 30 January is celebrated as Shaheed Diwas, or Martyr’s Day, in the memory of Mahatma Gandhi, The Father of the Nation fondly called Bapuji. He was assassinated by Nathuram Godse in the Birla House during his evening prayers on January 30, 1948.
- 13 July is celebrated as Martyr's Day in Jammu and Kashmir to commemorate the deaths of 22 people. On July 13, 1931, people were killed by royal soldiers while demonstrating adjacent to the Maharaja, Hari Singh of Kashmir.
- 17th November is celebrated as Martyr's Day in Odisha to observe the death anniversary of Lala Lajpat Ray, also known as the "Lion of Punjab". He also played an important role in the freedom struggle of India from the British dominion.
- 19th November is also celebrated as Martyr's Day in Jhansi. On November 19th, Rani Lakshmi Bai was born. She also sacrificed her life during the 1857 revolt.
March 23rd is also Ram Manohar Lohia's birth anniversary. He was an activist in the Indian independence movement and a socialist political leader.
Shaheed Diwas Quotes:
- “They may kill me, but they cannot kill my ideas. They can crush my body, but they will not be able to crush my spirit.” — Shaheed Bhagat Singh
- “Lovers, Lunatics and poets are made of same stuff.”― Shaheed Bhagat Singh
- “They may kill me, but they cannot kill my ideas. They can crush my body, but they will not be able to crush my spirit.” — Shaheed Bhagat Singh
Dare to Erade TB: Union Minister Dr Jitendra Singh while addressing the event on World TB Day 2022 announced the launch of “Dare to Erade TB” program.
Key Points:
- The program will be based on the Indian data and the formation of the Genome Sequencing Consortium for Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS) TB Surveillance.
- Union minister said that Indian Tuberculosis Genomic Surveillance Consortium (InTGS) is proposed on lines of the Indian SARS-CoV-2 Genomic Consortia (INSACOG) for Whole Genome Sequencing, (WSG) TB surveillance.
- He also stated that Dare2eraD TB will be the umbrella TB program of DBT comprising of following key initiatives-
- InTGS - Indian Tuberculosis Genomic Surveillance Consortium;
- InTBK Hub- Indian TB Knowledge Hub- Webinar Series;
- Host Directed therapies against TB and developing an evidence-based regimen for treating extra-pulmonary Tuberculosis.
- Dr. Jitendra Singh said that there is a need for a mass movement to get rid of Tuberculosis to realize the dream of Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi of a “TB Mukt Bharat” by the year 2025.
- Minister of State for Health Bharati Pravin Pawar noted in her speech at the event that the government has increased its capacity for early detection and treatment of tuberculosis cases.
- These capabilities, she said, have been reinforced through surveillance and contact tracing, and digital technology will effectively advise health personnel.
- The well-performing district and states of the country were awarded by Mansukh Mandaviya, Union Health Minister, for improving the levels to eliminate Tuberculosis.
Tuberculosis in India:
- Tuberculosis in India is one of the major public health problems of the country.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that the largest tuberculosis epidemic in the world is in India.
- In 2020, India had accounted for 26% of all TB-related cases worldwide.
- There are 192 cases of TB found per 1,00,000 population in the country.
About TB Day:
- World Tuberculosis (TB) Day is celebrated every year on 24 March to commemorate the date when Robert Koch announced his discovery of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the bacillus that causes TB in 1882.
- This Day is observed to educate people about TB and its impact around the world.
- The term tuberculosis was coined by Johann Schonlein in 1834.
- India has set the target to make the country TB free by 2025.
Theme of TB Day 2022:
- Theme of 2022 is ‘Invest to End TB. Save Lives.’
About Tuberculosis:
- Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that mostly affects the lungs of those who are sick.
- Sneezes and coughs emit microscopic droplets into the air, which carry tuberculosis-causing bacteria from one person to another.
BRICS Vaccine R&D Centre: Union Minister of Health and Family Welfare, Shri Mansukh Mandaviya recently launched the BRICS Vaccine Research & Development (R&D) Center and Workshop on Vaccine Cooperation through a video conference in New Delhi, Delhi.
Key Details:
- The launch ceremony was chaired by the Minister of Science and Technology of China Wang Zhigang.
- Speaking at the launch, Wang Zhigang asked the BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa) countries to focus on promoting the fair distribution of vaccines and to increase cooperation among the BRICS countries.
- The panel also discussed different techniques for collaborating and dealing with future pandemics.
- India has one of the world’s largest vaccine manufacturing industries.
- It exports vaccines to more than 150 countries meeting 65-70 percent of WHO vaccination demand.
- It also has one of the world's largest vaccine manufacturing industries.
- India will offer its vaccine manufacturing industry to develop vaccines for the BRICS nations as well as the rest of the world.
Significance of the Centre:
- The R&D Centre initiative will collaborate with countries, share experiences, build collaborations for mutual benefits and accelerate the development of vaccines of public health importance.
- This centre will also aid in the development of preclinical and clinical studies, basic R&D, and the strengthening of BRICS countries' laboratories in order to test vaccine candidates.
- It will assist in bringing together the BRICS countries' strengths in the field of vaccine production and research, enhancing the BRICS countries' ability to control and prevent infectious illnesses.
- The BRICS countries will also be able to assist other developing countries throughout the world in providing timely help.
Background:
- A BRICS Vaccine R&D Centre was proposed to be established in the 2018 Johannesburg Declaration.
- During the XIII BRICS Summit: New Delhi Declaration, 2021, the leaders reaffirmed their commitment to the early launch of the BRICS Vaccine R&D Centre.
Drone-based Mineral Exploration: India’s largest iron ore producer, National Mineral Development Corporation (NMDC) Ltd, recently signed a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with IIT Kharagpur for the purpose of drone-based mineral exploration.
Key points:
- The NMDC is increasingly dependent on technical innovation and the digitization of its exploration and mining database.
- Drones are currently used in agriculture, forestry, mining, urban planning, disaster management, surveillance, and transportation, among other industries, and the government has taken the first step in regulating and monitoring their use and operations in India.
- Key Details:
- With this MoU, NMDC becomes the first CPSE in India to conduct Drone-based Geophysical Surveys and Hyperspectral Studies for Mineral Exploration in the country.
- The collaboration between NMDC and IIT-Kharagpur will open a new era in mineral exploration for the country.
- Spectral products, algorithms and methods would be developed by IIT Kharagpur and NMDC for exploration using drones (UAV) for mining.
- This collaboration would also lead to the development of software spectral tools for the purpose of capacity-building programs on mining technology and mineral excavation.
- Mineral Exploration of NMDC for six decades has been exploring minerals for a wide range of minerals such as rock phosphate, copper, tungsten, diamond, magnetite, limestone, and beach sands amongst others right from the G4 reconnaissance level to the detailed G1 level of United Nations Framework Classification for Resources (UNFC).
Where is the mineral exploration being conducted?
- The mineral exploration is being conducted by NDMC in Madhya Pradesh as well as diamonds in Chhattisgarh’s Beloda-Belmundi block.
- NMDC is also the first CPSE to use Space Geophysics in Central Indian Diamond Province and the first to use online monitoring of exploration of data on the BHUVAN platform.
About BHUVAN platform:
- BHUVAN is a multi-purpose end-user satellite application platform.
- It is also known as the Indian version of Google Maps.
- ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization) is in charge of this platform.
- Users can explore a 2D/3D representation of the Earth’s surface with this software program.
- The browser has been designed specifically for viewing India.
- In comparison to other Virtual Globe Software, it provides more detailed images of Indian locations, with spatial resolutions up to 1 metre.
About NDMC:
- The NMDC Limited is a government-owned mineral producer, under the Ministry of Steel.
- It is the largest Iron Ore producer in India.
People In News
Padma Awards: President of India Shri Ram Nath Kovind presented the two Padma Vibhushan, eight Padma Bhushan and 54 Padma Shri Awards at the Civil Investiture Ceremony-I held at Rashtrapati Bhavan on 21 March 2022.
This year a total of 128 Padma Awards are being conferred, including two duo cases (in a duo case, the award is counted as one). The list of awardees comprises four Padma Vibhushan, 17 Padma Bhushan and 107 Padma Shri Awards.
The Civil Investiture CeremonyII is scheduled to be held on March 28.
Padma Vibhushan(4):
- Ms. Prabha Atre Art Maharashtra
- Shri Radheyshyam Khemka (Posthumous) Literature & Education Uttar Pradesh
- General Bipin Rawat Civil Service Uttarakhand (Posthumous)
- Shri Kalyan Singh Public Affairs Uttar Pradesh (Posthumous)
Padma Bhushan(17):
- Shri Ghulam Nabi Azad Public Affairs Jammu and Kashmir
- Shri Victor Banerjee Art West Bengal
- Ms. Gurmeet Bawa (Posthumous) Art Punjab
- Shri Buddhadeb Bhattacharjee Public Affairs West Bengal
- Shri Natarajan Chandrasekaran Trade and Industry Maharashtra
- Shri Krishna Ella and Smt. Suchitra Ella* (Duo) Trade and Industry Telangana
- Ms. Madhur Jaffery Others-Culinary
- Shri Devendra Jhajharia Sports Rajasthan
- Shri Rashid Khan Art Uttar Pradesh
- Shri Rajiv Mehrishi Civil Service Rajasthan
- Shri Satya Narayana Nadella Trade and Industry USA
- Shri Sundararajan Pichai Trade and Industry USA
- Shri Cyrus Poonawalla Trade and Industry Maharashtra
- Shri Sanjaya Rajaram (Posthumous) Science and Engineering Mexico
- Ms. Pratibha Ray Literature and Education Odisha
- Swami Sachidanand Literature and Education Gujarat
- Shri Vashishth Tripathi Literature and Education Uttar Pradesh
Padma Shri(107):
- Shri Prahlad Rai Agarwala Trade and Industry West Bengal
- Prof. Najma Akhtar Literature and Education Delhi
- Shri Sumit Antil Sports Haryana
- Shri T Senka Ao Literature and Education Nagaland
- Ms. Kamalini Asthana and Ms.Nalini Asthana* (Duo) Art Uttar Pradesh
- Shri Subbanna Ayyappan Science and Engineering Karnataka
- Shri J K Bajaj Literature and Education Delhi
- Shri Sirpi Balasubramaniam Literature and Education Tamil Nadu
- Srimad Baba Balia Social Work Odisha
- Ms. Sanghamitra Bandyopadhyay Science and Engineering West Bengal
- Ms. Madhuri Barthwal Art Uttarakhand
- Shri Akhone Asgar Ali Basharat Literature and Education Ladakh
- Dr. Himmatrao Bawaskar Medicine Maharashtra
- Shri Harmohinder Singh Bedi Literature and Education Punjab
- Shri Pramod Bhagat Sports Odisha
- Shri S Ballesh Bhajantri Art Tamil Nadu
- Shri Khandu Wangchuk Bhutia Art Sikkim
- Shri Maria Christopher Byrski Literature and Education Poland
- Acharya Chandanaji Social Work Bihar
- Ms. Sulochana Chavan Art Maharashtra
- Shri Neeraj Chopra Sports Haryana
- Ms. Shakuntala Choudhary Social Work Assam
- Shri Sankaranarayana Menon Chundayil Sports Kerala
- Shri S Damodaran Social Work Tamil Nadu
- Shri Faisal Ali Dar Sports J&K
- Shri Jagjit Singh Dardi Trade and Industry Chandigarh
- Dr. Prokar Dasgupta Medicine United Kingdom
- Shri Aditya Prasad Dash Science and Engineering Odisha
- Dr. Lata Desai Medicine Gujarat
- Shri Malji bhai Desai Public Affairs Gujarat
- Ms. Basanti Devi Social Work Uttarakhand
- Ms. Lourembam Bino Devi Art Manipur
- Ms. Muktamani Devi Trade and Industry Manipur
- Ms. Shyamamani Devi Art Odisha
- Shri Khalil Dhantejvi (Posthumous) Literature and Education Gujarat
- Shri Savaji Bhai Dholakia Social Work Gujarat
- Shri Arjun Singh Dhurve Art Madhya Pradesh
- Dr. Vijaykumar Vinayak Dongre Medicine Maharashtra
- Shri Chandraprakash Dwivedi Art Rajasthan
- Shri Dhaneswar Engti Literature and Education Assam
- Shri Om Prakash Gandhi Social Work Haryana
- Shri Narasimha Rao Garikapati Literature and Education Andhra Pradesh
- Shri Girdhari Ram Ghonju (Posthumous) Literature and Education Jharkhand
- Shri Shaibal Gupta (Posthumous) Literature and Education Bihar
- Shri Narasingha Prasad Guru Literature and Education Odisha
- Shri Gosaveedu Shaik Hassan (Posthumous) Art Andhra Pradesh
- Shri Ryuko Hira Trade and Industry Japan
- Ms. Sosamma Type Others - Animal Husbandry Kerala
- Shri Avadh Kishore Jadia Literature and Education Madhya Pradesh
- Ms. Sowcar Janaki Art Tamil Nadu
- Ms. Tara Jauhar Literature and Education Delhi
- Ms. Vandana Kataria Sports Uttarakhand
- Shri H R Keshavamurthy Art Karnataka
- Shri Rutger Kortenhorst Literature and Education Ireland
- Shri P Narayana Kurup Literature and Education Kerala
- Ms. Avani Lekhara Sports Rajasthan
- Shri Moti Lal Madan Science and Engineering Haryana
- Shri Shivnath Mishra Art Uttar Pradesh
- Dr. Narendra Prasad Misra (Posthumous) Medicine Madhya Pradesh
- Shri Darshanam Mogilaiah Art Telangana
- Shri Guruprasad Mohapatra (Posthumous) Civil Service Delhi
- Shri Thavil Kongampattu A V Murugaiyan Art Puducherry
- Ms. R Muthukannammal Art Tamil Nadu
- Shri Abdul Khader Nadakattin Others - Grassroots Innovation Karnataka
- Shri Amai Mahalinga Naik Others - Agriculture Karnataka
- Shri Tsering Namgyal Art Ladakh
- Shri A K C Natarajan Art Tamil Nadu
- Shri V L Nghaka Literature and Education Mizoram
- Shri Sonu Nigam Art Maharashtra
- Shri Ram Sahay Panday Art Madhya Pradesh
- Shri Chirapat Prapandavidya Literature and Education Thailand
- Ms. K V Rabiya Social Work Kerala
- Shri Anil Kumar Rajvanshi Science and Engineering Maharashtra
- Shri Sheesh Ram Art Uttar Pradesh
- Shri Ramachandraiah Art Telangana
- Dr. Sunkara Venkata Adinarayana Rao Medicine Andhra Pradesh
- Ms. Gamit Ramilaben Raysingbhai Social Work Gujarat
- Ms. Padmaja Reddy Art Telangana
- Guru Tulku Rinpoche Others - Spiritualism Arunachal Pradesh
- Shri Brahmanand Sankhwalkar Sports Goa
- Shri Vidyanand Sarek Literature and Education Himachal Pradesh
- Shri Kali Pada Saren Literature and Education West Bengal
- Dr. Veeraswamy Seshiah Medicine Tamil Nadu
- Ms. Prabhaben Shah Social Work Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu
- Shri Dilip Shahani Literature and Education Delhi
- Shri Ram Dayal Sharma Art Rajasthan
- Shri Vishwamurti Shastri Literature and Education J&K
- Ms. Tatiana Lvovna Shaumyan Literature and Education Russia
- Shri Siddhalingaiah (Posthumous) Literature and Education Karnataka
- Shri Kaajee Singh Art West Bengal
- Shri Konsam Ibomcha Singh Art Manipur
- Shri Prem Singh Social Work Punjab
- Shri Seth Pal Singh Others - Agriculture Uttar Pradesh
- Ms. Vidya Vindu Singh Literature and Education Uttar Pradesh
- Baba Iqbal Singh Ji Social Work Punjab
- Dr. Bhimsen Singhal Medicine Maharashtra
- Shri Sivananda Others - Yoga Uttar Pradesh
- Shri Ajay Kumar Sonkar Science and Engineering Uttar Pradesh
- Ms. Ajita Srivastava Art Uttar Pradesh
- Sadguru Brahmeshanand Acharya Swami Others - Spiritualism Goa
- Dr. Balaji Tambe (Posthumous) Medicine Maharashtra
- Shri Raghuvendra Tanwar Literature and Education Haryana
- Dr. Kamlakar Tripathi Medicine Uttar Pradesh
- Ms. Lalita Vakil Art Himachal Pradesh
- Ms. Durga Bai Vyam Art Madhya Pradesh
- Shri Jyantkumar Maganlal
- Vyas Science and Engineering Gujarat
- Ms. Badaplin War Literature and Education Meghalaya
About Padma Awards:
- Padma Awards are the highest civilian awards in India.
- These awards are conferred in three categories- Padma Vibhushan, Padma Bhushan, and Padma Shri.
- They are presented by the President of India.
- The Padma Awards are being awarded to the citizens since 1954.
- The awards are being presented under the categories such as social work, art, science and engineering, public affairs, medicine, trade and industry, civil service, education, sports, etc.
- Padma Vibhushan is awarded for exceptional and distinguished service.
- Padma Bhushan for distinguished service of a high order.
- Padma Shri for distinguished service in any field.
Abel Prize for 2022: the Abel Prize for the year 2022 has been awarded to American Mathematician Dennis Parnell Sullivan by the Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters.
Key Highlights:
- This award also includes prize money which amounts to 7 Million NOK (Norwegian Krone).
- He was awarded the prize for his groundbreaking contributions to topology in its broadest sense and in particular its algebraic, geometric and dynamical aspects.
What is Topology?
- Topology is a new field of mathematics that has to do with the properties of surfaces that do not change when they are deformed.
- It was born at the end of the 19th century.
- For instance, topologically, a circle and a square are the same; similarly, the surfaces of a doughnut and a coffee mug with one handle are topologically equivalent, however, the surface of a sphere and a coffee mug is not equivalent.
- Topology is important in math and various other fields like data economics, science and physics.
About Dennis P. Sullivan:
- Prof. Sullivan is from the City University of New York and the State University of New York at Stony Brook.
- He has won numerous awards, among them the Steele Prize, the 2010 Wolf Prize in Mathematics and the 2014 Balzan Prize for Mathematics.
- He is also a fellow of the American Mathematical Society.
About Abel Prize:
- The King of Norway presents the Abel Prize.
- It is given annually to an individual who has done a remarkable job in the mathematics field.
- It was established on 23 August 2001.
- This prize has been named after Niels Henrik Abel who was a famous Norwegian mathematician.
- It is directly modeled after the Nobel Prizes.
- Nobel Prize doesn’t have a section for mathematics, though some mathematicians have won this prestigious prize in other fields.
- The Fields Medal is an annual award that is also considered to be the ‘Mathematics Nobel’ but it is only awarded to those individuals who are below the age of 40.
- It is funded by the Norwegian Government.
- The laureates are selected by the Abel Committee, the members of which are appointed by the Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters.
- The award ceremony takes place in the Aula of the University of Oslo, where the Nobel Peace Prize was awarded between 1947 and 1989.
Note:
- The Abel Prize was first awarded in 2003 to Jean-Pierre Serre, a French mathematician, for his contribution to algebraic geometry, topology, and number theory.
- In 2007, S. R. Srinivasa Varadhan, who is an Indian-American citizen had won the Abel Prize for his contribution in probability theory and for creating a unified large deviation theory.
- In 2019, Karen Uhlenbeck became the first woman to win the Abel Prize, with the award committee citing "the fundamental impact of her work on analysis, geometry and mathematical physics.
Fellow of Royal Society of Edinburgh: Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw, the executive chairperson of Biocon and Biocon Biologics, has been elected as a fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (RSE) in Scotland.
Key Highlights:
- She will be joining RSE’s current fellowship of around 1,700 fellows who are recognized as being some of the greatest researchers and practitioners working in or with Scotland.
- The Biocon chief is among the 80 luminaries to be appointed to the RSE’s Fellowship this year.
About RSE:
- The Royal Society of Edinburgh (RSE) is one of the world’s oldest and most respected academic societies.
- It is Scotland’s National Academy established in 1783, for the advancement of learning and useful knowledge.
- Fellows are elected to join the RSE from across the fields of education, science, arts, business and public life in recognition of their impact on improving the world around them.
About Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw:
- Ms Kiran Mazumdar-Shaw is a pioneering biotech entrepreneur, a healthcare visionary, a global influencer, and a passionate philanthropist.
- She holds key positions in various industry, educational, government and professional bodies.
- She was elected a full-term member of the Board of Trustees of the prestigious Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), U.S., in 2018 and as a Member of the National Academy of Engineering, U.S., in 2019.
- She is also among the earliest Indian signatories to the Giving Pledge, a global commitment to dedicate majority of her wealth to philanthropy.
- As Founder of Biocon, an innovation-led global biopharmaceuticals enterprise, her vision and work have drawn global recognition both for the Indian industry and her company.
- The impact she has made as a leading woman in science has made her a role model globally.
- She is committed to equitable access to healthcare through affordable innovation as she pursues a path of making a difference in billions of lives globally.
- During the Covid-19 crisis, she has been championing the cause of the healthcare industry in finding innovative solutions to combat the pandemic.
Awards:
Her inspiring achievements have earned her several coveted titles and awards, both national and international.
- She has been recognized with two of India’s highest civilian honours, the Padma Shri (1989) and the Padma Bhushan (2005).
- She has been conferred with the Order of Australia, Australia’s highest civilian honour, in 2020 and appointed Knight of the National Order of the French Legion of Honour in 2016.
- She was named EY World Entrepreneur of the Year in 2020.
- In 2014, she was honoured with the Othmer Gold Medal by the U.S.-based Chemical Heritage Foundation.
- The same year, the Kiel Institute for the World Economy, Germany, awarded her the Global Economy Prize.
Places In News
Bihar Diwas 2022: Bihar is celebrating its 109th foundation day on March 22, 2021.
Key Highlights:
- Bihar Day (Bihar Diwas) is observed every year on March 22, marking the formation of the state of Bihar.
- It was on this day that the British carved out the state from Bengal in 1912.
- The day is a public holiday in Bihar.
- Three-day function will be organized on this occasion.
- Altogether 18 departments of the state and different organizations are participating in the mega event. A drone show will also be organized in which 500 drones will fly together.
Bihar Diwas 2022 Theme:
- The theme of Bihar Diwas 2022 is ‘Jal, Jeevan, Hariyali’.
- The theme of Bihar Day signifies the prosperity in the state which is also rich in its cultural heritage.
Background:
- Bihar Day was started and celebrated on large scale by Bihar Government in the tenure of Nitish Kumar.
- Bihar Diwas was first celebrated on a large-scale in 2010
History:
- On October 22, 1764, the Battle of Buxar was fought between the forces of the East India Company led by Hector Munro and the joint army of the Nawab of Bengal, the Nawab of Awadh and the Mughal King Shah Alam II.
- The battle was fought at Buxar and was a massive victory for the East India Company.
- The defeat resulted in the Mughals and Nawabs of Bengal losing control over the territories and the East India Company according to the Diwani rights – the right to administer the collection and management of revenues.
- The territories consisted of the current state of West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, Orissa, and Bangladesh.
- In 1911, King George V was coronated in Delhi and the capital of British India was shifted to Delhi.
- On March 21, 1912, Thomas Gibson Carmichael, the new governor of Bengal took charge.
- He announced that from March 22, 1912, the Bengal Presidency will be split into four subhas of Bengal, Orissa, Bihar, and Assam.
- Thus the state of Bihar was carved out from the Bengal Presidency of British India on March 22, 1912.
Note: Apart from India, it is also celebrated in countries including the United States, Germany, Britain (Scotland), Australia, Canada, Bahrain, Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Trinidad and Tobago and Mauritius.
About Bihar:
- Bihar is a state in East India, bordering Nepal and is the third-largest state by population across India.
- It is also the twelfth-largest state by territory.
- The state is having an area of 94,163 km2.
- It is surrounded by Uttar Pradesh in the west, Nepal in the north, northern part of West Bengal in the east and Jharkhand in the south.
- The plain is split by the river Ganges flows from west to east.
- The three main cultural regions of the state include Mithila, Magadh, and Bhojpur.
- Official languages of the state are Hindi and Urdu.
Note: The southern part of the state was carved out to form Jharkhand on November 15, 2000.
History of Bihar:
- In ancient and classical India, Bihar was once regarded as the epicenter of power, intellect, and culture in ancient and classical India. Magadha was the birthplace of India's first empire, the "Maurya Empire."
- Also, Bihar is considered the origin of the most widely adhered-to religion of the world called Buddhism.
AquaMAP Water Management and Policy Centre: The Principal Scientific Adviser to the Government of India, Prof. K. VijayRaghavan, at IIT Madras recently inaugurated the new water management and policy centre, called ‘AquaMAP’ to solve water problems in India.
Key points:
- He also launched its website https://aquamap.iitm.ac.in/.
- The aim of AquaMAP is to provide solutions regarding the challenges faced due to water problems by implementing smart water management practices.
- The water management practices will also be implemented across various fields across the nation.
- They will be used as scalable models for innovative management technologies.
- AquaMAP, a national water centre under which IIT Madras is collaborating with IIT Dharwad.
- It is collaborating on the broad theme of ‘Data Science for Water Security and Agriculture Sustenance.’
Aim of AquaMAP:
- AquaMAP looks to achieve the capability to address real-life water problems which are complex in nature through a consortium approach.
- It looks to establish itself as an entity that can deliver solutions with a wide range of applications and a broad impact.
- It intends to complete pilot studies in a minimum of six water innovation villages or towns, which will then be showcased as models which can be replicated for policy implementation and water management, within India.
- It will also attempt to address a minimum of three chronic water issues through various Grand Challenges and their transition into pilot projects.
- A state-of-the-art Hydro-Informatics Laboratory will also be set up under this project.
- A Community and Alumni Engagement Model will also be established.
AquaMAP Team:
- Ligy Philip, Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Madras, and dean (planning), IIT Madras, is the principal investigator of AquaMAP.
- 20 faculty members working on water-related issues and drawn from diverse departments such as Chemistry, Civil Engineering, Electrical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Management, Mechanical Engineering, and Humanities and Social Sciences will be supporting Ligy Philip.
- AquaMAP will also include a governing body, which will be chaired by the director of IIT Madras, as well as an advisory board, which will include many notable persons in the fields of water technology, policy, and management.
National e-Vidhan Application: Nagaland recently created history by becoming the first State Assembly in the country to implement the National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA) programme to become completely paperless.
The Nagaland Assembly Secretariat has attached a tablet or e-book on each table in the 60 members’ assembly amid the ongoing Budget session.
About National e-Vidhan Application (NeVA):
NeVA is a workflow system deployed on NIC Cloud, MeghRaj that assists the Chair of the House in conducting the proceedings of the House smoothly and also in conducting Legislative Business of the House in a Paperless manner.
NeVA is a device neutral and member-centric application designed to equip them to smartly handle diverse House Business by putting entire information regarding member contact details, list of business, rules of procedure, bulletins, notices, bills, starred/unstarred questions and answers, papers laid, committee reports, etc. in their handheld devices/ tablets and equipping all legislatures/departments to handle it effectively.
Aim of NeVA:
NeVA aims to connect the country's legislators together on a single platform, resulting in a vast data repository without the complexity of various apps.
Benefits of NeVA:
- Through the use of NeVA the process of sending out a request or notice for the data collection is completely eliminated.
- Each Member of the House has a secure page where they can submit questions and other notices.
- mNeVA is a user-friendly mobile version of NeVA that is accessible on both Android and iOS.
- mNeVA has made information about how legislatures conduct business available to the public which can be accessed any time and from any location.
The expenses for implementing NeVA are funded by the Centre and the state government on a 90:10 sharing basis.
About Nagaland:
- Nagaland is a mountainous state in northeast India, bordering Myanmar.
- It was formally inaugurated on December 1st, 1963, as the 16th State of the Indian Union.
- It is bounded by Assam in the West, Myanmar (Burma) on the east, Arunachal Pradesh and part of Assam in the North and Manipur in the South.
- Kohima is the capital of Nagaland.
- The Chief Minister and the Governor of Nagaland are Neiphiu Rio and Prof Jagdish Mukhi (additional charge) respectively.
About the Legislative Assembly of Nagaland:
- The Legislative Assembly of Nagaland (Vidhan Sabha) is the real executive and legislative body of the state.
- The 60-member of Vidhan Sabha are all elected members of the legislature who form the government executive.
- It is led by the Chief Minister.
- Unlike most states in India, Nagaland has been granted a great degree of state autonomy, as well as special powers and autonomy for Naga tribes to conduct their own affairs.
- Each tribe has a hierarchy of councils at the village, range, and tribal levels dealing with local disputes.
Carbon-Neutral Farming Methods: Kerala has become the first state in the country to introduce carbon-neutral farming practices in selected locations for better soil health.
Key Highlights:
- The government of Kerala government had budgeted 6 crores in the 2022-23 fiscal year for introducing carbon-neutral farming practices.
- In the first phase, carbon-neutral farming will be implemented in 13 farms under the Agriculture Department and tribal areas, and plans are underway to convert the State Seed Farm at Aluva to a carbon-neutral farm.
- In the second phase, model carbon-neutral farms will be developed in all the 140 Assembly constituencies.
Note:
- Agriculture and related land-use change are responsible for generating one-quarter of the world’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
- It can also lead to the conversion of valued habitats or eliminate biodiversity.
- Agricultural production also accounts for the majority of methane and nitrogen dioxide emissions.
- This mainly comes from enteric fermentation and cattle manure, over-application of fertiliser and flooding rice paddies.
About Carbon-Neutral Farming:
Carbon-Neutral Agricultural is a technique of reducing carbon emissions and aiding carbon storage in the soil by employing tactics such as -
- Integrated farming methods
- Changing the way the soil is watered,
- Limiting the indiscriminate application of fertilizers.
What is the Need for Carbon Farming?
- Offsets carbon emissions and reduces the volume of greenhouse gases (GHG) that agriculture releases into the atmosphere
- It results in improved soil health by increasing soil fertility, reducing soil salinity, and boosting microbial activity and soil biodiversity.
- It minimizes soil erosion and nutrient runoff while also purifying surface and groundwater.
- It has the immense potential to reverse climate change effects when implemented on a large scale.
- It improves crop yields as well as native vegetation, habitat, and animal health
- It provides financial incentives to farmers in the form of carbon credits
About Kerala:
- It is a state on the southwestern Malabar Coast of India.
- It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganization Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile states of Travancore-Cochin and Madras.
- It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Lakshadweep Sea to the west. Its capital is Thiruvananthapuram.
- The current Governor and Chief Minister of Kerala are Arif Mohammad Khan and Pinarayi Vijayan respectively.
Science and Technology
GSAT 7B Satellite: The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC) has given the Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) for Capital Acquisition proposals of Armed Forces amounting to Rs 8,357 crore.
Key Highlights:
- The AoN for procurement of a GSAT 7B satellite, along with equipment like Night Sight (image intensifier), 4X4 light vehicles, and Air Defence Fire Control Radar (light) was given at the meeting of 22nd March 2022 held under the Chairmanship of Raksha Mantri Shri Rajnath Singh.
- All of these proposals have been approved under ‘Buy (Indian IDDM)’ category with focus on indigenous design & development and manufacturing in India, as an impetus to ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’.
Note: IDDM stands for indigenously designed, developed and manufactured.
- The DAC also accorded consolidated AoN for procurements of Rs 380.43 crore from iDEX startups and MSMEs in a ground-breaking programme to encourage innovation.
- The DAC, to accelerate the pace of indigenisation, achieve self-reliance in defence and to facilitate Ease of Doing Business for defence industry approved effecting the following policy initiatives in the DAP-2020:
- All modernisation requirements of defence forces to be indigenously sourced with imports used only as a last option.
- To reduce financial burden on defence industry, the IPBG (Integrity Pact Bank Guarantee) requirement will be eliminated, and an Earnest Money Deposit (EMD) will be used as bid security and PCIP(Pre Contract Integrity Pact) coverage up to contract stage.
- EMD will be applicable only for proposals of Rs 100 Cr and above and MSMEs & Startups will be exempted from EMD.
- Vendors whose products are successfully trial evaluated will be provided a certificate to that effect.
- iDEX and Make II procedures have been simplified resulting in compressing timelines and ensuring early placement of contracts on successful iDEX and Make II vendors.
About GSAT 7 satellites:
- The GSAT 7 satellites are advanced satellites developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) to meet the communication needs of the defence services.
- The GSAT 7 satellite was launched in August 2013 from an Ariane 5 ECA rocket from Kourou in French Guiana.
- It is a 2,650 kg satellite which has a footprint of nearly 2,000 nautical miles in the Indian Ocean region.
- This satellite is mainly used by the Indian Navy for its communication needs.
- The GSAT 7 provides a gamut of services for military communication needs, which includes low bit voice rate to high bit rate data facilities, including multi-band communications.
- Named Rukmini, the satellite carries payloads in UHF, C-band and Ku-band.
- It helps the Navy to have a secure, real time communication link between its land establishments, surface ships, submarines and aircraft.
- The satellite was injected into a geosynchronous transfer orbit (GTO) of 249 km perigee (nearest point to earth), 35,929 km apogee (farthest point to earth) and an inclination of 3.5 degree with respect to the equator.
- The Army currently is using 30% of the communication capabilities of the GSAT 7A satellite, which has been designed for the Indian Air Force (IAF).
About DAC:
- The Defence Acquisition Council (DAC)is the highest decision-making body in the Defence Ministry for deciding on new policies and capital acquisitions for the three services (Army, Navy and Air Force) and the Indian Coast Guard.
- The Minister of Defence is the Chairman of the Council.
- It was formed, after the Group of Ministers recommendations on 'Reforming the National Security System', in 2001, post Kargil War (1999).
Objective of DAC:
- The main objective of the DAC is to ensure expeditious procurement of the approved requirements of the Armed Forces in terms of capabilities sought, and time frame prescribed, by optimally utilizing the allocated budgetary resources.
Monster Missile Hwasong-17: North Korea successfully test-fired the Hwasong-17 intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) recently.
- The Hwasong-17 missile was launched for testing from a Transporter Erector Launcher (TEL) vehicle.
About Monster Missile Hwasong-17:
- This is the world's largest intercontinental ballistic missile ever developed.
- The diameter of this missile is between 2.4 and 2.5 meters.
- When fully fuelled, it has a total mass of around 80,000 to 1,10,000 kg.
- This missile has the capability to deliver a nuclear warhead to any United States (US) location.
- The analysts have named this missile a ‘monster missile’.
- This missile was first shown to the public at a military parade commemorating the ruling Workers' Party's 75th anniversary in the year 2020.
- It was again displayed in 2021 in Pyongyang at a defense exhibition.
- Due to this missile’s size, it is being speculated that the Hwasong-17 capable of carrying numerous decoys and warheads, allowing it to effectively penetrate a country's missile defence system.
Ayurveda for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Ayush Ministry has recently launched the world’s first multicenter phase III clinical trial that will be assessing Ayurveda’s efficacy in Rheumatoid Arthritis treatment.
Key Details:
- The clinical trial will be conducted in accordance with stringent International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use – Good Clinical Practice guidelines.
- The trial will be closely monitored by Dr Daniel Erick Furst, a renowned rheumatologist at University of California Los Angeles in the United States of America.
- Dr. Edzard Ernst, currently the Director of Clinical Research at Arthritis Association of South California (AASC) and a vociferous critic of CAM, has endorsed the study as a model for future investigations on Complementary and Alternative Medicine(CAM).
- The trial will be conducted by the AVP Research Foundation, affiliated to the Arya Vaidya Pharmacy (Coimbatore) Ltd and the Central Council for Research in Ayurveda (CCRAS), Ministry of Ayush.
- The study is expected to begin in May 2022 and is expected to be completed in the next two years.
- The sample size has increased almost five times, from 48 patients to 240.
Where will the trials be conducted?
It will be conducted at three locations which are -
- Central Ayurveda Research Institute for Metabolic Disorders,
- Bengaluru, AVP Research Foundation, Coimbatore, and
- Raja Ramdeo Anandilala Central Ayurveda Research Institute for Cancer, Mumbai.
About Rheumatoid Arthritis:
- Rheumatoid arthritis is an inflammatory autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks the healthy cells by mistake.
- This causes inflammation in the body parts that are affected.
- This disease mainly occurs in the joints like the joints in the knees, wrists, and hands.
Sports
Badminton world rankings: For the first time, the All England Badminton Championship runner-up Lakshya Sen has broken into the top 10 of the men's singles badminton world rankings.
Key Highlights:
- The 20-year-old from Uttarakhand, climbed two spots to reach ninth in the latest standings.
- His silver medal winning feat at the All England Badminton Championships helped him break into the top 10 of the latest BWF World Ranking.
- He is now the highest-ranked Indian in the men's singles badminton, above world silver medallist Kidambi Srikanth at 12 and Tokyo Olympian B Sai Praneeth at 19.
- On 19th March 2022, Sen had become only the fifth Indian after Prakash Nath (1947), Prakash Padukone (1980, 1981), Pullela Gopichand (2001) and Saina Nehwal (2015) to reach the final of the prestigious tournament after outwitting defending champion Lee Zii Jia in a gruelling semifinal.
- The Indian Star shuttler defeated defending champion Lee Zee Jia and world bronze medallist Anders Antonsen before he lost in the final against Denmark's Viktor Axelsen.
- This was his third straight final appearance at a BWF World Tour event since winning the India Open and a second-place finish at the German Open.
- Along with Sen, Commonwealth Games silver medallists Satwiksairaj Rankireddy and Chirag Shetty also moved up a spot to equal their career-best ranking of seventh.
- The Chirag-Satwik duo won the India Open, finished third at the Super 1000 Indonesia Open and also represented India at Tokyo 2020.
- In the women's doubles, Treesa Jolly and Gayatri Gopichand also jumped 12 places to reach a career-best world number 34, riding on their maiden semifinal finish at the All England Championship.
- Double Olympic medallist P V Sindhu remained at world number 7, while Saina climbed two places to 23rd, following a second round defeat at All England.
About England Badminton Championships:
- The All England Open Badminton Championships is the world's oldest badminton tournament, held annually in England.
- With the introduction of the BWF's latest grading system, it was given Super Series status in 2007, upgraded to Super Series Premier status in 2011.
2022 All England Open:
- The 2022 All England Open (officially known as the Yonex All England Open Badminton Championships 2022 for sponsorship reasons) was a badminton tournament that took place at Utilita Arena Birmingham in Birmingham, England, from 16 to 20 March 2022.
- It had a total prize pool of $990,000.
- The 2022 All England Open was the fifth tournament of the 2022 BWF World Tour and was part of the All England Open Badminton Championships, which had been held since 1899.
- The tournament was organized by the Badminton England with sanction from the Badminton World Federation.
Indian Super League: Hyderabad FC recently clinched their maiden Indian Super League title.
Key Highlights:
- They won their maiden trophy after defeating Kerala Blasters in the penalty shoot-out in the summit clash.
- Hyderabad beat Kerala 3-1 in the shoot-out after the match ended 1-1 in the regulation and extra time.
- Goalkeeper Laxmikant Kattimani made three stunning saves.
- Joao Victor, Khassa Camara, and Halicharan Narzary scored for Hyderabad, while only Ayush Adhikari scored in the shoot-out as Kerala was eliminated for the third time in the finals.
2022 BNP Paribas Open Tennis Tournament: The 2022 BNP Paribas Open tennis tournament was held from March 07 to 20, 2022 at Indian Wells, California, US.
Key highlights:
- The 2022 BNP Paribas Open tennis tournament is also known as the 2022 Indian Wells Masters.
- The BNP Paribas Open is the largest two-week combined event outside of the four Grand Slams.
- It is the most-attended WTA 1000 and ATP World Tour Masters 1000 tennis tournament in the world.
List of winners:
Singles Category:
- Women’s singles - Iga ÅšwiÄ…tek (Poland)
- Men’s Singles - Taylor Fritz (United States)
Doubles Category:
- Women’s Doubles - Xu Yifan / Yang Zhaoxuan
- Men’s Doubles - John Isner / Jack Sock
F1 Bahrain Grand Prix 2022: Charles Leclerc (Ferrari- Monaco) has won the Formula One Bahrain Grand Prix 2022.
Key Highlights:
- The Formula One Bahrain Grand Prix 2022 was held at the Bahrain International Circuit, a motor racing circuit in the west of Bahrain.
- Carlos Sainz Jr. (Ferrari – Spain) came second while Lewis Hamilton (Mercedes-Great Britain) came third.
- This was the first Formula One race of 2022.
Arts
Mangarh: National Monuments Authority(NMA) Chairman Shri Tarun Vijay recently submitted a report to the Minister of Culture on declaring Mangarh hillock in Rajasthan as a monument of National Importance as tribute to 1500 Bhil tribal freedom fighters.
Key Highlights:
The report was submitted by him and his team to the Minister of State for Culture Shri Arjun Ram Meghwal at Indira Gandhi National Centre for Arts (IGNCA), New Delhi.
This report carries relevant details about the Mangarh hillock and recommendations by National Monuments Authority.
Mangarh Hillock:
- Mangarh Hillock is a hillock in the Aravalli range located in Banswara District, Rajasthan.
- It is situated near the Rajasthan-Gujarat border.
- It is a site of a tribal uprising where a massacre of over 1500 Bhil tribal freedom fighters took place in 1913.
- Hence, this place is also known as the Adivasi Jallianwala.
History:
On 17 November 1913, a gathering of local Bhils numbering about 1500 were brutally killed by the British army when they refused to disperse.
- The Bhils present were supporters of social reformer Govind Guru who was influenced by social reformers like Dayanand Saraswati.
- Govind Guru had led the “Bhagat movement” in the late 19th century among Bhil tribes in an effort to ’emancipate’ them by prescribing, among other things, adherence to vegetarianism and abstinence from all kinds of intoxicants.
- The Bhils rose in rebellion against the oppressive policies of the British.
- They began opposing taxes imposed by the British and forced labour imposed by the princely states of Banswara, Santrampur, Dungarpur and Kushalgarh.
- The British and princely kingdoms, worried by the tribal revolt made the decision to crush the uprising.
- Govind guru was captured and exiled from the area.
- He was imprisoned in Hyderabad jail and released in 1919 on grounds of good behaviour.
- But as he was exiled from his homeland, he settled in Gujarat where he died in 1931.
Sao Joao festival 2022: The people of Goa recently celebrated the Sao Joao festival.
Key Highlights:
- A large number of people participated in the boat parade in Siolim village of Goa’s Bardez taluka, marking the beginning of revelry in the ‘Sao Joao’ festival.
- Traditionally, people jump into the well but since the wells are fast disappearing, people prefer to celebrate it in swimming pools.
About the festival:
- Sao Joao festival is the feast of St John the Baptist with traditional enthusiasm after a two-year coronavirus-induced gap.
- The festival is dedicated to Saint John the Baptist, who baptised Lord Jesus on the river of Jordan and is celebrated at the onset of monsoon.
- Siolim, a village in North Goa, hosts a traditional canoe parade on the occasion of Sao Joao.
- The festival is marked to herald the monsoon season in the state every year in June.
- People are often seen having a great time by enjoying and dancing in the artificial rain which adds charm to the celebrations.
Economics
Udyami Bharat Programme: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently participated in Udyami Bharat Programme in New Delhi.
Key Points:
During the event, Mr Modi launched the following key initiatives:
- Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance(RAMP) scheme
- Capacity Building of First-Time MSME Exporters(CBFTE) scheme
- New features of Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP) to boost the MSME sector.
- Digital Equity Certificates were also issued to 75 MSMEs in Self Reliant India (SRI) Fund.
He transferred the assistance to beneficiaries of PMEGP, digitally, for 2022-23.
He announced results of MSME Idea Hackathon, 2022 and distributed National MSME Awards, 2022.
About RAMP scheme:
- The Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance(RAMP) scheme was launched with an outlay of around Rs 6000 crore.
- Its goal is to scale up the implementation capacity and coverage of MSMEs in the States, with impact enhancement of existing MSME schemes.
- It will complement the Aatmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan, by encouraging innovation, ideation, entrepreneurship, improving practices & process, incubating new business by developing quality standards, enhancing market access, deploying technological tools and Industry 4.0 for making MSMEs competitive and self-reliant.
About CBFTE Scheme:
- The Capacity Building of First-Time MSME Exporters (CBFTE) scheme aims to encourage MSMEs for offering products and services of international standards to global market.
- This will enhance the participation of Indian MSMEs at international value chain. CBFTE will help them in realizing their export potential.
New features of the PMEGP:
New features of Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP) include:
- For Manufacturing sector , an increase in maximum project cost from Rs 25 lakhs to Rs 50 lakhs for manufacturing sector
- For service sector, an increase in maximum project cost from Rs 10 lakhs to Rs 20 lakhs.
MSME Idea Hackathon, 2022:
- The Hackathon was organized with the aim of promoting and supporting the untapped creativity of individuals and promoting latest technologies & innovation among MSMEs.
- The selected incubatee ideas will be provided funding support of up to 15 lakhs per approved idea.
National MSME Awards 2022:
- The award recognises the contributions of MSMEs, Aspirational Districts, states/UTs, and Banks for their outstanding performance in terms of growth and development of MSME sector in India.
Chartered Accountants Day 2022: The Chartered Accountants’ Day or CA Day is held on 01 July every year in India.
Key Points:
- The day is aimed at acknowledging the contribution of chartered accountants in nation-building.
- It also honours the crucial role played by chartered accountants in the economic growth of the country.
- The year 2022 Chartered Accountants Day marks 74th anniversary of the establishment of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) by an Act of the Parliament.
History:
- The Chartered Accountants’ Day honors the founding of the ICAI.
- It is the second-largest accounting organization in the world and the country’s first national professional accounting body.
- It was created on July 1st, 1949, as a statutory body by the Indian Parliament under the Chartered Accountants Act.
- India celebrates this day each year to commemorate the founding of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI).
Significance:
- The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI)is a key player in the regulation of the accounting profession in India.
- Besides regulating the chartered accountancy profession, the ICAI carries out other duties in the field.
- These include education and examination of chartered accountancy course, formulation of accounting standards, prescribing standard auditing procedures, laying down ethical standards, exercising disciplinary jurisdiction, and giving inputs on policy matters to the government.
Importance of Chartered Accountants:
- Chartered Accountants have become a major part of the tax planning, capital budgeting and budget forecasting processes for GST implementation.
- They have become a key player in the running economy of the country.
- Every nation and business in today's globalised world aspires to work with foreign firms. Charter Accountants can help them with the laws of Foreign Exchange Management or even conduct business on an international level that will influence the outflow of foreign currency.
As APJ Abdul Kalam has rightly put it, “Chartered Accountants are the partners in nation building.” Not just in leveraging the economy, but they also minimise corruption by educating people and preventing them from engaging in corrupt practices.
- A CA will be knowledgeable and skilled in the areas of finance, taxation, and corporate law, among others, and will impart his or her knowledge and solutions to any financial problems.
About ICAI:
- The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) functions under the administrative control of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India (GOI).
- It was established on 1st July in the year 1949 under an Act passed in Parliament.
- It is the national professional accounting body of India and also the second biggest accounting organization in the world.
- It is the sole licensing and regulatory body for the financial audit and accounting profession in India, and its recommendations are followed by everyone – from the National Financial Reporting Authority (NFRA) to companies and accounting organizations.
- It’s affairs is managed by a Council as per the provisions of the Chartered Accountants Act, 1949 and the Chartered Accountants Regulations, 1988.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- The current President of ICAI Debashis Mitra.
Members:
- The body is managed in by a council comprising 40 members.
- Thirty two members of the council are elected by the chartered accountants while the remaining eight members are nominated by the central government.
47th GST Council Meeting: The 47th GST Council meeting was held in Chandigarh under the Chairmanship of Union Minister for Finance & Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman in Chandigarh.
Key Points:
- The meeting was held on meeting on 28th and 29th June, 2022.
- The GST Council has inter-alia made the following recommendations relating to changes in GST rates on supply of goods and services and changes related to GST law and procedure.
Recommendations relating to GST rates on goods and services:
- 18% of GST will be applied to bank cheque book and 12% will be applied on maps, atlas and globes.
- The rate rationalization decision implies that printing, writing and drawing ink will get costlier.
- Non-branded pre-packed lassi, curd, butter milk, food items and grains will now be a part of the GST.
- GST rates on medical items, including ostomy and orthopaedic appliances – splints and other fracture appliances, artificial body parts which are worn or implanted in the body has been reduced to 5%.
- The GST for transport of good and passengers via ropeway has been reduced from 18% to 5%.
- Also, the renting of truck which includes fuel cost will now stand at 12%.
- Electric vehicles whether or not fitted with a battery pack, are eligible for the concessional GST rate of 5%.
- As part of the revised rates, GST on LED lamps, lights and fixture, their metal printed circuits board, drawing and marking instruments will be increased from 12% to 18%.
- The GST rates have been increased for services supplied by a foreman in a chit fund, jobs related to leather goods and footwear, manufacturing of clay bricks,processing of hides and skins, contracts for roads, bridges, railways, metro among others.
All rate changes recommended by the 47th GST Council will be made effective from 18th July, 2022.
What is GST?
- Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an indirect tax (or consumption tax) used in India on the supply of goods and services.
- It is a comprehensive, multistage, destination-based tax.
- It is comprehensive because it has subsumed almost all the indirect taxes except a few state taxes.
- It is Multi-staged as it is the GST is imposed at every step in the production process, but is meant to be refunded to all parties in the various stages of production other than the final consumer.
- It is destination-based tax as it is collected from point of consumption and not point of origin like previous taxes.
- The tax came into effect from 1 July 2017 through the implementation of the One Hundred and First Amendment of the Constitution of India by the Indian government.
- The GST replaced the existing multiple taxes levied by the central and state governments.
Note: The tax rates, rules and regulations are governed by the GST Council which consists of the finance ministers of the central government and all the states.
Defence
840 Squadron: Eastern region of Indian Coast Guard (ICG), inducted the indigenously designed and developed Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) Mark III.
Key Points:
- The new air squadron known as 840 Squadron was established in Chennai, with an Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) Mark-III aircraft as its first aircraft.
- It will be the first ALH MK-III to be positioned in the Coast Guard Region East.
- The capabilities of the first ALH MK-III aircraft would boost the operational footprint of Unit.
- Three more ALHs will be added to the “840 Squadron” shortly.
- The Advanced Light Helicopter Mark III was received at the Coast Guard Air Station in Chennai, with ‘water cannon salute’.
About ALH MK- III:
- The ALH MK-III has been indigenously designed and developed by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) as part of the government’s ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative.
- It is powered by two Shakti engines.
- Modern radars are used to detect beyond the visual range of the aircraft.
- It is armed with a mounted Heavy Machine Gun for target neutralisation operations.
- It is equipped with surveillance radar, electro optic pod, medical urgent care unit, high-intensity searchlight, infrared suppressor, heavy machine gun, and glass cockpit.
The squadron’s operations area will encompass the entire Eastern Region due to its strategic importance and geographical location.
PADMA: Shri Rajnish Kumar, Controller General of Defence Accounts (CGDA), Ministry of Defence (MoD) inaugurated a Pay Roll Automation for Disbursement of Monthly Allowances (PADMA), an automated Pay & Allowances module for the Indian Coast Guard on June 28, 2022.
About PADMA:
- PADMA is an automated platform leveraging latest technology.
- It will provide seamless and timely disbursal of Pay & Allowances to around 15,000 Indian Coast Guard personnel.
- This module has been developed under the aegis of Defense Accounts Department and will be operated by Pay Accounts Office Coast Guard, Noida.
Significance:
- The foundation of CPS is being laid by the Defence Accounts Department Headquarters.
- The launch has marked the beginning of the Centralized Pay System (CPS) which is a one stop pay accounting solutions for all organisations under the MoD.
- It will not only strengthen the Digital India concept but it is also an 'Atmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative as the entire module has been designed and developed by Indian entrepreneurs assisted by domain experts.
About CPS in India:
In India, the Centralized Pay System (CPS) are Real Time Gross Settlelment (RTGS) and National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) systems which are both owned and operated by the Reserve Bank of India.
About ICG:
- Indian Coast Guard (ICG) is an armed force that protects India's maritime interests and enforces maritime law, with jurisdiction over the territorial waters of India, including its contiguous zone and exclusive economic zone.
- IGC was founded in 18 August 1978 by the Coast Guard Act, 1978 of Parliament of India an independent armed force of India.
- It works under the jurisdiction of Ministry of Defence.
- The moto of IGC is Vayam “Vayam Rakshamah” meaning “We Protect”.
- The Coast Guard works in close cooperation with the Indian Navy, the Department of Fisheries, the Department of Revenue (Customs) and the Central and State police forces.
- The Director General of IGC is V.S. Pathania(24TH DG of ICG).
835 Squadron (CG): On June 28, 2022, 835 Squadron (CG), an indigenous Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) MK III squadron, was commissioned into Indian Coast Guard at its Air Enclave in Porbandar, Gujarat
Key Highlights:
- The commissioning ceremony was presided over by DG, Coast Guard Shri VS Pathania which was attended by various military & civil dignitaries based at Porbandar and Gujarat area.
- The commissioning of this squadron marks a tremendous leap towards self-reliance in the field of Search and Rescue (SAR) and maritime surveillance, in line with Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi’s vision of ‘Aatmanirbhar Bharat’.
- It will give a major fillip to the abilities of the Indian Coast Guard in the Gujarat region and further strengthen the country’s maritime security.
- The 835 Sqn (CG) is commanded by Commandant Sunil Dutt.
Advanced Mark III (ALH Mark III) helicopters:
- The ALH MK III helicopters have been indigenously manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- They feature state-of-the-art equipment including advanced RADAR as well as Electro optical sensors, Shakti engines, full glass cockpit, high-intensity searchlight, advanced communication systems, automatic identification system as well as SAR homer.
- The features enable them to undertake maritime reconnaissance as well as carry out SAR at extended ranges even while operating from ships during both day and night.
- The aircraft has the ability to switch roles from an offensive platform with heavy machine gun to that of a benign one carrying a Medical Intensive Care Unit to facilitate transfer of critically ill patients.
So far, 13 ALH MK-III aircraft have been inducted in the Indian Coast Guard in a phased manner and four of these aircraft are positioned at Porbandar.
Since the induction, the squadron has flown over 1,200 hours and conducted numerous operational missions, including the maiden night SAR mission off Diu coast.
Dinkar Gupta: The Appointments Committee of the Cabinet (ACC) has appointed Senior Indian Police Service (IPS) officer and former Punjab Director-General of Police (DGP) Dinkar Gupta as the Director-General of National Investigation Agency (NIA).
Key Highlights:
- An officer of the 1987 batch of the IPS, Gupta will succeed Yogesh Chandra Modi.
- A notification from the Department of Personnel & Training (DoPT) said the Appointments Committee of the Cabinet (ACC) had approved the proposal of the Ministry of Home Affairs in this regard.
- According to the notification, the appointment will be with effect from the date of his joining the post and up to March 31, 2024, the date of his superannuation,or till further orders, whichever takes place earlier.
- The ACC has also approved the appointment of Swagat Das, IPS (CH:87), currently Special Director in the Intelligence Bureau, as Special Secretary (Internal Security) in the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
About Dinkar Gupta:
- The 1987 batch Indian Police Service (IPS) officer of Punjab cadre was removed as the State DGP and posted to the Police Housing Corporation after Charanjit Singh Channi replaced Captain (retd.) Amarinder Singh as Punjab’s Chief Minister in 2021.
- He has held the post of Director General of Police, Intelligence, Punjab, which involved the direct supervision of Punjab State Intelligence Wing, State Anti-Terrorist Squad (ATS) and Organized Crime Control Unit (OCCU).
Awards:
- He has been decorated with two police gallantry medals in 1992 and 1994.
- He was also decorated with the Police Medal for Meritorious Services by the President and the Presidents Police Medal for Distinguished Service (2010).
- In 1999, Gupta was awarded the British Chevening Gurukul Scholarship by the British Council at London School of Economics, London.
About NIA:
- The National Investigation Agency (NIA) is the primary counter-terrorist task force of India.
- The agency is empowered to deal with the investigation of terror related crimes across states without special permission from the states under written proclamation from the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The Agency came into existence with the enactment of the National Investigation Agency Act 2008 by the Parliament of India on 31 December 2008, which was passed after the deadly 26/11 terror attack in Mumbai.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- The branches of NIA are located in Hyderabad, Lucknow, Mumbai, Kolkata, Raipur, Guwahati, Kochi, Jammu, Chandigarh, Ranchi, Chennai and Imphal.
Tapan Kumar Deka: The Appointments Committee of the Cabinet (ACC) recently appointed Tapan Kumar Deka as Director, Intelligence Bureau for a period of two years, till June 2024.
Key Highlights:
- Deka is a 1988-batch Indian Police Service (IPS) officer.
- He will assume charge for a tenure of two years from the date of assumption of the charge of the post or until further orders, whichever is earlier, by granting extension in service under the provisions of FR 56(d) and Rule 16 (1A) of All India Services (Death-cum-Retirement Benefits) Rules, 1958.
- He will be in service during the remaining term of the present government as the next Lok Sabha election will conclude in May that year.
- He was set to retire in February 2023.
- He will assume office on July 1 after incumbent Arvinda Kumar retires on June 30.
About:
- Deka has spent most of the career in the Intelligence Bureau.
- He was an Additional Director in Intelligence Bureau when he was promoted to the rank of Special Director in the Wing in June last year.
- Deka has handled crucial cases like terrorism in Jammu and Kashmir, especially targeted killings in the Valley.
Samant Kumar Goel
- Meanwhile, RAW Secretary Samant Kumar Goel, whose two-year fixed term would have ended on June 30, 2021, was granted another one-year extension by the ACC.
- Mr. Goel is a 1984-batch IPS officer from the Punjab cadre.
Environment
Bird Village of Udaipur: Recognised as the “bird village” following community driven conservation efforts, Menar in Udaipur district in Rajasthan is set to be notified as the state’s new wetland.
Key Points:
- This will pave the way for getting the Ramsar site status for this village.
- The Forest Department of Rajasthan State Government has initiated the process for notification of Menar as a wetland, which will recognise its role in the storage of sediment and nutrients and enable the local authorities to maintain the Brahma and Dhandh lakes.
- Currently, Rajasthan has two wetlands recognised as Ramsar sites – Keoladeo Ghana in Bharatpur district and Sambhar Salt Lake in Jaipur district.
About Menar:
- Menar is a village located in Udaipur district, Rajasthan.
- It is situated 45 km away from Udaipur.
- It is recognised as bird village following community-driven conservation efforts.
- The village has two lakes – the Brahma and Dhandh.
- Lakes Brahma and Dhandh plays host to a large number of migratory birds in the winter season every year.
- Migratory and local birds include greater flamingo, white-tailed lapwing, bar headed goose, common teal, greenshank, pelican, marsh harrier pintail, wagtail, green sandpiper and red-wattled lapwing.
- These lakes are maintained as safe haven for birds by volunteers known as Pakshi Mitras (friends of birds).
About the wetland:
- A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded by water, either permanently or seasonally, where oxygen-free processes prevail.
- It is an area where water covers the soil, or is present either at or near the surface of the soil all year or for varying periods of time during the year, including during the growing season.
- Water saturation (hydrology) largely determines how the soil develops and the types of plant and animal communities living in and on the soil.
- Wetlands may support both aquatic and terrestrial species.
- The prolonged presence of water creates conditions that favor the growth of specially adapted plants (hydrophytes) and promote the development of characteristic wetland (hydric) soils.
Five major wetland types are generally recognized:
1. Marine (coastal wetlands including coastal lagoons, rocky shores, and coral reefs);
2. Estuarine (including deltas, tidal marshes, and mangrove swamps);
3. Lacustrine (wetlands associated with lakes);
4. Riverine (wetlands along rivers and streams); and
5. palustrine (meaning “marshy” - marshes, swamps and bogs).
Significance of wetland:
- Wetlands are a critical part of our natural environment.
- They mitigate floods, protect coastlines and build community resilience to disasters, reduce the impacts of floods, absorb pollutants and improve water quality.
- Wetlands are critical to human and planet life.
- More than 1 billion people depend on them for a living and 40% of the world’s species live and breed in wetlands.
- They are a vital source for food, raw materials, genetic resources for medicines, and hydropower.
- 30% of land-based carbon is stored in peatland.
- They play an important role in transport, tourism and the cultural and spiritual well-being of people.
- Many wetlands are areas of natural beauty, and many are important to Aboriginal people.
The Ramsar Convention:
- It was signed on 2nd February, 1971.
- It is one of the oldest inter-governmental accords signed by member countries.
- Its main objective is to preserve the ecological character of their wetlands of international importance.
- It is named after Ramsar, the Iranian city where the treaty was signed.
- Places chosen for conservation under it are given the tag ‘Ramsar site’.
- The aim of the Ramsar list is to develop and maintain an international network of wetlands which are important for the conservation of global biological diversity and for sustaining human life through the maintenance of their ecosystem components, processes and benefits.
Significance of Ramsar Tag:
- Ramsar tag makes it incumbent upon authority to strengthen the protection regime there and creates defenses against encroachment.
- It is like an International Organization for Standardization (ISO) certification.
International Asteroid Day 2022: World Asteroid Day (also known as International Asteroid Day) is observed to mark the anniversary of the Tunguska impact over Siberia, 1908.
Key Points:
- It is an annual UN-sanctioned global awareness campaign event observed on June 30th.
- The observance of this day raises public awareness about the hazards of an asteroid impact.
- It’s also a day to inform the public about crisis communication actions necessary in the event of a credible near-Earth object event.
Theme:
The theme of Asteroid Day 2022 is “small is beautiful.”
World Asteroid Day history:
- In December 2016, the UN General Assembly adopted a resolution in order to "observe each year at the international level the anniversary of the Tunguska impact over Siberia, Russian Federation, on 30 June 1908, and to raise public awareness about the asteroid impact hazard.”
- Tunguska event is the most harmful known asteroid-related event on Earth in recent history.
Significance:
- On World Asteroid Day or International Asteroid Day, the potentially catastrophic implications of an asteroid impact on Earth are highlighted.
- Also, the part asteroids have played in the creation of our cosmos, potential uses for their resources, how asteroids pave the way for more research, and how we might shield the earth from asteroids’ effects.
About Asteroids:
- They are small rocky bodies that orbit around the Sun.
- Considered minor planets, some asteroids even have a companion moon.
- Most of the asteroids are found in the asteroid belt.
- The asteroid belt is the region between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter.
- Asteroids are also leftover materials from the formation of the solar system.
- Size of asteroids vary and can be hundreds of miles in diameter and various asteroids are as small as pebbles also.
- The currently known asteroid count is 958,915.
Asteroid Classes:
The three classes of asteroids include:
- C-type (chondrite) – This most common type of asteroid consists of clay and silicate rocks.
- S-type (stony) – This asteroid consists of silicate rocks and nickel-iron.
- M-type (metallic) – Nickel-iron composes these asteroids.
Note: On 29 April 2020, the biggest asteroid passed relatively close to Earth. At a distance of 4 million miles, asteroid (52768) 1998 OR2 passed. That is it is about 16 times the Earth-Moon distance.
Impact of Asteroid collision:
- An asteroid collision would cause environmental impacts, such as shock waves, heat radiation, earthquakes, and tsunamis.
Indian Policy
Single-Use Plastics Ban: The Government of India (GoI) has announced the Single use plastic (SUP) ban from July 1, 2022.
Key Points:
- A gazetted notification was issued in 2021 by the Ministry for Environment, Forest and Climate Change (MoEFCC) announcing the plastic ban.
- The manufacturing, importation, stocking, distribution, sale, and use of a number of single-use plastic items including the polystyrene and expanded polystyrene, commodities will be prohibited beginning on July 1, 2022, according to the Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2021.
- The novel amendment is in line with PM Narendra Modi’s clarion call to phase out single-use plastic by 2022.
- It was in June 2018 that PM Narendra Modi had announced to eliminate all single-use plastic items from the country by 2022.
- Now the ministry has defined a list of items that will be banned from July 1, 2022.
Single Use Plastic ban Items List:
- The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) have announced a ban on – earbuds; cutlery items including plates, cups, glasses, forks, spoons, knives, balloon sticks; candy and ice-cream sticks;trays; sweet boxes; invitation cards; cigarette packs; PVC banners measuring under 100 microns; and polystyrene for decoration.
- This ban will not be applicable to commodities made of compostable plastic.
- The Ministry, in September 2021, had already banned the polythene bags under 75 microns expanding the limit from the earlier 50 microns.
- Permitted thicknesses of the plastic bags have been increased to 75 microns, from 50 microns, starting from September 30, 2021 and to 120 microns from December 31, 2022.
- As per the Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016, there is also a complete ban on sachets using plastic material for storing, packing, or selling Gutkha, tobacco, and pan masala.
Why particular items?
- As per the Ministry officials, the choice for the first set of single-use plastic items for the ban was based on the difficulty of collection and therefore recycling.
- The Ministry official further explained that the adversary isn't plastic per se, but rather plastic in the environment.
- Plastic that is left in the environment for a long time and does not decompose becomes microplastics, which are very dangerous since they infiltrate our food supplies first before making their way into our bodies.
- The specific objects that have been selected to be banned are bacause they are difficult to gather, especially considering that the majority are either little or thrown away into the environment, such ice cream sticks.
How will the ban be enforced?
- The single use plastic ban will be monitored by the CPCB from the Centre and by the State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) that will report to the Centre regularly.
- Directions to keep an eye on single use plastic ban have also been issued at the national, state, and local levels to not to supply the raw materials to industries engaged in the banned items.
- SPCBs and Pollution Control Committees will modify or revoke consent to operate issued under the Air/Water Act to industries engaged in single-use plastic items.
- Those violating single use plastic ban can be penalized under the Environment Protection Act 1986- which allows for imprisonment up to 5 years, a penalty up to Rs. 1 lakh, or both.
- Violators can also be asked to pay Environmental Damage Compensation by the SPCB.
- In addition, there are also municipal laws on plastic waste, with their own penal codes.
India is committed to taking action towards mitigating pollution caused by littered Single-Use Plastics.
What are Single-use Plastics?
- Single-use Plastics are also known as disposable plastics.
- They are plastic items that are used once and discarded. For E.g., plastics used in packaging of items, bottles (detergents, shampoo, cosmetics), coffee cups, cling film, polythene bags, face masks, trash bags, food packaging etc.
- Plastic has superseded other materials in the packaging sector because it is so practical and affordable.
- It takes hundreds of years to disintegrate.
- India ranks at 94 in the top 100 countries of single-use plastic waste generation as 9.46 million tonnes of plastic waste is generated every year, out of which 43% is single use plastic.
How are other countries tackling with single-use plastic?
- In 2022, 124 countries, parties to the United Nations Environment Assembly, including India, signed a resolution to draw up an agreement which will in the future make it legally binding for the signatories to address the full life of plastics from production to disposal, to end plastic pollution.
- EU bans certain single-use plastics for which alternatives are available.
- Bangladesh became the first country to ban thin plastic bags in 2002.
- China issued a ban on plastic bags in 2020 with a phased implementation.
Note: In the 4th United Nations Environment Assembly held in 2019, India had piloted a resolution on addressing single-use plastic products pollution, recognizing the urgent need for the global community to focus on this very important issue. The adoption of this resolution at UNEA 4 was thus a very significant step.
One Nation, One Dialysis: On June 26, 2022, Dr. Mansukh Mandaviya, the Union Minister for Health and Family Welfare, announced that the Central Government would shortly launch the "One Nation, One Dialysis" initiative.
Key Highlights:
- He announced the One Nation, One Dialysis Programme during his two-day visit to Tamil Nadu and Puducherry.
- It will be launched by the Government under the Pradhan Mantri National Dialysis Programme.
- Through this scheme, any patient in India can get a dialysis facility from anywhere in the country.
Key Points about One Nation, One Dialysis’Programme:
- In line with the idea of one nation and one service, the Central Government has been planning to introduce another service under the Pradhan Mantri National Dialysis Programme under the National Health Mission called "One Nation, One Dialysis."
- The One Nation, One Dialysis initiative will facilitate the dialysis facility for the needy patients anywhere in the country.
About National Dialysis Programme:
- In the Budget Speech of 2016-2017, the Union Finance Minister Nirmala sitharaman had announced the launch of a National Dialysis Programme under a public-private partnership at the district hospitals.
- The programme was launched by the Government of India (GoI) keeping in view the fact that every year about 2.2 lakh new patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) get added to the country resulting in additional demand for 3.4 crore dialysis each year.
Significance of One Nation, One Dialysis Programme:
- Every year, there is an increase in patients with end-stage renal diseases, which increases the demand for 3.4 crore dialysis treatments.
- The demand is not fully satisfied by the infrastructure at this time, despite India having approximately 4,950 dialysis centres, the most of which are private.
- Practically all families of patients who require dialysis suffer a financial catastrophe as a result of the high cost of care.
- A dialysis programme is found necessary both in terms of providing significant life-saving procedures and in terms of lowering patient poverty due to out-of-pocket expenses.
What is Dialysis?
- Dialysis is a medical procedure that performs some of the functions of healthy kidneys. When renal failure reaches its latter stage, it becomes necessary.
Dialysis maintains balance of body by:
- Removing waste, salt and extra water to prevent them from building up in the body.
- Keeping a safe level of certain chemicals in your blood, such as potassium, sodium and bicarbonate.
- Helping to control blood pressure.
Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI): The Union Cabinet chaired by the Prime Minister Shri Narendra Modi recently approved the categorization of the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) as an ‘International Organization’.
Key Points:
It also approved the signing of the Headquarters Agreement (HQA) with CDRI.
This agreement is for granting it the exemptions, immunities and privileges as contemplated under the United Nations (Privileges & Immunities) Act, 1947.
How will these affect CDRI?
Categorization of CDRI as an ‘International Organization’ and signing of the Headquarters Agreement (HQA) will provide CDRI a legal identity that is independent and global, enabling it to carry out its duties abroad effectively.
Associated Benefits to CDRI:
Deputing experts to other countries:
It will help the CDRI in deputing experts to countries which are vulnerable to disaster risk and seek for post disaster recovery. It will also bring in experts from member countries to India for similar purposes.
Deploy funds and receive contributions:
It can deploy funds at global level and receive contributions from member countries for its activities.
Making available technical expertise:
It will be able to assist countries to develop resilient infrastructure by providing technical expertise in accordance with their disaster and climate risks and resources.
Imparting assistance to countries:
It will help in imparting assistance to countries in adopting appropriate risk governance arrangements and strategies for resilient infrastructure.
Render support to member countries:
It will render all possible support to member countries in upgrading their systems to ensure disaster and climate resilience of existing and future infrastructure, while aligning with the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the Paris Climate Agreement and the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction.
Leveraging international engagement:
It will leverage international engagement to foster disaster resilient infrastructure at home
Assistance to Indian scientific and technical institution:
It will provide an opportunity to Indian scientific and technical institution and infrastructure developers to interact with global experts. It will help in building our own capacities and mechanisms to support disaster resilient infrastructure development.
This will be helpful in building the country's own capacities and mechanisms to support disaster resilient infrastructure development.
About CDRI:
- Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) is a global coalition of National governments, United Nations agencies and programmes, multilateral development banks and financing mechanisms, academic, research institutions and the private sector.
- It was launched in 2019 by the Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi at the 2019 United Nations Climate Action Summit at New York.
Members of CDRI:
Since its launch, 31 Countries, 6 International Organizations and 2 private sector organizations have joined as members of CDRI.
6 International Organizations are:
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
- World Bank Group)
- European Union
- European Investment Bank
- United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR)
Two Private Sector Organisations are:
- Private Sector Alliance for Disaster Resilient Societies
- Coalition for Climate Resilient Investment.
CDRI has steadily grown its membership by attracting drawing members from a variety of economically developed, developing, and disaster-prone nations.
Aims and objectives:
- CDRI aims to promote the resilience of new and existing infrastructure systems to climate and disaster risks in support of sustainable development.
- Its objective is to promote research and knowledge sharing in the fields of infrastructure risk management, standards, financing, and recovery mechanisms
Background:
- CDRI was first proposed by our Prime Minister during the 2016 Asian Ministerial Conference on Disaster Risk Reduction held in New Delhi.
- On 28th August, 2019, the Cabinet had approved the setting up of CDRI with its Secretariat in New Delhi along with a support of Rs. 480 crore to CDRI.
NITI Aayog-WEP report on THR: Government’s think-tank, NITI Aayog and the World Food Program (WFP) recently launched a report titled ‘Take Home Ration-Good Practices across the State/Union Territories’.
Key Highlights:
- The report was launched by Suman K. Bery, vice chairman of the NITI Aayog in the presence of CEO Amitabh Kant and Member (Health) Dr. V.K. Paul, Secretary of the Ministry of Women and Child Development, Indevar Pandey.
- The NITI Aayog-WEP report outlines a number of beneficial and creative techniques that the States and UTs have used to implement the Take Home Ration value chain.
Key Points:
- The Government of India (GoI) provides Take Home Ration (THR) under the Supplementary Nutrition component of the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) to fill the gap in nutrition among children as well as Pregnant and Lactating Women (PLW).
- It offers fortified rations for use at home for children aged 6 to 36 months as well as pregnant and lactating women, with the goal of bridging the nutrition gap among them.
Compilation of Innovations:
- The document on good practices compiles and collates innovations in Take Home Ration(THR) programmes in various States and Union Territories.
Generating catalogue of good practices:
- Aspects related to production, formulation, distribution, labelling, packaging, monitoring, quality assurance, and social and behavioural change have been reviewed to generate a catalogue of good practices.
Adopting good practices:
- This document will help State Governments/Union Territories to adopt good practices in their THR programmes.”
Suggestions made by the report:
- The NITI Aayog-WFP report made following recommendation:
- In order to realize the full potential of the THR, the report suggested that all components of this value chain need to function at optimum.
- It also suggested building a robust system for procurement, standardized process, full coverage, supply chain management & monitoring to ensure complete transparency, sustainability, leverages local ties, and bring a culture of collaboration and trust within a community.
About World Food Programme (WFP):
- The World Food Programme (WFP) is the food-assistance branch of United Nations.
- It is the largest humanitarian organization worldwide, that saves lives in times of need and utilises food aid to help people recover from war, natural disasters, and the effects of climate change create a road to peace, stability, and prosperity.
- It was established in 1961 by the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) and United Nations General Assembly (UNGA).
- It is headquartered in Rome, Italy.
- It is also a member of the United Nations Sustainable Development Group (UNSDG), a coalition of UN agencies and organizations aimed at fulfilling the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Indian polity
Vice President of India: The Election Commission of India (ECI)on July 5th 2022 issued the notification for the election of the Vice President of India.
Key Highlights:
- The term of office of Vice President M Venkaiah Naidu comes to an end on August 10.
- The election is scheduled for August 6, and July 19 is the last date for filing nominations.
Is Vice President of India a constitutional post?
- The office of vice president is the second-highest constitutional office after the president and ranks second in the order of precedence and first in the line of succession to the presidency.
- The vice president is also a member of the Parliament of India as the Chairman of the Rajya Sabha.
Office of the Vice President:
- Article 63 of the Indian Constitution states that “there shall be a Vice-President of India”.
- Under Article 64, the Vice-President “shall be ex officio Chairman of the Council of the States” (Rajya Sabha).
- Article 65 says that “in the event of the occurrence of any vacancy in the office of the President by reason of his death, resignation or removal, or otherwise, the Vice-President shall act as President until the date on which a new President…enters upon his office”.
What is the process of election of the Vice-President?
- Article 66 lays down the process of the election of the Vice-President.
- It says the Vice-President “shall be elected by the members of an electoral college consisting of the members of both Houses of Parliament in accordance with the system of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote and the voting at such election shall be by secret ballot”.
- Article 66(3) says “No person shall be eligible for election as Vice-President unless he —
- is a citizen of India;
- has completed the age of thirty-five years; and
- is qualified for election as a member of the Council of States”.
- He/she should not hold any office of profit under the Union government or any state government or any local authority or any other public authority.
Eknath Shinde: Shivsena rebel leader Eknath Shinde was recenlty sworn-in as the new Chief Minister of Maharashtra.
Key Highlights:
- He has become the 20th Chief Minister of the state.
- The oath of office to Mr. Shinde was administered by Governor Bhagat Singh Koshyari.
- Apart from Mr Shinde, BJP leader Devendra Fadnavis was also sworn-in as Deputy Chief Minister.
- The trust vote of the new government will be held on Saturday.
- The special session of the Assembly will be held on July 2 and 3.
- The Speaker will also be elected on the first day of the session.
Background:
- Shinde, had revolted against former Chief Minister Uddhav Thackeray on June 20, 2022.
- He was joined by 39 Sena MLAs and 11 Independents.
- The rebel MLAs had demanded that Mr. Thackeray quit the tripartite Maha Vikas Aghadi (MVA) and snap ties with the Congress and the Nationalist Congress Party (NCP) to return to the path of Hindutva.
International
European Union Candidate Status: The European Parliament recently approved the EU candidacy status for Ukraine, Moldova and Georgia in a convincing vote.
Key Points:
- This was announced by European Council President Charles Michel after discussions among leaders of the EU's 27 member states.
- A total of 529 votes were cast for the resolution to defer the status of the three countries, while 45 voted against the proposal.
- Another 14 politicians abstained.
- The European Parliament also approved EU candidacy for Georgia.
- In order to join the 27-member EU bloc, the three countries will be required to carry out a series of political and economic reforms.
- The European Council, which comprises the heads of all 27 EU governments, would have the final vote on Ukraine’s membership.
- The vote must be unanimous.
- However,according to diplomts, the process could take a decade to complete.
- The vote came as the U.S. said, it was sending 450 million dollar more in military aid to Ukraine, including some additional medium-range rocket systems.
About European Council (EC):
- EC is an executive body of the EU, responsible for proposing legislation, implementing decisions, upholding the EU treaties and managing the day-to-day business of the EU.
- The EU is a group of 27 countries that operate as a cohesive economic and political block.
- The Commission is divided into departments known as Directorates-General (DGs) that can be likened to departments or ministries headed by a director-general who is responsible to a commissioner.
Structure:
- It operates as a cabinet government, with 28 members of the Commission.
- There is one member per member state. These members are proposed by member countries and European Parliament gives final approval to them.
- One of the 28 members is the Commission President proposed by the European Council and elected by the European Parliament.
BRICS: Iran has submitted an application to become a member in the group of emerging economies known as the BRICS
Key Phighlights:
- Iran, which holds the world’s second-largest gas reserves, wants to join the BRICS group of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
- Argentina had also applied to join.
- Alberto Fernandez, the president of Argentina, who is presently travelling in Europe, has recently reaffirmed his country's intention to join the BRICS.
About BRICS:
- BRICS is an acronym for Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- The term BRIC was coined by Goldman Sachs economist Jim O’Neill in 2001 to describe the startling rise of Brazil, Russia, India, and China.
- Jim O’Neill claimed that claiming that by 2050 the four BRIC economies would come to dominate the global economy by 2050.
- The BRIC powers had their first summit in 2009 in Russia.
- South Africa joined in 2010.
Statistics:
- Of the BRICS nations, China is by far the largest economy, making up more than 70% of their combined 27.5 trillion US dollar GDP.
- According to IMF data, India accounts for about 13 percent and Russia as well as Brazil each account for about seven percent,
- BRICS account for more than 40 percent of the world’s population and about 26 percent of the global economy.
14th Prime Minister of Israel: Yair Lapid who is the leader of Yesh Atid Party has officially become the 14th prime minister of Israel.
Key Highlights:
- He has replaced Naftali Benett.
- Lapid's term could be the short one as he takes over the caretaker government ahead of Israel's election which was scheduled to take place on November 1.
- Israel's Parliament voted on June 30 to dissolve itself and send the country to the polls in November for the fifth time in less than four years.
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi also congratulated Yair Lapid for assuming the Premiership of Israel and said that he looks forward to furthering the bilateral strategic partnership as the two countries celebrate 30 years of full diplomatic relations.
About Yair Lapid:
- Yair Lapid, born 5 November 1963 is an Israeli politician and former journalist.
- He also previously served as the Alternate Prime Minister of Israel and the Prime Minister of Foreign Affairs from 2021 to 2022.
- Before entering politics, Yair Lapid was an author, TV presenter, and news anchor.
About Israel:
- Israel formally known as the State of Israel is a country in Western Asia.
- It is located on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea.
- It is regarded as the biblical Holy Land by Jews, Muslims and Christians.
- Its most sacred sites are in Jerusalem which is also the Capital of Israel.
- The currency used here is Israeli Shekel.
- The current President of Israel is Isaac Herzog.
International Day of Parliamentarism 2022: Every year 30 June is celebrated as International Day of Parliamentarism across the world.
Key Points:
- It marks day of establishment of Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU), the global organization of parliaments.
- The IPU was founded in Paris in 1889.
- The year 2022 is the 133th anniversary of IPU.
- On the occasion of the International Day of Parliamentarism, it is important to analyse the progress that parliaments have made toward a number of important objectives that include increasing the representation of women and young people in parliaments as well as embracing new technology.
Theme:
- In 2022, the Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU) and its Member Parliaments will mark the International Day of Parliamentarism under the theme of "Public Engagement."
- This follows the recent launch of the Global Parliamentary Report on Public engagement in the work of parliament.
History:
- It was established by United Nations General Assembly in 2018 by adopting n its resolution A/RES/72/278.
- The day seeks to unite all parliamentarians of the world.
- It recognized role played by parliaments in national plans and strategies and in ensuring greater transparency and accountability at national as well as global levels.
Significance:
- The Day celebrates parliaments and ways in which parliamentary systems of government improve everday lives of people throughout the world.
- It is also an opportunity for parliaments to identify challenges, and stock ways to address them effectively.
About IPU:
- Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU) is the world organization of parliaments.
- It is an international organization of national parliaments to promote democratic governance, accountability, and cooperation among its members.
- It connects national parliaments in order to promote greater accountability, transparency and participation at global level.
Key Facts about Parliaments:
Every nation in the world has a representative government, whether it be a presidential or parliamentary form.
A parliamentary system is of two categories:
- Bicameral-with two chambers of parliament
- Unicameral-with one chamber
Out of 193 countries, 79 are bicameral and 114 are unicameral.
Note: The World’s oldest parliament is Althingi, the Icelandic Parliament. It was founded in 930.
Importance of Parliament:
- Strong parliaments are a cornerstone of a democracy.
- They represent voice of people, allocate funds to implement laws and policies, pass laws and hold governments accountable to people.
National
National Statistics Day 2022: National Statistics Day is celebrated every year on 29th June to mark the birth anniversary of Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis, an Indian scientist and statistician.
Key Points:
- This year, National Statistics Day 2022 marks the 129th birth anniversary of Prof Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis.
- The Statistics Day 2022 is also being celebrated as a part of a week-long celebration in the Ministry, from June 27 to July 3, in commemoration of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav (AKAM), an initiative of the Government.
Theme for National Statistics Day 2022:
The theme for this year’s celebration is ‘Data for Sustainable Development’.
Importance this year's theme:
- The analysis of data is crucial currently in order to draw a conclusion.
- However, in the modern era, there is also a need for sustainable development to maintain a balance between all the variables of life.
- In order to predict and make informed judgments, data analysis is required.
- If used responsibly, new data sources, technology, and analytical methods—such as satellite data—can enable swifter, effective, and evidence-based decision-making, as well as more accurately and fairly gauge progress toward the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Additionally, this would help in gaining real-time insights into people’s well-being and in focusing humanitarian initiatives on vulnerable populations.
- The theme for the celebration would follow intensive and narrowly targeted conversations about filling the data gaps and improving data collection, processing, and dissemination.
Objective:
- Ministry of Statistics and Programme( MOSPI) commemorates National Statistics Day at the National level.
- The main Objective behind celebrating Statistics Day is the creation of public awareness, especially among the younger generation, on the role and importance of statistics in socio-economic planning and policy formulation for the development of the country.
Note: The world observes World Statistics Day on Ocober 20, every five years.
History:
- India celebrated the first National Statistics Day on 29th June, 2007.
- The Indian Government decided to to designate 29th June i.e., the birth date of Prof. P C Mahalanobis as National Statistics Day.
- On June 5th, 2007, the Indian Gazette initially published a notification about this.
National Statistics Day 2022: Significance
- The National Statistics Day is observed to create public awareness, especially in the younger generation to draw inspiration from Professor Mahalanobis about the role and importance of statistics in socio-economic planning and policy formulation.
- The Prof PC Mahalanobis National Award was created by to recognizes the outstanding contribution through high quality research in the field of applied and theoretical statistics benefiting the official statistical system.
- The names of the winners of Prof PC Mahalanobis National Award in Official Statistics are also announced on this day.
About Prof. Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis:
- Professor Prasanta Chandra Mahalanobis (29 June 1893– 28 June 1972), who was called ‘PCM’ by his colleagues, was a noted Indian scientist and applied statistician.
- He is also known as the Father of Indian Statistics.
- He introduced the Mahalanobis distance, a statistical measure, and random sampling.
- He was also one of the members of the first Planning Commission of India.
- He played a key role in shaping the first 5-year plan.
- He was instrumental in designing the way surveys are conducted today.
- He introduced the concept of pilot surveys and advocated the importance of sampling methods.
- He made pioneering studies in anthropometry in India.
- He also introduced a method for the estimation of crop yields using statistical sampling.
- Prof. Mahalanobis in 1931 set up the Indian Statistical Institute (ISI) at Kolkata.
- It was declared an autonomous “Institute of National Importance” through an act of Parliament in 1959, also celebrates June 29 as the “Worker Day”.
BHARAT-NCAP: Union Road Transport and Highways Minister Nitin Gadkari has approved the Draft GSR Notification to introduce Bharat NCAP (New Car Assessment Program).
Key Points:
- Under Bharat NCAP the automobiles in India shall be accorded Star Ratings based upon their performance in Crash Tests.
- Bharat-NCAP will serve as a consumer-centric platform which will allow customers to opt for safer cars based upon their star-ratings, while promoting a healthy competition among OEMs in India to manufacture safer vehicles.
Significance of Bharat NCAP:
- Star Rating of Indian Cars based on Crash Tests is extremely crucial not only to ensure structural and passenger safety in cars, but to also increase the export-worthiness of Indian automobiles.
- The testing protocol of Bharat NCAP shall be aligned with Global Crash Test Protocols factoring in the existing Indian regulations, allowing OEMs to get their vehicles tested at India’s own in-house testing facilities.
- With the goal of making India the top automotive hub in the world, Bharat NCAP will prove to be a crucial tool in growing the country's automotive industry.
Dak Karmayogi: Minister of Communications, Railways, and Electronics & IT Ashwini Vaishnav recently launched an e-learning portal of the Department of Posts named ‘Dak Karmayogi’.
Dak Karmayogi was launched at a function held at Stein Auditorium, Indian Habitat Centre on 28 July 2022. Shri Ashwini Vaishnaw and Electronics & Information Technology and Shri Devusinh Chauhan, Minister of State for Communications conferred the Meghdoot Awards to recognise the good performance of employees of the Department of Posts and motivate them in eight different categories during the event.
The Meghdoot awards were conferred to recognise the good performance of employees of Department of Posts and motivate them to maintain or improve their good work.
About ‘Dak Karmayogi’ portal:
- ‘Dak Karmayogi’ portal aims to enhance the competencies of about 4 lakh Gramin Dak Sevaks & Departmental employees.
- It will enable the trainees to access the uniform standardized training content online or in blended campus mode to enable them to effectively deliver a number of G2C services for enhanced customer satisfaction.
- The training videos and quizzes on the portal are available in 12 Indian languages to help postal trainees to access training content in vernacular languages.
- A system-generated course completion certificate will be emailed instantly to the trainee's registered email ID upon successful completion of the final summative assessment.
- The portal allows trainees to give their feedback, ratings and suggestions for each and every video and other learning content so that necessary enrichment can be ensured.
- This portal has been developed ‘In-House’ under vision of ‘Mission Karmayogi’.
- Mission Karmayogi was conceptualized by Prime Minister Narendra Modi with a view to bring efficiency in actions of all the employees of Government of India and transforming efficiency of bureaucracy with ‘Minimum Government’ and ‘Maximum Governance’.
Significance:
- Department of Posts has been imparting training to its employees through its network of 10 Postal Training Centres/Regional Training Centre and Rafi Ahmed Kidwai National Postal Academy (RAKNPA), a Central Training Institute.
- However, with the launch of this portal, Departmental employees and Gramin Dak Sevaks will be able to avail training ‘Any-time, Any-where’ and upgrade their Attitude, Skill and Knowledge (ASK), as per their convenience.
- The portal is expected to go a long way in being an enabler in providing better services by upgrading employees and Gramin Dak Sevaks.
About Mission Karmayogi:
- Mission Karmayogi is the National Programme for Civil Services Capacity Building (NPCSCB).
- It is the biggest bureaucratic reform initiative Indian Bureaucracy.
- This initiative was launched on September 20, 2020 by the Prime Minister Narendra Modi-led Union Cabinet.
- It will cover around 46 lakh central employees between 2020-2025.
- Mission Karmayogi will have the following six pillars:-
- Policy Framework
- Institutional Framework
- Competency Framework
- Digital Learning Framework (Integrated Government Online Training Karmayogi Platform (iGOT-Karmayogi)
- Electronic Human Resource Management System (e-HRMS)
- Monitoring and Evaluation Framework
- A special purpose vehicle (SPV) (non-profit company) is set up under the Companies Act 2013 to run this mission.
- This SPV will manage i-GOT Karmayogi which is the online training digital platform.
Aim:
- It aims to transform capacity-building in bureaucracy by bringing institutional and process reforms.
- The mission envisages preparing Indian civil servants for future by making them more constructive, proactive, creative, imaginative, innovative, progressive, professional, energetic, transparent and technology-enabled.
People In News
Ranjit Bajaj: Entrepreneur Ranjit Bajaj has been named chairman of advisory committee to assist the Supreme Court-appointed Committee of Administrators (CoA) which is running the day-to-day affairs All India Football Federation (AIFF).
Key Highlights:
- Ranjit Bajaj, the former owner of I-League side Minerva Punjab FC, will head the 12-member committee
- The CoA appointed a 12-member advisory committee that will oversee the day-to-day matters of various departments of the AIFF. departments of the AIFF.
- The advisory committee will send regular reports to all the members of the CoA for their information and approvals, if required.
Following are the members of the advisory committee:
- Ranjit Bajaj -- Chairman of the Advisory Committee and Integrity matters
- Gurslmran Brar -- Admin, Legal and Government Liaison matters
- Manoj Gupta -- Accounts and Finance matters
- Akshay Rohatgi -- Tournament and Logistics matters
- Sankalp Pujari -- Player status and Registration matters
- lndranil Oas -- Club Licensing and Academy Accreditation matters
- S Suresh -- Refereeing matters
- Savio Medeira -- National Teams (men and women) and Coaching matters
- Richard Hood -- Grassroots and Futsal matters
- Jaydeep Basu -- Media and Communication matters
- Pushpargha Chatterjee -- HR matters
- Oebashis Dey -- Member of the Advisory Committee
Additional Info:
- The CoA took charge of the AIFF in June 2022 after the Supreme Court removed the Praful Patel-led office bearers for not holding elections on time.
- Patel had exceeded his tenure of 12 years as AIFF chief.
- The CoA has been tasked to amend the AIFF constitution in line with the National Sports Code and hold elections.
- A seven-member joint team of the world football governing body FIFA and its Asian unit AFC is currently visiting India to help find a solution to the impasse.
About All India Football Federation:
- All India Football Federation (AIFF) is the governing body of association football in India.
- It was formed on 23 June 1937.
- The federation was one of founding members of the Asian Football Confederation, the overseer of football in Asia.
- It sanctions and runs all competitive football tournaments and leagues at a national level, namely the Indian Super League, I-League and Super Cup.
- It indirectly manages local football competitions through the state associations and is also responsible for managing the India national football team, as well as the women's team and the various youth national sides.
- The federation is currently based in Dwarka, Delhi.
Radha Iyengar Plumb: U.S. President Joe Biden recently nominated security expert Radha Iyengar Plumb to the post of Deputy Under Secretary of Defense for Acquisition and Sustainment.
Key Facts:
- She is the latest Indian-American to be named for a key position.
- Presently serving as the Chief of Staff to the Deputy Secretary of Defense, she was nominated for the top Pentagon position in June 2022.
- Prior to her appointment as Chief of Staff, she was the Director of Research and Insights for Trust and Safety at Google, leading their cross-functional teams on business analytics, data science and technical research.
- She has also previously served as the Global Head of Policy Analysis at Facebook, where she focused on high-risk and high-harm safety and critical international security issues.
Dak Karamyogi -Meghdoot Award: Minister of Communications, Railways, Electronics & IT Ashwini Vaishnav and Shri Devusinh Chauhan, Minister of State for Communications conferred the Meghdoot Awards to recognise the good performance of employees of the Department of Posts and motivate them in eight different categories.
The Department of post acknowledged the following people with the Meghdoot award for the year 2021.
- Shri Ashok Kumar Sahoo, GDS BPM, Cuttack South Division, Odisha Circle.
- Shri Prem Lal, Mail Runner, Mandi Division, Himachal Pradesh Circle.
- Shri Dhananjay T, Postal Assistant, Circle office, Karnataka Circle
- Shri Vijendra Singh Rana, Technical Supervisor, Mail Motor Service, Delhi Circle.
- Shri Sandeep Gundu kadgaonkar, ASP, Goa Region, Maharashtra Circle.
- Shri Randhir Kumar, Assistant Director, Circle office, Bihar Circle.
- Shri Challa Shri Nagesh, Deputy Manager, CEPT, Hyderabad.
- Shrimati K kalaivani, Assistant Director, Southern Region, Madurai, Tamil Nadu circle.
About Meghdoot Award:
- Meghdoot award was introduced in the year 1984.
- It is the highest award of the departmental post at the National level for overall performance and excellence.
- The awardees are facilitated with a medallion, certificate, and a cash prize of rupees 21000.
Ketanji Brown Jackson: The U.S. scripted history as Ketanji Brown Jackson was sworn in as the first Black woman to serve in the Supreme Court.
Key Highlighs:
- The 51-year-old’s appointment by Democratic President Joe Biden means ‘white men’ are not in the majority on the nation’s highest court for the first time in 233 years.
- Four of the Justices on the nine-member court are now women, making it the most diverse bench in history.
Places In News
One Health Pilot Initiative: The Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying (DAHD) recently launched the One Health pilot in Bengaluru, Karnataka.
Key Highlights:
- The Pilot project in Karnataka was launched by Secretary Atul Chaturvedi, Department of Animal Husbandry & Dairying.
- Key dignitaries and stakeholders from the Centre and state level across livestock, human, wildlife, and environment sectors were also a part of the inauguration.
- During the event, the capacity-building plan for Karnataka and the One Health brochure (Kannada) was also unveiled.
- The ‘One Health India’ program initiated by the Department aims to work with stakeholders from various sectors to improve livestock health, human health, wildlife health, and environmental health through technology and finance.
Which states are implementing the pilot projects?
- DAHD in collaboration with the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF) and The Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) as implementation partner is implementing the One-Health Framework undertaking project in the states of Karnataka and Uttarakhand.
- The pilot project in Karnataka will form the basis for development of the One Health Framework for India.
About the ‘One Health Pilot’:
- This project is aimed at improving national and State-level resource allocation and policy ecosystem on early prediction, detection, and diagnosis of zoonotic diseases through increased quality, availability, and utility of data evidence.
- The programme will bring stakeholders from animal, human and environment health on a common platform in order to formulate solutions for preventing outbreak of zoonotic disease like covid-19 pandemic in future.
- The department of animal husbandry and dairying would develop a national One Health roadmap, on the basis of learnings of “One Health Pilot Project” which will help in preventing future zoonotic disease outbreaks.
About Confederation of Indian Industry (CII):
- The Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) is a non-governmental trade association and advocacy group.
- It was founded in 1895.
- It engages business, political, academic, and other leaders of society to shape global, regional, and industry agendas.
- It is a membership-based organization.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi, India.
- The current Director-General (DG) is Chandrajit Banerjee.
About Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation (BMGF):
- It is an American private foundation. It was launched in 2000 by Bill Gates and Melinda French Gates.
- It is based in Seattle, Washington.
- As of 2020, it is reported as the second largest charitable foundation worldwide.
MEDISEP Scheme: Kerala state government has issued orders regarding the implementation of a medical insurance “MEDISEP” scheme.
Key Highlights:
- The Pinarayi Vijayan government issued orders giving sanction to implement the much awaited cashless medical assistance through Oriental Insurance Company Ltd from July 1, 2022.
- The orders have been issued for government employees and pensioners and the deduction of premium from the salary of June 2022 and pension of July 2022.
- MEDISEP scheme is applicable to government employees, pensioners/family pensioners and their eligible family members and employees and pensioners of universities that receive grant in aid from the state government and the local self-government institutions.
Key Points about the scheme:
- MEDISEP is being implemented through the public sector insurer, Oriental Insurance Company.
- The scheme is expected to benefit more than 30 lakh people, including government employees, pensioners and their families, teaching and non-teaching staff of aided schools and colleges, and part-time contingent employees.
- The scheme provides cashless medical assistance through an insurance company selected through the competitive bidding process.
- As per the scheme, the premium on behalf of the employees and pensioners towards MEDISEP shall be paid by the government in advance and will be recouped from the salary of employees and pensioners.
- The annual premium of the employees and the pensioners will be Rs 4,800 + 18% GST for the policy period of 2022-24, and the monthly premium of Rs 500 would be deducted from the salary/pension.
- The scheme is applicable to universities and local self-government institutions as well.
- The scheme is also applicable to directly recruited personal staff of the chief minister, ministers, opposition leader, the chief whip, Speaker, deputy speaker and chairman of the financial committees.
About Kerala:
- It is a state on the southwestern Malabar Coast of India.
- It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile states of Travancore-Cochin and Madras.
- It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Lakshadweep Sea to the west. Its capital is Thiruvananthapuram.
- The current Governor and Chief Minister of Kerala are Arif Mohammad Khan and Pinarayi Vijayan respectively.
Science and Technology
CAPSTONE: NASA recently launched CAPSTONE, a microwave oven-sized CubeSat weighing just 55 pounds (25 kg).
About CAPSTONE:
- CAPSTONE, short for Cislunar Autonomous Positioning System Technology Operations and Navigation Experiment, is designed to test a unique, elliptical lunar orbit.
- The satellite was launched on Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket from the Rocket Lab Launch Complex 1.
- It is heading toward an orbit intended in the future for Gateway, a Moon-orbiting outpost that is part of NASA’s Artemis program.
- As a pathfinder for Gateway, CAPSTONE aims to help reduce risk for future spacecraft by validating innovative navigation technologies, and by verifying the dynamics of the halo-shaped orbit.
- The orbit is known as a near-rectilinear halo orbit (NRHO).
- It is significantly elongated, and is located at a precise balance point in the gravities of Earth and the Moon.
- This offers stability for long-term missions like Gateway.
Key details of the Mission:
- CAPSTONE will enter NRHO, where it will fly within 1,600 km of the Moon’s North Pole on its near pass and 70,000 km from the South Pole at its farthest.
- The spacecraft will repeat the cycle every six-and-a-half days and maintain this orbit for at least six months to study dynamics.
Mission objectives:
The main objectives of the mission are as follows:
- To verify the characteristics of a cis-lunar near rectilinear halo orbit for future spacecraft
- To demonstrate entering and maintaining this unique orbit that provides a highly-efficient path to the Moon’s surface and back
- To demonstrate spacecraft-to-spacecraft navigation services that allow future spacecraft to determine their location relative to the Moon without relying exclusively on tracking from Earth
- Lay a foundation for commercial support of future lunar operations
- To gain experience with small dedicated launches of CubeSats beyond low-Earth orbit, to the Moon, and beyond
What is NASA Artemis program?
- The Artemis program is a human spaceflight program led by NASA to explore the Moon, aiming for its first touchdown on the lunar South Pole by 2025.
- The Artemis program began in December 2017 as part of successive efforts to revitalize the U.S. space program.
- The Artemis program is carried out predominantly by NASA and U.S. commercial spaceflight contractors, in partnership with the European Space Agency and the space agencies of several other nations.
- With Artemis missions, NASA will land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon, using innovative technologies to explore more of the lunar surface than ever before.
- Long-term objectives for Artemis are laying the foundations for the extraction of lunar resources, and eventually making crewed missions to Mars and beyond feasible.
Hermit Spyware: A new spyware called “Hermit” has recently been discovered by Lookout, a cloud-based security company.
This spyware is capable of affecting both Android and iOS devices.
About Hermit Spyware:
- Hermit is a commercial spyware that is known to be used by governments with victims in Italy, Kazakhstan and northern Syria.
- The spyware was first detected in Kazakhstan in April 2022 after the government violently suppressed protests against government policies.
- It was also deployed in north-eastern Kurdish region of Syria and by Italian authorities for an anti-corruption investigation.
How is Hermit distributed?
- Hermit is a modular spyware that hides its malicious capabilities in packages downloaded after it's deployed.
- These modules work in conjunction with the permissions the core apps have.
- These modules give Hermit the ability to attack a rooted device, record audio, make and reroute phone calls, as well as gather information including call logs, contacts, photographs, the position of the device, and SMS messages.
- Hermit tricks the users by serving up the legitimate webpages of the brands it impersonates as it kickstarts malicious activities in the background.
GSAT-24: Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has successfully launched India's communication satellite GSAT-24.
Key Points:
- The satellite was successfully launched into geostationary orbit from Kourou in French Guiana by the Ariane 5 rocket (South America).
- GSAT-24 is built by ISRO for NewSpace India Limited (NSIL).
- It was the 25th Indian satellite launched by Arianespace and the 11th of the GSAT (Geosynchronous Satellite) series.
- It was launched by French company Arianespace.
Note: Alongwith GSAT-24, Ariane 5 launcher also carried two satellites, MEASAT-3d for the Malaysian operator MEASAT. With this, the total payload of the launcher was approx. 10,863 kg.
Features of GSAT-24:
- GSAT-24 is a 24-Ku band communication satellite weighing 4180 kg with pan-India coverage for meeting Direct-to-Home (DTH) application needs.
- This was the first demand driven communication satellite mission undertaken by NSIL post space sector reforms.
- It will provide high-quality television, telecommunications and broadcasting services over India.
- The 15-year mission life of GSAT-24 is configured on ISRO’s tried-and-true I-3k Bus.
Background:
- NSIL, a Central Public Sector Enterprise (CPSE) of Government of India (GoI) under the Department of Space (DOS), has leased the entire satellite capacity to Tata Play (formerly Tata Sky).
- The commercial arm of ISRO, NSIL was established in March 2019.
- NSIL was required to carry out operational satellite missions on a “demand driven” model as part of the “space reforms” announced by the government in June 2020.
- Under this model, NSIL is responsible for building, launching, owning, and operating satellites as well as providing services to its devoted customer.
Sports
World Sports Journalist Day 2022: World Sports Journalists Day is observed on 2nd of July every year to celebrate the services of sports journalists for the promotion of sports.
Key Points:
- Sports journalism is a form of reporting that focuses on matters pertaining to any subject or topic related to sports.
- It is an essential component of every media organization.
- Sports journalists are employed by a variety of media outlets, such as print, broadcast, and online.
- There are several local and national journalism organisations active in sports reporting.
History:
- The International Sports Press Association (AIPS) established the World Sports Journalist Day in 1994.
- Furthermore, the day commemorates the formation of the AIPS organisation that took place back on July 2, 1924, during the Summer Olympics in Paris.
- Over the years, the accomplishments of numerous sports media professionals have been honoured on this day.
Significance:
- The goal of World Sports Journalist Day is to support and honour all sports journalists for their exceptional work. The journalists are encouraged to serve as positive role models for future generations and are motivated to pursue careers in sports media.
- On this day, many media organisations conduct special events to felicitate their sports journalists.
About International Sports Press Association (AIPS):
- The International Sports Press Association (AIPS) was founded on July 2, 1924.
- It is the peak professional body representing the international sports media, with more than 9,500 members worldwide.
- It is made up of 160 Member Associations and is comprised of four Continental Sections, each with its own history and leadership. Continental Sections include Asia, America, Europe and Africa.
- AIPS was built with the belief of enhancing the cooperation between its member associations in defending sport and professional interests and strengthening the friendship and solidarity between sports journalists of all countries.
- Its headquarters are based in the Olympic capital Lausanne, Switzerland.
44th Chess Olympiad: Prime Minister Narendra Modi recently launched the historic torch relay for the 44th Chess Olympiad at Indira Gandhi Stadium, New Delhi.
Key Highlights:
- The International Chess Federation, FIDE, introduced the Chess Olympiad Torch, a component of the Olympic heritage, for the first time this year.
- India is the first country to have the Chess Olympiad Torch Relay.
- FIDE President Arkady Dvorkovich handed over the torch to Prime Minister, who in turn handed it over to Grandmaster Vishwanathan Anand.
About the torch:
- This torch will be taken to 75 cities in a span of 40 days before the final culmination at Mahabalipuram near Chennai.
- At every location, chess grandmasters of the state will receive the torch.
- It will then head over to the FIDE Headquarters, Switzerland.
44th Chess Olympiad:
- Asia will once again host the prestigious Chess Olympiad thanks to India, which is hosting it for the first time after a 30-year absence.
- The 44th Chess Olympiad will be held in Chennai from 28th July to 10th August, 2022.
Background:
- Philippines last hosted it from Asia in 1992.
- India, who made its debut at the event in 1956 Moscow (27th position), has a gold medal (joint winners with Russia in 2020) and two bronze medals (2021, 2014) from the Chess Olympiad.
- While the 2020 and 2021 editions were held virtually owing to the Covid 19 pandemic, the 2022 edition will be the first over-the-board Chess Olympiad being held since 2018 in Georgia.
About FIDE:
- The International Chess Federation (FIDE) is an international organization based in Switzerland.
- It connects the various national chess federations and acts as the governing body of international chess competition.
- It was founded on 20 July 1924, Paris, France.
- It is headquartered in Lausanne, Switzerland.
- The current President os FIDE is Arkady Dvorkovich.
Qosanov Memorial 2022: Indian women’s discus thrower, Navjeet Dhillon won the gold medal at the Qosanov Memorial 2022 athletics meet in Almaty, Kazakhstan.
Key Highlights:
- Navjeet Dhillon, who is looking to seal her place in the Indian team for Commonwealth Games, won the women’s discus throw with a 56.24m effort.
- Local athlete Karina Vasilyeva with 44.61m and Uzbekistan’s Yulianna Shchukina with 40.48m followed Navjeet Dhillon on the podium.
- Ace sprinter Sekar Dhanalakshmi ran her personal best time to win 200m gold at the Qosanov Memorial Athletics which is a World Athletics bronze-level event.
- She ran a creditable sub-23 second, clocking 22.89s to better her earlier personal best of 23.14s she had come up last year.
- She is only the third Indian woman to run sub-23s after national record holder Saraswati Saha (22.82s) and Hima Das (22.88s).
- In 100 mteter race, India’s Dutee Chand won silver by finishing race in 11.49 seconds. Olga Safronova of Kazakhstan won the gold in 11.40s. India’s MV Jilna won bronze in 11.61s.
- Overall India won 15 medals on the day, including seven golds.
Novak Djokovic: Novak Djokovic recently became the first player in history to win 80 matches in all four Grand Slams.
Key Facts:
- The Serbian defeated Kwon Soon-woo 6-3, 3-6, 6-3, 6-4 on Centre Court his 80th win in Wimbledon.
- By winning his 80th match at Wimbledon, the former world No. 1 tennis player made Wimbledon history.
- The six-time champion made history by becoming the first male competitor to win 80 or more games at all four grand slams in the Open Era.
Number of matches won by Novak Djokovic at each Grand Slam:
- Roland Garros – 85
- Australian Open -82
- US Open – 81
- Wimbledon -80
A seventh title would tie him with Pete Sampras' record and put him just one title behind Roger Federer as the second-most successful male singles player in the history of the oldest grand slam.
