Export Management
Concept of export management
Export business is prevalent around the globe and in recent times it has grown at much faster rate due to globalisation process. Export means transaction of products and services from one nation to other following legal rules for trade purposes. Export goods are given to international end users by domestic producers. Export management is the use of managerial process to the serviceable area of exports. It is basically associated with export activities and type of management that brings harmonization and incorporation of an export business. Export management is concerned with export orders and accomplish objectives to successfully complete in time as per the requirements given by the overseas buyers. The main purpose of export management is to secure export orders and to make certain for timely delivery of goods as per agreed norms of quality and other specifications including terms and conditions agreed to between the exporter and the importer.
The nature of export management
Export management can be appraised with reference to functional area of export and the administrative process involved in export management.
Categorization of Export
The export can be grouped into many sections such as Merchandise Exports, Services Exports, Project Exports, and Deemed Exports.
A merchandise export is related with the export of physical goods, for example, readymade garments, engineering goods, furniture, and works of art. Service Exports denotes to the export of goods that don't exist in physical form, that is, professional, technical or general services. Examples of the exports would include export of computer software, architectural, entertainment or technical consultancy services. Project export means to develop a project by a business firm in a different nation. It is viewed as systematically evolved work plan devised to achieve a specific objective within a specific period of time. Deemed Exports refer to those transactions by the recipient of the goods in which the goods are made in India. The necessary condition is that such goods are manufactured in India. This category of export has been introduced by the Export Import Policy of the Government of India. Some of the examples of goods that are considered as Deemed Exports, as given in Export-Import Policy (2002-07) are supply of goods against duty free licenses, Supply of goods to projects financed by multilateral or bilateral agencies/Funds notified by the Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance, Government of India and supply of goods to the power, oil and gas including refineries.
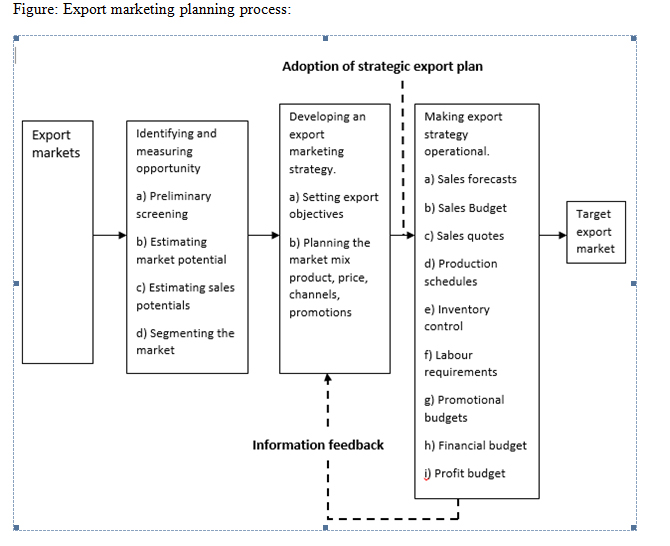
Function of Export Manager
Export manager has important role in managing business for international orders. They must be competent to perform export business. The conventional management structures with functional classification such as purchases, marketing, finance, accounts, administration, cannot make certain efficiency in export management through all stages in the export phases. Therefore, export manager is needed to successfully conduct export business operation. The basic role of an export manager is to bring about synchronization and integration of the export transaction from within the established management structures and concerned external agencies to guarantee timely delivery of goods as per the specifications of purchaser. The export manager is accountable for the successful completing of the order in terms of time, cost and technical performance. He must provide the guidance necessary to connect the people and groups from dissimilar departments working on the export order, into one team in a managerial organisation and provide the drive necessary to complete the task on time and within cost. He must have good understanding of the techniques applied in export planning, financial management, inventory management, merchandising, risk management, foreign exchange operations, exchange control, negotiation with banks information systems, communication, personnel management and industrial relations, co-ordination and control. The efficiency of export manager will depend upon the extent of authority delegated to him by the senior management.
Process of Export Management
When it is decides to develop export business, the primary function is to make good plan to secure an export order. After confirming the order to the consumer, it is necessary to develop an organization structure for it and form competent team of personnel for its implementation. Export Manager has great responsibility to manage all operation in timely manner. The success of the export order depends, on his efficient management and handling of export orders. He must maintain liaison with the importer, prepare plans for its implementation and issue necessary executive instructions to the export employees. He has also to develop an information system so that there is continuous flow of information on the progress of the order. In case, if progress is not satisfactory and some tasks are not performed as per prescribed schedules, export manager has duty to evaluate the variances and tasks suitable corrective measures, if necessary, for the purpose and ultimately submit report on the progress of work to the top management. The major functions of the export manager in managing orders are: procurement of export order, planning for export order execution, direction for exports, export order execution, importer liaison, export order evaluation, reprogramming, reporting on export order execution.
Development of Export Strategies
Once a detailed market analysis has been completed, company should develop a method of market entry. The indirect methods of market entry usually need less marketing investment, but company could lose considerable control over the marketing process. Direct exporting may require huge capital investment in marketing, but there is more control over export strategies. Corporate presence is a choice for companies with successful test marketing. In Direct Exporting, Company or individual can access directly to customers and sell them products in foreign markets by establishing an export department within your organization. Selling through company's sales department creates a chance to establish healthy relationship with the abroad market and buyer. In addition to selling directly to the market, company can penetrate and may also choose to use an export manager to handle other parts of the world. In fact, in some countries, it is not necessary to sell directly to the end-user; company must use a local agent or representative. Other direct exporting options are Manufacturer's Representative or Sales Agents. They are the persons who are responsible for closing the sale and taking orders on a commission basis. They do not take financial responsibility or collect payment for the goods sold, and they assume no risk or responsibility for the product. Foreign Distributor/Importer is another option for exporting who buys the product and is always responsible for payment of the export item. They presume financial risk and generally provide support and service for the product. Distributors often buy to fill their own inventories and typically carry a range of non-competitive, but complementary products. Overseas Retailers are also involved in exporting products.
Indirect Exporting is preferable for complex task and also cover the risk of direct exporting. An Export Management Company functions as an "off-site" export sales department, representing company's product along with a variety of non-competitive manufacturers. The Export Management Company searches for business for company and usually provides the array of services like it performs market research and develops a marketing strategy, locates new and utilizes existing foreign distributors or sales representatives, to put your product into the foreign market, functions as an overseas distribution channel or wholesaler, takes title to the goods and operates on a commission basis. Another indirect exporting option is through Export Trading Company which is analogous to Export Management Companies. The ETC is more likely to take title to the product and pay directly, but like an EMC, they can also act as an export department. Usually, there is less responsibility on the part of the ETC towards the supplier and they tend to be demand driven and transaction oriented. Licensing offers a small business the advantages of rapid entry into foreign markets as well as reducing the capital requirements to establish manufacturing facilities overseas. Other option is Franchise agreements that tend to give the franchiser more control over marketing, since it is the company's reputation and existing market relationship that adds value to the product. Agreements with foreign manufacturers to produce company product, as opposed to exporting to the overseas region is known as contract manufacturing. It is an easy foreign market entry method when your manufacturer is already producing company product for the domestic market.
Benefits of Exporting
Main benefit of export is the possession which is specific to the firms' international experience, asset and capacity of the exporter to offer distinct product or low cost product with in the values chain. An assortment of investment risk and market potential is recognized as the site benefit of the particular market combination. Some companies have lower level of ownership advantage therefore they may not enter into the foreign markets. In case a company's products and company's ownership equipped with the international advantage and ownership advantage, the entry can be made through low risk model. Another benefit is that low investment is needed in exporting of goods than the other modes of international trade and development. In export of products, the managers perform the various operational control however it does not have the option over the control of marketing activities of the company. The consumer of exported goods is far away from the exporter though the different intermediaries can manage the risk.
Problems and issues in export management
Major barriers of export management include language, high risk, government control, difference in laws, difficulty in payment, custom duty, and lack of information. Other problems of export management are evil effects of foreign trade, economic dependence, disadvantage of agriculture country, international rivalry. Researchers said that there is high risk in foreign trade instead of internal business because goods are transported to other countries through sea, air in which there is environmental threat and products may be damaged from poor climate, rocks etc. Usually international trade is under governmental control and licence is must for doing international trade. In export, management, there are differing law in each country therefore traders have to face many problems in conducting business. Export management become difficult when information flow is not smooth. It is very difficult to assess the financial position of businessman located in other country. It is observed that developed nations get advantage through export business but developing countries may suffer loss as they cannot manufacture goods at rapid rate and managerial process is also not very smooth. Another problem is dependency on other country for raw material and if imports are stopped due to some reasons, country has to suffer a lot in terms of finance. Export management is not smooth due to low labour productivity, less technological advancement and laziness.
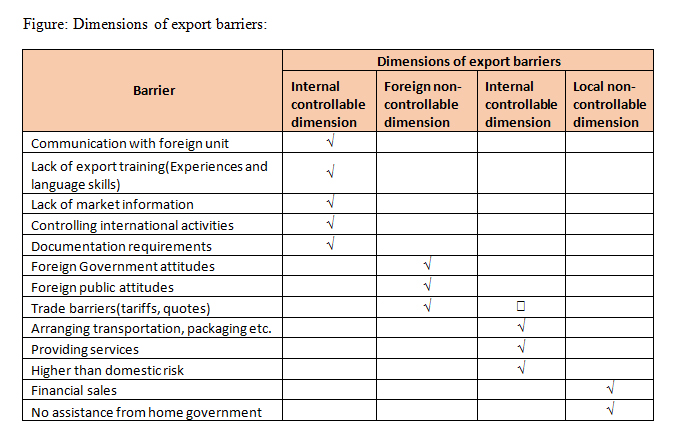
In order to reduce issues of export trade, it is suggested that traders must know various language for good conversation. Export managers must have knowledge of exchange rates. They must modernize the process of foreign trade and standardize the products. In addition to this there are some major disadvantages highlighted in the export of goods such as financial management, communication technology improvements, and customer demand and management mistakes. To reduce the risk of transaction process of exporting the goods and exchange rate fluctuation, it is necessary to have more capacity for managing the financials for coping up the efforts. Presently, customers can directly communicate with the suppliers with the aid of communication technology which has improved the way of purchasing goods. It leads more clearness in transaction and purchasing of goods and vendors are responsible for following the real time demand for submitting the transaction details.
It is summarized that exporting is common way for manufacturers to do business in foreign market. Success of export management requires the enthusiastic, honest and positive support of all the functional managers in the organisations. Good export management gets the export order completed within the time and as per the budget allocated for particular project.

