Basics of Cyber Security
In the age of technical modernization, array of new opportunity and potential sources of efficiency for organisations of all sizes emerge but these new technologies have also brought unparalleled threats to economy and populace all over the world. Security measures must be taken to ensure safety and reliability of organizations. Hacking of data and information has become almost a practice in organizations. Therefore it is necessary to understand the features of cyber security. Cyber security is described as the protection of systems, networks and data in cyberspace. It is a critical concern for all businesses. Cyber technology is documented as modern ways for investors and common people to effortlessly, economically and efficiently access ample of source and opportunities to accomplish their task. In parallel, it also attracts fraudsters to apply fake schemes. Internet media is a major resource for developing serious crime. As Internet is growing rapidly, online criminals try to present fraudulent plans in many ways. Cyber-attacks are current method of creating fear in a technology driven world.
Cyber security is basically related to the internet. Since last many years, specialists and policy makers have shown more concerns about protection of information and communication technology systems from cyber attacks that are purposeful attempts by unauthorized persons to access ICT systems in order to achieve the target of theft, disturbance, damage, or other illegal actions. Cyber security is the detection, analysis and mitigation of vulnerabilities and diminished trust in "virtual" computer-based entities and services occurring because of globalisation of supply chains, exponentially increasing intricacy of devices and computer code, increasingly open, global networks and devices and accidental and purposeful exploitations and barriers by human and institutional actors. Many professionals anticipate the number and severity of cyber attacks to increase over the next several years.
The act of protecting ICT systems and their contents has come to be known as cyber security. A broad and debatable concept, cyber security can be a constructive term. It generally refers to a set of activities and other measures intended to protect from attack, disruption, or other threats to computers, computer networks, related hardware and devices software, and the information they hold and communicate, including software and data, as well as other elements of cyberspace. It is also related to the state or quality of being protected from such threats. Cyber security is the broad field of endeavour aimed at implementing and improving those activities and quality. It has been documented in studies that Cyber security is the activity to protect information and information systems (networks, computers, data bases, data centres and applications) with suitable procedural and technological security measures. Firewalls, antivirus software, and other technological solutions for safeguarding personal data and computer networks are indispensable but not adequate to guarantee security.
The scope of Cyber Security expands to the security of IT systems within the enterprise as well as to the broad digital networks upon which they rely including cyber space itself and critical infrastructures. Cyber Security has imperative role in the development of information technology as well as Internet services. For national security, it is essential to augment cyber security and shield critical information infrastructures and economic welfare. Society has become dependent on cyber systems for varied of human activities such as commerce, finance, health care, energy, entertainment, communications, and national defence. Several researches are being conducted in this stream and results showed that the level of public concern for privacy and personal information has increased since 2006. Internet users are more concerned about security of sensitive information which they share and want to be forgotten when there is no lawful grounds to retain their personal information
Cyber security is also associated with the technical term, information security, which is explained in federal law as protecting information and information systems from illegal access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or damage in order to provide integrity, confidentiality and availability. Integrity denotes to guarding against improper information modification or destruction, and includes ensuring information non repudiation and authenticity. Confidentiality signifies preserving authorized restrictions on access and disclosure, including ways of protecting personal privacy and proprietary information. Availability indicates ensuring timely and reliable access to and use of information. Cyber security concentrates on protecting computers, networks, programs and data from unintended or unauthorized access, change or destruction. Governments, military, corporations, financial institutions, hospitals and other businesses gather process and store huge confidential information on computers and pass on that data across networks to other computers. With the growing volume and complexity of cyber attacks, more attention is necessary to protect sensitive business and personal information, as well as protect national security.
Elements of national Cyber security programme:
Challenges of cyber security: There are some new risks to cyberspace such as smart Phones pretence Security Challenges Development like smart phones and cloud computing mean people are considering a whole new set of problem link to inter-connectivity that required new regulation and new thinking. The cyber security issue is quite similar in countries in world that use information and communication technology because they deploy similar hardware and software. Some of the commonalities are that all countries use TCP/IP as the protocols for communication, and all are dependent on the same operating Systems (Windows, UNIX, Linux, and others), software applications (Firefox, Skype, Microsoft Office and many others) and the large router manufactures (Cisco and Juniper). Since the technology is analogous then the problems created by the technology are also of same kind. The cyber security issue in urbanized nations has been well recognized and it is a huge problem. Some problems are associated to critical information infrastructure (CIIP), SCADA (supervisory control and data acquisition) systems and government networks, while others are related to the Internet infrastructure and host devices like desktop computers, smart phones, and Internet enabled devices.
The massive information produced and stored by the vast numbers of machines that will be connected to the Internet, will necessitate the development of security technologies that remain efficient at this scale and that can detect potential risks among an ever-expanding constellation of unstructured and highly heterogeneous datasets. This is a major challenge in cyber security management. More connections also pose challenge to cyber security. Each new object connected to the Internet will represent an additional entry point to the digital ecosystem that will have to be secured. This will prove particularly difficult for autonomous machines such as robots and smart meters that operate in public spaces and can be easily tampered with, or for devices that are produced in such large quantities that security features need to remain elementary to reduce price (Roman et al., 2011).
Threats to Cyber Security: Threats to cyber security can be generally divided into two general categories that include actions aimed at to damage or destroy cyber systems that is cyber attacks and actions that try to exploit the cyber infrastructure for illegal or damaging purposes without destructive or compromising that infrastructure that is cyber exploitation. While some intrusions may not result in an instant impact on the operation of a cyber-systems, such as when a Trojan Horse penetrates and establishes itself in a computer, such intrusions are considered cyber-attacks when they can subsequently permit actions that obliterate or corrupt the computer's capacities. Cyber exploitation includes using the Internet and other cyber systems to commit fraud, to steal, to recruit and train terrorists, to breach copyright and other rules limiting distribution of information, to convey controversial messages that comprises of political and hate speech and to put up for sale child pornography or other banned materials.
The matter of cyber security is prominent at global scale. Miscreants attack on cyberspace in several ways. Many hackers are just copycats but not inventive. They try to access any of a number of hacker websites to download malicious code (malware) developed by other, even if the majority of the world's systems are previously immunized against that particular attack. Another way that hackers gain illegal access to a system is through social engineering. Social engineering denotes to deception against other humans. A hacker may formulate a plan to trick another person into providing a username and password. This is often accomplished by preying on the unsuspecting individual's readiness to help or by taking advantage of a trusting relationship. Scanner is one of the effectual tools that hackers use to obtain valuable information about weaknesses in networks and systems. Other powerful way to attack on cyber security is cracking password. Password cracking involves creating plain text passwords from their cryptographic hashes. Once the plain text password is garnered, access can be had. Password cracking can be done through a "dictionary" approach entails checking the unencrypted result against a dictionary of words. A "hybrid" algorithm extends the dictionary approach by adding numbers and special characters to the mix. Some hackers use rule-based method when the executor knows information about the organization's password policy, perhaps learned through social engineering.
IP spoofing is also used by hackers to disrupt the system which is a technique to gain hidden, unauthorized access to a target resource. They do this by impersonating a trusted resource. Particularly, a DoS attack may change address information in the IP header of a message to make the target resource think the message is coming from a recognized, friendly port. When this practice is deployed in at mass level, the attack can effectively dominate the target machine's resources and make the machine lethargic or stop processing altogether. Trojan Horses is well known hacking virus that corrupt the computer system and it is very dangerous for cyberspace. "Trojan horse" to connote a malicious, security breaking program that is disguised as something benign. Malicious attacks follow a common process of events from origin to mission success: a target has to be researched; the malware devised, delivered, installed and activated; the control channel has to be established; and the mission itself must be completed. Such a process goes by several names, most of which are a variant of "kill chain" because of the many points or links in the chain.
Lifecycle of a cyber attack, often called a kill-chain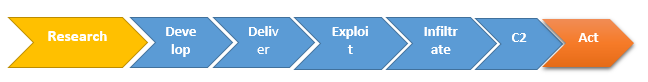
The extraordinary development of cyberspace has brought unparalleled economic growth, opportunity, and affluence. However, it also invites fraudulent with entirely new threat and felony opportunities. The interests of industry and governments in securing and facilitating cyber-based transactions and activities are basically aligned. All firms want a protected digital infrastructure for business operations. To ensure the continued feasibility of the infrastructure and expansion of their sector, technology companies are highly stimulated to design and build security into their products and systems. Governments need a safe global digital infrastructure for financial growth, wealth, efficiency, and security.
Principles of cyber security: The Information Technology Industry Council (ITI) provides complete set of cyber security principles for industry and government. ITI comprise the world's leading technology companies, both producers and consumers of cyber security products and services. ITI has developed six principles to improve cyber security.
To be successful, Company must make efforts to boost cyber security through following way:
- Organizations must leverage public-private partnerships and build upon existing initiatives and resource commitments. Through partnership with government, the IT industry has provided leadership, resources, innovation, and stewardship in every aspect of cyber security since many years. Cybersecurity efforts are most effectual when leveraging and building upon these existing initiatives, investments, and partnerships.
- Organizations reflect the borderless, interconnected, and global nature of today's cyber environment. Cyberspace is international and unified system that spans geographic borders and traverses national jurisdictions. Countries should exercise leadership to encourage the use of bottom-up, industry-led, globally accepted standards, best practices, and assurance programs to promote security and interoperability
- Firms must be able to adapt rapidly to emerging threats, technologies, and business models and be based on effective risk management. Efforts to improve cyber security must be based on risk management. Security is a means to realize and make sure continued trust in various technologies that comprise the cyber infrastructure. Cyber security efforts must help an organization's ability to appropriately understand, assess, and take steps to manage ongoing risks in this environment.
- Efforts to improve cyber security must focus on awareness. The principle of cyber security is to focus on raising public awareness. Cyberspace's owners include consumers, businesses, governments, and infrastructure owners and operators. Cyber security efforts must help these stakeholders to be attentive of the risks to their property, reputations, operations, and sometimes businesses, and better understand their important role in helping to address these risks.
- Efforts to improve cyber security must more directly focus on bad actors and their threats. The unified, global, and digital nature of the cyber infrastructure also has presented cyber criminals with completely new crime opportunities. Security practices serve to counter these opportunities and allow cyber-based transactions and activities to occur.
- In cyberspace, as in the physical world, adversaries use instruments to do crime, spying, or warfare. Cyber security policies must allow governments to better use current laws, efforts, and information sharing practices to respond to cyber actors, threats, and incidents domestically and internationally
Ways to Improve Cyber Security
Cyberspace is a worldwide and interrelated sphere that covers geographic borders and national jurisdictions. To support the growth, operation, maintenance, and security of this area, information technology companies continually innovate and spend in the development of internationally deployable products and services. Cyberspace's stakeholders such as consumers, businesses, governments, and infrastructure owners and operators, search for a consistent, secure experience in cyberspace. Efforts to improve cyber security should mirror cyberspace's borderless nature and be based on internationally established standards, best practices, and international assurance programs. This approach will augment security, because nationally focused efforts may not have the advantage of the best peer-review processes conventionally found in global standards bodies, because proven and effectual security measures must be deployed across the whole global digital infrastructure, and because the need to meet multiple, conflicting security requirements in multiple jurisdictions raises enterprises' costs, demanding valuable security resources. Cyber security standards also improve interoperability of the digital infrastructure, because security practices and technologies can be better united across borders. It also allow more private-sector resources to be used for investment and innovation to address future security challenges and increase international trade in cyber security products and services that can be sold in multiple markets. Best practices in cyber security allow countries to obey with their international commitments, such as the World Trade Organization (WTO)'s Technical Barriers to Trade Agreement (TBT), which calls for non-discrimination in the preparation, acceptance, and application of technical rules, standards, and conformity assessment procedures; evading unnecessary obstacles to trade; synchronizing specifications and procedures with international standards as far as possible; and the clearness of these measure.
Companies must have Password Management to prevent from cyber-attack. Strong passwords are first defensive technique when it comes to controlling access to protected systems and information. It is important to recognize the idiosyncrasies and limitations of account administration when it comes to operating systems, database servers and applications. The following should be explored and analysed systematically before establishing policy in a formal way:
- Procedures for protecting password files and administrator accounts
- Random password generation, one-time passwords and two-factor authentication
- Length of a password's life
- Password expiration and renewal
- Procedures for cleansing ex-employee access
- Length and qualities of acceptable passwords
Antivirus is an effective cyber security management policy that checks the vulnerabilities exist for an organization's resources before formalizing processes and procedures. This is especially factual for exposures to the outside Internet, community. Once weaknesses are acknowledged, the policy will specify both commercial and internally developed solutions to avoid the introduction of malicious code on the company's perimeter defence systems, servers and desktops, how deployment is to unfold, and who is responsible for deployment. Incident handling also prevent cyber-attacks. Policy must be devised to cover practical steps that an organization needs to take when a cyber-security incident occurs. Recognized incident handling tasks are aimed first at securing information assets, minimizing damage as speedily as possible. Backup and Recovery also protect cyber threat. Policy needs to highlight the primary importance of backup and recovery processes for desktops, file servers and mainframes. Responsibilities should be clearly acknowledged. Batch processing and storage capacity plans needs to be vital parts of the operational planning process. A plan for disaster recovery from offsite backups should be considered.
Maintaining Cyber Security for Small Business
For small business owners, Broadband and information technology are dominant factors to reach new markets and increase productivity and competence. Conversely, businesses must need effective cyber security strategy to shield their own business, their customers, and their data from growing cyber security threats. In order to retain cyber security, following factors must be considered:
- Train employees in security principles: It is necessary to establish basic security practices and policies for workers, such as requiring strong passwords, and establishing proper Internet use guiding principle that detail penalties for violating company cyber security policies. Establish rules of behaviour describing how to deal with and protect customer information and other vital data.
- Protect information, computers and networks from cyber attacks: It is very important to keep clean machines and have the latest security software, web browser, and operating system and secure with the best defences against viruses, malware, and other online threats. Set antivirus software to run a scan after each update. Install other key software updates as soon as they are available.
- Provide firewall security for Internet connection: A firewall is a set of related programs that prevent outsiders from accessing data on a private network. Company must assure that the operating system's firewall is enabled or install free firewall software available online. If employees work from home, ensure that their home system(s) are protected by a firewall.
- Create a mobile device action plan: Mobile devices can create considerable security and management challenges, particularly if they hold confidential information or can access the corporate network. Require users to password protect their devices, encrypt their data, and install security apps to prevent criminals from stealing information while the phone is on public networks. Be sure to set reporting procedures for lost or stolen equipment.
- Make backup copies of important business data and information: Companies are instructed to maintain backup of the data on all computers at regular basis. Critical data includes word processing documents, electronic spreadsheets, databases, financial files, human resources files, and accounts receivable/payable files. Backup data automatically if possible, or at least weekly and store the copies either offsite or in the cloud.
- Control physical access to computers and create user accounts for each employee: It is very important to control cybercrime. Companies must prevent the access or use of business computers by unauthorized individuals. Laptops can be particularly easy targets for theft or can be lost, so lock them up when unattended. Make sure a separate user account is created for each employee and require strong passwords. Administrative privileges should only be given to trustworthy IT staff and key personnel.
- Secure Wi-Fi networks: If there is a Wi-Fi network for workplace, make sure it is secure, encrypted, and hidden. To hide Wi-Fi network, establish wireless access point or router so it does not broadcast the network name, known as the Service Set Identifier (SSID). Password protects access to the router.
- Employ best practices on payment cards: Company must work with banks or processors to guarantee the most trusted and validated tools and anti-fraud services which are being used. Executives may also have additional security obligations pursuant to agreements with their bank or processor. Isolate payment systems from other, less secure programs and don't use the same computer to process payments and to surf Internet.
- Limit employee access to data and information, limit authority to install software: Company must assign experts for data usage. It must not allow any one employee with access to all data systems. Employees should only be given access to the precise data systems that they need for their jobs, and should not be able to install any software without permission.
- Passwords and authentication: Company must facilitate employees to use unique passwords and change passwords every three months. Consider implementing multi-factor authentication that requires additional information beyond a password to gain entry. Verify with vendors that handle sensitive data, especially financial institutions, to see if they offer multi-factor authentication for account.
To summarize, Cyber security is need of organization in technologically advanced business climate. In a situation of global connection and cyber terrorism, the security of information assets is vital to all private business, public organization and individual household. With the expansion of the internet as a global infrastructure for business and as a new device for politics, espionage and military activities, cyber security has become central theme for national and international security. The objective of a cyber-security management system is to shield the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information assets. Two appropriate cyber security management system technologies are effective that include perimeter defence and encryption. These concepts and solutions are consistent and joined together in practical application. A thoroughly conceived and consistently rendered cyber security management policy facilitates to move the application of these technologies forward. The concepts of policy and technology are basic to an effectual cyber security management system. Good cyber security can maintain privacy in an electronic environment, but information that is shared to assist in cyber security efforts might sometimes include personal information that at least some observers would regard as private. Cyber security is an effectual way of protecting against undesired observation and gathering of intelligence from an information system.

