Management Accounting: concept, need, importance and scope
Concept: Management accounting is wide arena of accounting. The phrase Management Accounting includes two words, Management and Accounting. It refers to Accounting for the Management. Management accounting is the procedure to develop management reports and accounts that present precise and timely financial and statistical information required by managers to make day-to-day and short-term decisions. Management accounting can be seen as accounting associated with management. Basically it is deep study of managerial characteristic of financial accounting, "accounting in relation to management function". It demonstrates how the accounting function can be re-oriented so as to fit it within the structure of management activity. The prime task of management accounting is to reform the whole accounting system so that it may serve the operational needs of organization. Alleyne,P. and Weekes-Marshal, D, (2011) explained management accounting practices as array of methods considered for businesses so as to support the organisation’s infrastructure and management accounting processes. It is associated with tax accounting, financial accounting, managerial accounting and internal auditing. Johnson and Kaplan (1987) stated that management accounting systems evolved to encourage and assess the efficiency of internal processes and not to measure the overall profits of the organization. Drury (1996) avowed that further advances in management accounting were associated with the scientific management movement.
The area of organizational movement covered by management accounting has developed through four identifiable stages. Stage one is earlier to 1950. Its focus was on cost determination and financial control, through the use of budgeting and cost accounting technologies. Stage two belonged to the period of 1965. During this stage, main focus had shifted to the provision of information for management planning and control, through the use of such technologies as decision analysis and responsibility accounting. Stage 3 was the period of 1985 in which main concentration on the lessening of waste in resources used in business processes, through the use of process analysis and cost management technologies and Stage four belonged to 1995, in which attention had shifted to the creation of value through the effective use of resources, through the use of technologies which scrutinize the drivers of customer value, shareholder value, and organizational improvement.
Evolutionary stages of management accounting (Source: IFAC, 1998):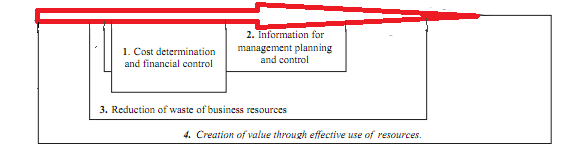
Management accounting creates monthly or weekly reports for an organization's internal audiences such as department managers and the chief executive officer. These reports characteristically demonstrate the amount of available cash, sales revenue generated, amount of orders in hand, state of accounts payable and accounts receivable, outstanding debts, raw material and inventory, and also comprises of trend charts, variance analysis, and other statistics. An effectual management accounting system offers superior quality, timely information to relevant persons. Although emergence of information technology have made the provision of information cheaper than ever, the cost of further refining an information system still needs to be weighed against the benefits that are expected to result from such modification. According to Hilton (2008), Management accounting is still a new discipline, as a result, its theory and devices are still growing as new ways are found to provide information that helps management. Robert N. Anthony described that “Management Accounting is concerned with accounting information, which is useful to the management”. Other theorists, Brown and Howard stated that “Management Accounting is concerned with the efficient management of a business through the presentation to management of such information that will facilitate efficient planning and control”. The Certified Institute of Management Accountants explained that management accounting is an vital part of management concerned with recognizing, presenting and inferring information to formulate strategy, planning and controlling activities, decision taking, optimizing the use of resources, disclosure to shareholders and others, external to the entity, disclosure to employees and safeguarding assets. The information in the management accounting system is used for Measurement, Control and Decision-making.
Management literature showed that Management Accounting is a contemporary instrument to management. It offers the techniques for interpretation of accounting data. Accounting should serve the needs of management. Management is associated with decision-making. Therefore the role of management accounting is to make possible the process of decision-making by the management. It is apparent that Managers need information about business activities to plan, accurately, for the future and make decisions for achieving the goals of the enterprise. The main function of Management Accounting is to lessen the ambiguity and assist the management in the decision making process.
Importance of Management Accounting
In complex business, it is imperative to perform systematic management planning. Delegation of authority and decentralization of decision-making process has become important to conduct business. The functions of management are no longer private. A system of information is required to assist the management to investigate, evaluate and verify the functioning of each division or unit for decision-making to accomplish the goals of the business. Management Accounting has great importance to fulfil the needs of the management. Management Accounting measures and reports appropriate information to the management and facilitates in accomplishing corporate objectives. It is significant that the information given to the management should be pertinent and issue based to facilitate the management to focus on the real issue to reach at a specific conclusion. Management accounting on the basis of the information available decide its goal and tries to realize the way through which it can reach the objective.
Need of management accounting: Management accounting is required to recognize the financial situation of the business, it reports to those inside the organisation for planning, directing, motivating, and controlling and performance evaluation. It gives special emphasis on decision affecting the future. It is needed to prepare plan.
Functions of Management Accounting in Management Process
Management Accounting has brought out apparent shift in the aim of accounting. The main emphasis is Management Accounting is on analysing and interpreting to assist the management to secure better results. In this way, Management Accounting eradicates intuition, which is not at all dependable, from the field of business management to the cause and effect approach. Major functions of the management include planning, organizing, directing and controlling. Management accounting facilitates in the performance of each of these functions in numerous ways.
Provides data: Management accounting is significant source of data to plan. The accounts and documents are a repository of a huge quantity of data about the past development of the firms, which are a must predict the future.
Modifies data: The accounting data needed for managerial decisions is accurately compiled and classified.
Analyses and interprets data: The accounting data is analysed significantly for successful planning and decision-making. For this purpose the data is presented in a comparative form. Ratios are calculated and likely trends are projected.
Serves as a means of communicating: Management accounting provides effective way for communicating management plans upward, downward and outward through the organization. Originally, it identifies the viability and steadiness of the various segments of plan. At later stages it keeps all parties informed about the plans that have been agreed upon and their roles in these plans.
Facilitates Control
Management accounting assists to translate given objectives and strategy into specific goals for accomplishment by a particular time and secures effective success of these goals in a capable manner. This can be possible through budgetary control and standard costing which is an integral part of management accounting.
Uses also qualitative information: Management accounting does not control itself to financial data to assist the management in decision making but also uses such information which may not be capable of being measured in economic terms. Such information may be collected form special surveys, statistical compilations, engineering records.
Management accounting can be detailed through a set of concepts classified in terms of the characteristic function of management accounting within the management process in organizations, the way in which the utility of the result of the management accounting process can be tested, measures which can be used to assess the value of the processes and work technologies used in management accounting and ability to necessarily related with the efficacy of the management accounting function overall. Conceptual framework can be used to explain best practice in management accounting because it concentrates on capabilities necessary for effective performance of the unique work of the function, evaluations of the organizational value of the work outcomes of the function and the worth of the function's work processes and technologies in securing such results.
conceptual framework for management accounting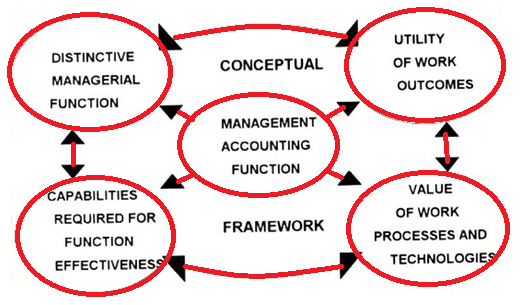
Major benefits of Management Accounting
Management accounting offers better Services to Customers. The cost control device is management accounting that facilitates in reduction in prices of the Product. It helps in making judgment. It is process of measuring performance. The techniques of budgetary control standard costing enable the measurement of performance. In standard costing, standards are decided and then actual cost is compared with standard cost. It facilitates the management to find out deviations between standard cost and actual cost. Management accounting increase efficiency of the business. The targets of different departments of the enterprise are determined in advance and the accomplishment of these goals is taken as a device to gauge their competence. Management accounting serves as effective management control. The Tools and techniques of the management accounting are supportive to the management in planning controlling and coordinating activities of the business, getting of standard and assessing actual performance. Through management accounting, firms get maximum profits. In this process, every possible effort are made to control unnecessary expenses. Management accounting gives safety and security from trade cycle. The Information received from the management accounting gives information over the past trade cycle. The management tries to determine the Causes of trade cycle and its influence. Consequently, management accounting tries to defend the organization from the effect of trade cycle.
Scope of Management Accounting
Management accounting is related with management of accounting information in resourceful way for the administration. Its scope is immense and includes all aspects of business operations. The following areas can accurately be recognized as falling within the compass of management accounting.
Financial Accounting: Management accounting is strongly associated with the rescheduling of the information provided by financial accounting. Therefore, management cannot get full control and synchronization of operations without a correctly designed financial accounting system. Cost Accounting: Standard costing, marginal costing, opportunity cost analysis, differential costing and other cost methods play a constructive role in operation and control of the business undertaking.
Revaluation Accounting: This is related with fact that capital is maintained together in actual terms and profit is calculated with this fact in mind.
Budgetary Control: This includes framing of budgets, comparison of actual performance with the budgeted performance, computation of variances, finding of their causes.
Inventory Control: It consists of control over inventory from the time it is acquired till its final disposal.
Statistical Methods: These procedures include Graphs, charts, pictorial presentation, index numbers and other statistical methods make the information more inspiring and understandable.
Interim Reporting: This includes groundwork of monthly, quarterly, half-yearly income statements and the related reports, cash flow and funds flow statements, scrap reports.
Taxation: This comprises of computation of income according to the tax laws, filing of returns and making tax payments.
Office Services: This includes upholding of appropriate data processing and other office management services, reporting on best use of mechanical and electronic devices.
Internal Audit: This includes development of a suitable internal audit system for internal control.
The primary objective of Management Accounting is to exploit profits or reduce losses. This is performed through the presentation of statements in such a way that the management can make remedial policy or take good decision. The way in which the Management Accountant satisfies the various needs of management is explained below:
Storehouse of Reliable Data: Management wants consistent data for Planning, Forecasting and Decision-making. Management accounting collects the data from different sources and stores the information for appropriate use, as and when required. Although the main source of data is financial statements, Management Accounting is not limited to utilize financial data only. While preparing a sales budget, the management accountant uses the past data of the products sold from the financial records and makes projections based on the customer surveys, population figures and other consistent information to assess the sales budget. Management accounting uses qualitative information, dissimilar to financial accounting to prepare its reports, collect and alter the data for the specific purpose.
Modification and Presentation of Data: Whenever Data is collected from financial statements and other sources, it is not readily reasonable to the management. The data is tailored and presented to the management in manner that it is constructive to the management. If sales data is required, it can be categorized according to product, geographical area, season-wise, type of consumers and time taken by them to make payments. Likewise, if production figures are required, these can be grouped according to product, quality, and time taken for mechanized process. Management Accountant changes the data in accordance with the needs of the management for particular issue to be resolved.
Communication and Coordination: Targets are conversed to the different branches for their accomplishment. Coordination among the different departments is necessary to get huge success. The targets and performances of different departments are well communicated to the concerned departments to boost the efficiency of the various sections and enhance productivity of organization. Variance analysis is a significant device to focus on serious matters to control and accomplish the desired outcomes.
Financial Analysis and Interpretation: Management accounting is needed in strategic decision making. High level managerial executives do not have good technical knowledge. Such as, there are various alternatives to produce. Management Accountant provides relevant facts and figures about different policies and appraises them in financial terms.
Control: In any organization, it is a good practice to develop a system of monitoring the performance of all divisions and departments so that differences from the desired path can be visible without interruption and corrective action can be taken. This process is called control. The intent of this function ‘control’ is to make possible achievement of the goals in competent manner. To perform this function, management accounting gives significant information in a systematic and efficient manner. However, the role of accountant is misinterpreted. Many consider the accountant as a controller of their performance. The main function of control is effectual communication and assists the managers to accomplish their goals in effectual way.
Supplying Information to Various Levels of Management
In management ladder, relevant information is needed to take wise decision-making and execute policy. Senior management takes major policy decisions and allocate power to lower staff for day-to-day decisions. Supply of right information, at proper time, increases competence at all levels.
Reporting to Management
Reporting is vital function of management accounting in order to attain the targets. The reports are accessible in the form of graphs, diagrams and other statistical methods in order to understand easily. These reports may be monthly, quarterly, and half-yearly. These reports are useful in giving continuous review of the working of the business.
Helpful in taking Strategic Decisions: There are complex decisions in respect of make or buy, discontinuance of a product line, investigating new market areas. It is quite difficult to decide in such arena without systematic accounting information.
Limitations of management accounting: Though accounting management offers numerous benefits to organization to maintain financial process and serve as an effective discipline to improve the managerial performance, there are several drawbacks in the system. Management Accounting is mainly based on estimates. It does not deal with actuals, alone, and thus total precision is not guaranteed under Management Accounting. Management Accounting is absolutely a tool for management, but cannot substitute management. Management Accounting obtains information from Financial Accounting, Cost Accounting and other records. The strength and weakness of these essential information providers become the strength and weakness of Management Accounting. The installation of Management Accounting is an expensive process so all the organizations especially small firms cannot manage to pay for it. The emergence of Management Accounting is the combination of a number of themes like statistics, economics, engineering and management theory. Any insufficient grounding in any one or more of the subjects is bound to have an adverse effect on the consideration and solution of the problems, relating to management performance. Though the main role of Management Accounting is removal of intuitive approach, there is always a temptation to take an easy course of arriving at decisions, by intuition, instead of taking the convoluted path of scientific decision-making. When organization implements a system of Management Accounting, there is a radical change in the established pattern of the activity of the management workers. It results in rescheduling of personnel as well as their activities. This is bound to encounter opposition from some quarter or other. It is observed that management accounting is novel approach and is in a stage of development. Therefore, it has numerous difficulties which a relatively new discipline has to undergo.
To summarize, management accounting is essential in tactical planning. The aim of management accounting is to provide internal users with the basis to make knowledgeable business decisions. Management accounting information is generally not openly reported and is forward looking rather than historical. It is established in literature that management accounting emphasizes on the information that management requires for specific intra firm resource allocation and it is an application of appropriate techniques and concepts in processing historical and projected economic data of an entity to help management to establish plans for reasonable economic objectives and making rational decisions. .

